Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: LaBoy C, Siziopikou KP. Mucinous. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastmalignantmucinous.html. Accessed August 18th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Breast neoplasm with mucinous component that comprises > 90% of tumor, usually with favorable prognosis
Essential features
- Rare tumor occurring in older women
- Epithelial clusters that lie within secreted mucin (type A) or large sheets of tumor cells with neuroendocrine features and mucin production (type B)
- Mucinous component must be > 90% of tumor to be pure and have favorable prognosis
- ER and PR hormone receptor positive and HER2 negative (luminal A subtype)
Terminology
- Colloid carcinoma
- Mucinoid carcinoma
- Gelatinous carcinoma
- Mucoid carcinoma
- Mucinous adenocarcinoma
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- < 5% of breast carcinomas have mucinous component; of these, only 2% are pure mucinous carcinoma
- F > M, sixth through eighth decades
Sites
- Most are unifocal and can occur in any quadrant
Pathophysiology
- Occurs through ER positive pathway, although it lacks gains of 1q, loss of 16q and PIK3CA mutations, which are typical of low grade neoplasms (Breast 2020;49:87)
- Lesions express hormone receptors while lacking HER2 and basal markers
Etiology
- Multifactorial, with factors including hormones (early menarche, nulliparity or exogenous hormone use), genetics and diet
Clinical features
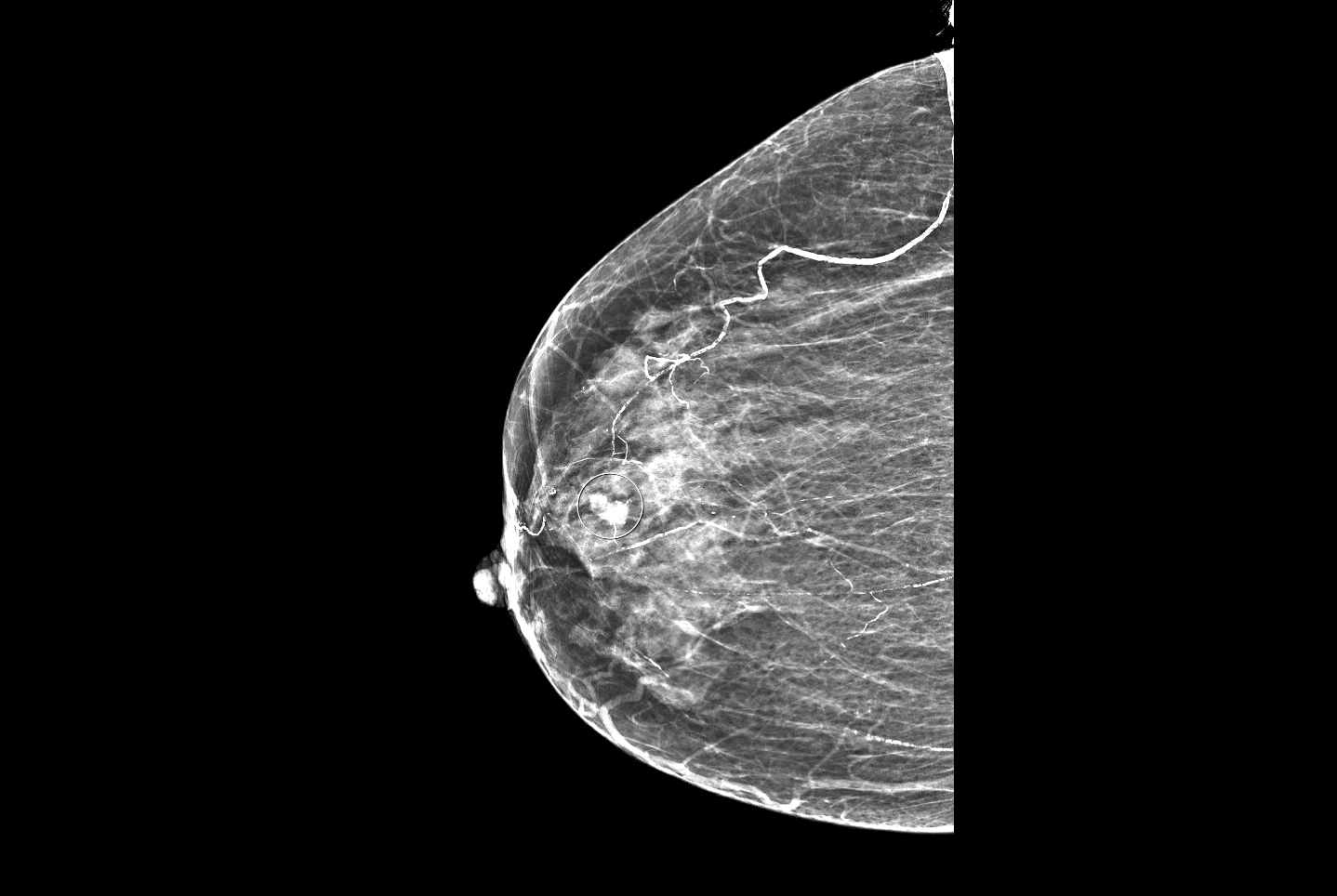
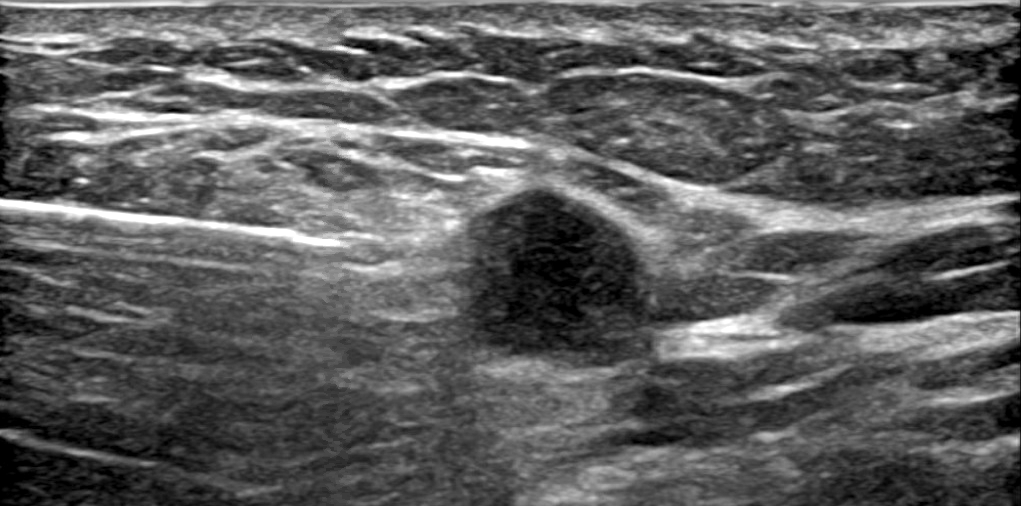
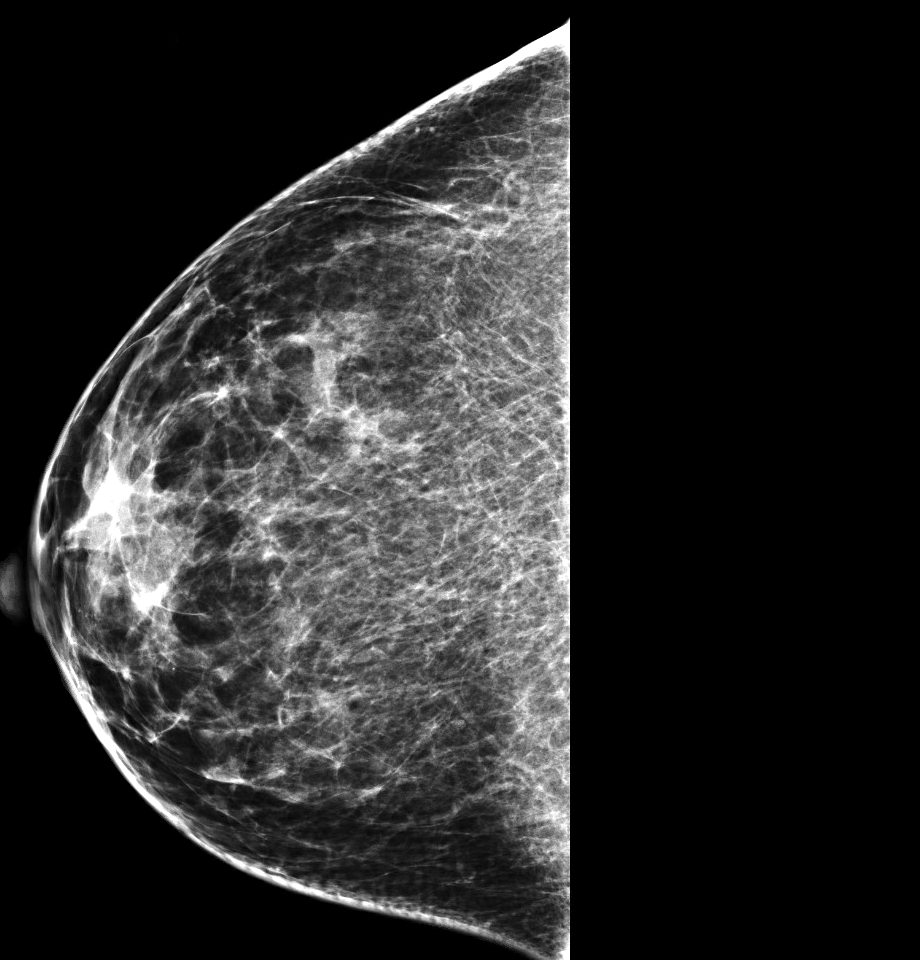
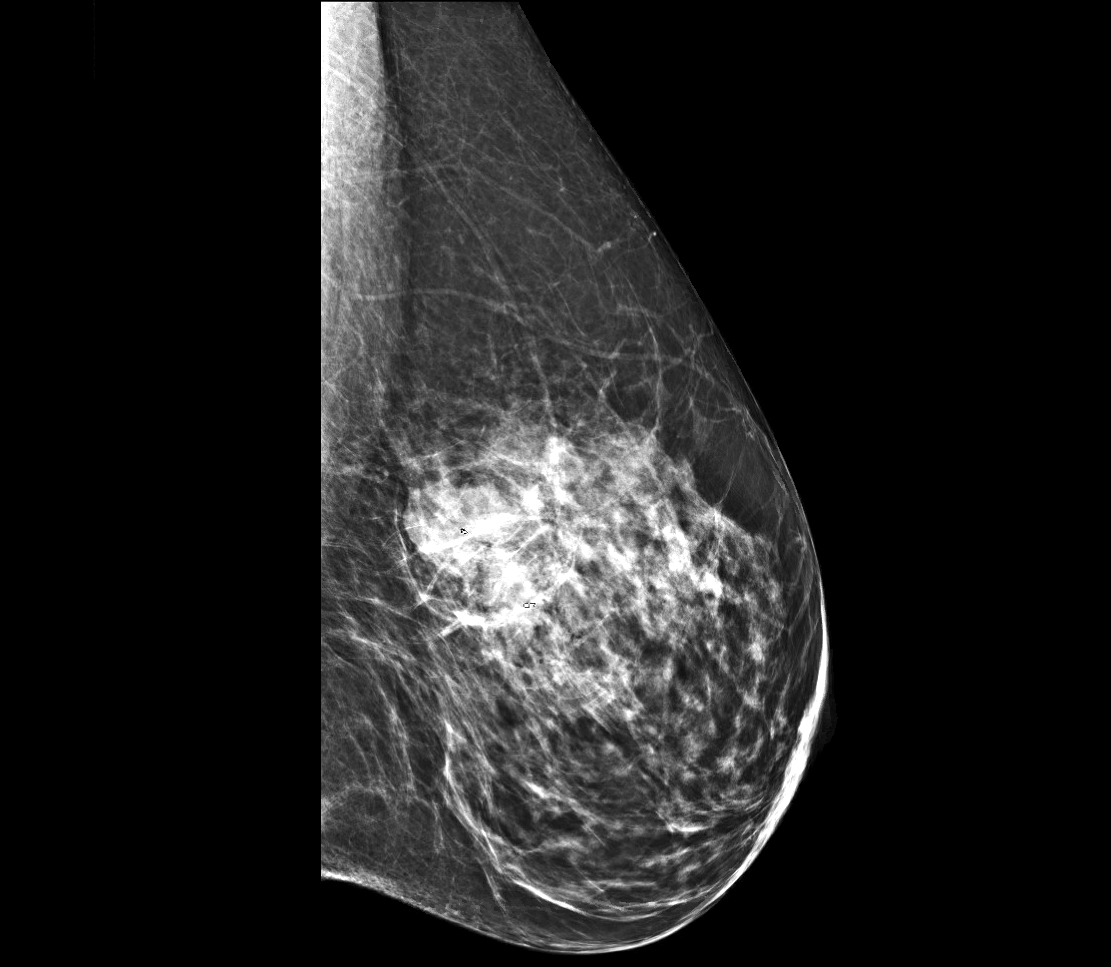
- Imaging can vary from a well circumscribed mass (more likely to be pure) to an irregular, spiculated mass (more likely to have mixed mucinous component) (Breast 2020;49:87)
- Due to potential circumscription seen on imaging, may be mistaken for benign process
Diagnosis
- More often palpable mass that appears as abnormality on mammography (StatPearls: Mucinous Breast Carcinoma [Accessed 8 January 2021])
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Prognosis dependent on extent of mucinous involvement; pure mucinous carcinoma has favorable prognosis with 10 year survival rate of 90.4% (Breast 2020;49:87)
- No prognostic significance between type A and type B
- Patients tend to have localized disease with low recurrence rate and rare involvement of axillary lymph nodes (Breast 2020;49:87)
