Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1Cite this page: Kuo E, Gonzalez RS. Mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/pancreasmcn.html. Accessed October 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Benign or potentially low grade malignant cystic epithelial neoplasm composed of cells which contain intracytoplasmic mucin (ICD-O: 8470/0 [Accessed 18 February 2021])
- WHO classification:
- MCN with low grade dysplasia (adenoma)
- MCN with high grade dysplasia (carcinoma in situ)
- MCN with invasive carcinoma
Essential features
- Cystic neoplastic lesion that is a precursor to pancreatic adenocarcinoma
- May harbor invasive carcinoma
- Presence of associated ovarian type stroma
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Almost always women (> 95%); mean age of 45 years (Ann Surg 2008;247:571)
Sites
- Distal pancreas (> 95%) (Ann Surg 2008;247:571)
- Can also occur in the liver and gallbladder
- Metastases usually restricted to abdominal cavity; metastases to ovary may simulate primary ovarian tumors
Pathophysiology
- Ectopic ovarian stroma is thought to be seeded from primordial ovarian cells at early stages of embryonic development
- Cysts are later formed by hormones and growth factors released by the ovarian stroma (Am J Surg Pathol 1999;23:410)
Etiology
- No known etiology
Clinical features
- Usually a single lesion (Gut Liver 2015;9:571)
- May present as abdominal pain or acute pancreatitis (Ann Surg 2008;247:571)
- Majority are slow growing and asymptomatic (Gastroenterology Res 2014;7:44)
Diagnosis
- Cytology and lab analysis of pancreatic cyst fluid from endoscopic ultrasound guided FNA
- Histology of pancreatic resection
Laboratory
- Elevated carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and presence of KRAS mutation in cyst fluid supports a mucinous cyst (includes MCN and intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm) (Ann Gastroenterol;26:122)
Radiology description
- Thick walled, single, septated cyst in the body or tail of the pancreas (Gut Liver 2015;9:571)
- May have nodules or calcifications
Prognostic factors
- Prognosis is excellent unless there is invasive carcinoma with extracapsular or diffuse intracapsular infiltration (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:179, Ann Surg 2008;247:571)
