Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Ely KA. Sclerosing polycystic adenoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/salivaryglandssclerosingpolycysticadenoma.html. Accessed August 29th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Rare salivary gland disorder, first described in 1996 (Am J Surg Pathol 1996;20:161)
- Resembles fibrocystic changes and sclerosing adenosis of the breast (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:630)
- Exact nature of the disease is unknown but recent evidence suggests that it is neoplastic (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:e33)
Essential features
- Resembles fibrocystic changes and sclerosing adenosis of the breast (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:630)
- Composed of irregularly distributed bilayered ducts and acini within a sclerotic stroma (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:630)
Terminology
- Sclerosing polycystic adenosis
- Sclerosing adenosis
- Polycystic adenosis
- Sclerosing polycystic sialadenopathy
ICD coding
- ICD-10: K11.8 - Other diseases of salivary glands
Epidemiology
- Occurs over a wide age range (9 - 84 years); mean: 40 years
- Slight female predominance (F:M = 3:2) (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:e33)
Sites
- Parotid gland (around 70%), occasional examples in the submandibular glands and oral cavity (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:e33)
Pathophysiology
- Originally believed to be a reactive, nonneoplastic process resembling fibrocystic changes of the breast but evidence suggests it is likely neoplastic (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:630)
- Recurrence rate of up to 30% (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:939)
- Demonstration of clonality in 6 cases using the human androgen receptor assay (HUMARA) (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:939)
- Targeted next generation sequencing demonstrated mutations in genes that are well established to be drivers in human neoplasms (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:630)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Slow growing mass, may have pain or altered sensation (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:e33)
Diagnosis
- Best made on histologic examination of excisional material
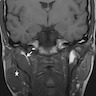
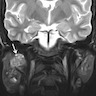
Radiology description
