Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Flow cytometry description | Flow cytometry images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Reid J, Rezk SA. Follicular hyperplasia. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphnodesfollicularhyperplasia.html. Accessed October 5th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Follicular hyperplasia is a benign proliferation of lymphoid follicles, which can develop wherever lymphoid tissue is present (Surg Neurol 2008;70:514)
Essential features
- Most common type of reactive lymphadenopathy (Mod Pathol 2013;26:S88)
- Associated with varying degrees of paracortical or sinus hyperplasia (Mod Pathol 2013;26:S88)
- A descriptive term that refers to an exaggerated response to antigenic stimulation, characterized by an increased number of germinal centers with variably sized mantle zones (Ann Diagn Pathol 2020;44:151421)
- Follicular hyperplasia represents stimulation of the B cell compartment of the lymph node
Terminology
- Follicular hyperplasia, reactive follicular hyperplasia (RFH), follicular lymphoid hyperplasia (FLH)
ICD coding
- ICD-10: R59.9 - enlarged lymph nodes, unspecified
Epidemiology
- Follicular hyperplasia is seen in pediatric and young adults but may also be encountered in all ages, including the elderly (Mod Pathol 1991;4:24)
Sites
- Majority of cases with follicular hyperplasia occur in lymph nodes
- However, it can affect extranodal organs
