Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Fisher H, Asadbeigi SN. Atypical Spitz tumor (Spitz melanocytoma). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumormelanocyticatypicalspitz.html. Accessed September 26th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Atypical Spitz tumor (AST) is a classification of Spitz tumors that shares genetic and morphological characteristics between Spitz nevi and Spitz melanoma; it has variable potential for malignant progression
Essential features
- Nevus that consists of epithelioid and spindled melanocytes and contains sufficient morphological and genetic atypia to distinguish from Spitz nevus but is insufficient for a diagnosis of melanoma
- Has a higher risk of sentinel lymph node involvement but typically has an indolent behavior (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2015;139:1263)
- Potential for malignancy is difficult to discern
- Often contains HRAS mutation or tyrosine kinase fusions involving ROS1, NTRK1, NTRK3, ALK, BRAF, RET, MET and MAP3K8
Terminology
- Spindle and epithelioid cell nevus with atypia and metastasis
- Spitzoid tumor of uncertain malignant potential
- Benign juvenile melanoma (historical)
- Atypical Spitzoid melanocytic tumor
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Can occur at any age but the majority of cases occur in childhood and into the second decade of life (Cancer 1977;40:217, Cancer 2009;115:631)
- Rare congenital cases have been reported (Cancer 2009;115:631)
- More common in the White population (Br J Dermatol 2019;181:366)
- May have slight predilection for women (Cancer 1977;40:217, Cancer 2009;115:631)
Sites
- Can occur anywhere on the skin but is most common on the lower limbs (Cancer 2009;115:631)
Pathophysiology
- Cell proliferation mediated by mutations in genes associated with Spitz tumor, such as kinase fusion or inactivation of CDKN2A
Clinical features
- Often larger than Spitz nevus, often > 1 cm (Front Oncol 2022:12:889223, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2015;139:1263, Histopathology 2022;80:122)
- Usually presents as a dome shaped papule or nodule; may be plaque or polyploid, with or without ulceration (J Am Acad Dermatol 2015;73:777, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2015;139:1263)
- Variable pigmentation, from amelanotic to black or multicolored (Br J Dermatol 2019;181:366, Dermatopathology (Basel) 2022;9:136, Cancer 2009;115:631)
- Variable symmetry and circumscription (Histopathology 2022;80:122)
- Asymmetry is more associated with AST than Spitz nevus (J Am Acad Dermatol 2015;72:37)
- History of a rapid, recent growth in a lesion that was previously stable (Histopathology 2022;80:122)
- Dermoscopy
- Nearly 20% showed a characteristic appearance of an amelanotic nodule with hypopigmentation, dotted vessels and white lines (J Am Acad Dermatol 2015;73:777)
- Overall, dermoscopic appearance may be nonspecific or consist of a combination of starburst, globular, homogenous or atypical vascular patterns (J Am Acad Dermatol 2015;73:777)