- Component of micropapillary pattern is associated with worse prognosis, with increased rate of lymph node metastasis (Breast J 2018;24:339)
- Acellular mucin seen in postneoadjuvant chemotherapy specimens does not correlate with residual disease
- Only when residual neoplastic epithelium is identified is the patient classified as partial response and staged with residual disease by measuring the extent of extracellular mucin (Histopathology 2018;72:965)
Case reports
- 25 year old woman with slow growing mass radiologically diagnosed as fibroadenoma (Int J Surg Case Rep 2018;53:58)
- 48 year old woman with lump in right breast (Int J Surg Case Rep 2018;42:242)
- 55 year old woman with large left breast mass (Cureus 2018;10:e3606)
- 67 year old woman with swelling of the left breast (Iran J Pathol 2015;10:231)
- 75 year old woman with multiple masses in the left breast (J Med Radiat Sci 2020;67:155)
Treatment
- Surgical excision and adjuvant hormone therapy
- Cases associated with worse prognosis, such as micropapillary variant, may warrant neoadjuvant chemotherapy (Breast J 2018;24:339, Histopathology 2018;72:965)
- HER2 positivity is associated with tamoxifen resistance and should be treated with chemotherapy, anti-HER2 therapy and endocrine therapy via an aromatase inhibitor (Medicine (Baltimore) 2020;99:e20996)
