Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Lin DM. Parathyroid adenoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/parathyroidpthadenoma.html. Accessed October 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Benign neoplasm derived from parathyroid parenchymal cells
- Typically involves one gland
Essential features
- Incidence increasing due to biochemical testing
- Diagnosis confirmed by a drop in parathyroid hormone (PTH) after surgical removal
- Atypical parathyroid adenoma displays histology concerning for but not diagnostic of malignancy and requires clinical follow up after excision
- Can be mistaken for thyroid follicular neoplasm by fine needle aspiration
ICD coding
- ICD-10: D35.1 - Benign neoplasm of parathyroid gland
Epidemiology
- Incidence has increased over the past 50 years due to routine biochemical testing
- Accounts for over 85% of cases of primary hyperparathyroidism worldwide (N Engl J Med 2011;365:2389)
- Women more frequently affected than men
- Age range is broad but commonly 30s - 60s (Lloyd: WHO Classification of Tumours of Endocrine Organs, 4th Edition, 2017)
Sites
- Parathyroid gland, inferior glands slightly more common than superior
- Can also occur where ectopic / supernumerary parathyroid tissue may be found (thyroid gland, thymus, retroesophageal area, mediastinum, vagus nerve, carotid sheath)
- Double adenomas can occur, usually involving both superior parathyroid glands (Surg Pathol Clin 2019;12:1007)
Etiology
- Most are sporadic cases of unknown etiology
- Associated syndromes: hyperparathyroidism jaw tumor syndrome (HRPT2 gene germ line mutation), multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN1 more likely to have adenomas than MEN2A and MEN2B) (Surg Pathol Clin 2019;12:1007)
- Risk factors: radiation exposure, long term lithium therapy (Endocr Rev 2019;40:711, Front Oncol 2019;9:1092)
Clinical features
- Often detected early in asymptomatic patients due to routine serologic testing (see laboratory findings below)
- Symptoms of hyperparathyroidism: nephrolithiasis, osteopenia, osteitis fibrosa cystica, weakness, fatigue and psychiatric disturbances can occur if not detected early
- Rarely presents as a palpable mass (J Med Case Rep 2019;13:332)