- Benign and malignant Spitzoid lesions show significant dermoscopy overlap (Lancet Child Adolesc Health 2019;3:646)
Diagnosis
- Biopsy
- Modified ABCD (asymmetry, border irregularity, color variegation, diameter > 6 mm) and dermoscopy are used for detection of Spitzoid lesions but biopsy is necessary to evaluate the degree of atypia (Lancet Child Adolesc Health 2019;3:646)
- Any asymmetrical, raised or nodular lesion should be biopsied for evaluation of atypia (Br J Dermatol 2017;177:645)
Prognostic factors
- Tends to be indolent
- Presence of tumor deposits in sentinel lymph nodes tends not to alter prognosis (Hum Pathol 2013;44:87, Clin Exp Dermatol 2022;47:1464)
- Increased risk for metastatic progression is associated with
- Homozygous 9p21 deletion
- TERT promoter mutations
- MAP3K8 kinase rearrangements (Front Oncol 2022:12:889223)
- Older age
- Lesion diameter exceeding 1 cm
- Ulceration
- Subcutaneous fat involvement
- Mitotic activity > 6/mm2 (Histopathology 2022;80:122)
- Intermediate risk of metastasis associated with (Front Oncol 2022:12:889223)
- 6p25 gain: intermediate risk
- 11q13 gain: intermediate risk
- Favorable prognosis is associated with HRAS amplification (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2015;139:1263)
- Recurrence is infrequent if excised completely but risk may increase with homozygous 9p21 deletion or MAP3K8 fusion (Histopathology 2022;80:122)
Case reports