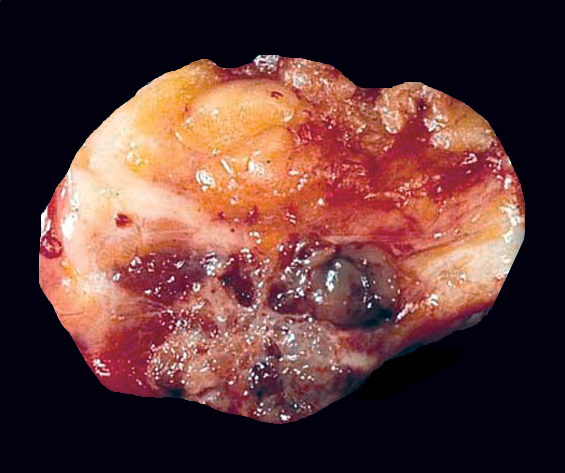
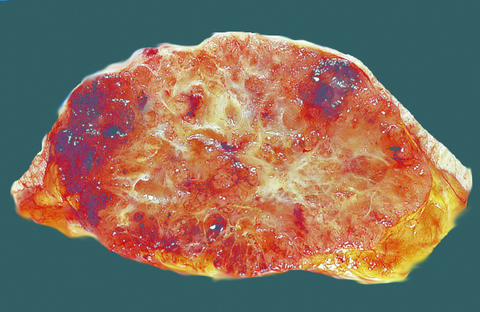
Gross description
- Well circumscribed mass of variable size (from < 1 cm to > 20 cm) with gelatinous cut surface
Gross images
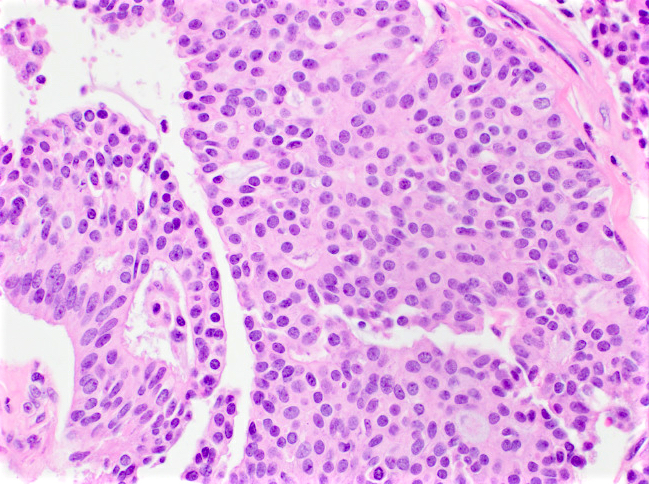
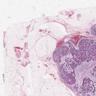
Microscopic (histologic) description
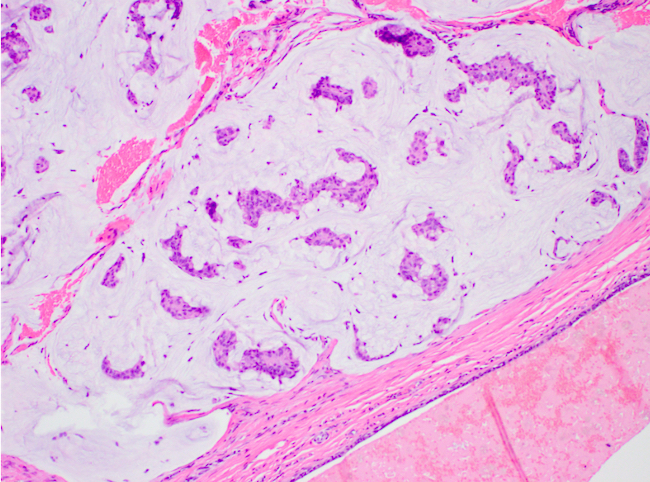
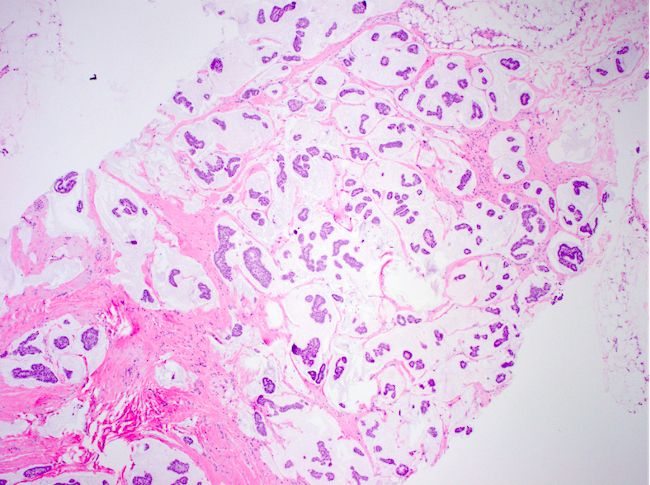
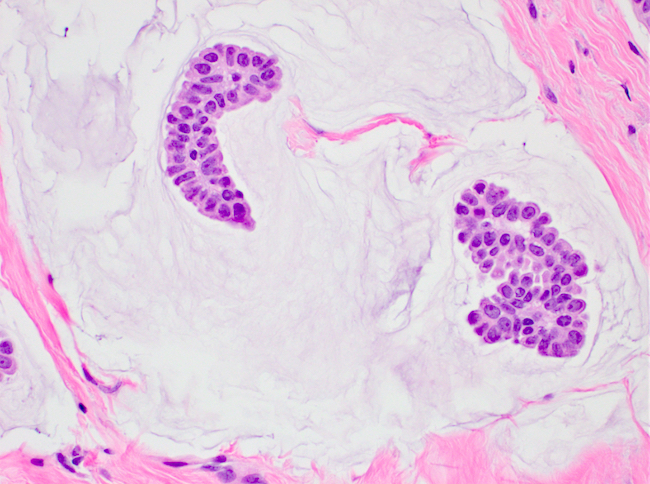
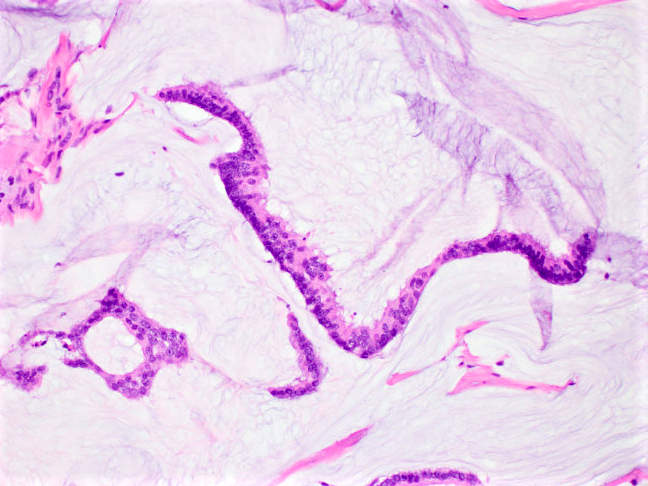
- Clusters / nests of tumor cells with low or intermediate nuclear grade floating in pools of extracellular mucin
- Mucin pools separated by fibrous septa with capillaries
- Considered pure when mucinous component comprises > 90% of the tumor, which is associated with favorable prognosis
- Otherwise, tumor is mixed (mucinous component comprises 50 - 90% of tumor) or has mucinous features (mucinous component comprises < 50% of tumor), both of which have less favorable prognosis
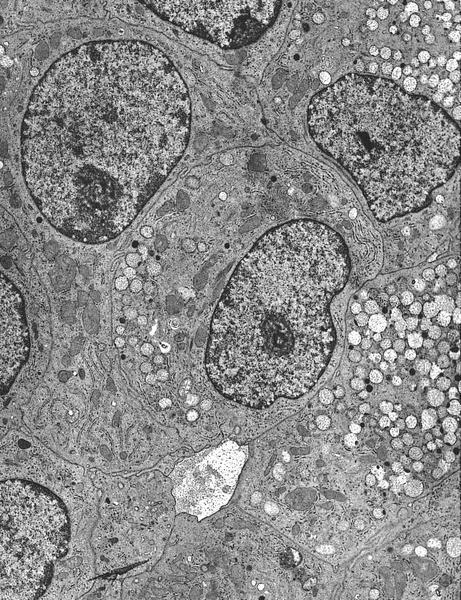
- Capella type A: abundant extracellular mucin production with scattered small epithelial clusters, strips or cribriform structures floating in pools of mucin
