Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Albahra S, Hosler GA. Angiofibroma / fibrous papule. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocyticangiofibroma.html. Accessed September 17th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Benign fibrohistiocytic tumor consisting of dermal dendritic cells
Essential features
- Common benign lesion composed of stellate, factor XIIIa positive stromal cells
- Most common variant referred to as fibrous papule when present on the central face
Terminology
- Solitary angiofibroma on the central face referred to as fibrous papule
- Multiple angiofibromatous lesions in tuberous sclerosis referred to as adenoma sebaceum
- On the penis, referred to as pearly penile papules
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Middle aged adults (J Invest Dermatol 1965;45:194)
- Multiple facial lesions can be seen in tuberous sclerosis, multiple endocrine neoplasia type I (MEN 1), neurofibromatosis II and Birt-Hogg-Dubé
Sites
- Central face, particularly on the nose
Pathophysiology
- Unknown at this time
Etiology
- Unclear
- Thought to represent a proliferative reactive process of dermal dendritic cells (J Cutan Pathol 1989;16:194)
Clinical features
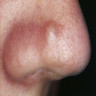
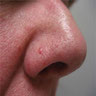
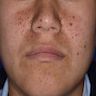
- Dome shaped, skin colored papules measuring a few millimeters
- Asymptomatic
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis can be made on biopsy
- Dermoscopy may show milky white or pink background with telangiectasia (StatPearls: Cutaneous Angiofibroma [Accessed 3 December 2021])