- 2 year old girl with a lower lip mass, harboring ROS1 kinase mutation and ALK variant (JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2020;146:203)
- 7 year old girl with 12 mm ALK positive pedunculated pigmented nodule of the right ankle (J Cutan Pathol 2018;45:136)
- 9 year old boy with 14 mm ALK positive pedunculated pigmented nodule of the thigh (J Cutan Pathol 2018;45:136)
- 16 year old girl with AST with Homer Wright-like rosettes (Am J Dermatopathol 2018;40:903)
- 40 year old woman with enlarging red polypoid lesion on right forearm, with ALK fusion (Hum Pathol 2018:80:99)
- Case series including 13 ASTs with MAP3K8 fusions (Mod Pathol 2020;33:846)
Treatment
- Complete excision
- Re-excision of the lesion regardless of the margin status of the biopsy (J Cutan Med Surg 2020;24:144)
- Typically, without sentinel lymph node biopsy due to lack of prognostic value (JAMA Dermatol 2013;149:1348)
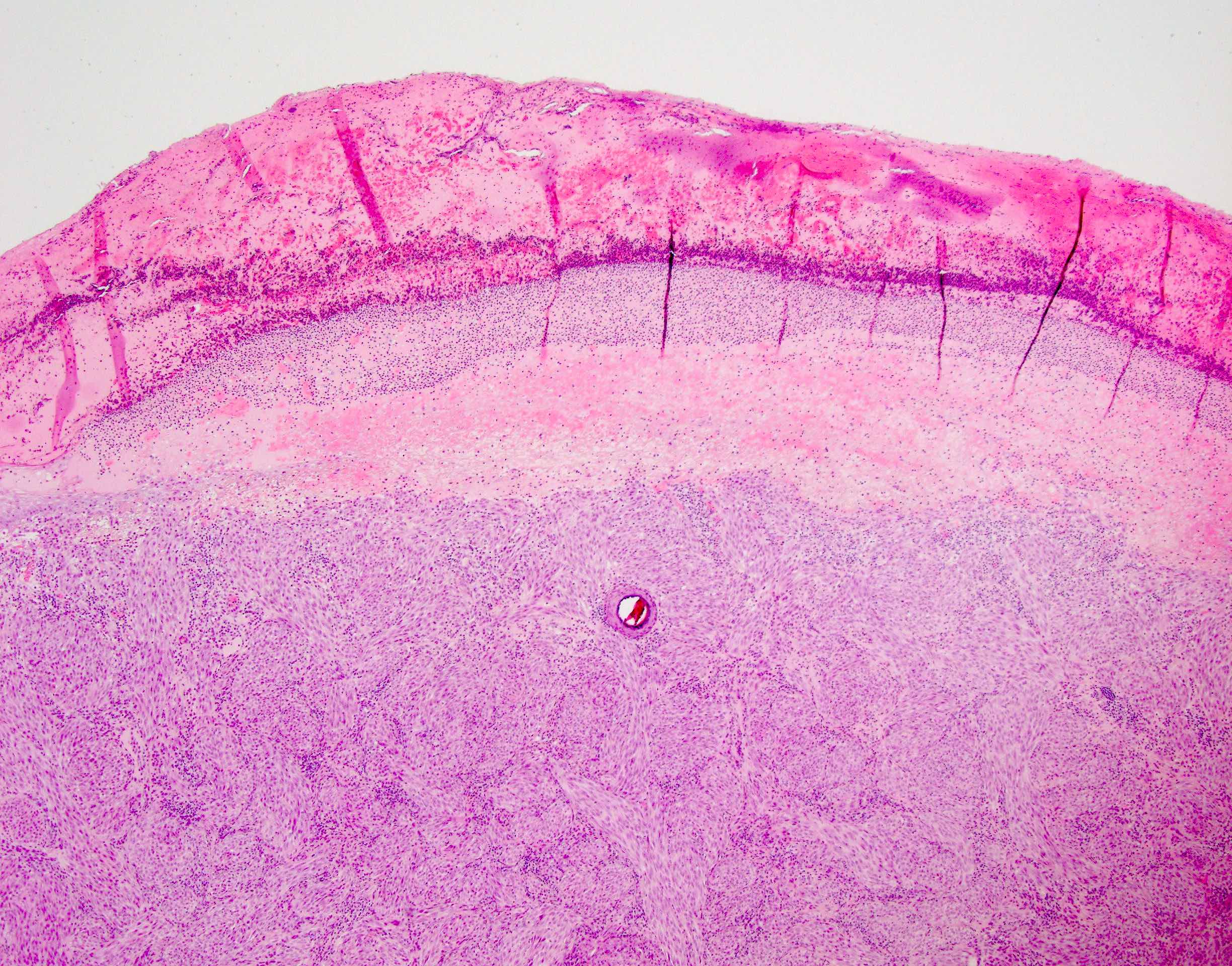
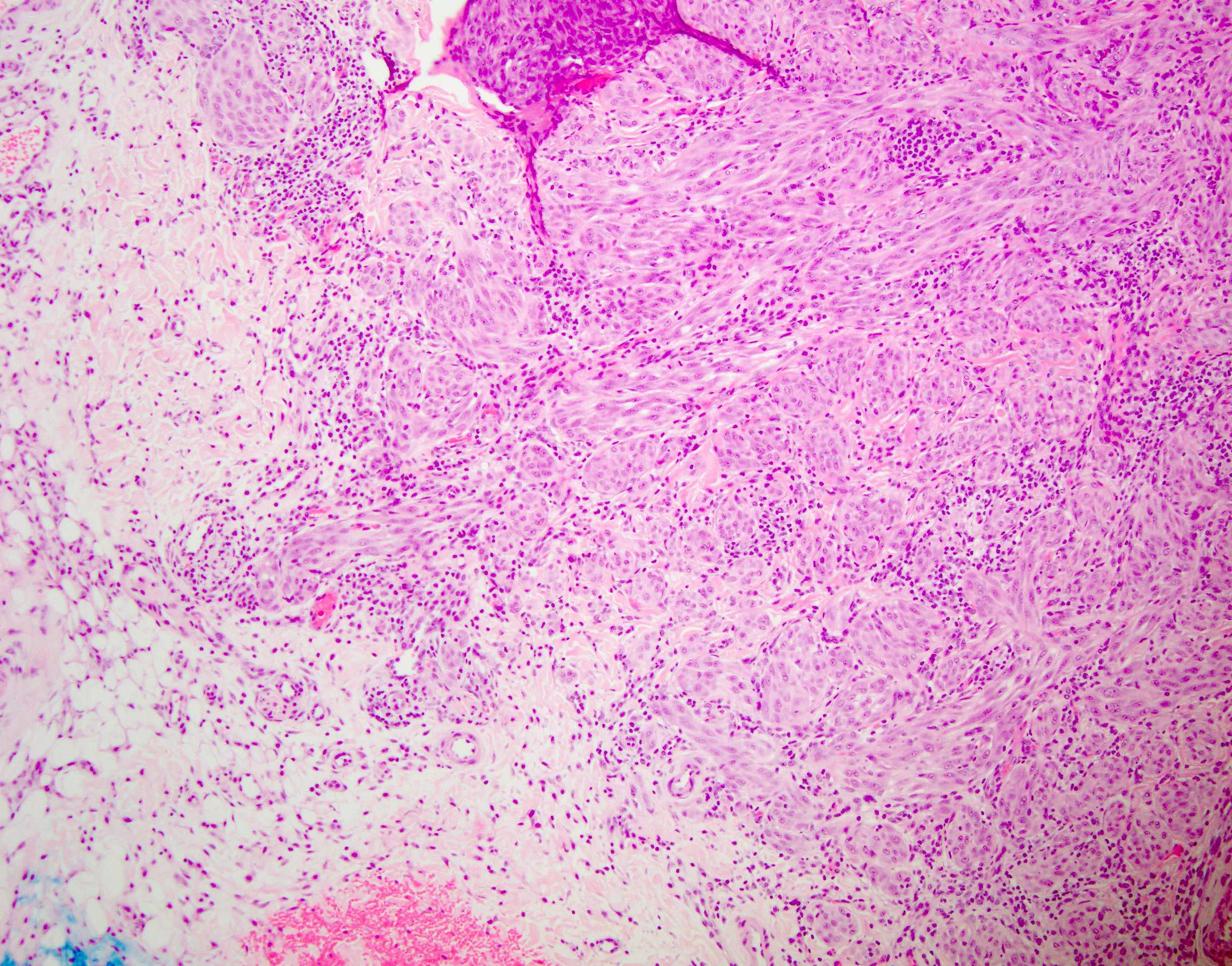
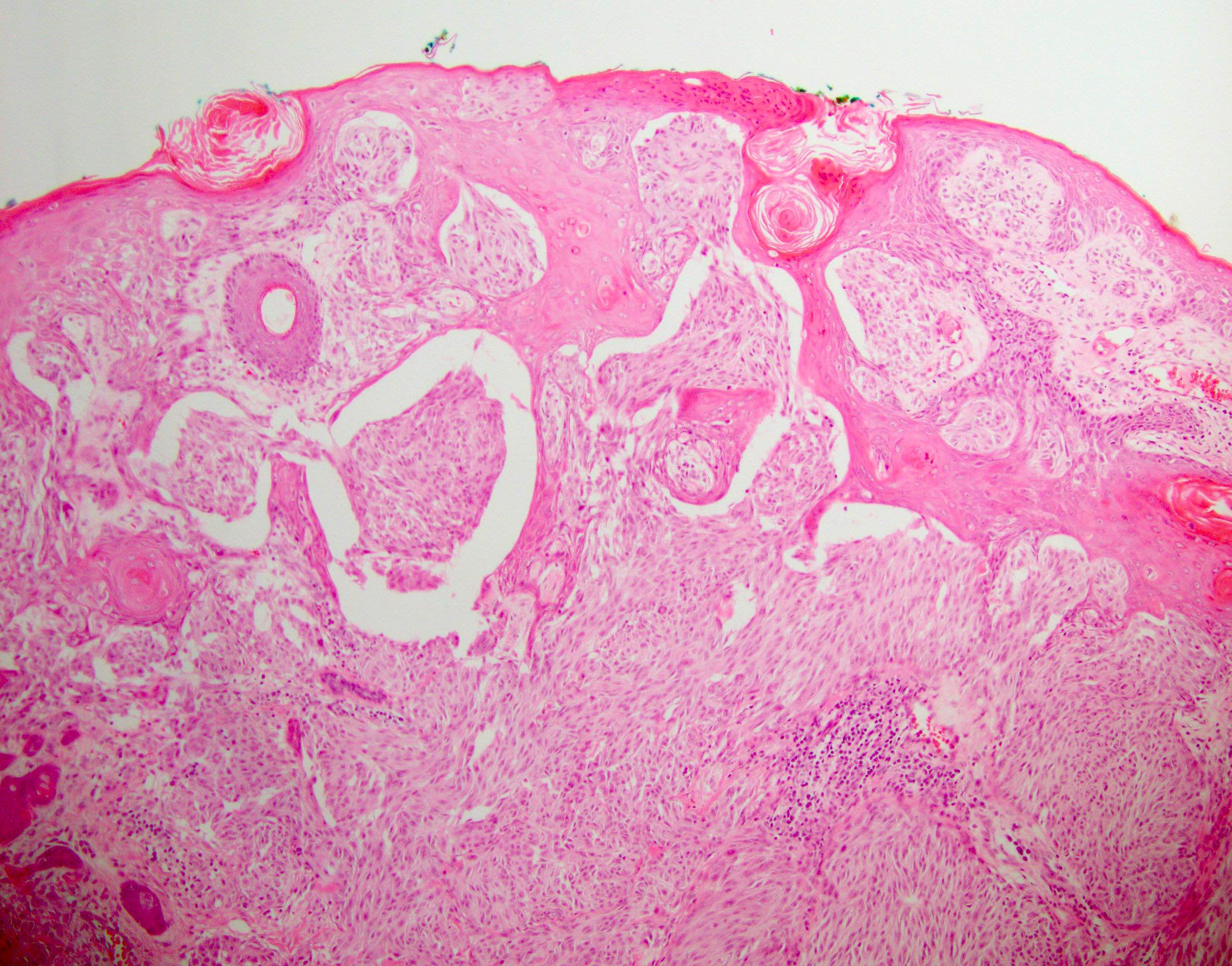
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Can be junctional, compound or dermal but compound form is more common
- Greater degree of atypia compared to benign Spitz nevus (cytological atypia or architectural overlap with dysplastic nevus) and involves 1+ features atypical for Spitz nevus; not enough atypia to be equivocal to melanoma
- Overlap features with benign Spitz nevus
- Spitzoid cytomorphology
- Junctional component with vertically oriented nests and retraction artifact
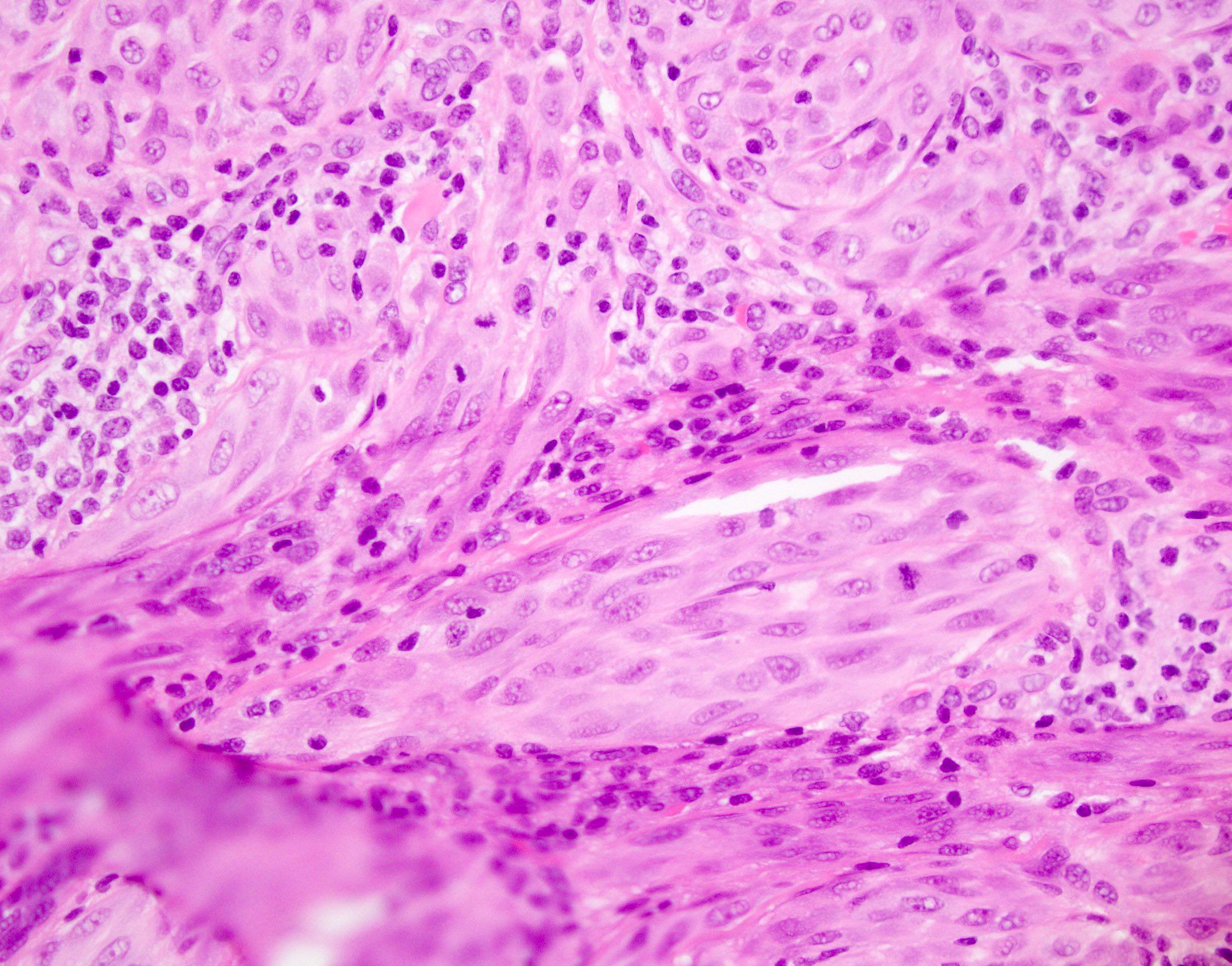
