Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Muller KE. Lymphocytic / diabetic mastitis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastlymphocyticmastitis.html. Accessed May 14th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Histologic triad of keloidal type fibrosis, lymphocytic inflammation and epithelioid myofibroblasts
- Associated with type I (insulin dependent) diabetes or other autoimmune diseases
Essential features
- Young to middle aged women presenting with breast mass(es)
- Histologic triad of keloidal type fibrosis, lymphocytic infiltrates and epithelioid stromal myofibroblasts
- Associated with type I (insulin dependent) diabetes or other autoimmune diseases
Terminology
- Lymphocytic mastopathy / diabetic mastopathy
- Sclerosing lymphocytic mastitis / lobulitis
- Diabetic fibrous breast disease
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Uncommon, < 1% benign breast disease (Arch Surg 2000;135:1190)
- Usually women, may occur in men, premenopausal, average age 45 years (Ann Plast Surg 2017;78:471, Am J Clin Pathol 2000;113:541, Arch Surg 2000;135:1190)
- Often associated with longstanding type I diabetes (insulin dependent) or other autoimmune disease (Hashimoto thyroiditis, Graves disease, pernicious anemia, rheumatoid arthritis, Sjögren syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus) but may occur in type II diabetes or nondiabetic patients (Diabetes Care 2002;25:121, Hum Pathol 1994;25:819, Hum Pathol 1992;23:780, Ann Plast Surg 2017;78:471)
Sites
- Breast
Pathophysiology
- Unknown
- Theories include:
- Hyperglycemia leads to stromal matrix expansion and accumulation of glycosylation end products and a B cell inflammatory response (Hum Pathol 1992;23:780)
- Immunologic response to exogenous insulin (Hum Pathol 1994;25:819)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Associated with insulin dependent diabetes (type I > II), autoimmune disorders and endocrine disorders
