Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Asa SL. Pituicytoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cnstumorpituicytoma.html. Accessed August 25th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Pituicytomas are tumors that arise from the pituicytes of the neurohypophysis and pituitary infundibulum
- 4 subtypes
- Pituicytoma
- Oncocytic pituicytoma (first described as spindle cell oncocytoma in 2002) (Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:1048)
- Granular cell pituicytoma
- Ependymal pituicytoma
- Pituicytoma derives from light and dark normal pituicytes, oncocytic pituicytoma derives from oncocytic pituicytes, the granular cell subtype derives from granular pituicytes and the ependymal subtype derives from the elongated ependymal pituicytes (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1694)
- These tumors and cells are characterized by the expression of the transcription factor TTF1
Essential features
- Pituicytoma belongs to the group of TTF1 expressing tumors of the neurohypophysis and infundibulum
- Histologic features include fascicles of spindle cells or epithelioid cells expressing TTF1, S100 protein and GFAP
- Surgical resection is curative; excellent outcome
Terminology
- Not recommended
- Infundibuloma
- Low grade glioma of sellar and suprasellar region
- Pilocytic astrocytoma
- Spindle cell oncocytoma of adenohypophysis
- Granular cell tumor / myoblastoma / schwannoma / neuroma
- Pituitary ependymoma / sellar ependymoma
Epidemiology