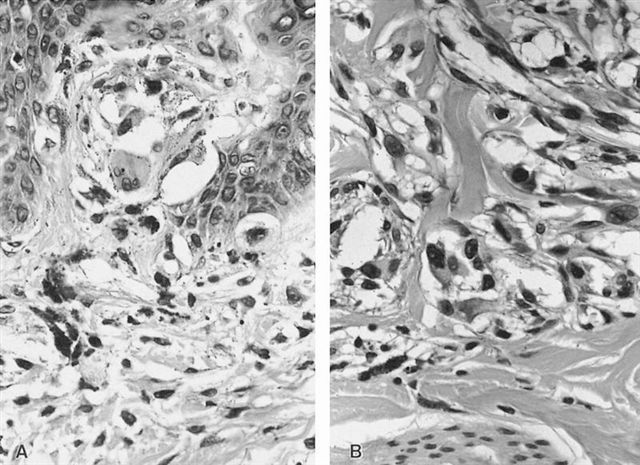
- Intranuclear pseudoinclusion
- Eosinophilic nucleoli
- Epidermal hyperplasia
- Vertical junctional nests
- Overlap features with melanoma
- Large size (> 10 mm)
- Asymmetry
- Poor circumcision
- Ulceration
- Deep dermal component
- Absence of maturation
- Increased dermal mitosis in deep or peripheral component
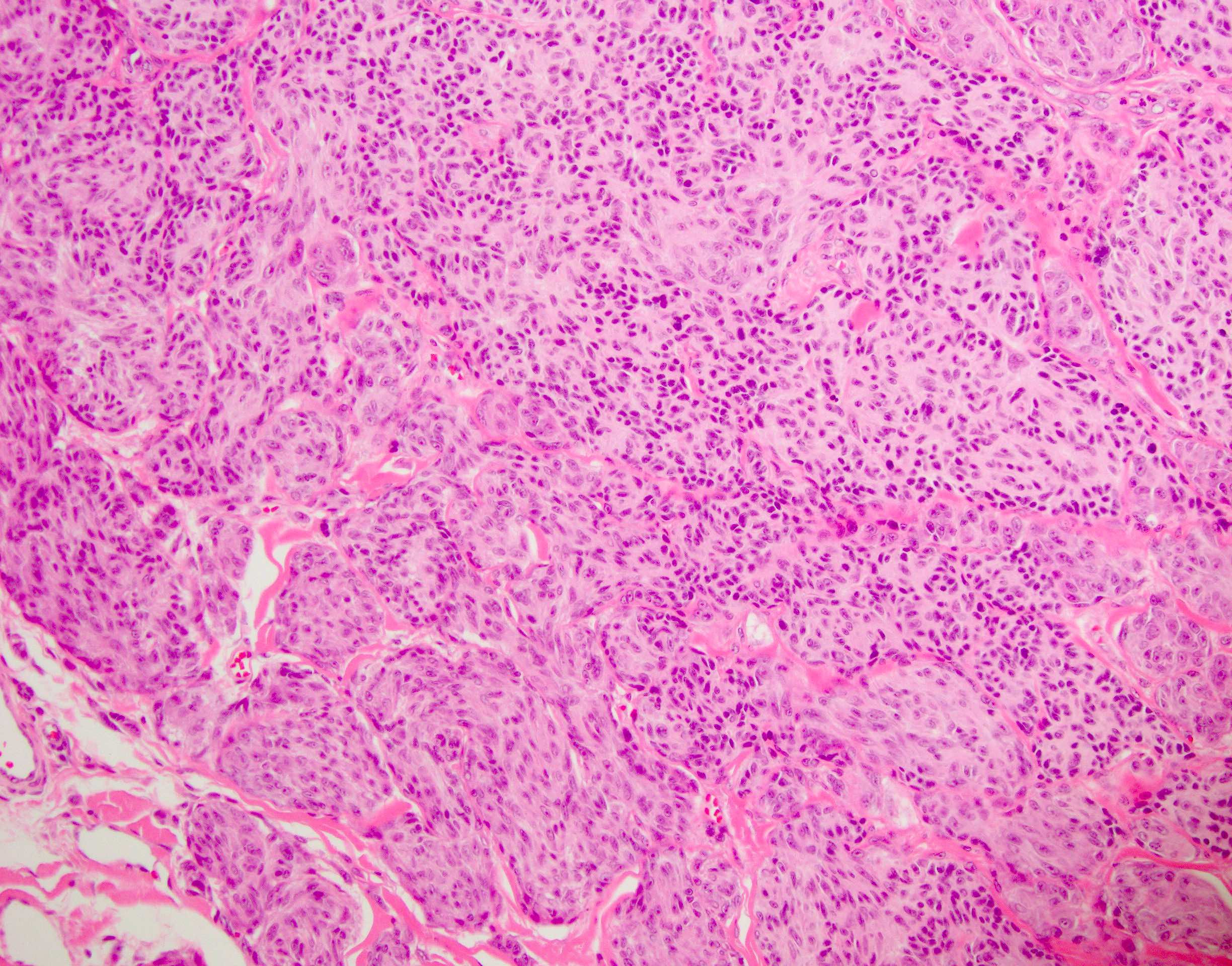
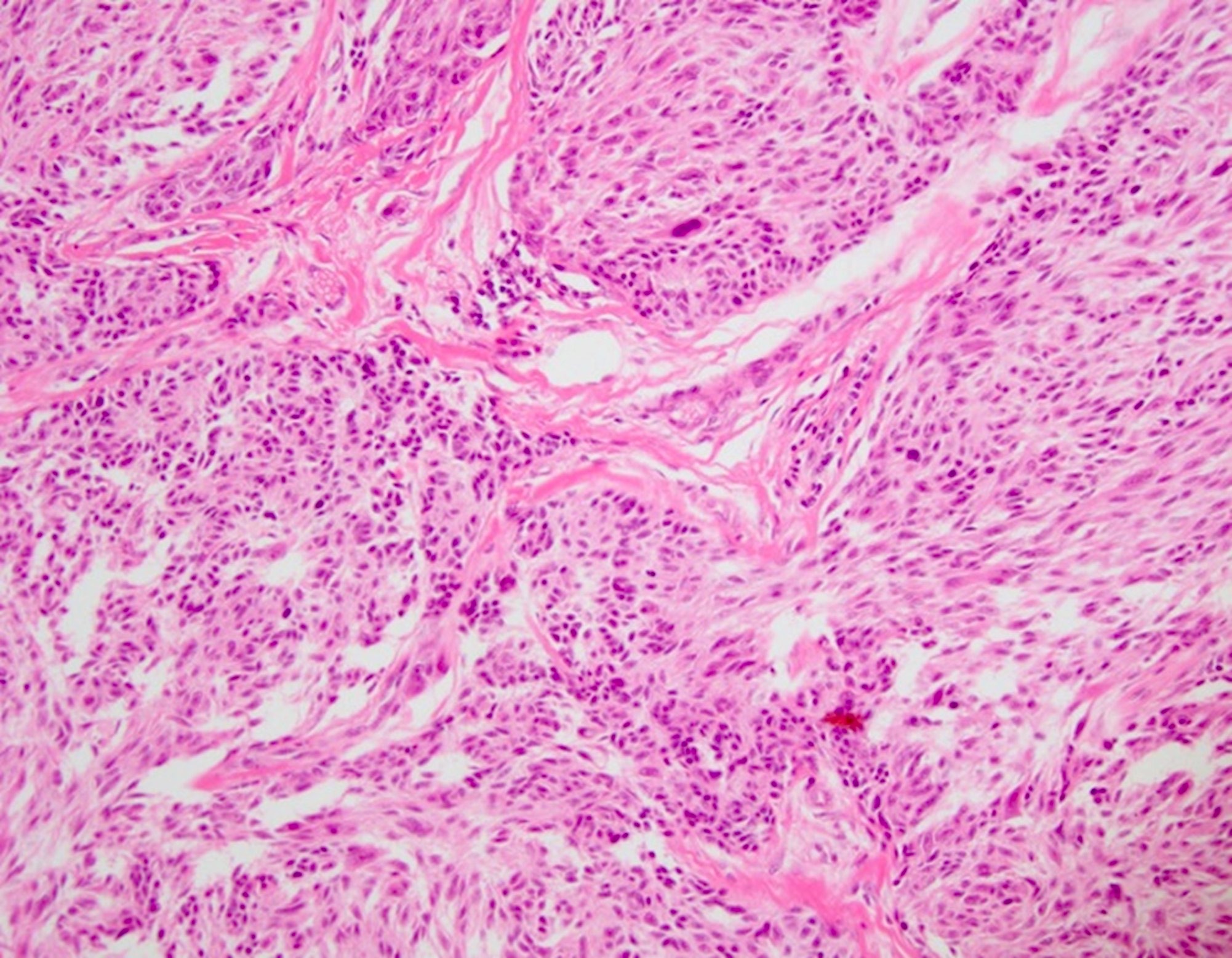
- Primarily epithelioid, spindle or mixed melanocytes that may present with (Front Oncol 2022:12:889223)
- Large tumor consisting of cellular fascicles of melanocytes
- Expansile growth with compression of stroma
- Most commonly asymmetrical
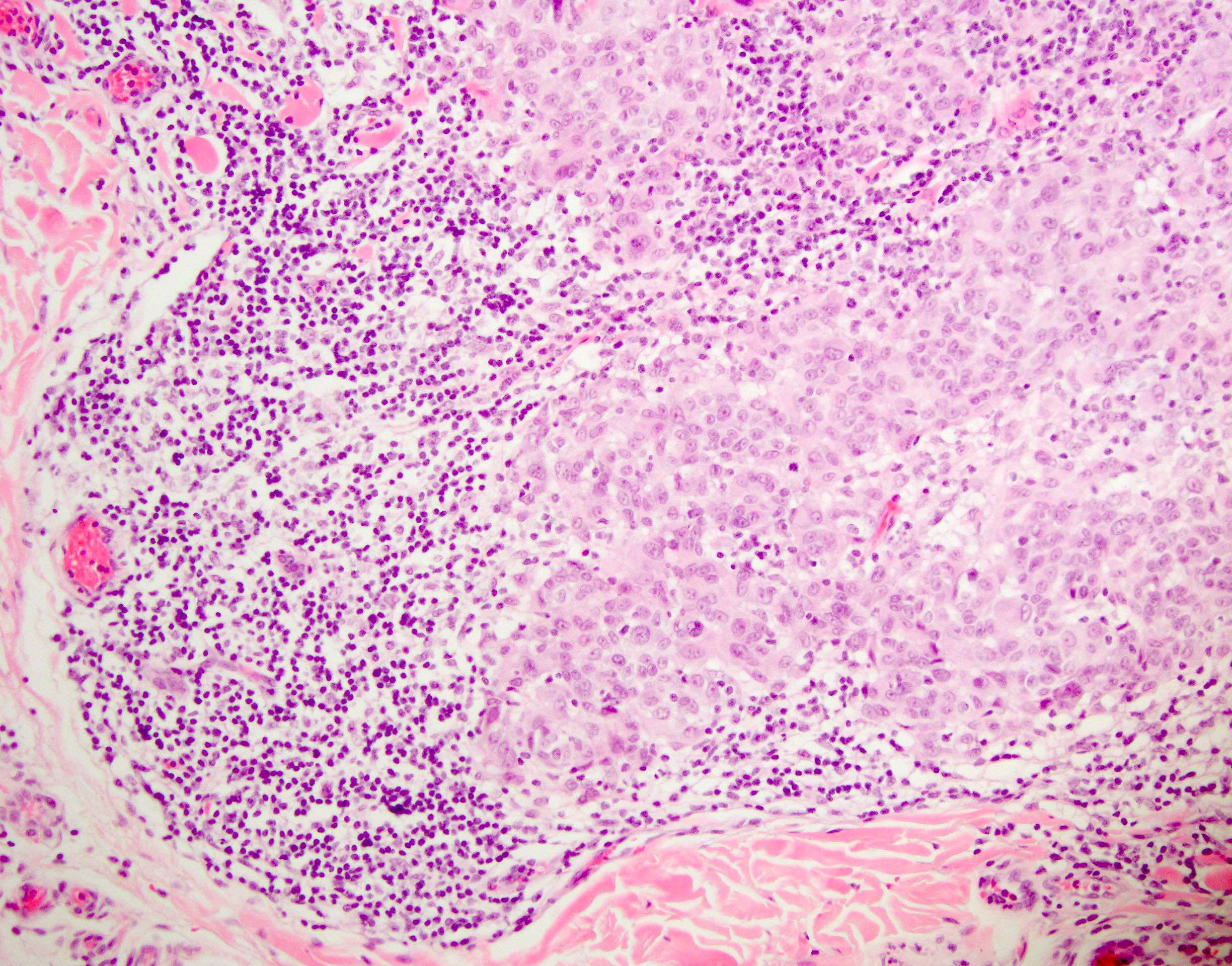
- Lymphocytic infiltrate
- Fewer Kamino bodies
- Pagetoid spread (often peripheral)
- Junctional nests with vertical orientation of cells (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2015;139:1263)
- Average Breslow depth: 2.4 mm (Cancer 2009;115:631)
- ASTs with ALK fusion (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:491)
- Wedge shaped with large diameter
- Plexiform growth of intersecting fusiform melanocytes
- ASTs with NTRK1 fusion (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:491)
- Smaller nests
- Presence of Kamino bodies and rosette formation
- ASTs with MAP3K8 fusion
