Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Udoh AI, Qiu S. Inflammatory aural / otic polyp. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/earinflammatoryotic.html. Accessed May 6th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Proliferation of granulation tissue with chronic inflammatory cells in response to a longstanding inflammatory process usually lacking epithelial proliferation
- Commonly associated with cholesteatoma (80% of cases)
Essential features
- Proliferation of granulation tissue with chronic inflammatory cells in response to a longstanding inflammatory process
- Associated with cholesteatoma in 80% of cases
- More common in children but occurs in all ages
- May perforate tympanic membrane and appear to originate from the external auditory canal; with time, may destroy ossicles
- The otologic tissue specimen submitted as polyp should be evaluated with the knowledge of the spectrum of diseases known to clinically mimic aural polyp disease (see Diagrams / tables)
Terminology
- Aural polyp
- Otic polyp
- Inflammatory aural polyp
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Uncommon lesion that usually affects young ages
- M:F = 2:1
- May perforate tympanic membrane and appear to originate from the external auditory canal; with time, may destroy ossicles
- More common in children but occurs in all ages
- Usually associated with cholesteatoma (in at least 80% of cases) (Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2018;70:505)
- May be associated with chronic otitis media (Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp 2003;54:161)
Sites
- Usually arises from the middle ear
- May extend into the external auditory canal if tympanic membrane perforated
Pathophysiology
- Complex interplay of inflammatory processes, tissue remodeling and cellular proliferation within the ear canal or middle ear
- Chronic inflammation and irritation of the mucosal lining of the ear, often secondary to conditions such as chronic otitis media or repeated trauma, lead to the accumulation of inflammatory cells, cytokines and growth factors within the affected tissues; this triggers a cascade of cellular responses, including fibroblast activation, angiogenesis and tissue remodeling, which contribute to the development of otic polyps
Etiology
- Chronic otitis media with or without cholesteatoma may be associated with the formation of an aural polyp, which is usually confined to the middle ear and external auditory canal (EAC) but may sometimes protrude outside the EAC
Clinical features
- The most common symptoms of an aural polyp are otorrhea, diminished hearing and a visible mass in the ear; otalgia and bleeding or sensation of mass are far less common
- In longstanding cases, partial or complete destruction of the ossicles may occur
- Usually confined to the middle ear and external auditory canal (EAC) but may sometimes protrude outside the EAC
- Commonly unilateral, bilateral cases can occur
