Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Peripheral smear description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Flow cytometry description | Flow cytometry images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Saluja K, Thakral B. MDS with single lineage dysplasia. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/myeloproliferativera.html. Accessed September 14th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Myelodysplastic syndrome with single lineage dysplasia (MDS SLD) is defined as persistent unexplained cytopenias (anemia [most common], neutropenia or thrombocytopenia) or bicytopenia with ≥ 10% dysplastic cells in 1 myeloid lineage
Essential features
- Per 2016 revised WHO classification, MDS SLD includes:
- Peripheral blood with anemia (Hb < 10 g/dL) or neutropenia (< 1.8 x 109/L) or thrombocytopenia (< 100 x 109/L) or bicytopenia with < 1% blasts
- Bone marrow (BM) with ≥ 10% dysplastic cells in one myeloid lineage
- MDS with erythroid dysplasia only and 5 - 14% ring sideroblasts in absence of SF3B1 mutation
- Reference: Blood 2016;127:2391
Terminology
- According to 2008 WHO classification, it was known as refractory cytopenia with unilineage dysplasia (refractory anemia, refractory neutropenia or refractory thrombocytopenia)
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Incidence: 7 - 20% of all MDS cases
- Median age of onset: 65 - 70 years
- M = F
Sites
- Peripheral blood and bone marrow
Etiology
- Risk factors:
- Benzene exposure (J Natl Cancer Inst 2012;104:1724)
- Cigarette smoking (also in part due to benzene in cigarette smoke)
- Agricultural solvents or chemicals
- Family history of hematopoietic neoplasms
- Inherited hematological disorders, such as Fanconi anemia, dyskeratosis congenita, Shwachman-Diamond syndrome (SDS) and Diamond-Blackfan anemia