- Epithelioid with higher grade features (J Cutan Pathol 2019;46:878)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- No single IHC result can be used for the definitive identification, though it is suggested that the combination of Ki67 proliferative index, HMB45 and p16 results may be useful in distinguishing Spitz neoplasms (Front Oncol 2022:12:889223)
- Melanocytic markers such as SOX10, MITF, MelanA
- Ki67 proliferative index: 2 - 10% (intermediate between Spitz nevus and Spitz melanoma) (Front Oncol 2022:12:889223, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2015;139:1263)
- BAP1: distinct subtype of ASTs express BAP1 (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:818)
- ALK1 in ASTs with ALK fusion
Negative stains
- Infrequent or diffuse PRAME staining may be useful in distinguishing AST from melanoma (J Cutan Pathol 2020;47:1123, J Cutan Pathol 2022;49:709)
- BRAF V600E
- p16: variable due to homozygous or heterozygous loss of 9p21 (Front Oncol 2022:12:889223)
- HMB45: variable or diminished in dermis (Front Oncol 2022:12:889223)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Often demonstrates HRAS mutations, similar to approximately half of all Spitz neoplasms (Am J Dermatopathol 2009;31:107)
- Tyrosine kinase fusions are common in all varieties of Spitz neoplasms: ROS1, NTRK1, NTRK3, ALK, BRAF, RET, MET and MAP3K8 (Front Oncol 2022:12:889223, Nat Commun 2014:5:3116)
- Present in ~56% of ASTs (Nat Commun 2014:5:3116)
- ALK present in ~15 - 20% of diagnosed ASTs (Front Oncol 2022:12:889223, Am J Dermatopathol 2017;39:181, Nat Commun 2014:5:3116)
- MAP3K8 translocation tends to be more common in AST and Spitz melanoma than Spitz nevus (Front Oncol 2022:12:889223)