- May rarely occur in association with aspirin exacerbated respiratory disease (AERD), formerly Samter triad (rhinosinusitis with polyposis, asthma and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug [NSAID] intolerance) (Otol Neurotol 2012;33:774, Wenig: Atlas of Head and Neck Pathology, 3rd Edition, 2015)
- Aural polyps in association with AERD / Samter triad are often bilateral (Head Neck Pathol 2018;12:328)
Diagnosis
- High resolution computed tomography (HRCT) shows loss of pneumatization of mastoid air cells
- In large polyps completely obstructing the external ear, radiographic studies are an invaluable aid in identifying the origin of the polyp
- Key histologic findings: a well circumscribed mass with granulation tissue, mixed inflammation and abundant plasma cells
Radiology description
- See Diagnosis
Prognostic factors
- In the absence of an infectious cause, local surgical excision is curative
- Recurrence is more common in the setting of AERD / Samter triad
Case reports
- 39 year old man with a history of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and bilateral aural polyps (J Laryngol Otol 2002;116:288)
- 52 year old woman with a history of chronic rhinosinusitis with sinonasal polyps found to have bilateral aural polyps (Int J Otolaryngol 2009;2009:464958)
- 57 year old woman with a history of AERD / Samter triad and bilateral otorrhea (Otol Neurotol 2012;33:774)
Treatment
- Surgical excision
- Possibly mastoid exploration
Gross description
- Polypoid, soft to rubbery, tan-white to pink-red lesion
Microscopic (histologic) description