- Classic pituicytoma represents ~0.07% of all primary sellar neoplasms (Eur J Endocrinol 2007;156:203)
- ~50% of posterior pituitary tumors (World Neurosurg 2021;145:148)
- Usually in adults: 40 - 60 years
- No obvious male or female predominance
- Exceptional in children (3% of posterior pituitary tumors)
Sites
- Sella and suprasellar region
Pathophysiology
- TTF1 expression indicates an origin from neurohypophysis and infundibulum (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1694)
- Given the low incidence of diabetes insipidus, an origin from the lower infundibulum was proposed (Pituitary 2012;15:227)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Main signs and symptoms at onset (World Neurosurg 2021;145:148)
- Headache
- Visual field defects
- Hypopituitarism
- Occurrence of polydipsia and polyuria (diabetes insipidus) is rare
- Apoplexy is exceptional
- Pituicytoma can also present in association with primary tumors of adenohypophyseal cells (collision tumors)
Diagnosis
- Evidence of a sellar and suprasellar (or suprasellar only) lesion involving the infundibulum
- Usually no excess of pituitary hormones
- Diagnosis is made on histology
- Reference: World Neurosurg 2021;145:148
Laboratory
- Low serum levels of pituitary hormones
- Increase in prolactin due to pituitary stalk compression
- Occasional increase in growth hormone or adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) / peripheral cortisol due to coexistence of a pituitary neuroendocrine tumor