- MET, RET and MAP3K8 considered less common than the other tyrosine kinase fusions (Front Oncol 2022:12:889223)
- Deep deletion with limited additional copy number of CDKN2A and no additional mutations (Histopathology 2022;80:122)
- Array comparative genomic hybridization tends to show 1+ chromosomal gains / losses (Front Oncol 2022:12:889223)
- May have homozygous or heterozygous loss of 9p21 (Front Oncol 2022:12:889223)
- Tumors with BRAF V600E and NRAS Q61 mutations are not classified in Spitz tumors anymore (Histopathology 2022;80:122)
Videos
Common histological features associated with Spitz nevus
Sample pathology report
- Skin, left cheek, shave biopsy:
- Atypical Spitz tumor (see comment)
- Comment: The sections show nests of melanocytes involving the epidermis and upper dermis. The melanocytes are nested and show some pagetoid scatter. The melanocytes show pink-lavender cytoplasm with large nuclei. The nucleoli are conspicuous and eosinophilic. Mitotic figures are present in superficial dermis (2/10 high power fields). The nests show some maturation. Immunohistochemistry shows diffuse positivity with SOX10. HMB45 shows loss of staining with maturation. p16 shows preserved nuclear staining in majority of the melanocytes and PRAME is negative within the nevomelanocytes. BRAF V600E immunohistochemistry is negative. The overall histology is consistent with atypical Spitz tumor. The margins are involved and a complete excision is recommended.
