Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive stains | Negative stains | Flow cytometry description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Perry AM. Indolent T cell lymphoma of the GI tract. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphomanonBindolentTcell.html. Accessed May 14th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Clonal T cell lymphoproliferative disorder (T-LPD) that involves the mucosa of gastrointestinal (GI) tract
Essential features
- Rare, clinically indolent clonal T cell lymphoproliferative disease confined to the GI tract
- Can involve all GI sites, with small intestine and colon being most commonly involved
- Most patients are middle aged men, frequently presenting with diarrhea
- Nondestructive infiltrate of small, monotonous lymphoid cells that can be CD4+ / CD8- or CD4- / CD8+
- Poor response to chemotherapy; chronic course with frequent relapses and prolonged survival
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 9702/1 - indolent T cell lymphoproliferative disorder of the gastrointestinal tract
Epidemiology
- Rare, approximately 50 reported cases (Int J Surg Pathol 2019;27:102, Leuk Res 2020;91:106336)
- Most commonly diagnosed in fifth and sixth decade, with a broad age range (23 - 79 years)
- M:F = 2.4:1
- No specific risk factors identified
Sites
- Most commonly involves small intestine and colon but any GI site can be involved (Blood 2013;122:3599)
- Rarely associated with regional (abdominal) lymphadenopathy
- Occasional reports of bone marrow involvement
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Most common presenting symptoms are abdominal pain and diarrhea (Blood 2013;122:3599)
- Other symptoms / signs include vomiting, weight loss, signs of malabsorption
- Disease can clinically mimic inflammatory bowel disease
- Some patients had a history of Crohn's disease
- Chronic course with frequent relapses
- Prolonged survival with persistent disease
- 4 reported cases in the literature of progression to aggressive T cell lymphoma, with poor outcome (Int J Surg Pathol 2019;27:102)
Diagnosis
- Biopsy of affected GI site