- References: World Neurosurg 2021;145:148, Endocrine 2020;70:15
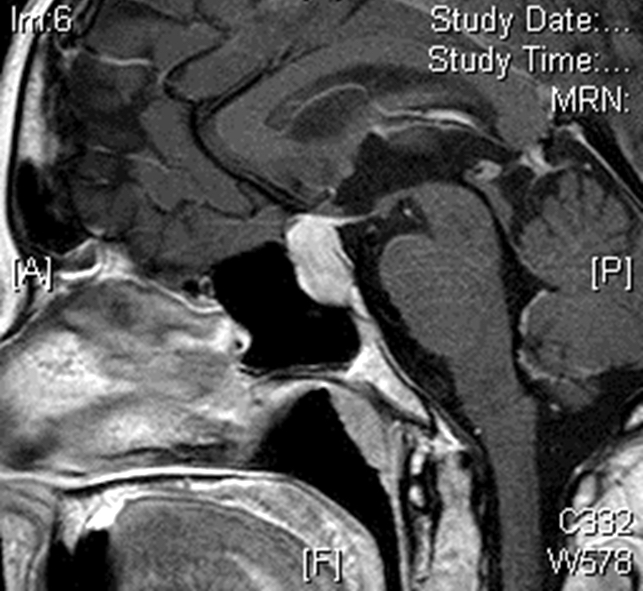
Radiology description
- Can be suspected when exclusively suprasellar and the anterior hypophysis is spared
- Indistinguishable from other clinically nonfunctioning primary sellar tumors when it involves the sellar and suprasellar region
- MRI features: isointense on T1 weighted sequences and often inhomogeneous intensity on T2 weighted sequences; homogenous or heterogeneous contrast enhancement
- Reference: World Neurosurg 2021;145:148
Prognostic factors
- Behaves as a benign tumor when completely resected
- Recurrence can occur when incompletely excised
- Oncocytic tumors have higher frequency of recurrence, possibly due to rich vascularity and adhesion
- Radiation therapy has been reported for recurrent / residual disease
- Metastasis has not been reported
- 1 recurrent case showed nuclear atypia and mitoses (Pathology 2011;43:389)
- Unclear relevance of atypia and increased proliferation as a prognostic factor (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2019;7:69)
Case reports
- 26 year old man presented with decreased libido, hypopituitarism and visual disturbances (Neurosurgery 2004;54:753)
- 41 year old woman with nausea, headache and fatigue (Endocr Pathol 2014;25:436)
- 47 year old woman with a history of Cushing disease and a left sided intrasellar lesion (J Surg Case Rep 2020;2020:rjaa104)