Case reports
- 39 year old woman with a dome shaped papule on the nose (J Cutan Pathol 2009;36:381)
- 45 year old woman with multiple facial papules since her 20s (JAAD Case Rep 2019;5:368)
- 63 year old man with a flesh colored papule on the left nasal ala present for many years (J Cutan Pathol 1991;18:284)
Treatment
- For cosmetic purposes, can be removed by excisional / shave biopsy or electrosurgery
Clinical images
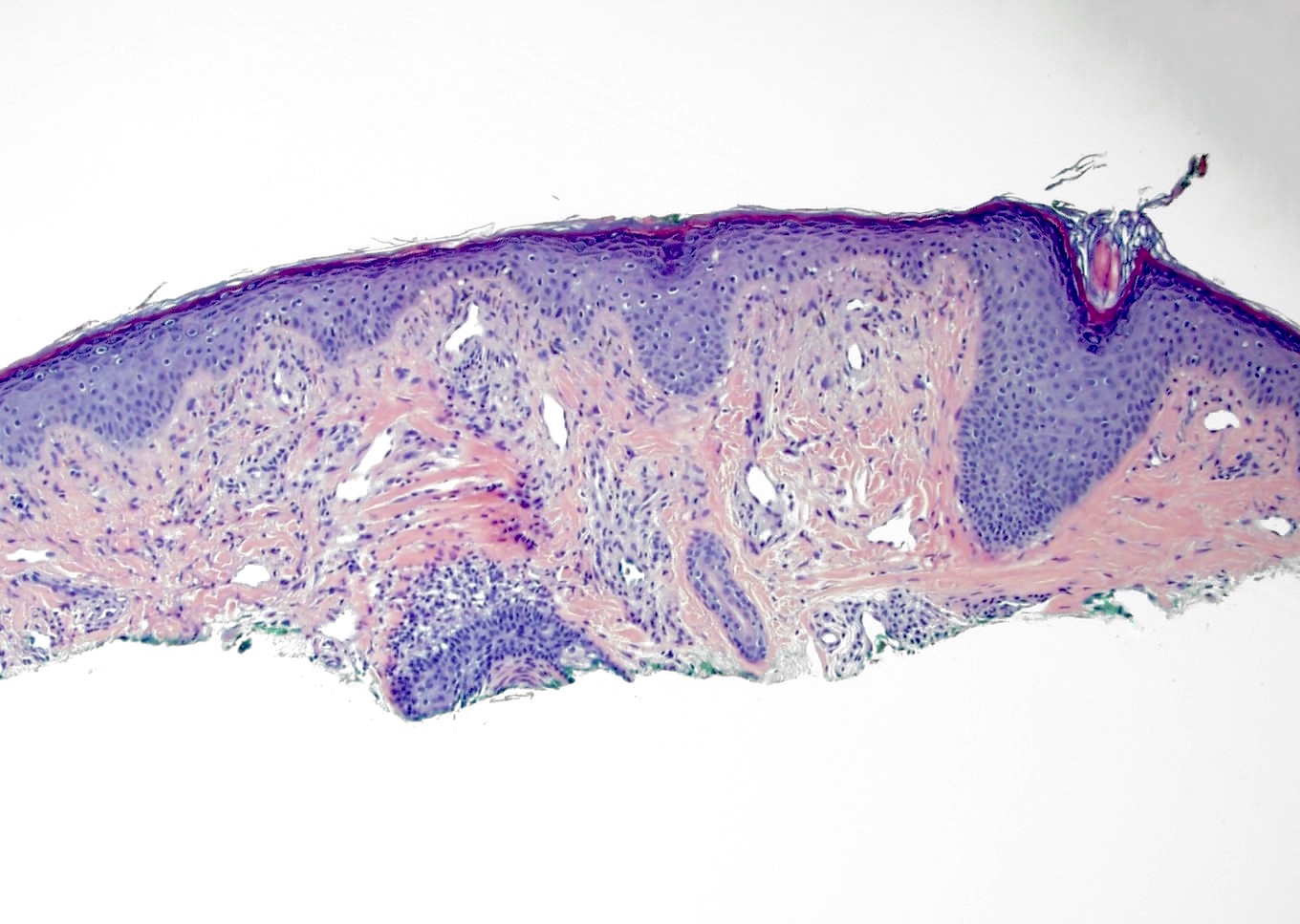
Microscopic (histologic) description
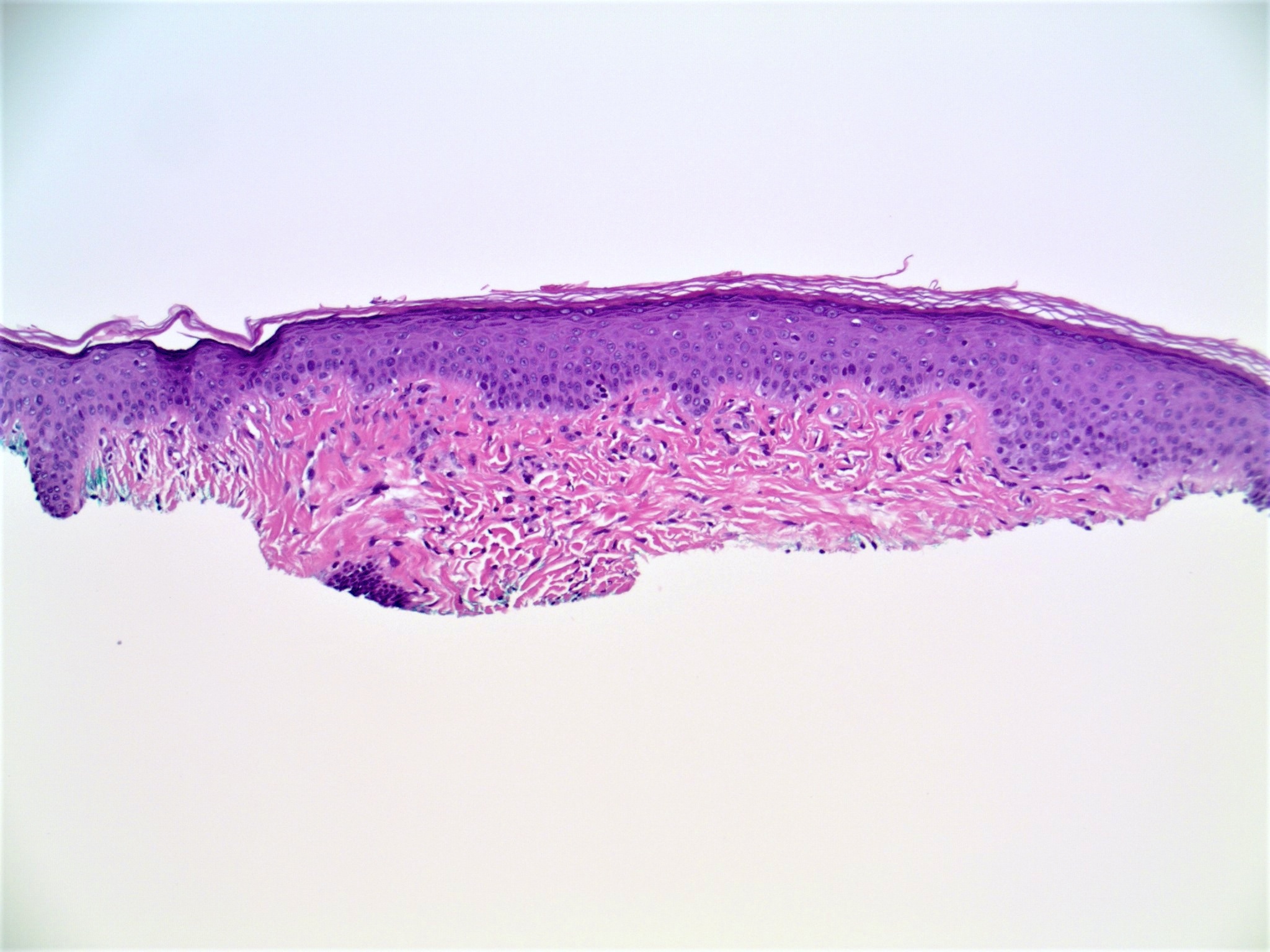
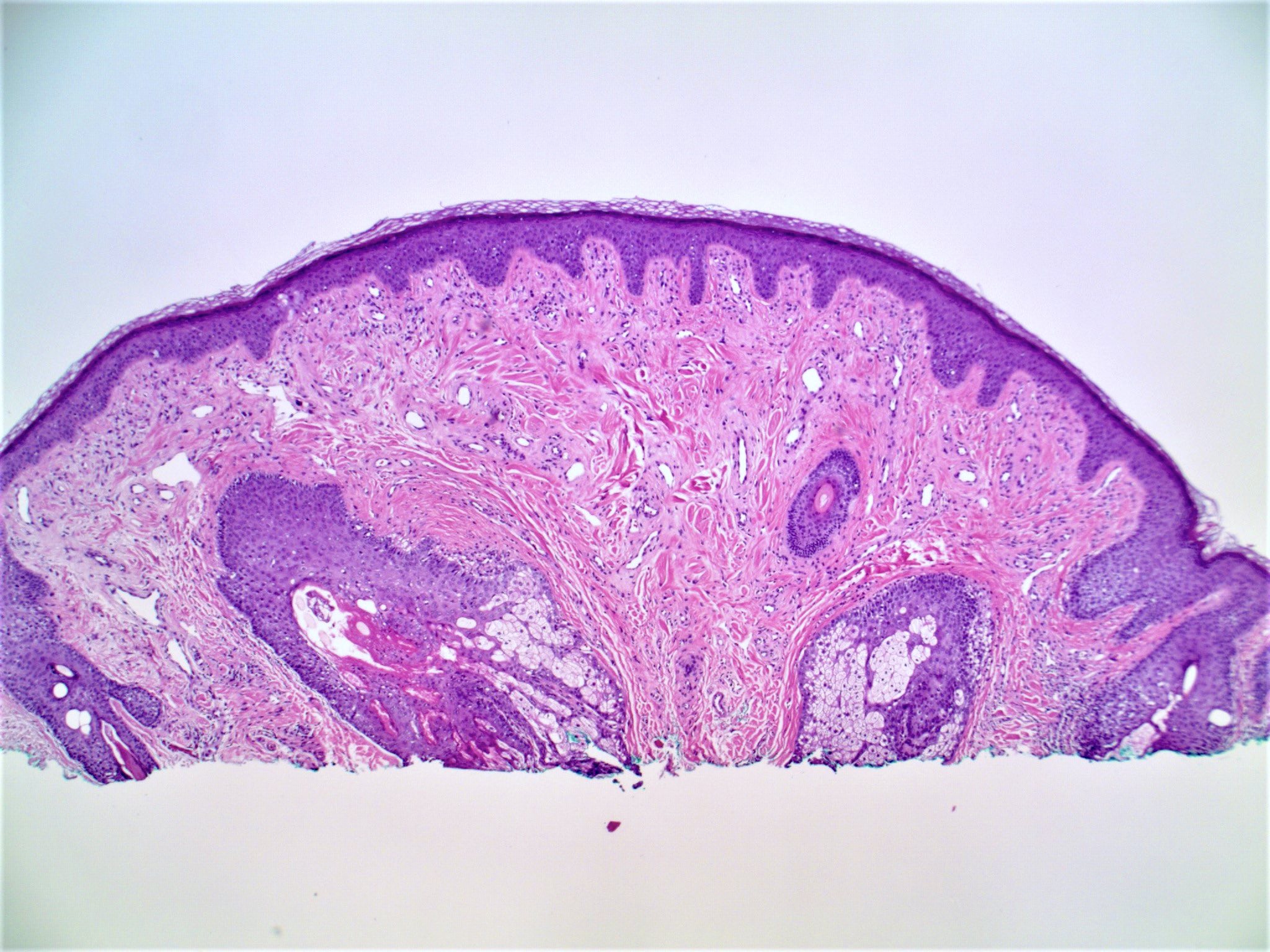
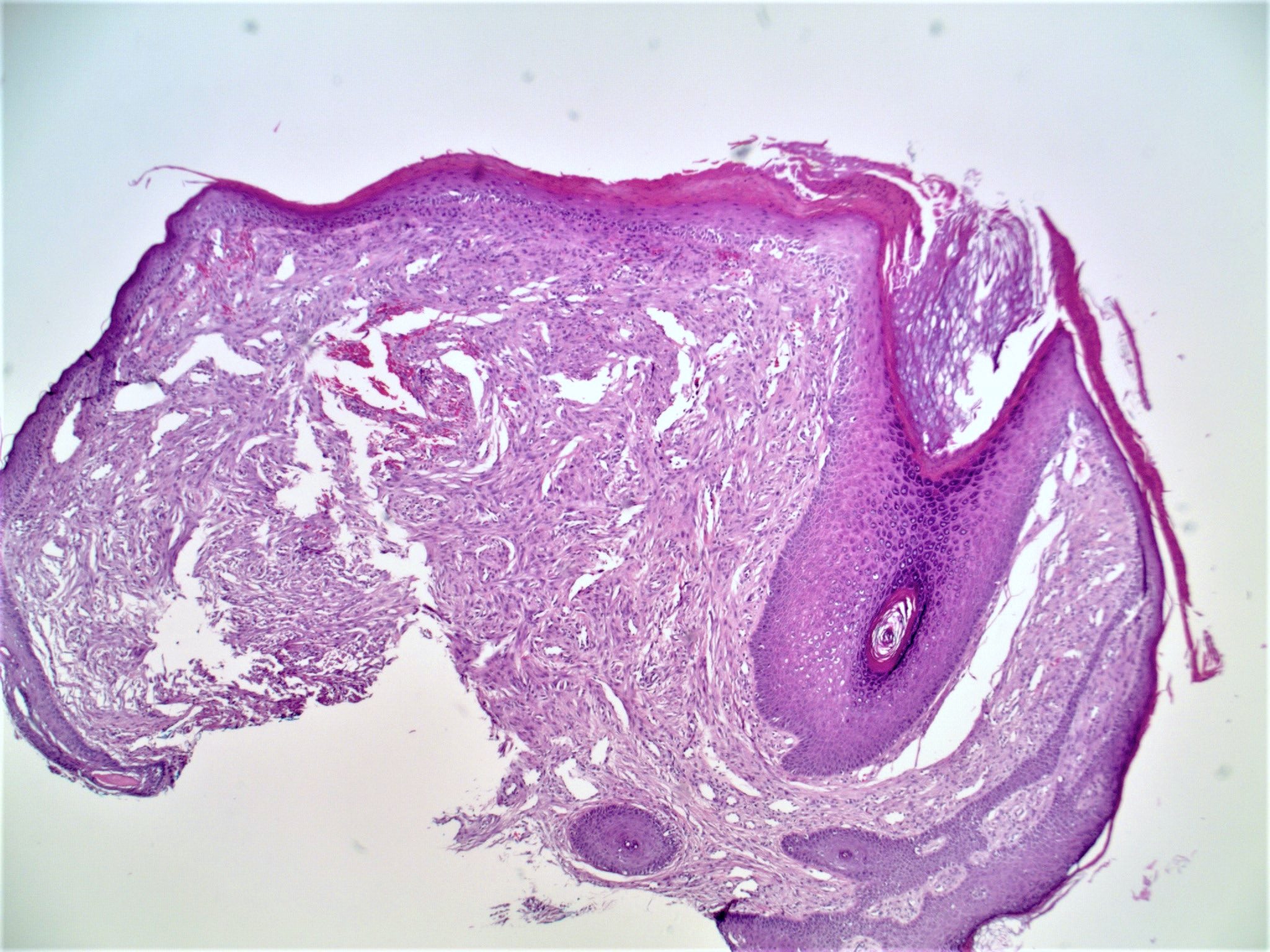
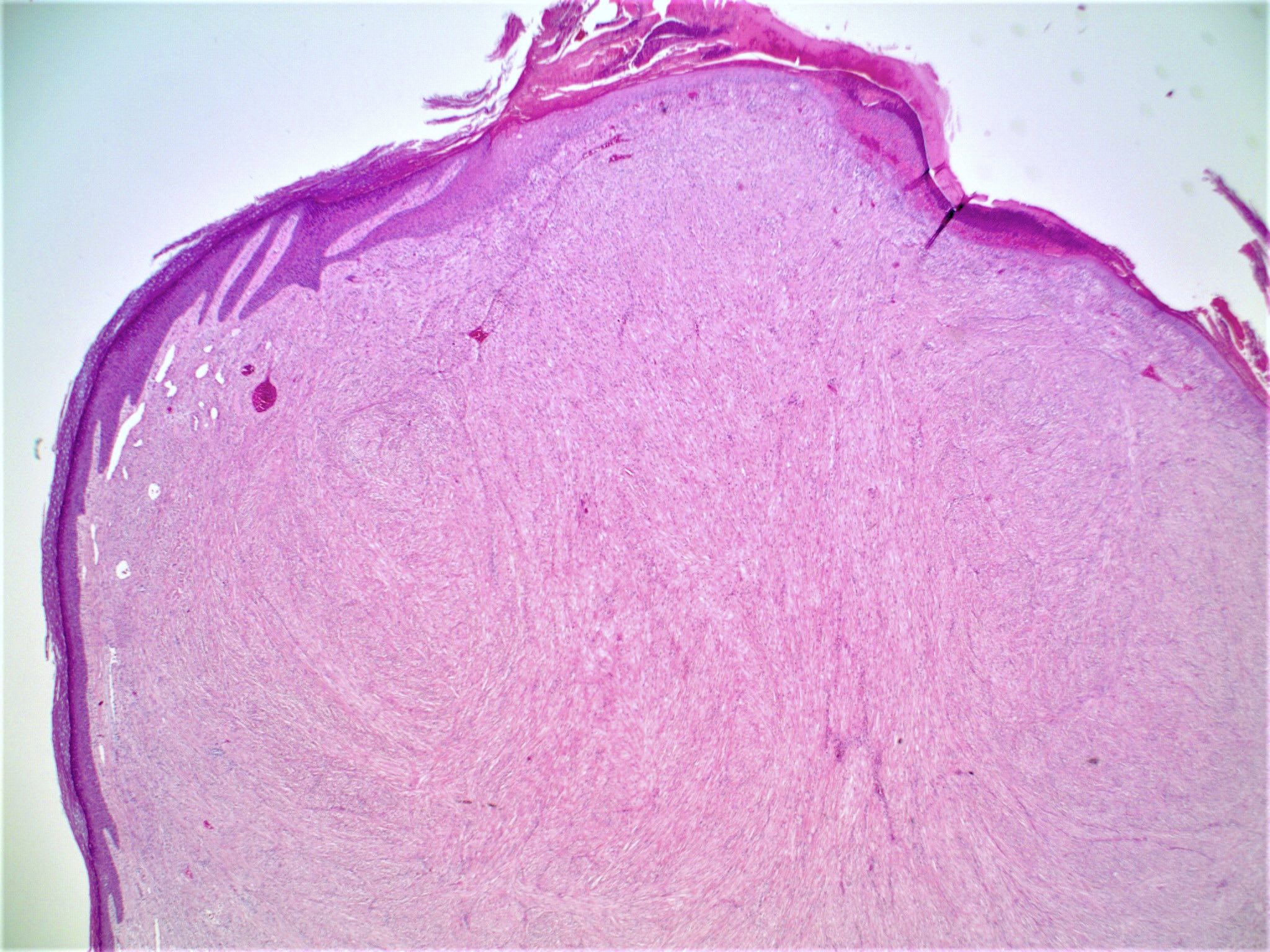
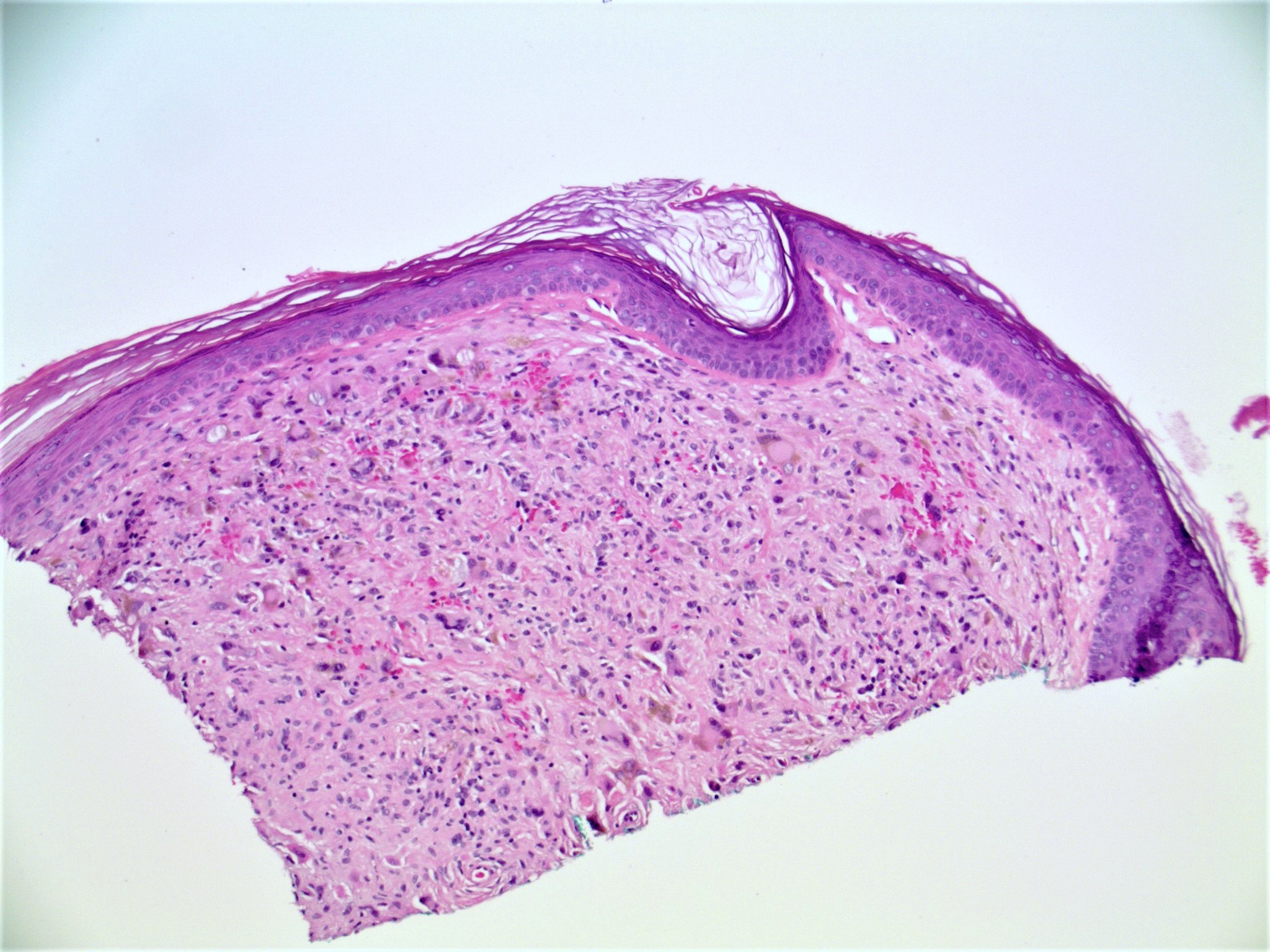
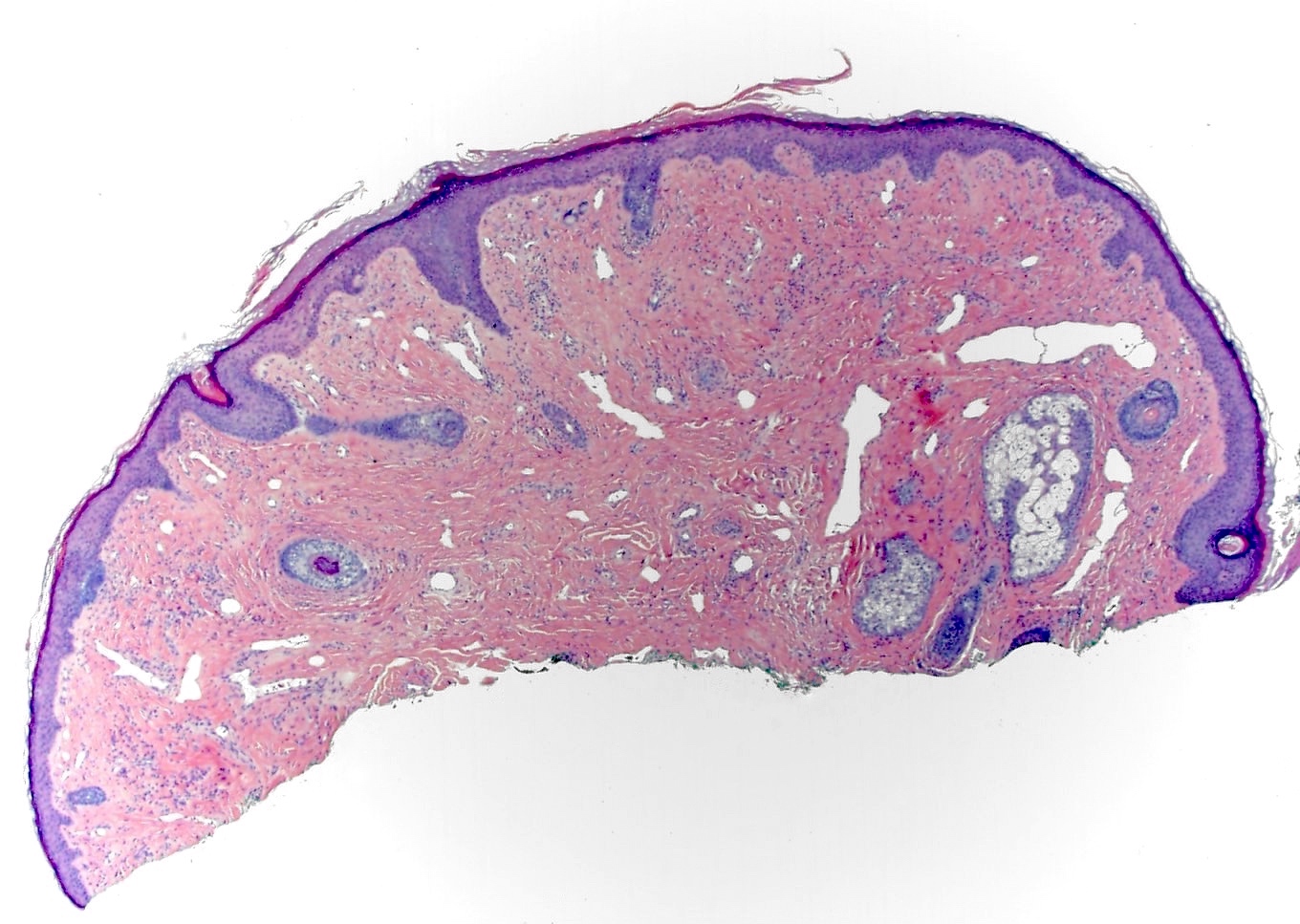