Diagnosis
- Various imaging techniques can identify parathyroid nodules, including CT, MRI and ultrasound
- Technetium 99 sestamibi scintigraphy (99mTc) (see radiology description below)
- Intraoperative parathyroid hormone (PTH) rapidly decreases after the abnormal gland is removed
Laboratory
- Serum parathyroid hormone (PTH) and calcium elevated, though usually not as high as in parathyroid carcinoma
- Needle washouts after FNA can be used for PTH measurements (Diagn Cytopathol 2020 Aug 24 [Online ahead of print])
- Hypophosphatemia and hypophosphaturia (J Med Case Rep 2019;13:332)
Radiology description
- Nodule posterior to thyroid gland
- 99mTc sestamibi:
- Sestamibi accumulates in the mitochondria rich oxyphil cells of the parathyroid
- Increased focal uptake may indicate an adenoma (J Nucl Med 1992;33:1801)
Prognostic factors
- Normally can be cured by surgical removal but recurrences can happen if not properly localized and excised
- Atypical adenomas are considered tumors of uncertain malignant potential and should be followed up clinically (Surg Pathol Clin 2019;12:1007)
Case reports
- 24 year old pregnant woman with parathyroid adenoma and acute necrotizing pancreatitis (BMC Endocr Disord 2019;19:82)
- 52 year old woman with giant parathyroid adenoma (J Med Case Rep 2019;13:332)
- 54 year old woman with parathyroid lipothymoadenoma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1993;117:312)
- 56 year old woman with cystic parathyroid adenoma (BMC Endocr Disord 2020;20:53)
- 57 year old man with a parathyroid adenoma (Endocr J 2019;66:379)
- 61 year old woman with retrotracheal parathyroid adenoma (Radiol Case Rep 2020;15:672)
Treatment
- Parathyroidectomy
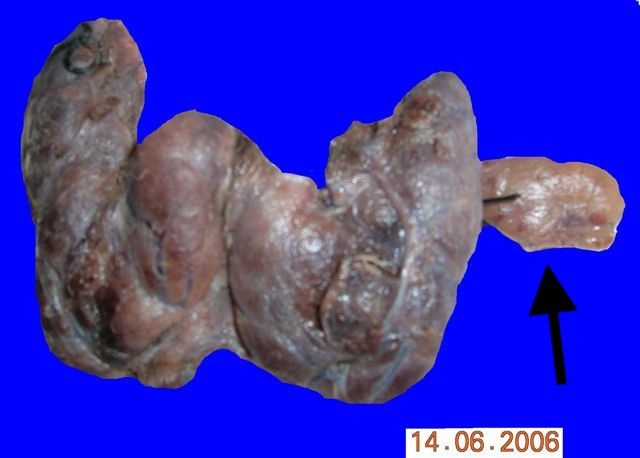
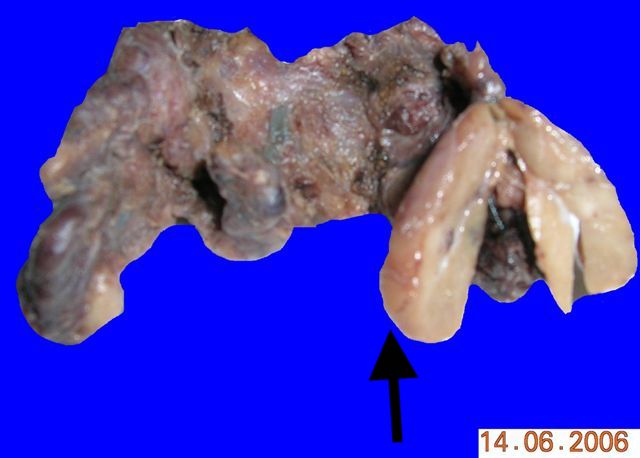
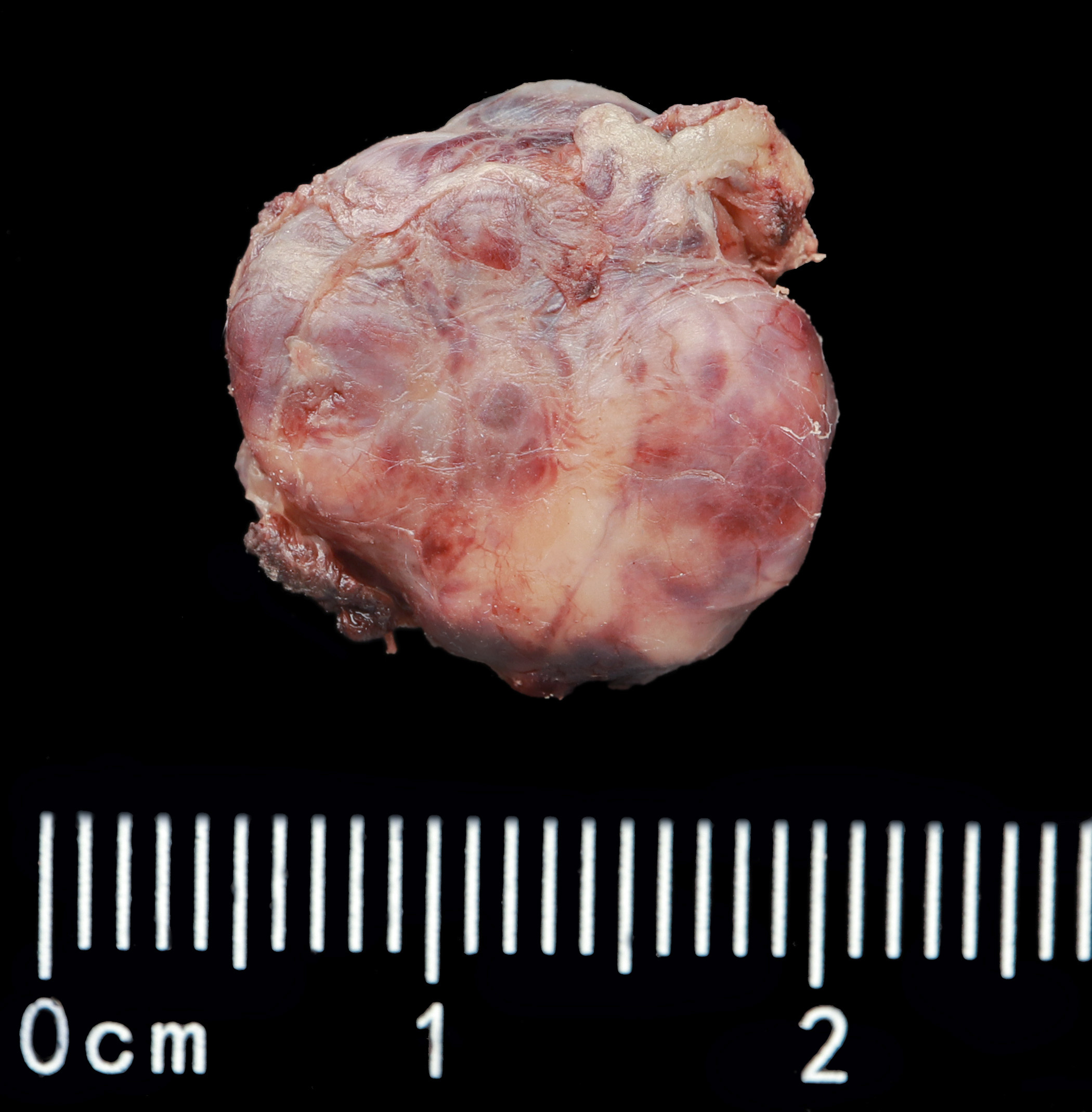
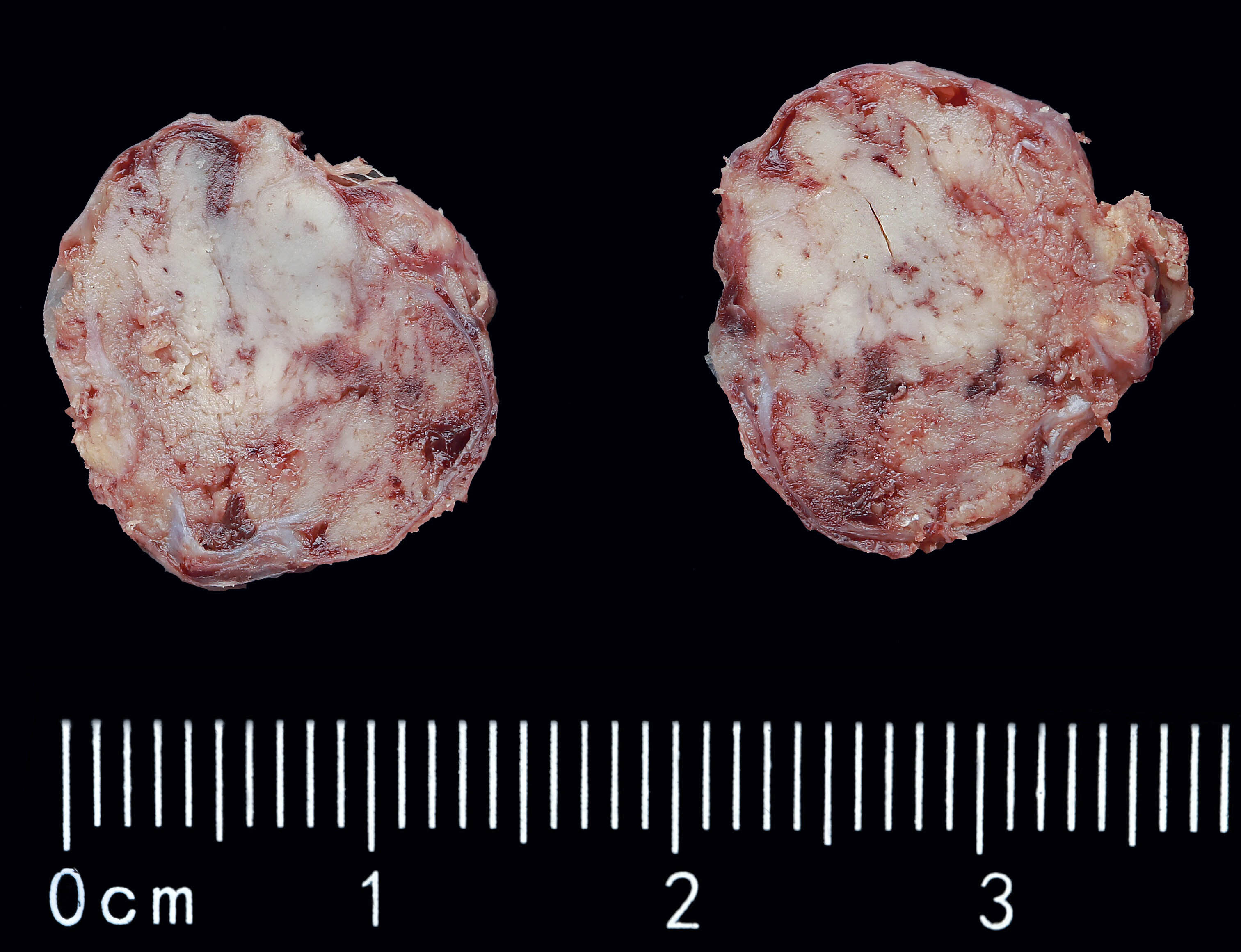
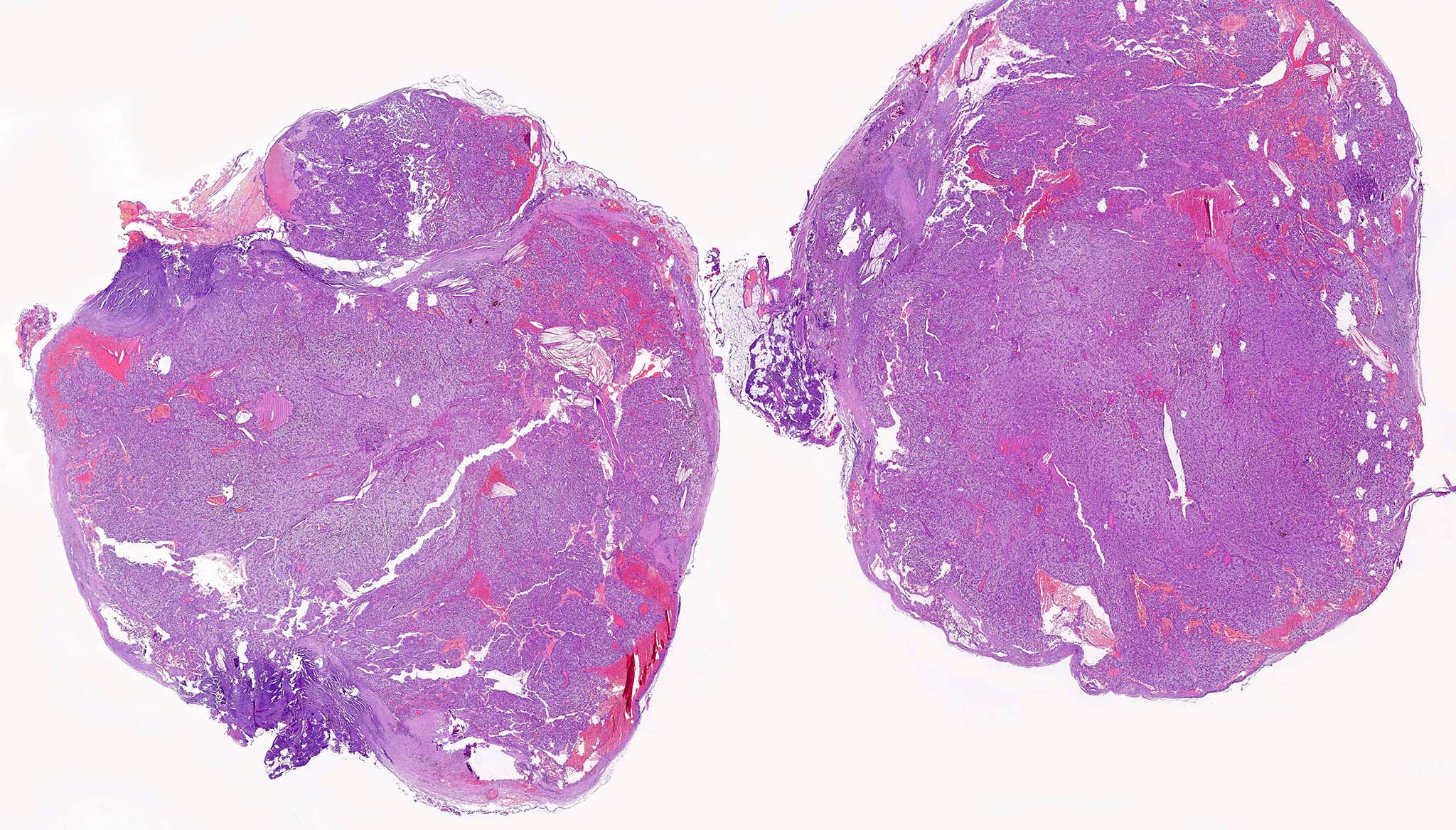
Gross description
- Variable size, from < 1 cm to > 10 cm (Rosai: Tumors of the Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands, Series 4)
- Term “microadenoma” has been used to describe tumors measuring < 6 mm
- Weight > 40 mg (Endocr Pathol 2018;29:113)
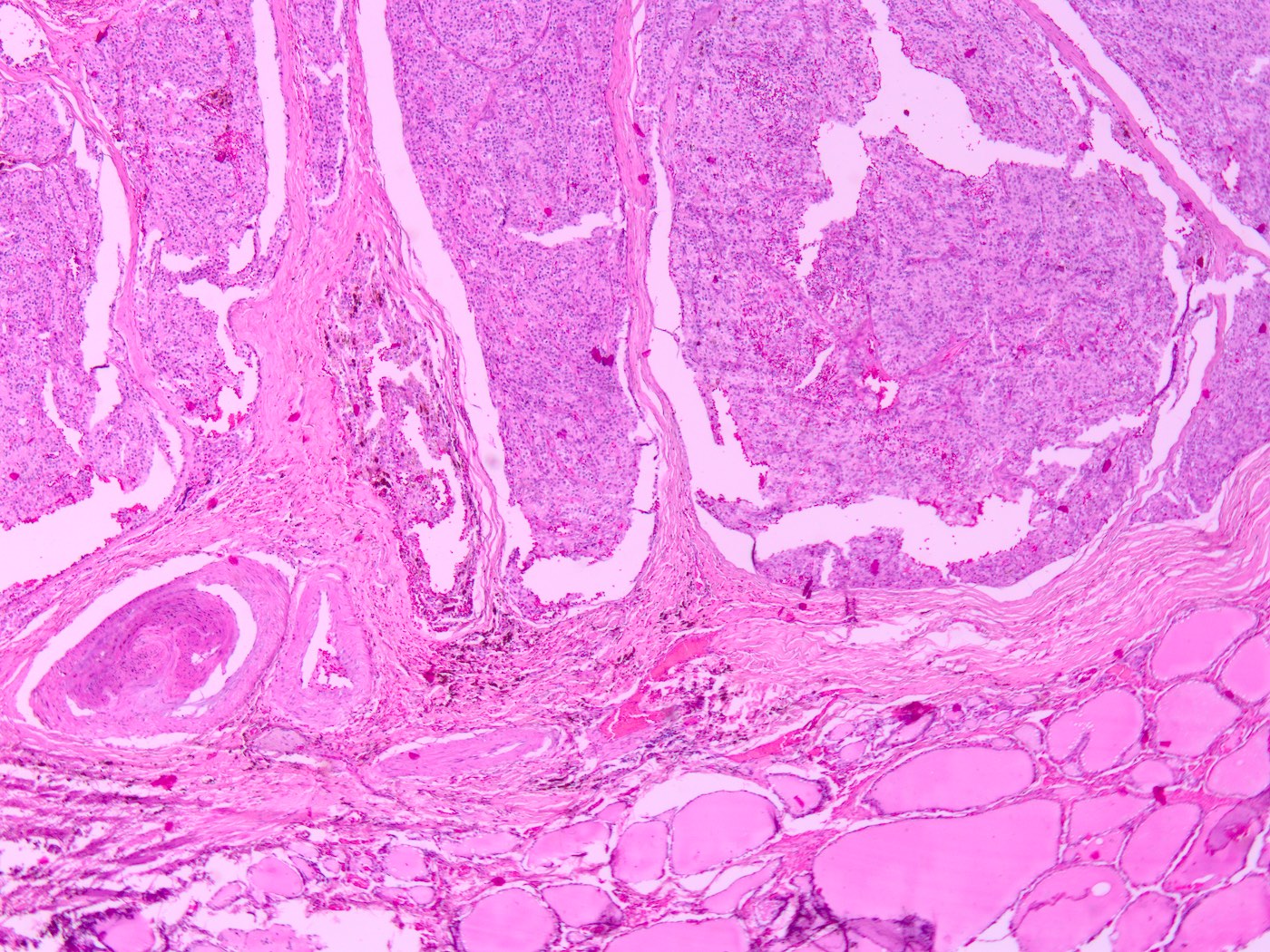
- Solid yellow / tan, well circumscribed ovoid nodule
