Cite this page: Tranesh GA, Qu H. Other cysts. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocyticcystadenoma.html. Accessed August 26th, 2025.
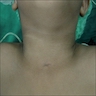
Branchial cleft cyst
[Pending]
Bronchogenic cyst
Definition / general
Sites
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
Case reports
Treatment
Clinical images
Images hosted on other servers:
Gross description
Gross images
Images hosted on other servers:
Microscopic (histologic) description
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
Cytology description
Positive stains
Negative stains
Differential diagnosis
- Bronchogenic cysts presenting in the skin are very rare, with < 70 cases reported
Sites
- Most are present at birth on the precordium or overlying the suprasternal notch
- Occasionally occur near shoulder, back, scapula, neck, abdomen or chin or present at a later age
Pathophysiology
- Believed to form from buds or diverticula that separate from foregut during development of the tracheobronchial tree
- May be intrapulmonary or peripheral
- Cutaneous bronchogenic cysts may result from subsequent sequestration outside the chest cavity following fusion of the mesenchymal bars of the sternum or from active migration prior to fusion
Clinical features
- 80% males
- Variable presentation as cutaneous cystic nodule, sinus or papillomatous growth
- Usually asymptomatic but may be tender or painful
- Rarely are multiple
Case reports
- 2 year old boy with scapular cyst (Dermatol Online J 2012;18:12)
- 21 year old woman with multiple cysts on neck and scalp (Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat 2008;17:69)
Treatment
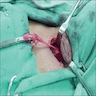
- Treatment is surgical resection, if clinically indicated
Clinical images
Images hosted on other servers:
Gross description
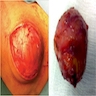
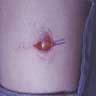
- Skin nodule
Gross images
Images hosted on other servers:
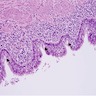
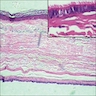
Microscopic (histologic) description
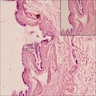
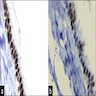
- Cutaneous bronchogenic cyst occurs within dermis or subcutaneous tissue
- Lining is usually thrown into small folds
- Epithelium is invariably ciliated, pseudostratified cuboidal or columnar, with mucus secreting goblet cells in 50% of cases
- May have nonciliated cuboidal, columnar and stratified squamous epithelium
- Smooth muscle supports the mucosa in 8% of cases
- Lymphoid follicles are found in 25% of cases and appear to be part of a secondary inflammatory response
- Occasionally seromucinous glands or cartilage are present
- Cutaneous lung tissue heterotopia, in which fully developed bronchioles and alveoli are present, is considered a variant
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
Cytology description
- Ciliated columnar cells with abundant cytoplasm and eccentric nuclei in proteinaceous or clean background (J Cutan Aesthet Surg 2010;3:181)
Positive stains
Negative stains
Differential diagnosis
- Heterotopic rests
- Mature cystic teratoma
- Thyroglossal duct cyst
Cutaneous ciliated cyst
Definition / general
Epidemiology
Sites
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
Case reports
Treatment
Gross description
Gross images
Images hosted on other servers:
Microscopic (histologic) description
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
Positive stains
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
Differential diagnosis
Additional references
- Also called cystadenoma, cutaneous Müllerian cyst
- Usually extremities of teenage girls
- May have Müllerian derivation in females, distinct fetal eccrine duct origin in males
Epidemiology
- Solitary lesion which presents shortly after menarche on limb of young women (12 - 42 years)
- Also described in males and at atypical sites including back, shoulder, scalp, cheek
Sites
- Thigh > buttock > calf > foot
Pathophysiology
- Lesions on limbs of young females are generally thought to be of Müllerian (paramesonephric) derivation, representing a migration abnormality of fetal development (heterotopia)
- Cysts arising at other sites and in males may represent metaplasia of lining of a pre-existent simple cyst of sweat duct derivation or have an entirely different histogenesis
Clinical features
- Located in deep dermis or subcutaneous tissue
- Usually asymptomatic
Case reports
- 16 year old girl with cutaneous ciliated cyst on finger (Am J Dermatopathol 2012;34:335)
- 18 year old woman with cutaneous ciliated cyst over knee (J Cutan Aesthet Surg 2011;4:158)
- 48 year old woman with cystic lesion on right heel (Dermatol Online J 2011;17:6)
Treatment
- Surgical excision
Gross description
- Soft to cystic, solitary, movable, nontender, fluctuant swelling
Gross images
Images hosted on other servers:
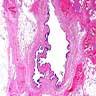
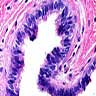
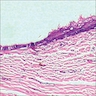
Microscopic (histologic) description
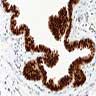
- Unilocular or multilocular cyst with intraluminal papillary projections of lining resembling fallopian tube
- Cuboidal to columnar ciliated epithelium with frequent pseudostratified foci
- Deep to the epithelium lie well vascularized parallel bundles of collagen but smooth muscle is not present
- Occasional: squamous metaplasia, intercalated dark cells
- Rare: mucin secreting cells, apocrine-like features
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
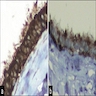
Positive stains
- Cytokeratin, EMA, ER, PR
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Ultrastructurally, cilia have characteristic morphology with a central pair of microtubules, 9 radially orientated pairs of microtubules, basal bodies, cross striated rootlets
Differential diagnosis
- Branchial and thymic cysts
- Bronchogenic cyst
- Mature cystic teratoma
- Thyroglossal duct
Additional references