- Slightly raised dermal lesion composed of collagenous stroma with increased vasculature
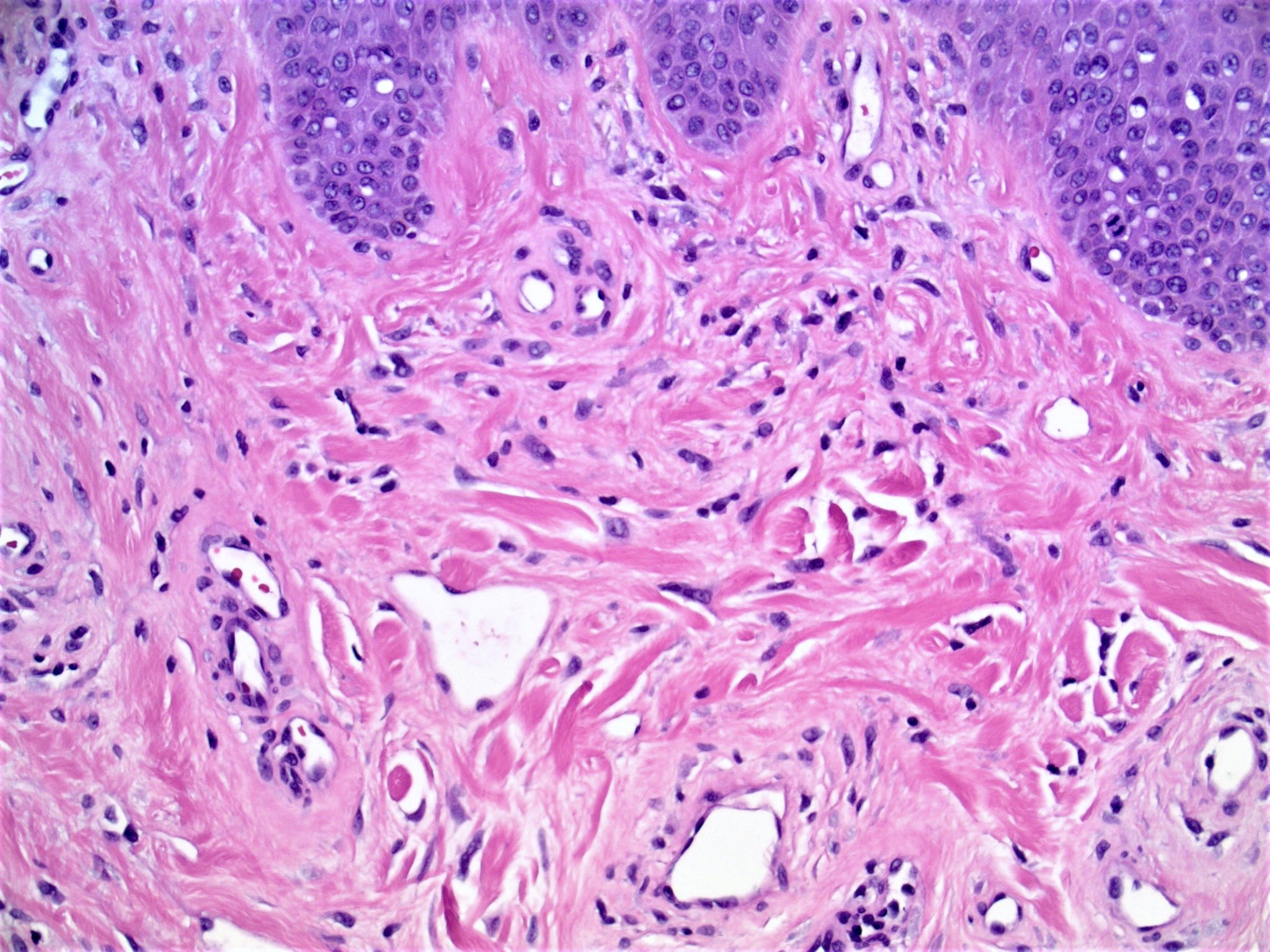
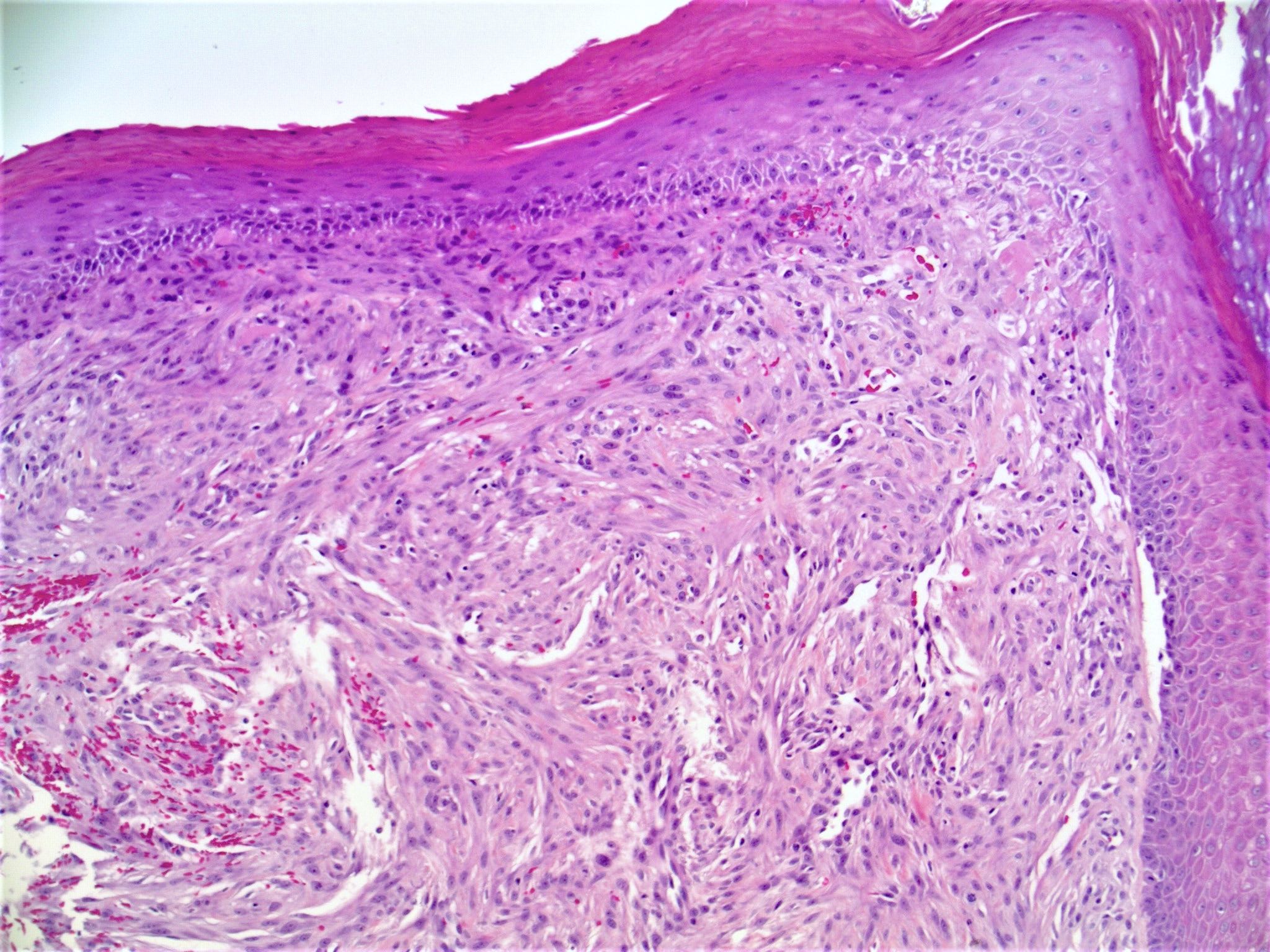
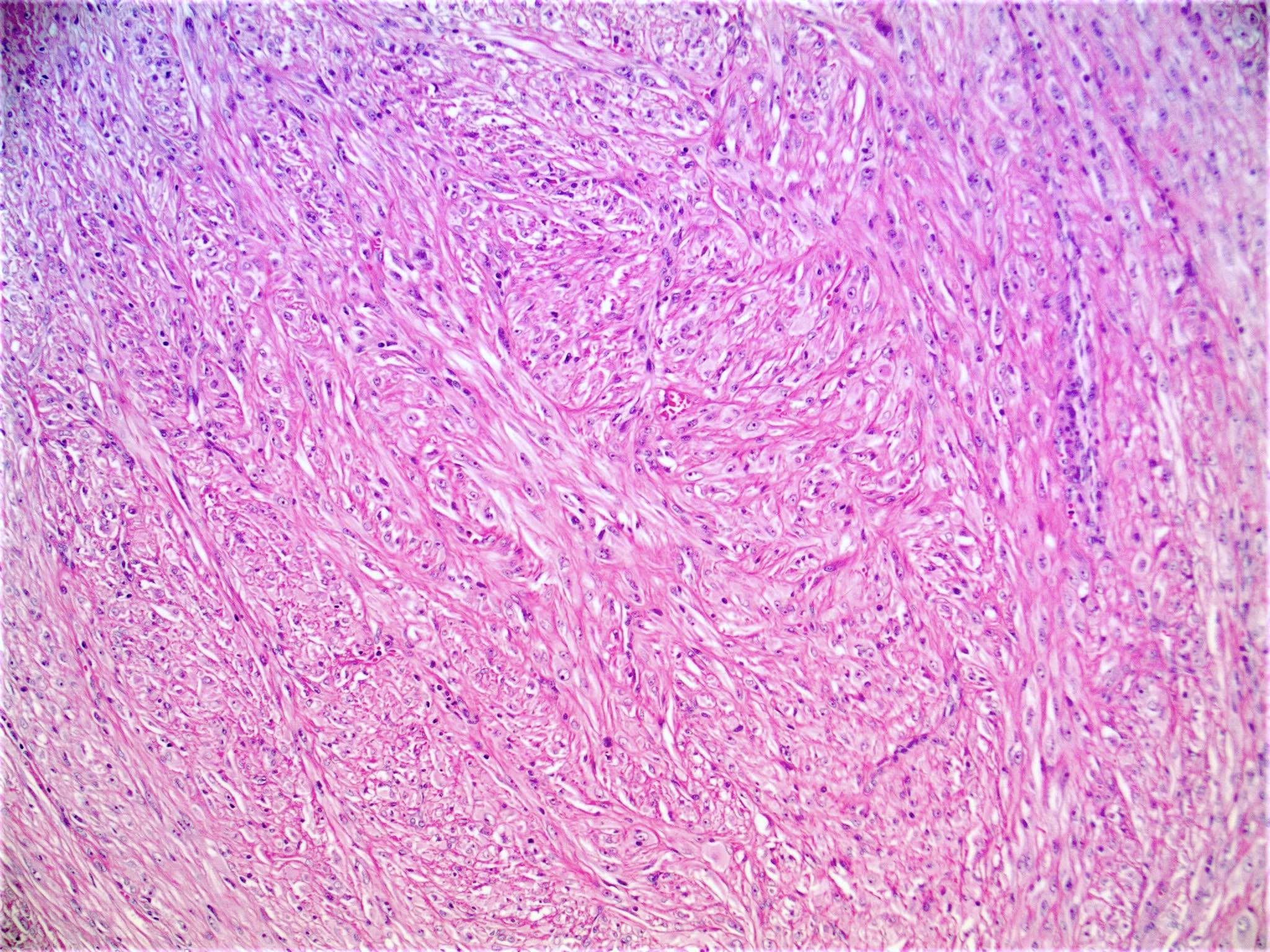
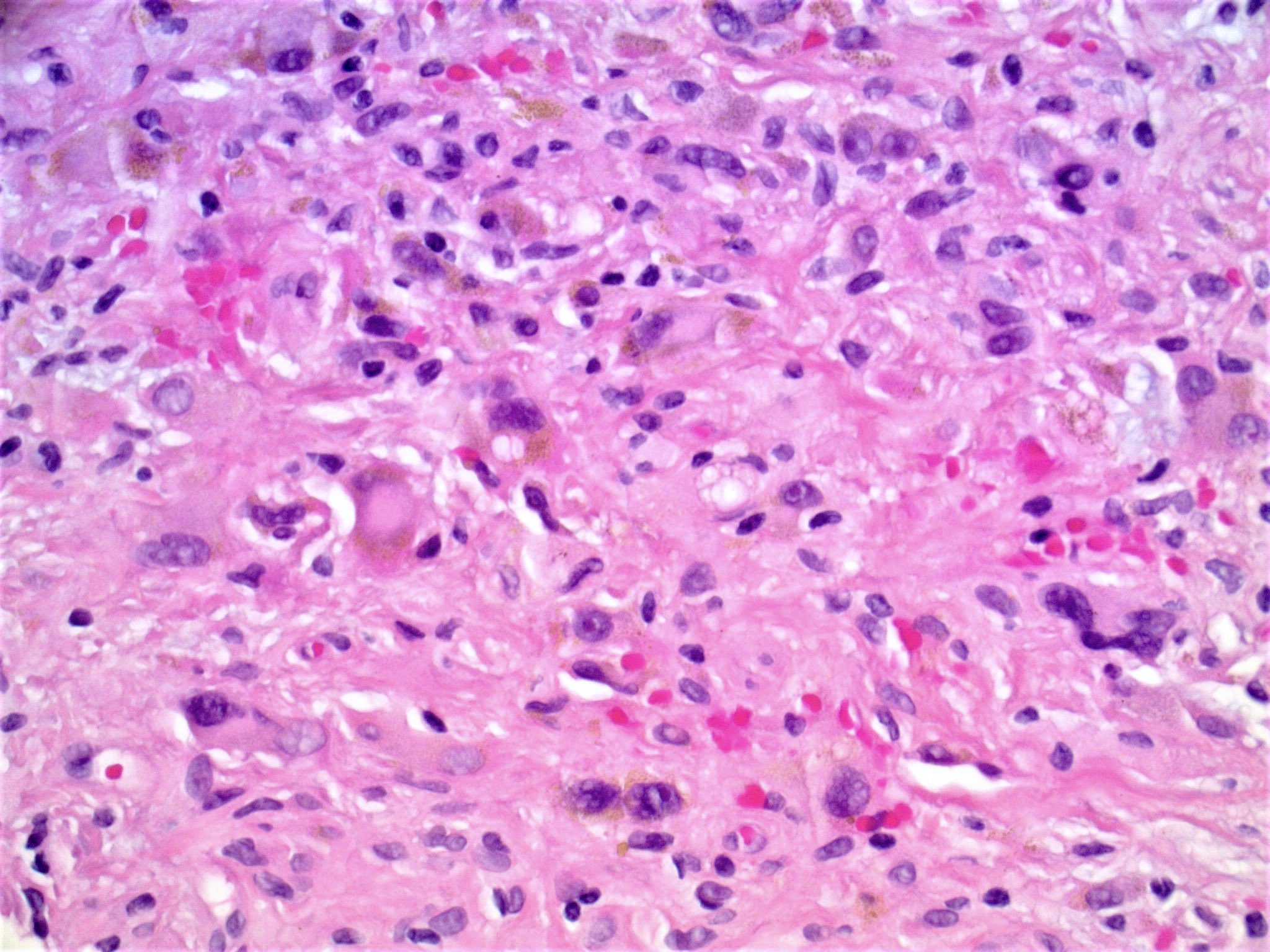
- Increased stromal cells with varying morphology
- Cells can be plump, spindle shaped, stellate or multinucleate
- Mitotic figures are rare
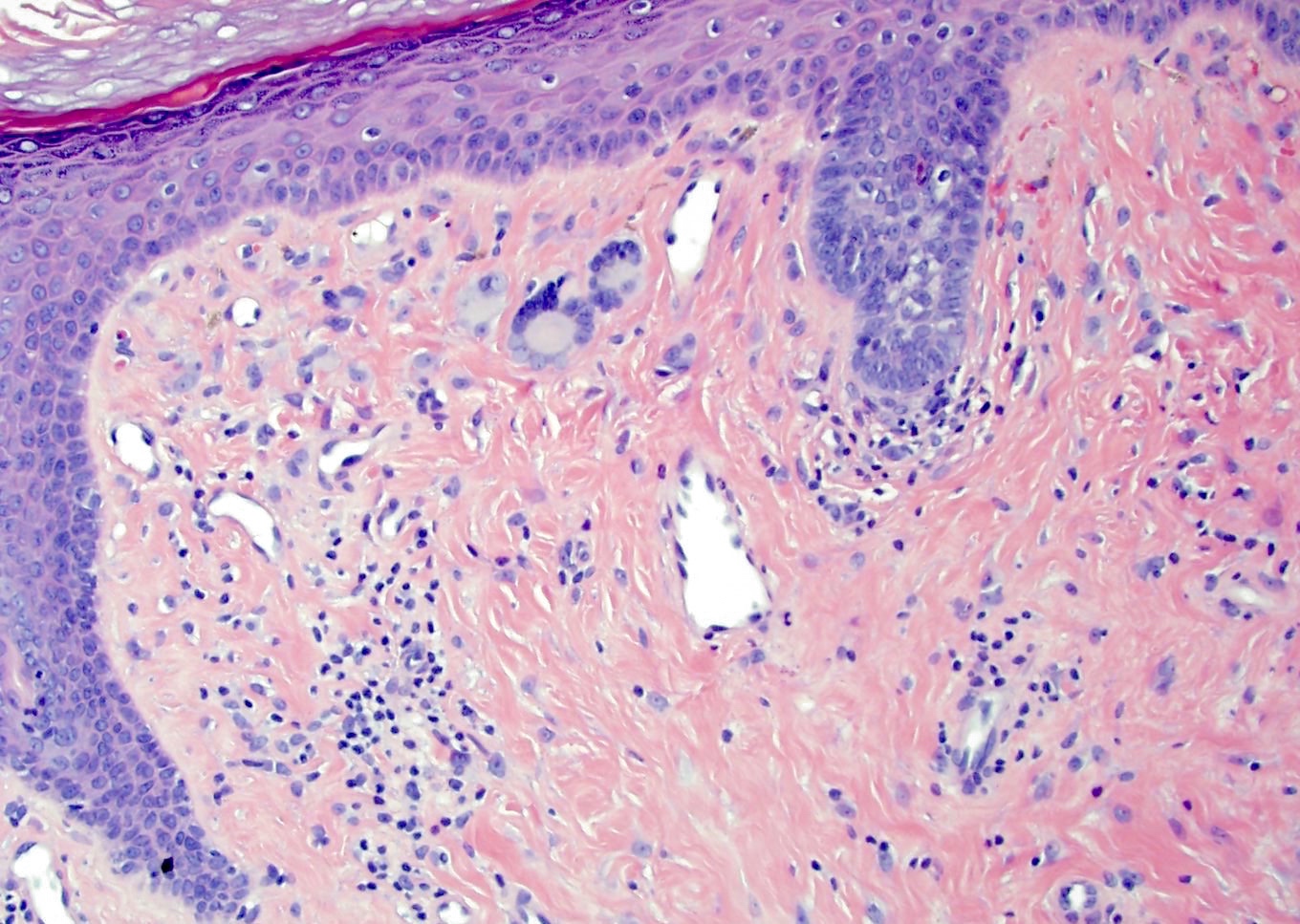
- Epidermis uninvolved but can appear flattened or atrophic
- Can have overlying junctional melanocytic hyperplasia
- Useful clue in partially / limited biopsies
- However, overdiagnosis (atypical junction melanocytic hyperplasia or melanoma in situ) is a pitfall that should be avoided
- Histologic variants exist:
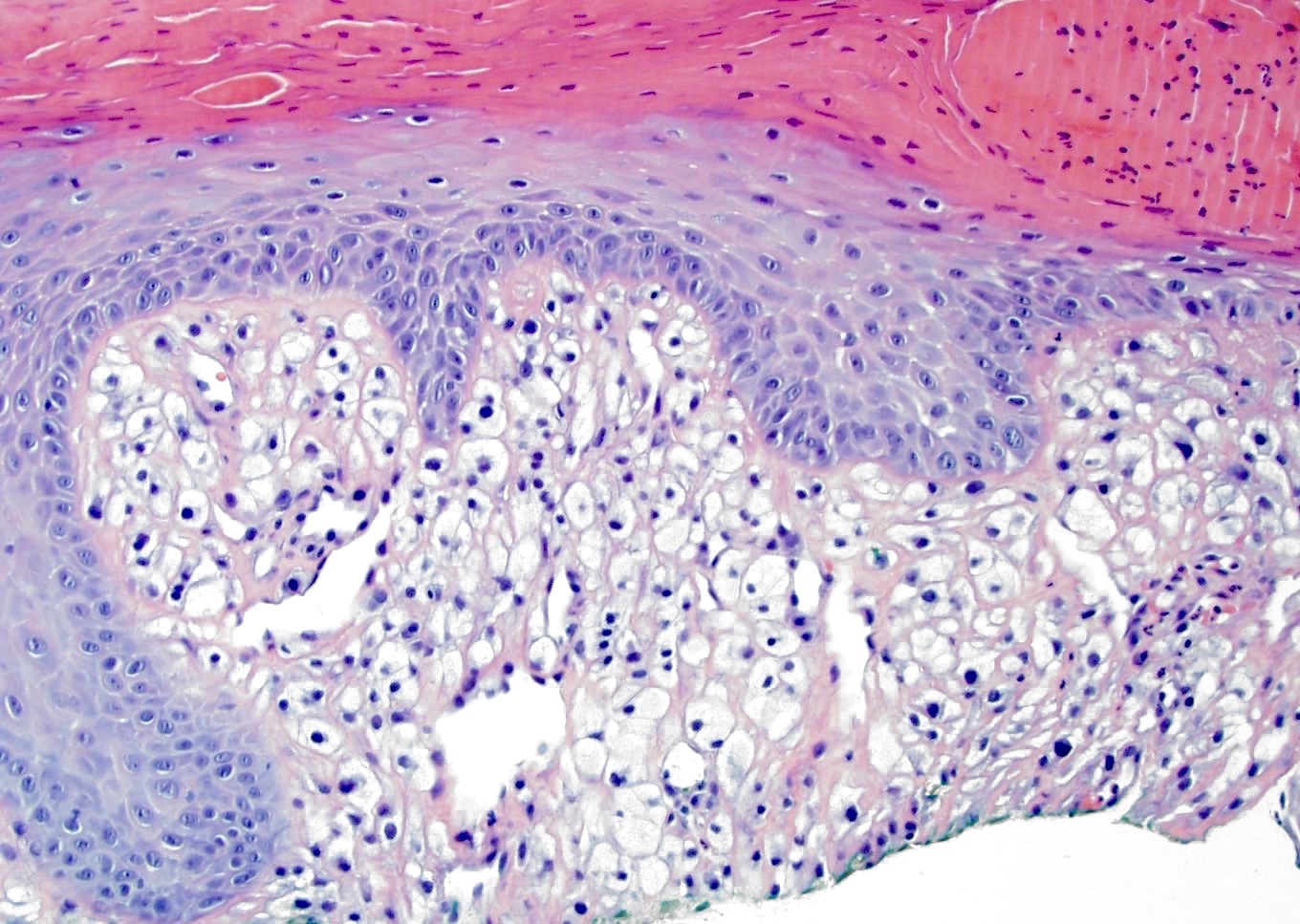