- Firm, palpable, nontender, mobile masses or diffuse nodularity at presentation common (Am J Clin Pathol 2000;113:541, Ann Plast Surg 2017;78:471)
Diagnosis
- Needle core biopsy or surgical excision with histologic examination
Laboratory
- Correlate with serologic markers for diabetes and other autoimmune diseases
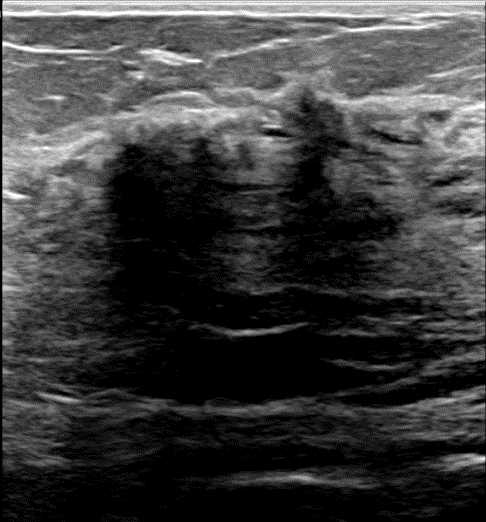
Radiology description
- Mammography: frequently negative; may show asymmetric density or dense breast tissue, discrete mass not seen (Breast J 2007;13:607)
- Ultrasound: irregular shaped mass(es), indistinct margins, parallel orientation to chest wall, hypoechogenicity, posterior shadowing (Clin Imaging 2019;53:204, Breast J 2000;6:183)
Prognostic factors
- Recurrence rates vary; 10 - 30% (Am J Clin Pathol 2000;113:541, Ann Plast Surg 2017;78:471)