- 61 year old man presented with progressively worsening visual acuity, normal pituitary lab values and a mixed solid cystic, intra and suprasellar lesion (Surg Neurol Int 2018;9:145)
- 71 year old man with a previous diagnosis of sellar meningioma and a recurrent lesion on surveillance imaging after 16 years (Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2020;102:e87)
Treatment
- Complete surgical excision is curative
- Radiotherapy administered in a few patients with unclear benefits
- References: World Neurosurg 2021;145:148, Pituitary 2012;15:227
Gross description
- Usually white, gray or light yellow soft tissue fragments; hemorrhagic changes can be seen
Frozen section description
- Fascicles of spindle cells in fibrillary background reminiscent of glioma
- Possible ill defined whorls reminiscent of sellar meningioma
- Bipolar cells similar to schwannoma
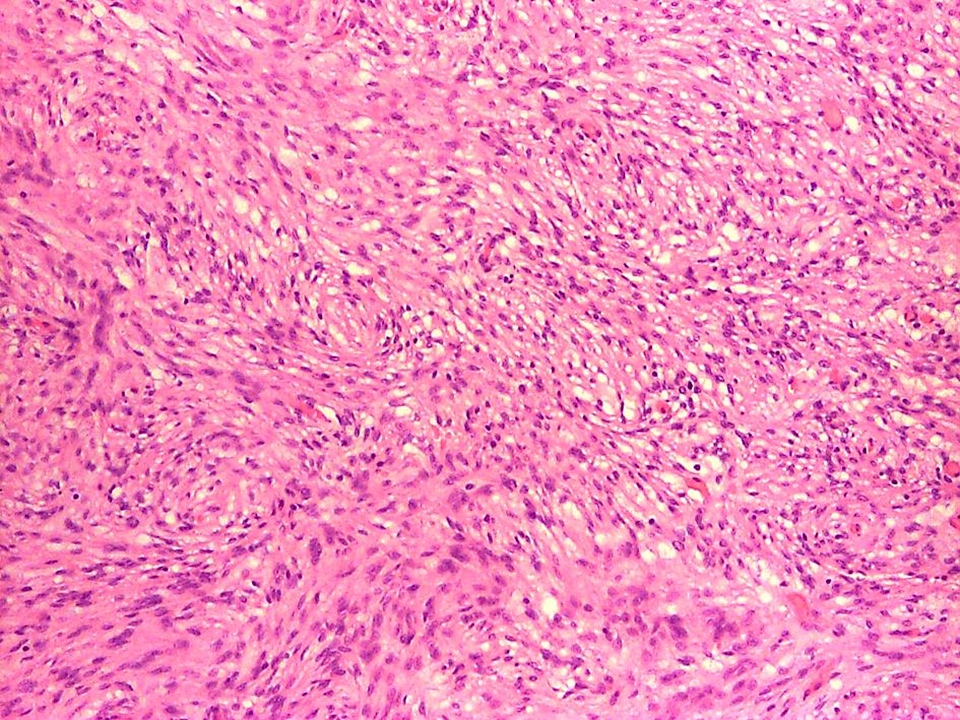
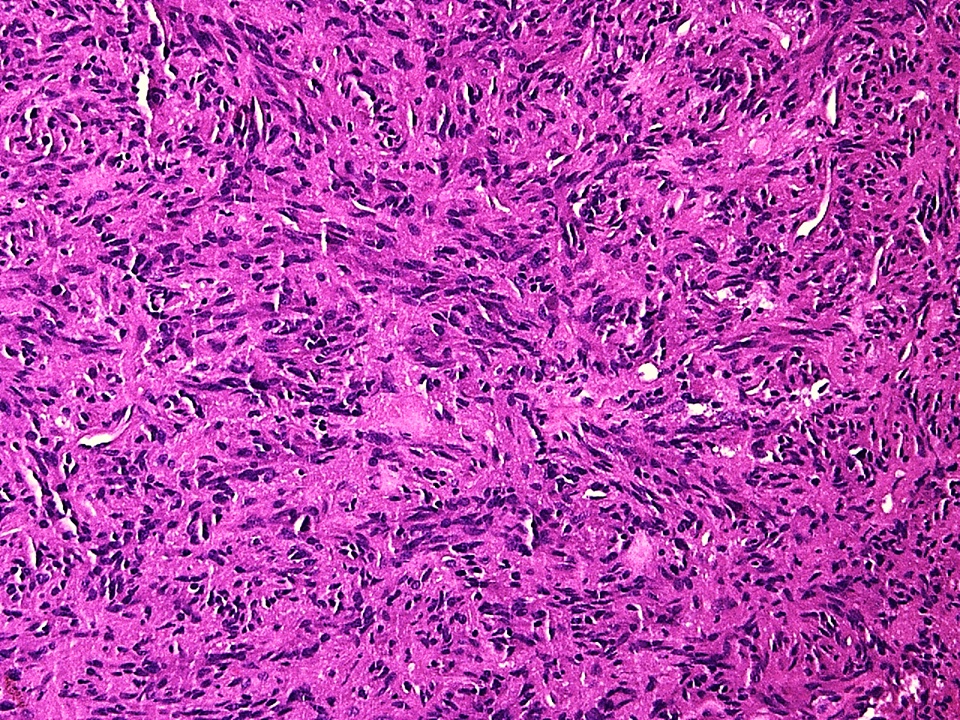
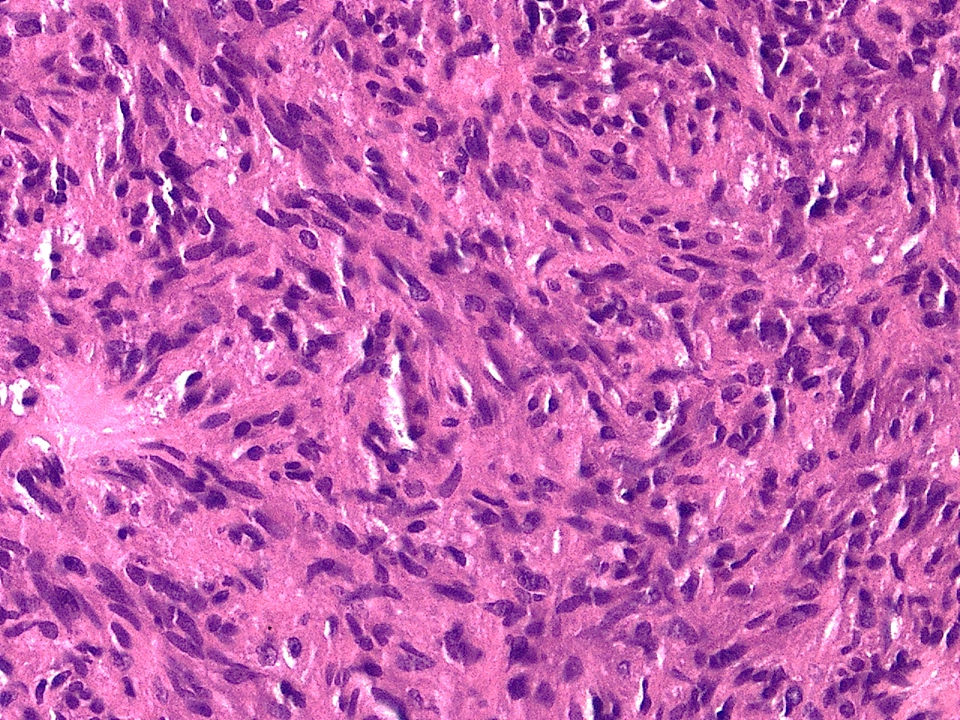
Microscopic (histologic) description
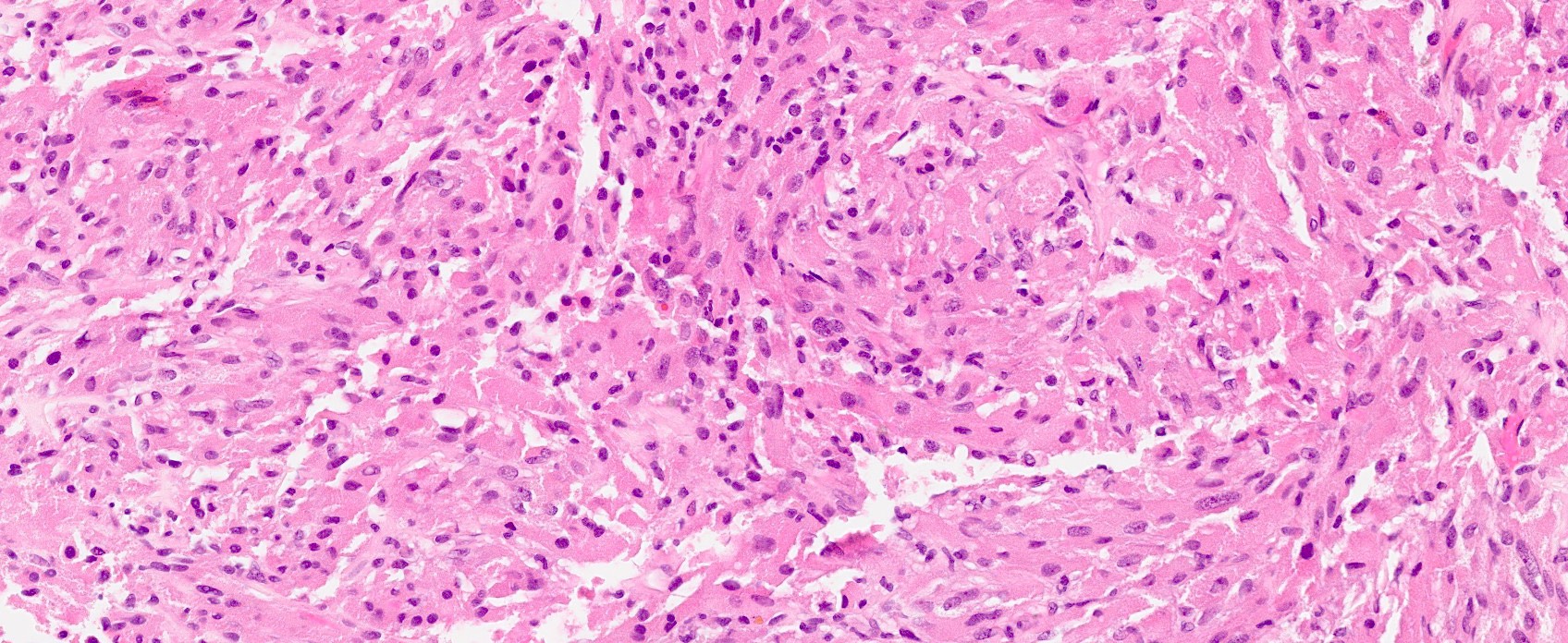
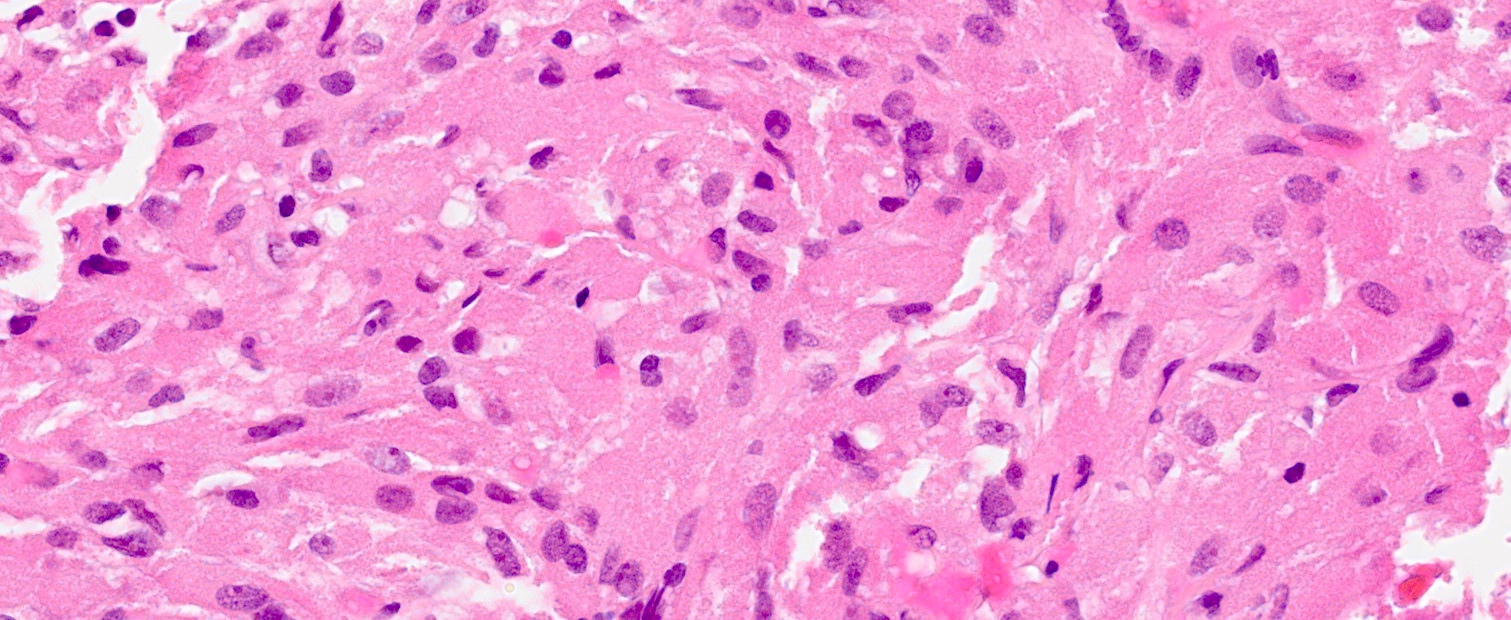
- Sheets and short fascicles of spindle, bipolar tumor cells; storiform pattern can be present
- Variants distinguished based on cytologic features
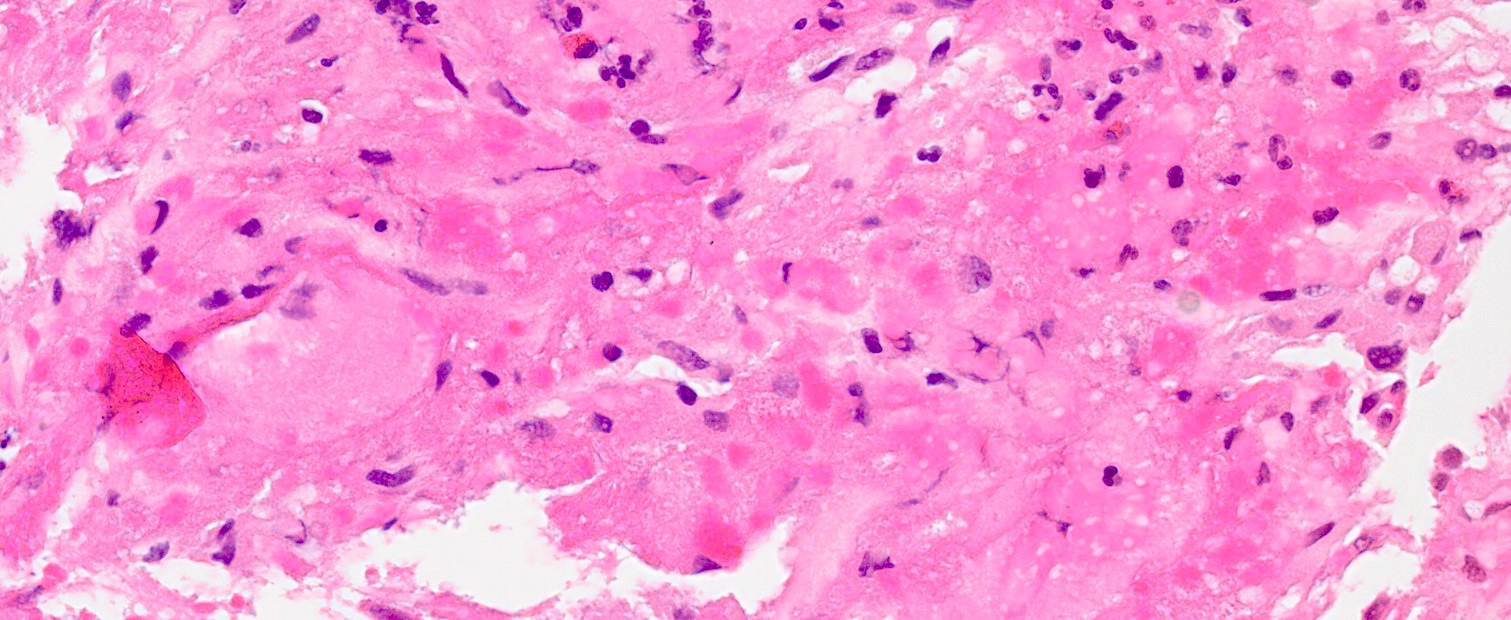
- Oncocytic tumors have epithelioid cells with oncocytic cytoplasm
- Granular cell variants have large cells with granular cytoplasm
- Ependymal variants have elongated cells with ependymal cell-like features
- Mixed morphologies are not uncommon
- Rarely, focal chronic inflammation
