Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Choy B. Adult cystic nephroma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/kidneytumorcysticnephroma.html. Accessed September 16th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Uncommon multilocular cystic tumor without a grossly appreciable solid component
- Classified as part of mixed epithelial and stromal tumor (MEST) family with MEST at opposite end of spectrum, by the 2016 World Health Organization (WHO) Classification
Essential features
- Mainly occurs in adult women
- Well circumscribed, multicystic tumors with no apparent solid component
- Versus MEST - variable solid and cystic components
- Noncommunicating cysts lined by single layer epithelium separated by septa with hypocellular fibrous to hypercellular spindle cell stroma
- Most benign but very rare local recurrence and malignant transformation
- Stromal cells typically positive for ER / PR
Terminology
- Renal epithelial and stromal tumor (REST) (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:489)
- Multilocular cystic nephroma
- Multilocular renal cyst (term not recommended, does not reflect neoplastic nature of entity)
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8959/0 - benign cystic nephroma
Epidemiology
- M:F = 1:8 (Semin Diagn Pathol 1998;15:2, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2004;128:1404, Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:489, Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1591)
- Age, peak incidence 50 - 60 years (Semin Diagn Pathol 1998;15:2, Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1591)
Sites
- Confined to kidney
- Located at poles of kidney, close to hilum or closely associated with pelvicalyceal system (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2004;128:1404, Urology 2008;71:1142)
Etiology
- Possible role of hormones in pathogenesis (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:489)
Clinical features
- Often incidentally found
- Others present with abdominal / flank pain, hematuria, urinary tract infection, palpable mass (Urology 2008;71:1142)
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis by histologic examination of tissue
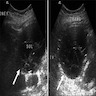
Radiology description
- Ultrasound (Urol Ann 2013;5:13, J Kidney Cancer VHL 2017;4:1):
- Multiple anechoic spaces traversed by thin septa and without vascularity
- Rarely, calcifications seen in septa
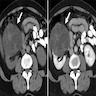
- CT (Urology 2008;71:1142, Urol Ann 2013;5:13):
- Well circumscribed, fluid density mass with multiple septations
- Enhancement of septations following contrast but contrast does not accumulate within individual loculi and calcification may be seen
- Most classified into Bosniak category III
- MRI (Urol Ann 2013;5:13):
- T1 hypointensity and T2 hyperintensity
Prognostic factors
- Mostly benign with rare local recurrence reported (Int J Surg Pathol 2015;23:238)
- Rarely aggressive
- Sarcomatous transformation (Semin Diagn Pathol 1998;15:2, Hum Pathol 2007;38:1432)
- Carcinomatous transformation (Int Braz J Urol 2006;32:187)
Case reports
- 48 year old woman with adult cystic nephroma (Turk J Urol 2018;44:373)