- More than 75% of lymphadenopathies are generally localized but commonly involve head and neck regions (StatPearls: Adenopathy [Accessed 7 October 2022])
Pathophysiology
- Reactive follicular hyperplasia is caused by stimulation of the B cell compartment and by abnormal cell growth of secondary follicles (Mod Pathol 2013;26:S88)
Etiology
- Causes of reactive follicular hyperplasia are often unknown; however, it can be caused by bacterial and viral infections, as well as immune mediated disorders (Miranda: Atlas of Lymph Node Pathology, 1st Edition, 2013)
Clinical features
- Lymphadenopathies such as follicular hyperplasia can present clinically as pain, swelling, warmth, tenderness, fever and chills (StatPearls: Adenopathy [Accessed 7 October 2022])
- Nonspecific reactive follicular hyperplasia involving younger patients often resolves spontaneously (Mod Pathol 2013;26:S88)
Diagnosis
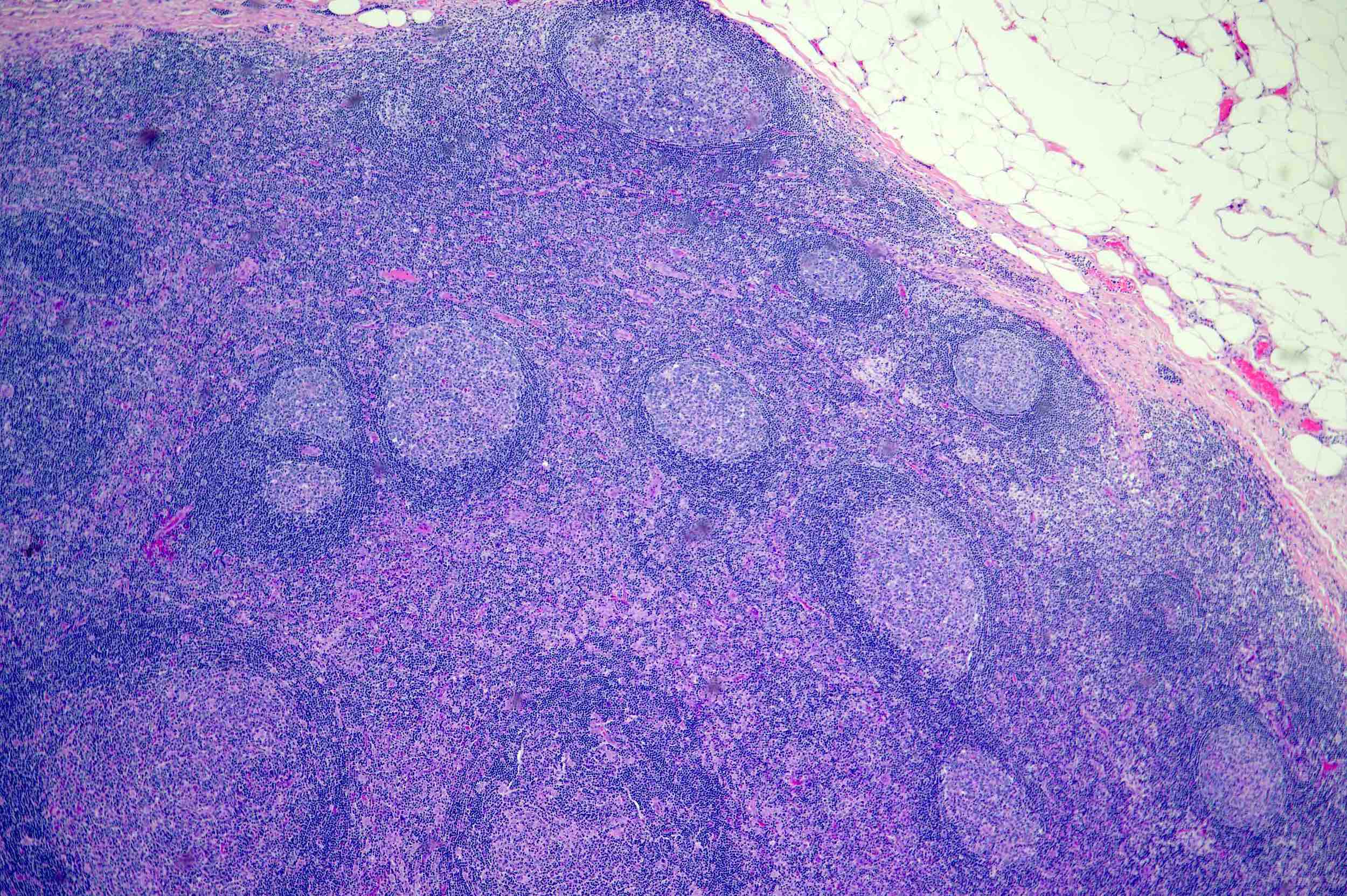
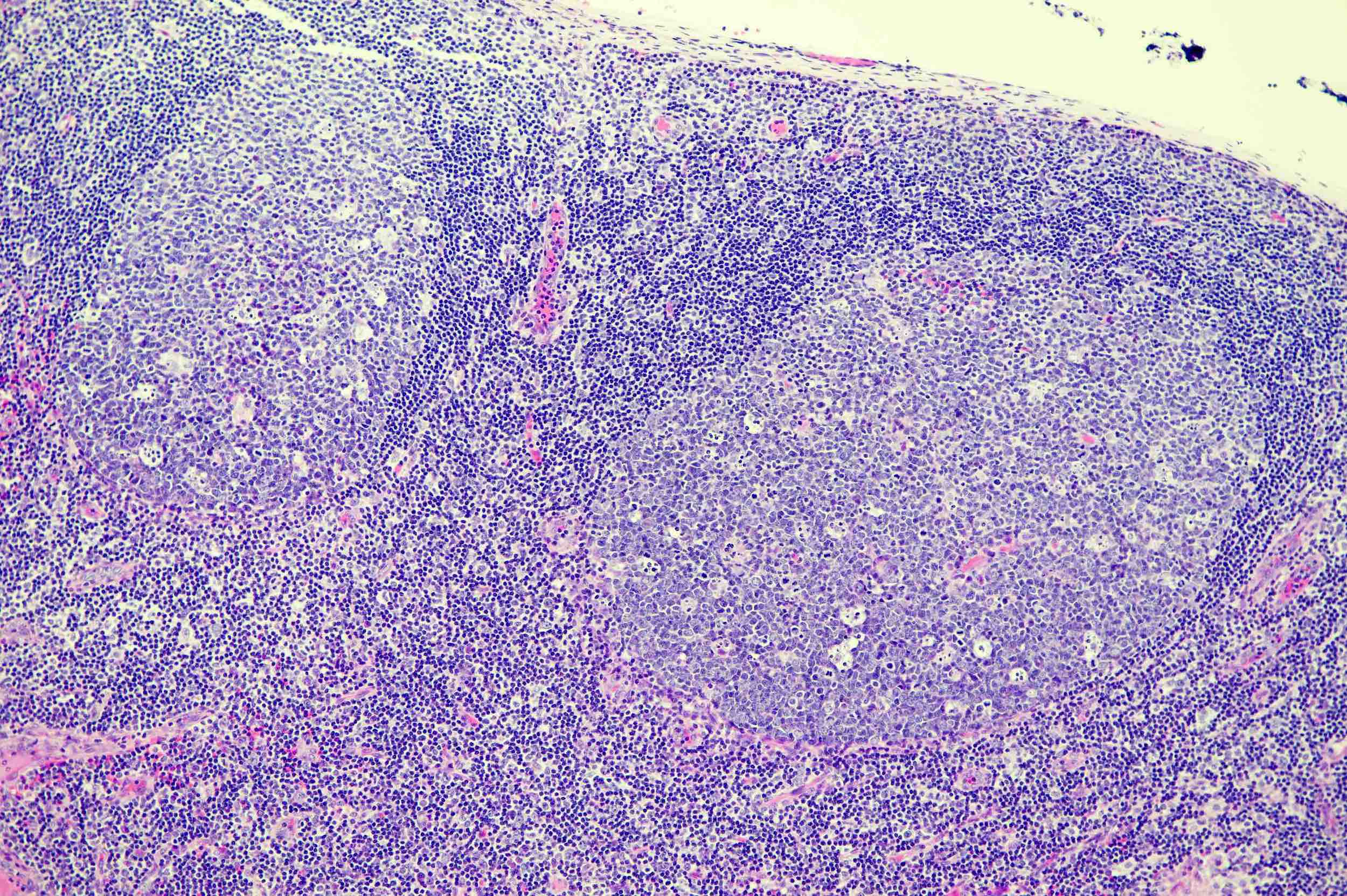
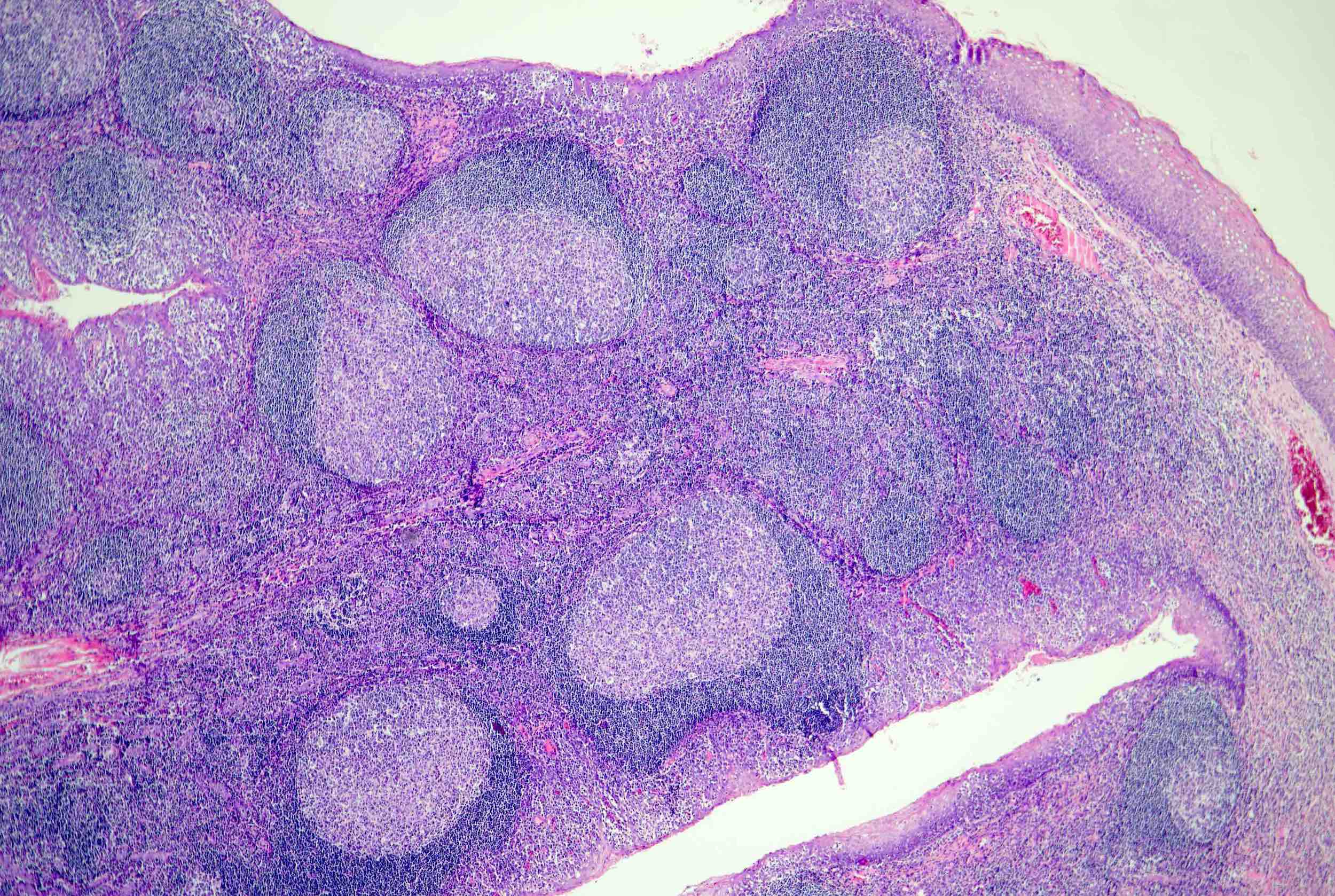
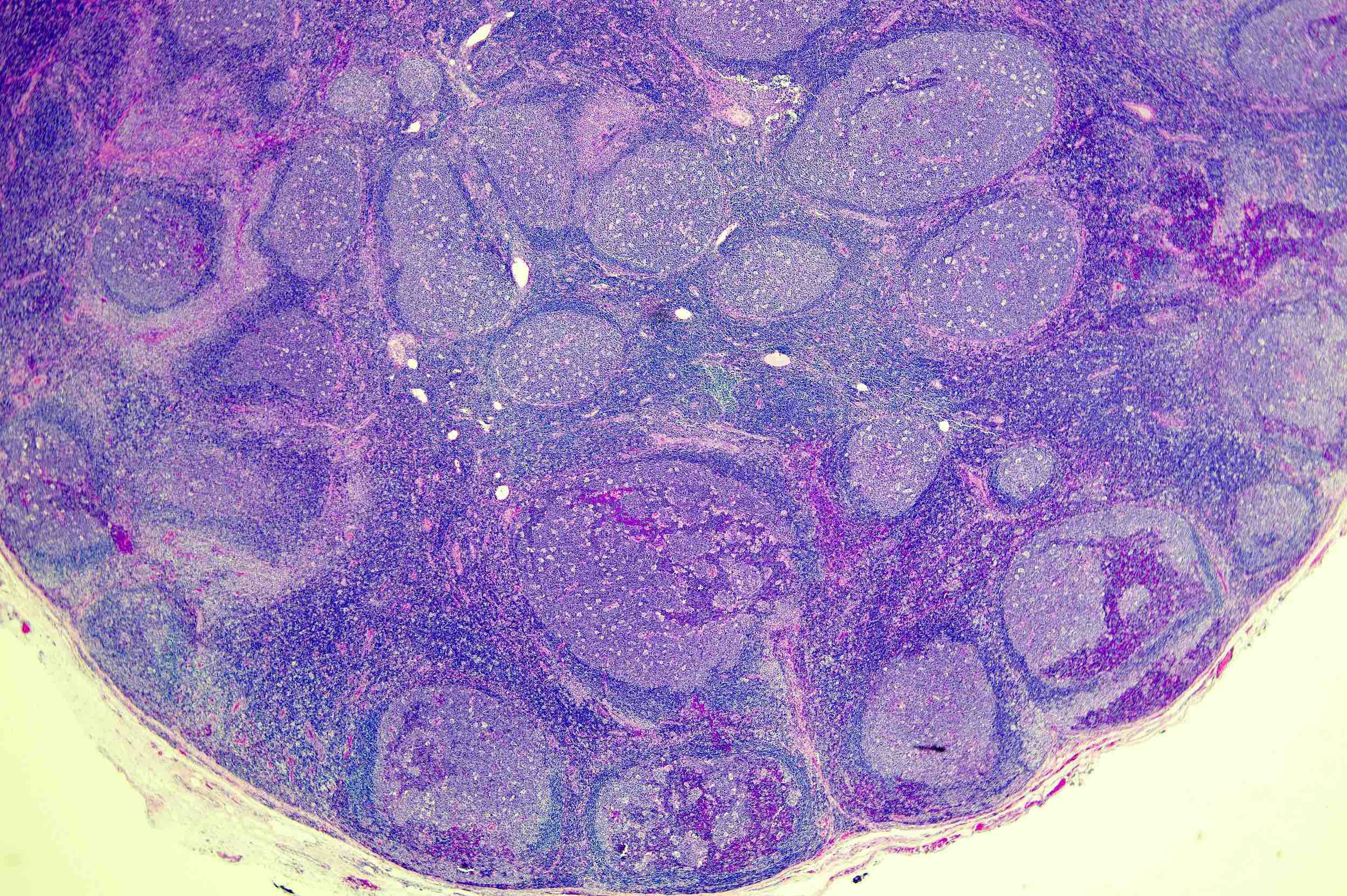
- Morphologically, follicular hyperplasia can be diagnosed by observation of specific histological features such as expansion of germinal center, moderate to high mitotic rate, distinct mantle zone, polarization of the germinal center, variably shaped and sized follicles, tingible body macrophages and mixture of cell types in germinal center (Mod Pathol 2013;26:S88)
- Lymph nodes with reactive follicular hyperplasia show a lower follicular density than is seen in follicular lymphoma