- No invasion into adjacent structures
Gross images
Frozen section description
- Identification of parathyroid tissue is usually sufficient for intraoperative management, rather than trying to distinguish adenoma from hyperplasia
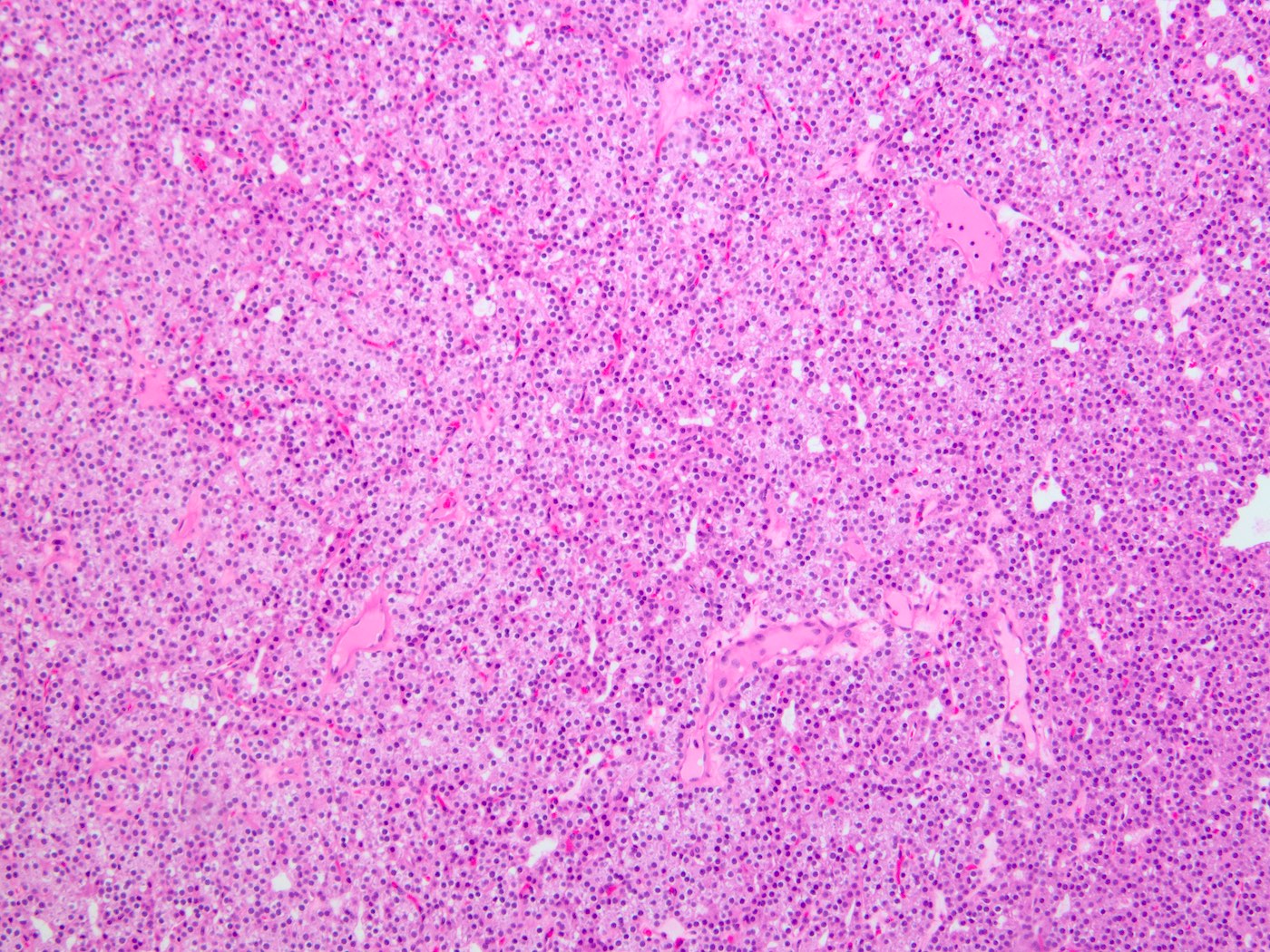
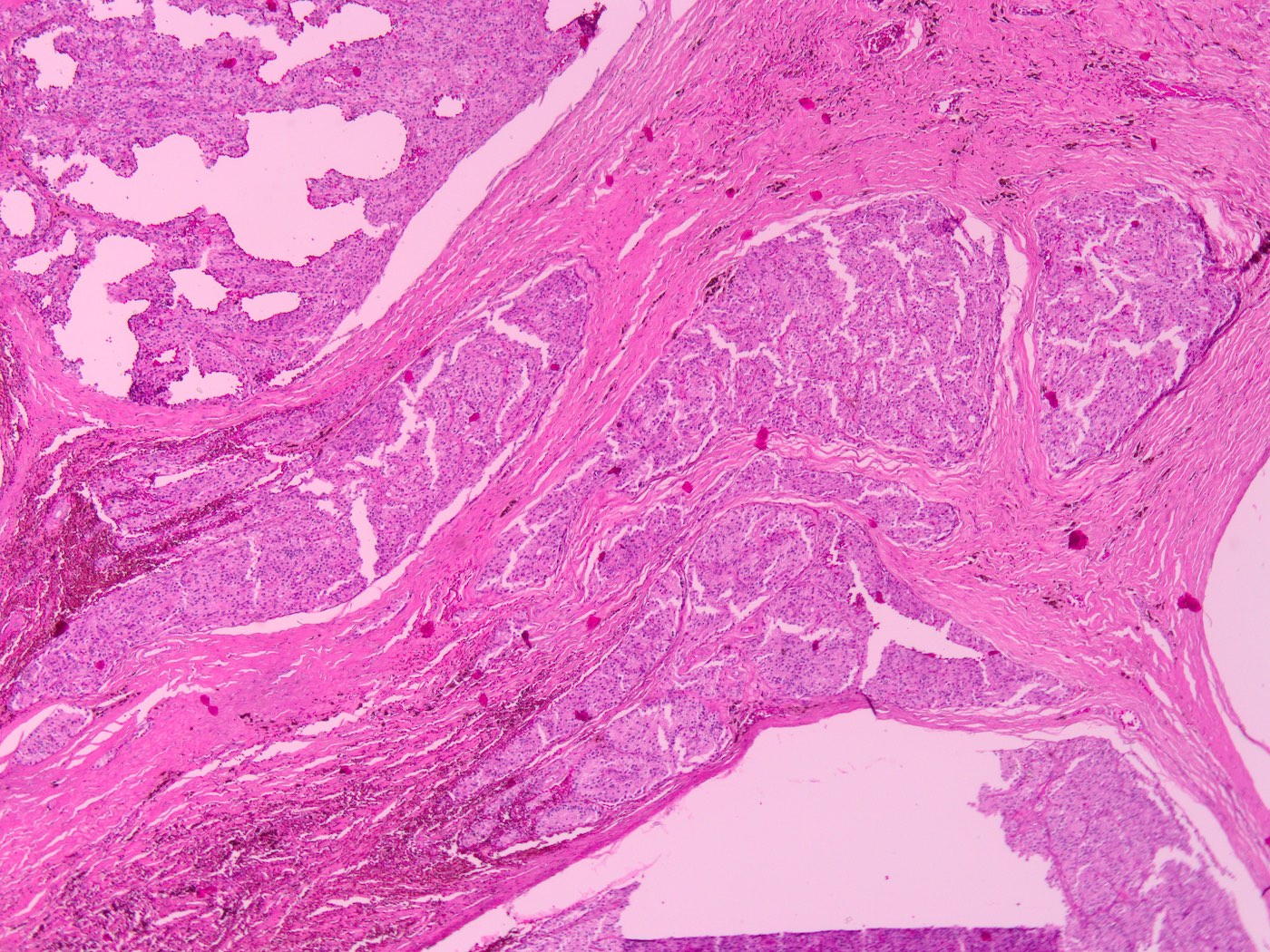
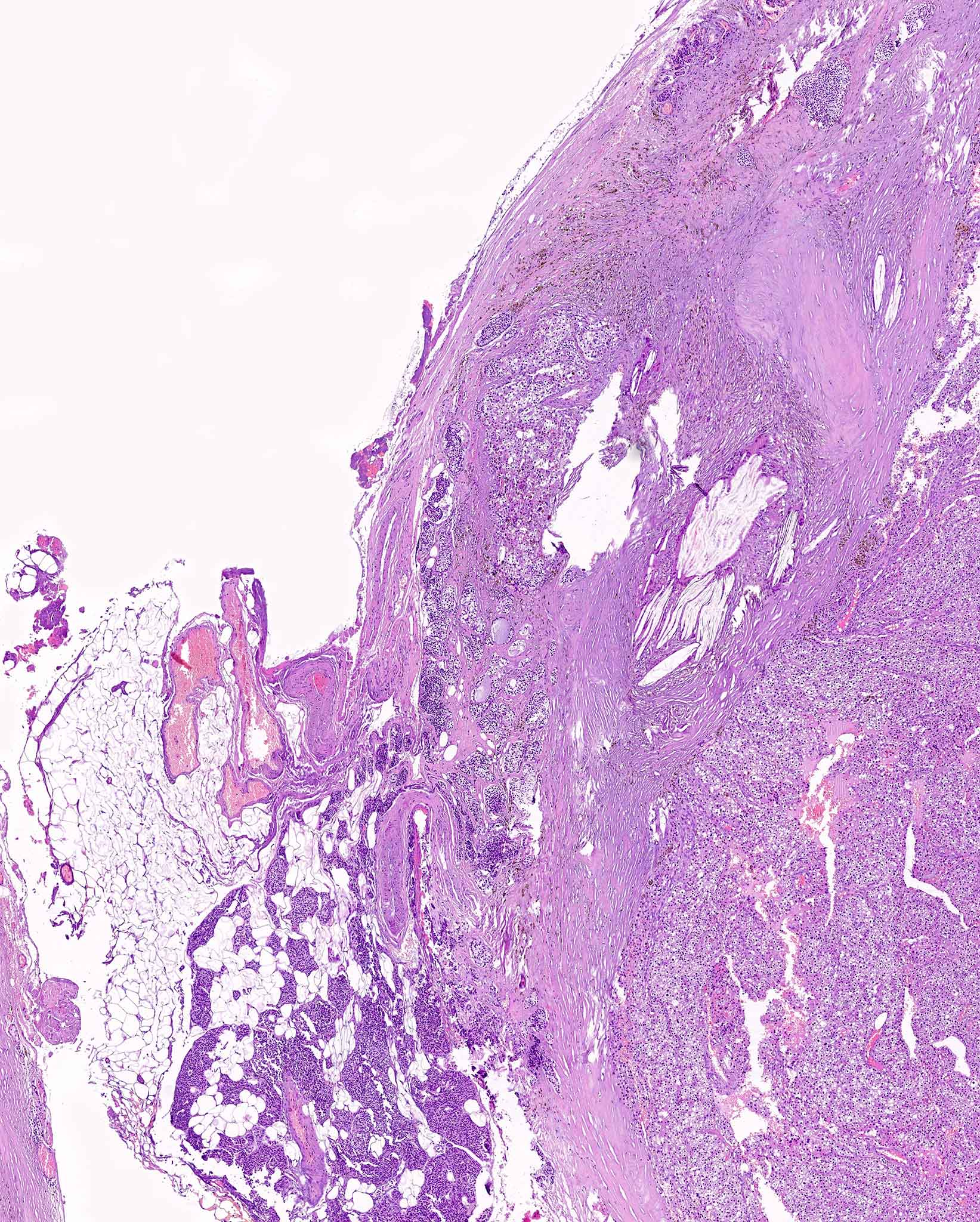
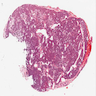
Microscopic (histologic) description
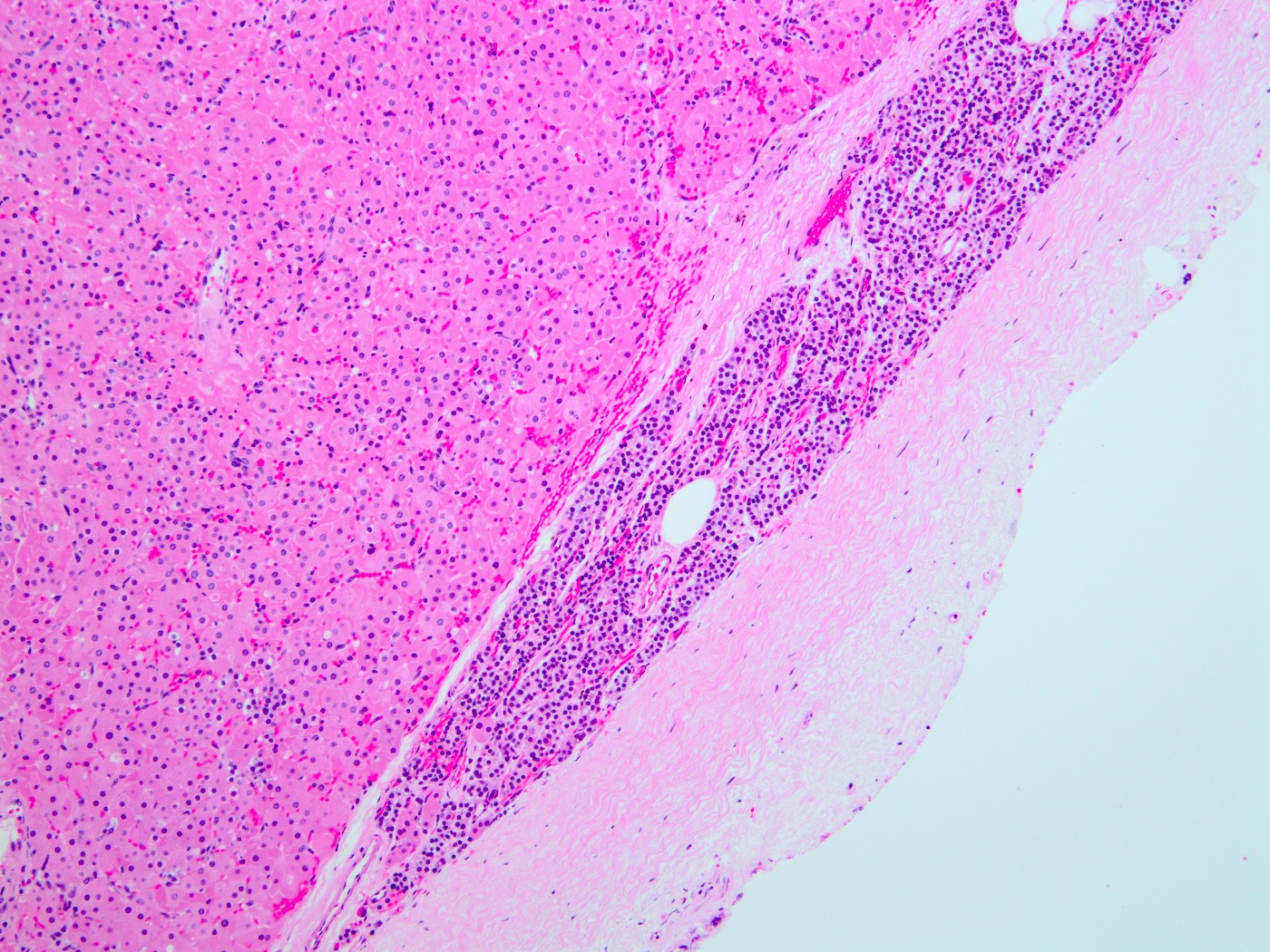
- Well circumscribed, frequently with thin fibrous capsule
- Absent or reduced stromal adipocytes
- Compressed nonneoplastic parathyroid tissue may be seen at edge
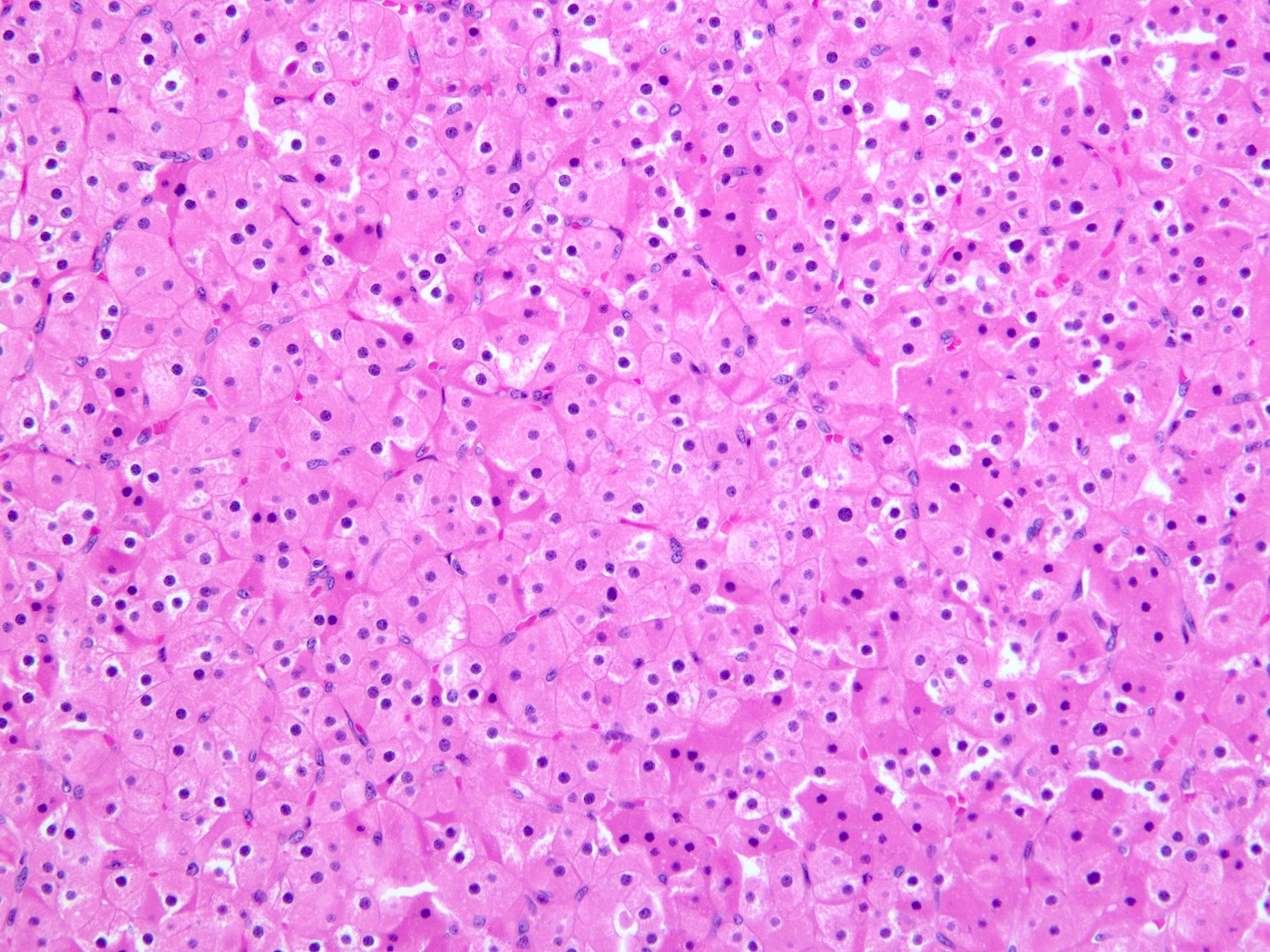
- Most commonly composed of chief cells (round nucleus, little granular cytoplasm)
- Follicle formation is not rare
- Mitoses and bizarre nuclei (endocrine atypia) may be focally present
- Variants:
- Oxyphilic / oncocytic adenomas: composed entirely of oncocytic cells with abundant, eosinophilic granular cytoplasm (Surg Pathol Clin 2019;12:1007)
- Water clear cell adenoma: cells have clear, glycogen containing cytoplasm (Surg Pathol Clin 2019;12:1007)