- 57 year old woman with local recurrence of adult cystic nephroma (Int J Urol 2004;11:329)
- 59 year old woman with ureteral invagination of multilocular cystic nephroma (adult cystic nephroma) (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7:5271)
- 65 year old woman with cystic renal cell carcinoma arising from multilocular cystic nephroma (adult cystic nephroma) (Int Braz J Urol 2006;32:187)
- 66 year old man with adult cystic nephroma (Rare Tumors 2015;7:5860)
Treatment
- Nephron sparing surgery whenever feasible
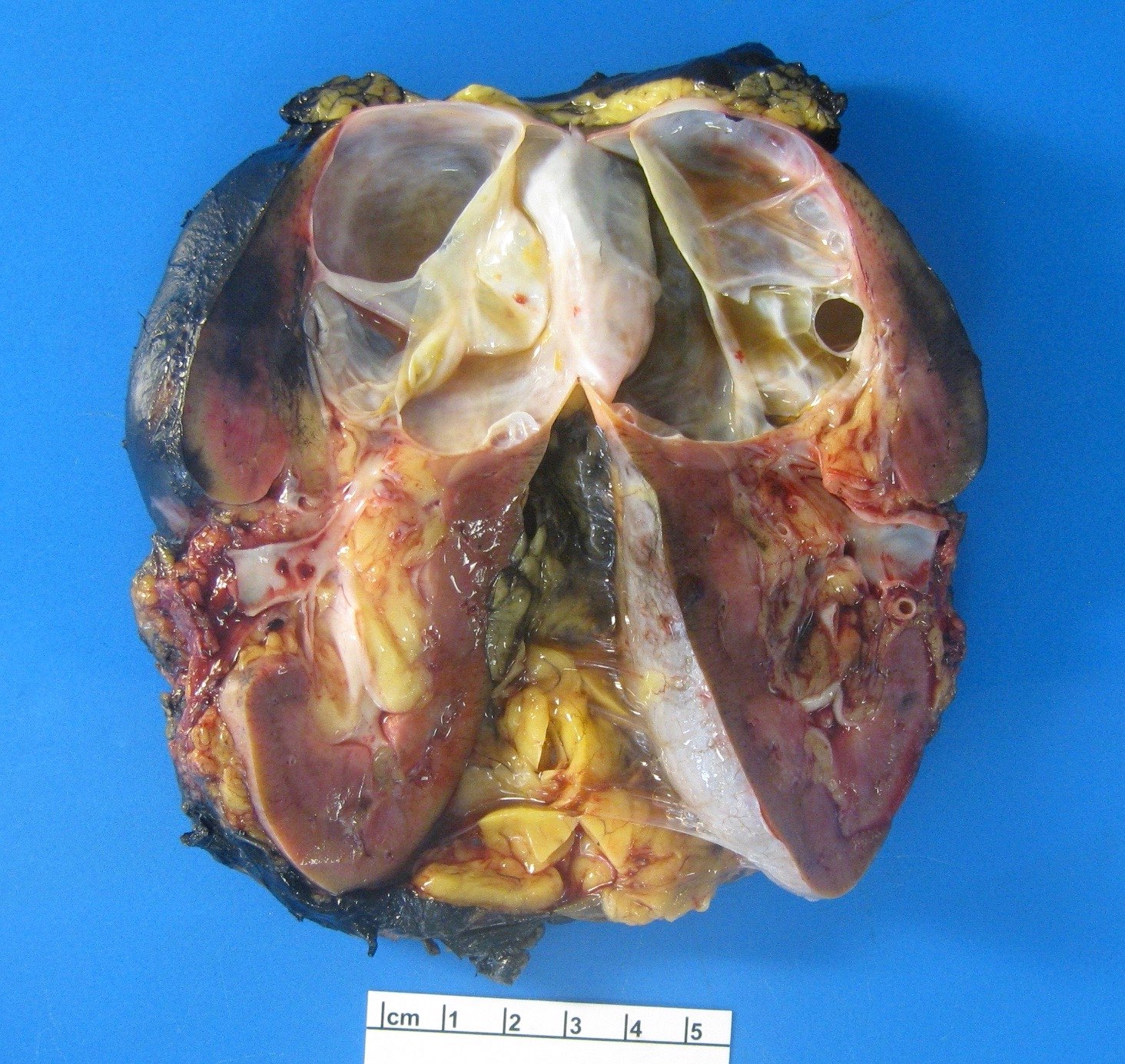
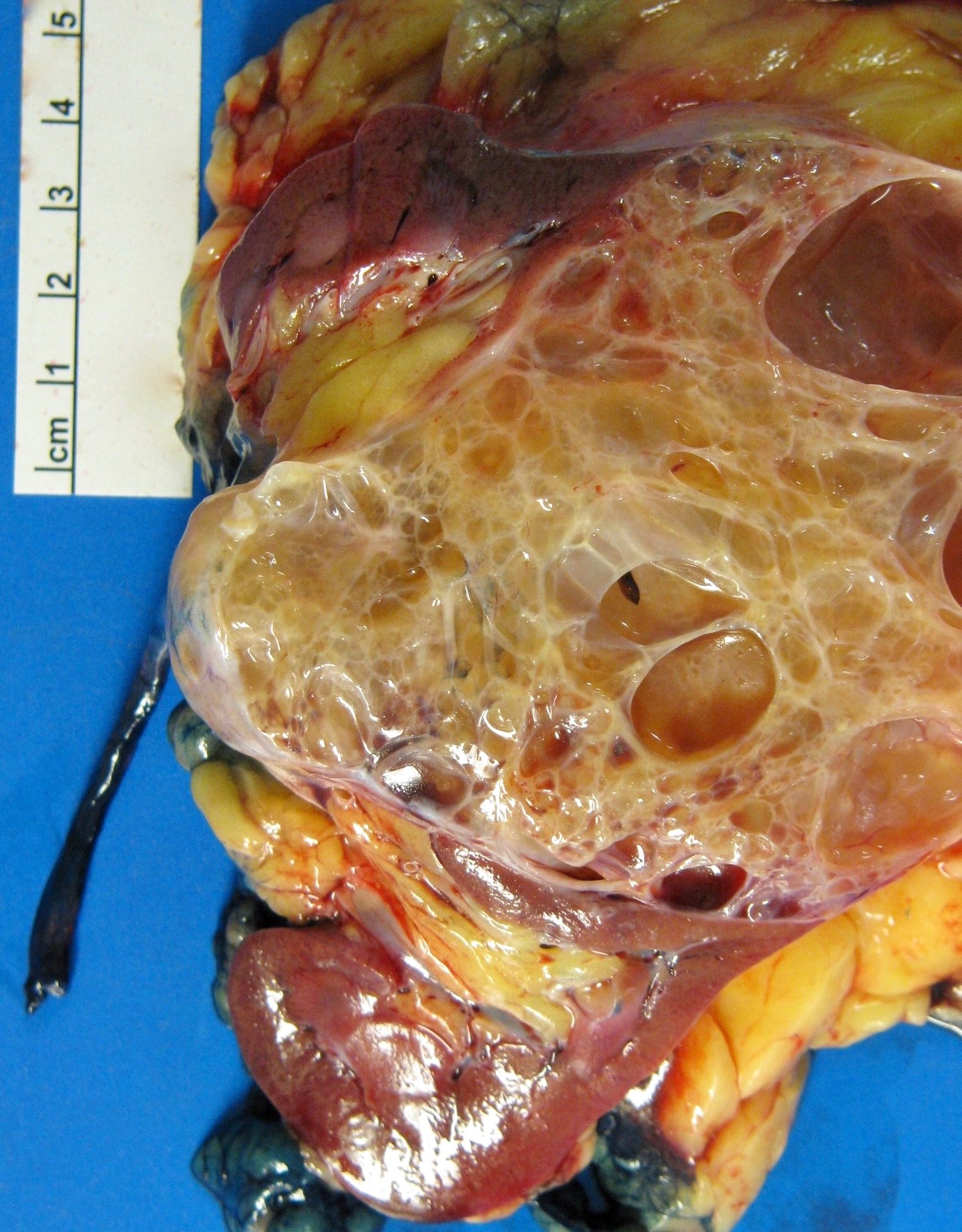
Gross description
- Unilateral but rarely bilateral (Urology 2008;71:1142, Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:72)
- Well circumscribed, multilocular cystic mass
- Median size: 6.8 cm (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1591)
- Noncommunicating thin walled cysts of varying sizes
- Smooth and glistening linings
- Filled with serous to serosanguinous fluid
Gross images
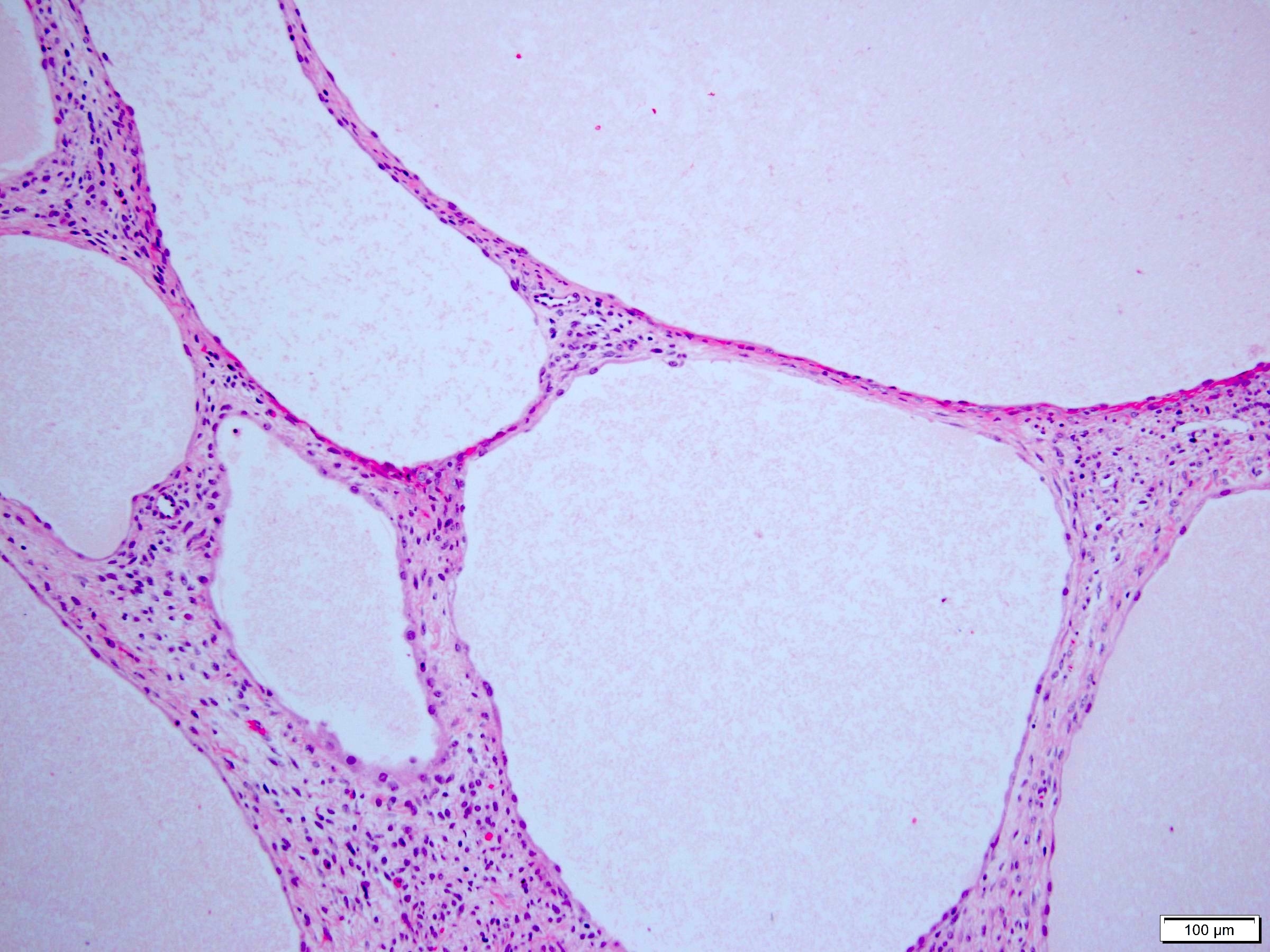
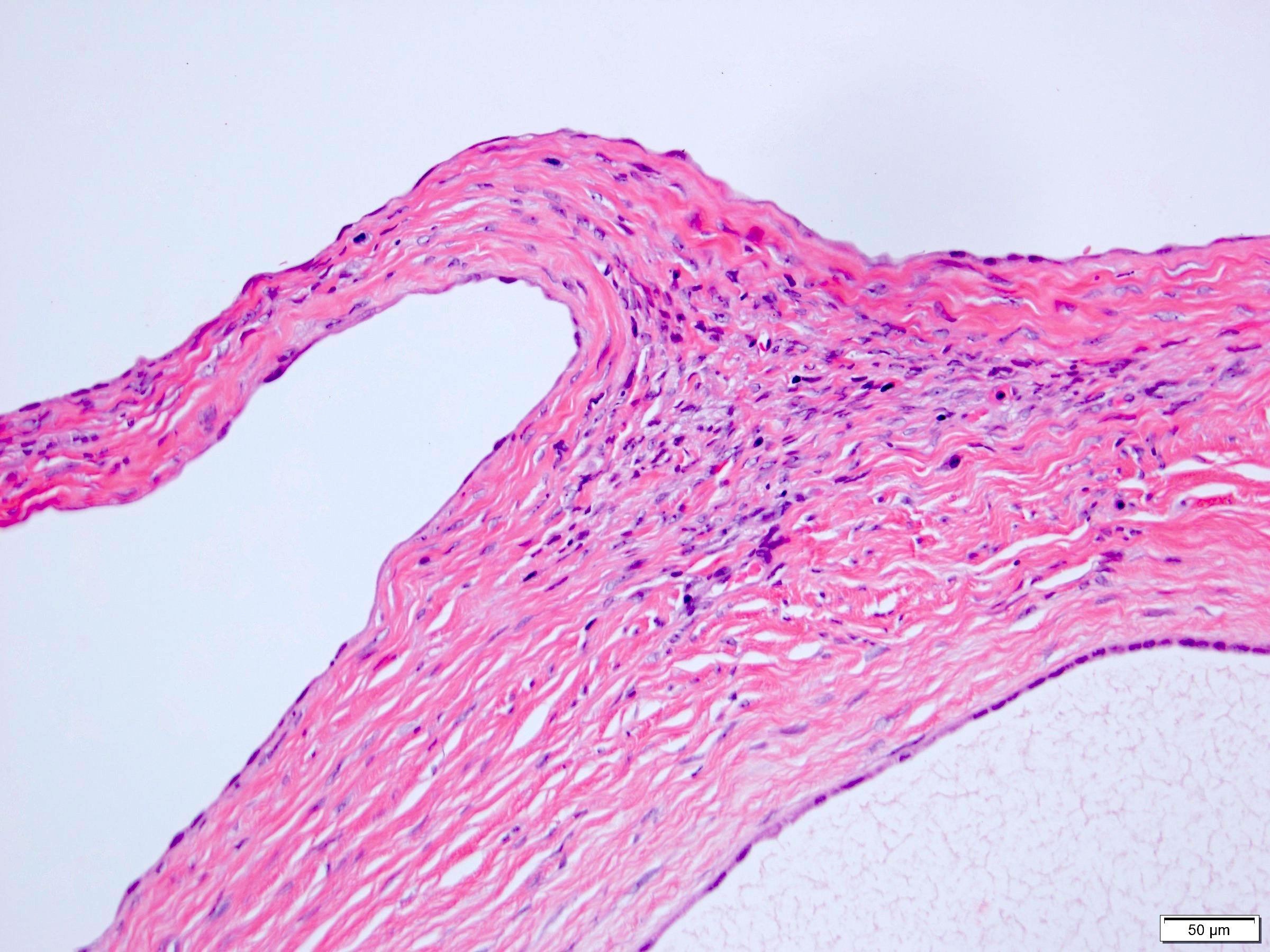
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Many with at least a partial pseudocapsule
- Entirely composed of cysts separated by septa (Semin Diagn Pathol 1998;15:2, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2004;128:1404, Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:489, Eur Urol 2008;54:1237, Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1591)
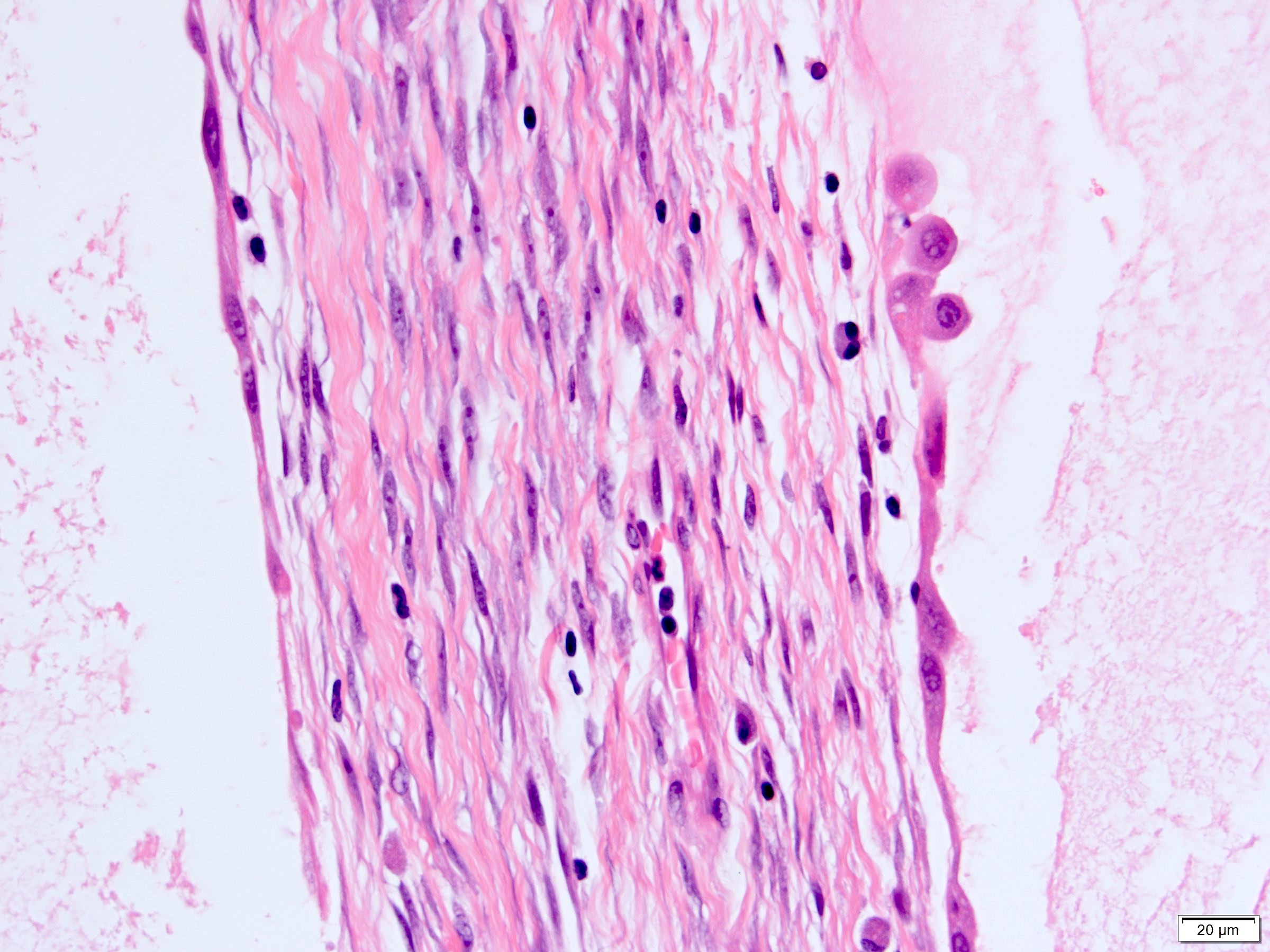
- Stroma:
- Hypocellular to hypercellular
- Collagenous and fibrous to edematous and myxoid
- Areas of hyalinized stroma with contours resembling ovarian corpora albicantia