- No associated increased risk of lymphoma (Mod Pathol 2003;16:223)
Case reports
- 29 year old woman with diabetic mastopathy (Cureus 2020;12:e7003)
- 32 year old woman with bilateral diabetic mastopathy (Ann Plast Surg 2017;78:471)
- 37 year old woman with lymphocytic mastitis mimicking breast carcinoma (Malays J Med Sci 2013;20:83)
- 47 year old woman with lymphocytic mastitis and invasive carcinoma (BJR Case Rep 2016;2:20150234)
- 50 year old woman with metabolic syndrome and lymphocytic mastitis (Breast Care (Basel) 2012;7:493)
Treatment
- Conservative management
- Surgical excision (partial mastectomy, mastectomy) an option if symptomatic, especially if multiple and bilateral masses present (Breast J 2006;12:559, Ann Plast Surg 2017;78:471)
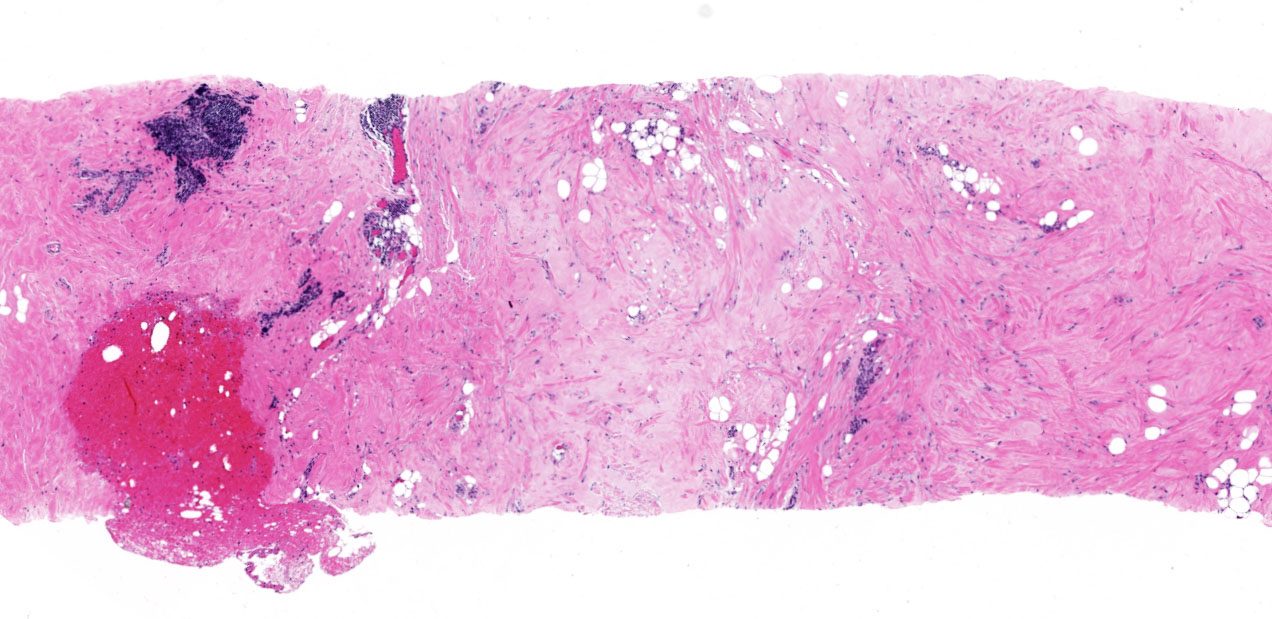
Gross description
- Firm, ill defined, homogenous, tan-white or white-gray cut surface
- Size variable, up to 6.0 cm
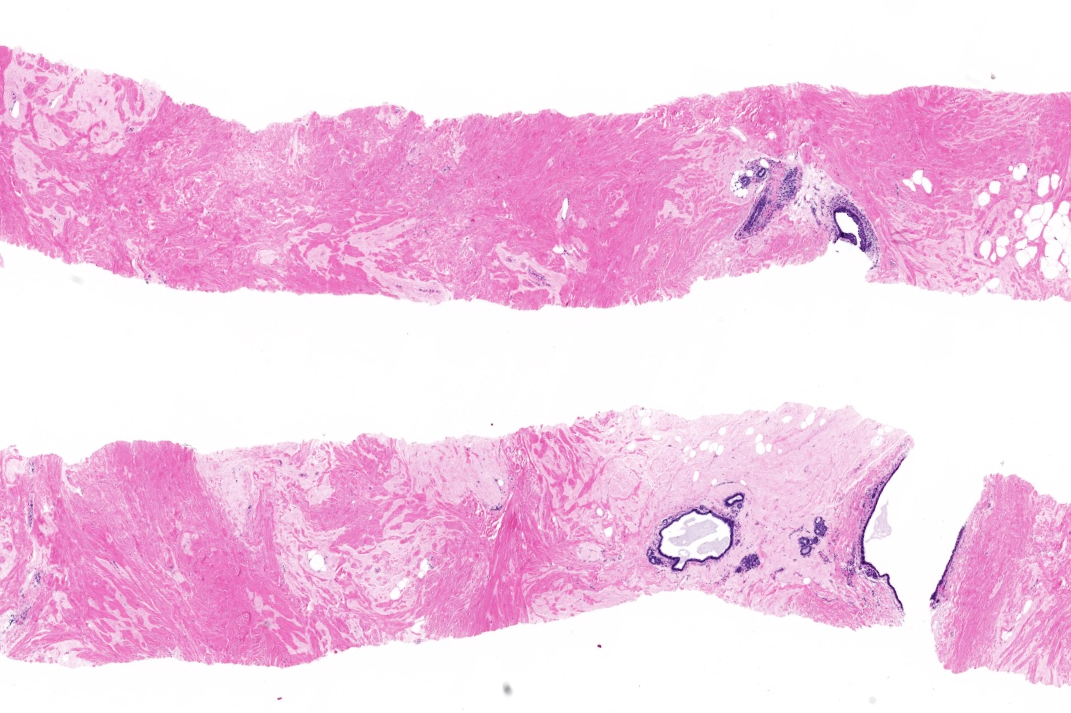
