Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Frozen section images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Khattak MT, Anjum S, Ud Din N. Angiomyofibroblastoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissueangiomyofibroblastoma.html. Accessed September 15th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Rare, benign, well circumscribed mesenchymal tumor that usually presents in young to middle aged women, predominantly in vulvovaginal area (Gynecol Minim Invasive Ther 2022;11:185, Mod Pathol 1996;9:284, Heliyon 2020;6:e04123)
Essential features
- Benign myofibroblastic tumor that most commonly occurs in the lower genital tract of women
- Histologically, a well circumscribed tumor that has alternating areas of hypercellularity and hypocellularity with stromal edema, abundant blood vessels and spindle to epithelioid stromal cells (J Surg Case Rep 2020;2020:rjaa051, BMJ Case Rep 2019;12:e229486, Diagnostics (Basel) 2022;12:357, Gynecol Minim Invasive Ther 2022;11:185)
- Immunoreactivity for desmin, estrogen receptor / progesterone receptor and occasionally for CD34 (Gynecol Minim Invasive Ther 2022;11:185)
Terminology
- Angiomyofibroblastoma (Pathologica 2021;113:70, Diagnostics (Basel) 2022;12:357)
ICD coding
- ICD-10: D21.9 - benign neoplasm of connective and other soft tissue, unspecified
Epidemiology
- Rare, benign soft tissue tumor (Gynecol Minim Invasive Ther 2022;11:185)