Laboratory
- Leukocytosis, neutrophilia or lymphocytosis may be present in association with infections
Prognostic factors
- Prognosis of follicular hyperplasia is mostly excellent
Case reports
- 51 year old woman with asymptomatic firm mass in the left posterior maxillary site (BMC Oral Health 2019;19:243)
- 55 year old Caucasian woman with swelling in her left posterior hard palate (J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2009;37:79)
- 74 year old edentulous woman with maxillary denture presenting with palatal swelling (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2003;96:172)
- Reactive follicular hyperplasia in the lymph node lesions in 21 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (Pathol Int 2000;50:304)
Treatment
- Localized lymph node enlargement without any additional symptoms will usually spontaneously regress
- Generalized lymphadenopathy usually requires additional investigation for etiology
Gross description
- Typically < 1 cm in size
- Cut surface is tan-pink homogenous
- No gross appearance of hemorrhage or necrosis
- Reference: Mod Pathol 2013;26:S88
Microscopic (histologic) description
- H&E sections of the lymph node show hyperplastic follicles with expanded germinal centers and paracortical regions
- Follicles exhibit normal polarization
- No significant cytologic atypia is identified
- Immunostains reveal a normal staining pattern and distribution
- Reference: Mod Pathol 2013;26:S88
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Polymorphous lymphocytes and tingible body macrophages
- Cytology to histopathology correlation is ~90%
Positive stains
- BCL6 shows densely populated germinal centers with well defined and regular borders and strong staining of follicular center cells but only rare BCL6+ cells in the interfollicular areas (Hum Pathol 1999;30:403)
- CD21, CD23 and CD35 highlight the enlargement of the dendritic meshwork (ScienceDirect: Follicular Hyperplasia [Accessed 29 September 2023])
- Ki67 highlights a predominance of large transformed germinal center cells that have a high mitotic rate (ScienceDirect: Follicular Hyperplasia [Accessed 29 September 2023])
- CD10 stains only follicular center cells and is typically much stronger in follicular lymphoma than in most follicular hyperplasias (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:846, ScienceDirect: Follicular Hyperplasia [Accessed 29 September 2023], Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2000;8:263)
- HGAL also stains germinal center B cells, as does GCET1 (Nat Commun 2013;4:1338)
Negative stains
- BCL2, helpful in distinguishing from follicular lymphoma (Weidner: Modern Surgical Pathology, 2nd Edition, 2009)
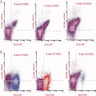
Flow cytometry description
- Polytypic B cell population with positive CD10 and CD23; typically, it is a subset that is CD10 positive