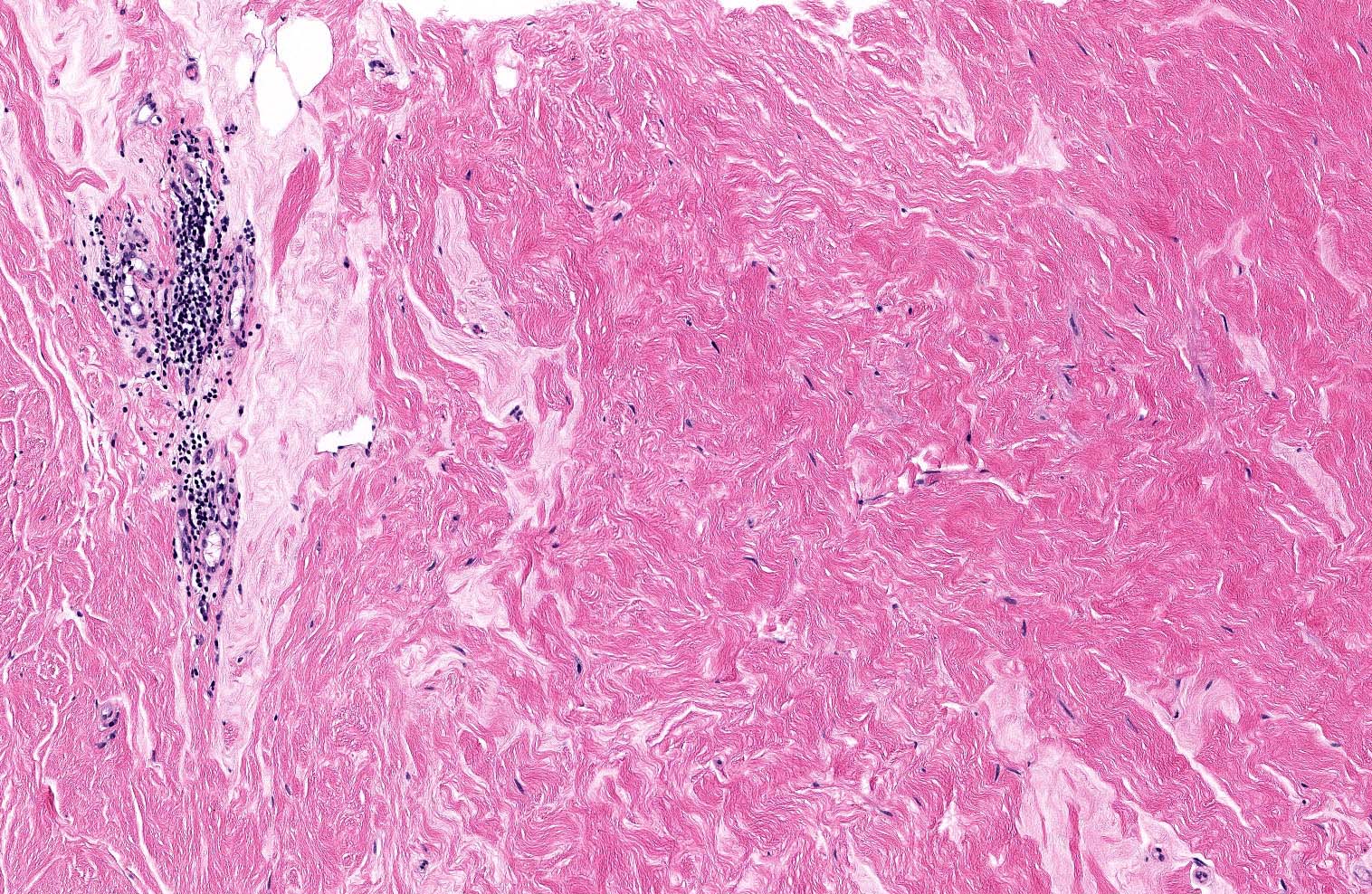
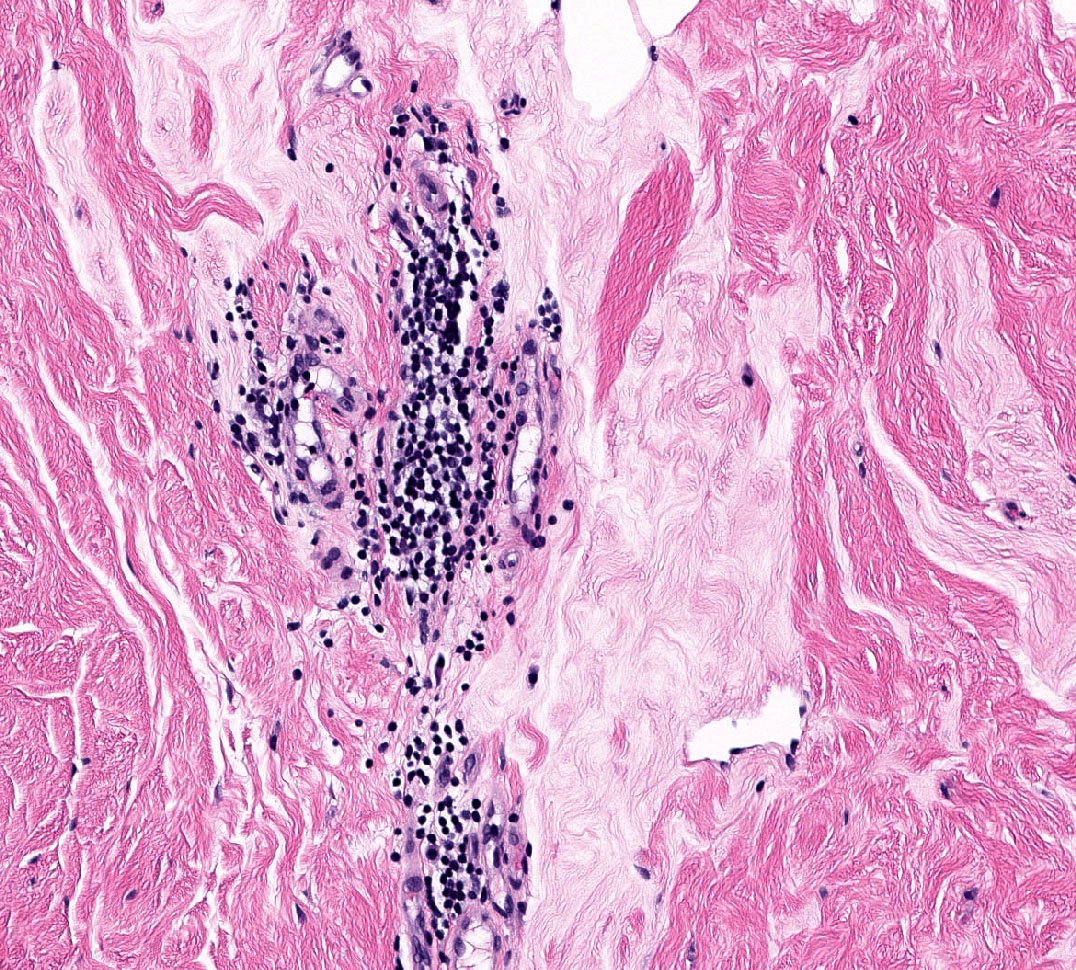
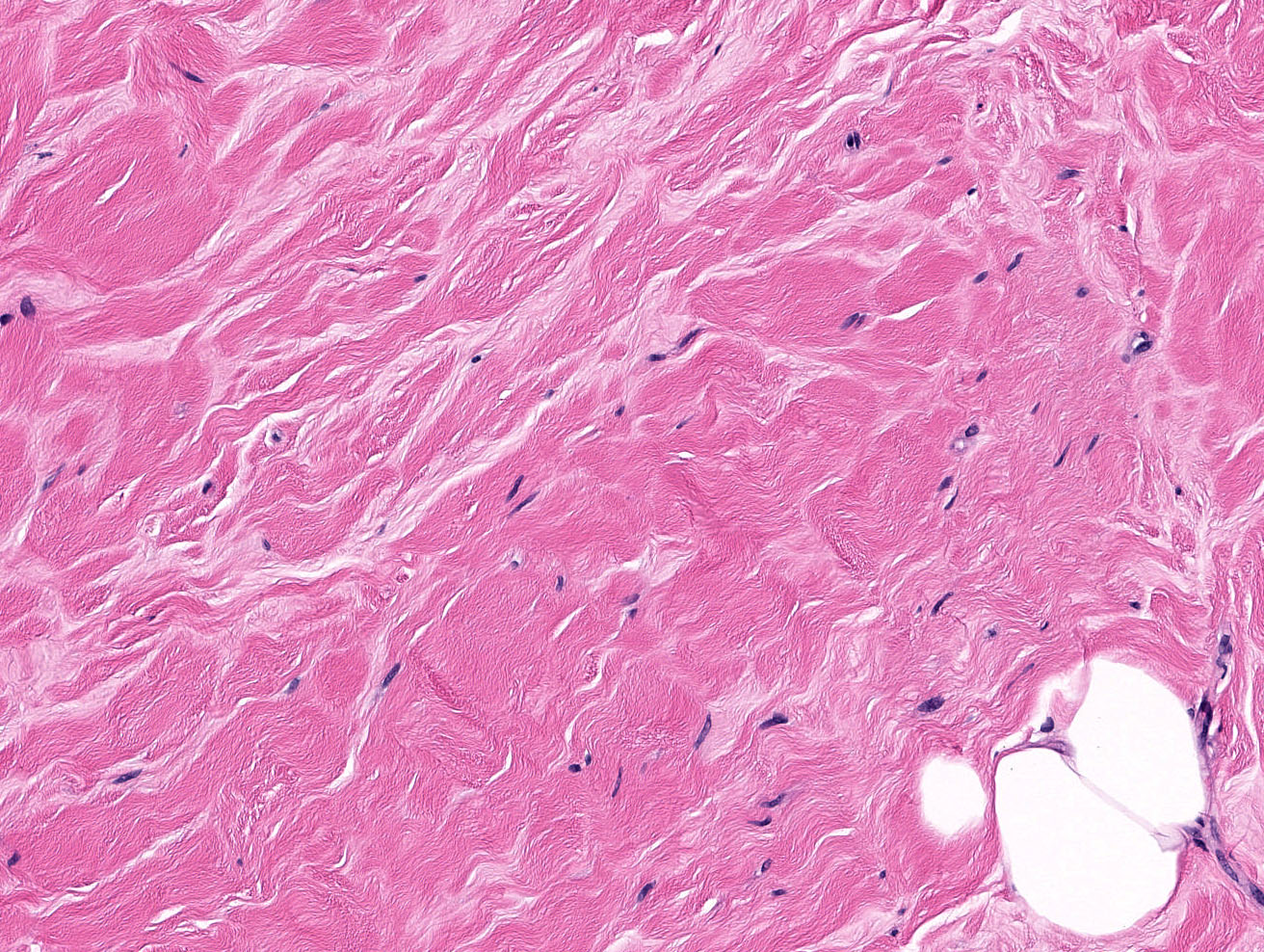
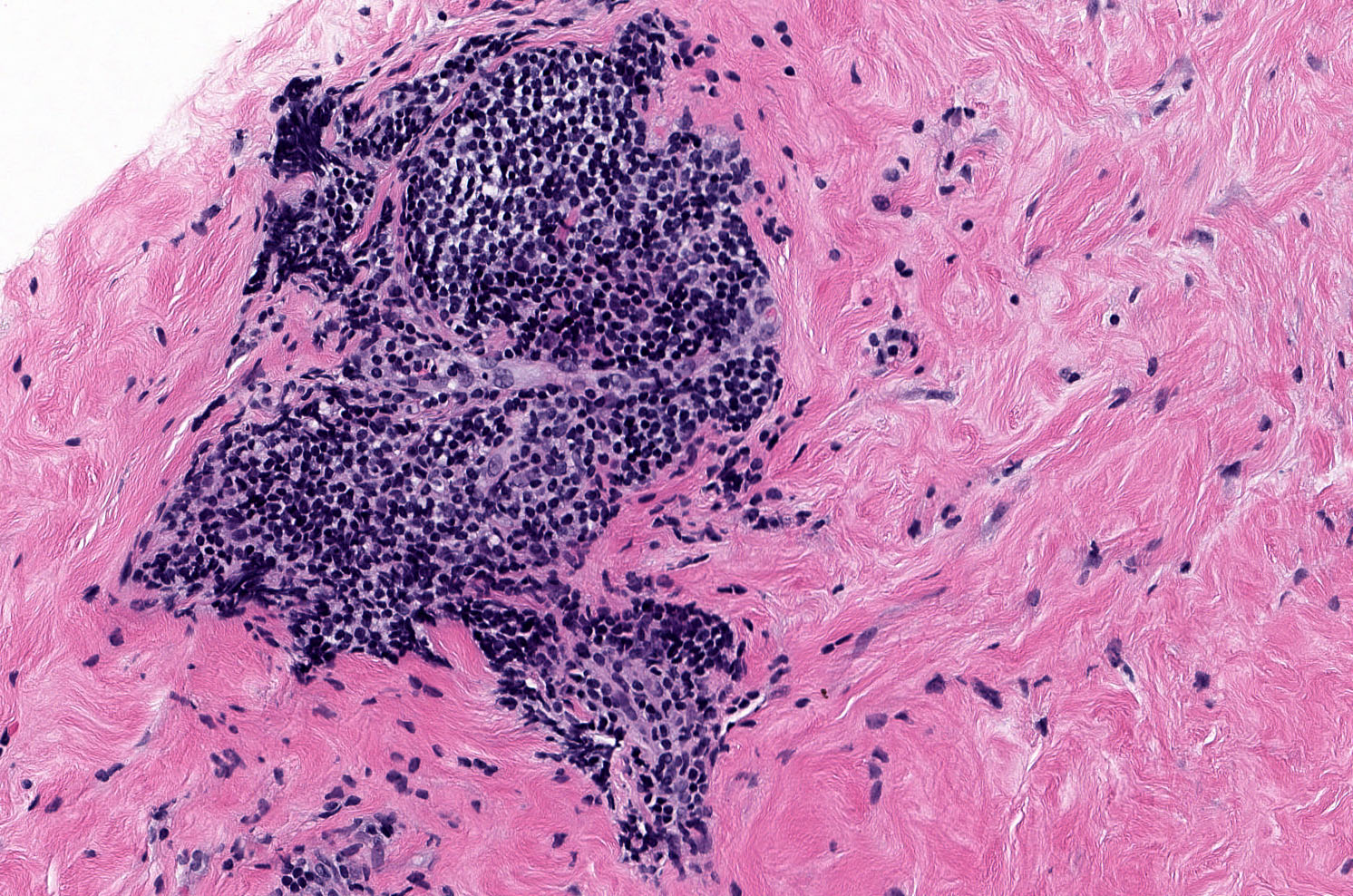
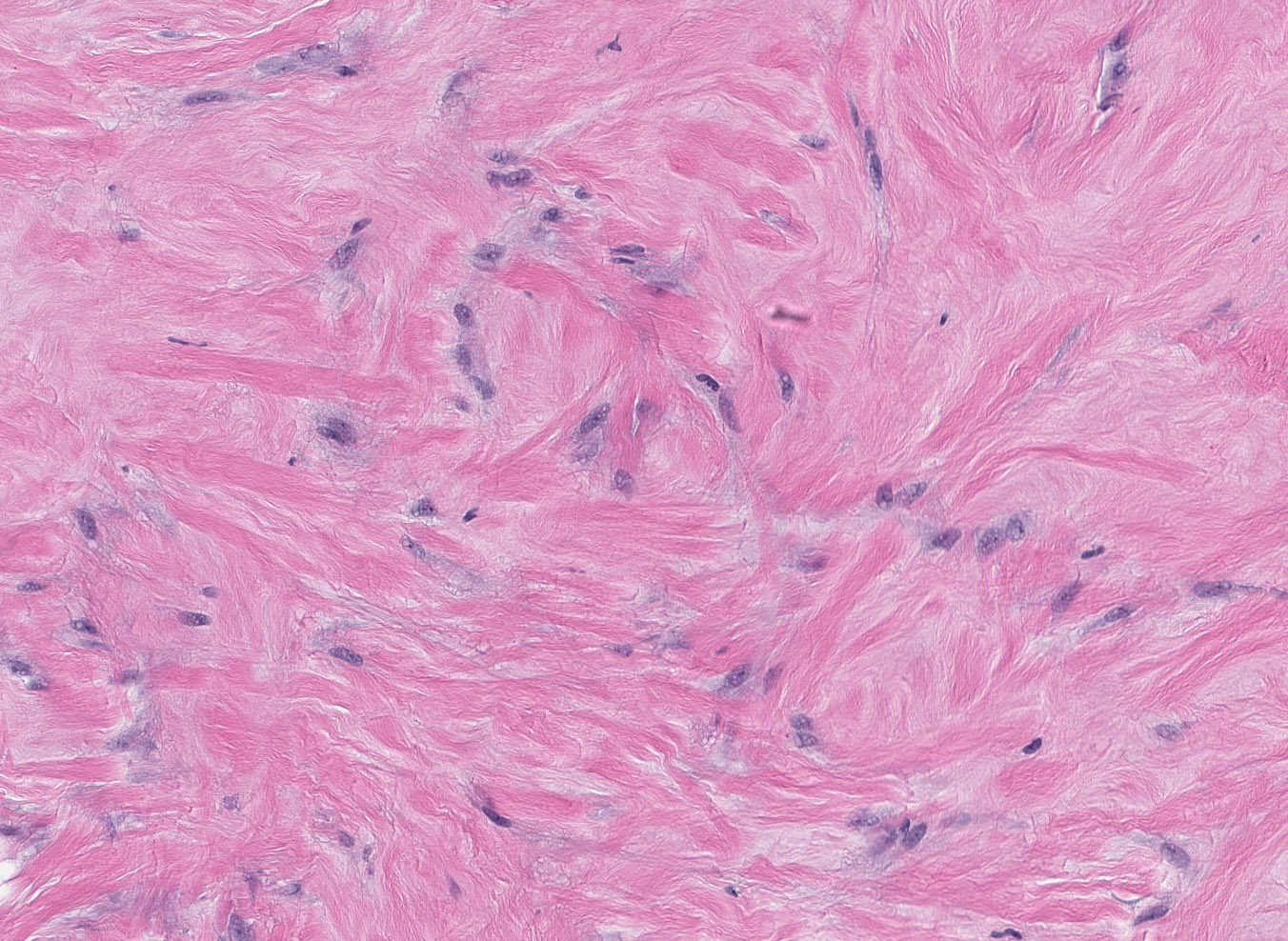
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Triad of dense, keloidal type fibrosis, periductal, perilobular and perivascular lymphocytic infiltrates and epithelioid stromal myofibroblasts
- Epithelioid characteristics of myofibroblasts include enlarged cells with round to polygonal nuclei, prominent nucleoli and abundant cytoplasm
- Epithelioid features of myofibroblasts may be subtle or absent
- Stromal mitoses absent
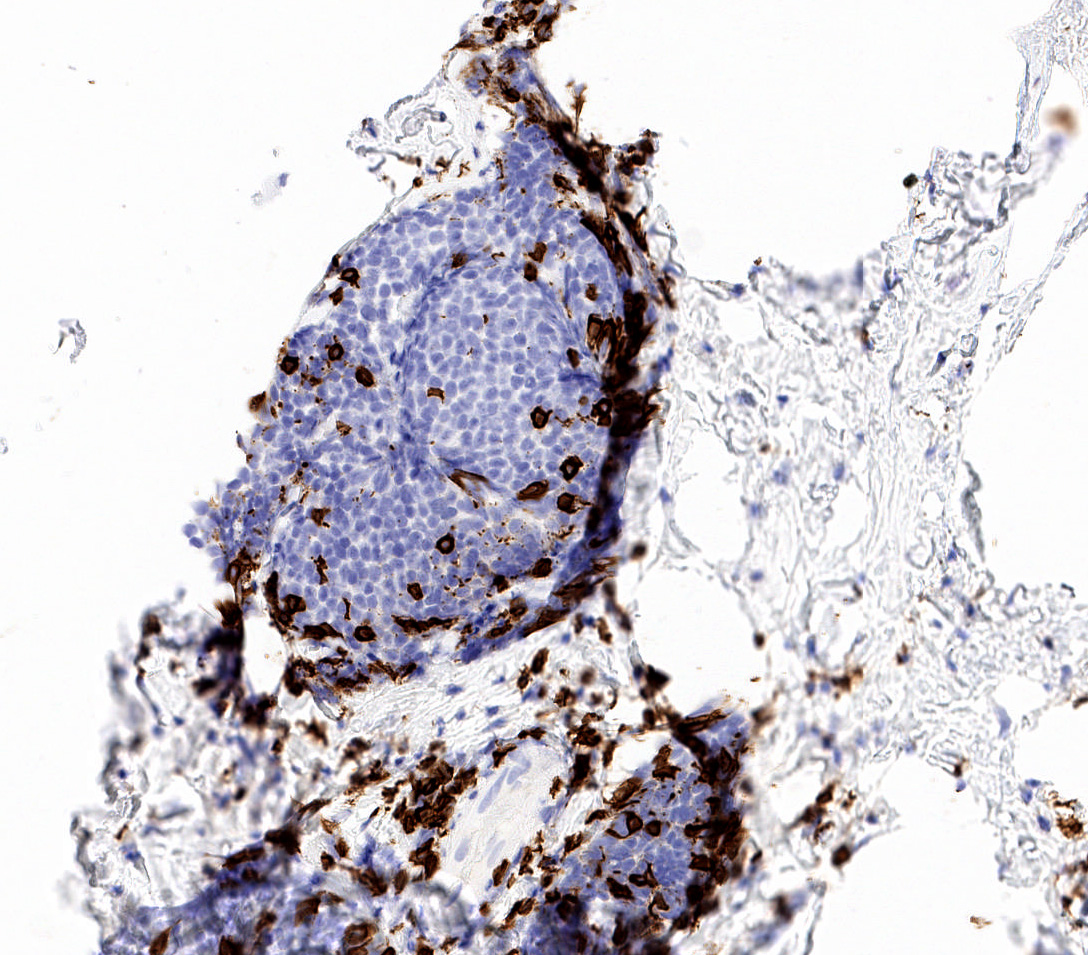
- Mature lymphocytic infiltrates are nonclonal, predominantly B lymphocytes and lack germinal centers (Mod Pathol 2003;16:223)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Clusters of ductal cells, lymphocytes and epithelioid fibroblasts in fragments of dense connective tissue (Acta Cytol 1997;41:1349)