- Granular cell change: stromal cells with coarse cytoplasmic granules (J Cutan Pathol 1991;18:284)
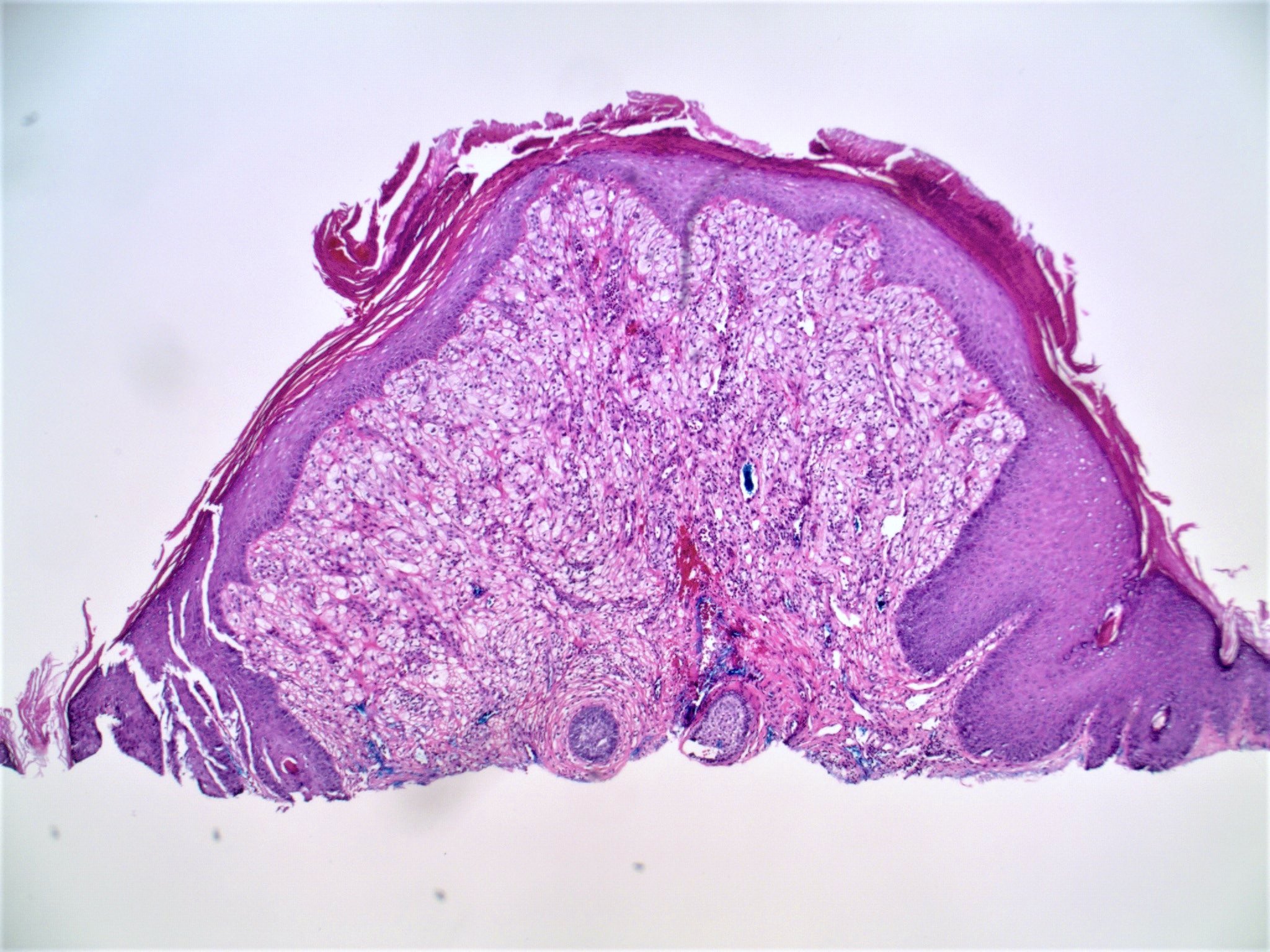
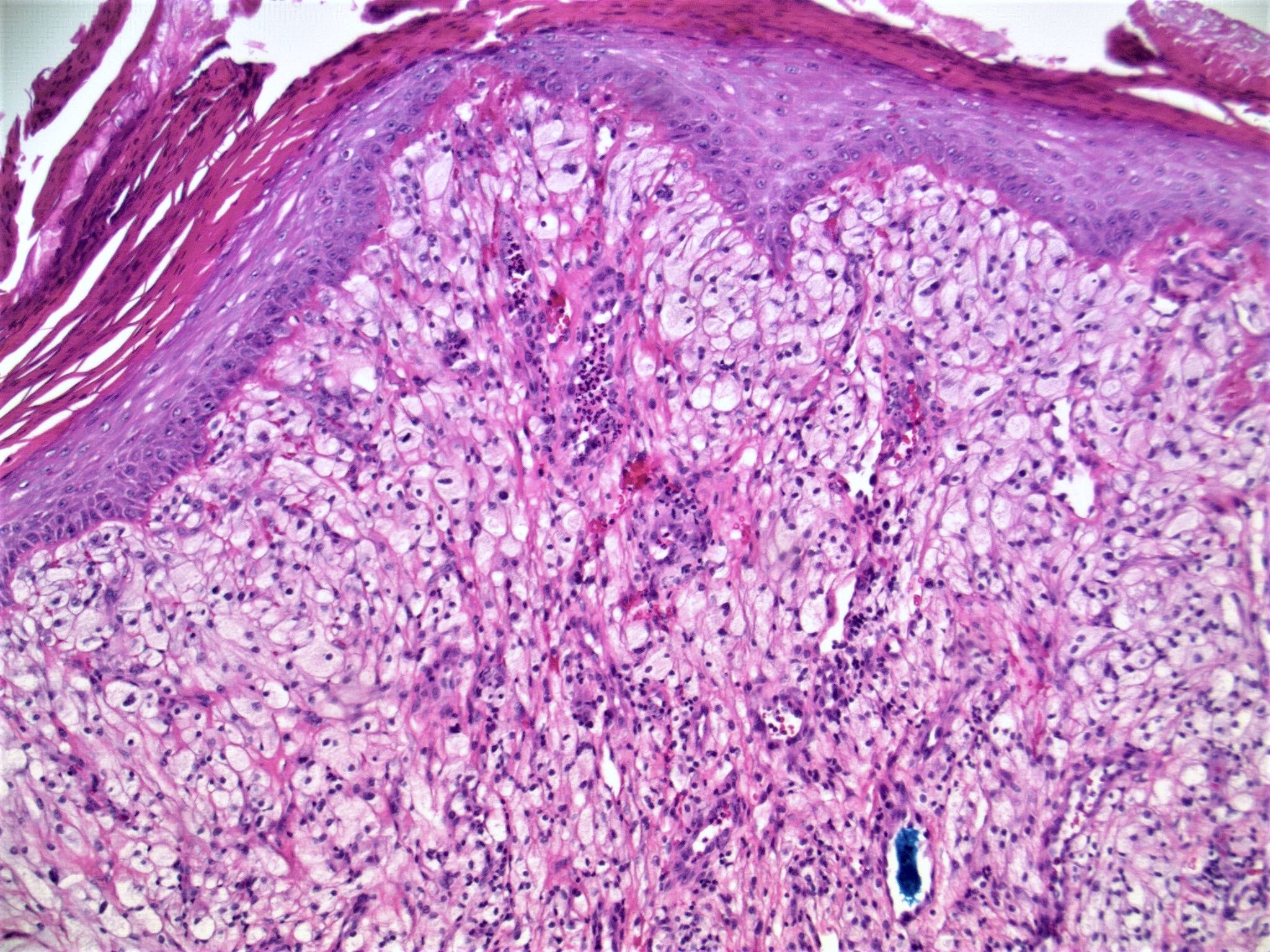
- Clear cell change: stromal cells with clear vacuolated cytoplasm (J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2007;21:1267)
- Other rare variants include hypercellular, pigmented, pleomorphic, inflammatory and epithelioid fibrous papules (J Cutan Pathol 2005;32:424)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Gregory A. Hosler, M.D., Ph.D.
Contributed by Hillary Rose Elwood, M.D.
Positive stains
- Factor XIIIa: positive in stellate stromal cells (J Am Acad Dermatol 1988;19:1102)
- CD34: may also be positive (J Am Acad Dermatol 1996;35:342)
- NKI-C3: positive in clear cell variant (Am J Dermatopathol 2005;27:296)
Negative stains