- Spindle cells; closely packed areas resemble ovarian stroma
- Cellular foci embedded with epithelial elements ranging from handful of cells with no lumen to tiny cysts with pinpoint lumens and to slightly larger cysts
- Steroidogenic cells: small clusters of polygonal cells with amphophilic cytoplasm and round nuclei, frequently around epithelial component
- Calcifications, multinucleated giant cells, foamy or hemosiderin laden macrophages and focal chronic inflammation
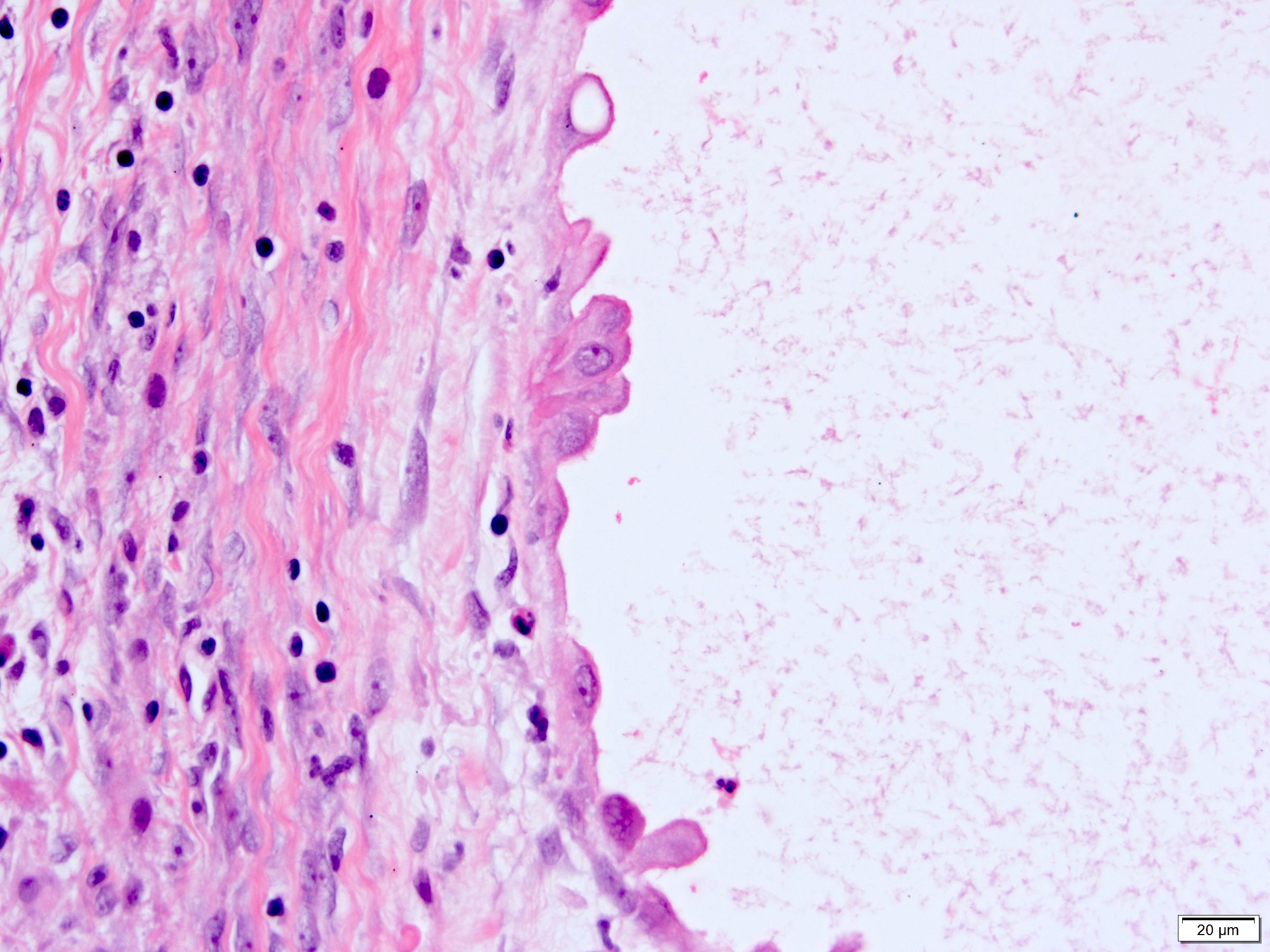
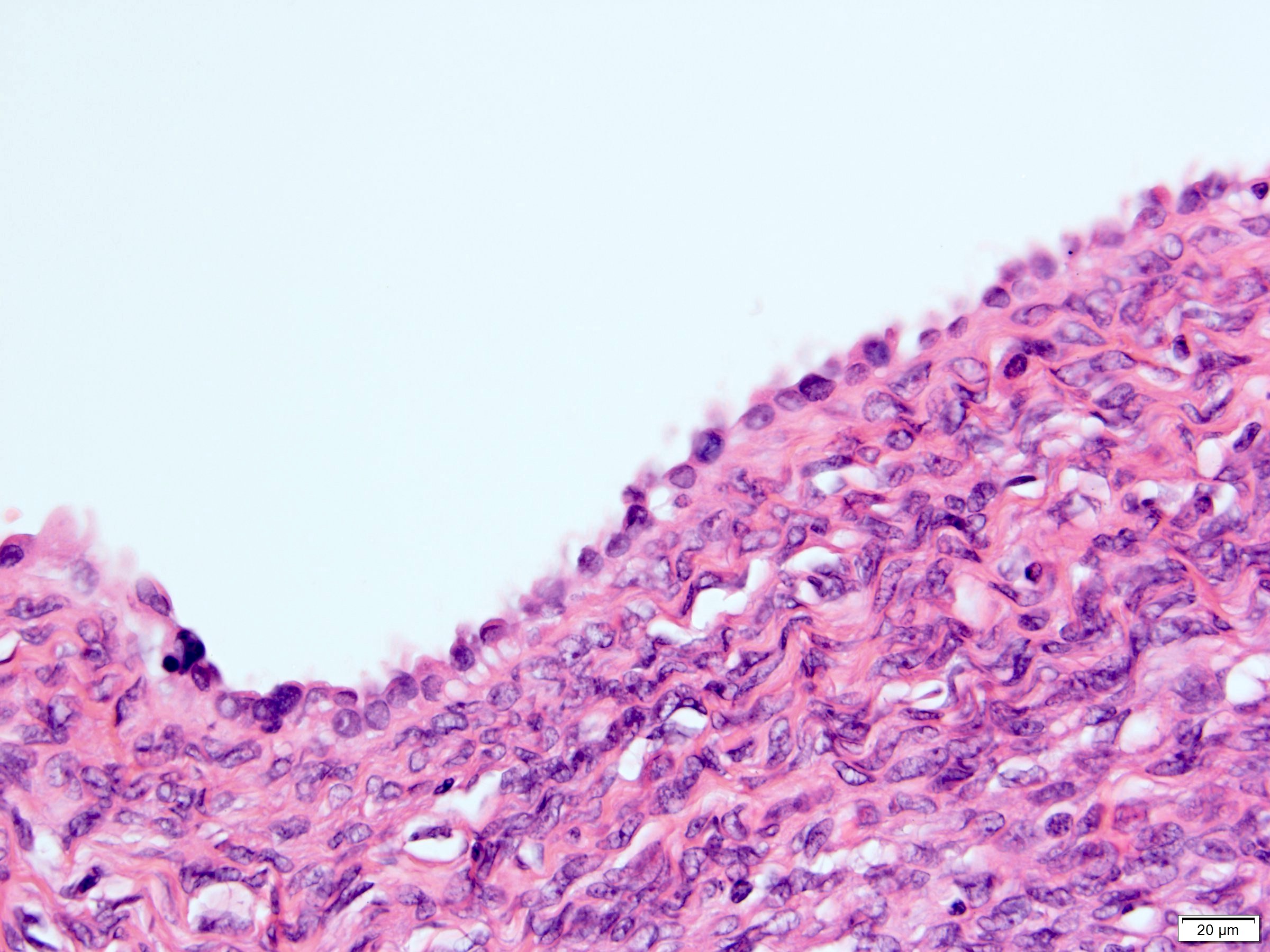
- Epithelium:
- Cells lining cysts
- Mostly arranged in single layer with various morphology: flat, cuboidal, hobnail, clear cell
- Rarely, foci of blunt and delicate papillae or foci of multiple layers of epithelium
- Minimal cytologic atypia
- Rare necrosis, no mitosis
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- FNA (Diagn Cytopathol 1992;8:349, Diagn Cytopathol 1996;14:60, Acta Cytol 2008;52:91, Acta Cytol 2010;54:233):
- Hypocellular specimen
- Small papillary clusters of epithelial cells
- Cells with eccentrically placed, hyperchromatic, irregular nuclei, prominent nucleoli and cytoplasmic vacuoles
- Background of red blood cells, histiocytes and rare neutrophils
- No necrosis
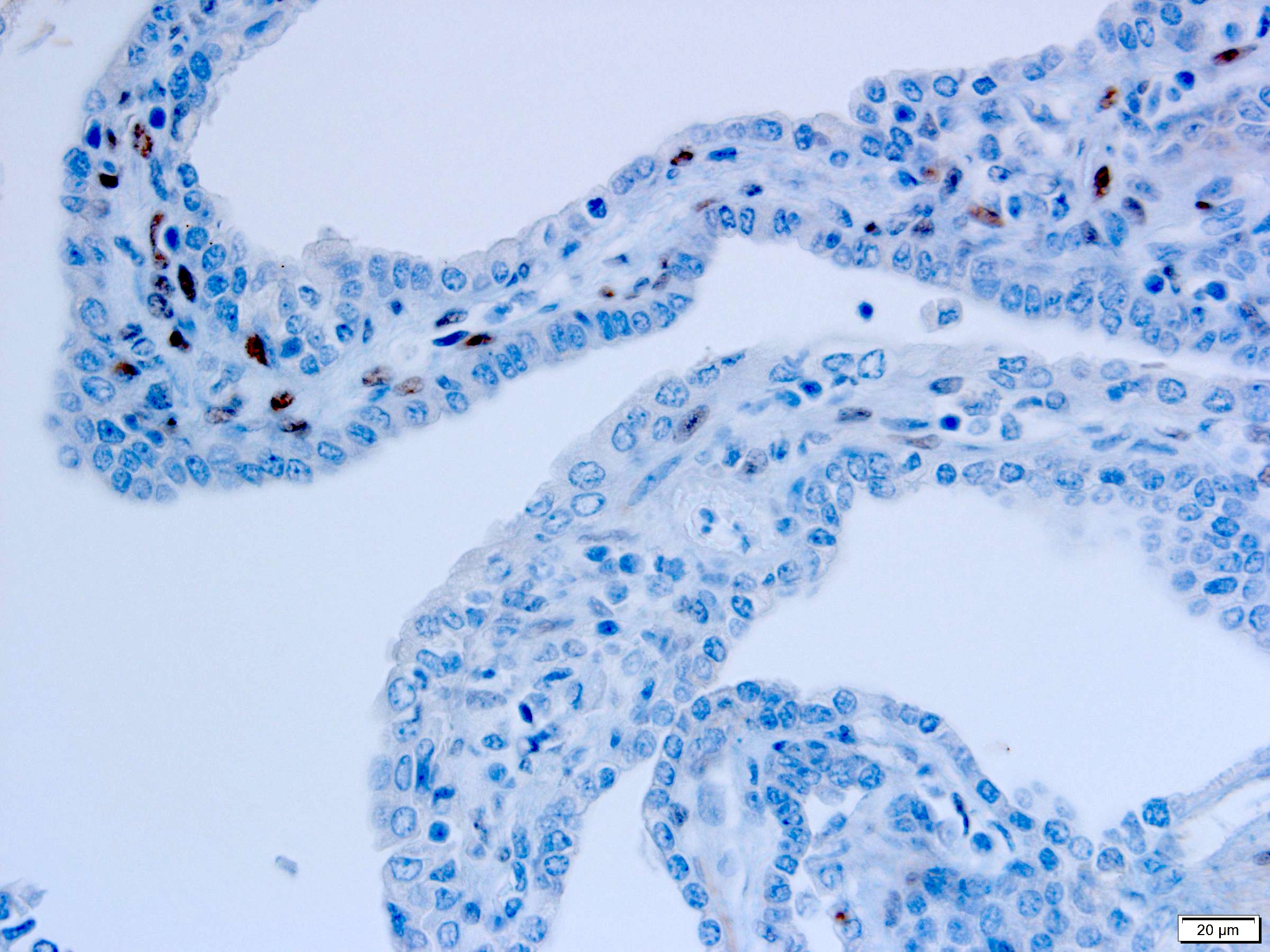
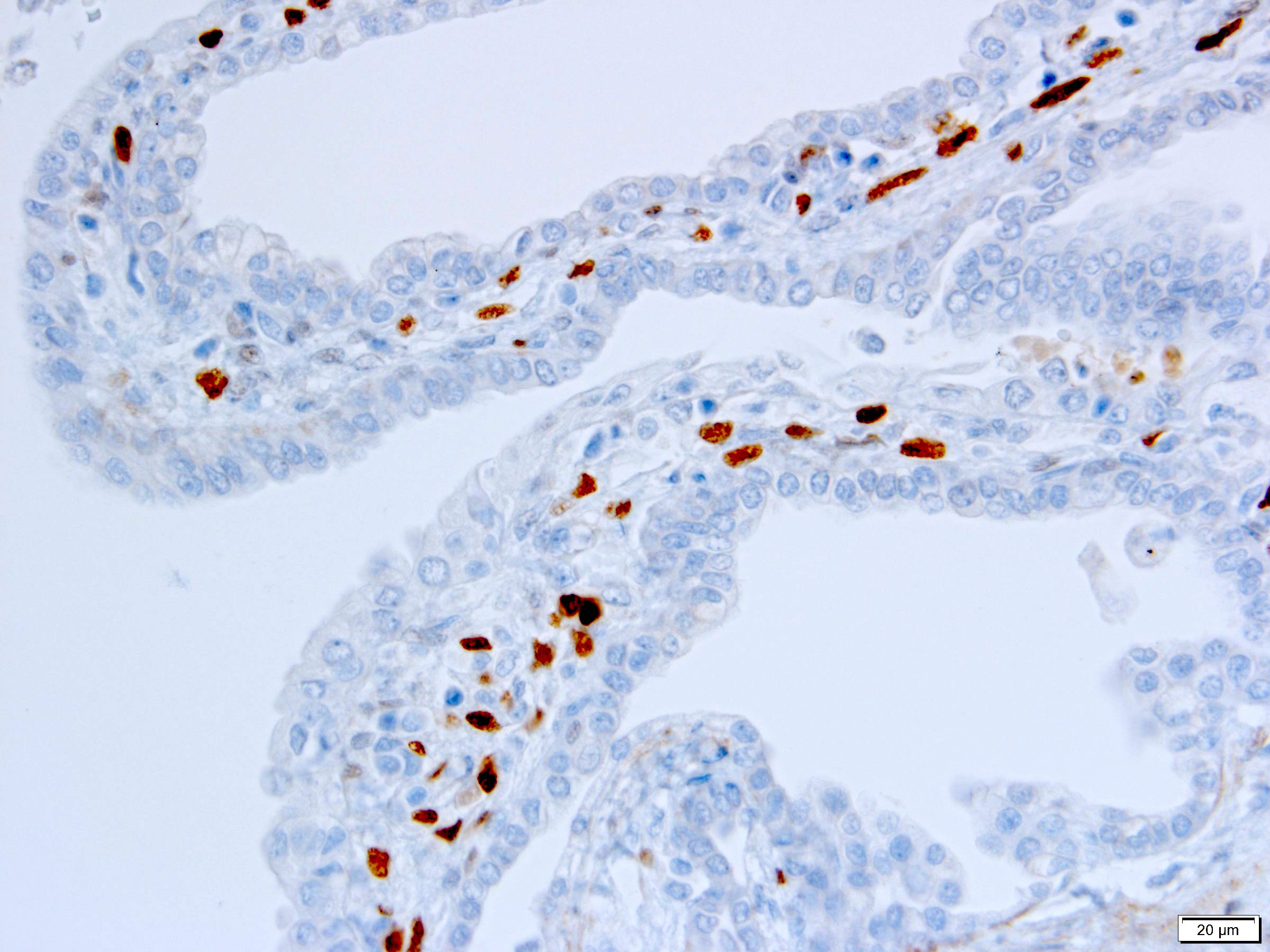
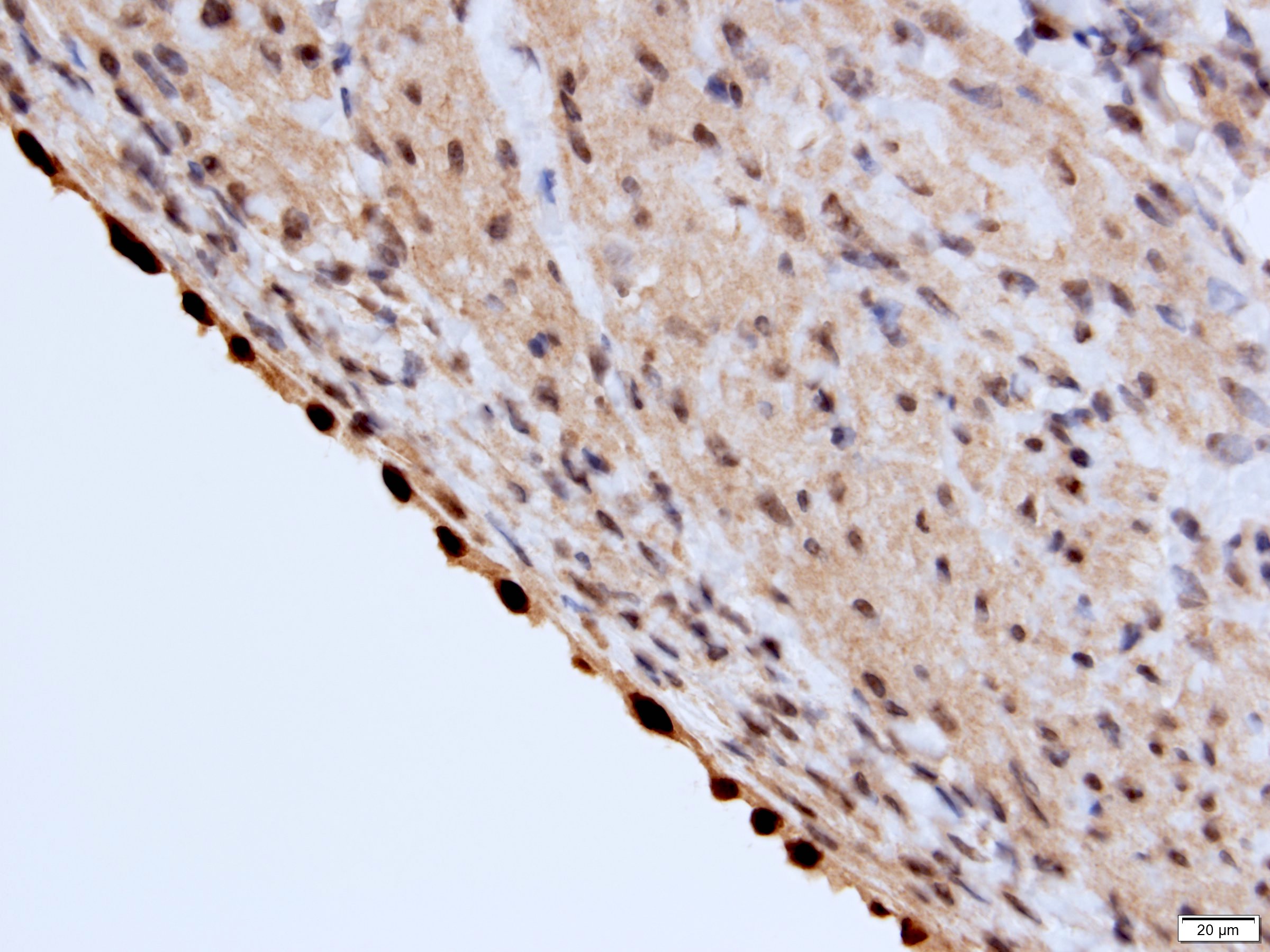
Positive stains
- Stroma:
- SMA: strong and diffuse, 95% (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1591, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2004;128:1404, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2006;130:80)