- M:F = 1:10 (J Med Case Rep 2015;9:248)
- In women of reproductive age, ranging from third to ninth decade of life, median age of 45 years (J Med Case Rep 2015;9:248)
Sites
- Vulvovaginal area, predominantly the vulva (Gynecol Minim Invasive Ther 2022;11:185, Int J Gynecol Pathol 2017;36:300)
- Occasionally perineum and pelvis in women, scrotum, inguinal area and perineum in men (Gynecol Minim Invasive Ther 2022;11:185, Heliyon 2020;6:e04123, J Surg Case Rep 2020;2020:rjaa051, Front Surg 2022;9:808488, J Med Case Rep 2015;9:248)
- Rarely retroperitoneum, extremities, mediastinum and nasal cavity (Indian J Surg Oncol 2017;8:210, Medicine (Baltimore) 2016;95:e5484, Coll Antropol 2013;37:301)
Pathophysiology
- Cell origin remains unclear (Gynecol Minim Invasive Ther 2022;11:185, J Med Case Rep 2015;9:248)
- Positivity for estrogen receptor / progesterone receptor suggests hormonal role in development (Gynecol Minim Invasive Ther 2022;11:185, Case Rep Obstet Gynecol 2018;2018:8579026)
- RNA sequencing based MTG1::CYP2E1 fusion detected (Histopathology 2022;81:841, Mod Pathol 2021;34:2222)
Etiology
- Relationship with tamoxifen therapy (Int J Gynecol Cancer 2006;16:581)
Clinical features
- Asymptomatic, slowly progressing, well defined mass (Gynecol Minim Invasive Ther 2022;11:185, Front Surg 2022;9:808488)
- Often misinterpreted as a Bartholin gland cyst (Diagnostics (Basel) 2022;12:357)
Diagnosis