- Evaluation of CD38 by flow cytometry can be helpful in distinguishing follicular hyperplasia from follicular lymphoma (Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2009;76:315)
- Clonal B cell populations may be present in the histologically reactive setting of follicular hyperplasia (Am J Clin Pathol 2004;121:464)
- Combined analysis of CD20 and BCL2 by flow cytometry can distinguish follicular hyperplasia and follicular lymphoma; it may be particularly helpful if samples are limited or B cell clonality is questionable (Am J Clin Pathol 2000;114:258)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Unlike follicular lymphoma, there is no evidence of t(14;18)(q32;q21) or IGH::BCL2 fusion sequences found in cases with follicular hyperplasia
- IgH rearrangement was not identified in follicular lymphoma and was mainly found in lymphoplasmacytoid and follicular lymphoma (Oncotarget 2017;8:77009)
Videos
Histopathology lymph node: follicular hyperplasia
Sample pathology report
- Lymph node, excision:
- Reactive follicular hyperplasia; no carcinoma or lymphoma (see comment)
- Comment: The H&E sections of the lymph node show hyperplastic follicles with expanded germinal centers and paracortical region. The follicles exhibit normal polarization. No significant cytologic atypia is identified. The immunostains reveal a normal staining pattern and distribution. The histological and immunohistochemical features are consistent with a reactive follicular hyperplasia. Clinical and microbiological correlation is recommended for complete interpretation.