- Absent pericellular reticulin fibers
- Absent Rosenthal fibers, granular bodies and hyalinized blood vessel walls
- Lack of Herring bodies
- Usually negligible mitotic activity
- Rarely, increased cellularity, severe nuclear atypia and high mitotic count
- References: Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:362, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1694
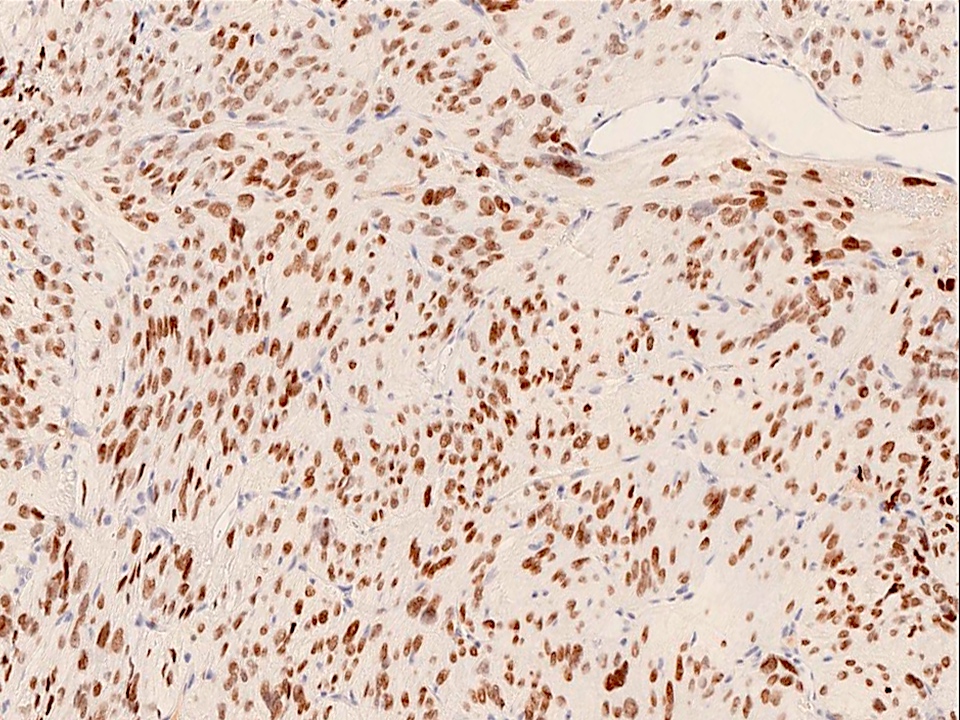
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Aggregates of spindle cells with fibrillary to fine cytoplasm, usually thin walled, delicate vessels and neuropil-like background; features can be reminiscent of meningioma (Diagn Cytopathol 2020;48:342)
Positive stains
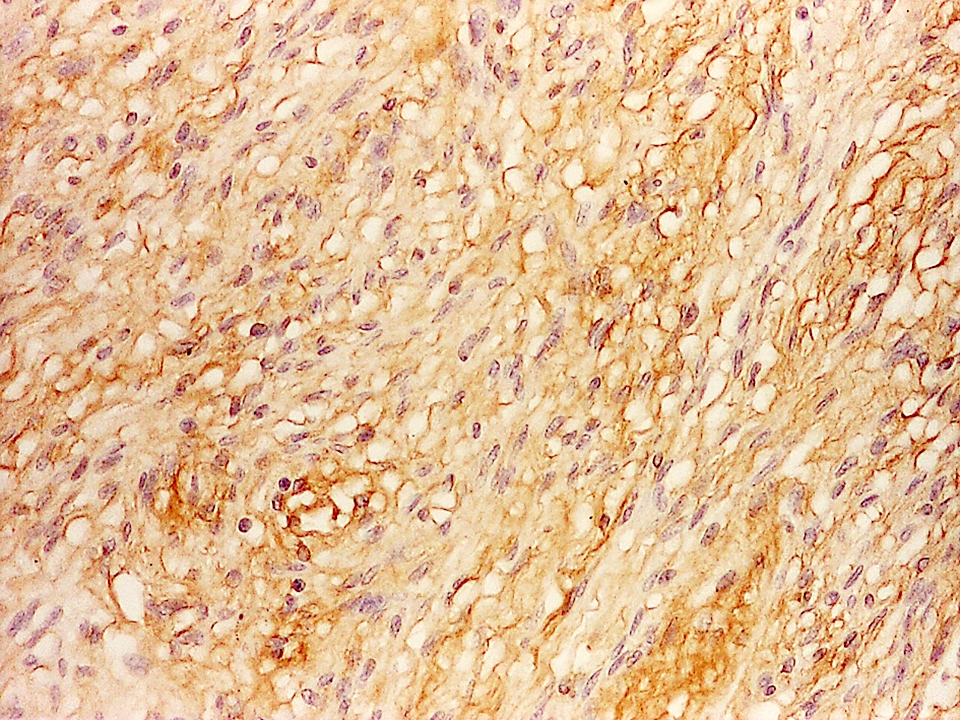
- TTF1
- Vimentin, S100
- Variable GFAP (expressed in all cases)
- CD56 (NCAM), galectin3, BCL2, focal SSTR2A (20% of cases)
- Low Ki67 labeling index
- References: Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:362, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1694
Negative stains
- Pituitary hormones (GH, PRL, ACTH, TSH beta subunit, FSH beta subunit, LH beta subunit and common alpha subunit)
- Pituitary transcription factors (Pit1, SF1 and Tpit)
- Synaptophysin, neurofilament proteins, collagen type IV (absent around single tumor cells)
- EMA
- Cytokeratins
- Smooth muscle actin, CD34, CD38
- Vasopressin
- Reference: Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1694
Electron microscopy description
- Elongated or oval tumor cells