- Histopathological examination (Front Surg 2022;9:808488, Heliyon 2020;6:e04123)
Radiology description
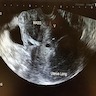
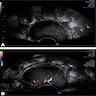
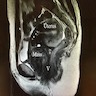
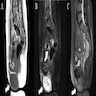
- Ultrasonography: solid, well demarcated, vascularized lesion, hyperechoic areas with irregular and small hypoechoic cystic areas scattered within homogenous echogenic stroma (Case Rep Obstet Gynecol 2018;2018:7397121, Case Rep Obstet Gynecol 2018;2018:8579026, J Med Case Rep 2015;9:248)
- MRI: solid vascularized lesions with well defined margins
- Heterogeneous signal intensity on T2 weighted; persistent enhancement on dynamic gadolinium enhanced (Case Rep Obstet Gynecol 2018;2018:8579026, J Med Case Rep 2015;9:248, Gynecol Oncol Rep 2021;36:100751, Front Surg 2022;9:808488, Mol Clin Oncol 2017;7:407)
- Color Doppler: slight intralesional or peripheral vascularization (J Med Case Rep 2015;9:248)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Rare local recurrences even with marginal excision (Gynecol Minim Invasive Ther 2022;11:185, Gynecol Oncol Rep 2021;36:100751, Diagnostics (Basel) 2022;12:357, Int J Pharm 2018;547:235)
Case reports
- 22 year old woman with rare case of huge vulvar angiomyofibroblastoma (Gynecol Oncol Rep 2021;36:100751)
- 25 year old woman with recurrent angiomyofibroblastoma of the vagina (Exp Ther Med 2016;11:1893)