- Features associated with invasive carcinoma include increased cyst size (> 5 cm), intracystic papillary nodules > 1 cm in size and elevated serum CA19-9 (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:179)
- Less than 20% of cases have invasive carcinoma (Gut Liver 2015;9:571, Ann Surg 2008;247:571)
Case reports
- 38 year old woman with anaplastic carcinoma and mucinous cystic neoplasm of the pancreas during pregnancy (World J Gastroenterol 2008;14:132)
- 46 year old man with pancreatic mucinous cystic neoplasm with sarcomatous stroma metastasizing to liver (World J Surg Oncol 2013;11:100)
- 52 year old Japanese woman with anaplastic carcinoma combined with mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the pancreas (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1997;121:1104)
- 65 year old man (JOP 2012;13:687)
Treatment
- Surgical resection is indicated for all MCNs (Gut Liver 2015;9:571, Gastroenterology Res 2014;7:44)
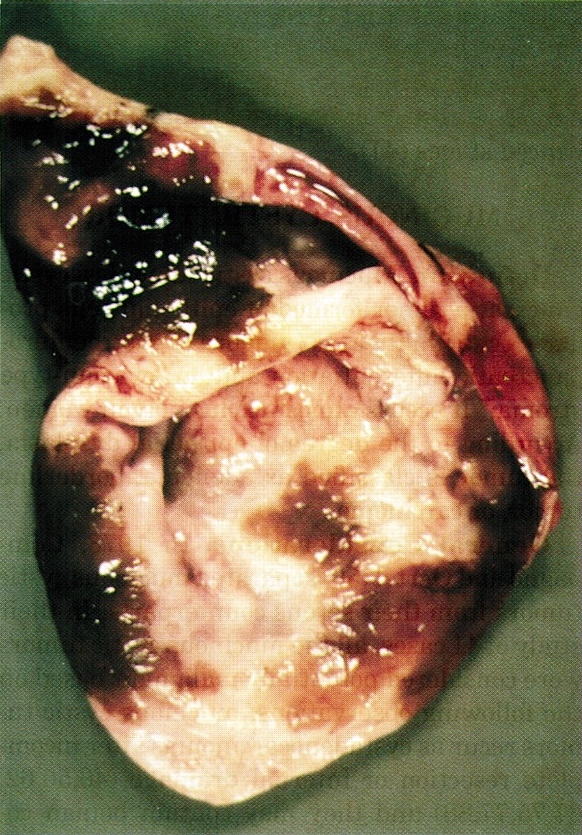
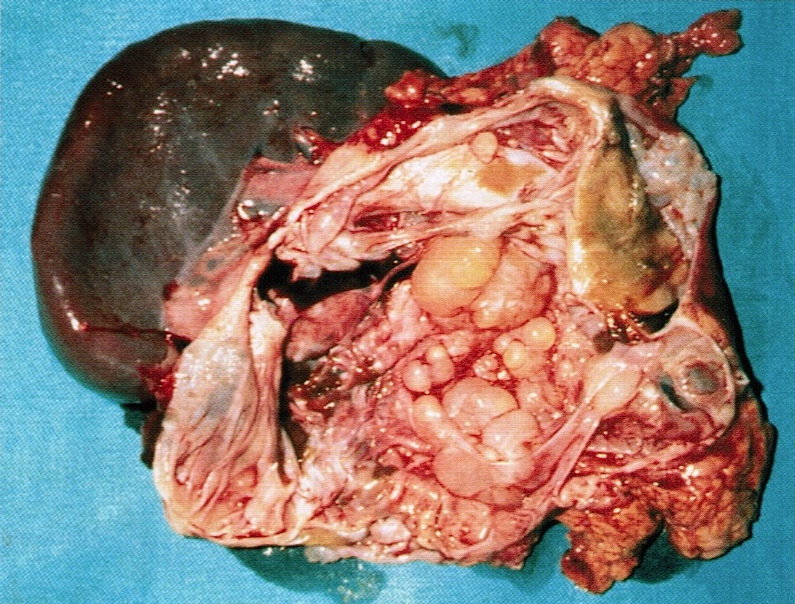
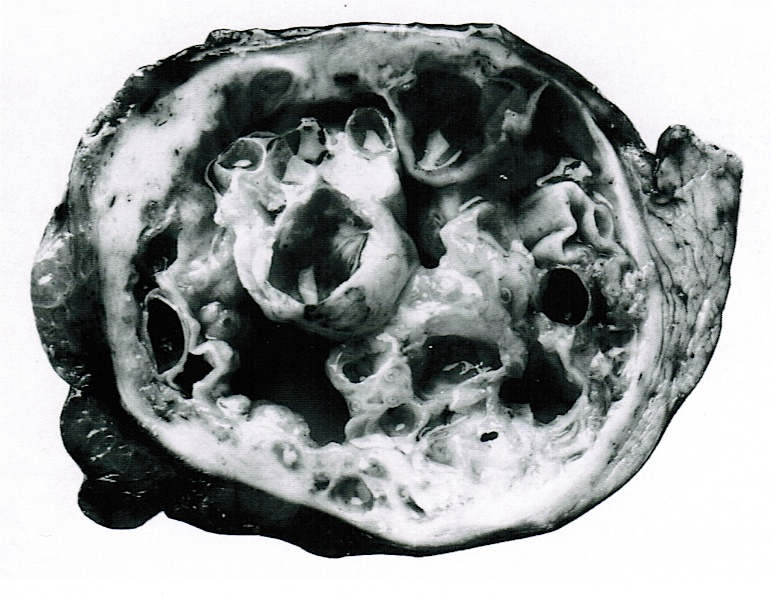
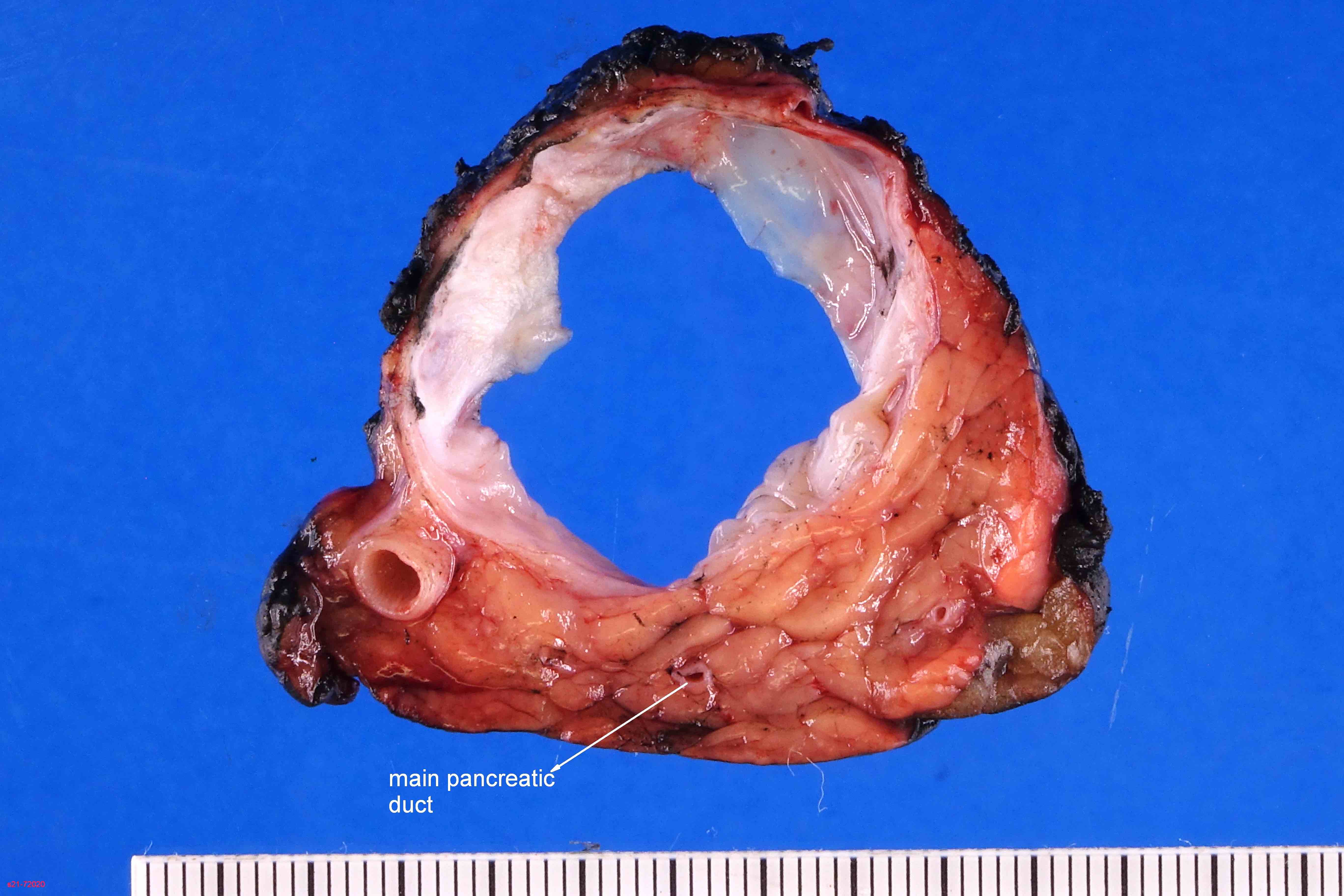
Gross description