- Focal accumulations of intermediate filaments
- No interdigitating cell membranes
- Oncocytic variant has abundant mitochondria rich in lamellar cristae
- No secretory granules
- References: Neurosurgery 2004;54:753, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1694
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Molecular genetics studies have been restricted to the 3 most common subtypes (pituicytomas, granular cell and oncocytic pituicytomas)
- Close clustering on methylation studies indicates a single spectrum (Nature 2018;555:469, Acta Neuropathol 2021;142:1025)
- 2 epigenomic DNA methylation subgroups with only subtle overall methylation differences (Acta Neuropathol 2021;142:1025)
- Variable somatic alterations causing MAPK pathway activation in pituicytomas and oncocytic tumors
- Pathogenic FGFR1, HRAS, BRAF, NF1, CBL, MAP2K2, PTEN and TSC1 variants (Acta Neuropathol 2021;142:1025)
- Rare tumors had accompanying TERT promoter mutation
- SND1 and FAT1 gene mutations also identified (Oncotarget 2016;7:37054)
- Close clustering on methylation studies indicates a single spectrum (Nature 2018;555:469, Acta Neuropathol 2021;142:1025)
- Whole miRNA signature shows global downregulation of miRNA expression (Neurochem Res 2019;44:2360)
- Chromosome 1 alterations in oncocytic tumors including 1p deletion (4/5 cases) and 1p gain (1/5 cases) (J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2021;80:45)
- Copy number alterations identify a less favorable group with reduced progression free survival (Acta Neuropathol 2021;142:1025)
