Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Fels Elliott DR, Gill RM. HCC - lymphocyte rich. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/livertumorlelhcc.html. Accessed August 14th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Rare subtype of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) designated by the WHO; characterized by a dense lymphoid infiltrate with more lymphocytes than tumor cells
Essential features
- Striking lymphocytic infiltrate is a defining feature
- Not associated with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) or microsatellite instability
Terminology
- May be called lymphoepithelioma-like HCC when the tumor is poorly differentiated (Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2017;46:365)
ICD coding
- ICD-10: C22.7 - other specified carcinomas of liver
Epidemiology
- Incidence ≤ 1% of HCC
- Based on a review of 42 cases reported in the literature, there appears to be a male predominance (M:F = 2.8:1), with mean age of 58 years (range: 39 - 81 years) (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:304, Hepatology 1998;27:407, Histopathology 2000;37:523)
Sites
- Liver
Etiology
- Approximately half of cases have underlying cirrhosis or chronic infection with hepatitis B / C (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:304)
Clinical features
- Very rare tumor with limited clinical and outcome data
Diagnosis
- Imaging modalities for diagnosis of HCC: multiphasic computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Tissue biopsy is indicated if imaging is not diagnostic of HCC
Laboratory
- Elevation in serum alpha fetoprotein (AFP)
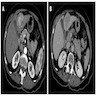
Radiology description
- Dynamic perfusion pattern of arterial hyperenhancement and venous or delayed phase washout is characteristic of HCC
Prognostic factors
- May have better prognosis in comparison to classic HCC (Am J Pathol 2017;187:1438, Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:304)
- Majority of patients present with low stage disease, a single lesion, and without vascular invasion (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:304)
- Prognostic factors for HCC: stage (TNM), single lesion (versus multifocal), size, vascular invasion, portal vein thrombosis, severity of underlying liver disease (Liver Int 2009;29:502, J Surg Oncol 2018;117:644)