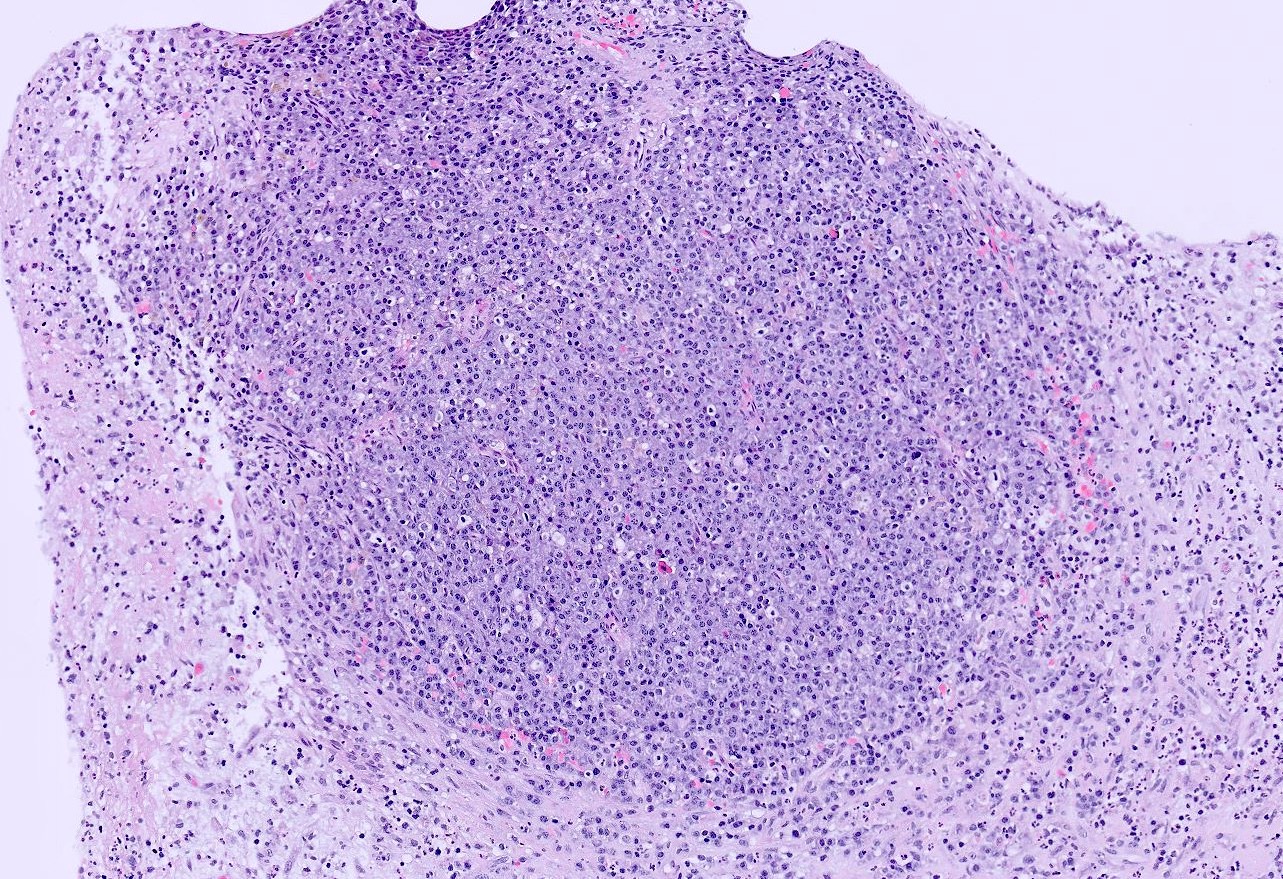
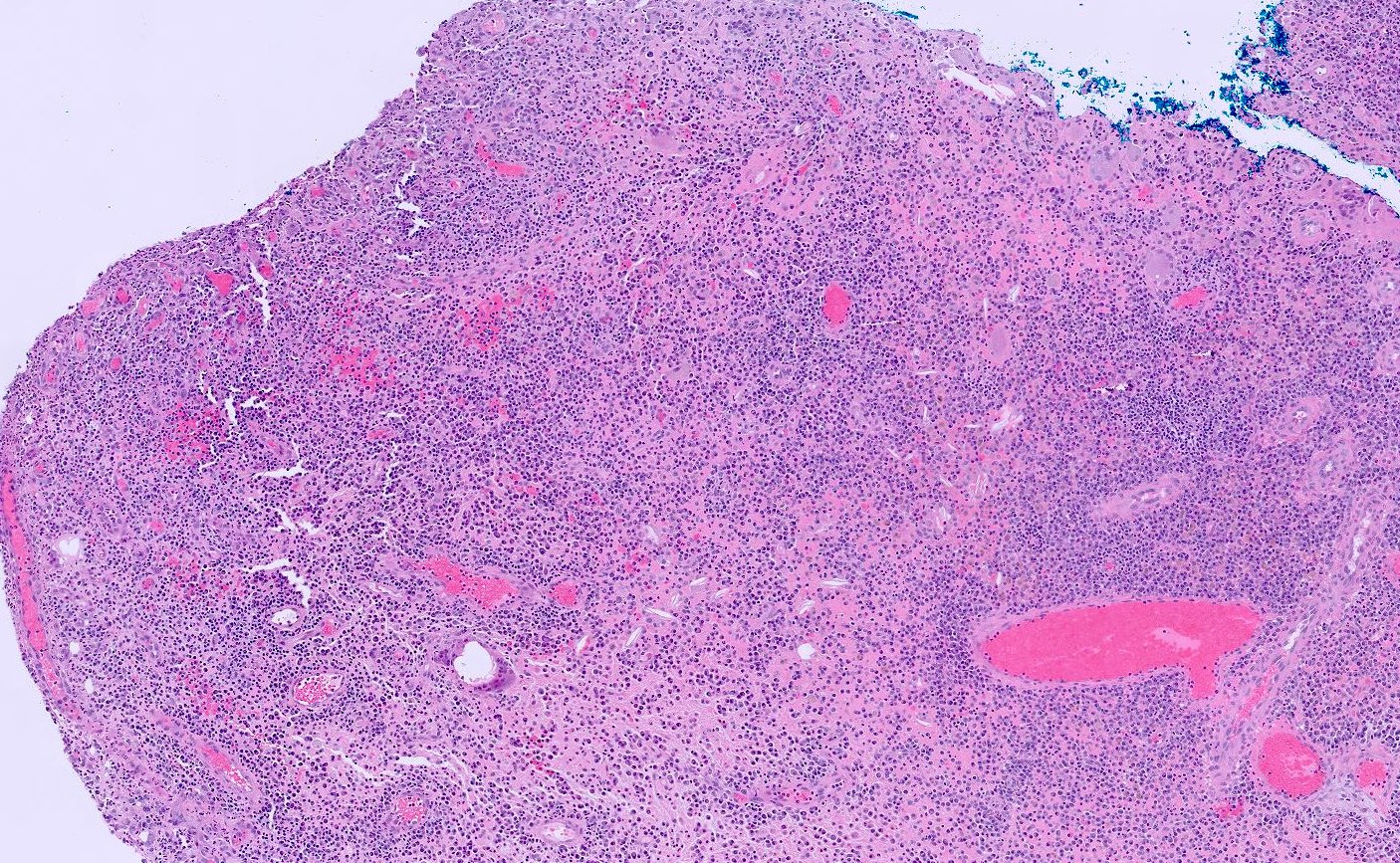
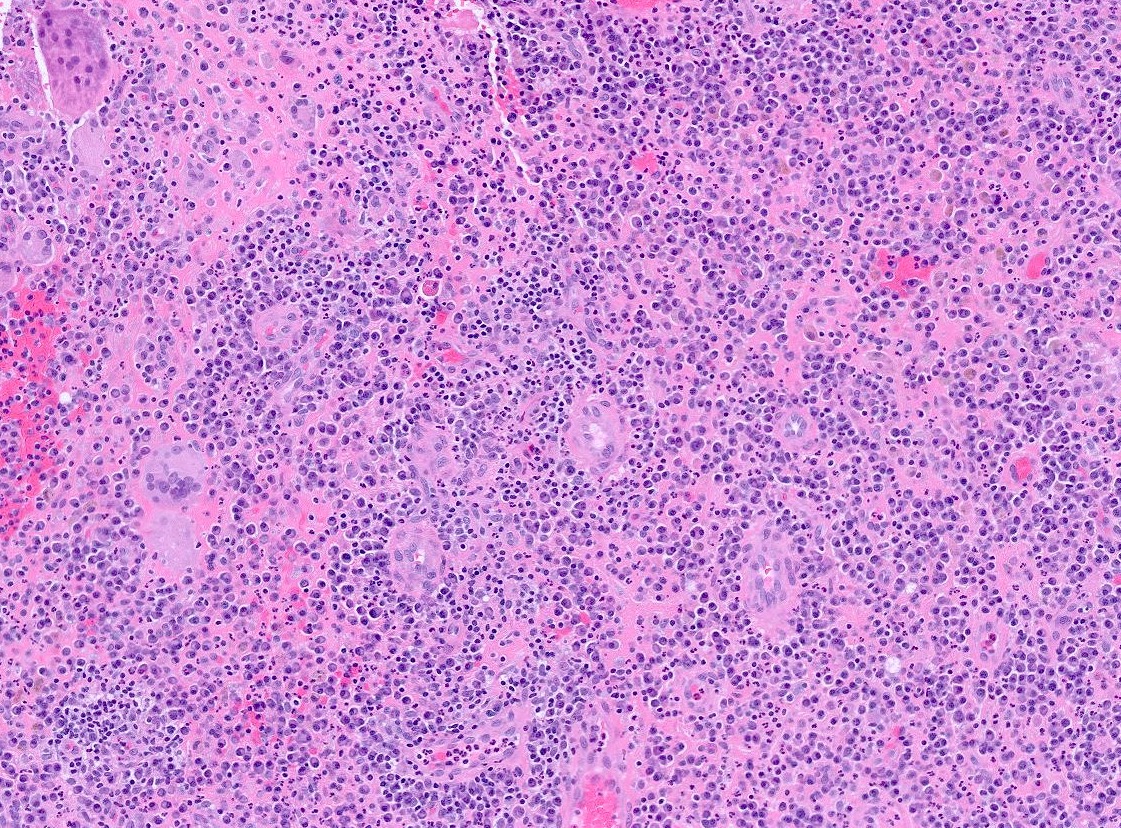
- Cellular polypoid mass primarily consisting of a chronic inflammatory cell infiltrate, including mature lymphocytes, plasma cells, histiocytes and eosinophils
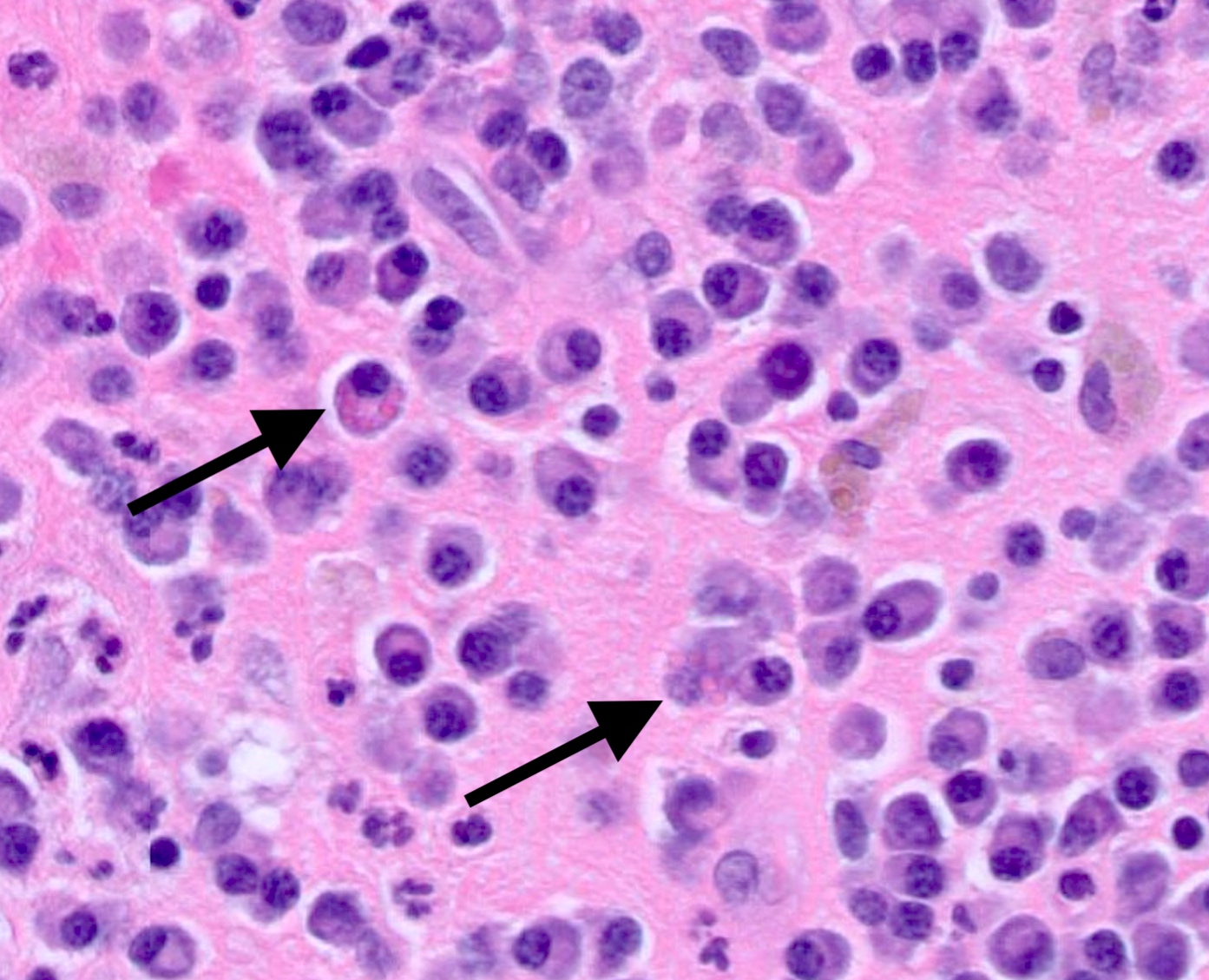
- Relative to the plasma cells, Russell bodies or Mott cells containing large eosinophilic immunoglobules can be seen and are indicative of a benign plasma cell proliferation
- Polymorphonuclear leukocytes may be present
- Stroma includes granulation tissue varying in appearance from edematous and richly vascularized to fibrous with a decreased vascular component
- Multinucleated giant cells may be present
- Cholesterol granulomas and calcific debris (tympanosclerosis) may be present
- When the epithelium is present, it appears as pseudostratified columnar or cuboidal cells with or without cilia and may demonstrate squamous metaplasia (Wenig: Atlas of Head and Neck Pathology, 3rd Edition, 2015)
- Finding of granulation tissue reaction and keratin in an aural polyp is a good predictor for the presence of a cholesteatoma or cholesteatomatous chronic otitis media (Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp 2003;54:161)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Nonspecific
- Cytokeratin positive in epithelial cells within the otic polyp
Negative stains
- Special stains for microorganisms (fungi, spirochetes, mycobacteria, protozoa and parasites) are negative but are indicated to rule out an infectious cause