- These cases should also be separately designated as myeloid neoplasms with germline predisposition (Curr Opin Hematol 2021;28:86)
- Acquired aplastic anemia (Blood 2002;100:786)
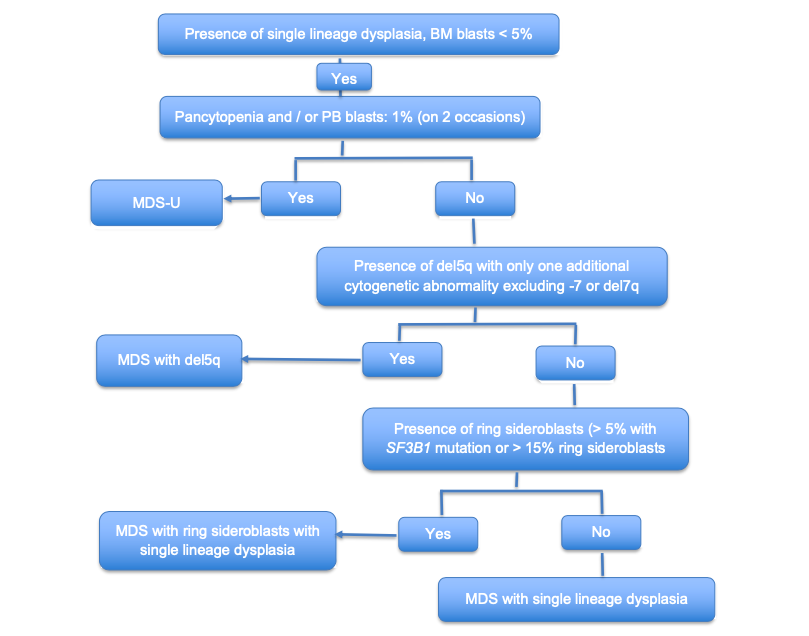
Diagrams / tables
Clinical features
- Clinical presentation may include fatigue, infection or petechiae related to the type and degree of cytopenia(s)
Diagnosis
- MDS is a comprehensive diagnosis made by review of complete clinical history, complete blood count, peripheral blood smear findings, bone marrow morphology assessment, flow cytometry immunophenotyping (if available), cytogenetics and molecular findings
- Review of:
- Complete clinical history (personal and family history), history of chemotherapy or radiation exposure
- Medications that can contribute to cytopenia or dysplasia
- Peripheral blood smear for blasts percentage, absolute monocyte count, monocyte percentage, degree of dysplasia and number of lineages involved
- Bone marrow morphology should include cellularity, blast percentage, degree of dysplasia, ring sideroblasts percentage (if any), presence or absence of fibrosis
- Flow cytometry to evaluate for aberrancies in CD34 positive myeloblast population and abnormal myelomonocytic maturation; in addition, any monoclonal B cell population or immunophenotypically abnormal T cells or NK cell population, if present, can also be assessed
- Cytogenetic abnormality in the absence of morphologic criteria, such as gain of chromosome 8, del 20q and loss of Y chromosome, is not considered definitive evidence of MDS, according to the WHO 2016 revised classification; in the setting of persistent cytopenia of undetermined origin, other MDS defining cytogenetic abnormalities are considered presumptive evidence of MDS, even in the absence of definitive morphologic features
- MDS associated somatic mutations identified alone in the absence of morphologic features of dysplasia are not considered diagnostic evidence of MDS, according to the current WHO 2016 revised classification