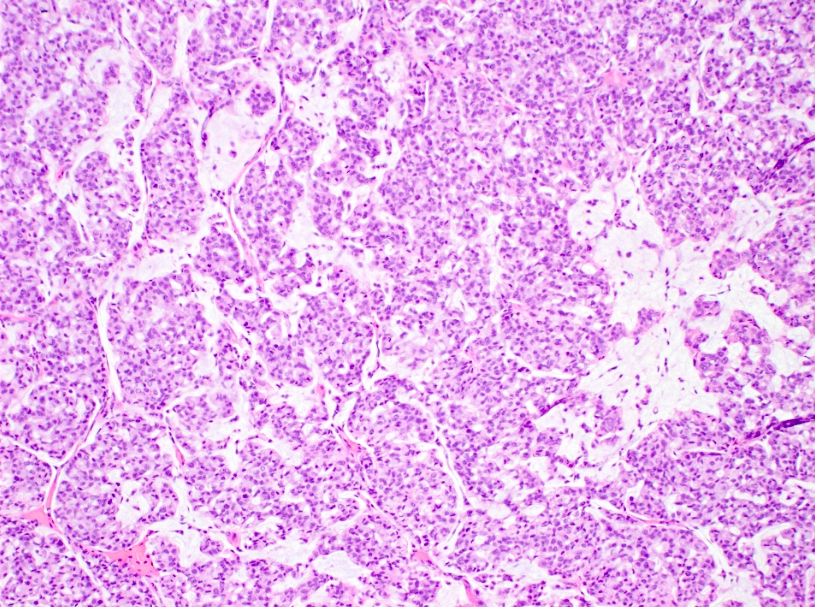
- Capella type B: large sheets of tumor cells with mucin production and neuroendocrine features
- Micropapillary pattern
- Clusters of tumor cells with intermediate to high grade nuclei, occasional hobnailing and reverse polarity; more likely to be HER2 positive, which in turn has a worse prognosis (more likely to have lymph vascular space invasion and metastasis to lymph nodes) (Breast J 2018;24:339)
- PIK3CA and TP53 mutations more frequent with recurrent gains of 8q (Histopathology 2019;75:139)
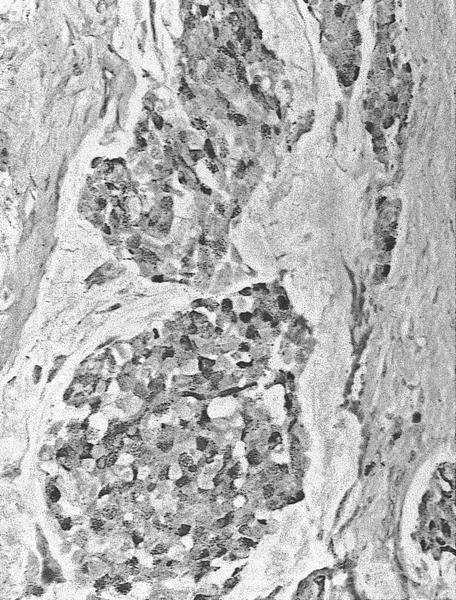
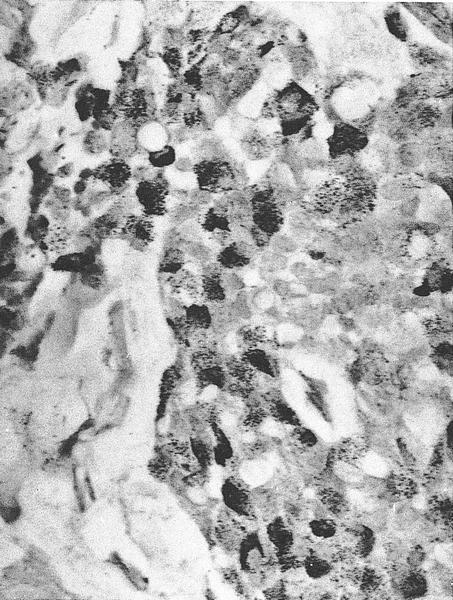
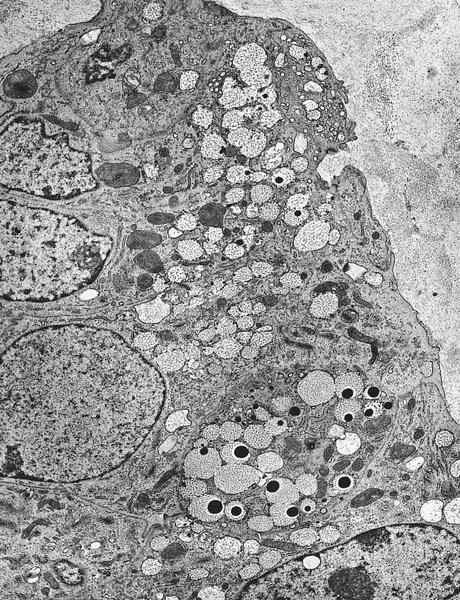
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Carissa LaBoy, M.D., Mark R. Wick, M.D. and AFIP images
Virtual slides
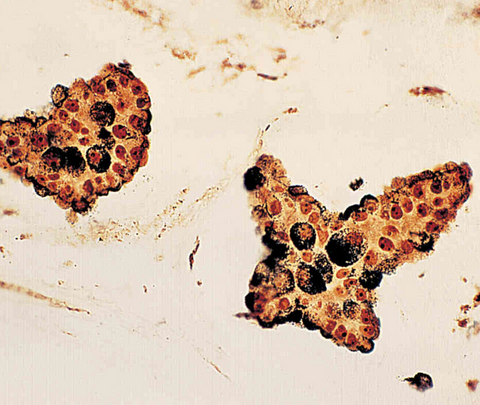
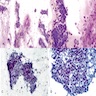
Cytology description
- Small to intermediate sized cohesive groups of epithelial cells with low grade nuclei floating within pools of extracellular mucin
- Mucinous carcinoma type B displays neuroendocrine differentiation in discohesive clusters with plasmacytoid cells with low grade nuclei (Cytopathology 2016;27:193)