- Limited published descriptions
- T2 weighted MRI: small cystic areas show high signal intensity
- Ultrasound: hypoechoic, well circumscribed with microcysts (Head Neck Pathol 2012;6:247)
Prognostic factors
- Local recurrence rate up to 30% (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:939)
- Solitary case of an invasive component arising following multiple recurrences over decades (Virchows Arch 2014;464:621)
Case reports
- 7 and 33 year old sisters present with firm nodules of the right parotid gland (Pathol Res Pract 2014;210:342)
- 49 year old man with left palatal swelling (Contemp Clin Dent 2019;10:676)
- 79 year old woman with a sinonasal mass (Hum Pathol 2013;44:1937)
Treatment
- Complete, conservative local resection followed by prolonged surveillance (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:e33)
Gross description
- Well delineated, pale, firm, rubbery nodules embedded within normal salivary gland
- May be multinodular (Am J Surg Pathol 1996;20:161)
Frozen section description
- Well circumscribed proliferation of scattered dilated, variably sized ducts lined by hyperplastic epithelium in a vague nodular pattern
- Foci of apocrine change
- Dense stroma
- Because a definitive diagnosis may not be possible at the time of frozen section, a descriptive interpretation such as "sclerotic fibrous material with benign appearing glandular elements" could be rendered (Pathology 2016;48:93)
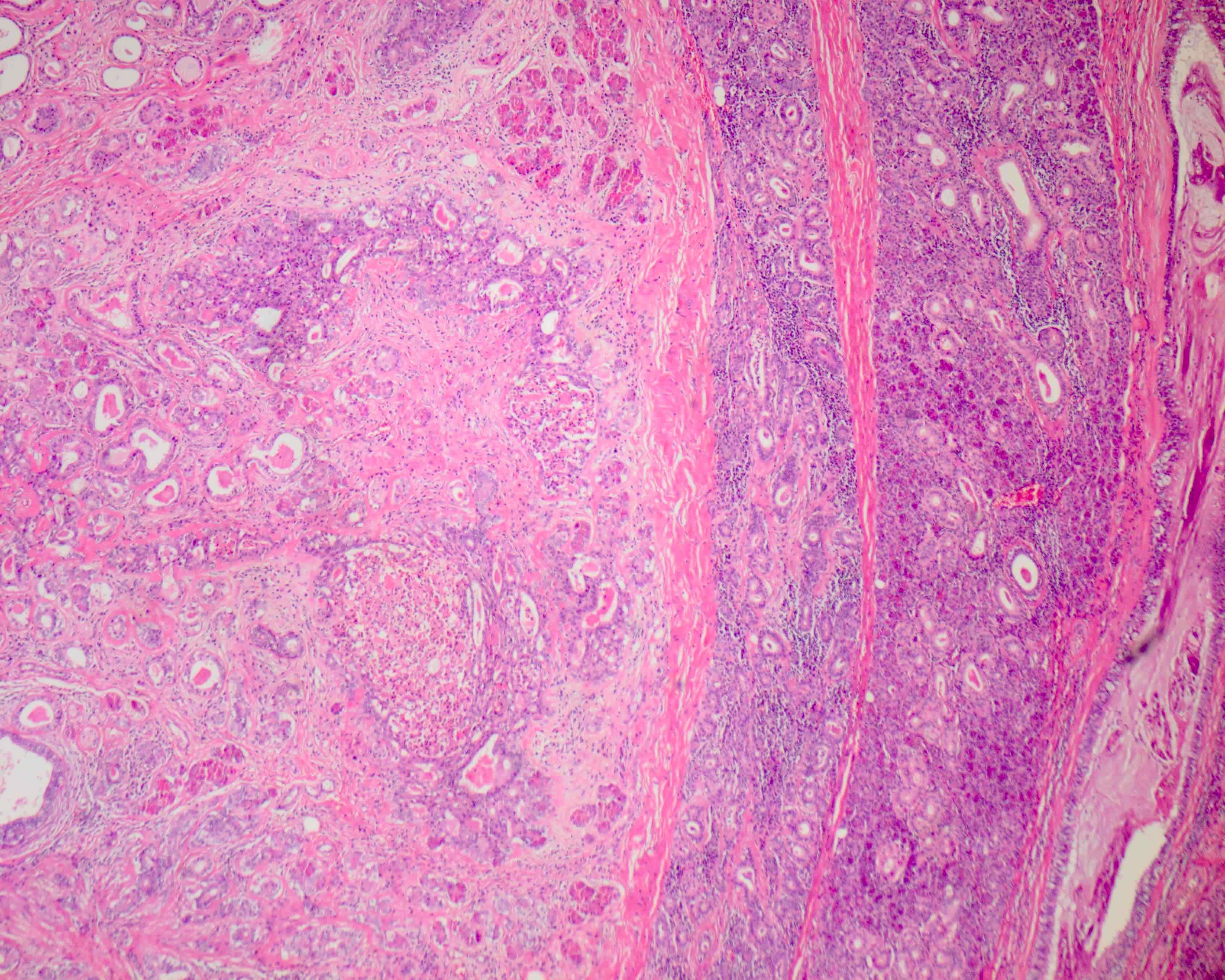
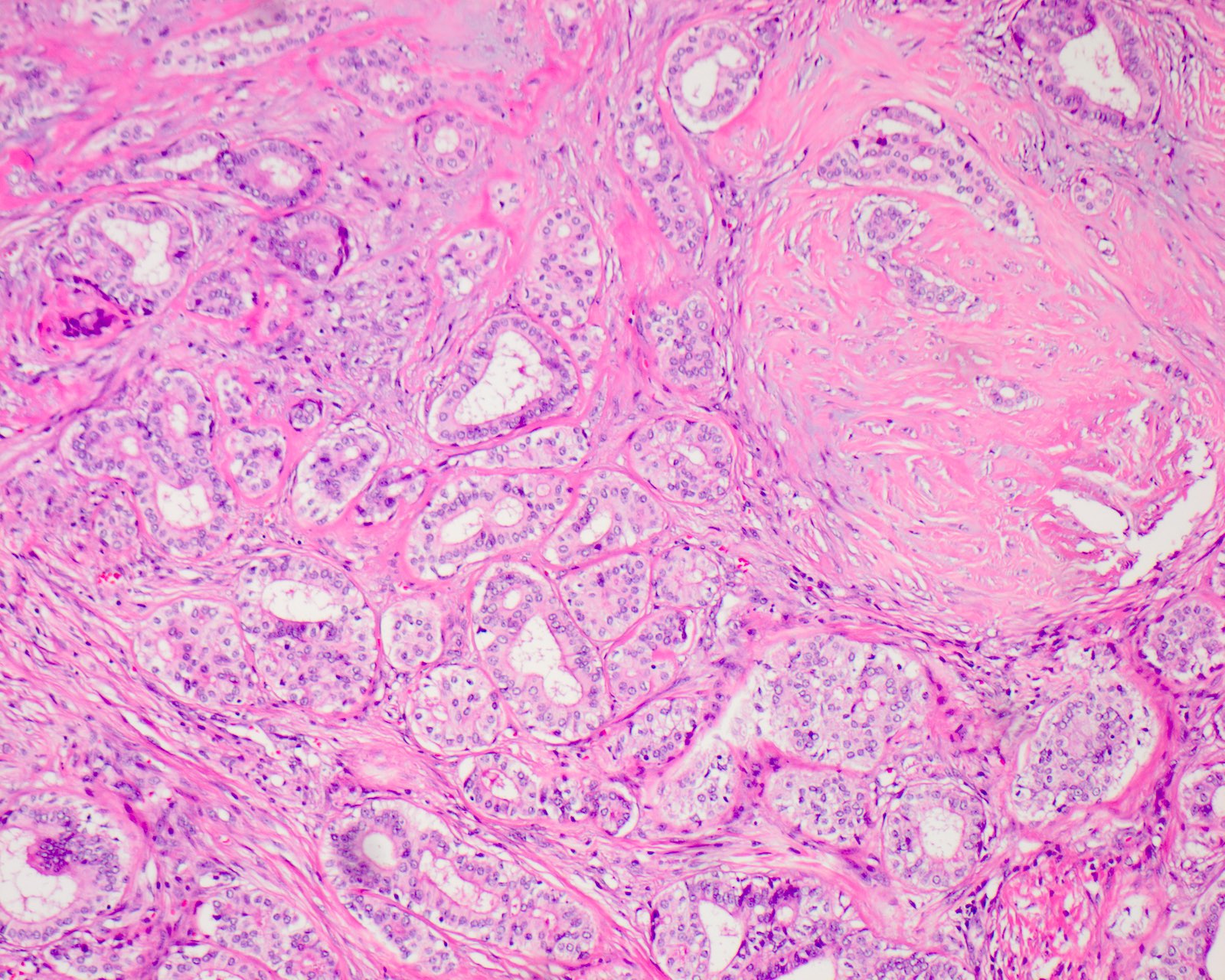
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Circumscribed with preservation of lobular architecture (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:939)
- Composed of irregularly distributed bilayered ducts and acini within a sclerotic stroma (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:630)
- Ducts range from small tubules to ectatic spaces; may contain secretory material or foamy macrophages (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:630)
- Ductal cells can have vacuolated, foamy, apocrine and mucous appearances (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:939)
- Hyperplastic ductal epithelium forming solid, microcystic and cribriform structures (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:e33)
- Small eosinophilic globules of basement membrane-like material in some cribriform areas (i.e. collagenous spherulosis) (Am J Surg Pathol 1996;20:161)