- References: Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2015;2015:294, Pathobiology 2019;86:7
Laboratory
- Peripheral blood cytopenias with anemia (Hb < 10 g/dL) or neutropenia (< 1.8 x 109/L) or thrombocytopenia (< 100 x 109/L) or bicytopenia and < 1% blasts
Prognostic factors
- Prognosis in MDS is determined using IPSS-R diagnostic scoring system, which takes into account cytogenetic findings, bone marrow blast percentage, hemoglobin, platelet count and absolute neutrophil count (ANC)
- 5 risk groups:
- Very low risk: ≤ 1.5
- Low: > 1.5 - 3.0
- Intermediate: > 3.0 - 4.5
- High: > 4.5 - 6.0
- Very high: > 6.0
- References: Blood 2012;120:2454, J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2015;13:261
IPPS-R scoring for MDS
| Prognostic variables | Score value | ||||||
| 0 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 | |
| Karyotype | Very good | - | Good | - | Intermediate | Poor | Very poor |
| Percentage of bone marrow blasts | ≤ 2% | - | > 2% to < 5% | - | 5 - 10% | > 10% | - |
| Hemoglobin (Hb) (g/dL) | ≥ 10 | - | 8 to < 10 | < 8 | - | - | - |
| Platelets (x109/L) | ≥ 100 | 50 to < 100 | < 50 | - | - | - | - |
| Absolute neutrophil count (ANC) (x109/L) | ≥ 0.8 | < 0.8 | - | - | - | - | - |
Cytogenetic prognostic group:
| |||||||
Case reports
- 46 year old man and his daughter presented with a novel germline frameshift GATA2 mutation presenting as congenital sensorineural hearing loss and familial MDS (Int J Hematol 2021;114:286)
- 53 year old man with history of shortness of breath, dizziness and fatigue (pernicious anemia with spuriously normal vitamin B12 level might be misdiagnosed as myelodysplastic syndrome) (Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 2014;14:e141)