Prognostic factors
- No specific prognostic factors identified
Case reports
- 42 year old man with indolent T cell lymphoproliferative disease of GI tract (Hum Pathol 2014;45:421)
- 59 year old woman with a history of diarrhea and weight loss (Br J Haematol 2014;167:265)
- 67 year old man presenting with lower abdominal pain and diarrhea, with multiple colon polyps (Dig Liver Dis 2004;36:218)
Treatment
- Poor response to conventional chemotherapy and immunotherapy; so far, there is no successful treatment
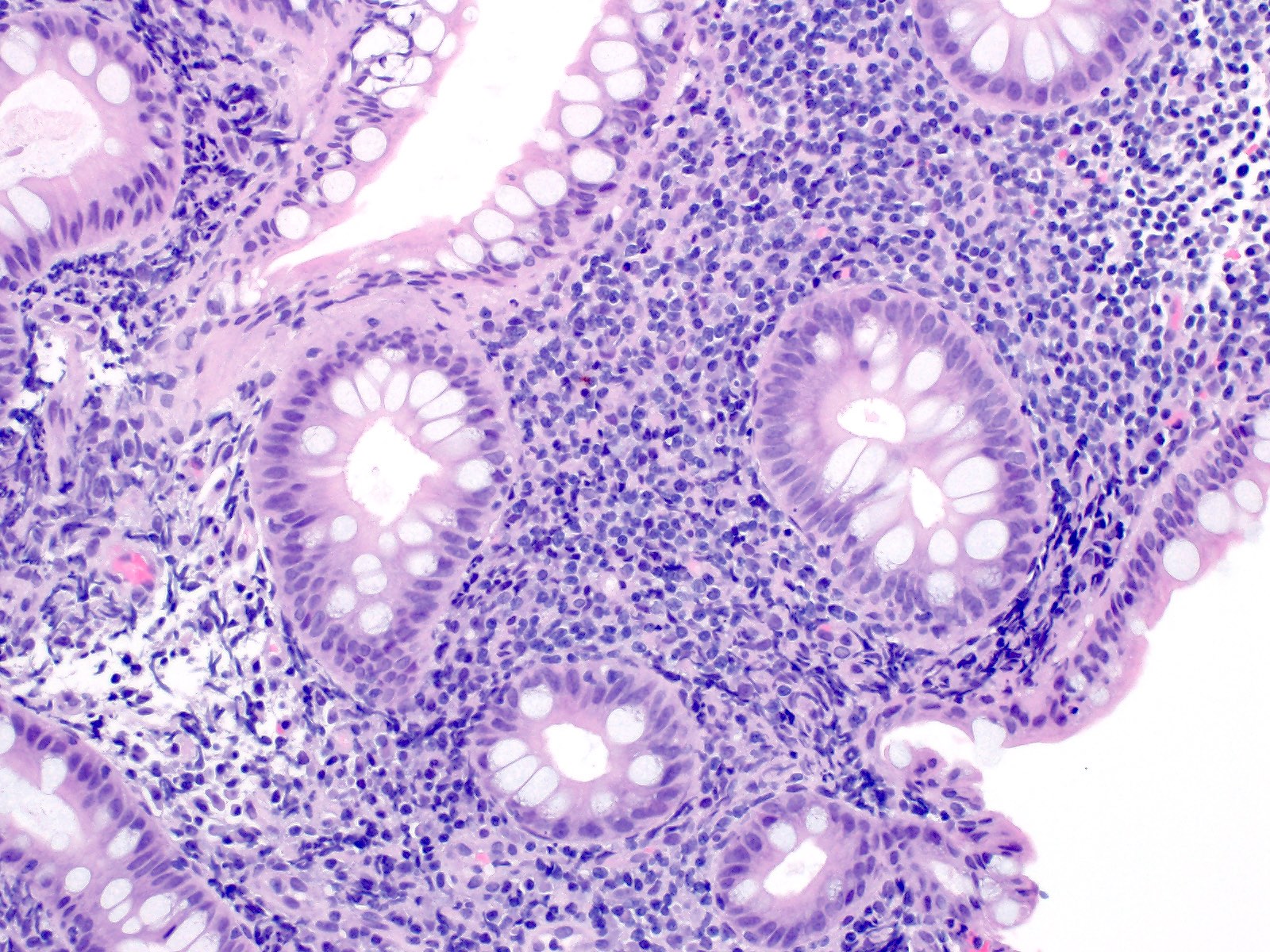
Microscopic (histologic) description
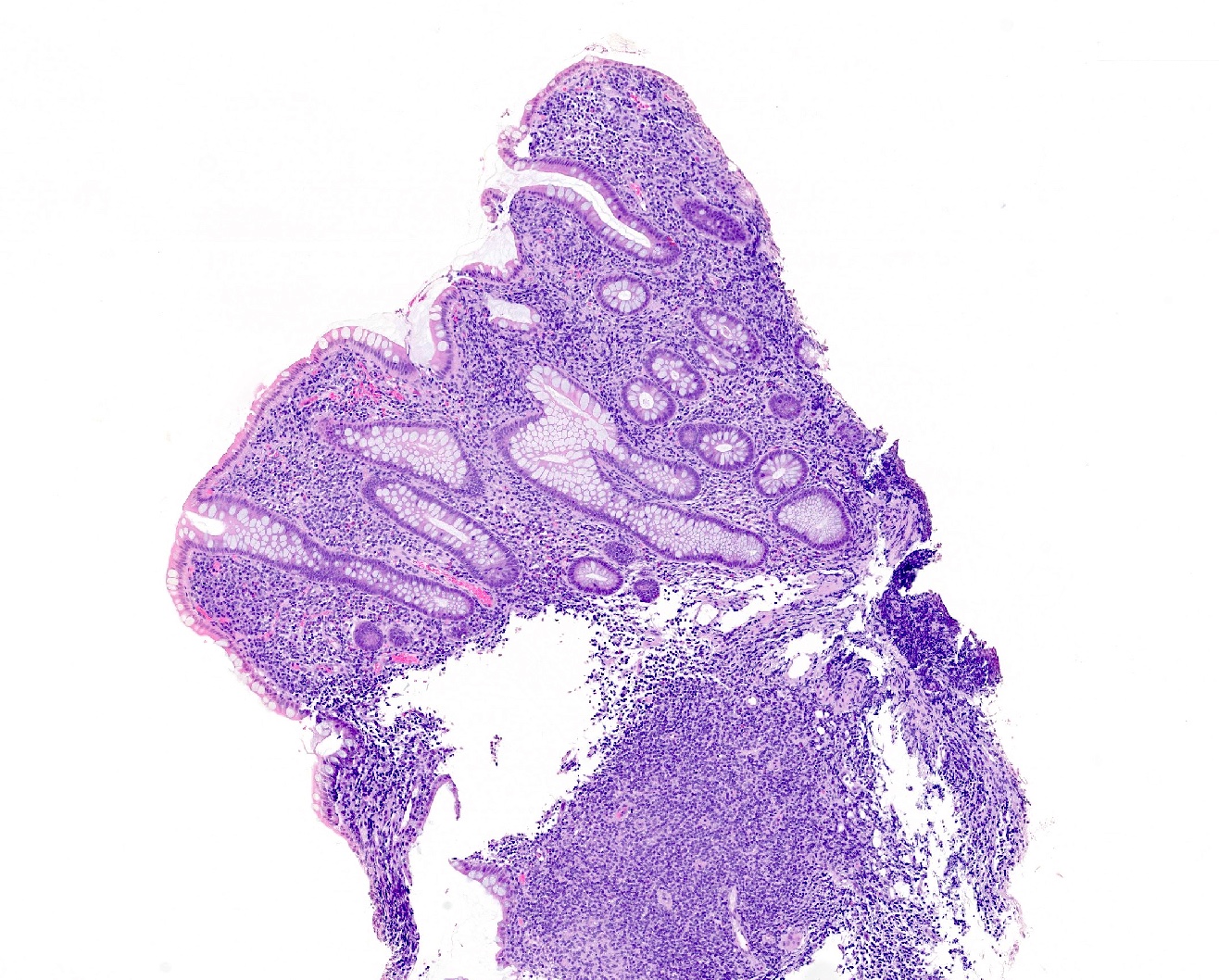
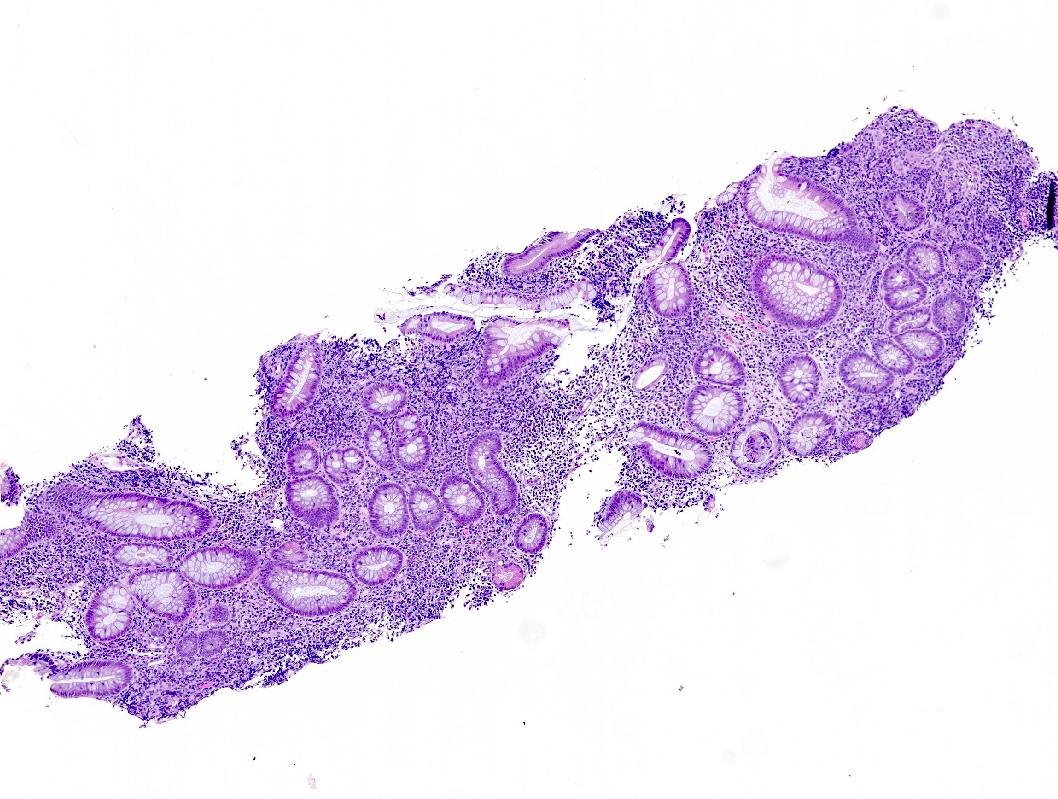
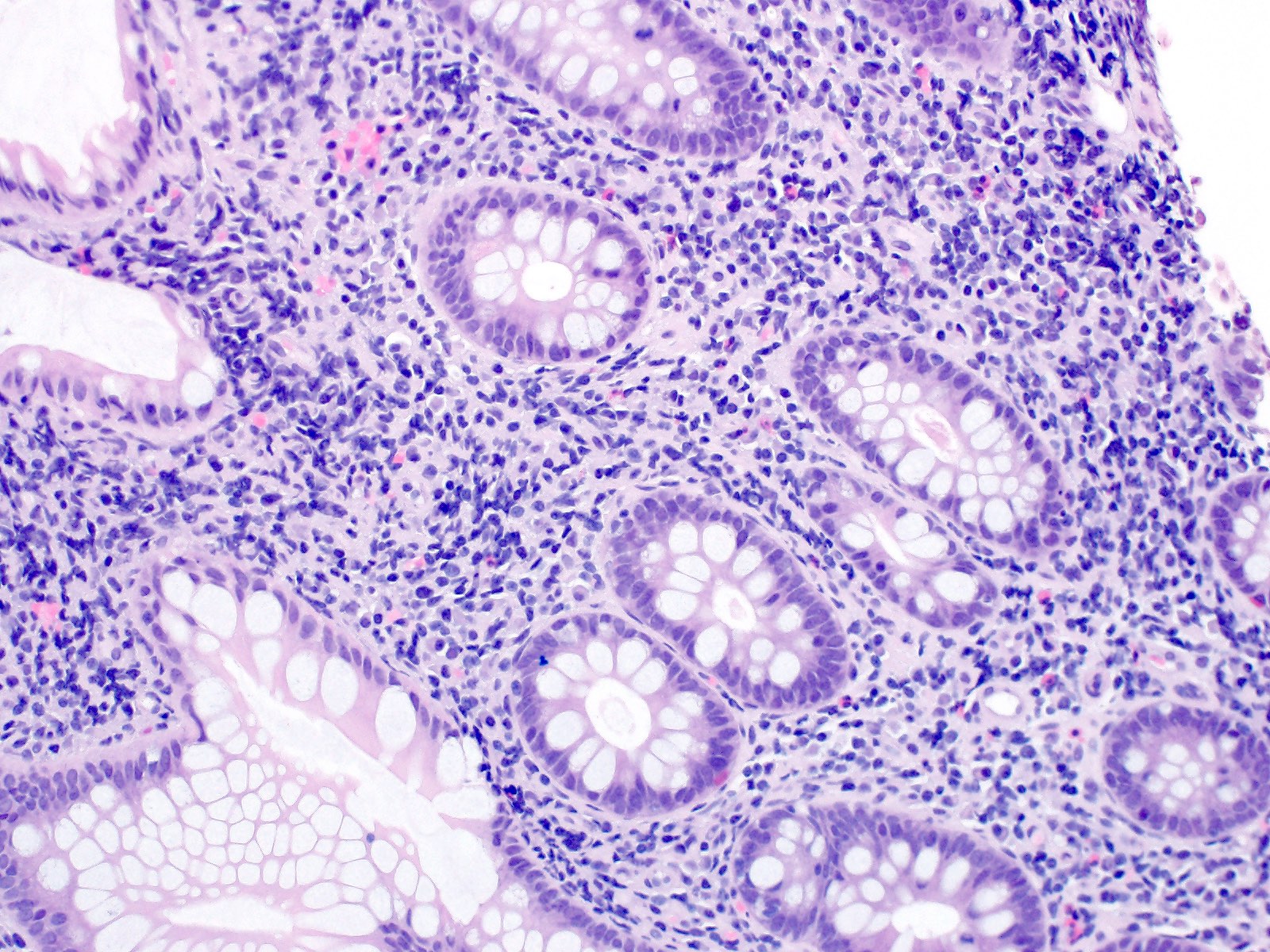
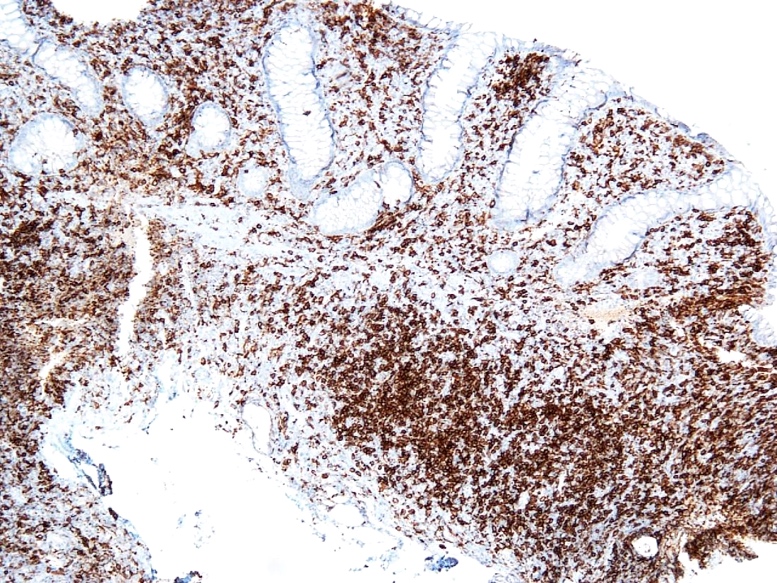
- Dense lymphoid infiltrate in the lamina propria / mucosa, occasionally extending into the submucosa (Blood 2013;122:3599)
- Infiltrate is nondestructive; adjacent glands are displaced and distorted
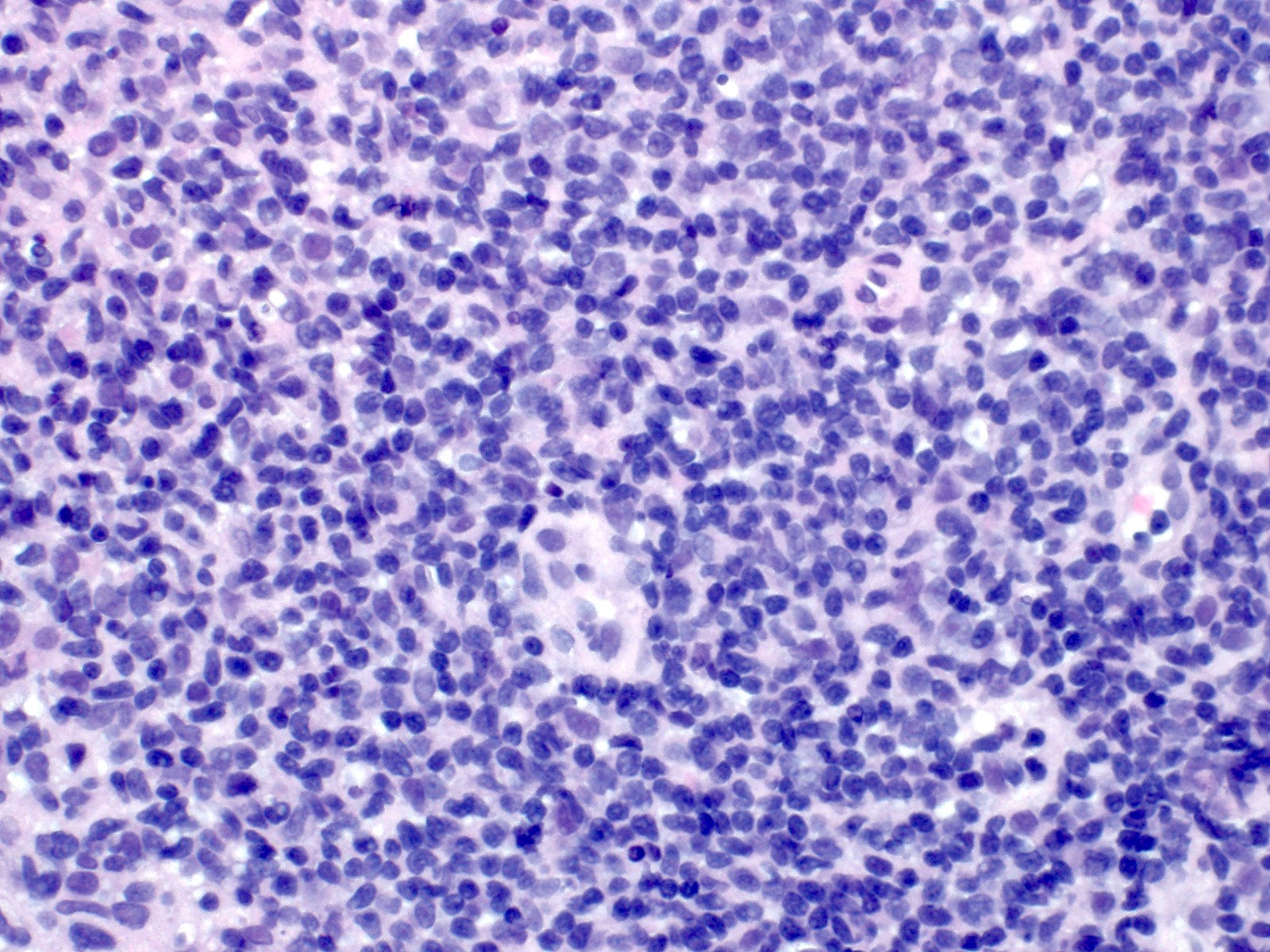