- Desmin and caldesmon: more variable, 42% and 60%, respectively (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1591, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2004;128:1404)
- ER and PR, 50% and 95%, respectively (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1591, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2004;128:1404, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2006;130:80, Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:489)
- CD10: mainly in spindle cells around epithelial elements, 81% (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1591, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2004;128:1404, Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:489)
- FOXL2: in ovarian type stroma, 90% (Hum Pathol 2014;45:1010)
- Epithelium:
Negative stains
- HMB45 (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2004;128:1404, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2006;130:80, Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1591)
- MelanA: may show positivity in steroidogenic cells (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1591)
- Inhibin and SF1: may show positivity in steroidogenic cells (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:489, Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1591)
- GATA3: epithelial coexpression with PAX8, 32% (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1591)
- S100 (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2004;128:1404)
- Neuron specific enolase (NSE) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2004;128:1404)
- Cathepsin K (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1591)
- WT1: may show positivity in stromal cells (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2006;130:80, Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1591)
- CD34: may show positivity in pericystic stromal cells (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2006;130:80, Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1591)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Similar mRNA expression profile between adult cystic nephroma and MEST supports these tumors to represent opposite ends of same disease spectrum (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:72)
- Highest differentially expressed gene: insulin-like growth factor 2
- Lowest differentially expressed gene: carbonic anhydrase II
- No DICER1 mutations as seen in pediatric cystic nephroma (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:472)
Sample pathology report
- Left kidney, mass, partial nephrectomy:
- Adult cystic nephroma, measuring 6.5 cm in greatest dimension (see comment)
- Surgical margins, negative for tumor
- Comment: The sections show a well circumscribed tumor composed of multiple cysts lined by flattened or cuboidal epithelium. Immunohistochemistry was performed to show the septal stroma is positive for ER and PR. The morphologic and immunohistochemical findings support the diagnosis of adult cystic nephroma.
Differential diagnosis
- Mixed epithelial and stromal tumor (MEST):
- Part of the MEST family with adult cystic nephroma at the opposite end of spectrum, on basis of comparable clinical features (sex and age distribution), overlapping morphologic findings and similar immunohistochemical profile