- 55 year old man with history of fatigue and generalized weakness (zinc induced copper deficiency: a diagnostic pitfall of myelodysplastic syndrome) (Pathology 2014;46:246)
Treatment
- Low grade MDS can be observed if the patient is asymptomatic with mild cytopenias
- ESA (erythropoietin stimulating agent) to treat anemia
- Hypomethylating agents (azacitidine or decitabine) if the patient is symptomatic, with or without moderate to severe cytopenias
- Reference: Cancers (Basel) 2021;13:784
Gross description
- Adequate morphologic assessment for MDS requires high quality, good stained aspirate smears prepared from fresh aspirate specimen (< 2 hours); bone marrow core biopsy should be of adequate length (≥ 1.5 cm) and good quality peripheral blood smear
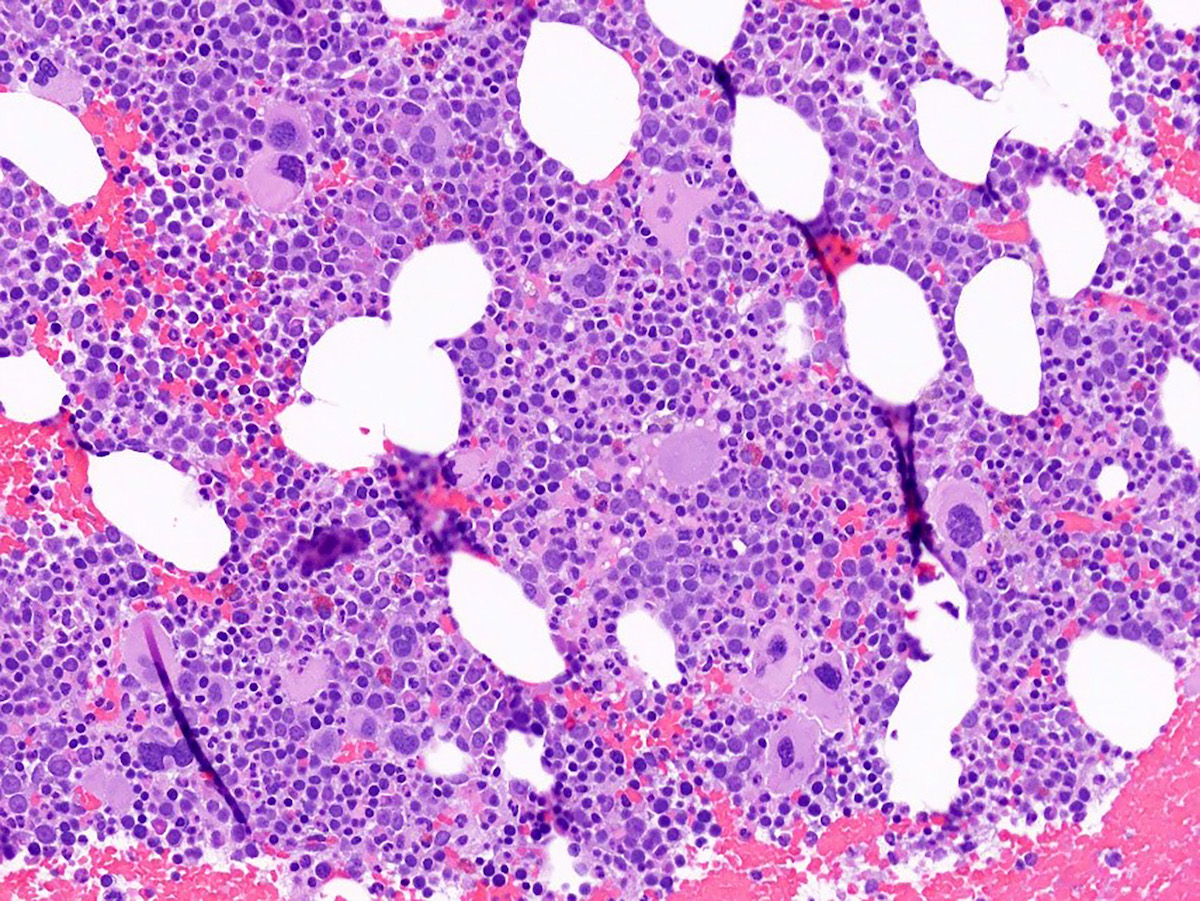
Microscopic (histologic) description
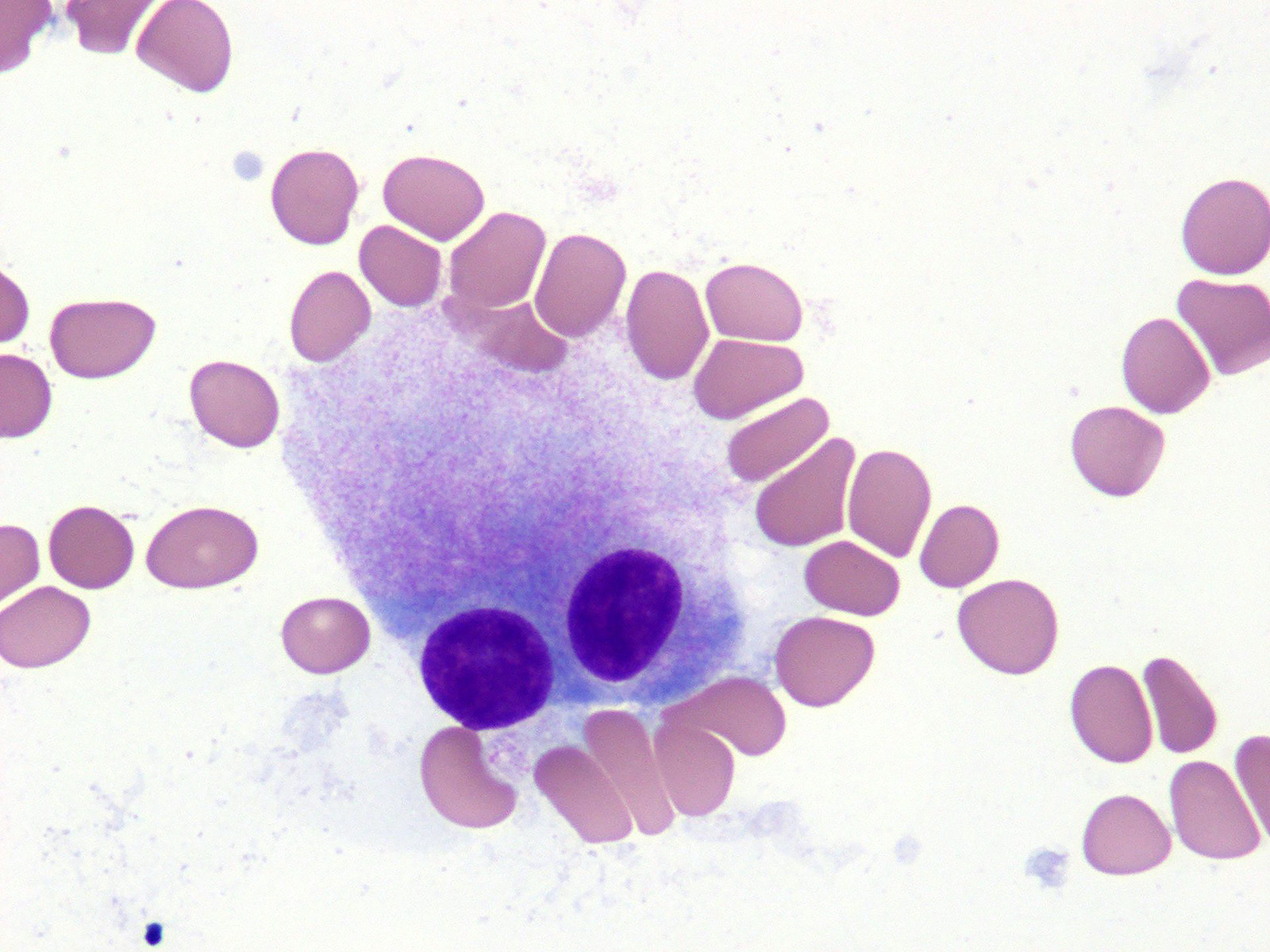
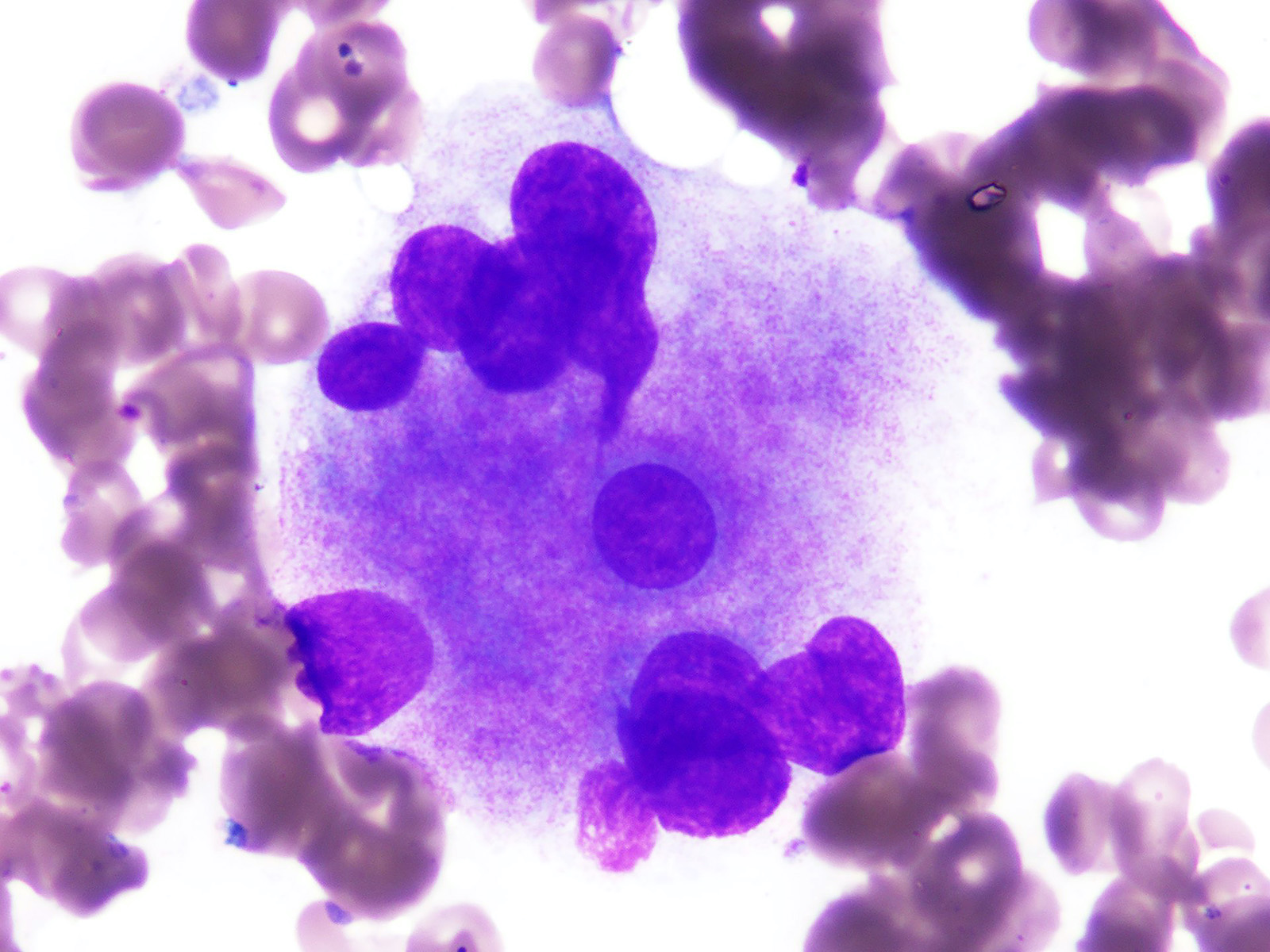
- Morphologic features of dysplasia in erythroid, myeloid or megakaryocytic lineages
| Dyserythropoiesis | Dysgranulopoiesis | Dysmegakaryopoiesis |
| Nuclear budding or multinucleation | Small or unusually large size granulocytes | Micromegakaryocytes |
| Internuclear bridging | Nuclear hyposegmentation (pseudo Pelger-Huët) | Nuclear hypolobation |
| Karyorrhexis | Nuclear hypersegmentation | Multinucleation or widely separated nuclear lobes |
| Megaloblastoid changes | Hypogranularity; agranularity | |
| Presence of ring sideroblasts | Pseudo Chediak-Higashi granules | |
| Cytoplasmic vacoulization | Auer rod |
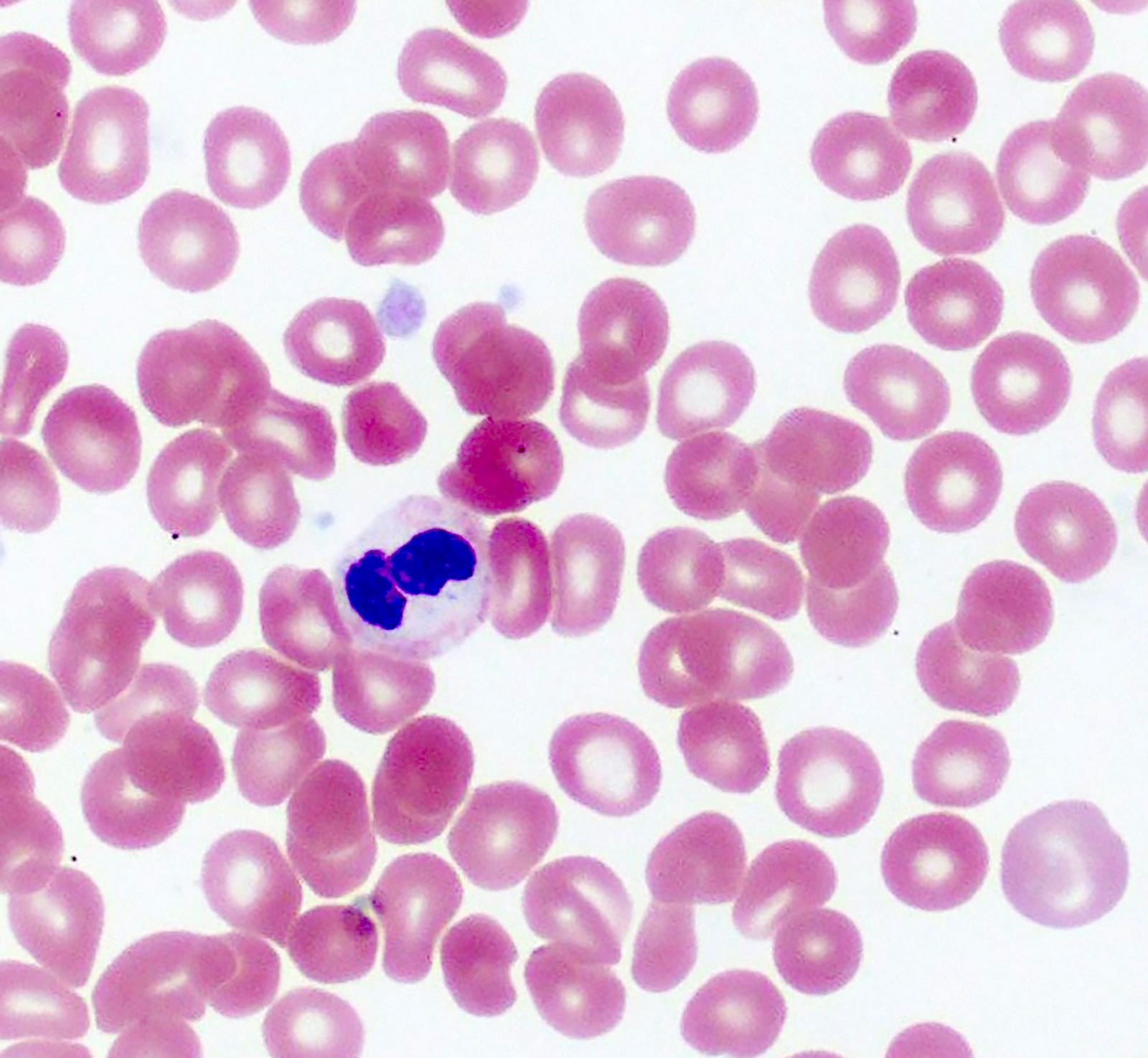
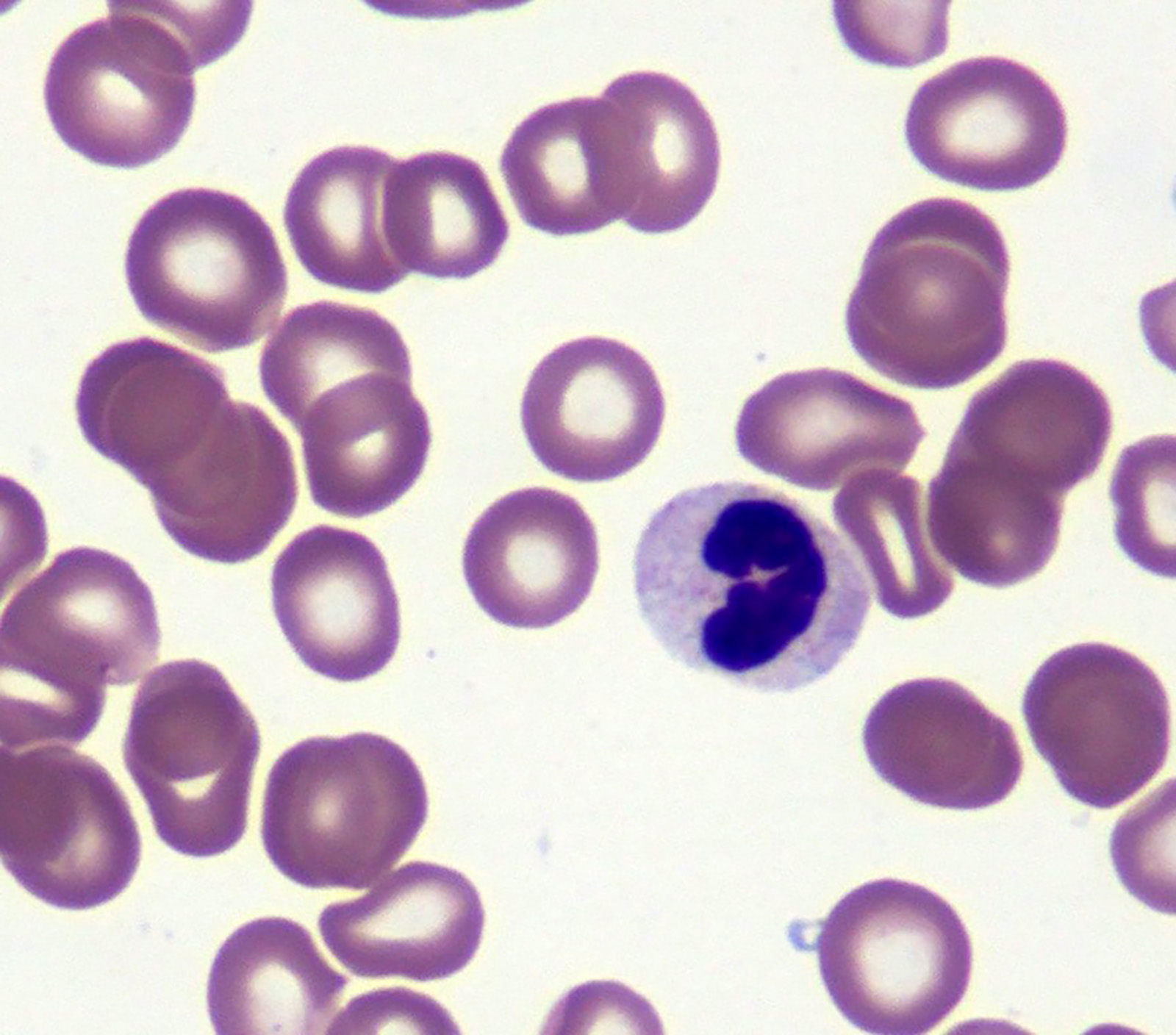
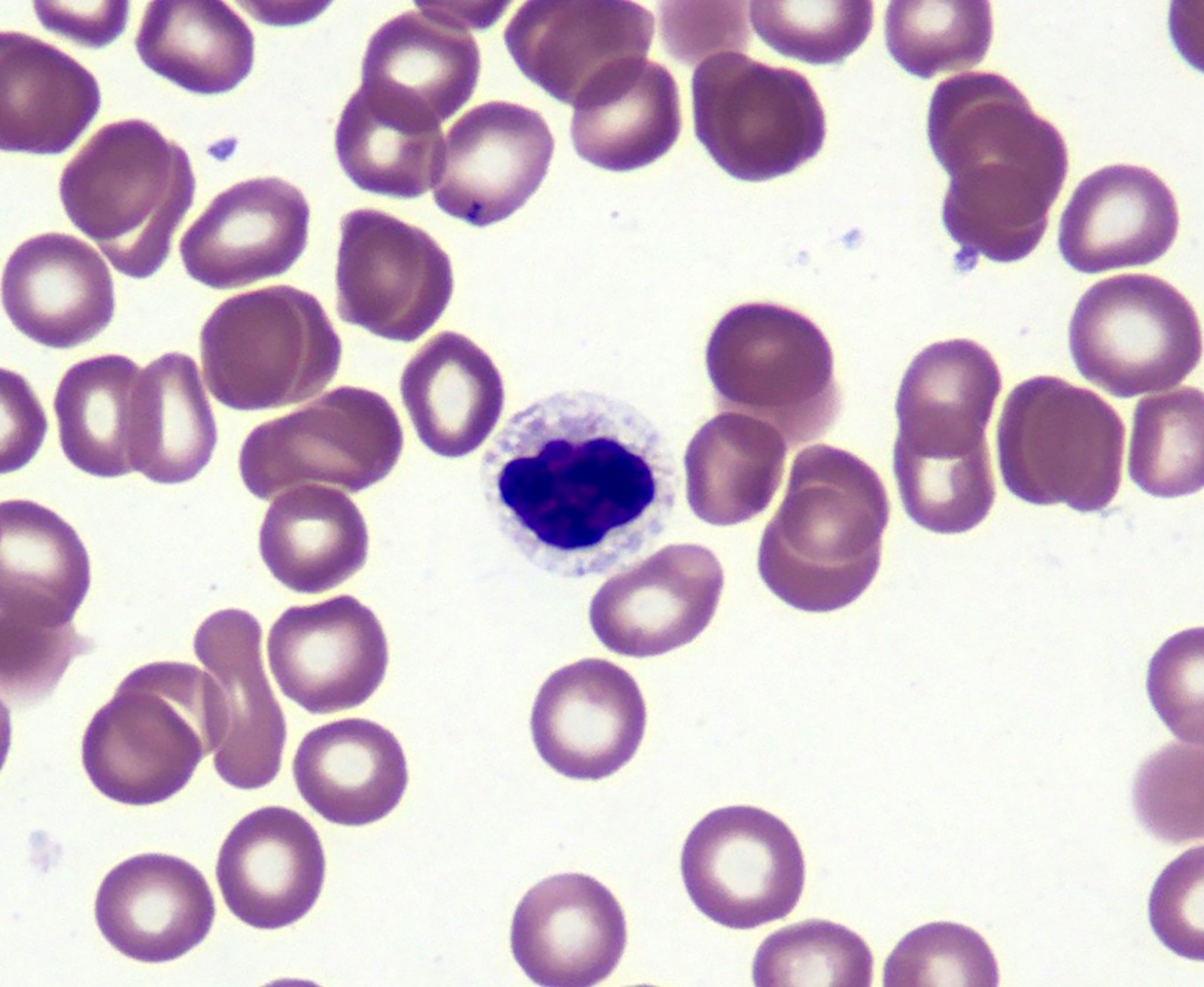
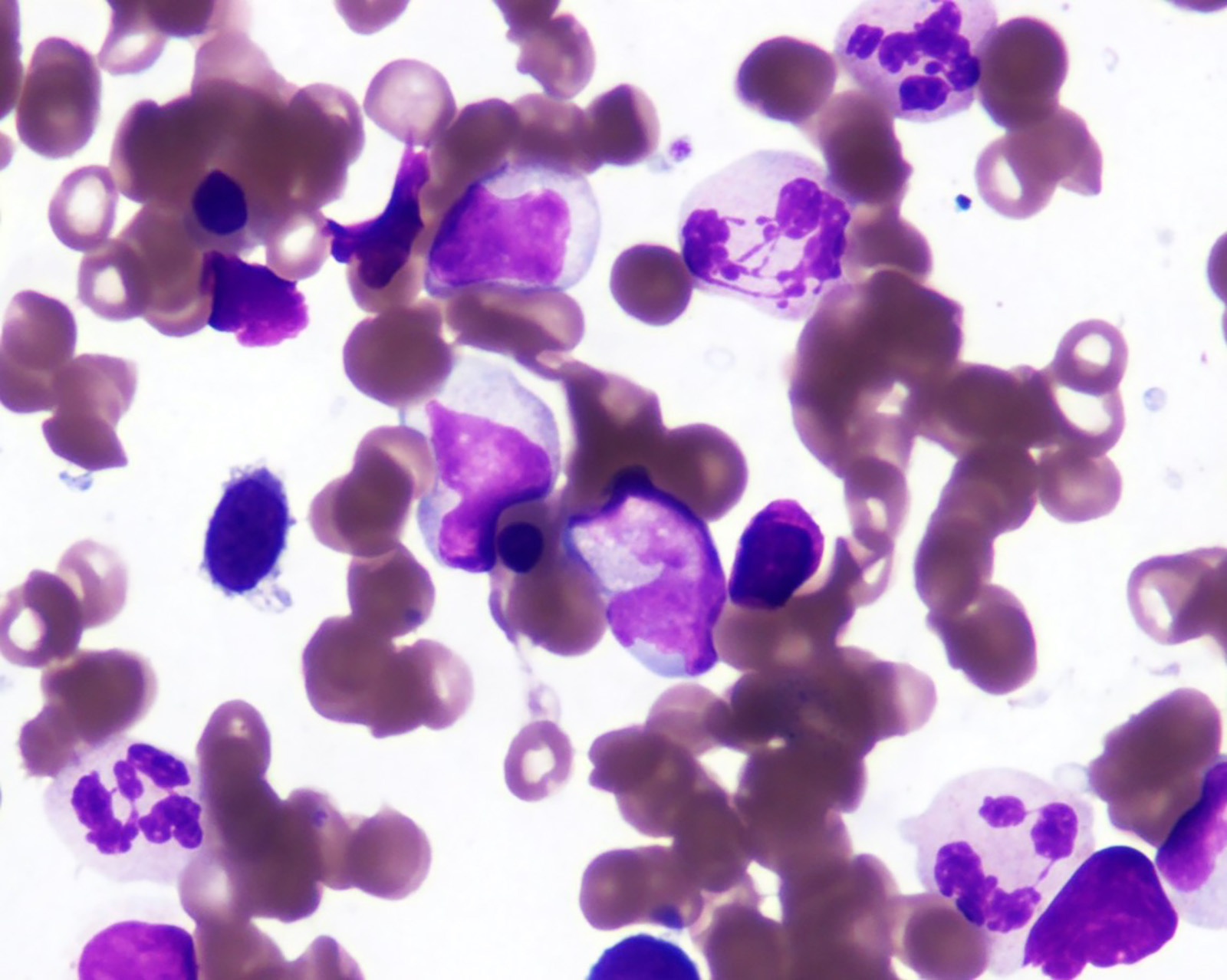
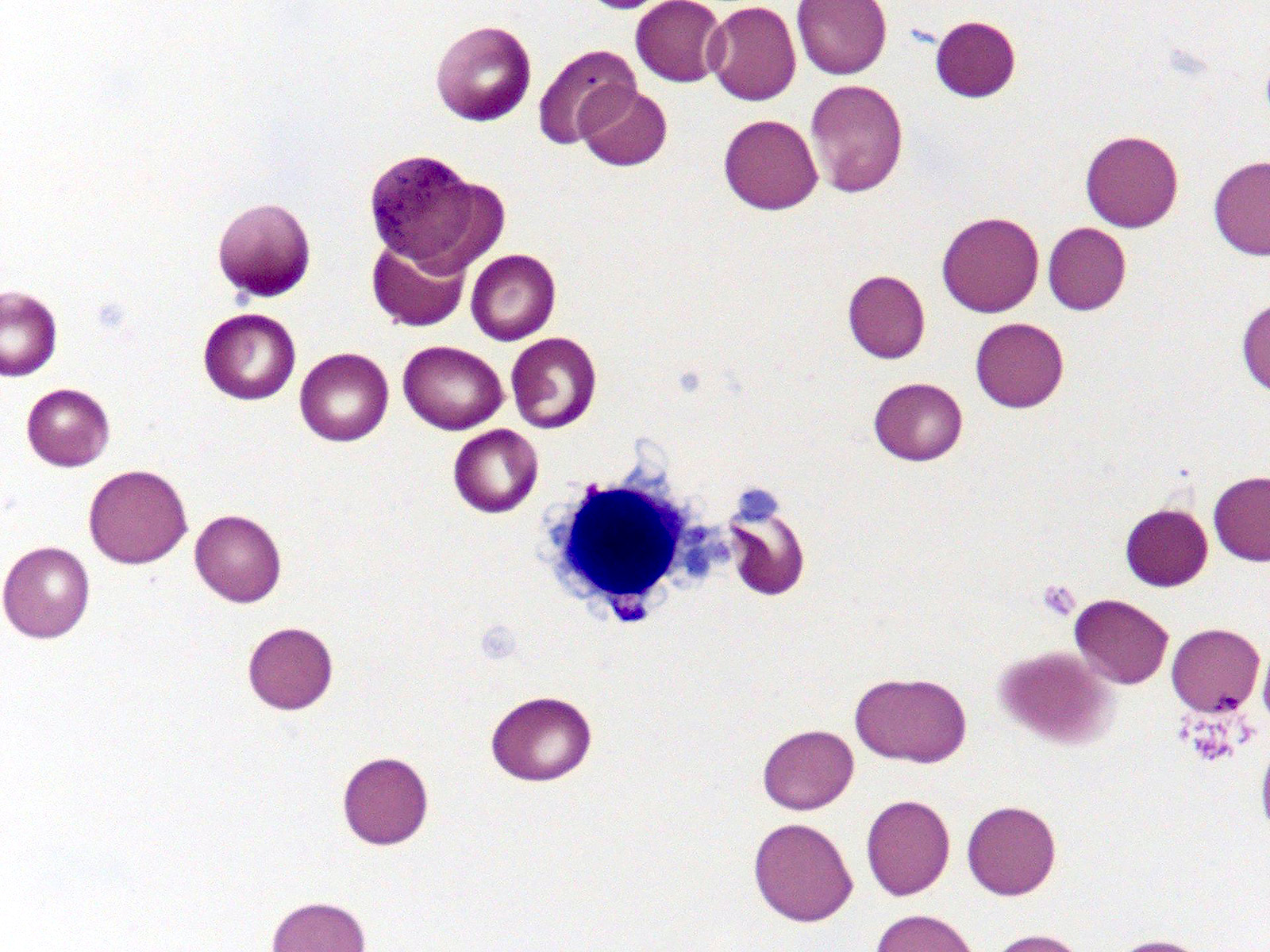
Microscopic (histologic) images
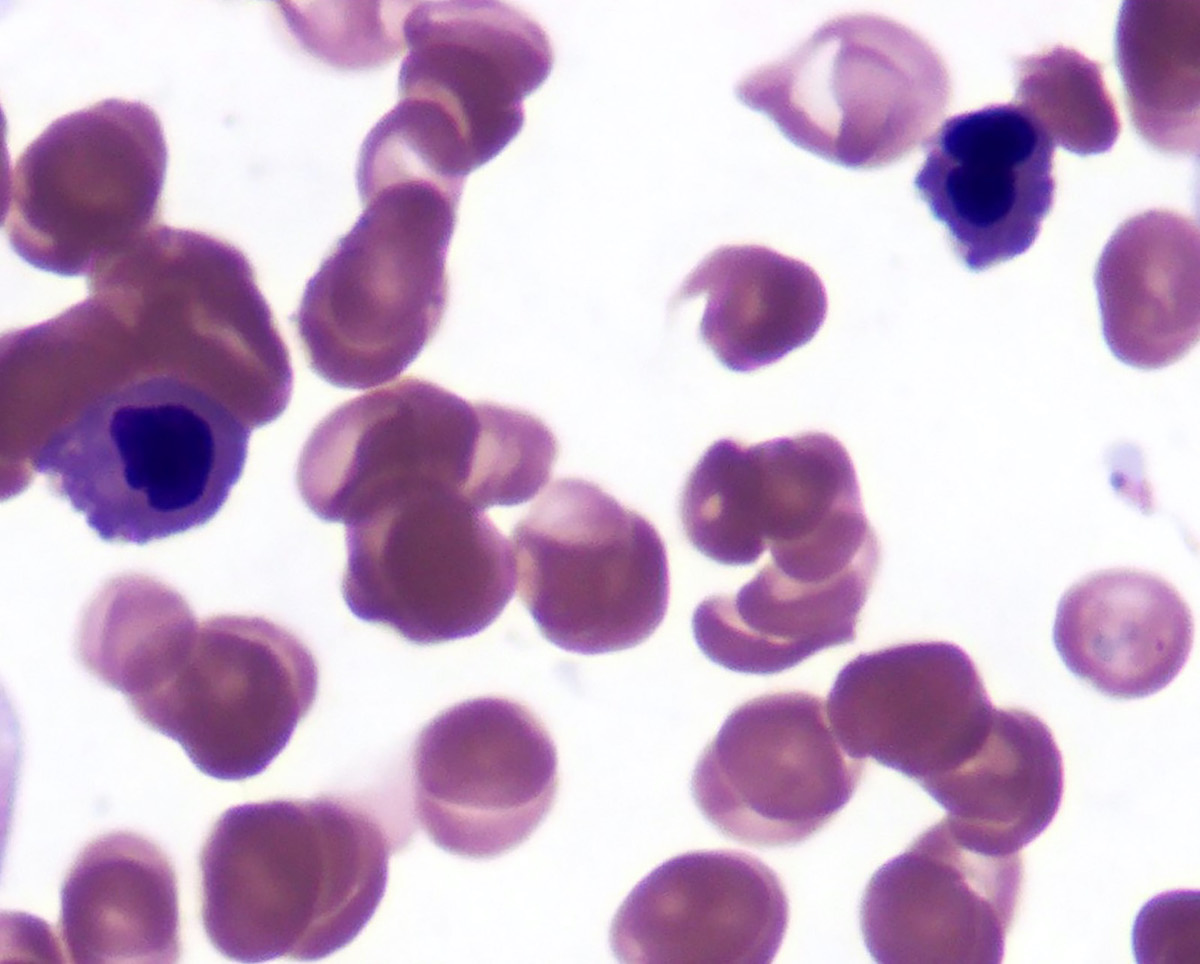
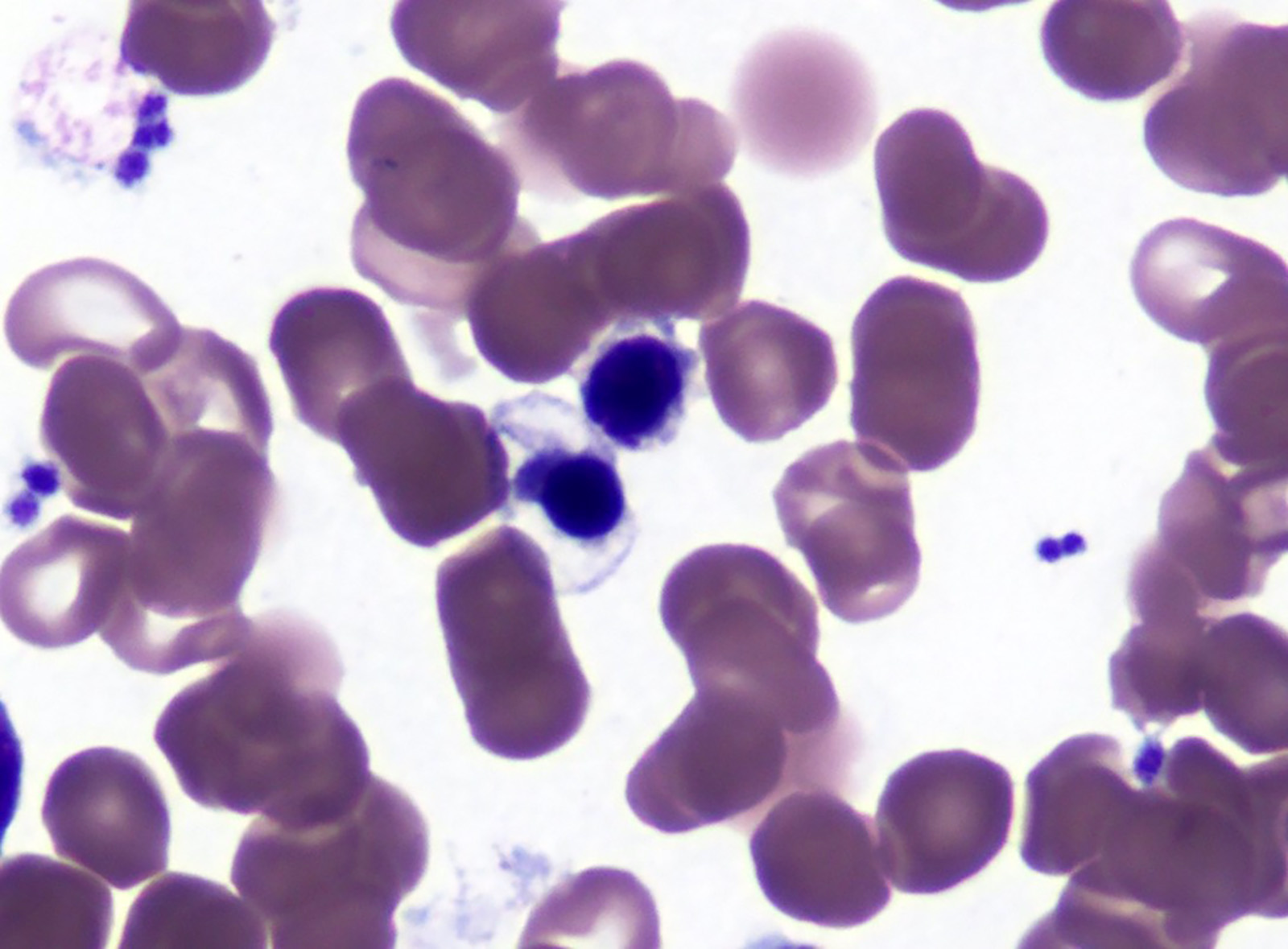
Peripheral smear description
- Red blood cells are usually normocytic or macrocytic and normochromic with anisopoikilocytsois