- 27 year old man with angiomyofibroblastoma of the inguinal region (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2000;124:1679)
- 28 year old woman with angiomyofibroblastoma arising from the fallopian tube (Obstet Gynecol 1999;94:833)
- 32 year old woman with giant pelvic angiomyofibroblastoma (Diagn Pathol 2014;9:106)
- 42 year old man with scrotal angiomyofibroblastoma (Front Surg 2022;9:808488)
- 48 year old woman with angiomyofibroblastoma of the foot (Indian J Surg Oncol 2017;8:210)
- 62 year old man with angiomyofibroblastoma mimicking an inguinal hernia (Postepy Dermatol Alergol 2019;36:223)
- 64 year old postmenopausal woman with vaginal angiomyofibroblastoma (Arch Gynecol Obstet 2005;273:129)
- 74 year old man with polypoid angiomyofibroblastoma of the nasal cavity (Coll Antropol 2013;37:301)
- 80 year old woman with angiomyofibroblastoma of the vulva with sarcomatous transformation (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:1104)
Treatment
- Complete surgical resection is curative (J Surg Case Rep 2020;2020:rjaa051, Gynecol Minim Invasive Ther 2022;11:185)
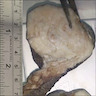
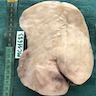
Gross description
- Subcutaneous, sharply demarcated, unencapsulated
- Usually < 5 cm, ranging from 0.5 - 12 cm
- Soft to rubbery, spongy to firm consistency and tan-pink or yellow cut surface (Gynecol Minim Invasive Ther 2022;11:185, Gynecol Oncol Rep 2021;36:100751, Heliyon 2020;6:e04123, Diagnostics (Basel) 2022;12:357, J Surg Case Rep 2020;2020:rjaa051, Mol Clin Oncol 2017;7:407)
