Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Findeis S, Huang H. Ductal adenocarcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/prostateprostaticduct.html. Accessed May 12th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Rare subtype of prostatic carcinoma composed of large glands lined by tall columnar cells with pseudostratified nuclei
Essential features
- Frequently mixed with acinar adenocarcinoma
- Similar mortality rate to Gleason score 8 - 10 acinar adenocarcinoma for usual ductal adenocarcinoma
Terminology
- Prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma, ductal carcinoma
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8500/3 - ductal adenocarcinoma
- ICD-10: C61 - malignant neoplasm of prostate
- ICD-11: 2C82.0 & XH7KH3 - adenocarcinoma of prostate & infiltrating duct carcinoma, NOS
Epidemiology
- Accounts for 3.2% of all prostate cancers
- Most are mixed with acinar adenocarcinoma; pure ductal carcinoma incidence: 0.4 - 0.8% of prostate cancers (Histopathology 2012;60:59, Cancer 1986;57:111)
Sites
- Prostate
- Most common in peripheral zone but also can be in the urethra and transition zone (Virchows Arch 2013;46:429)
Pathophysiology
- Unknown
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Periurethral tumor may cause hematuria and urinary tract symptoms; peripheral tumors have clinical features similar to acinar adenocarcinoma
- More likely to present with distant disease than acinar adenocarcinoma (J Urol 2010;184:2303)
- Can metastasize, including to unusual visceral metastases (including penis and testis) (Cancer 2020;126:3667, Urol Oncol 2008;26:368, Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:67, Cancer 2002;94:2610)
Diagnosis
- Similar to other prostate cancers, often diagnosed through transrectal needle biopsies
- Periurethral tumor may be diagnosed by transurethral resection of the prostate