- Granulocytes may show hypogranularity, uneven distribution of cytoplasmic granules, pseudo Pelger-Huët anomaly
- Blasts are usually < 1%
- Subset of platelets may be hypogranular
Positive stains
Flow cytometry description
- Flow cytometry abnormalities in MDS (Oncotarget 2017;8:73483, Leukemia 2012;26:1730, Haematologica 2009;94:1066, Haematologica 2013;98:201):
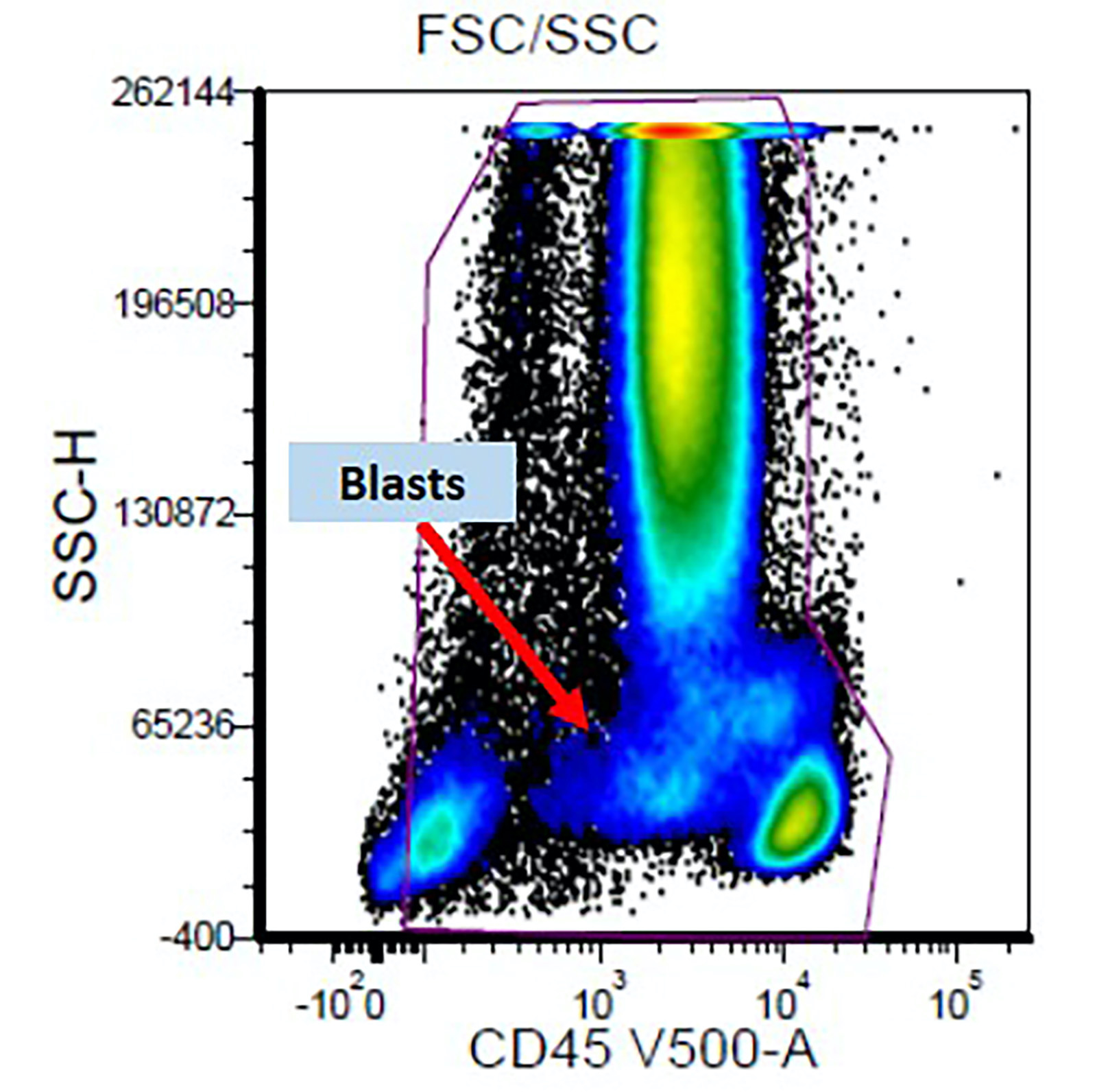
- Detection of an aberrant myeloblast population by flow cytometry helps in distinguishing reactive / nonclonal causes of dysplasia from clonal causes of MDS
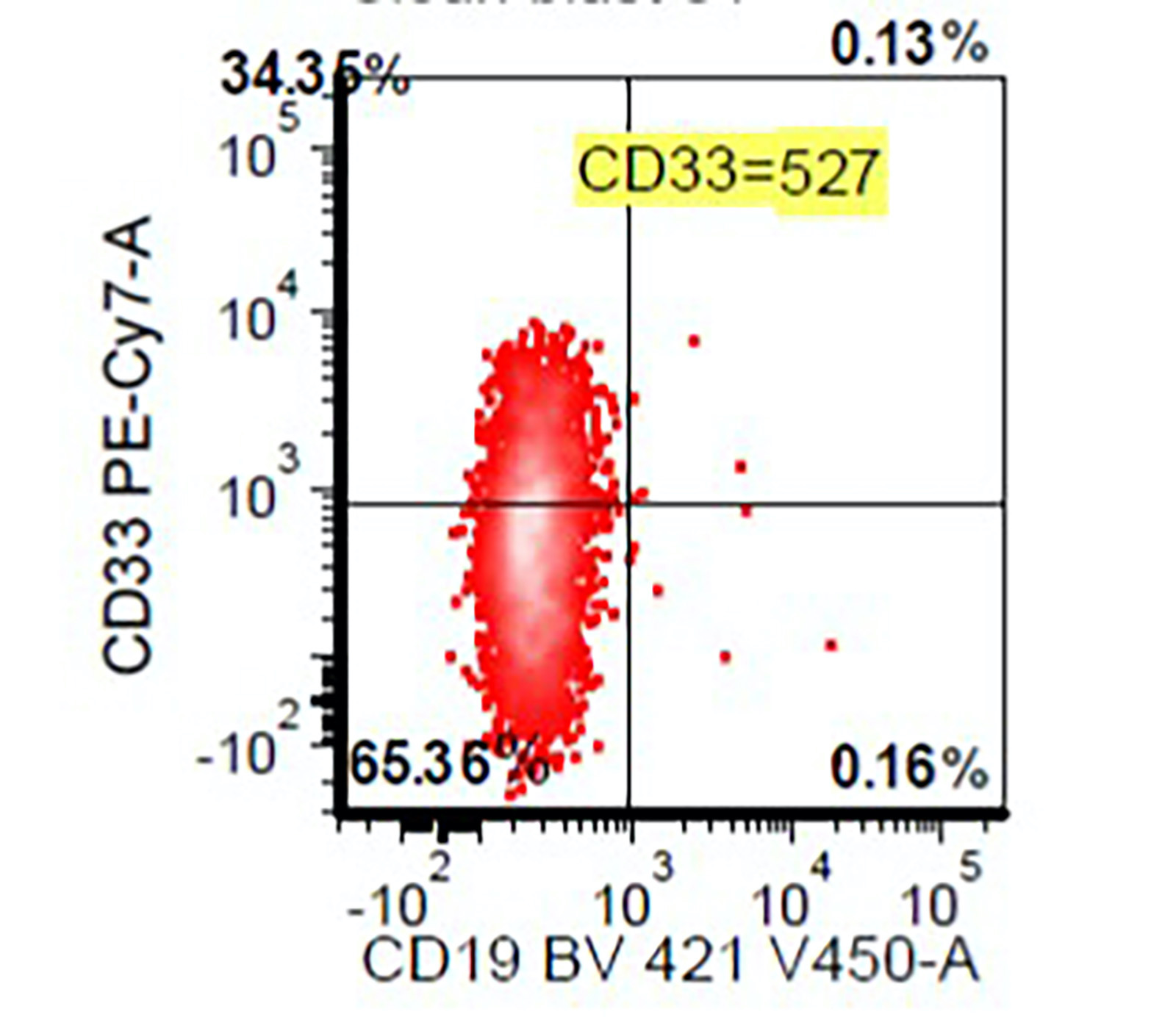
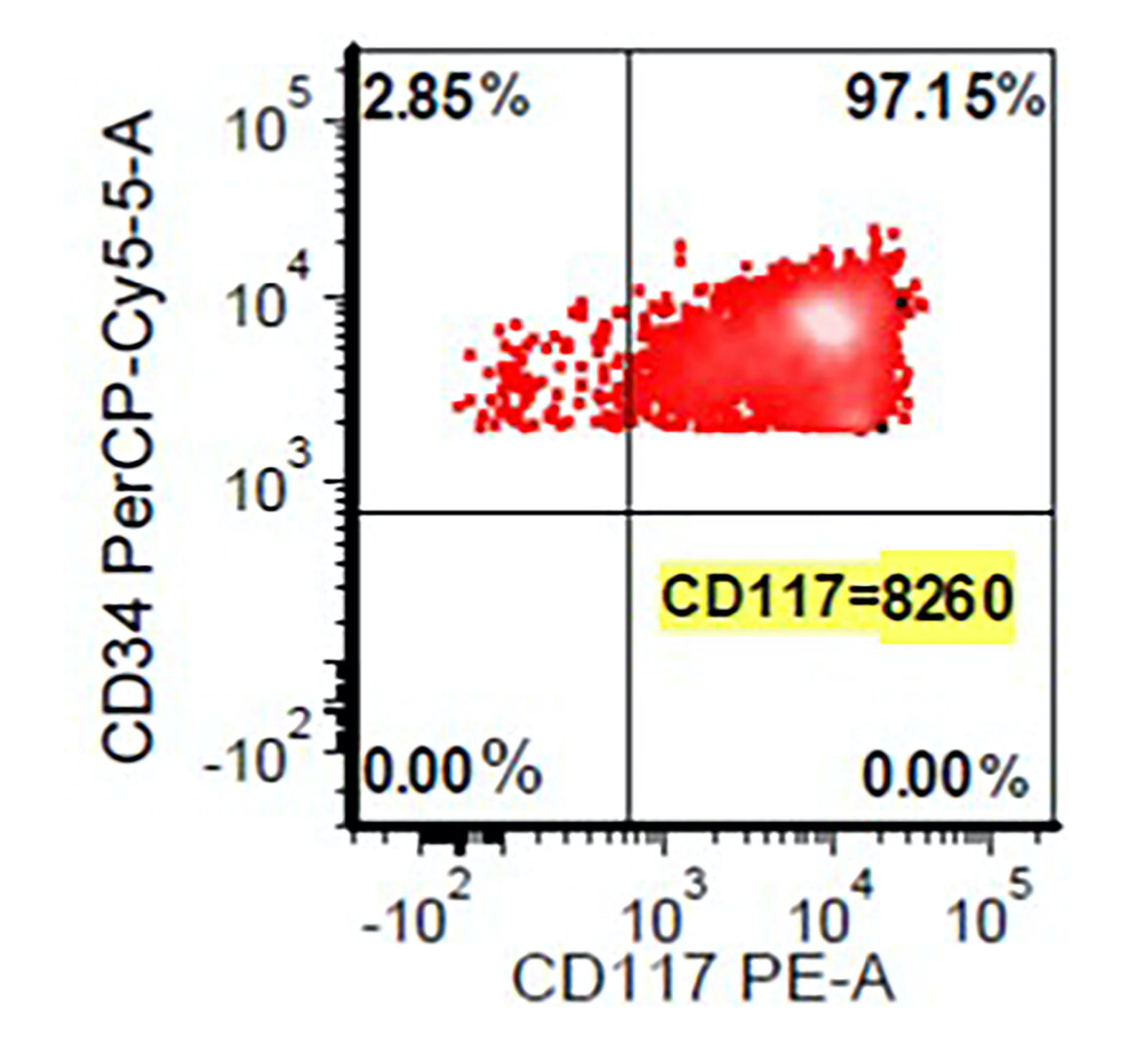
- Abnormal CD34 positive myeloblast population: altered CD45 and side scatter (CD45 / side scatter), increased blasts (> 2%), increased intensity of CD13, CD34, CD117, CD123, decreased intensity of CD38 or HLA-DR, substantial increase in cells with CD4, CD15, CD64 or CD65 expression, aberrant expression of lymphoid antigens (CD2, CD5 or CD7) and decreased hematogones
- Abnormal myelomonocytic maturation:
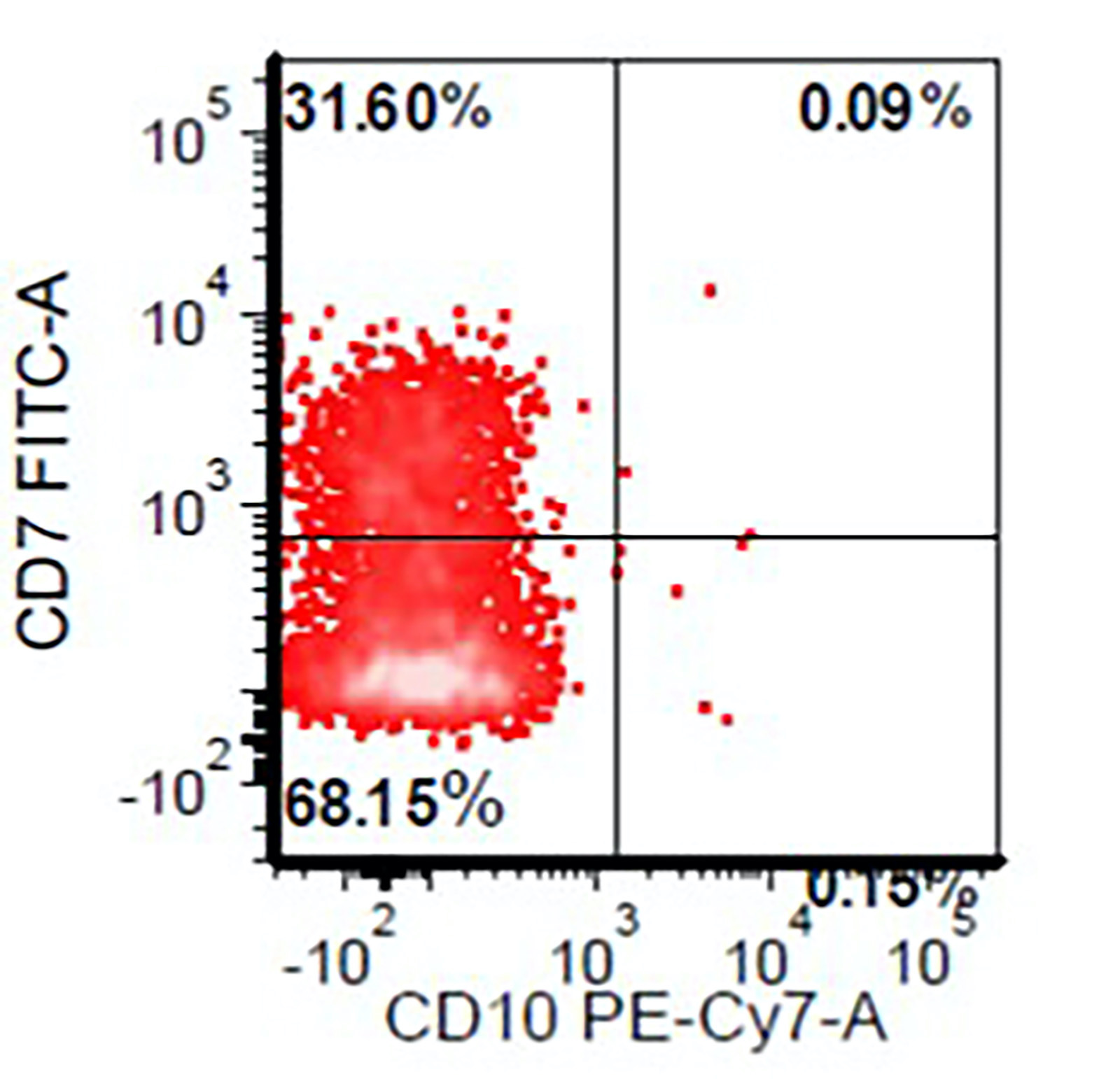
- Myeloid cells: decreased side scatter of granulocytes, abnormal maturation patterns of CD11b, CD13 and CD16 expression, lack of CD10 expression on neutrophils
- Monocytes: decreased CD45 and side scatter, decreased expression of HLA-DR, CD13, CD14 and CD36; increased expression of CD15 or CD16, aberrant expression of CD56 (bright) and CD2
- Detection of an aberrant myeloblast population by flow cytometry helps in distinguishing reactive / nonclonal causes of dysplasia from clonal causes of MDS
Flow cytometry images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Cytogenetics findings (J Clin Oncol 2012;30:820):
- Conventional karyotyping should be performed in all MDS cases at diagnosis, as it defines prognosis