- Rarely large pedunculated mass (Gynecol Minim Invasive Ther 2022;11:185)
Gross images
Frozen section description
- Spindle cells or cords of epithelioid cells around abundant blood vessels with thin to thick vascular walls embedded in loose stroma (Heliyon 2020;6:e04123)
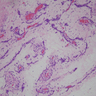
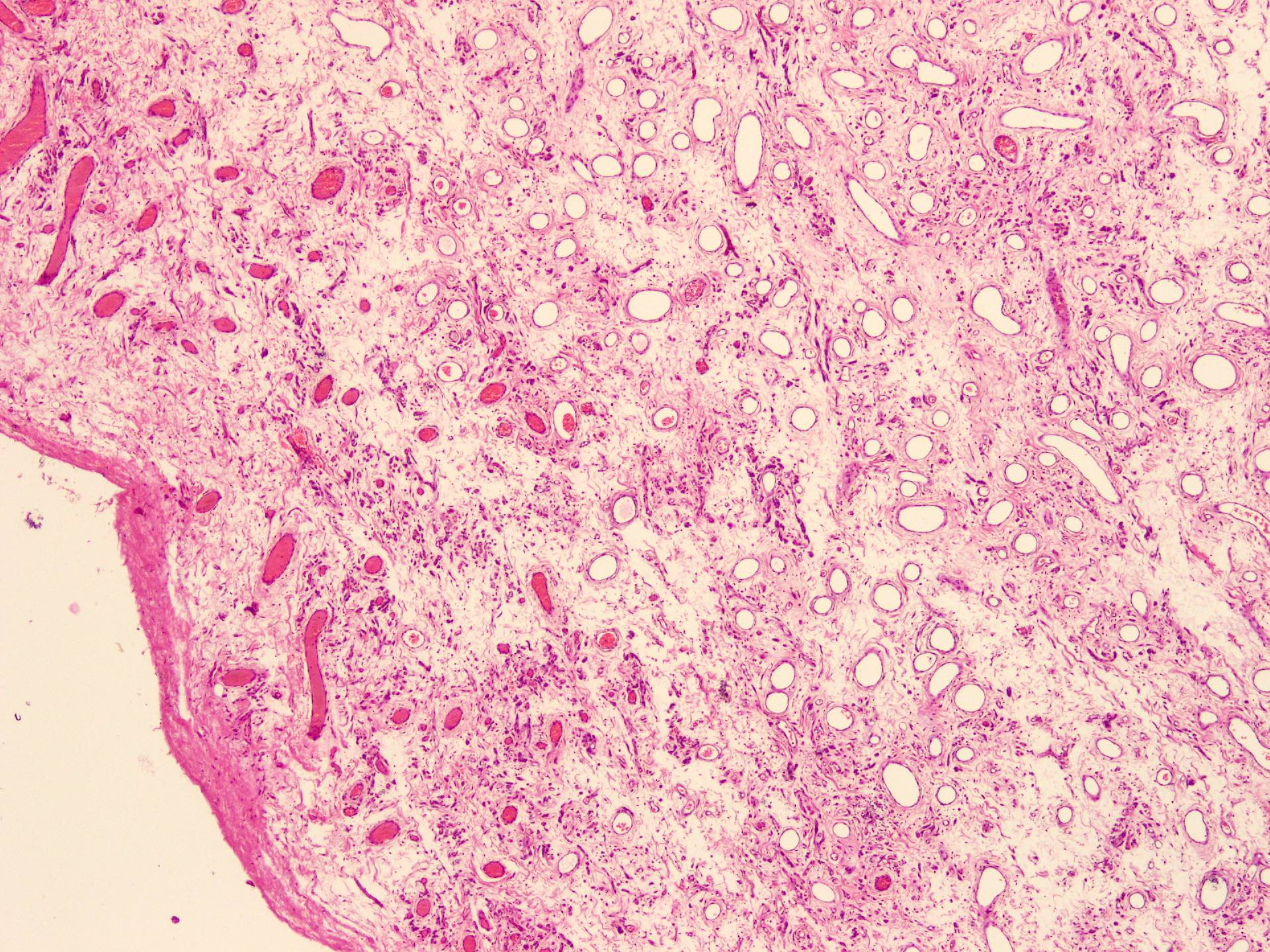
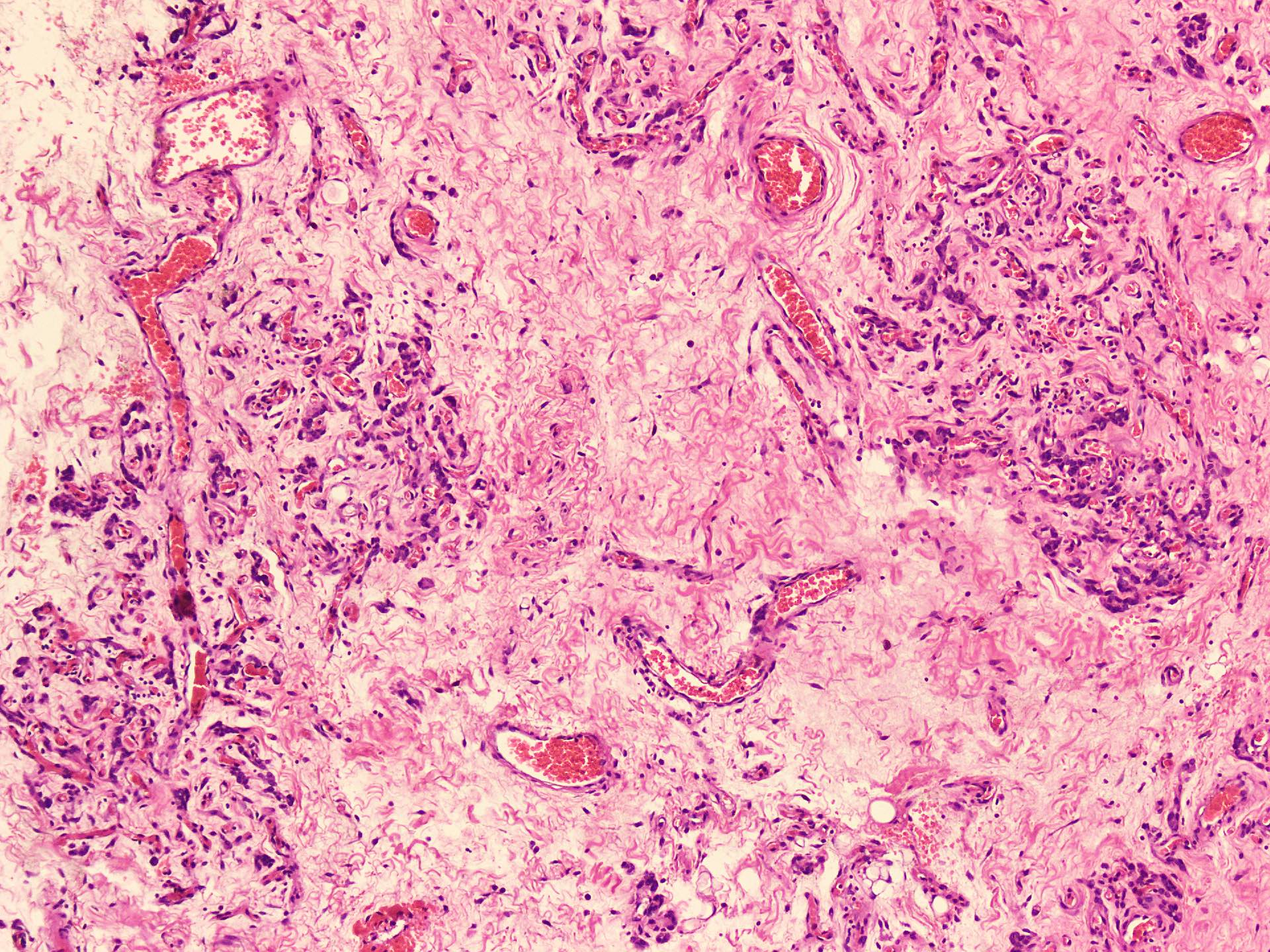
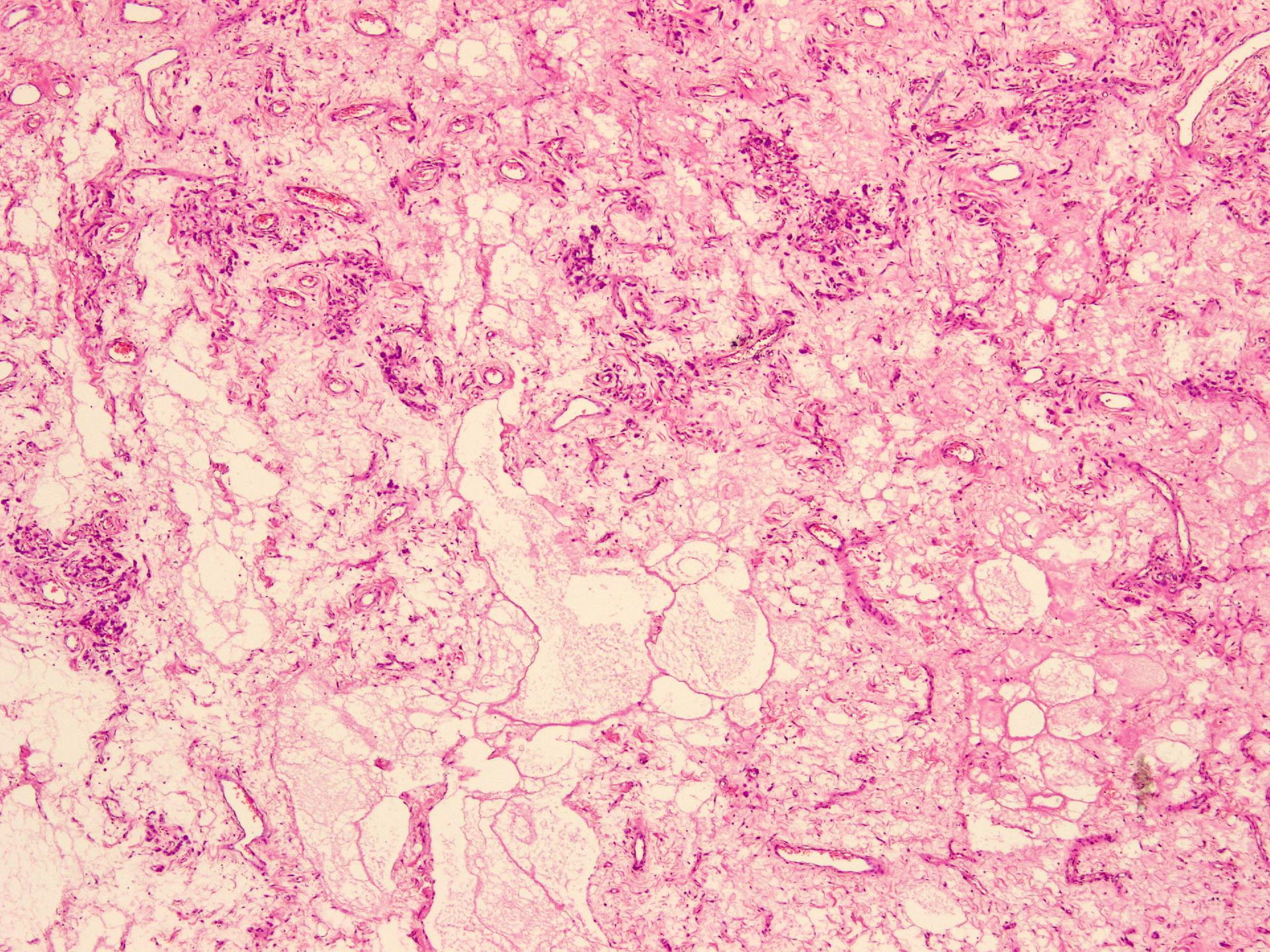
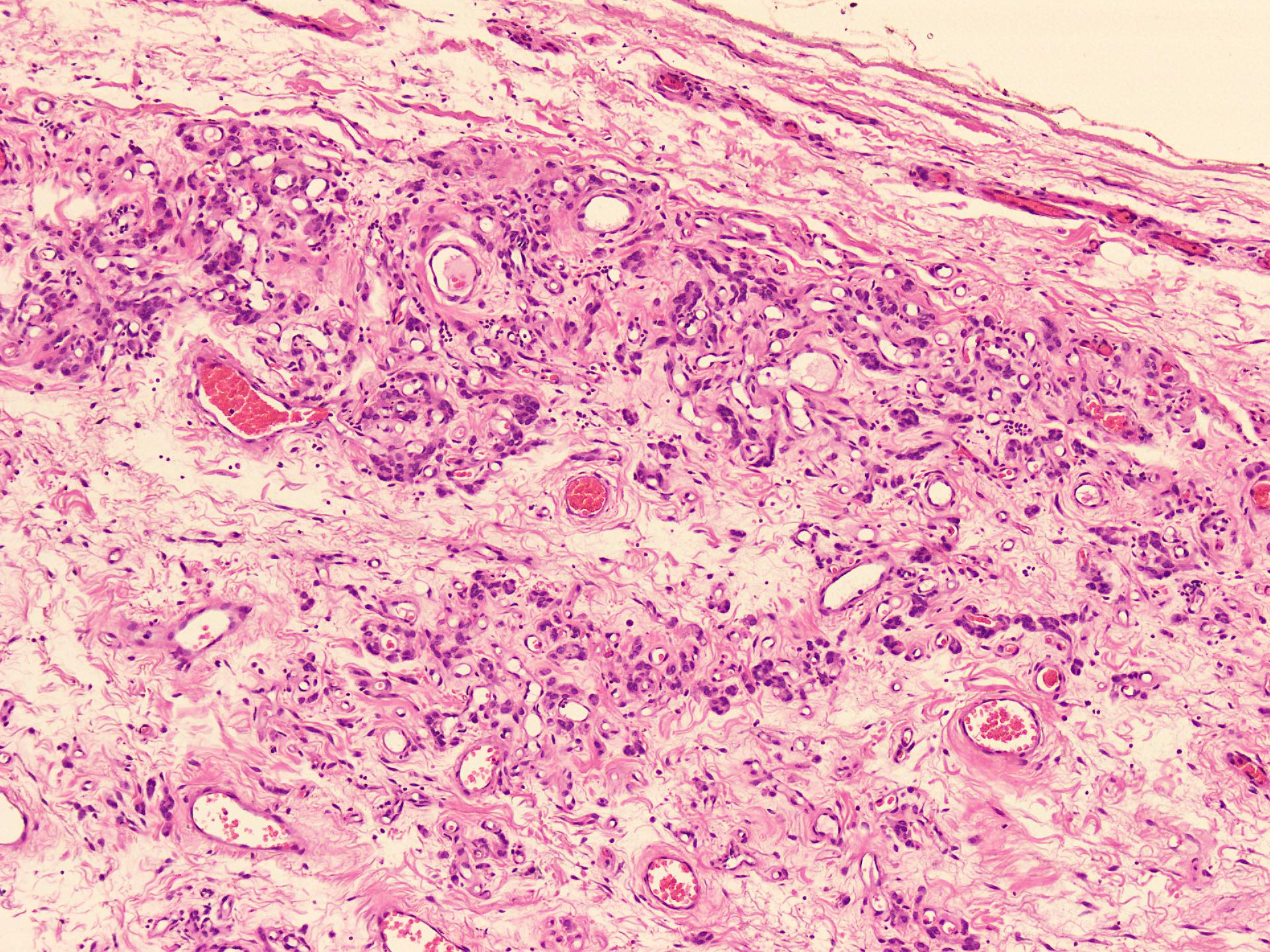
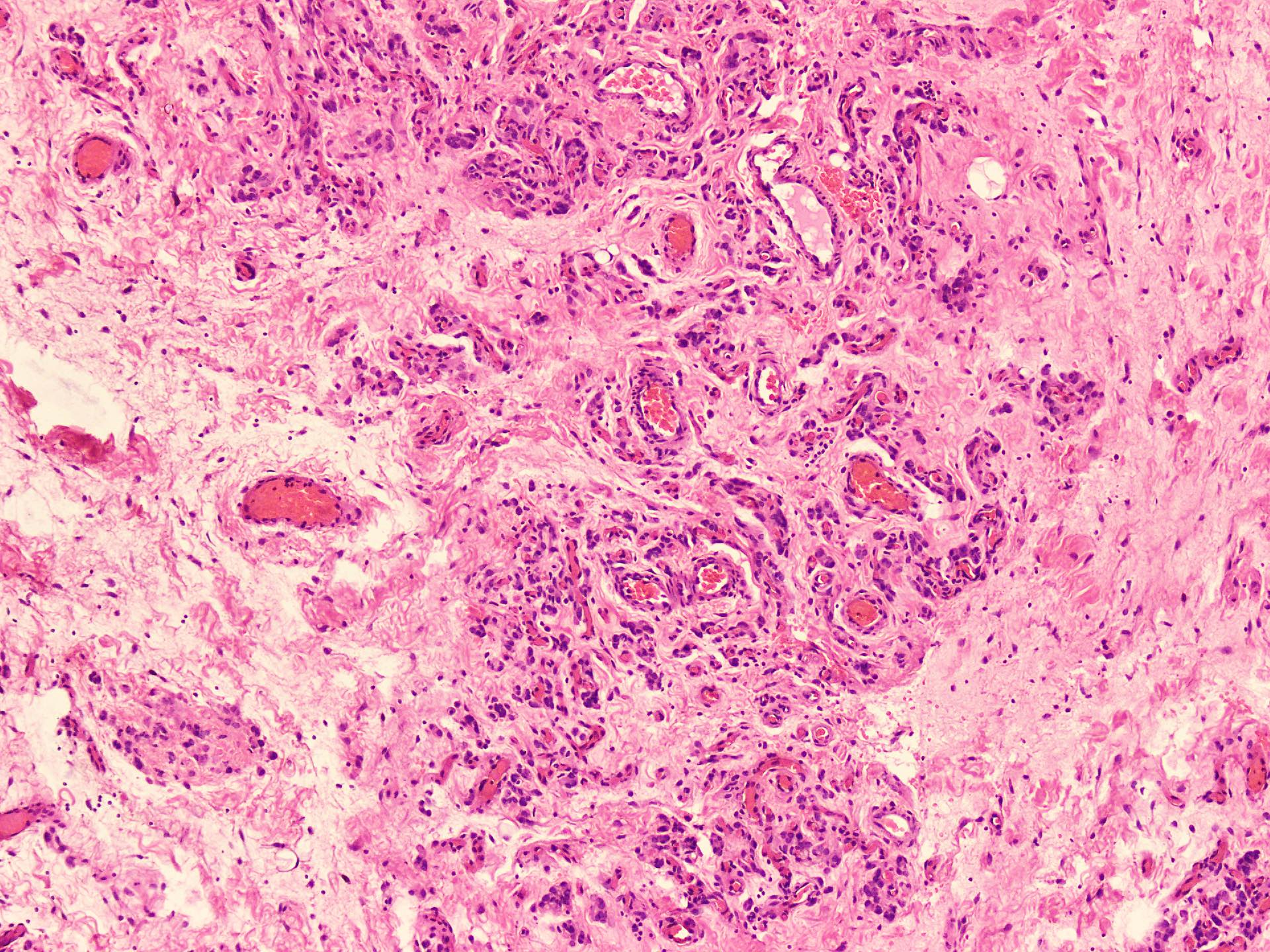
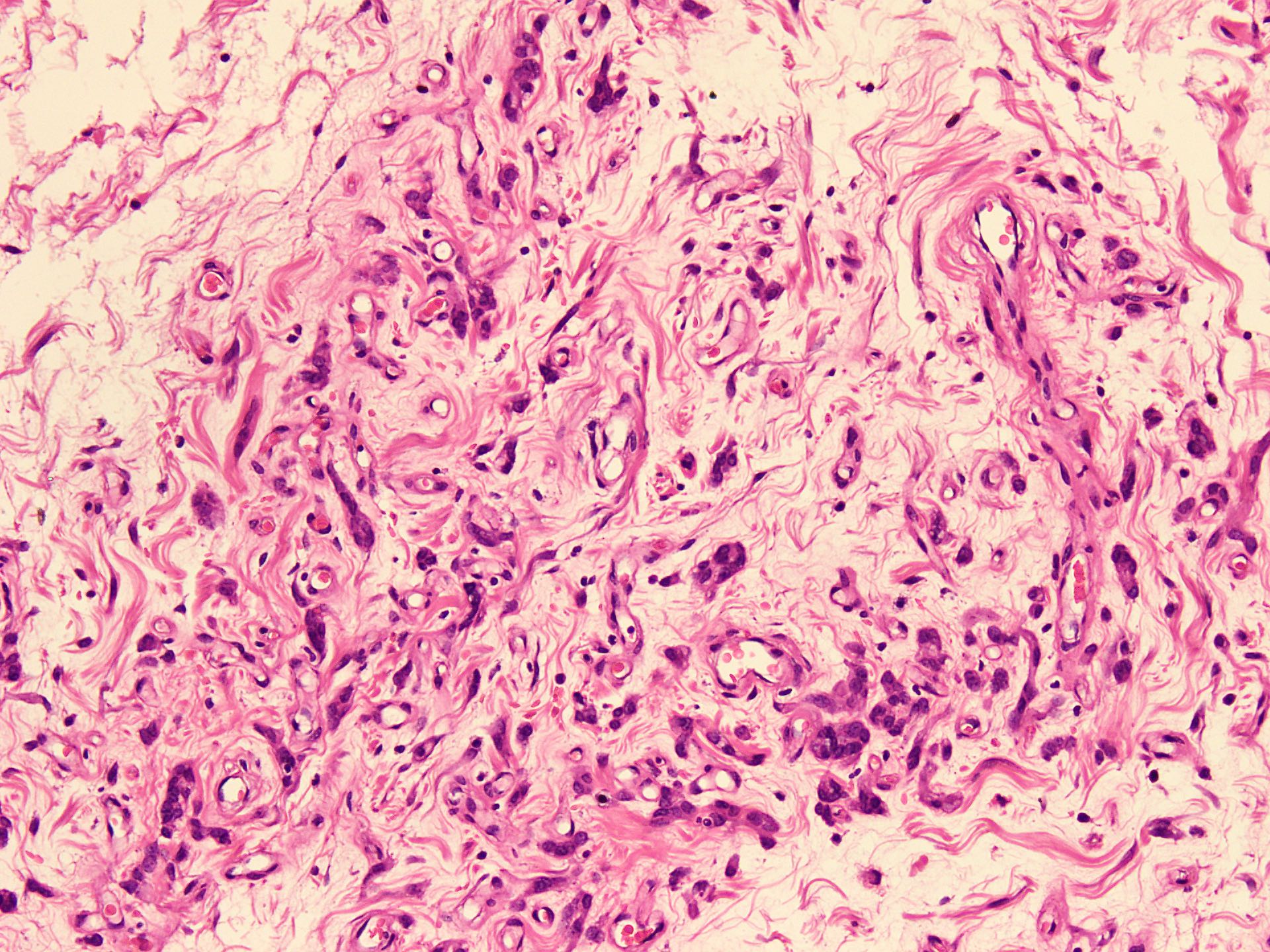
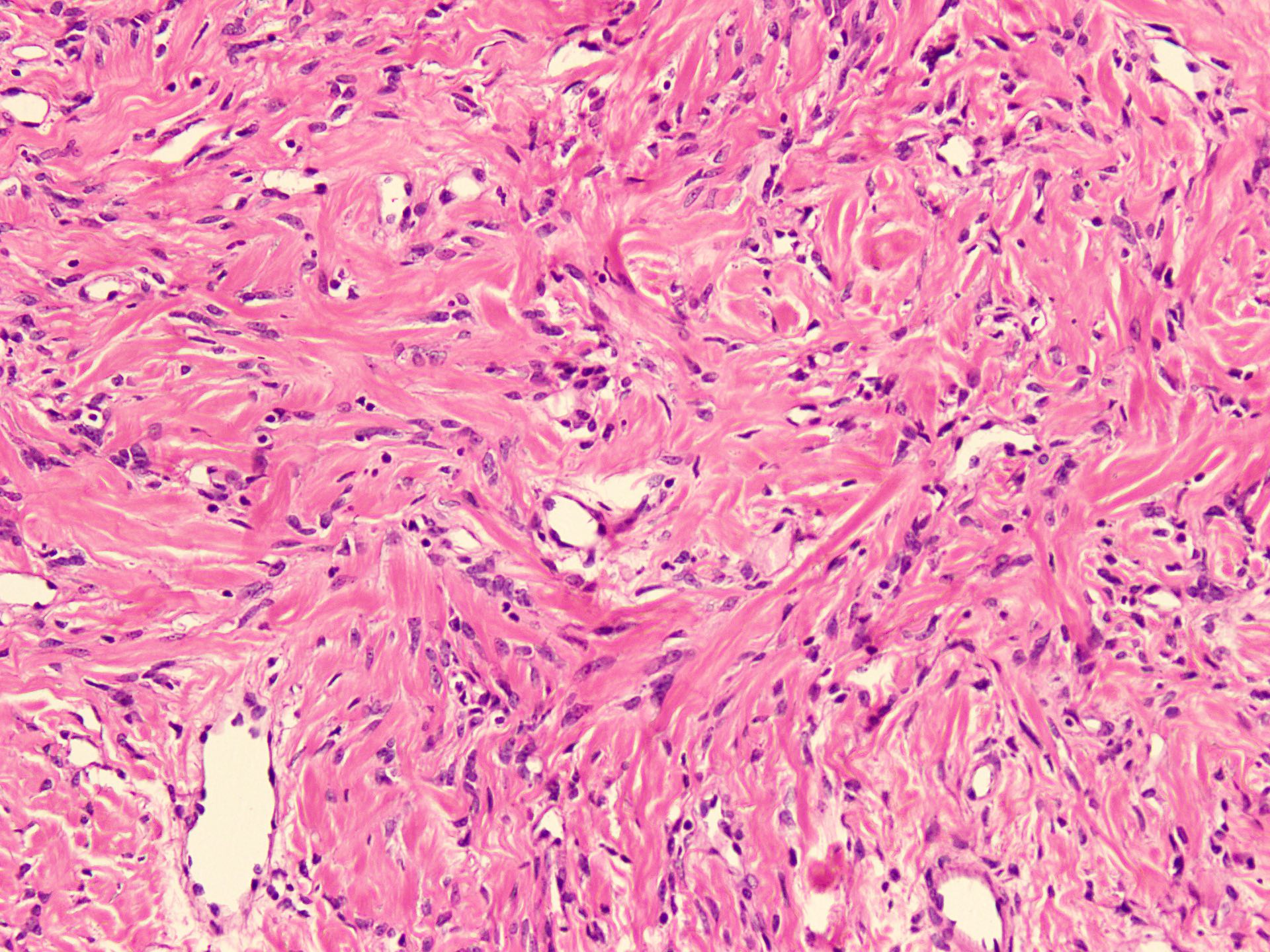
Microscopic (histologic) description
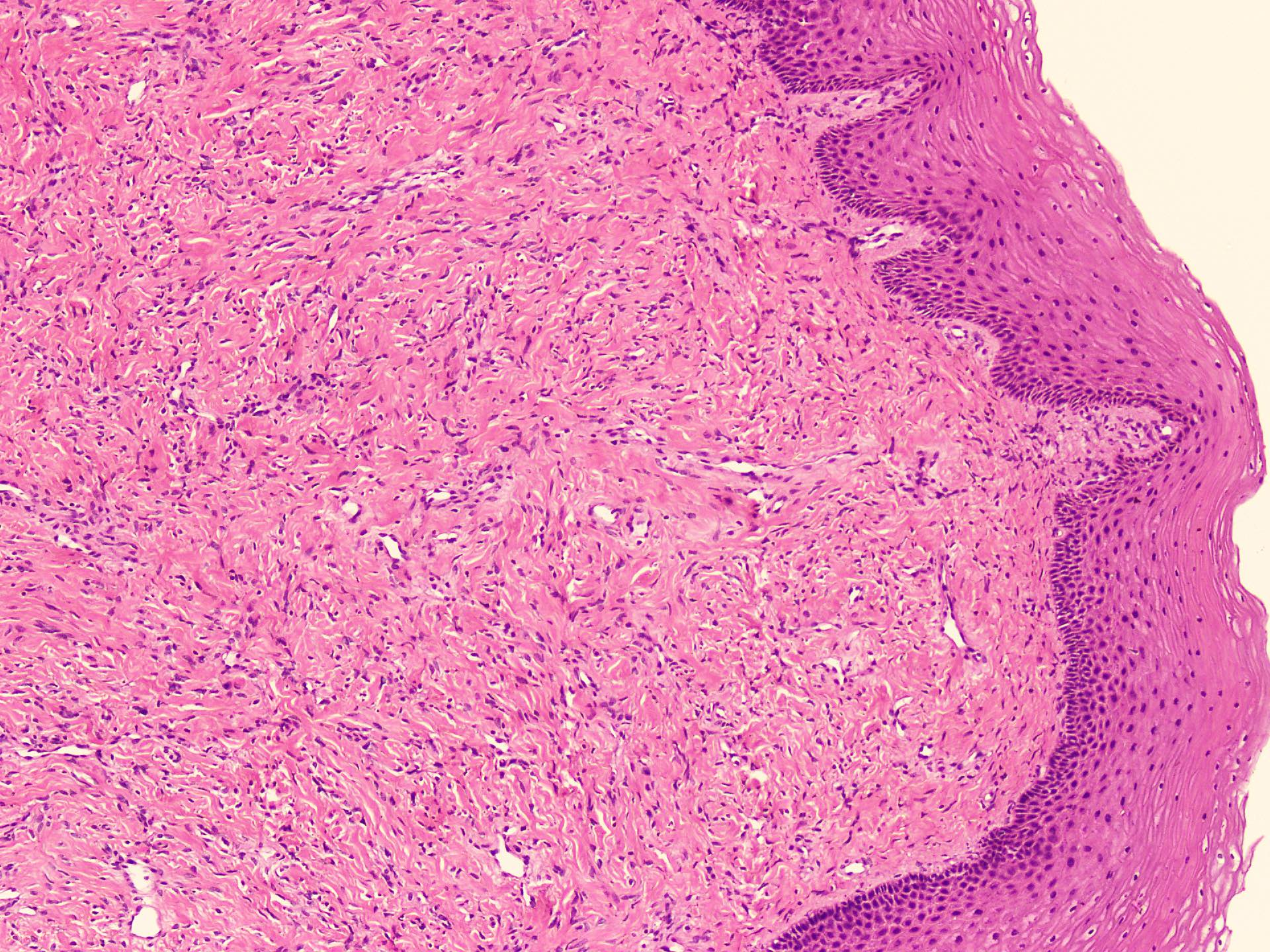
- Sharply circumscribed, unencapsulated (J Surg Case Rep 2020;2020:rjaa051, BMJ Case Rep 2019;12:e229486, Diagnostics (Basel) 2022;12:357)
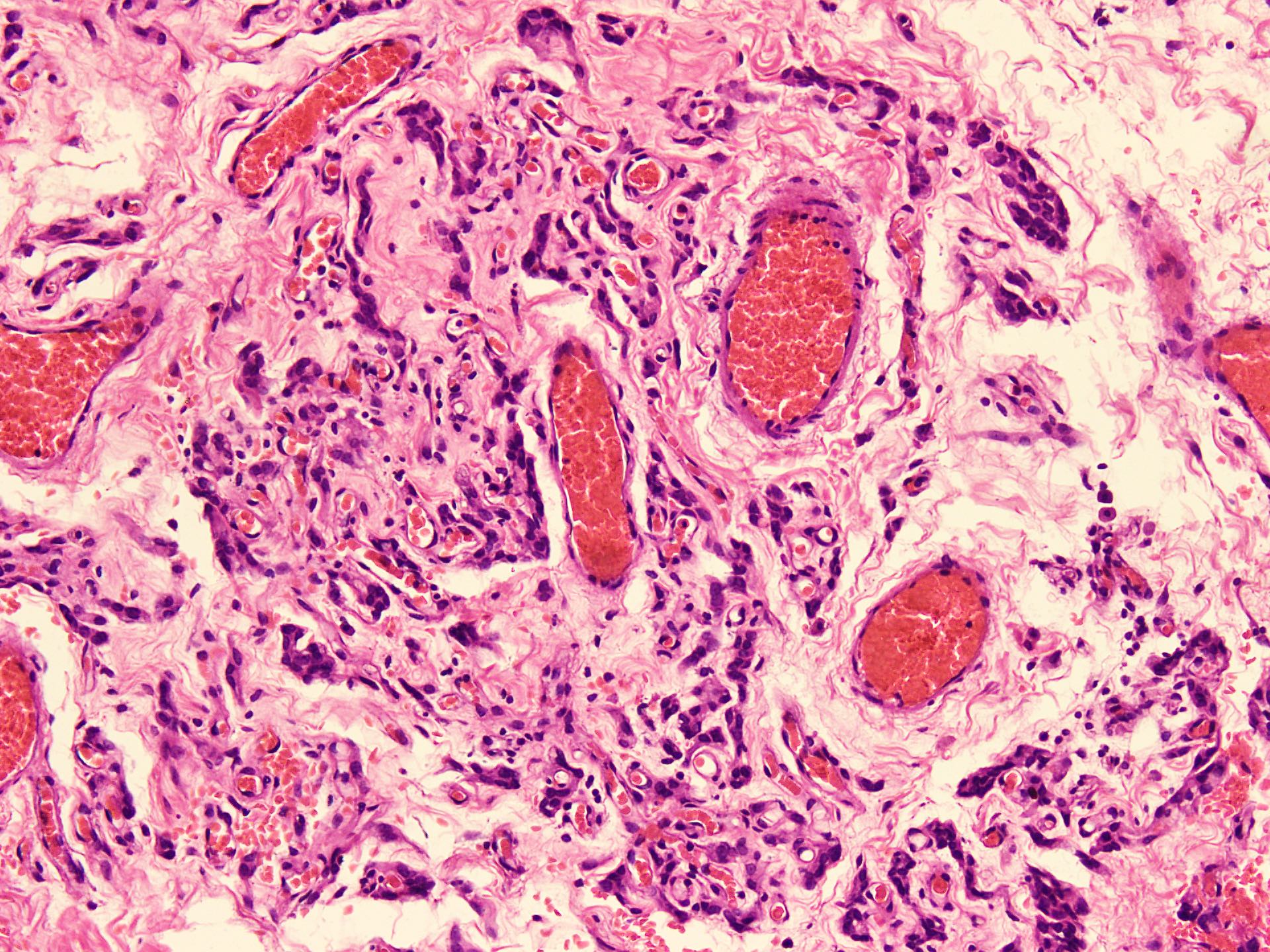
- Hypercellular and hypocellular areas, abundant irregularly distributed capillary sized blood vessels or small veins in myxoedematous to fibrous collagenous stroma (J Surg Case Rep 2020;2020:rjaa051, BMJ Case Rep 2019;12:e229486, Diagnostics (Basel) 2022;12:357)
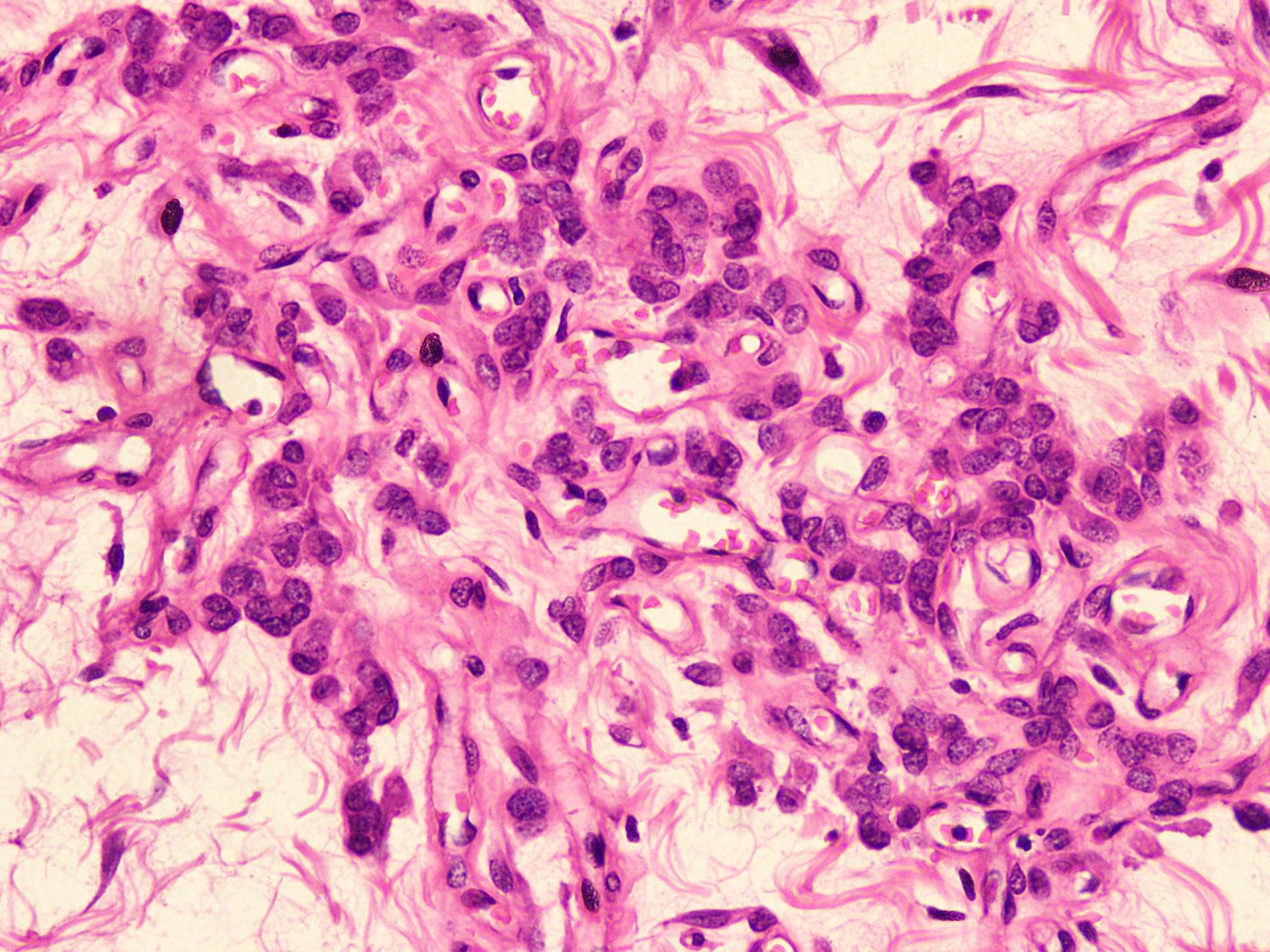
- Bland spindle to epithelioid to plasmacytoid tumor cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm arranged in a nest, a cord-like pattern or singly and concentrated around blood vessels and between fat cells (Diagnostics (Basel) 2022;12:357, Gynecol Minim Invasive Ther 2022;11:185)