Laboratory
- PSA can be highly variable
- More likely to have a PSA < 4.0 ng/mL; has a mean lower PSA at presentation compared with acinar adenocarcinoma (J Urol 2010;184:2303, Urology 2015;86:777)
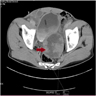
Radiology description
- Not diagnostically helpful at this time; however, pure ductal adenocarcinoma may be seen as a noncystic mass with periurethral distribution or a multicystic mass (Abdom Radiol (NY) 2022;47:1929)
Prognostic factors
- Similar mortality rate to acinar carcinoma with Gleason score of 8 - 10 (Urology 2015;86:777)
- Similar to acinar adenocarcinoma, cribriform features in ductal adenocarcinoma have been shown to have more aggressive behavior (Ann Diagn Pathol 2019;39:59)
- Is an aggressive subtype and has a high risk of biochemical failure due to similar genetic changes to castration resistant acinar adenocarcinoma (Eur Urol 2021;79:298, Hum Pathol 2017;69:1, Nat Rev Urol 2021;18:337)
- Has worse outcome compared to prostatic acinar adenocarcinoma (Eur Urol 2021;79:298)
Case reports
- 64 year old man with mixed acinar and macrocystic ductal prostatic adenocarcinoma (Lancet Oncol 2021;22:e37)
- 67 year old man with gastric metastasis (mixed ductal and acinar) (Urol Case Rep 2016;7:28)
- 76 year old man with ductal carcinoma which mimicked a urethral polyp (Pathology 2007;39:476)
- 86 year old man with ductal adenocarcinoma presenting with syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) (J Cancer Res Ther 2012;8:308)
- 29 men with metastatic prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma to the penis (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:67)
Treatment
- Hormonal therapy, radiation or surgery
- Tends to have a worse outcome compared to prostatic acinar adenocarcinoma (Eur Urol 2021;79:298)
Gross description