- S100 and cytokeratins
Electron microscopy description
- Stellate stromal cells with ultrastructural features of fibroblasts, rather than melanocytic or Schwann cell differentiation (Am J Dermatopathol 1979;1:349)
- Fibrous papule was previously suggested to represent fibrosed dermal nevi (Am J Dermatopathol 1979;1:345)
Videos
Fibrous papule (angiofibroma)
by Dr. Gardner
Sample pathology report
- Skin, nasal tip, shave biopsy:
- Fibrous papule
Differential diagnosis
- Adenoma sebaceum (angiofibroma of tuberous sclerosis):
- Fewer bizarre dermal stromal cells than in fibrous papule
- Vessels are smaller and likely to show more concentric fibrosis
- Pearly penile papules:
- Absence of pilosebaceous follicles
- Multiple in number and located on the penis
- Angioma:
- Proliferation of ectatic vessels
- Lacks stellate stromal cells
- Fibrosing / sclerotic nevus:
- Lacks stellate cells and cellular stroma
- S100 positive
- Pleomorphic fibroma:
- Pleomorphic cells can resemble those occasionally present in fibrous papule
- More commonly located on the truck and extremities
- Lacks vascularity
- Scar:
- Horizontal orientation of fibroblasts with vertically oriented blood vessels
Practice question #1
Practice answer #1
B. Factor XIIIa. The spindle cells of fibrous papule express factor XIIIa. Although NKI-C3 may be positive in the clear cell variant of fibrous papule, it is negative in classic variant shown here. S100, MART1 and cytokeratins are negative.
Comment Here
Reference: Angiofibroma / fibrous papule
Comment Here
Reference: Angiofibroma / fibrous papule
Practice question #2
Multiple facial fibrous papules are associated with what hereditary condition?
- Brooke-Spiegler syndrome
- Cowden syndrome
- Gardner syndrome
- Reed syndrome
- Tuberous sclerosis
Practice answer #2
E. Tuberous sclerosis. Multiple facial fibrous papules are classically associated with the autosomal dominant neurocutaneous syndrome of tuberous sclerosis. Angiofibromatous lesions found in patients with this syndrome are referred to as adenoma sebaceum (a misnomer, as there is no adenomatous proliferation of sebaceous glands). Other hereditary conditions also associated with multiple facial fibrous papules include multiple endocrine neoplasia type I (MEN 1), neurofibromatosis II and Birt-Hogg-Dubé.
Comment Here
Reference: Angiofibroma / fibrous papule
Comment Here
Reference: Angiofibroma / fibrous papule