- Lipoadenoma (hamartoma): contains stromal (adipose) and parenchymal (usually chief cells) elements; most of the tumor is adipose tissue (Surg Pathol Clin 2019;12:1007)
- Atypical adenoma: contains borderline features concerning for (but not diagnostic of) malignancy (Surg Pathol Clin 2019;12:1007)
- Dense fibrous bands with hemosiderin
- Prominent nuclear atypia with spindled nuclei
- Notable mitotic activity
- Adherence to adjacent tissue
- Necrosis
- Solid or trabecular growth
- No evidence of lymphovascular invasion, perineural invasion, invasion into adjacent structures or metastasis
Microscopic (histologic) images
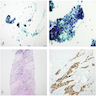
Cytology description
- Cellular aspirates with uniform small cells in sheets, 3D clusters and trabecular arrangements
- Round dark nuclei with smooth nuclear borders and without nucleoli
- Salt and pepper chromatin (Diagn Cytopathol 2020 Aug 24 [Online ahead of print])
- No colloid unless adjacent thyroid tissue is also aspirated
- More monotony than normal thyroid tissue
- Can be mistaken for a thyroid follicular neoplasm (Diagn Cytopathol 2017;45:526)
Cytology images
Positive stains
- Parathyroid hormone, synaptophysin, chromogranin A, GATA3, CAM 5.2, CK7, CK8, CK18 and CK19 (Endocr Pathol 2018;29:113)
- GATA3 (Diagn Cytopathol 2020 Aug 24 [Online ahead of print])
- Polyclonal PAX8 is nonspecific because monoclonal PAX8 is negative in parathyroid (Endocr Pathol 2018;29:91)
- CDC73 (parafibromin)
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Oxyphil cells are mitochondria rich (J Nucl Med 1992;33:1801)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- CDC73 (HRPT2) in patients with hyperparathyroidism jaw tumor syndrome (Endocr Pathol 2018;29:113)
- MEN1 in multiple endocrine neoplasia and sporadic adenomas
- For fine needle aspiration samples, the Veracyte Afirma Gene Expression Classifier contains a cassette to distinguish parathyroid from thyroid tissue (Diagn Cytopathol 2017;45:526)
- Mutations in CCND1 (cyclin D1), ZFX, EZH2 (Surg Pathol Clin 2019;12:1007)
Videos
Oncocytic adenoma
Parathyroid pathology
Sample pathology report
- Right lower parathyroid, parathyroidectomy:
- Chief cell adenoma, 250 mg
Differential diagnosis
- Histology:
- Parathyroid hyperplasia:
- Typically involves all 4 glands
- Diffuse enlargement rather than nodular growth with compressed rim of normal tissue
- Distinction between hyperplasia and adenoma may be difficult on routine histology and definitive diagnosis is based on intraoperative PTH findings
- Parathyroid carcinoma:
- Definitive evidence of invasion or metastasis (vascular invasion, perineural invasion, invasion into adjacent structure)
- Atypical mitotic figures
- Paraganglioma:
- Parathyroid hyperplasia:
- Cytology:
- Normal thyroid tissue and follicular neoplasms:
- Less defined cell membranes with no visible intracellular lipid droplets (Endocr Pathol 2018;29:113)
- Positive for TTF1 and thyroglobulin and negative for PTH and neuroendocrine markers (Endocr Pathol 2018;29:113)
- Serum calcium and PTH not elevated
- Normal thyroid tissue and follicular neoplasms:
Practice question #1
Practice answer #1
Practice question #2
Which of the following features is seen in parathyroid carcinoma but not adenoma?
- Adherence to adjacent thyroid
- Nuclear atypia
- Necrosis
- Perineural invasion
Practice answer #2