- Acini contain numerous, coarse eosinophilic, periodic acid-Schiff positive, intracytoplasmic granules (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:939)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Interpretation is challenging and frequently misdiagnosed
- Cohesive sheets and aggregates of cells
- Moderate to abundant finely granular eosinophilic cytoplasm
- Round to oval nuclei
- Evenly distributed chromatin with indistinct nucleoli (Diagn Cytopathol 2017;45:640)
Positive stains
- Epithelial cells:
- Cytokeratin (AE1 / AE3 and CAM5.2) (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:939)
- PR: 80% (Virchows Arch 2002;440:29)
- Myoepithelial cells:
- Acinar cells with coarse eosinophilic cytoplasm
- Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS), diastase resistant
- GCDFP-15 (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:939)
Negative stains
- Epithelial cells:
Electron microscopy description
- Cells have abundant cytoplasm filled by electron dense granules of various sizes consistent with zymogen granules (Virchows Arch 2002;440:29)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Genetic alterations in PI3K pathway
- PTEN mutations, PIK3CA mutations and PIK3R1 alterations (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:630)
Sample pathology report
- Parotid, right, excision:
- Sclerosing polycystic adenoma (see comment)
- Comment: Sections show a well demarcated nodule of densely collagenized stroma intermingling among a proliferation of acini and tubules. The latter are lined by cells which vary from vacuolated to foamy to apocrine to mucinous. Some ducts possess a hyperplastic epithelium with atypia reminiscent of ductal carcinoma in situ. Acini are remarkable for prominent eosinophilic intracytoplasmic granules which are highlighted upon PAS stain. No invasive growth is recognized.
Differential diagnosis
- Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis:
- Submandibular gland
- Fibrosis is not nodular
- Dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate with lymphoid follicles (Pathology 2016;48:93)
- Atrophic parenchyma without ductal hyperplasia or acinar cells with coarse PAS+ zymogen-like granules (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:e33)
- Polycystic (dysgenetic) disease:
- Bilateral
- Composed of a honeycombed lattice network of cysts replacing the entire parenchyma (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:154)
- No acinar proliferation and little fibrosis