- Cytogenetic abnormalities are seen in 50 - 60% of MDS; these abnormalities usually include del20q, gain in chromosome 8 or abnormalities in chromosome 5 and 7
- MDS SLD with isolated thrombocytopenia, the presence of cytogenetic or molecular abnormality is helpful in distinguishing MDS from immune mediated thrombocytopenia
MDS defining cytogenetic abnormalities
Unbalanced cytogenetic abnormalities
|
Balanced cytogenetic abnormalities
|
- Molecular findings (Int J Lab Hematol 2020;42:671, Blood 2012;119:3578, Leuk Res 2015;39:6):
- Recurrent somatic mutations are identified in 80 - 90% of MDS cases
- Most commonly mutated genes in MDS include RNA splicing (SF3B1, SRSF2, U2AF1 and ZRSR2) or epigenetic regulation of gene expression via DNA methylation (TET2, DNMT3A, IDH1 and IDH2) or genes involved in histone modification (ASXL1 and EZH2)
- Specific mutations associated with morphologic features and MDS include SF3B1 mutation with ring sideroblasts and mutations in ASXL1, RUNX1, TP53 and SRSF2 are associated with severe granulocytic dysplasia
- Acquired clonal mutations identical to those seen in MDS (TET2, DNMT3A, SF3B1, ASXL1 and JAK2) can also occur in hematopoietic cells of apparently healthy older individuals without MDS; thus, the presence of MDS associated somatic mutations alone are not considered diagnostic of MDS even in patients with unexplained cytopenia
Genes commonly mutated in MDS
| SF3B1 | RNA splicing | 20 - 30% | Favorable |
| TET2 | DNA methylation | 20 - 30% | Neutral |
| ASXL1 | Histone modification | 15 - 20% | Adverse |
| SRSF2 | RNA splicing | 15% | Adverse |
| DNMT3A | DNA methylation | 10% | Adverse |
| RUNX1 | Transcription factor | 10% | Adverse |
| U2AF1 | RNA splicing | 5 - 10% | Adverse |
| TP53 | Tumor suppressor | 5 - 10% | Adverse |
| EZH2 | Histone modification | 5 - 10% | Adverse |
| ZRSF2 | RNA splicing | 5 - 10% | Neutral |
| STAG2 | Cohesion complex | 5 - 7% | Adverse |