- Low cellularity coupled with bland nuclear features and potentially scant background mucin can make the FNA diagnostically challenging (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2011;135:1533)
Cytology images
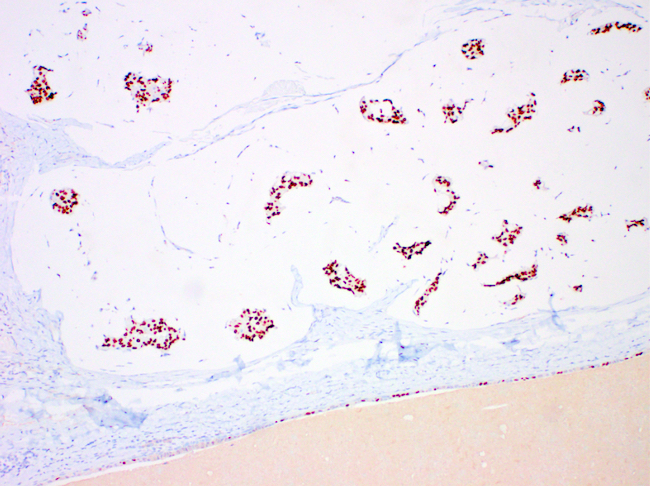
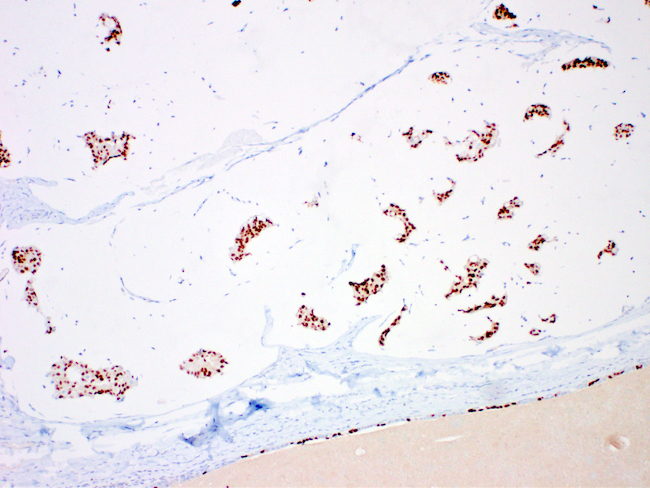
Positive stains
- ER (94%), PR (80%) (Int J Surg Case Rep 2018;42:242)
- MUC2
- Type B: chromogranin, synaptophysin, neuron specific enolase (NSE) (Maedica (Bucur) 2015;10:14)
- WT1
- GATA3
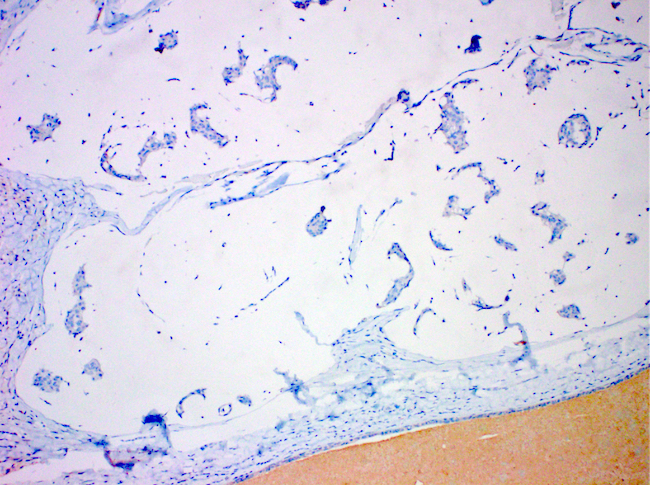
Negative stains
- HER2 (up to 7% are positive) (Medicine (Baltimore) 2020;99:e20996, Int J Surg Case Rep 2018;42:242)
- AR often negative (Breast 2020;49:87)
- MUC1 (membrane bound mucin)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Categorized as luminal A with favorable prognosis
- Lacks 1p gains and 16q losses and somatic mutations of PIK3CA and AKT1, which are common in other ER+, HER2- invasive breast carcinomas (J Natl Cancer Inst 2019;111:737)
- More often diploid (J Natl Cancer Inst 2019;111:737)
Videos
Review of mucinous carcinoma
Sample pathology report
- Left breast, needle localized lumpectomy:
- Invasive mucinous carcinoma, grade 1 (1+2+1), measuring 1.4 cm in greatest dimension (see synoptic report)