- Similar to prostatic acinar adenocarcinoma
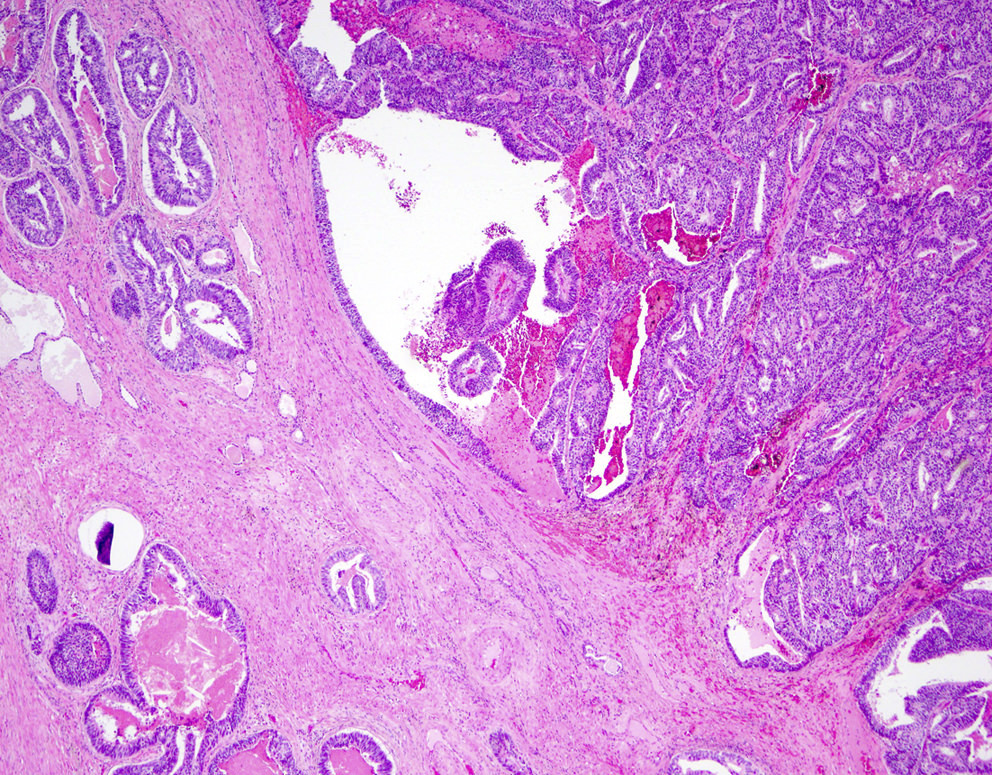
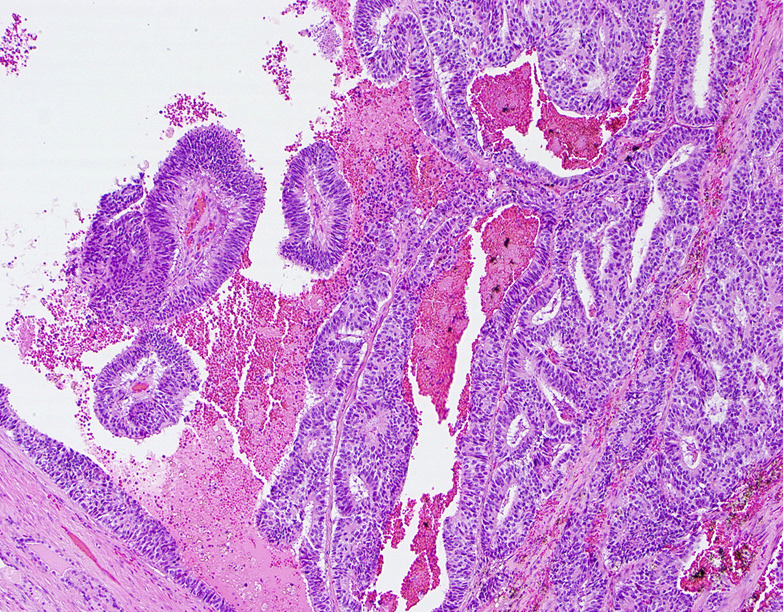
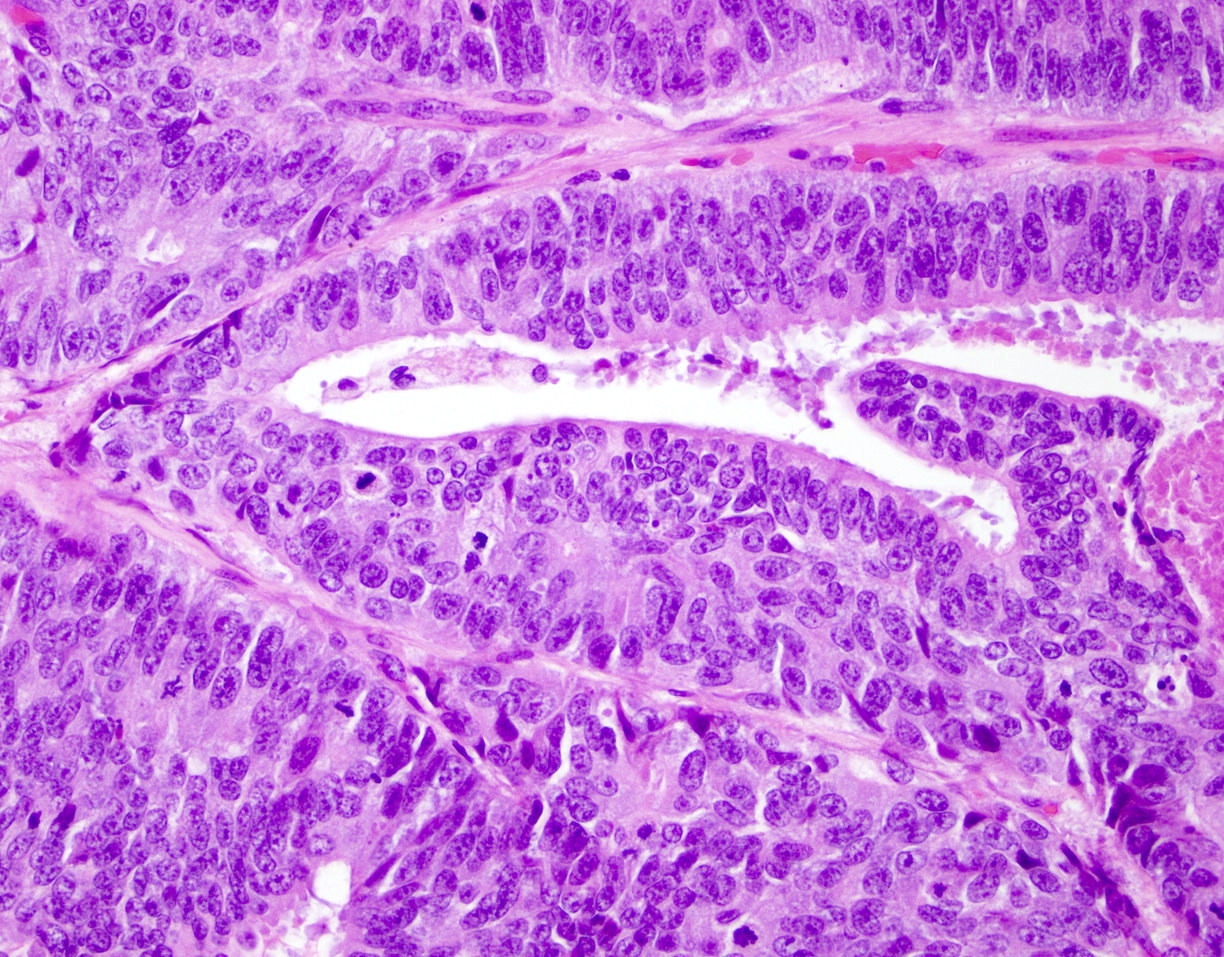
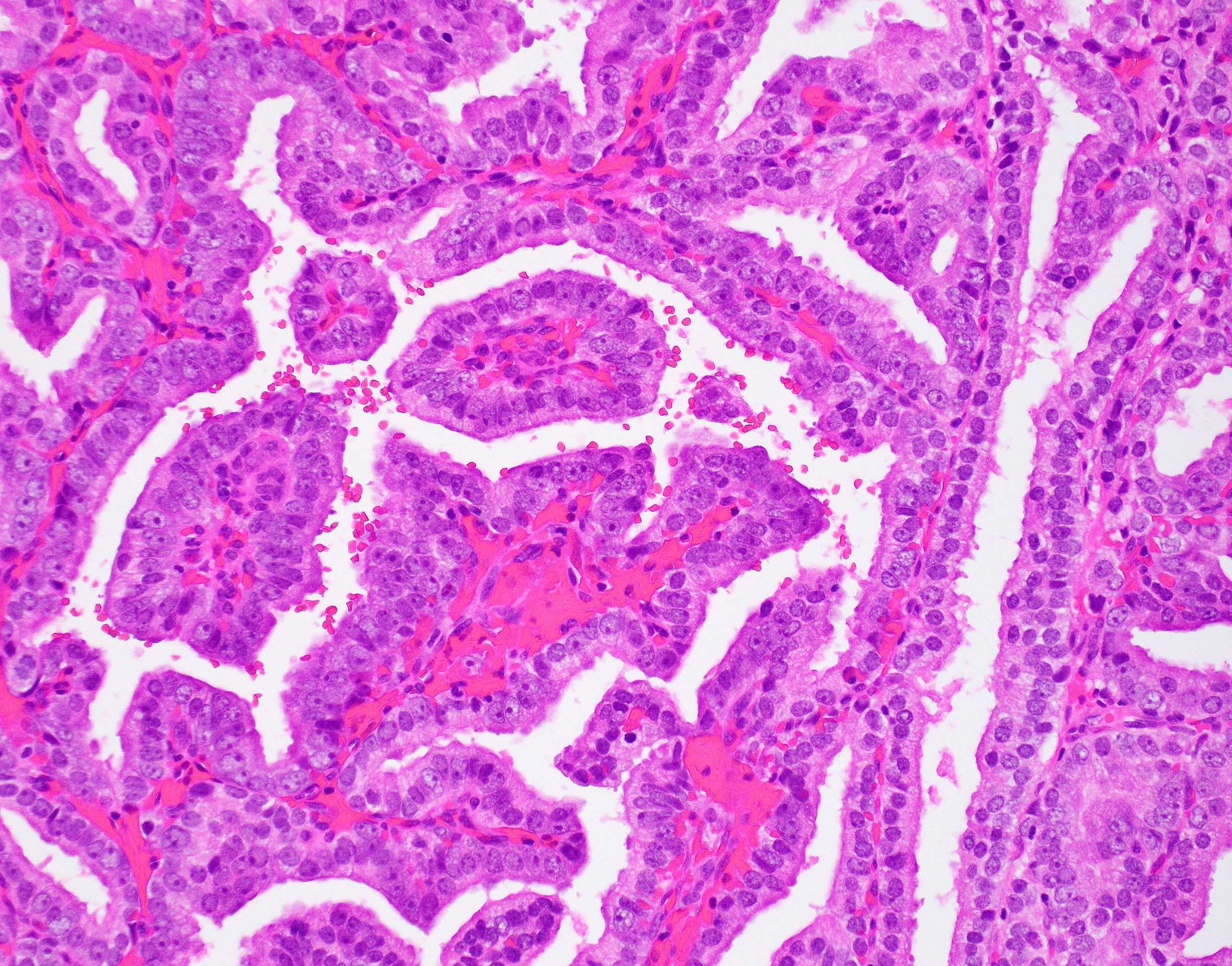
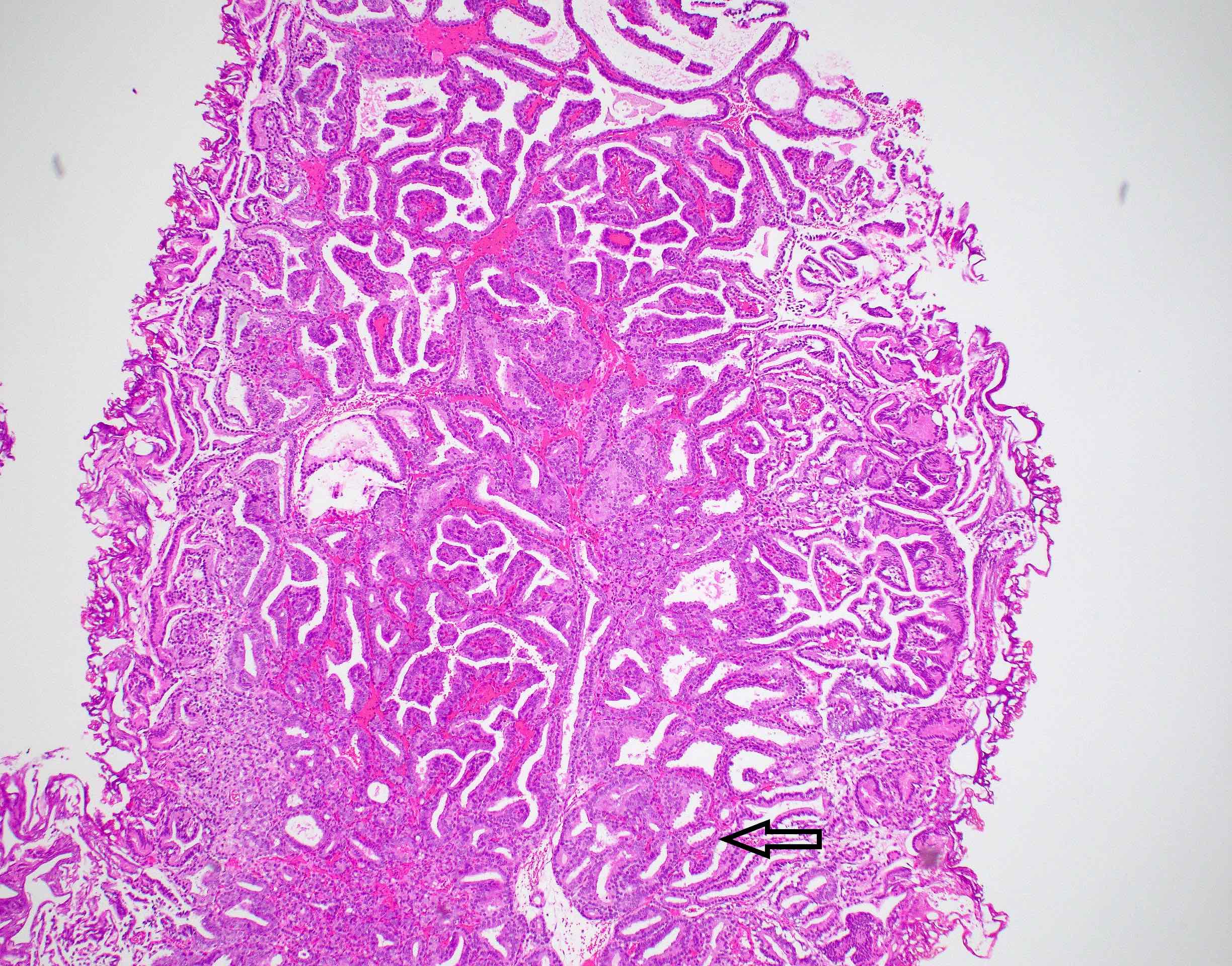
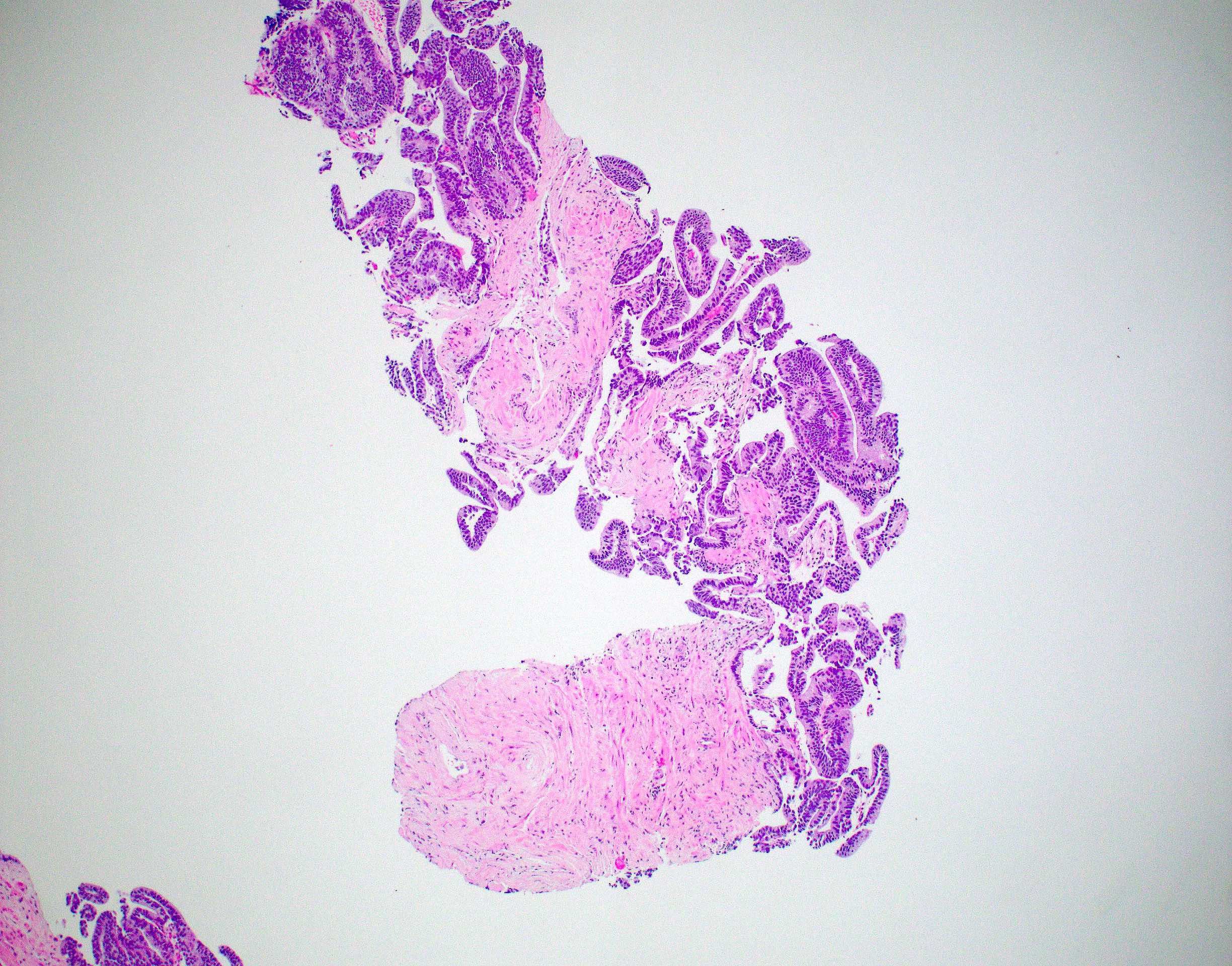
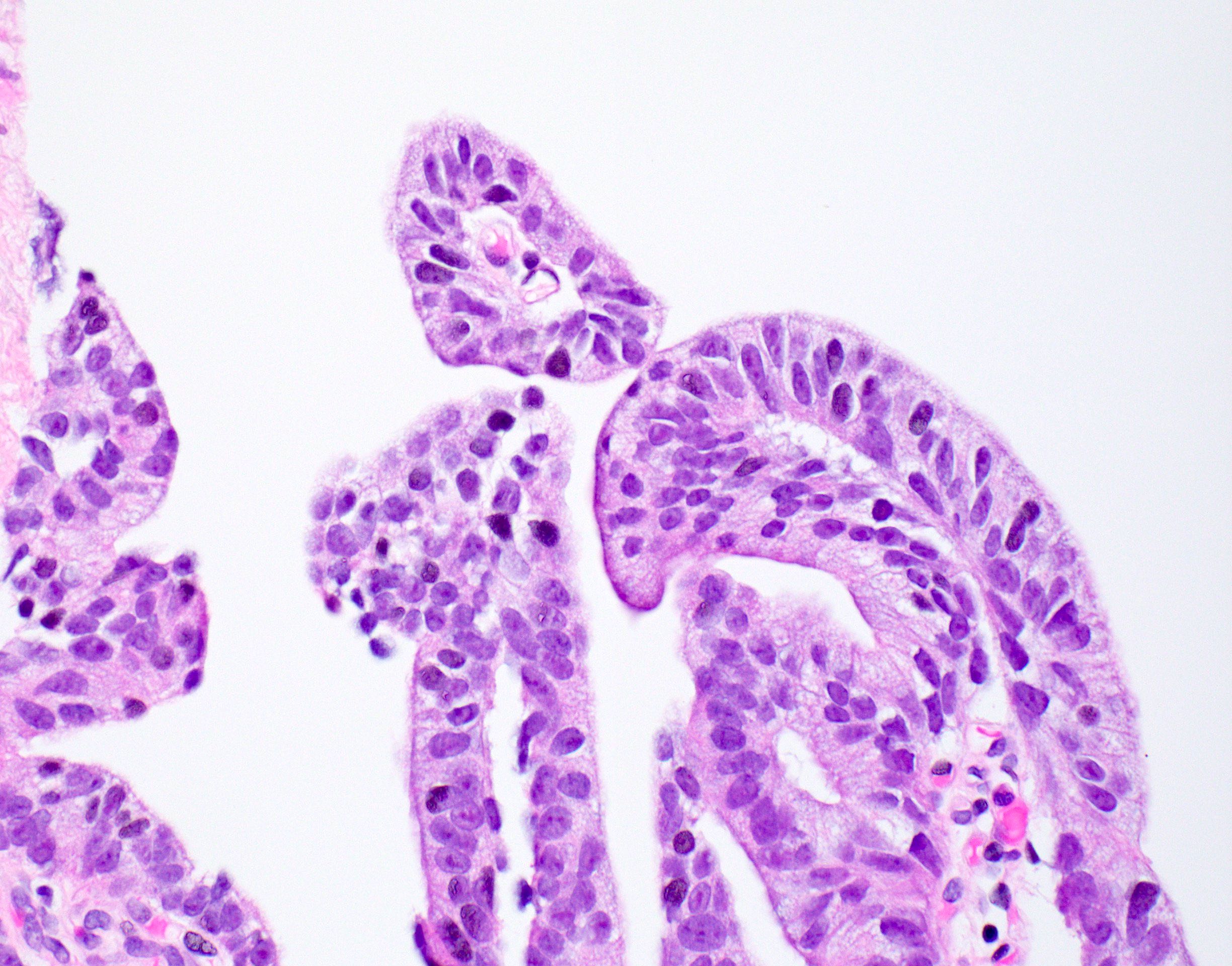
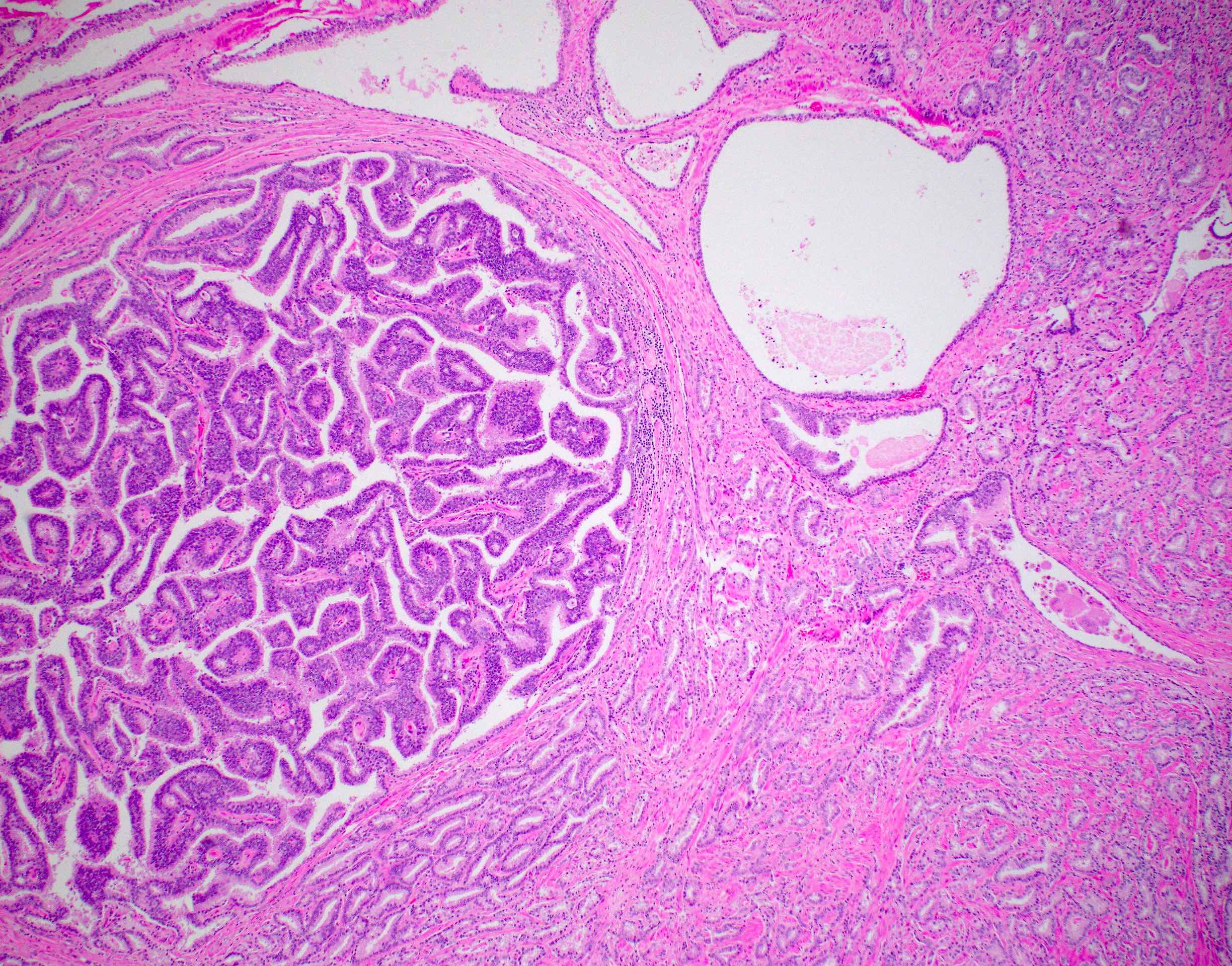
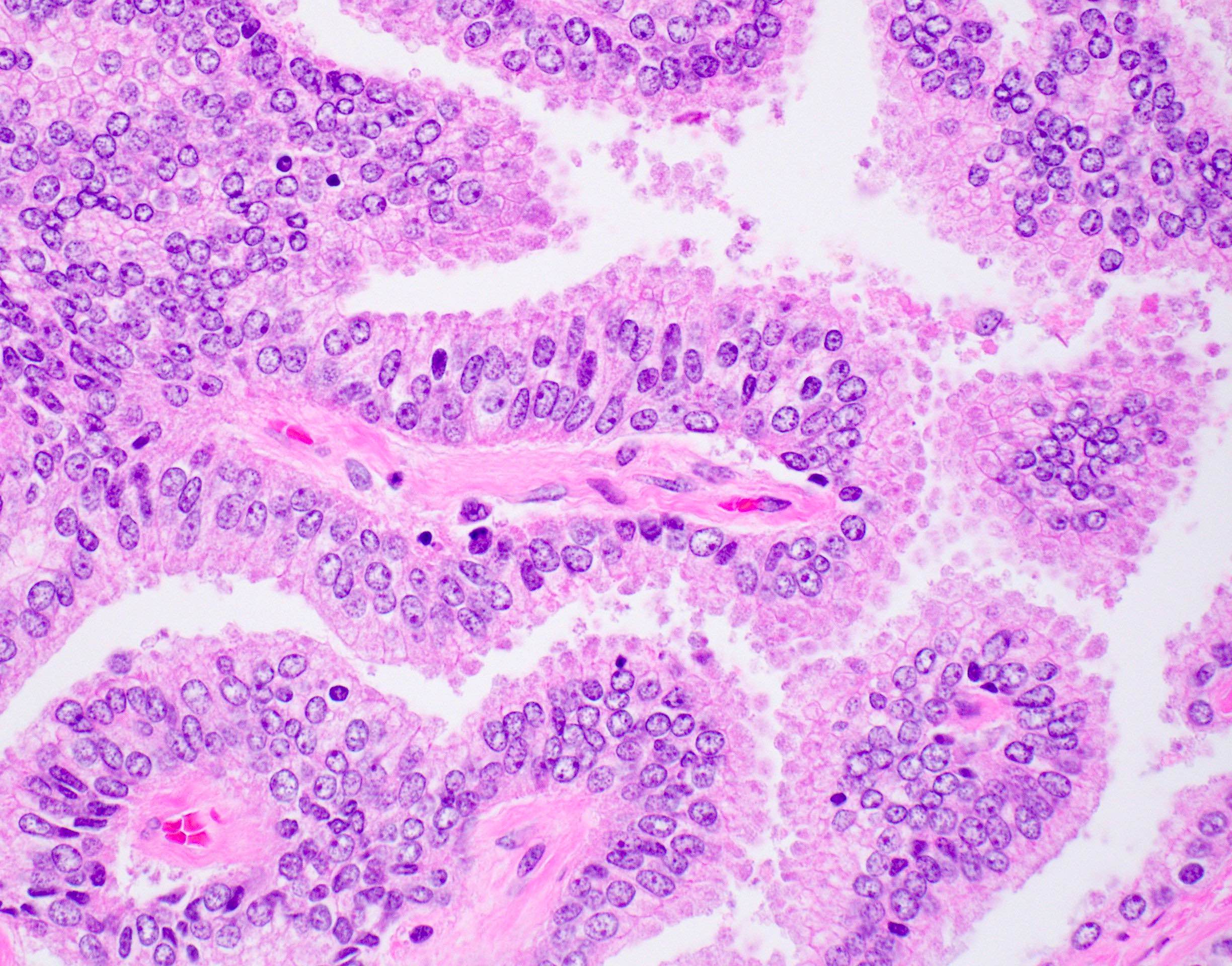
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Large glands composed of tall columnar cells which often have pseudostratified nuclei
- Patterns include cribriform, papillary, solid and prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia-like pattern
- Cribriform: similar to acinar adenocarcinoma, cribriform pattern in ductal adenocarcinoma has been shown to be more likely to have extraprostatic extension, seminal vesicle invasion, lymphovascular invasion and advanced pathologic stage (Ann Diagn Pathol 2019;39:59)