- Cytology usually insufficient for diagnosis (Arch Surg 2000;135:1190)
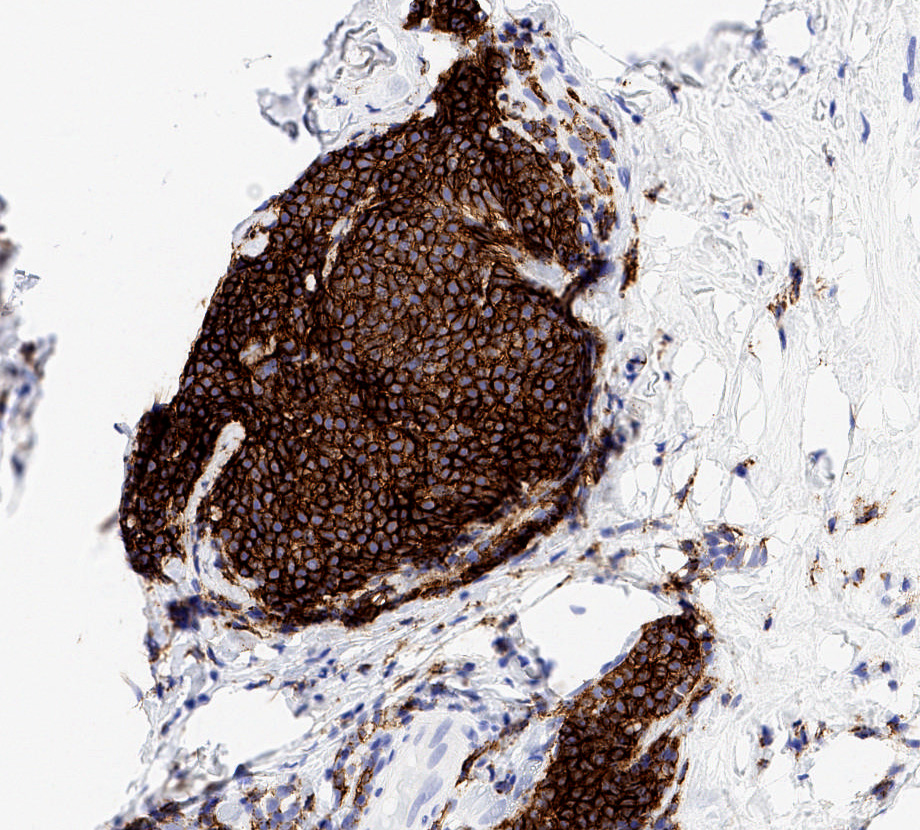
Positive stains
Negative stains
- Cytokeratins, p63 (useful in differential of invasive carcinoma)
- Nuclear beta catenin (useful in differential of fibromatosis)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Lymphocytes are not clonal (Mod Pathol 2003;16:223)
Sample pathology report
- Left breast, needle core biopsy:
- Breast tissue with dense stromal keloidal type fibrosis, epithelioid myofibroblasts and perilobular lymphocytic inflammation (see comment)
- Comment: The histologic findings are compatible with lymphocytic / diabetic mastopathy in the appropriate clinical context.
Differential diagnosis
- Invasive carcinoma:
- Epithelioid myofibroblasts may be mistaken for carcinoma tumor cells