- Immunohistochemical stain:
Block Stain Result 1 CD3 Positive in T cells CD20 Positive in B cells CD10 Positive in germinal center cells BCL6 Positive in germinal center cells BCL2 Positive in nongerminal center cells CD21 Highlight follicular dendritic meshwork
- Interpretation: There is a reactive follicular hyperplasia with no evidence of a malignant lymphoma.
Differential diagnosis
- Follicular lymphoma:
- Progressive transformation of germinal centers (PTGCs):
- Morphologically, the nodules seen in PTGCs are 3 - 4 times larger than those of reactive follicular hyperplasia
- Germinal center B cells are BCL2 negative
- Hyaline vascular Castleman disease:
- Regressed germinal centers
- Sclerotic vessels
- Prominent mantle zones with onion skin appearance
- Morphological features such as twinning (2 or more germinal centers inside each follicle) and lollipop sign (a radially penetrating sclerotic blood vessel in the germinal center)
- Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (NLPHL):
- Immunophenotypically, NLPHL expresses CD45, EMA and 50% of the cases with MUM1
- Morphologically distinct NLPHL can be seen with neoplastic lymphocyte predominant (LP) cells in the background of small lymphocytes and epithelioid histiocytes
- Both follicular hyperplasia and NLPHL may show a nodular proliferation at low power; however, NLPHL nodules are more irregular and have a moth eaten appearance due to the presence of clusters of epithelioid histiocytes (Pediatr Blood Cancer 2018;65:10.1002/pbc.26753)
- Follicular neoplasia in situ:
- Can be an incidental finding in a background of follicular hyperplasia (Blood 2011;118:2976)
- Pediatric variant of follicular lymphoma (PFL):
- Biologically different from common follicular lymphoma (FL)
- PFL cases have been reported exclusively in male patients in both children and young adults
- Most common site of PFL cases is head / neck region
- Morphologically, PFL cases demonstrate blastoid cytologic features with a high proliferation rate by Ki67
- By immunohistochemistry, PFL is positive for germinal center markers (CD10, BCL6, LMO2, HGAL)
- BCL2 expression by immunohistochemistry varies depending on the anatomic site: testicles (negative), lymph nodes (18% weakly positive), tonsils (63% of cases are positive)
- Majority of PFL cases demonstrate clonal immunoglobulin gene rearrangement by PCR analysis
- Absence of BCL2::IGH translocation by FISH
- MAP kinase pathway involvement has been reported in 50% cases with PFL (Blood 2016;128:1093)
- TNFRSF14 mutations have been reported in cases of PFL (Blood 2016;128:1093)
Practice question #1
When differentiating follicular hyperplasia from follicular lymphoma, which immunohistochemical stain is most helpful?
- BCL2
- BCL6
- CD10
- Ki67
- MUM1
Practice answer #1
A. BCL2. Follicular hyperplasia distinguishes itself from follicular lymphoma by lack of BCL2 expression whereas follicular lymphoma is classically positive for BCL2 expression.
Comment Here
Reference: Follicular hyperplasia
Comment Here
Reference: Follicular hyperplasia
Practice question #2
Practice answer #2
A. Polarization of germinal centers is typically seen in follicular hyperplasia along with features such as low density of follicles, variably sized follicles, mixture of cell types in the germinal centers, tingible body macrophages, moderate to high mitotic rate, intact nodal architecture. Answer B is incorrect because positive staining of BCL2 in the germinal center is seen in follicular lymphoma. Answers C and D are incorrect because multilobated popcorn cells and Reed-Sternberg (RS) cells are seen in Hodgkin lymphoma. Answer E is incorrect because twinning of the follicle is seen in Castleman disease.
Comment Here
Reference: Follicular hyperplasia
Comment Here
Reference: Follicular hyperplasia