- Large (mean 10 cm)
- Typically unilocular megacysts that do not communicate with ductal system, though up to 15% communicate with main pancreatic duct (Gut Liver 2015;9:571)
- Cyst wall is papillary, trabecular or thickened
- Has mucoid / watery cyst contents
- Must sample solid areas within the cyst
Gross images
Contributed by Diana Agostini-Vulaj, D.O., Wei Chen, M.D., Ph.D., Nakul Anush Ravish, M.B.B.S. and AFIP
Images hosted on other servers:
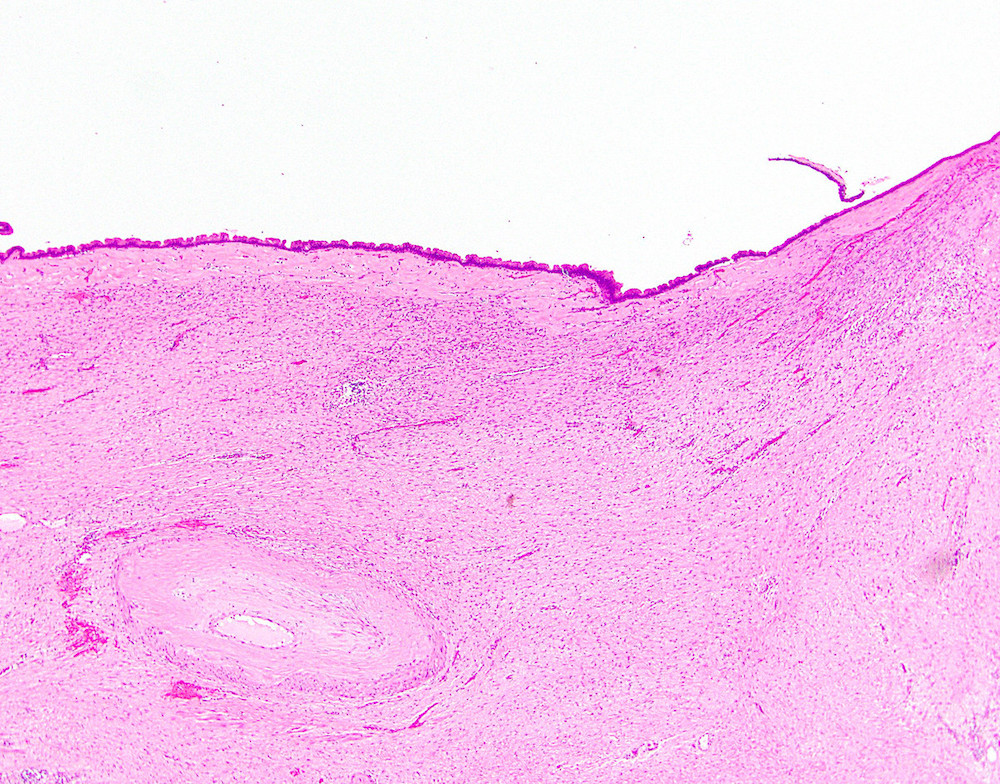
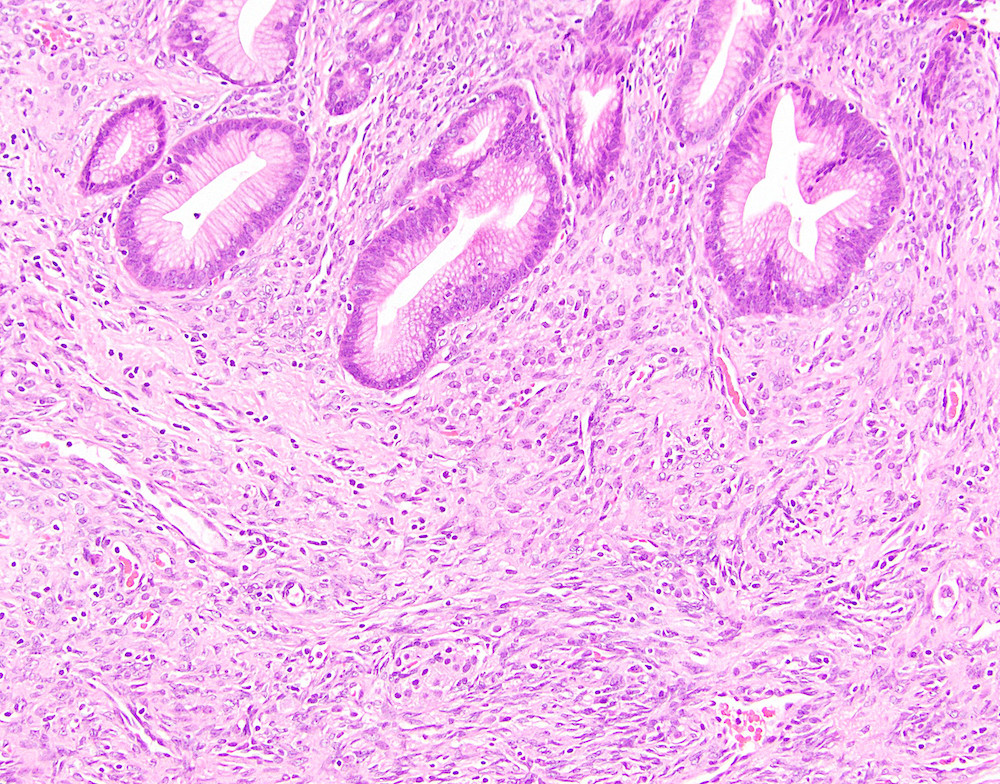
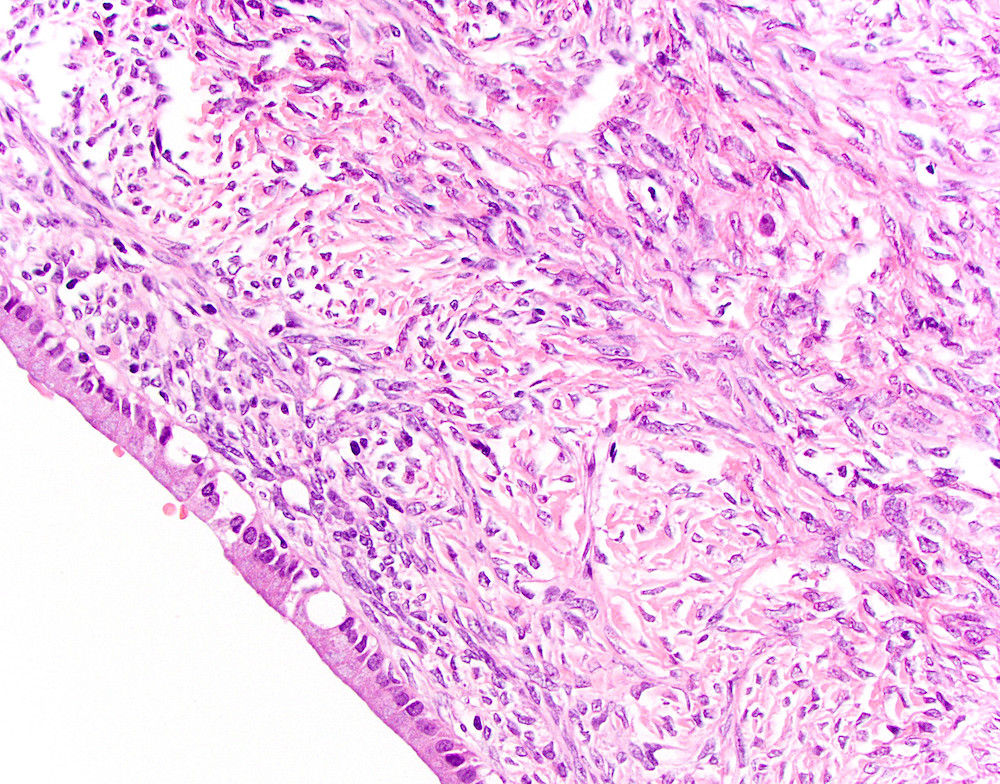
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Large cyst lined by intestinal, pseudopyloric or gastric foveolar type epithelium that often form papillae, surrounded by characteristic dense ovarian type stroma (Gut Liver 2015;9:571)
- Epithelial lining has variable atypia (none, low grade, high grade); scattered neuroendocrine cells may be present
- Invasive adenocarcinoma may or may not be present; must sample extensively to rule out an invasive component (Gut Liver 2015;9:571, Am J Surg Pathol 1999;23:1320)
- Calcifications are common