- Supportive of invasive carcinoma: cytokeratin positive, gland formation if invasive ductal carcinoma, mitoses, background of in situ carcinoma, lacks keloid-like fibrosis
- Low grade fibromatosis-like metaplastic carcinoma:
- Cytokeratin and p63 positive, infiltrative, background of in situ carcinoma, rare mitoses
- Fibromatosis:
- Beta catenin nuclear expression
- Lacks keloid-like fibrosis
- Amyloid:
- Stromal amyloid is amorphous and acellular, lacks epithelioid myofibroblasts
- Congo red positive
- MALT Lymphoma:
- Clonal B cells
- Lacks keloid-like fibrosis and epithelioid myofibroblasts
Additional references
Board review style question #1
For the breast stroma shown, which of the following is true?
- Lesion is associated with increased risk of developing lymphoma
- Lymphocytes are predominantly T cells and are clonal
- Patient may have insulin dependent diabetes or an autoimmune disorder
- Spindle cells in the stroma show beta catenin nuclear expression
Board review style answer #1
C. Patient may have insulin dependent diabetes or an autoimmune disorder
Comment Here
Reference: Lymphocytic / diabetic mastitis
Comment Here
Reference: Lymphocytic / diabetic mastitis
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is true regarding diabetic / lymphocytic mastopathy?
- All patients have a history of diabetes
- Characteristic histologic triad includes dense keloid-like fibrosis, epithelioid myofibroblasts and periductal, perilobular and perivascular lymphocytic inflammation
- If surgically excised, these lesions never recur
- Typical mammographic finding is an infiltrative mass lesion
Board review style answer #2
B. Characteristic histologic triad includes dense keloid-like fibrosis, epithelioid myofibroblasts and periductal, perilobular and perivascular lymphocytic inflammation
Comment Here
Reference: Lymphocytic / diabetic mastitis
Comment Here
Reference: Lymphocytic / diabetic mastitis