- Characteristic congophilic laminated spheroliths (Histopathology 1987;11:953)
- Lacks recurrences
- Pleomorphic adenoma:
- Chondromyxoid stroma and prominent myoepithelial component
- Lacks acinar cells and definitive lobular growth pattern (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:e33)
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma:
- Invasive growth pattern
- Lacks scar-like hyalinized fibrous sclerosis
- Absence of acinar cells with prominent brightly eosinophilic granules
- More numerous mucous cells
- Lacks a myoepithelial cell layer (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:e33)
- Acinic cell carcinoma:
- Loss of lobular architecture
- Smaller PAS+ eosinophilic granules
- Less varied architecture and cell population
- Lacks a myoepithelial cell layer (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:e33)
- Intraductal carcinoma (low grade salivary duct carcinoma / low grade cribriform cystadenocarcinoma):
- More complex cystic pattern
- May have invasive growth (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:154)
- Lacks acinar cells with PAS+ granules (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:e33)
- Ductal cells lack foamy, vacuolated, mucous, clear, squamous and columnar cytomorphology (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:e33)
Practice question #1
A 50 year old woman presents with a slow growing parotid mass. Calponin and p63 immunostains highlighted a subset of the cells. Elsewhere in the lesion, acini containing large, brightly eosinophilic, periodic acid-Schiff positive, intracytoplasmic granules were identified. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Acinic cell carcinoma
- Sclerosing polycystic adenoma
- Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis
- Pleomorphic adenoma
Practice answer #1
Practice question #2
Which of the following immunohistochemical patterns support a diagnosis of sclerosing polycystic adenoma?
- p63+ in epithelial and myoepithelial cells; HER2 / neu+ and PR- in epithelial cells
- p63+ in myoepithelial cells; HER2 / neu- and PR+ in epithelial cells
- p63+ in epithelial and myoepithelial cells; HER2 / neu- and PR-
- p63+ in myoepithelial cells; HER2 / neu+ and PR+ in epithelial cells
Practice answer #2
B. p63+ in myoepithelial cells; HER2 / neu- and PR+ in epithelial cells
Comment Here
Reference: Sclerosing polycystic adenoma
Comment Here
Reference: Sclerosing polycystic adenoma