- Margins negative with invasive carcinoma > 0.5 cm from all margins
Differential diagnosis
- Mucocele-like lesion:
- Ruptured cyst with detached strips of bland epithelium lined by myoepithelial cells floating within extravasated mucin
- Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma:
- Cribriform, papillary or micropapillary carcinoma lining the cysts with mucin production
- ER and PR-
- Invasive micropapillary carcinoma:
- Nests of tumor cells floating in spaces, mucin production absent
- Metastasis:
- Correlate with clinical and radiologic history, such as colorectal, lung and gynecologic
- Expression profile dependent on origin
- Solid papillary carcinoma:
- Nests of cells with neuroendocrine features, fibrovascular cores and possible mucin production; may potentially be precursor to mucinous carcinoma
- Invasive ductal carcinoma, no special type, with mucinous features:
- Histologic features are those of pure mucinous carcinoma but mucinous component does not fulfill > 90% criteria
- May be initial diagnosis on core needle biopsy for pure mucinous carcinoma
- Due to limited material sampled on core needle biopsy, amount of mucinous component is more reliably assessed on excision specimen
Practice question #1
Practice answer #1
A. ER+, PR+, HER2-
Mucinous carcinomas are ER+, PR+ and largely HER2-, making them a luminal A lesion, which is associated with a favorable prognosis.
Comment Here
Reference: Breast - Mucinous
Mucinous carcinomas are ER+, PR+ and largely HER2-, making them a luminal A lesion, which is associated with a favorable prognosis.
Comment Here
Reference: Breast - Mucinous
Practice question #2
Practice answer #2
C. > 90%
To be considered a pure mucinous carcinoma with a favorable prognosis, the mucinous component must comprise > 90% of a breast carcinoma. If it comprises 50 - 90% of the tumor, it is termed mixed. If the mucinous component is < 50%, the tumor is termed invasive ductal carcinoma with mucinous features. The latter two diagnoses do not have as favorable a diagnosis.
Comment Here
Reference: Mucinous carcinoma
To be considered a pure mucinous carcinoma with a favorable prognosis, the mucinous component must comprise > 90% of a breast carcinoma. If it comprises 50 - 90% of the tumor, it is termed mixed. If the mucinous component is < 50%, the tumor is termed invasive ductal carcinoma with mucinous features. The latter two diagnoses do not have as favorable a diagnosis.
Comment Here
Reference: Mucinous carcinoma