- Variable solid and cystic components
- Morphologically diverse epithelial and stromal elements
- Pediatric cystic nephroma:
- Almost exclusively occurs in children with higher prevalence in males
- Similar macroscopic and microscopic findings
- Most harbor DICER1 mutations (J Med Genet 2010;47:863, Mod Pathol 2014;27:1267, Hum Pathol 2016;48:81)
- Angiomyolipoma (AML) with epithelial cysts (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:593, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2016;140:594):
- Cystic partially differentiated nephroblastoma:
- Most occur in patients < 24 months old
- Nephroblastematous tissue (e.g. blastema, immature stromal cells, primitive epithelial elements) present
- Multilocular cystic neoplasm of low malignant potential:
- Clusters or nests of tumor cells with abundant clear cytoplasm and small nuclei without prominent nucleoli (WHO / ISUP grade 1 or 2) present in cystic septa
- Occasional small papillae may be seen
- No cellular stroma
- Carbonic anhydrase IX+, PR-
- Tubulocystic renal cell carcinoma:
- Strong male predominance (≥ 7:1)
- Small to medium sized tubules admixed with cystically dilated larger tubules lined by cells with enlarged irregular nuclei and prominent nucleoli (WHO / ISUP grade 3)
- Clear cell renal cell carcinoma with extensive cystic change:
- Expansile solid nodules of tumor cells with clear cytoplasm altering septal configuration
- Carbonic anhydrase IX+, PR-
Practice question #1