- Binucleated or multinucleated stromal cells may be present (Diagnostics (Basel) 2022;12:357, Mills: Sternberg's Diagnostic Surgical Pathology, 6th Edition, 2015)
- Rarely entrapped mucosal glands, nerves and fat (massive, denoted as lipomatous variant) (Diagnostics (Basel) 2022;12:357, Hum Pathol 1997;28:1046)
- Rare, slight nuclear pleomorphism, hyperchromasia and degenerative changes, scattered mast cells and lymphocytes in the stroma (Diagnostics (Basel) 2022;12:357)
- Mitotic activity absent or sparse (Diagnostics (Basel) 2022;12:357)
- Rarely may contain atypical cells and increased mitotic activity (so called malignant angiomyofibroblastoma) or sarcomatous areas close to leiomyosarcoma or undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (so called dedifferentiated angiomyofibroblastoma) (Diagnostics (Basel) 2022;12:357)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
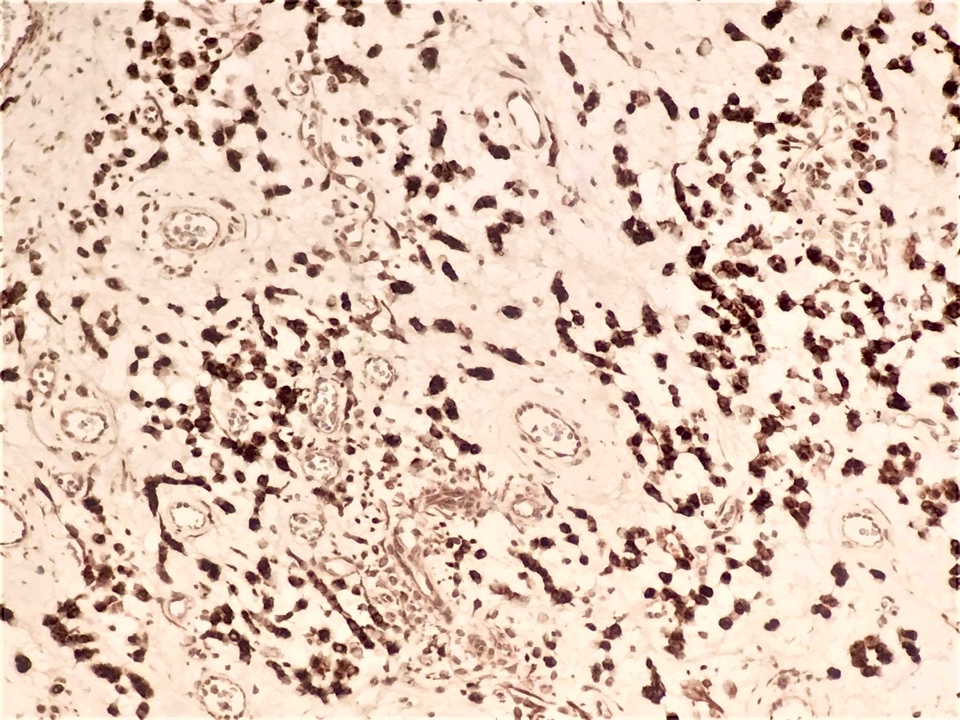
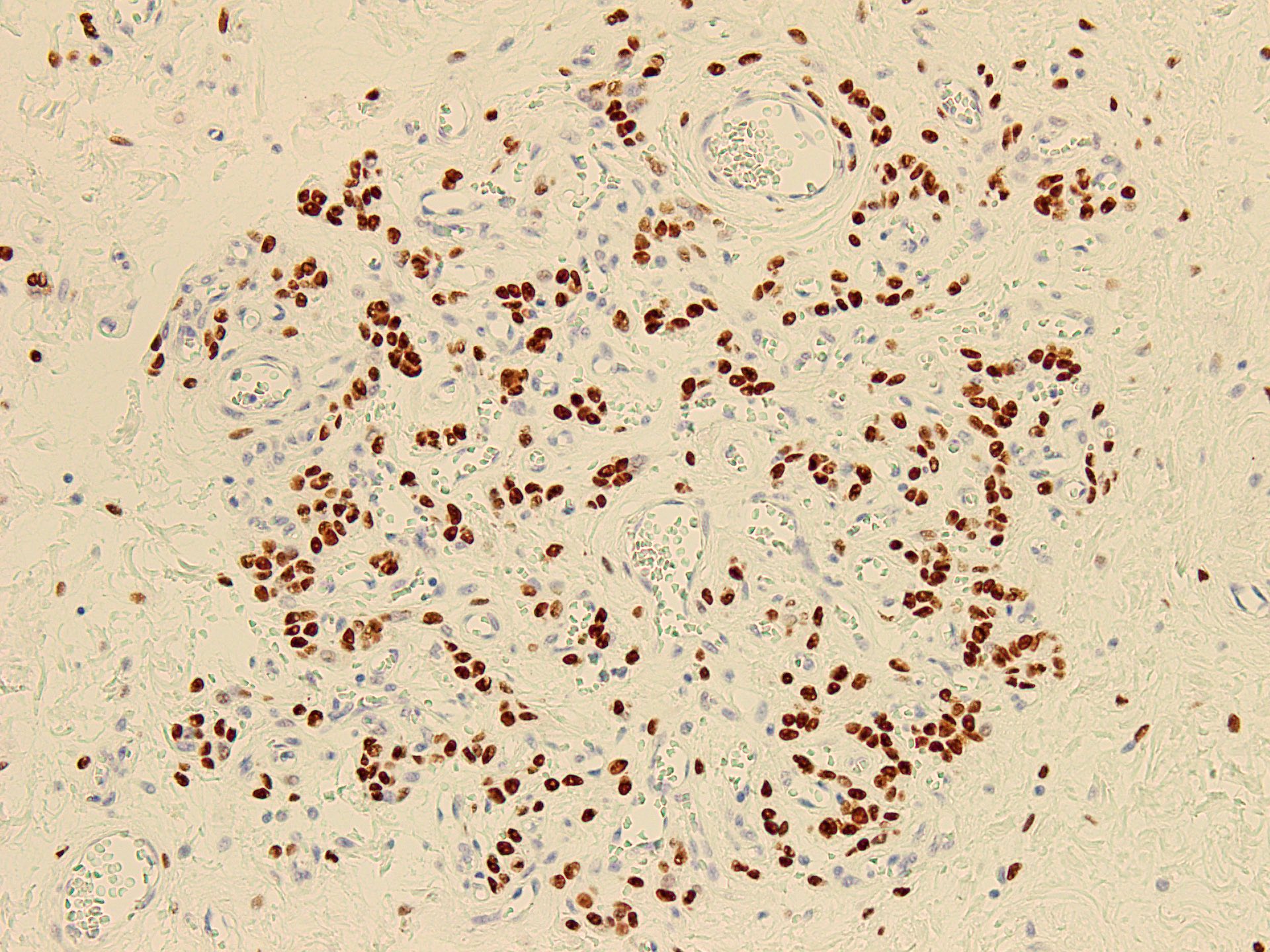
- Desmin (50 - 60% of cases), estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor in stromal cells, smooth muscle actin in stromal cells (up to 40% of cases) (Diagnostics (Basel) 2022;12:357, Gynecol Minim Invasive Ther 2022;11:185, J Ultrason 2019;19:158, Gynecol Oncol Rep 2021;36:100751, Postepy Dermatol Alergol 2019;36:223)