- Cribriform pattern is composed of intraglandular epithelial bridging with slit-like lumens instead of the punched out lumens of cribriform acinar adenocarcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:615)
- Papillary: true fibrovascular cores (Histopathology 2014;65:216)
- Solid: often not columnar shaped (Mod Pathol 2018;31:S71)
- Not specific; must see together with the other ductal patterns for diagnosis (Mod Pathol 2018;31:S71)
- Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia-like: assigned as Gleason pattern 3 (Histopathology 2012;60:59, Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:1060)
- Cribriform: similar to acinar adenocarcinoma, cribriform pattern in ductal adenocarcinoma has been shown to be more likely to have extraprostatic extension, seminal vesicle invasion, lymphovascular invasion and advanced pathologic stage (Ann Diagn Pathol 2019;39:59)
- Arises in primary periurethral ducts or in peripheral prostatic ducts
- Frequently is mixed with an acinar component (Virchows Arch 2013;46:429)
- Most ductal adenocarcinoma is considered to be Gleason pattern 4 (5 if with comedonecrosis) (scored via the Gleason scoring system)
- Cytoplasm is typically amphophilic, although it can be clear (Med Princ Pract 2010;19:82)
- May have desmoplastic stromal reaction, hemorrhage, edema and inflammation (Mod Pathol 2018;31:S71)
- May have intraductal spread (Mod Pathol 2018;31:S71)
- Other unusual patterns that have been reported are foamy gland, Paneth cell-like neuroendocrine, micropapillary and cystic papillary (Pathology 2010;42:319)
- Associated with seminal vesical invasion and less likely to be confined to the prostate than acinar adenocarcinoma with a Gleason score < 7 (Hum Pathol 2010;41:281, Virchows Arch 2013;46:429)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by He Huang, M.D., Ph.D. and Sarah Findeis, M.D.
