Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1Cite this page: Ginter PS. Low grade adenosquamous. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastmalignantadenosquamous.html. Accessed September 12th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Rare variant of metaplastic carcinoma comprised of an intimately admixed combination of bland, well developed glands and solid squamous cell nests within a fibrotic or cellular spindle stroma
- First reported in 1917 (Br J Surg 1917;5:417)
- Formally recognized in 1987 (Am J Surg Pathol 1987;11:351)
Essential features
- Rare variant of metaplastic carcinoma with low grade cytomorphology
- Largely clinically indolent but may be locally aggressive
- Diagnosis is based primarily on morphologic features, which can be challenging in small samples
- Immunostaining patterns can be variable and unreliable
- May arise in association with other breast lesions
Terminology
- Syringomatous squamous tumor or infiltrative syringomatous adenoma
ICD coding
- ICD-10: C50.919 - malignant neoplasm of unspecified site of unspecified female breast
Epidemiology
- 0.2 to 1%
- Median age: fifth decade; range: 20 - 85 years
- Females; only one case report in male
Sites
- Breast parenchyma
Pathophysiology
- Unknown at this time
- Association with other proliferative and sclerosing breast lesions has led some to suggest they represent precursors (Pathology 2014;46:402)
Etiology
- Multifactorial
Clinical features
- Frequently presents as a palpable mass, typically < 5 cm (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1009, Am J Surg Pathol 1993;17:248)
- May be associated with benign lesions, including
- Papilloma
- Adenomyoepithelioma
- Radial scar / complex sclerosing lesions
- Collagenous spherulosis
- Fibroadenoma or phyllodes tumor
- Indolent course with a favorable prognosis (Am J Surg Pathol 1993;17:248)
- May be locally aggressive and recurrences occur with incomplete excision (Am J Surg Pathol 1993;17:248)
Diagnosis
- Most frequently diagnosed via surgical resection
- Difficult to diagnose by fine needle aspiration, core biopsy or frozen section (Histopathology 2006;49:603)
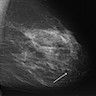
Radiology description
- Nonspecific radiologic appearance
- Mammography:
- Round or irregular solid mass or density (Can Assoc Radiol J 2013;64:339, Histopathology 2006;49:603)
- Calcifications may be present (Can Assoc Radiol J 2013;64:339)
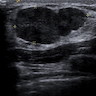
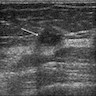
- Ultrasound:
- Solid, irregular hypoechoic mass with irregular borders on (Can Assoc Radiol J 2013;64:339, Histopathology 2006;49:603)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Indolent course with a favorable prognosis (Am J Surg Pathol 1993;17:248)
- Local recurrence is common, particularly if incompletely excised (Am J Surg Pathol 1993;17:248)
- Lymph node metastases and distant metastases are rare (Am J Surg Pathol 1993;17:248)
Case reports
- 42 year old woman presented with a palpable mass (Medicine (Baltimore) 2017;96:e8785)
- 49 year old woman with a palpable mass (Ultrasound Q 2018;34:88)
- 52 year old man with axillary low grade adenosquamous carcinoma (Front Oncol 2020;10:1714)
- 67 year old woman with mass around a residual localization wire fragment (Lab Med 2015;46:241)
- 69 year old woman with a palpable mass (Korean J Pathol 2014;48:229)
Treatment
- Surgical excision with negative margins (Am J Surg Pathol 1987;11:351)
- Radiotherapy is standard for patients with breast conserving surgery
- Role of chemotherapy is indeterminate
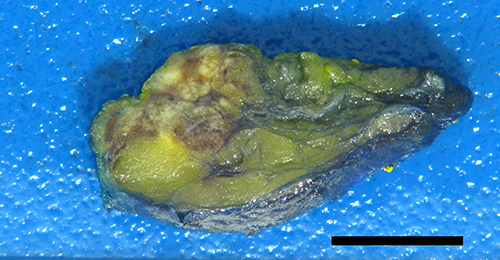
Gross description
- Firm to hard, white or pale yellow tumor with ill defined borders (Am J Surg Pathol 1993;17:248)
- Typically measures < 5 cm (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1009, Am J Surg Pathol 1993;17:248)
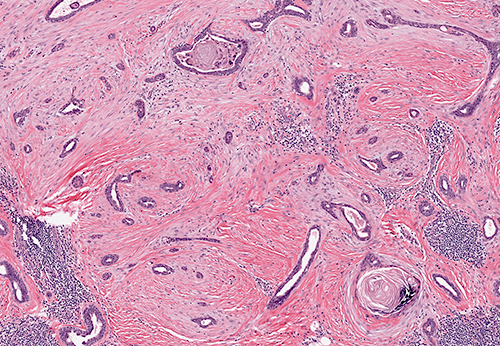
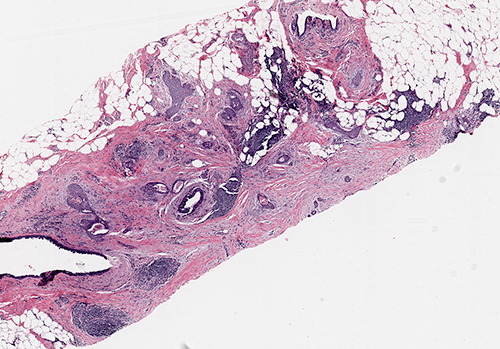
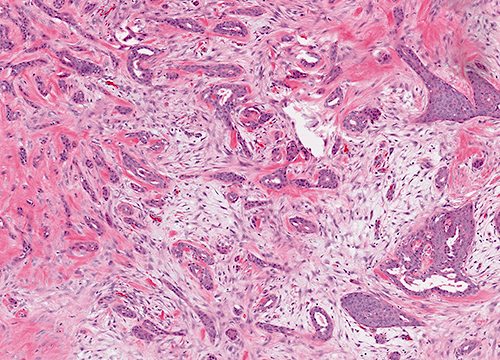
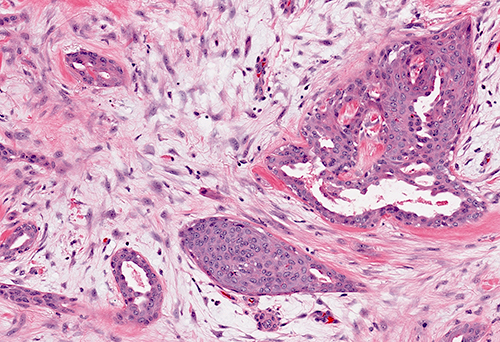
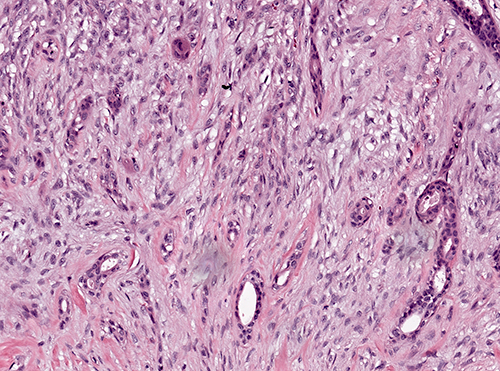
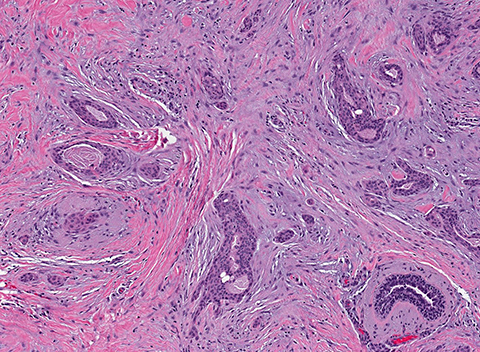
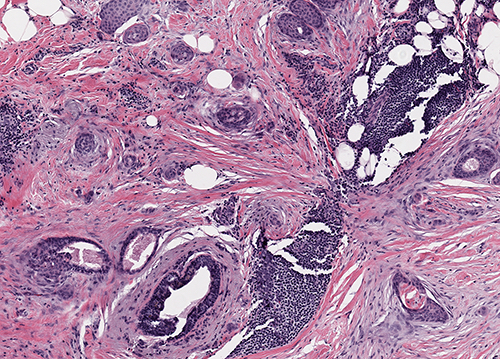
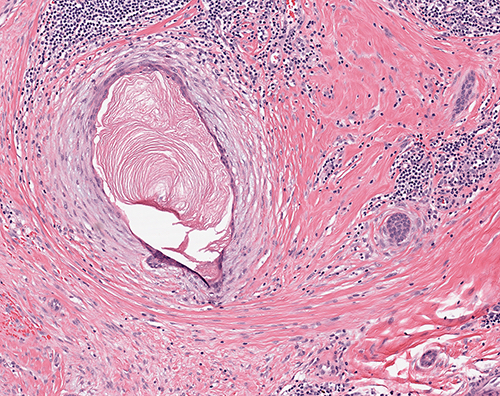
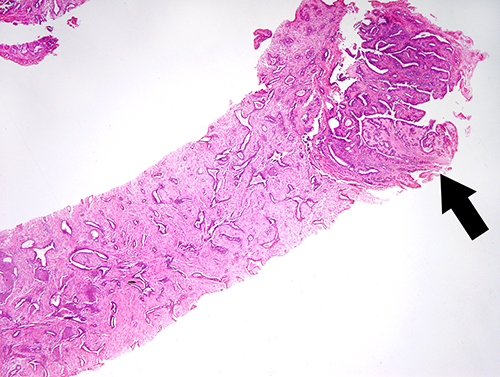
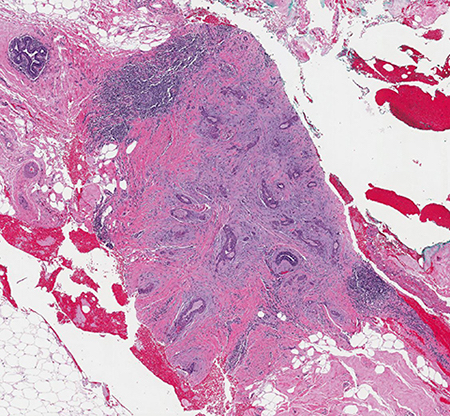
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Infiltrative glandular elements with a variable degree of squamous differentiation (Am J Surg Pathol 1987;11:351, Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1009)
- Glands are lined by cytologically bland epithelial cells and may be angulated, compressed or ovoid (Am J Surg Pathol 1993;17:248, Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1009)
- Luminal keratin debris may be present (Am J Surg Pathol 1993;17:248)
- Associated stroma may be fibrotic or cellular (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1009)
- In cases with cellular stroma, the bland spindled cells frequently demonstrate a circumferential distribution around the neoplastic glands (Am J Surg Pathol 1993;17:248, Am J Surg Pathol 1987;11:351)
- Infrequent epithelial and stromal mitoses