- IDH1 p.R132H mutation and KIAA1549::BRAF oncogene fusion are absent (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1694)
Sample pathology report
- Pituitary gland / sellar region, surgical excision:
- Pituicytoma (subtype if relevant) (WHO grade 1) (see comment)
- Comment: Pituicytoma belongs to the group of TTF1 expressing tumors of the posterior hypophysis and infundibulum. It rarely recurs when incompletely removed; follow up is recommended.
- Immunohistochemically, the tumor cells show TTF1 nuclear expression, diffuse vimentin and S100 expression. Immunostains for keratins, synaptophysin, chromogranin and biomarkers of adenohypophyseal neuroendocrine cells are negative.
Differential diagnosis
- Normal neurohypophysis and infundibulum:
- Vasopressin positive
- Herring bodies and axons absent in pituicytoma
- Sellar schwannoma:
- TTF1 negative
- Pericellular collagen IV
- Pilocytic astrocytoma:
- Rosenthal fibers and granular bodies
- Often vascular with features of endothelial proliferation
- Meningioma:
- Pituitary neuroendocrine tumor:
- Rarely, spindle cells
- Chromogranin and synaptophysin positive, as well as pituitary transcription factors and hormones
- TTF1 negative
Practice question #1
A middle aged man presented with hypopituitarism. Imaging showed a sellar and suprasellar enhancing lesion. The microscopic image above is from the surgical specimen. Which of the following immunostains is typically positive in these tumor cells?