- Occasionally CD34 around blood vessels (Gynecol Minim Invasive Ther 2022;11:185, Diagnostics (Basel) 2022;12:357, Postepy Dermatol Alergol 2019;36:223)
Negative stains
- Factor XIIIa, keratin, S100 protein, Leu7, GFAP, CD68 (Mod Pathol 1996;9:284, Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:1104)
- Sarcomatous component if present is negative for desmin, SMA and CD34 (Diagnostics (Basel) 2022;12:357)
Electron microscopy description
- Features of fibroblasts or myofibroblasts, stromal cells adhered via primitive junctions and contain intermediate filaments without focal density in the cytoplasm (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:1104, Pathol Int 1998;48:292)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- RNA sequencing based MTG1::CYP2E1 fusion transcript (Histopathology 2022;81:841)
Videos
Histopathology
Sample pathology report
- Vulva, wide local excision:
- Angiomyofibroblastoma (see comment)
- Comment: Histological examination reveals a well circumscribed, unencapsulated tumor with alternating hypercellular and hypocellular areas set in edematous to collagenous stroma. Numerous thin walled blood vessels and bland looking spindled to epithelioid cells, arranged singly or in small nests or cords concentrating around blood vessels are seen. No mitotic activity, nuclear atypia or necrosis is noted. It is a benign condition and has been completely excised.