- Frequent peripheral lymphoid aggregates and intratumor lymphocytic infiltrates (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1009)
- May be associated with benign lesions, such as intraductal papilloma, adenomyoepithelioma, radial / complex sclerosing lesions, collagenous spherulosis and fibroepithelial tumors (Mod Pathol 2003;16:893, Virchows Arch 1995;427:243, Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1009)
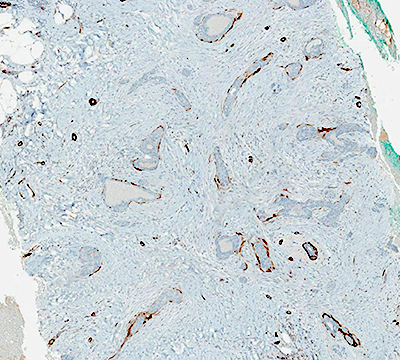
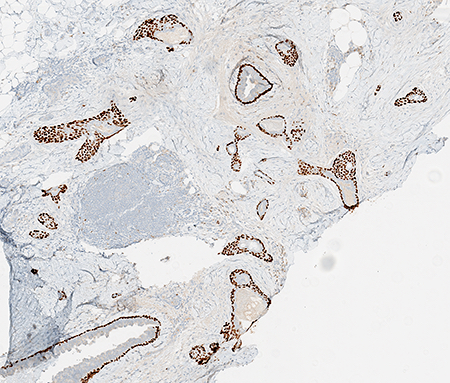
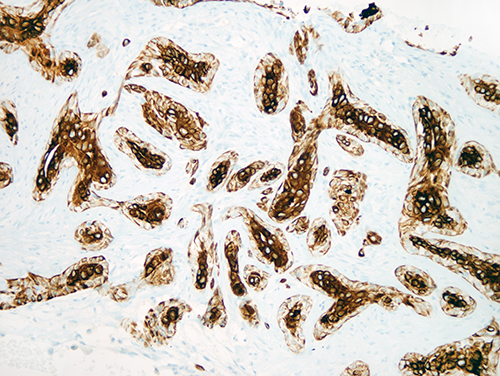
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Variable cellular yield; not reliable as a surrogate for considering malignancy
- Irregularly clustered cells, angulated sheets and tubular structures with monomorphic cytology (Acta Cytol 2014;58:427, Diagn Cytopathol 2012;40:713, Diagn Cytopathol 1999;20:13)
- Whorl-like arrangements of epithelial cells may hint of squamous differentiation
- Individually dispersed, atypical cells may be seen
- Background may show mildly atypical naked nuclei and spindle cells (representing the stromal component)
- Combination of epithelial and spindle elements is distinctive and should raise the possibility of low grade adenosquamous carcinoma
- Accurate cytological identification is challenging
Positive stains
- Luminal cells show varying immunoreactivity for p63 (highlighting squamous differentiation) (74%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1009)
- Glandular component often shows core staining, where luminal cells demonstrate greater intensity of cytokeratin staining compared with the basal cells (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1009)
- CK AE1 / AE3 (57%)
- CK5/6 (58%)
- CK7 (50%)
- Distinctive stromal lamellar staining pattern, frequently seen with SMMHC (53%) and calponin (57%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1009)
- Inconsistent staining patterns
- Commonly utilized diagnostic markers of limited use
Negative stains
- Often triple negative: ER, PR, HER2 (Mod Pathol 2010;23:951)
- Variable degrees of circumferential complete, discontinuous and absent myoepithelial cell markers (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1009)
Electron microscopy description
- Glandular and squamous differentiation (Am J Surg Pathol 1993;17:248)
- Squamous cells resemble acrosyringium of eccrine sweat gland (Am J Surg Pathol 1993;17:248)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Harbor recurrent PIK3CA mutations (Mod Pathol 2010;23:951, Histopathology 2018;73:273)