- Chromogranin
- Cytokeratin CAM5.2
- Neurofilament
- TTF1
- Vasopressin
Practice answer #1
D. TTF1. TTF1 is positive since this is pituicytoma, a tumor derived from posterior pituitary cells known as pituicytes, which derive from the medial basal hypothalamus, which expresses TTF1. Answers A and C are incorrect because these are not neural or neuroendocrine cells; therefore, they are negative for chromogranin and neurofilament. Answer B is incorrect because they are not epithelial and therefore are negative for cytokeratins, unlike adenohypophyseal cells. Answer E is incorrect because vasopressin is produced by neurons of the hypothalamus, not by these modified glial cells.
Comment Here
Reference: Pituicytoma
Comment Here
Reference: Pituicytoma
Practice question #2
Which of the following is correct regarding pituicytoma?
- Patients present with headaches, visual field disturbances and hypopituitarism
- Patients present with syndrome of antidiuresis (SIAD)
- Surgery is not curative
- These tumors are not responsive to radiotherapy
Practice answer #2
A. Patients present with headaches, visual field disturbances and hypopituitarism. Answer B is incorrect because patients with pituicytoma do not have features of vasopressin excess / antidiuresis but may have diabetes insipidus. Answers C and D are incorrect because surgery can be curative if complete resection is possible but if not, radiotherapy can provide control of growth.
Comment Here
Reference: Pituicytoma
Comment Here
Reference: Pituicytoma