| IDH1 / IDH2 | DNA methylation | 5% | Neutral |
| CBL | Signaling | 5% | Adverse |
| NRAS | Transcription factor | 5% | Adverse |
| BCOR | Transcription factor | 5% | Adverse |
Sample pathology report
- Bone marrow, right posterior iliac crest, core biopsy, clot section, aspirate smears, touch imprint and peripheral blood smear:
- Myelodysplastic syndrome with single lineage dysplasia, 1% blast (see comment)
- Comment: Flow cytometry immunophenotyping performed on bone marrow aspirate shows an aberrant myeloblast population (0.8% of total events) with the following immunophenotype: CD7 partial, CD13+, CD33+, CD34+, CD117 inc and CD38 dec. Hematogones are absent. No monoclonal B cells or immunophenotypically abnormal T cells are identified.
- Review of peripheral blood smear shows moderate macrocytic anemia with slight anisopoikilocytosis and no circulating blast.
- Cytogenetic study shows a normal female karyotype: 46,XX[20]
- Next generation sequencing identified mutations in U2AF1 and TET2 genes.
- The current bone marrow specimen shows hypercellular (80%) bone marrow with erythroid predominant trilineage hematopoiesis, dyserythropoiesis, 3% ring sideroblasts and no increase in blasts; this is consistent with myelodysplastic syndrome with single lineage dysplasia (WHO 2016 revised classification).
Differential diagnosis
Characteristics of ICUS, CHIP / ARCH, CCUS and MDS
(ICUS) | (CHIP / ARCH) | (CCUS) | (MDS) | |
| Clonality | ||||
| Cytopenia | ||||
| Dysplasia | ||||
| Bone marrow blasts | ||||
| Cytogenetic abnormality | ||||
| Typical number of mutated genes | ||||
| Commonly mutated genes | NA | |||
| Typical VAF (variants with allele frequency) | ||||
| Risk of developing MDS or acute myeloid leukemia | Very low | Low | High | NA |
- MDS with ring sideroblasts and single lineage dysplasia:
- Characterized by unilineage dysplasia and distinguished from MDS SLD by presence of ≥ 15% ring sideroblasts or ≥ 5% ring sideroblasts, if SF3B1 mutation is present
- MDS unclassifiable:
- Cases with single lineage dysplasia in presence of 1% blasts in peripheral blood on 2 separate occasions or by presence of pancytopenia
- Nonclonal causes of dysplasia:
- Drugs, medications and toxin exposure
- Growth factor therapy
- Viral infection
- Immunological disorders
- Vitamin deficiencies: B12, folate (Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 2014;14:e141)
- Copper deficiency or zinc excess (Pathology 2014;46:246)
- References: Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book 2019;39:400, Am J Clin Pathol 2019;152:347, Eur J Haematol 2021;106:500, Blood Adv 2021;5:2272
Additional references
Practice question #1
A 50 year old man presented with macrocytic anemia with no known medical history. Serum vitamin B12 and folate levels are normal. A bone marrow biopsy shows hypercellular (80%) bone marrow with erythroid predominance, dyserythropoiesis and 10% ring sideroblasts with 2% blasts on aspirate smears. Peripheral blood smear review shows macrocytic anemia and no circulating blasts. Cytogenetics shows a diploid karyotype. Next generation sequencing identified mutation in the U2AF1 gene. According to the current WHO 2016 revised classification, how should this case of MDS be classified?
- Myelodysplastic syndrome, unclassifiable
- Myelodysplastic syndrome with del5q
- Myelodysplastic syndrome with ring sideroblasts
- Myelodysplastic syndrome with single lineage dysplasia
Practice answer #1
D. Myelodysplastic syndrome with single lineage dysplasia
Comment Here
Reference: MDS with single lineage dysplasia
Comment Here
Reference: MDS with single lineage dysplasia
Practice question #2
Which of the following RNA splicing gene is commonly mutated in MDS?
- ASXL1
- RUNX1
- SF3B1
- STAG2
- TP53
Practice answer #2