- Mutations in PTEN, GNAS, KIT and CDKN2A have also been described (Mod Pathol 2010;23:951, Histopathology 2018;73:273)
- TP53 mutations are absent (Mod Pathol 2010;23:951, Histopathology 2018;73:273)
- Gains in 6p, 7pq and 8q; losses of 1p, 6p, 6q, 8p and 9p; no amplifications by microarray comparative genomic hybridization (Mod Pathol 2010;23:951)
Sample pathology report
- Left breast, 3 o'clock, lumpectomy:
- Low grade adenosquamous carcinoma (see comment and synoptic report)
- Ductal carcinoma in situ
- Comment: Low grade adenosquamous carcinoma is grade 1 (2, 2, 1), measures 1.7 cm in greatest dimension, is associated with a sclerotic papilloma, is present less than 1 mm from the inked surgical margin and is ER negative (< 1%), PR negative (< 1%) and HER2 negative (0). No lymphovascular invasion identified. Ductal carcinoma in situ is solid type with intermediate nuclear grade and is present as a single 0.2 cm focus associated with the low grade adenosquamous carcinoma. Ductal carcinoma in situ is present > 2 mm from the inked surgical margin.
Differential diagnosis
- Tubular carcinoma:
- Radial scar with squamous metaplasia:
- Heterogeneous, positive staining for ER
- Syringomatous adenoma:
- Morphologically similar to low grade adenosquamous carcinoma
- Composed of tubules and solid nests with comma-like or tail-like extensions and squamous cysts embedded in desmoplastic stroma
- More superficial, involving the nipple areolar complex
- Lacks lymphoid aggregates
- Multinucleated giant cell reactions to ruptured cysts may be seen
- Some authors suggest these are identical entities (Histopathology 2014;65:9)
- High grade adenosquamous carcinoma:
- Shows both squamous and glandular components with moderate to high cellularity and nuclear atypia
- Mitotic activity is moderate to high
- Areas of necrosis may be present
Additional references
Practice question #1
Practice answer #1
D. May be associated with other breast lesions. Multiple reports have demonstrated an association of low grade adenosquamous carcinoma with other breast entities (i.e. papilloma, adenomyoepithelioma, radial scar / radial sclerosing lesions and fibroepithelial tumors). Low grade adenosquamous carcinoma is frequently ER negative. Low grade adenosquamous carcinoma demonstrates variable degrees of circumferential myoepithelial cell markers and immunohistochemistry is consistently inconsistent in this entity, limiting use. Low grade adenosquamous carcinoma is associated with a good prognosis.
Comment Here
Reference: Low grade adenosquamous
Comment Here
Reference: Low grade adenosquamous