- May have mural nodules with features of giant cell tumor, malignant fibrous histiocytoma or anaplastic carcinoma
Microscopic (histologic) images
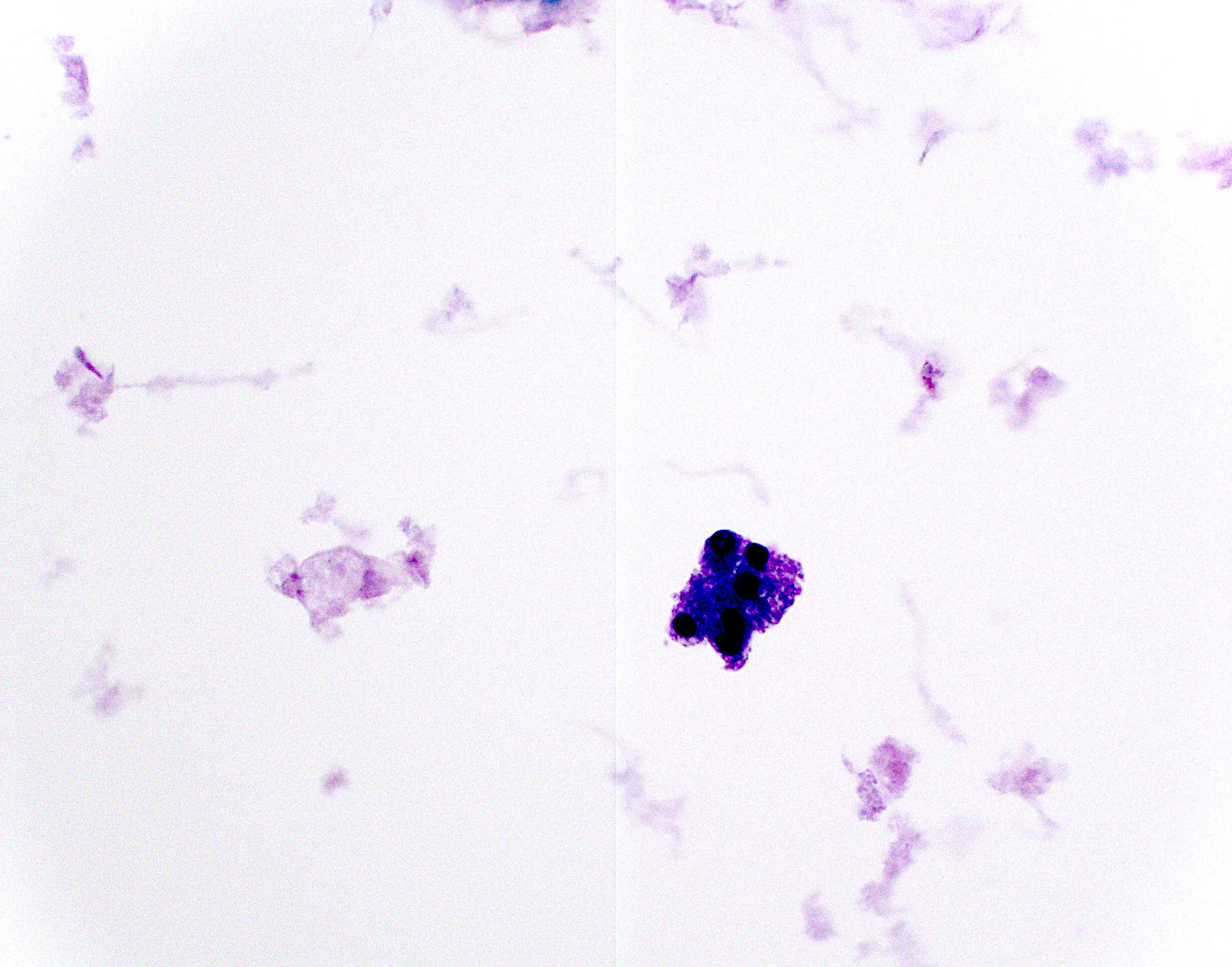
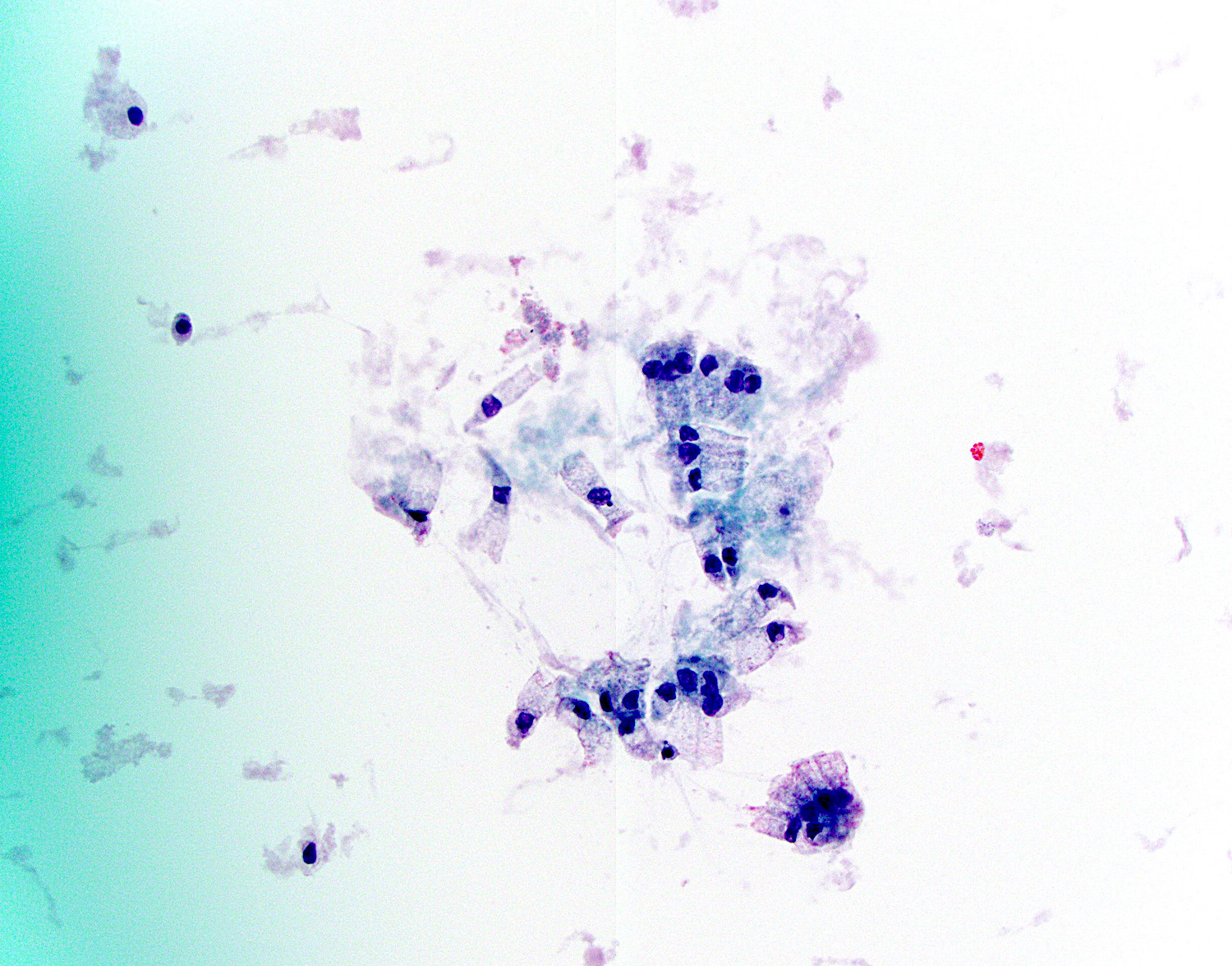
Cytology description
- Cyst aspirates are usually acellular with thick, gelatinous mucus
- Clusters of 3 dimensional atypical glandular cells with hyperchromasia predict at least moderate dysplasia (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2009;133:388)
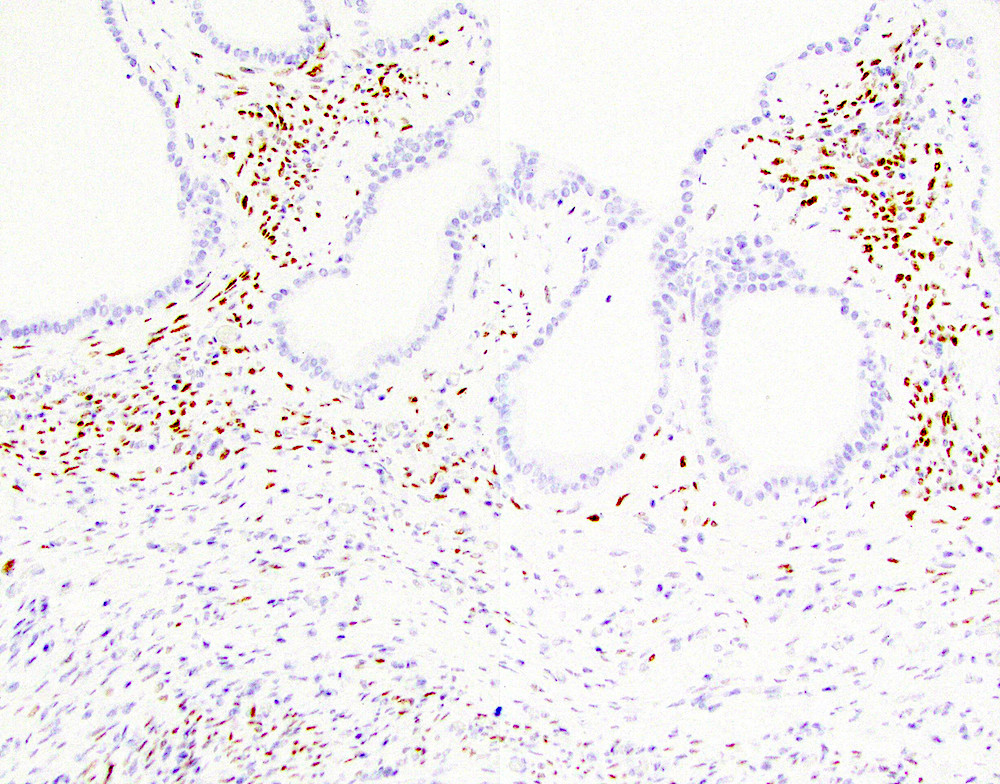
Positive stains
- Ovarian type stroma: CD10, ER, inhibin, PR, smooth muscle actin (SMA) and vimentin (Gut Liver 2015;9:571)
- Epithelium stains carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), CK7, CK8, CK18 and CK19 (Gut Liver 2015;9:571)
- Gastric type epithelium stains MUC5AC (Gut Liver 2015;9:571)
- DPC4 (MADH4, SMAD4), MUC5AC present in situ areas (usually lost in invasive disease) (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:1544, Gut Liver 2015;9:571, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2015;139:24)
- Invasive component stains MUC1
- Cyst fluid may stain positive for Alcian blue and mucicarmine