Case reports
- 37 year old woman with chronic hepatitis B and C infection (Medicine (Baltimore) 2017;96:e9416)
- 58 year old man with elevated serum AFP (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10:7893)
- 78 year old woman with a liver mass (J Liver Cancer 2021;21:69)
- 79 year old man with a liver mass (World J Surg Oncol 2013;11:97)
- 81 year old woman with chronic hepatitis C infection (World J Gastroenterol 2015;21:10468)
Treatment
- Surgical resection
- Radiofrequency ablation
- Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE)
- Transplantation (e.g., Milan criteria, modified by some institutions) (Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017;14:203)
Gross description
- Majority present as a solitary lesion (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:304)
Microscopic (histologic) description
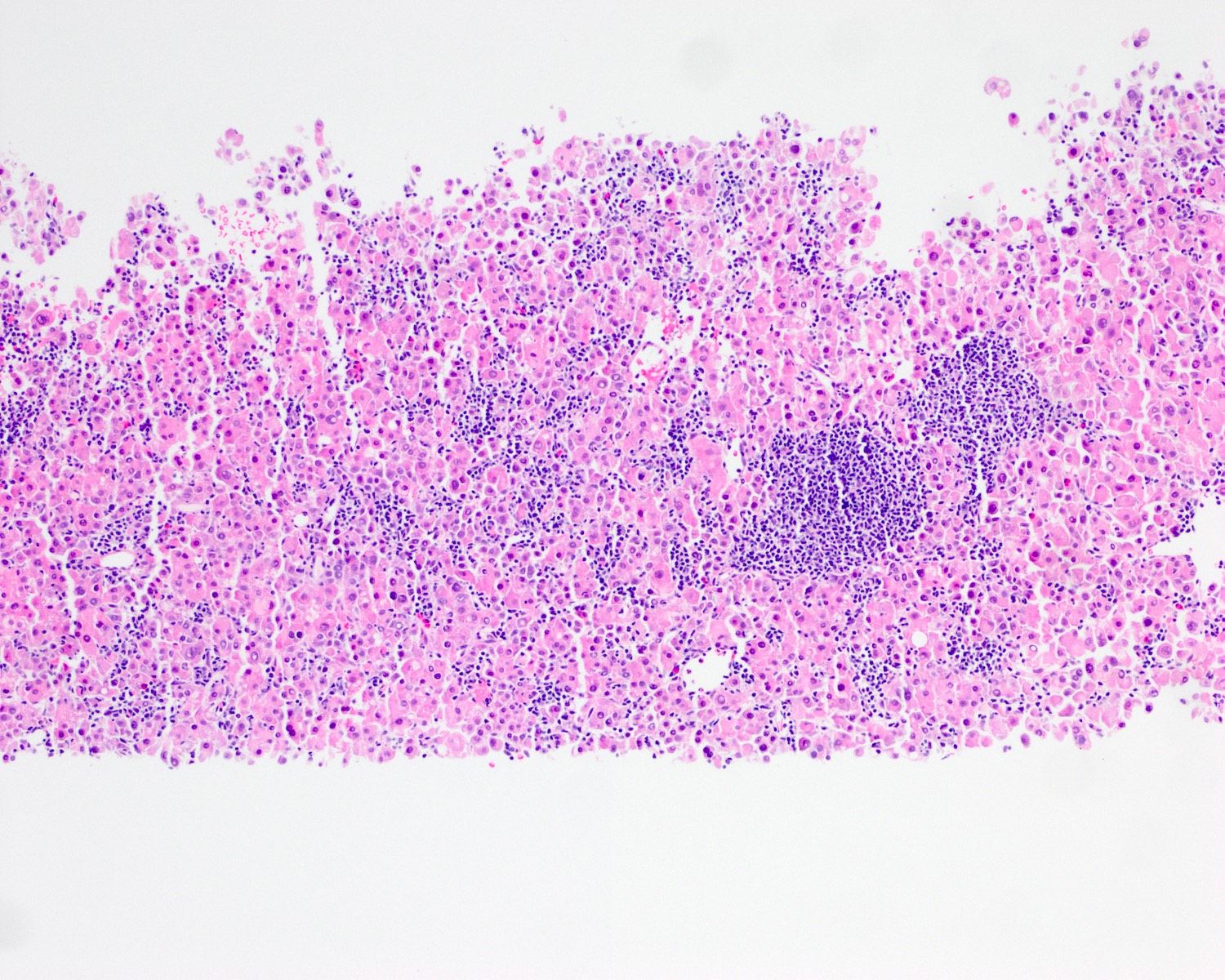
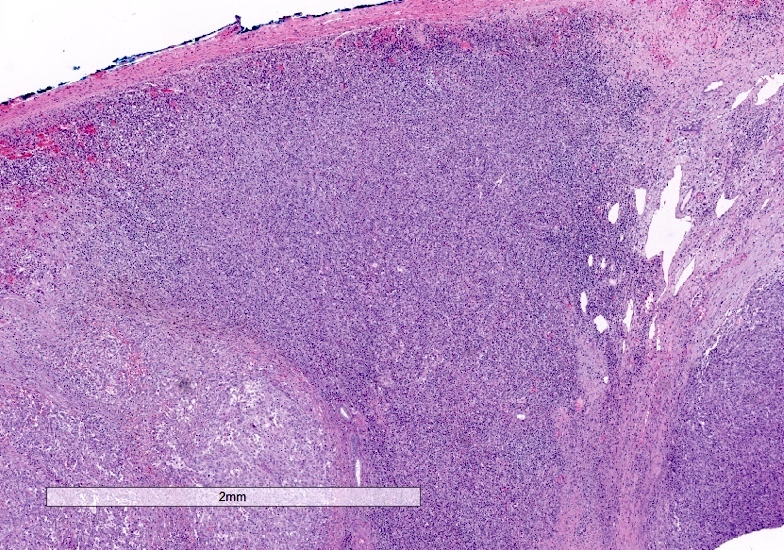
- Cords and trabeculae of tumor cells in a dense lymphoid stroma (lymphocytes outnumber tumor cells in most fields)
- Lymphoid infiltrate predominantly T cells with scattered B cells and germinal centers
- May show piecemeal necrosis
- Histologic grade usually well to moderately differentiated
- If poorly differentiated, the term lymphoepithelioma-like HCC may be used (Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2017;46:365)
- May have focal syncytial growth
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
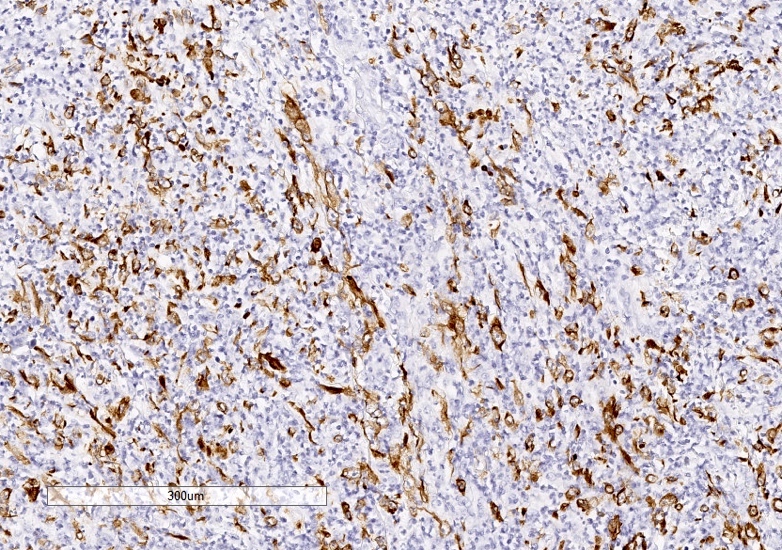
- Cytokeratin
- Hepatocellular markers (arginase1, glypican 3, HepPar1) variably positive
- Majority of lymphocytes are CD3+ / CD8+ cytotoxic T cells (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:304)
Negative stains
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Most cases negative for EBV in situ hybridization (ISH); EBV positivity reported in one study (Diagn Mol Pathol 2004;13:183)
- Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes not associated with microsatellite instability (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:304)