Videos
Infected aural polyp ear wax removal
Sample pathology report
- Soft tissue, middle ear, left, biopsy:
- Inflammatory aural / otic polyp
- Soft tissue, middle ear, left, polypectomy:
- Otic polyp
- No malignancy identified
Differential diagnosis
- Paraganglioma:
- Well differentiated nonepithelial neoplasm
- Found in the middle ear in 30% of cases
- Histologically, classic organoid (zellballen) or nesting pattern oval chief cells
- Uniform nuclei with dispersed chromatin
- Expresses neuroendocrine markers but negative for cytokeratins
- Cholesteatoma:
- Chronic inflammation without a polypoid mass
- Keratinizing squamous epithelium with keratin debris
- Prominent granular layer and inflammation
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis:
- Middle ear neuroendocrine tumor:
- Rare, benign middle ear epithelial neoplasm
- Tumor is white, gray or red-brown, with soft or rubbery consistency
- Histologically, the tumor exhibits cuboidal to columnar cells with distinct cell borders and eosinophilic cytoplasm
- Neoplastic cells coexpress keratins (AE1 / AE3, CAM5.2) and neuroendocrine markers
- Plasmacytoma:
- Similar dense plasma cell component
- Not commonly found in the middle ear
- Monoclonal by immunocytochemistry or in situ hybridization of kappa or lambda light chains
- Does not contain mature plasma cells or Russell bodies
Board review style question #1
Which of the following statements regarding otic polyps is true?