Cytology description
- Sheets of columnar cells with some gland formation or papillary architecture with inconspicuous nucleoli (Acta Cytol 2013;57:184)
- Abundant cytoplasm, oval nuclei, flat or folded sheets, peripheral nuclear palisading (Am J Clin Pathol 2006;126:302)
Positive stains
- PSA, PSAP, AMACR (77%), NKX3.1, androgen receptor (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:889)
- PSMA
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- PTEN loss by IHC was less frequent compared with pure acinar carcinoma; TMPRSS2::ERG gene fusion is infrequent (Mod Pathol 2009;22:359, Prostate 2015;75:1610)
- PTEN, RB1 and TP53 alterations, in a case report of ductal adenocarcinoma having neuroendocrine phenotype (BMC Med Genomics 2021;14:245)
- Low rates of ERG rearrangement by IHC and FISH (Prostate 2015;75:1610)
- Considerable gene expression overlap with acinar adenocarcinoma; however, early research suggests that prolactin receptor protein is overexpressed in ductal (compared to acinar) adenocarcinoma (Mod Pathol 2009;22:1273)
- High percentage of DNA damage repair pathway alterations (JCO Precis Oncol 2019;3:PO.18.00327)
- Often the genomic profile is similar to castration resistant prostatic acinar adenocarcinoma (Nat Rev Urol 2021;18:337)
- MAP3K1 homozygous deletion (case report) (IJU Case Rep 2021;4:176)
- Most often are clonally related, in cases of mixed acinar and ductal adenocarcinoma (Prostate 2022;82:576)
- Aneuploidy (Prostate 2022;82:576)
Sample pathology report
- Prostate, radical prostatectomy:
- Prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma, Gleason score 4+4=8, grade group 4 (see synoptic report)
Differential diagnosis
- Acinar adenocarcinoma, Gleason pattern 4:
- Cuboidal tumor cells with smooth and rounded luminal space
- Lack of true papillary structure
- Both can have patchy p63 / HMWCK basal cells (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:889)
- Intraductal adenocarcinoma:
- Can be quite difficult to distinguish as there is some morphological overlap
- Preserved basal cells, highlighted by p63, HMWCK or CK5/6
- Note that p63 / HMWCK basal cells may stain in a patchy pattern for ductal adenocarcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:889)
- Cuboidal neoplastic cells, rounded luminal spaces and lack of true papillae (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:615)
- May show more nuclear pleomorphism
- High grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia:
- Micropapillary frond without fibrovascular stalks of true papillae
- No comedonecrosis, large glands or back to back glands
- Features that point to ductal adenocarcinoma: stromal reaction, crowded glands, expansile morphology, necrosis and other ductal adenocarcinoma morphologies (Mod Pathol 2018;31:S71)
- Preserved basal cells, highlighted by p63, HMWCK or CK5/6
- Low Ki67 (Hum Pathol 2005;36:531)
- Metastatic carcinoma from other primary site:
- Potential other primary sites include nearby colon and bladder
- Stains to rule out other possible primaries
- Prostatic urethral polyp:
- Especially on needle core biopsy since it can look relatively bland (Am J Surg Pathol 1999;23:1471, Med Princ Pract 2010;19:82)
- No nuclear atypia and basal cells are present (Mod Pathol 2018;31:S71)
- AMACR-, p63+ and CK7+ (Pathology 2007;39:476)
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
C. NKX3.1+, CK20-, PSA+. Ductal adenocarcinoma is CDX2-, CK7-, CK20-, PSA+, PSAP+, AMACR+ (77%), NKX3.1+.
Comment here
Reference: Ductal adenocarcinoma
Comment here
Reference: Ductal adenocarcinoma
Board review style question #2
You suspect prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma but your differential includes high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (HGPIN). Which of the following features favor ductal adenocarcinoma over HGPIN?
- Comedonecrosis
- Micropapillary formation
- Stronger AMACR staining pattern
- Very high PSA serum levels
Board review style answer #2
A. Comedonecrosis. Other answer choices: both can have AMACR positivity. Micropapillary pattern (and not true papillary fibrovascular cores) is more associated with HGPIN.
Comment here
Reference: Ductal adenocarcinoma
Comment here
Reference: Ductal adenocarcinoma