- S100P in epithelium (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2015;139:24)
- SF1 in stroma (Pathol Int 2016;66:281)
Negative stains
- MUC1 (except in invasive components) (Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:466, Gut Liver 2015;9:571)
- MUC2 (except for faint staining of goblet cells)
- DPC4 (MADH4, SMAD4) staining is lost in invasive MCNs (Gut Liver 2015;9:571)
- pVHL (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2015;139:24)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- KRAS mutations noted in in situ or invasive areas, inactivating SMAD4 and TP53 mutations in more advanced MCNs (Gut Liver 2015;9:571)
- Negative for GNAS mutations
Sample pathology report
- Pancreas and duodenum, Whipple resection:
- Mucinous cystic neoplasm with low grade intraepithelial neoplasia (8.3 cm) (see comment)
- Negative for high grade intraepithelial neoplasia or malignancy.
- Focal background chronic pancreatitis
- Margins of resection unremarkable.
- Seven benign lymph nodes.
- Comment: The gross cystic lesion was entirely submitted for microscopic analysis.
- Pancreas and duodenum, Whipple resection:
- Focal adenocarcinoma arising from a mucinous cystic neoplasm (see synoptic report)
Differential diagnosis
- Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm:
- Usually at the head of pancreas and communicates with the duct system (MCNs usually do not communicate with the main pancreatic duct)
- IPMNs may be positive for GNAS mutations while MCNs will be negative (Gut Liver 2015;9:571)
- Both have elevated CEA and KRAS mutation in cyst fluid
- Ovarian mucinous tumors:
- Similar clinical and histologic appearance
- Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, large duct variant:
- Will have smaller cysts, clustering of ducts and myxoid stroma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2009;133:423)
- Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma:
- Usually not cystic, shows irregular infiltrative glands with nuclear atypia, no ovarian type stroma
- Pancreatic pseudocyst:
- Mimics MCN when MCN has denuded cyst lining
- MCN cystic fluid has high CEA content and viscosity, high expression of microRNAs, lower amylase (< 250 U/L) and elastase I than pseudocyst, although values may vary within different loculi of same neoplasm (Am J Clin Pathol 1993;100:425, Ann Gastroenterol 2013;26:122, Gastroenterology Res 2014;7:44)
- Serous cystadenoma:
- Has low levels of CEA
Practice question #1
Which of the following findings on fine needle aspiration of a pancreatic cyst are most consistent with a mucinous cystic neoplasm?
- Decreased CEA, decreased amylase, no KRAS mutation, no GNAS mutation
- Elevated CEA, elevated amylase, KRAS mutation, GNAS mutated
- Elevated CEA, highly elevated amylase, no KRAS mutation, no GNAS mutation
- Elevated CEA, variable amylase, KRAS mutation, no GNAS mutation
Practice answer #1
D. Mucinous cystic neoplasms have elevated CEA, variable amylase, KRAS mutation and no GNAS mutation. If a GNAS mutation is present, then the findings will favor an IPMN (answer B). Decreased CEA and amylase with no KRAS or GNAS mutations favor a serous cystadenoma (answer A). An elevated CEA and amylase without KRAS or GNAS mutations will favor a pancreatic pseudocyst (answer C).
Comment Here
Reference: Mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN)
Comment Here
Reference: Mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN)