Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Asghari T, Chundriger Q, Ud Din N. Cellular angiofibroma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissuecellularangiofibroma.html. Accessed September 15th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Cellular angiofibroma (CAF) is a benign, cellular and richly vascularized fibroblastic neoplasm of the genital tract
Essential features
- Benign, well circumscribed lesion arising in the superficial soft tissue of the genital region
- Characterized by bland spindle shaped cells arranged without any pattern in a stroma with wispy collagen, numerous medium sized thick walled vessels and a variable adipocytic component
- Complete excision is curative with extremely rare recurrence and even rarer sarcomatoid transformation
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Peak incidence in the fifth decade of life in women and the seventh decade in men
- M = F
Sites
- Women: usually in vulva, occasionally in vagina
- Men: inguinoscrotal region
- Rare extragenital sites
- Retroperitoneum (BMC Womens Health 2023;23:57, Acta Med Port 2017;30:882)
- Pelvis and lumbar region (Mod Pathol 2011;24:82)
- Anus (ACG Case Rep J 2020;7:e00471)
- Prostate (Case Rep Pathol 2014;2014:871530)
- Urethra (BMJ Case Rep 2018;2018:bcr2018225386)
- Trunk
- Hypopharynx (Medicine (Baltimore) 2019;98:e18385)
- Oral mucosa
Etiology
- Long term use of estrogen therapy may be related to the occurrence of CAF (Gynecol Oncol 2001;81:326)
Clinical features
- Women: slow growing, painless mass, mostly mimicking Bartholin cyst (Mod Pathol 2011;24:82, Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1426, Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:636)
- Men: may cause hernia or hydrocoele (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1426, Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:6)
- Tumors at rare sites may present with local pain and mass effect (Acta Med Port 2017;30:882)
Diagnosis
- Suggested by characteristic clinical presentation and supporting radiology and diagnosed by histopathological findings
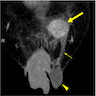
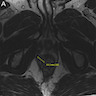
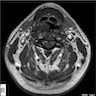
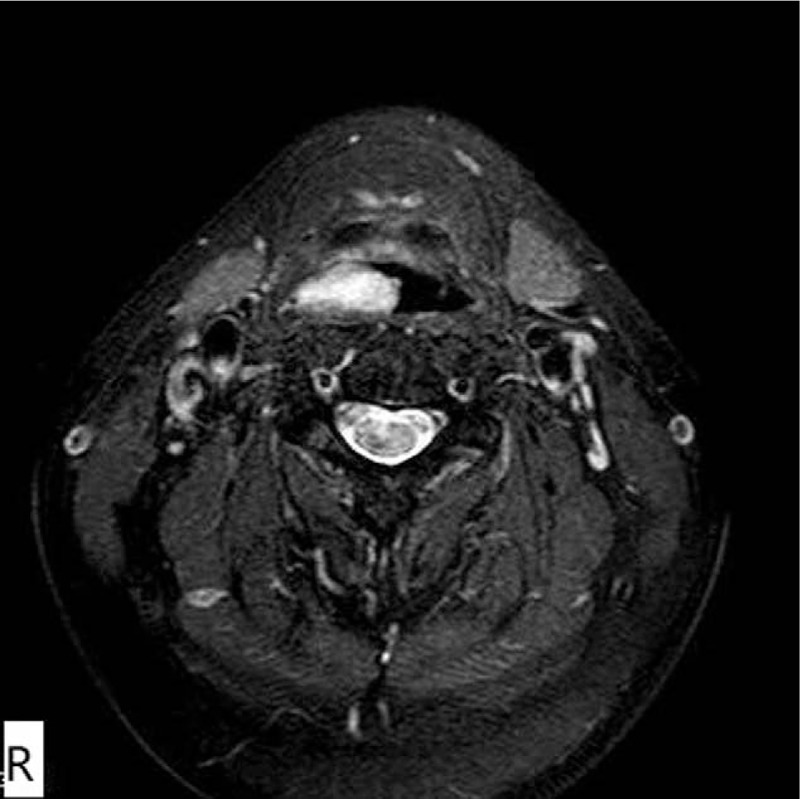
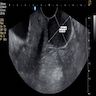
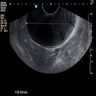
Radiology description
- Ultrasound: hypoechoic mass (BMJ Case Rep 2020;13:e235241)
- MRI: CAF demonstrates heterogeneous increased signal intensity on T2 weighted imaging and heterogeneous contrast enhanced pattern due to hypervascularity (IJU Case Rep 2020;3:69)
- CT: hyperintense on post contrast images (IJU Case Rep 2020;3:69)
- Cases with intratumoral fat component show heterogeneous appearance on both CT and MRI
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Clinically benign with a limited capacity for local recurrence
- Only rare cases show nuclear atypia and sarcomatous transformation (Mod Pathol 2011;24:82)
- Complete local excision is effective in preventing recurrence and damage to surrounding tissues (BMJ Case Rep 2020;13:e235241)
Case reports
- 54 year old man complained of a mass moving through his throat for 1 month (Medicine (Baltimore) 2019;98:e18385)
- 63 year old man with painless right epididymal mass (Asian J Androl 2018;20:95)
Treatment
- Complete local excision by shelling out is the treatment of choice
- Presence of atypical / sarcomatous features do not predispose to a malignant or aggressive biological behavior or recurrence (BMJ Case Rep 2020;13:e235241)
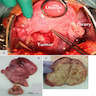
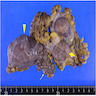
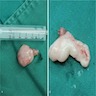
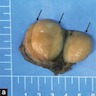
Gross description
- Circumscribed dermal or subcutaneous round, oval or lobulated masses, measuring a few centimeters in diameter (larger in men)
- Size ranges from 0.6 cm to 25 cm
- Consistency varies from soft to rubbery, with a solid grayish pink to yellowish brown cut surface (Asian J Androl 2018;20:95, Medicine (Baltimore) 2019;98:e18385)
- Foci of hemorrhage or necrosis are exceptional
Gross images
Frozen section description
- Frozen section examination of the lesion or margins is not required for diagnosis or to declare margin clearance
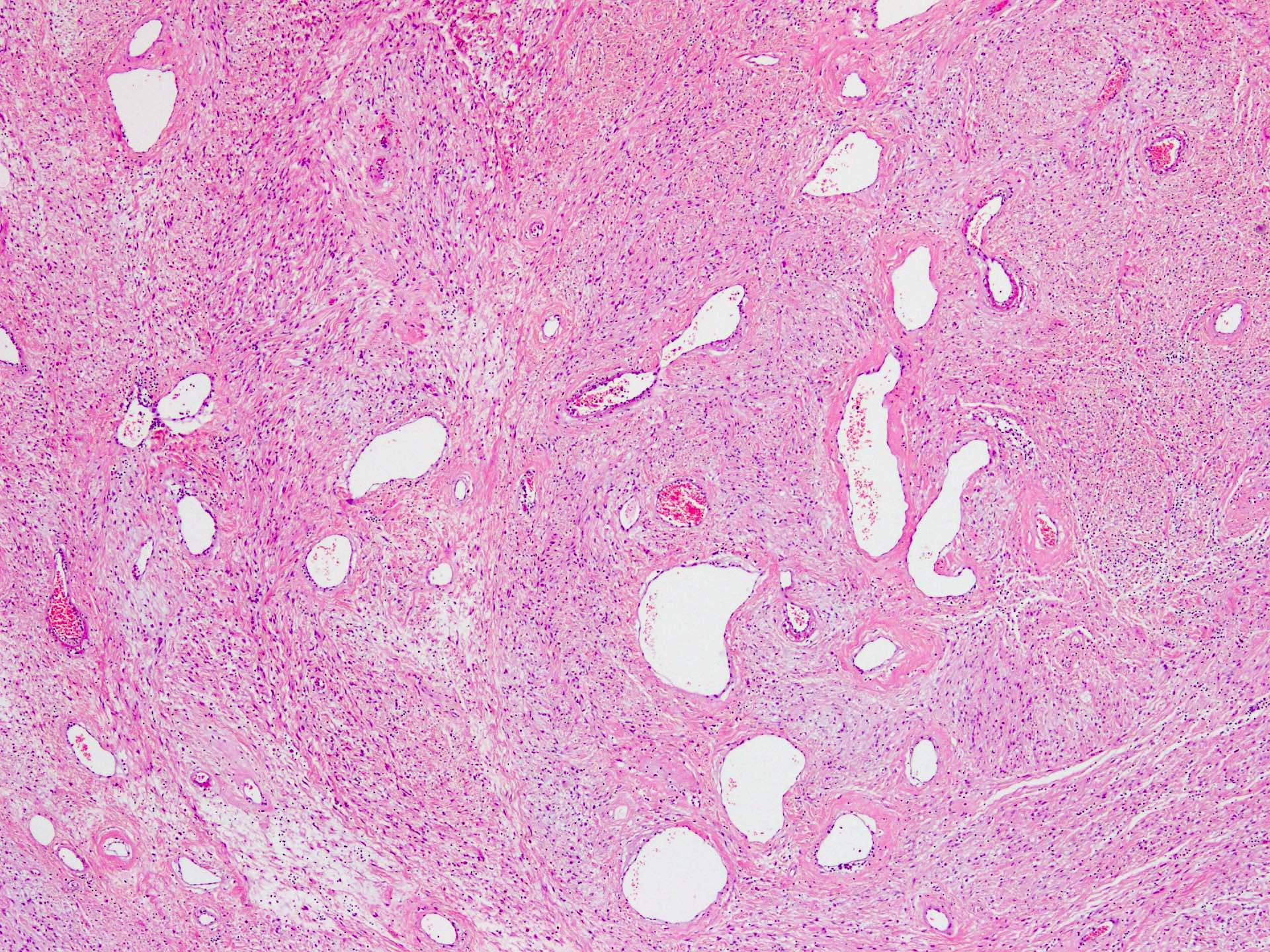
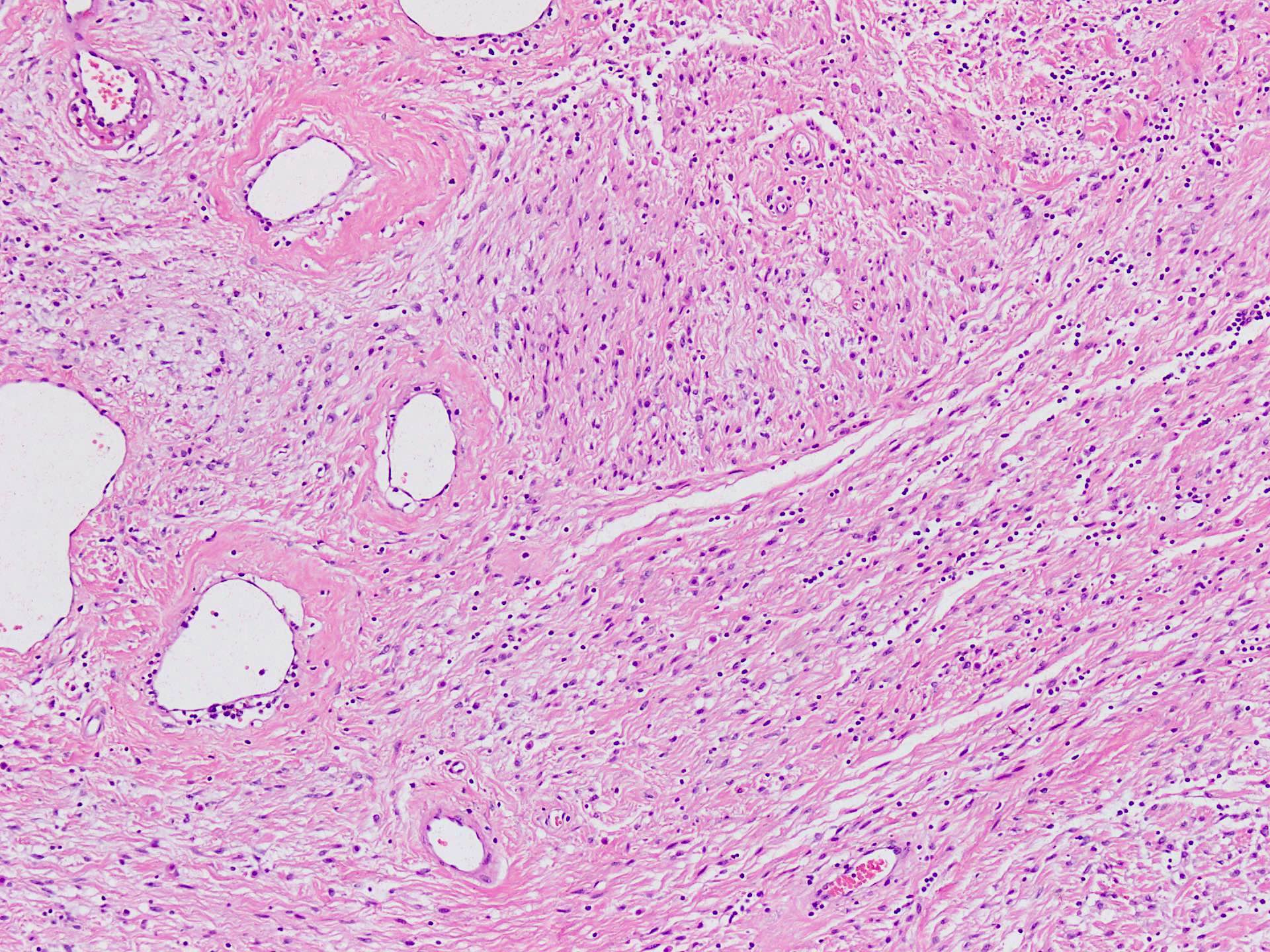
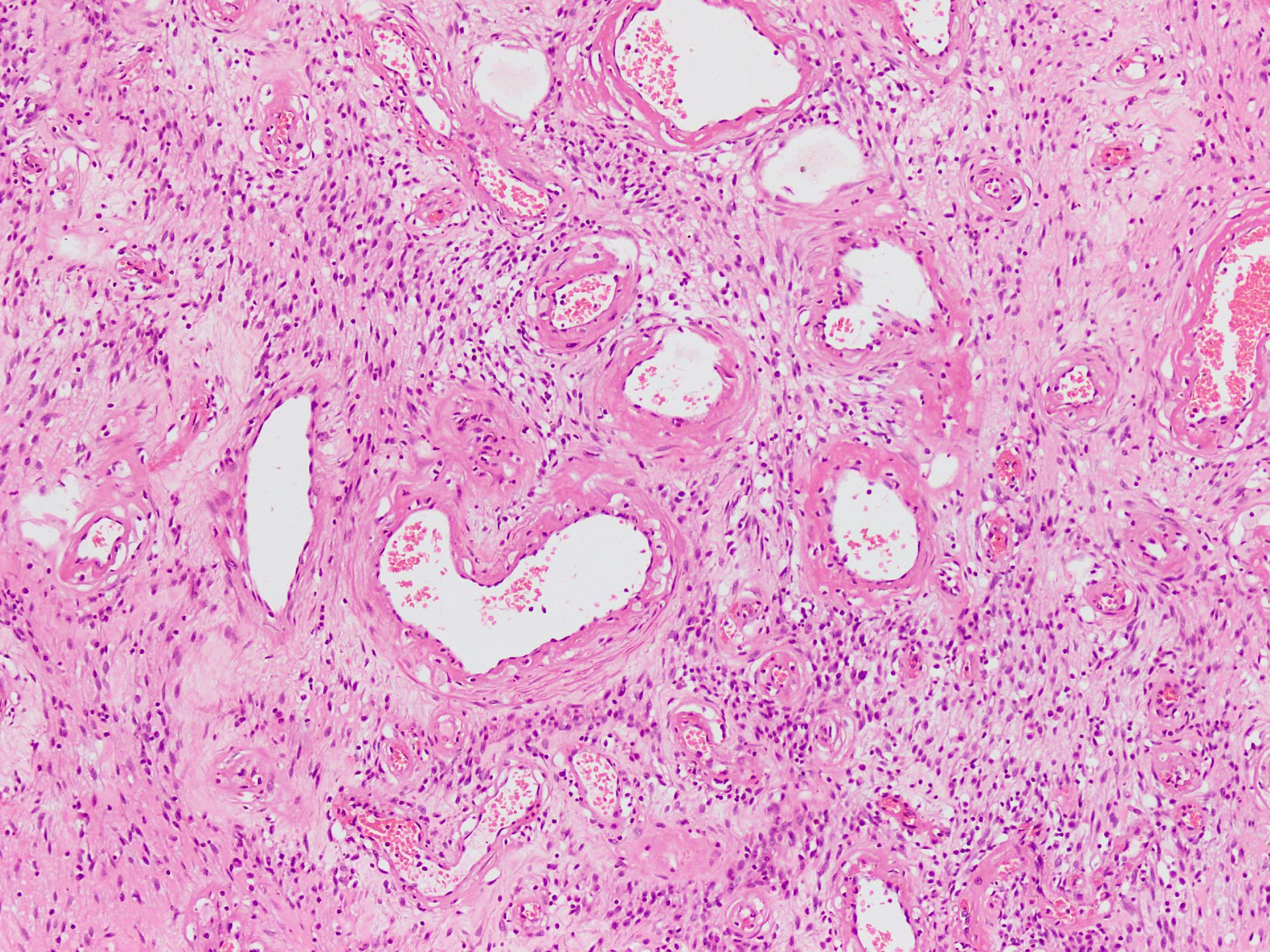
Microscopic (histologic) description
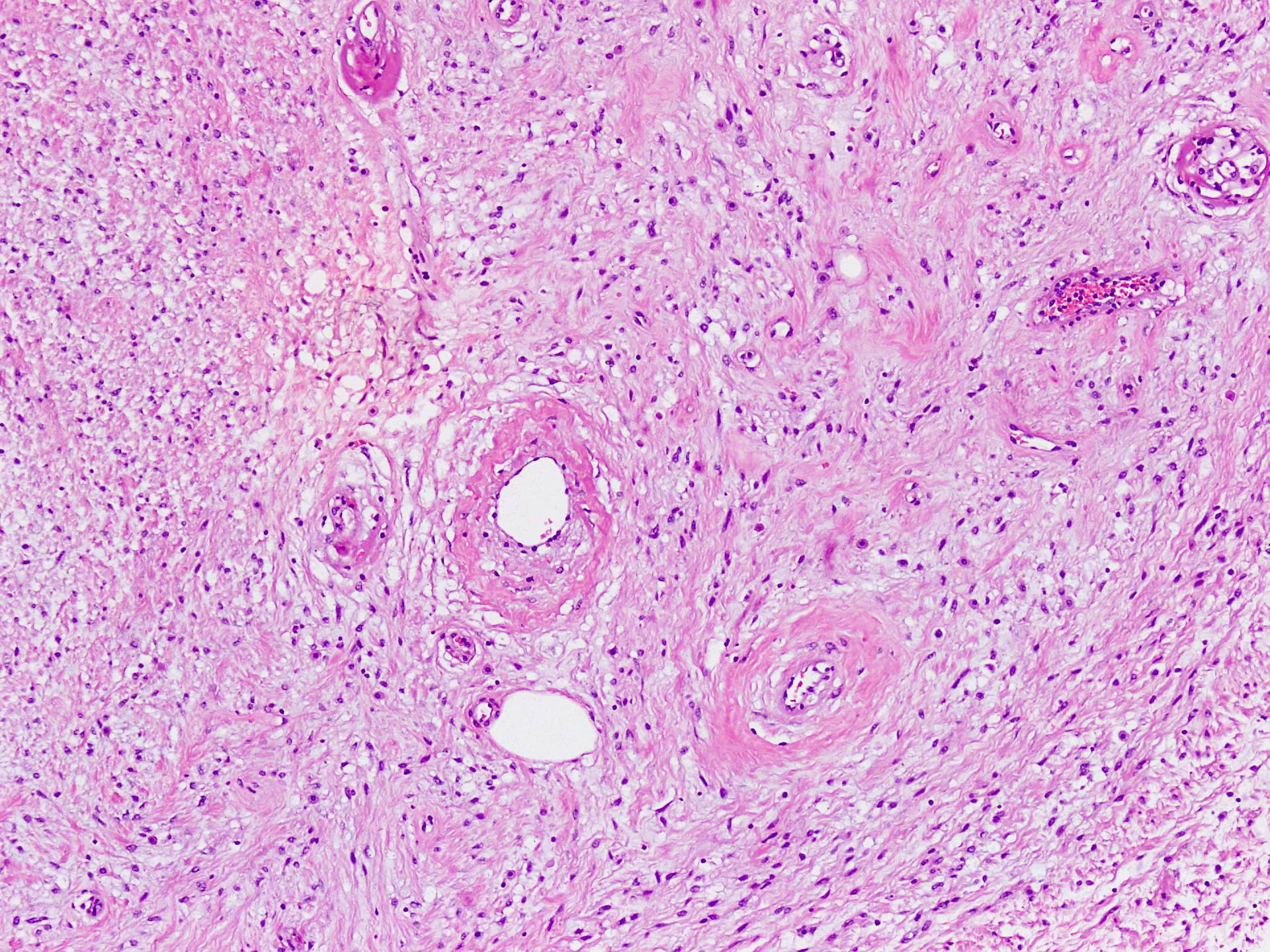
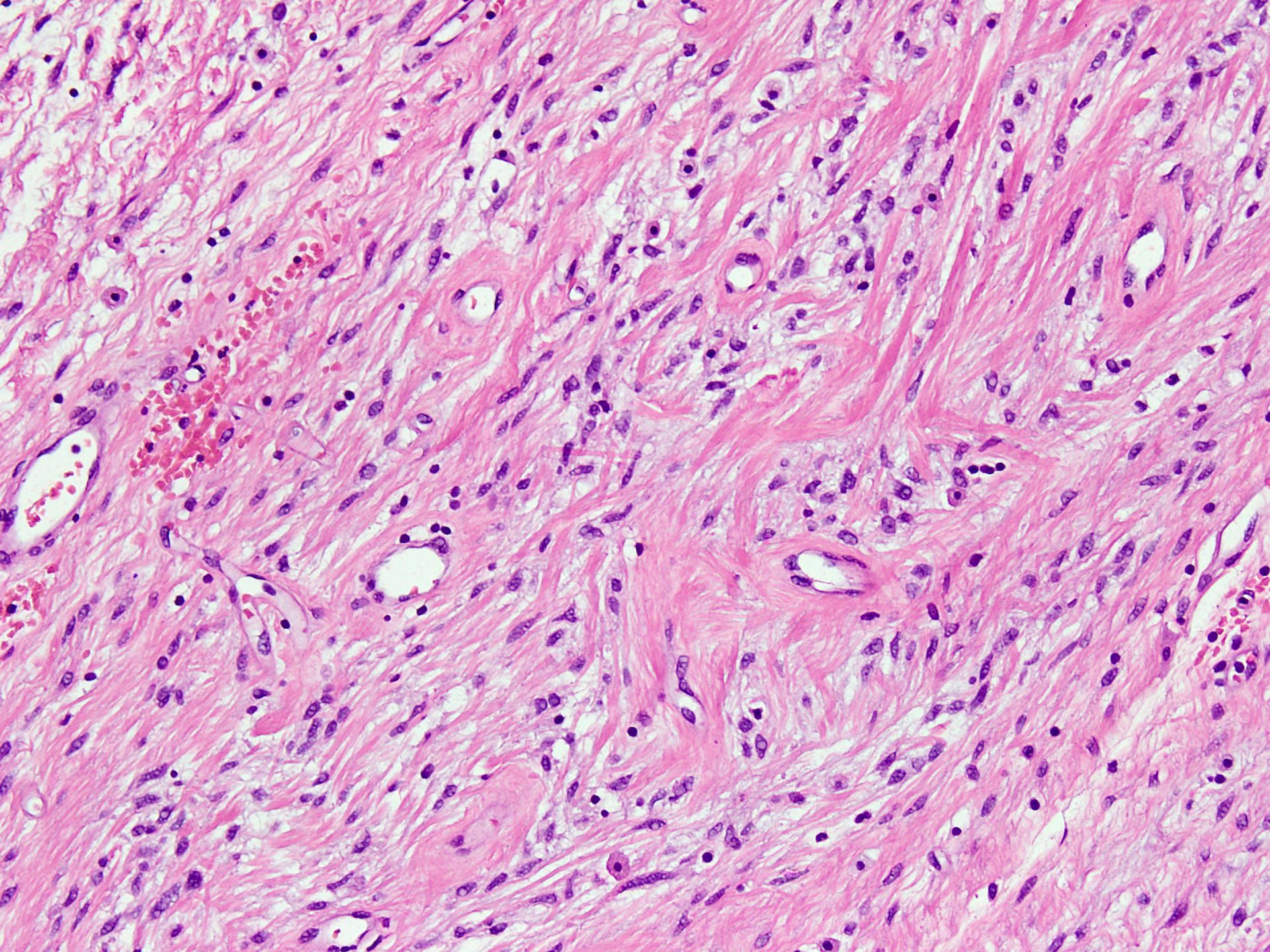
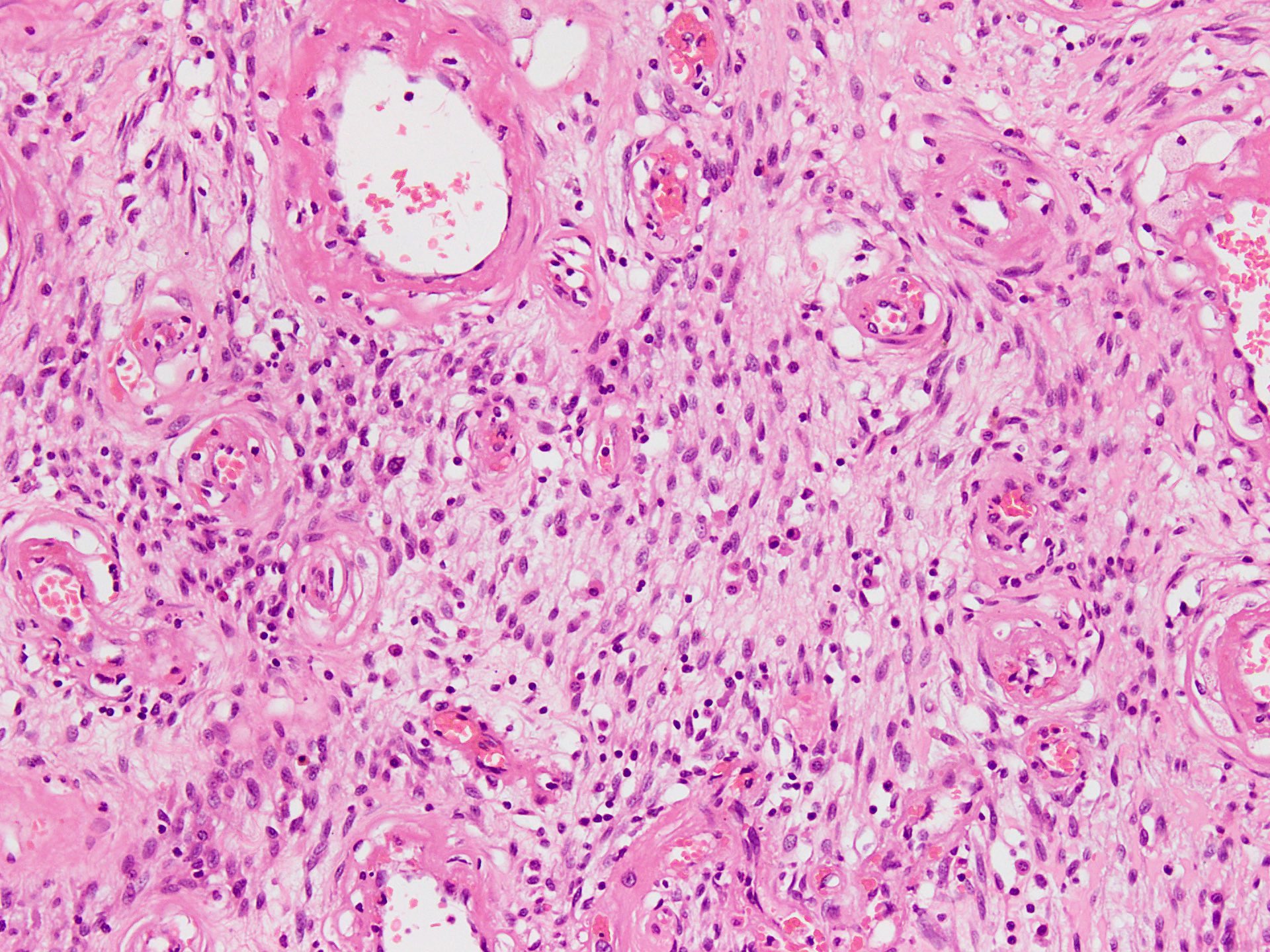
- Well circumscribed, unencapsulated dermal or subcutaneous lesions that may be more infiltrative in men
- The 2 components present are spindle cells and medium sized thick to variably hyalinized blood vessels (Diagn Pathol 2015;10:114)
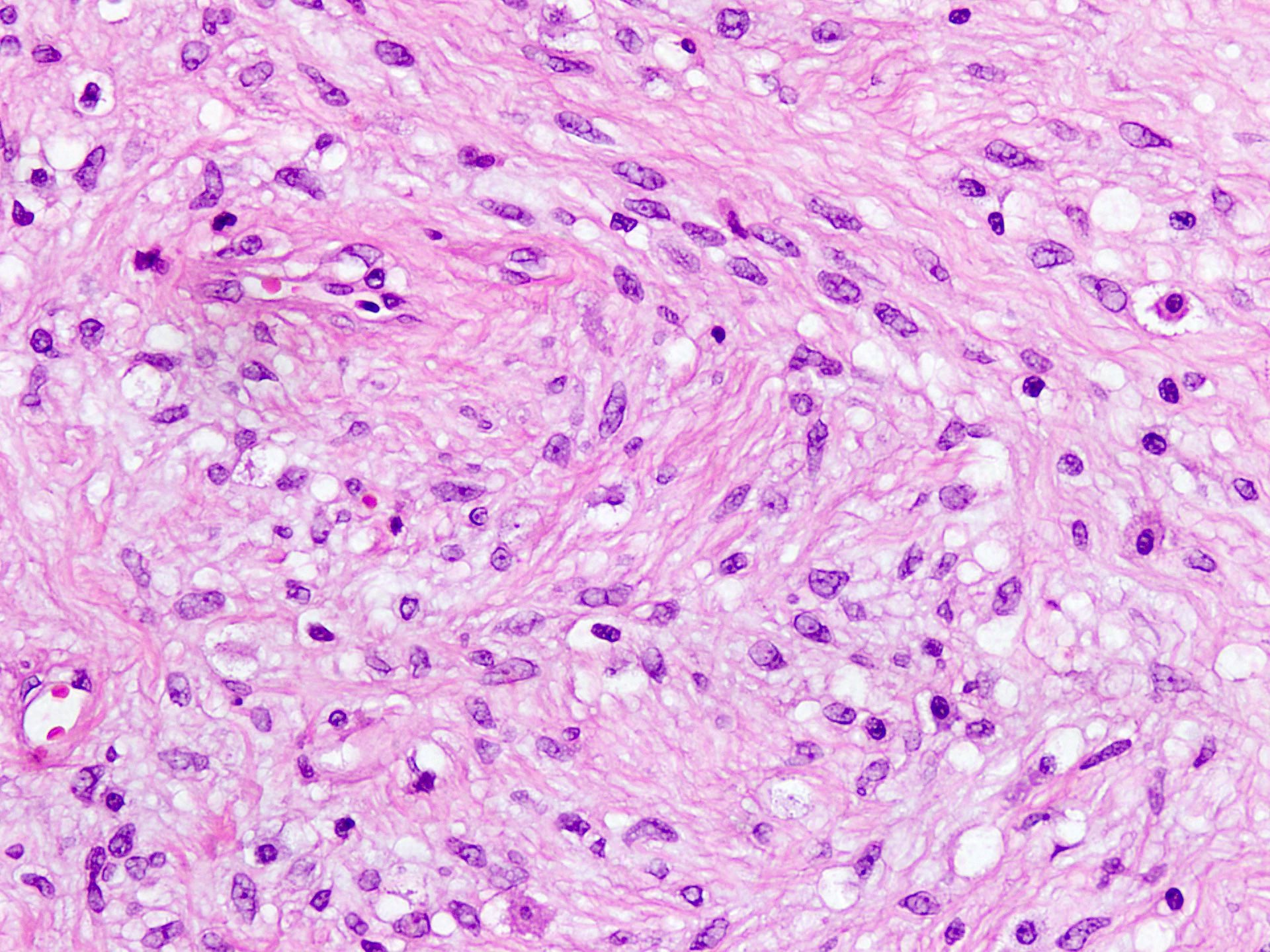
- Spindle / fusiform cells have bland cytologic features and may be arranged in fascicles, short whorls at random (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1426)
- Stroma can be fibrous to myxoid and contain delicate pale short to thick collagen fibers
- Mature fat can be seen in ~25% of cases (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors: Expert Consult, 7th Edition, 2019)
- Variable stromal edema, hyalinization or myxoid change is often seen, especially in men
- Stroma may show scattered lymphocytes and perivascular lymphoid aggregates, mast cells are frequent
- Necrosis or hemorrhage are not usually observed and mitotic activity is low (< 1/10 high power fields)
- Rarely, sarcomatous features may be seen as well as scattered cells with marked nuclear atypia or areas that mimic liposarcoma (both well differentiated and pleomorphic types) (Lindberg: Diagnostic Pathology - Soft Tissue Tumors, 3rd Edition, 2019)
- Occasional reports show abrupt transition to a discrete nodule with sarcomatous features or multivacuolated lipoblasts, pleomorphic and hyperchromatic spindle cells that morphologically resemble pleomorphic liposarcoma, atypical lipomatous tumor or pleomorphic spindle cell sarcoma
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
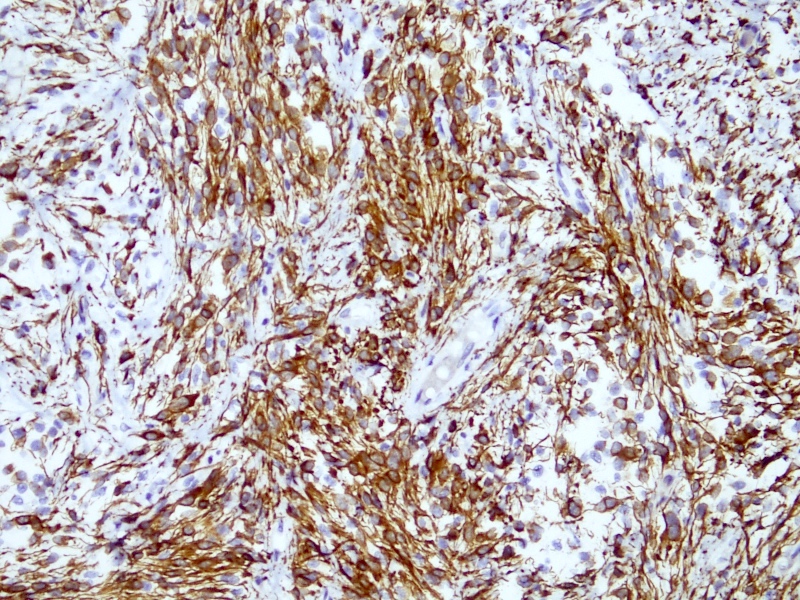
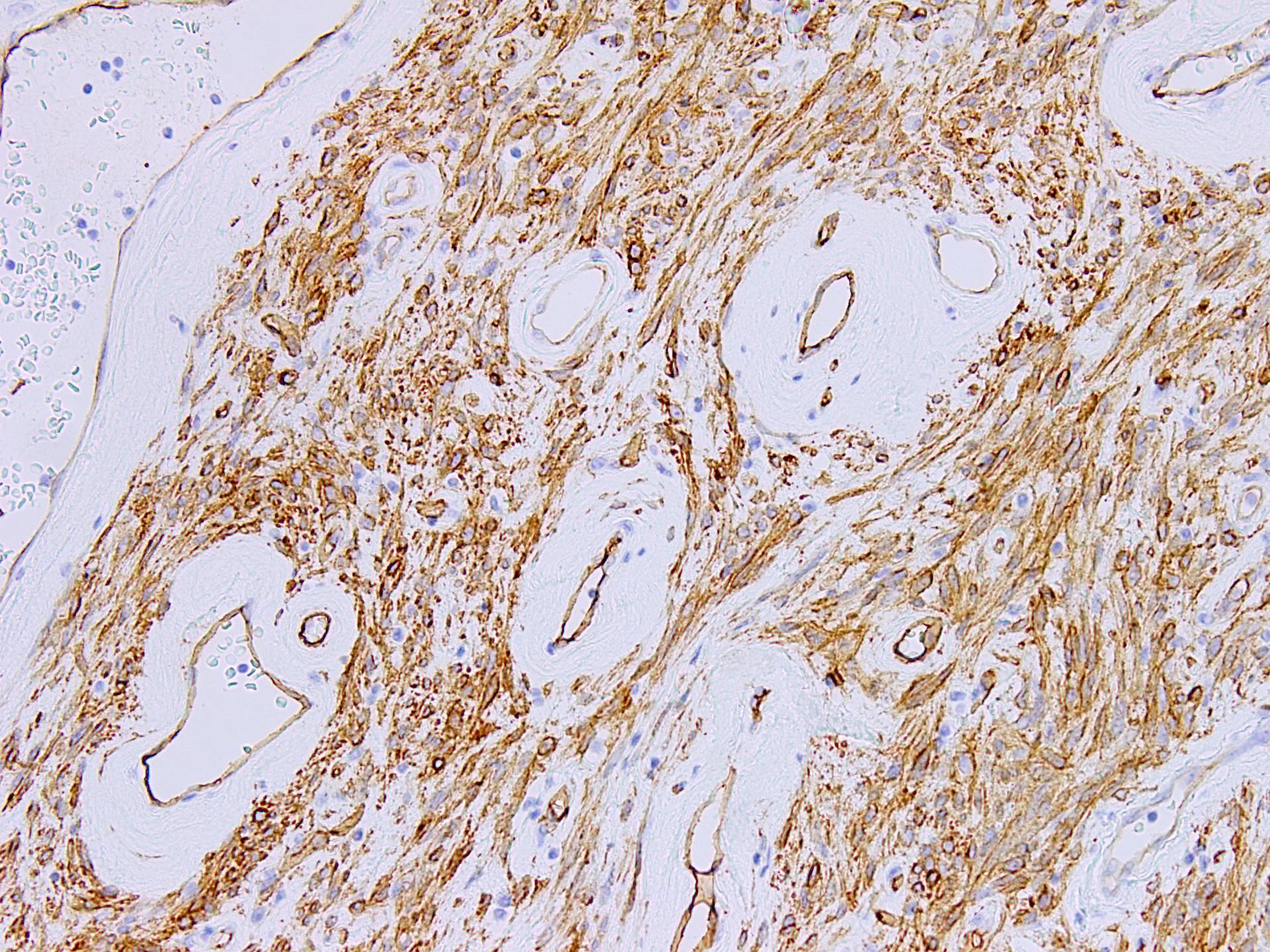
- CD34 (30 - 60%)
- Smooth muscle actin (minority of cases) (Diagn Pathol 2015;10:114)
- Desmin (minority of cases) (Diagn Pathol 2015;10:114)
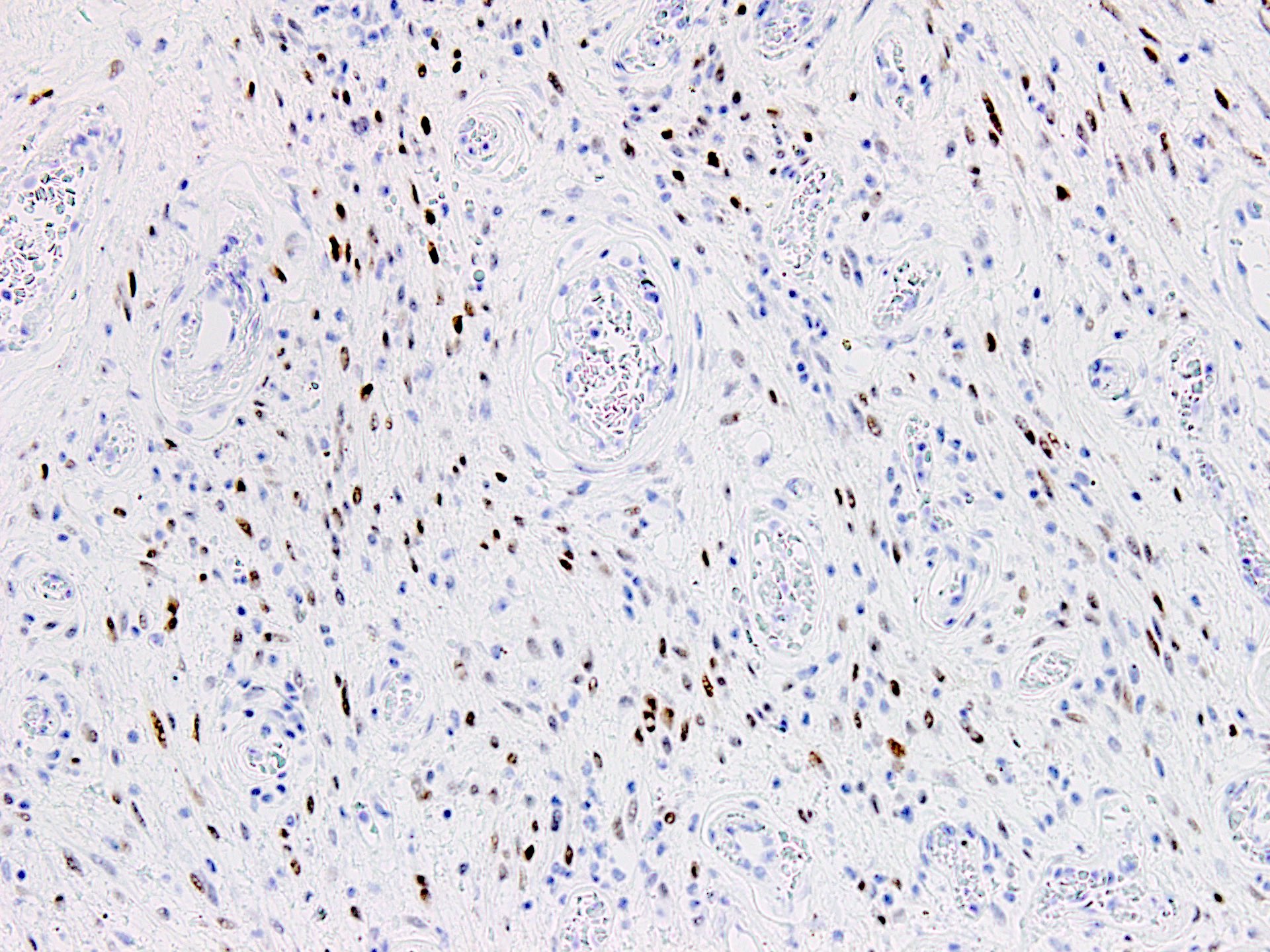
- ER
- PR
Negative stains
- EMA
- Cytokeratin (AE1 / AE3 and CAM 5.2)
- S100
- RB1 (loss of expression) (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7:8972)
- Caldesmon
- STAT6
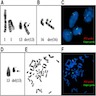
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Deletions of RB1, located at chromosome 13q14, is the most common genetic abnormality (Diagn Pathol 2017;12:17, Case Rep Pathol 2014;2014:871530)
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Videos
Cellular angiofibroma of the genitals
Sample pathology report
- Vaginal mass, excision specimen:
- Cellular angiofibroma, completely resected with clear margins (see comment)
- Comment: This tumor shows classic combination of benign spindle cells with admixed population of thick hyalinized medium sized blood vessels, which given with the site is compatible with a diagnosis of cellular angiofibroma. Any atypical or sarcomatous component is not identified. These are benign lesions and complete excision is generally considered curative with very low chances of local recurrence.
Differential diagnosis
- Aggressive angiomyxoma:
- Large, infiltrative, gelatinous masses with poor demarcation
- Extends deeper into the soft tissues
- Paucicellular, myxoid lesions with smooth muscle and lesional cells that appear to be radiating from thick medium to large blood vessels
- Variable CD34, desmin, smooth muscle actin, ER and PR
- Angiomyofibroblastoma:
- Vulvar, well marginated lesions of reproductive aged and early postmenopausal women
- Alternating areas of high and low cellularity
- Epithelioid cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm that are commonly seen aggregated around blood vessels
- Spindle cells morphology may also be seen, particularly in postmenopausal cases
- Variable CD34, desmin, smooth muscle actin, ER and PR
- Solitary fibrous tumor:
- Cellular lesion with short spindle cells in a collagenous background
- Hemangiopericytoma-like vasculature is the characteristic feature
- STAT6 positivity is highly specific for this entity
Additional references
Practice question #1
A 40 year old woman presented with vaginal swelling. Intraoperatively, a circumscribed nodular mass was seen and the cut surface showed a gray-white to yellow multinodular lesion. Microscopically, the tumor was well circumscribed, composed of bland spindle cells and had the striking presence of hyalinized blood vessels as shown in the photomicrograph above. What is the correct diagnosis?
- Angiomyofibroblastoma
- Cellular angiofibroma
- Leiomyoma
- Solitary fibrous tumor
Practice answer #1
B. Cellular angiofibroma. The tumor shows bland spindle cells and a prominent component of hyalinized blood vessels, which is characteristic of cellular angiofibroma. There is no perivascular arrangement as seen in angiomyofibroblastoma, no interlacing fascicles of cells as seen in leiomyoma and the blood vessels do not show hemangiopericytoma-like pattern to call it solitary fibrous tumor. Answer A is incorrect because angiomyofibroblastoma shows presence of epithelioid to spindle cells, which are prominently arranged around blood vessels. Answer C is incorrect because leiomyoma is composed of interlacing fascicles of smooth muscle without hyalinized vessels or another spindle cell component. Answer D is incorrect because solitary fibrous tumor shows characteristic staghorn-like blood vessels and not hyalinized ones.
Comment Here
Reference: Cellular angiofibroma
Comment Here
Reference: Cellular angiofibroma
Practice question #2
A 65 year old man presented with inguinal pain and swelling that was slow growing in nature. MRI showed a hyperintense lesion in the inguinal region that was attached to the spermatic cord. Excision was done and a diagnosis of cellular angiofibroma was made. Which of the following statements is correct regarding this entity?
- Excision followed by radiation is curative
- It is a locally aggressive neoplasm
- RB1 gene deletion is characteristic
- STAT6 is positive by immunohistochemistry
Practice answer #2
C. RB1 gene deletion is characteristic. RB1 gene deletion, which is located at chromosome 13q14, is characteristic of cellular angiofibroma. Answer B is incorrect because cellular angiofibroma is a benign lesion that does not require radiation or any other aggressive therapy in most cases. Answer A is incorrect because complete surgical excision is curative and local recurrence is extremely rare. Answer D is incorrect because STAT6 positivity by immunohistochemistry is a feature of solitary fibrous tumor, which surrogates the genetic abnormality (NAB2::STAT6 fusion) in this tumor.
Comment Here
Reference: Cellular angiofibroma
Comment Here
Reference: Cellular angiofibroma