- Lymphocyte rich hepatocellular carcinoma has been shown to have focal amplification of chromosome 11q13.3, which is considered to be an immune checkpoint signature, making them a promising target for immunotherapy (J Pathol 2019;249:166)
Sample pathology report
- Liver, mass, core biopsy:
- Lymphocyte rich hepatocellular carcinoma (see comment)
- Comment: The tumor shows histologic features of lymphocyte rich hepatocellular carcinoma with nests and cords of hepatoid cells within a dense lymphoid stroma. The tumor cells are positive for pancytokeratin, HepPar1 and glypican 3, and negative for CK7, CK19 and mucicarmine. EBV in situ hybridization is negative.
Differential diagnosis
- Lymphoepithelioma-like cholangiocarcinoma:
- Classic HCC with increased lymphocytes:
- Tumors with only mild to moderate increase in lymphocytes should be classified as conventional HCC
- Lymphoma (primary hepatic lymphoma or secondary involvement by systemic disease):
- Dense infiltrate of atypical B or T cells
- No intermixed neoplastic hepatocytes
- Positive hematolymphoid markers (depends on the entity), negative cytokeratin and hepatocellular markers
- Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor:
- Tumor of myofibroblasts with plasma cells, lymphocytes and eosinophils
- ALK+ spindle cells (subset)
- IgG4 related disease:
- Abundant IgG4+ plasma cells, systemic disease, elevated serum IgG4
- Inflammatory variant of angiomyolipoma:
- Inflammatory pseudotumor-like follicular / fibroblastic dendritic cell sarcoma:
- Inflammatory pseudotumor (nonneoplastic):
- Mixed inflammation, granulomas, necrosis / abscess, rule out AFB, T. pallidum, parasites
- No intermixed neoplastic hepatocytes
Additional references
Practice question #1
Practice answer #1
Practice question #2
Which of the following features is characteristic of lymphocyte rich hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)?
- Cytokeratin is usually negative
- Has a worse prognosis in comparison to classic HCC
- It is one of the more common variants of HCC
- Lymphocytes outnumber tumor cells in most fields
- Most cases are positive for Epstein-Barr virus in situ hybridization
Practice answer #2
D. Lymphocytes outnumber tumor cells in most fields
Comment Here
Reference: Lymphocyte rich hepatocellular carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Lymphocyte rich hepatocellular carcinoma