A 6 cm predominantly well circumscribed, multicystic mass was incidentally found in a 55 year old woman. Sections of the partial nephrectomy showed the above histologic features. The stromal component is positive for ER and PR (shown above). What is the likely diagnosis?
- Adult cystic nephroma
- Angiomyolipoma with epithelial cysts
- Cystic partially differentiated nephroblastoma
- Multilocular cystic neoplasm of low malignant potential
Practice answer #1
A. Adult cystic nephroma. Adult cystic nephroma is a well circumscribed, predominantly cystic mass. Angiomyolipoma with epithelial cysts shares overlapping histologic features but the stroma is immunopositive for melanocytic markers. Cystic partially differentiated nephroblastoma typically occurs in children. Multilocular cystic neoplasm of low malignant potential has nests of tumor cells with abundant clear cytoplasm and small nuclei without prominent nucleoli. None of the above choices, except for adult cystic nephroma, demonstrate immunoreactivity for ER and PR.
Comment Here
Reference: Adult cystic nephroma
Comment Here
Reference: Adult cystic nephroma
Practice question #2
Practice answer #2
C. Often indolent with very rare malignant transformation. Adult cystic nephroma is considered benign with very rare reports of local recurrence or malignant transformation. The tumors usually present as unilateral tumors and typically seen in adult women. Unlike pediatric cystic nephroma, neither adult cystic nephroma nor mixed epithelial and stromal tumor has been found to have DICER1 mutations.
Comment Here
Reference: Adult cystic nephroma
Comment Here
Reference: Adult cystic nephroma