- Infiltrate is composed of monomorphic small lymphoid cells with scant pale cytoplasm, slightly irregular nuclear contours, mature chromatin, inconspicuous nucleoli
- Cases with oral involvement manifest as ulcers with an underlying lymphocytic infiltrate
- Typically no necrosis, ulceration or angiocentricity / angiodestruction (Blood 2013;122:3599)
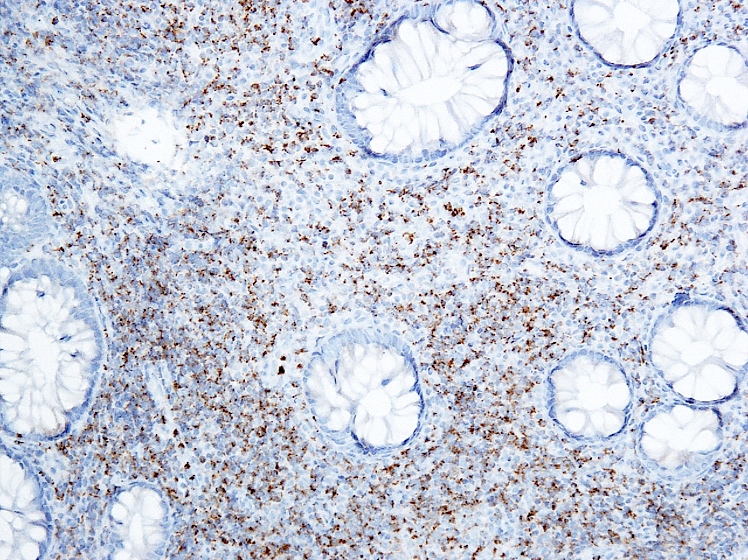
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
Flow cytometry description
- Immunophenotype similar to mature T lymphocytes
- Aberrant loss of CD7 is rarely seen
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Clonal TCR gene rearrangements present by PCR testing
- t(9;17)(p24.1;q21.2) STAT3-JAK2 fusion found as recurrent abnormality, mainly in CD4+ cases (Blood 2018;131:2262)
- Genetic alterations are common, including recurrent mutations and novel rearrangements, often involving JAK-STAT pathway genes (Haematologica 2020;105:1895)
Differential diagnosis
- Intestinal T cell lymphoma:
- Both enteropathy associated T cell lymphoma (EATL) and monomorphic epitheliotropic intestinal T cell lymphoma (MEITL) show infiltrative and destructive lymphoid infiltrates