Differential diagnosis
- Benign Spitz nevus:
- Factors favoring AST over Spitz nevus (J Am Acad Dermatol 2015;72:37)
- Asymmetry
- Ulceration or epidermal consumption (Front Oncol 2022:12:889223)
- Lack of cytological maturation
- Expansile nests and pushing lower border
- Increased cellularity
- Nuclear pleomorphism
- High N:C ratio
- Atypical and deep mitoses
- High mitotic rate
- Fewer, smaller Kamino bodies (Front Oncol 2022:12:889223)
- Factors favoring AST over Spitz nevus (J Am Acad Dermatol 2015;72:37)
- Spitzoid melanoma:
- Older patients
- Distinction can be very challenging with only light microscopy; all of the following features can be present in both AST and Spitz melanoma but are more common in melanoma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2015;139:1263, Am J Dermatopathol 2012;34:478)
- High grade cytologic atypia
- Poor nesting and prominent pagetosis in junctional component
- Deep, numerous, atypical and marginal mitosis
- Intravascular invasion
- High cellular density
- Lack of maturation
- Consumption of epidermis
- Infiltrative pattern
- Immunohistochemistry
- Molecular findings
- Presence of TERT, BRAF and CDKN2A alterations are supportive of Spitz melanoma diagnosis (Pediatr Dermatol 2022;39:409)
- FISH: aberration in 9p21,6p25,11q13 and 8q24
- Chromosomal microarray (comparative genomic hybridization): multiple (> 3) and complex chromosomal abnormalities
- Lack of tyrosine kinase mutation
- Lack of HRAS mutation
- Cellular neurothekeoma:
- Epithelioid fibrous histiocytoma:
- Negative melanocytic marker
- Lack of junctional component
- Dysplastic Clark nevus:
- Commonly in older population with sun damaged skin
- Lack of distinct spindle and epithelioid morphology seen in Spitz neoplasms
Practice question #1
A 17 year old patient with an ulcerated pink papule on the face underwent a shave biopsy, which showed a tumor with cells staining strongly positive for MelanA and HMB45. The tissue was sent for molecular study. The presence of which alteration is more indicative of a malignant process?
- ALK
- GNAQ
- HRAS
- TERT
Practice answer #1
D. TERT. The sections show a melanocytic proliferation with Spitzoid cytomorphology. Atypical features such as frequent mitosis and pushing borders are present, which can be seen in both ASTs and Spitz melanomas. The presence of TERT is supportive of a Spitz melanoma diagnosis. Answers A and C are incorrect because ALK fusion and HRAS deletion are common in Spitz lesions and can be observed in benign, atypical and malignant lesions. Answer B is incorrect because GNAQ mutation is common in blue nevi.
Comment Here
Reference: Atypical Spitz tumor (Spitz melanocytoma)
Comment Here
Reference: Atypical Spitz tumor (Spitz melanocytoma)
Practice question #2
Which immunohistochemical pattern is more indicative of an atypical Spitz tumor rather than a benign Spitz nevus?
- HMB45 positivity in junctional melanocytic nests
- Negative BRAF V600E in melanocytic nuclei
- p16 positivity in 40% of melanocytes
- Weak PRAME positivity in 5% of melanocytes
Practice answer #2
C. p16 positivity in 40% of melanocytes. Complete or extensive loss of p16 is more supportive of an atypical or malignant Spitz neoplasm. CDKN2A homozygous deletion can lead to p16 loss, which is indicative of a higher grade or malignant lesion. Answer B is incorrect because BRAF V600E immunohistochemistry is generally negative in Spitzoid lesions and its positivity should raise suspicion of melanoma. Answer A is incorrect because HMB45 shows a loss of staining with descent and the positivity of the stain only in the junctional component is supportive of benignity. Answer D is incorrect because weak and focal PRAME positivity (1+) is not strongly supportive of an atypical lesion and can be observed in benign Spitz nevi.
Comment Here
Reference: Atypical Spitz tumor (Spitz melanocytoma)
Comment Here
Reference: Atypical Spitz tumor (Spitz melanocytoma)