Differential diagnosis
- Aggressive angiomyxoma:
- Epidemiology: women in third to fourth decade of life
- Site: slow growing mass in vulvovaginal and pelviperineal region
- Radiology: well defined tumor with infiltrative borders and distinctive layering or swirled pattern
- Grossly: ill defined borders, frequently > 10 cm
- Histologically: hypocellular lesion with infiltrative margins and entrapped adipose tissue, skeletal muscle and nerves, myxoid stroma, wispy collagen fibers, hyalinized blood vessels and extravasated red blood cells, invasion into skeletal muscle and fat
- High frequency of local recurrence after surgery
- IHC:
- Positive stains:
- CD34 (strongly) (J Int Med Res 2020;48:300060520936414)
- Desmin (moderately positive) (J Int Med Res 2020;48:300060520936414)
- ER and PR (100% of cases) (Goldblum: Rosai and Ackerman's Surgical Pathology, 11th Edition, 2017)
- Negative stains:
- S100 (J Int Med Res 2020;48:300060520936414, Postepy Dermatol Alergol 2019;36:223)
- Ki67: < 1% of tumor cells (J Int Med Res 2020;48:300060520936414)
- Variable expression of HMGA2 (Diagnostics (Basel) 2022;12:357)
- SMA (27 - 95% of cases) (Diagnostics (Basel) 2022;12:357)
- Positive stains:
- FISH rearrangement of HMGA2 locus identified in ~33% of tumors (Diagnostics (Basel) 2022;12:357, Gynecol Oncol Rep 2021;36:100751, Int J Surg Case Rep 2021;83:105948, SAGE Open Med Case Rep 2019;7:2050313X19843391, Diagn Interv Imaging 2013;94:657, Postepy Dermatol Alergol 2019;36:223, Oman Med J 2016;31:456, J Pak Med Assoc 2020;70:1304)
- Cellular angiofibroma:
- Epidemiology: middle aged women
- Site: asymptomatic, round to lobulated, slow growing lesion with well circumscribed borders
- MRI: well marginated mass containing fat with high cellular density
- Grossly: usually 1.2 - 2.5 cm
- Histologically: short fascicles of monotonous bland spindle shaped mesenchymal cells, numerous small to medium sized blood vessels with mural hyalinization and edematous to fibrous stroma
- Limited infiltration of the surrounding adipose tissue and rare mitotic figures
- IHC (BMJ Case Rep 2020;13:e235241, BMJ Case Rep 2019;12:e229486, Diagn Pathol 2015;10:114, Postepy Dermatol Alergol 2019;36:223, Diagnostics (Basel) 2022;12:357, Medicine (Baltimore) 2022;101:e30293):
- Superficial myofibroblastoma:
- Epidemiology: wide age range (23 - 80 years), mean age of 53.5 years in women
- Site: lower female genital tract, frequently vulvovaginal region
- Radiology: well demarcated, polypoid / nodular mass
- Grossly: measures 1.2 - 2.5 cm
- Histologically: spindled and stellate shaped cells arranged in various architectural patterns in collagenized or myxoid stroma, grenz zone usually identified deep within the surface epithelium
- IHC:
- Positive stains: ER / PR in 80 - 100% of cases, desmin in 75 - 100%, SMA in 0 - 45% of cases, CD34 in 50 - 85% of cases (Case Rep Pathol 2019;2019:1582714, BJR Case Rep 2016;3:20160052, Radiol Case Rep 2021;16:3690, IJU Case Rep 2020;3:69, SAGE Open Med Case Rep 2017;5:2050313X17726936)
Additional references
Practice question #1
A 38 year old woman presented with a gradually growing nodule in left labium majus. On physical examination, there is a well demarcated, firm, subcutaneous mass protruding from the left labium majus. Radiology shows well demarcated subcutaneous mass. Histology is shown in the image above. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this case?
- Aggressive angiomyxoma
- Angiomyofibroblastoma
- Cellular angiofibroma
- Epithelioid leiomyoma
- Superficial myofibroblastoma
Practice answer #1
B. Angiomyofibroblastoma. The history of slow growing subcutaneous nodule in vulvovaginal areas in this middle aged woman suggests a soft tissue lesion. In this area, the most common mesenchymal tumors include aggressive angiomyxoma, angiomyofibroblastoma and cellular angiofibroma. The alternating hypocellular and hypercellular areas with prominent blood vessels and tumor cells concentrating around these vessels seen on the photomicrograph are characteristic features of angiomyofibroblastoma. In contrast, the aggressive angiomyxoma have low cellularity with abundant hyalinized blood vessels, extravasated red blood cells and plump stromal cell scattered in mucin rich stroma. Cellular angiofibroma and superficial myofibroblastoma also lack this characteristic, alternating cellularity pattern.
Comment Here
Reference: Angiomyofibroblastoma
Comment Here
Reference: Angiomyofibroblastoma
Practice question #2
A 27 year old woman noticed a small gradually increasing nodule in her vulvar region. Physical examination revealed a firm, well demarcated nodule in right labium majus. Reactivity of which of the following markers would help you to reach final diagnosis?
- Desmin
- Keratin
- NSE
- SMA
- S100
Practice answer #2
A. Desmin. The differential diagnosis of gradually increasing subcutaneous nodules in vulvovaginal areas in young women includes site specific mesenchymal tumors (i.e., aggressive angiomyxoma, angiomyofibroblastoma and cellular angiofibroma). The alternating areas of cellularity with prominent blood vessels and tumor cells concentrating around these vessels as seen on photomicrographs are characteristic features of angiomyofibroblastoma. This tumor commonly shows reactivity for desmin and ER / PR receptors. They are negative for keratin, NSE and S100, while SMA can be rarely positive.
Comment Here
Reference: Angiomyofibroblastoma
Comment Here
Reference: Angiomyofibroblastoma