- In contrast, indolent T-LPD shows a nondestructive infiltrate
- In EATL, the adjacent noninvolved intestinal mucosa shows morphological features of enteropathy, including villous blunting and intraepithelial lymphocytes but indolent T-LPD cases are not associated with celiac sprue or adjacent morphological evidence of enteropathy
- Celiac sprue:
- In cases of indolent T-LPD that involve duodenum, differential diagnosis includes celiac sprue
- Distribution of lymphocytes in indolent T-LPD is not characteristic for celiac sprue (no clustering at the tip)
- There are no other histologic features of sprue (i.e. villous atrophy, hyperplastic and elongated crypts, increase in plasma cells in lamina propria)
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD):
- Crypt distortion is present in indolent T-LPD
- However, other morphological features that are usually present in IBD are absent, including cryptitis, crypt abscesses, basal plasmacytosis and Paneth cell hyperplasia
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 52 year old man presents with a 10 year history of intermittent abdominal pain and diarrhea, which usually resolves in several weeks without treatment. Colonoscopy revealed erythematous irregular mucosa throughout the entire length of colon. Biopsy was taken and infiltrate is demonstrated in the image. The infiltrate involves mainly lamina propria, it is nondestructive and is positive for CD8 and TIA1 immunohistochemical stains. Molecular study was performed and showed clonal T cell gene rearrangement. Which of the following is true about this disease?
- Infiltrate is destructive and frequently involves the entire thickness of bowel wall
- It is successfully treated with CHOP chemotherapy
- Most cases are CD4- / CD8-
- Oral cavity is the most common site of involvement
- Subset of cases show STAT3-JAK2 fusion
Board review style answer #1
E. Subset of cases show STAT3-JAK2 fusion
Comment Here
Reference: Indolent T lymphoproliferative disease of the GI tract
Comment Here
Reference: Indolent T lymphoproliferative disease of the GI tract