- Composed primarily of keratinized squamous epithelium
- Often associated with a history of cholesteatoma
- They commonly arise from the tympanic membrane
- Typically present with sudden sensorineural hearing loss
- Usually become malignant if untreated
Board review style answer #1
B. Often associated with a history of cholesteatoma. Otic polyps are associated with cholesteatoma in 80% of cases.
Answer C is incorrect because otic polyps commonly arise from the mucosa of the middle ear or external auditory canal, rather than the tympanic membrane itself.
Answer E is incorrect because otic polyps are typically benign growths composed of granulation tissue, inflammatory cells and sometimes hypertrophic mucosa. Malignant transformation has not been reported in the literature.
Answer D is incorrect because otic polyps may lead to conductive hearing loss due to obstruction of the external auditory canal or middle ear space. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss is not a typical presentation of otic polyps.
Answer A is incorrect because otic polyps are primarily composed of granulation tissue, which consists of fibroblasts, blood vessels and inflammatory cells, such as lymphocytes and plasma cells. Keratinized squamous epithelium is not a predominant component of otic polyps.
Comment Here
Reference: Inflammatory aural / otic polyp
Comment Here
Reference: Inflammatory aural / otic polyp
Board review style question #2
A 55 year old woman presents with recurrent episodes of unilateral otorrhea, hearing loss and a sensation of fullness in the affected ear. Examination reveals a pink, fleshy mass protruding into the external auditory canal. Histopathological examination demonstrates hyperplastic squamous epithelium and numerous dilated vessels infiltrated by chronic inflammatory cells. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- Cerumen impaction
- Cholesteatoma
- Otic polyp
- Otitis externa
- Squamous cell carcinoma
Board review style answer #2
C. Otic polyp. It arises from the middle ear but may extend into the external auditory canal if perforated. The mass appears fleshy and is composed of granulation tissue, mixed inflammation and abundant plasma cells.
Answer E is incorrect because squamous cell carcinoma typically presents as a nonhealing ulcer often associated with bleeding, pain and hearing loss.
Answer A is incorrect because while cerumen impaction can cause symptoms such as hearing loss and fullness in the ear, it typically does not present as a fleshy mass. Additionally, cerumen impaction does not demonstrate the histopathological findings described in the question stem, such as hyperplastic squamous epithelium and dilated vessels infiltrated by chronic inflammatory cells.
Answer B is incorrect because cholesteatoma is a benign but locally destructive growth of keratinizing squamous epithelium with keratin debris and inflammation. It is typically not described as a fleshy mass.
Answer D is incorrect because otitis externa, also known as swimmer's ear, refers to inflammation of the external auditory canal. While otitis externa can present with otorrhea, hearing loss and a sensation of fullness in the ear, it typically does not manifest as a fleshy mass.
Comment Here
Reference: Inflammatory aural / otic polyp
Comment Here
Reference: Inflammatory aural / otic polyp