Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Epithelial type | Mixed epithelial mesenchymal type | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Staging | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Oliveira RC, Cipriano MA. Hepatoblastoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/livertumorhepatoblastoma.html. Accessed August 25th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Malignant primary hepatic blastomatous tumor that reiterates the hepatic development
- Variable combination of epithelial and mesenchymal components
Essential features
- Most frequent liver tumor in children
- Tumor cells recapitulating the embryological stages of hepatic development
- Epithelioid pattern or mixed epithelioid and mesenchymal pattern
- Mainly staged using the PRETEXT (PRE-Treatment EXTent of tumor) system
Epidemiology
- Most frequent liver tumor in children
- 1 - 1.5 cases per million
- Majority of cases (80 - 90%) between 5 months to 6 years old
- Remaining cases in prenatal / neonatal and older children
- Adult tumors are very rare (Surg Oncol 2016;25:339)
- Slight male predominance
Sites
- Liver; some authors refer a preference to the right lobe or state that the tumor starts at the right hepatic lobe (J Hepatol 2012;56:1392)
Pathophysiology
- Current hypothesis is that hepatoblastoma arises from primary hepatoblasts or multipotent hepatic progenitor cells
Etiology
- Majority of cases are sporadic
- Some cases are associated with familial adenomatous polyposis (APC mutations), Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome and trisomy 18 (Pediatr Blood Cancer 2018;65:e26892)
- Strong association with low birth weight, especially if < 1,000 g and parental smoking
Clinical features
- Usually presents with abdominal enlargement, mass or pain
- Anorexia and weight loss may be reported
- Jaundice is an uncommon feature
Epithelial type
- 56% of hepatoblastomas are epithelial type
Fetal pattern (31%)
- Tumor cells in trabeculae 2 - 3 cells thick (resembling fetal liver), separated by sinusoids lined by CD34+ endothelial cells
- Tumor cells are same size or smaller than in nonneoplastic liver
- Distinct cell membranes, uniform, polyhedral, slightly higher nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio, inconspicuous nucleoli and may contain bile
- Minimal pleomorphism, no / rare mitotic figures
- Have dark and light foci related to amount of glycogen and fat
- Extramedullary hematopoiesis common; no portal tracts, bile ducts or ductules at the periphery
- Reduced reticulin, rare mitosis
- Cholangoblastic if ductular differentiation (CK7 / 19 positive) prominent
- Crowded fetal type: crowded cells and 2+ mitotic figures/10 HPF
Embryonal pattern (19%)
- Sheets, ribbons, rosettes, papillary patterns or trabeculae of variable thickness with immature appearance, discohesive small cells with poorly defined cell borders, basophilic cytoplasm, high N:C ratio, prominent nucleoli, coarse chromatin and increased mitotic figures
- Extramedullary hematopoiesis, necrosis and vascular lakes are common; no fat, glycogen or bile
Macrotrabecular pattern (3%)
- Frequent trabeculae > 10 cells thick throughout the tumor, variable cytologic features
Small cell undifferentiated / anaplastic pattern (3%)
- Most primitive form
- Definition: 70%+ small cell areas; however, even small foci should be reported because associated with poor prognosis
- Discohesive sheets of small uniform keratin+ cells with minimal cytoplasm, indistinct cell borders, oval hyperchromatic nuclei, variable prominent nucleoli and increased mitotic figures (Mod Pathol 2003;16:930)
- Resembles small cell carcinoma at other sites
- May have mucoid stroma, hyalinized septae; bile
- Loss of INI1 associated with rhabdoid phenotype
Mixed epithelial mesenchymal type
Definition / general
Positive stains
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
Molecular / cytogenetics description
Differential diagnosis
- 44% of hepatoblastomas are mixed epithelial mesenchymal type
- Mixture of fetal / epithelial and mesenchymal cell types
- Teratoid (34%) or not (10%)
- Mesenchymal component has spindle oval cells with minimal cytoplasm, frequent osteoid, fibrous septa, myxoid zones, hemorrhage and necrosis
- Teratoid features are keratinized squamous epithelium, intestinal epithelial, skeletal muscle, mature bone and cartilage, melanin and neuroectodermal structures
Positive stains
- Alpha fetoprotein (negative in small cell type), chromogranin (fetal, epithelial subtypes, usually focal), CK8 / 18 (fetal, epithelial subtypes), CK19 (embryonal subtypes)
- Also EMA, HepPar1 (negative in small cell type), polyclonal CEA (canalicular pattern), vimentin
- Variable hCG, occasional HMB45 and melanin
- Beta catenin (nuclear) in small cell and embryonal types, delta-like protein (DLK), glypican 3 (negative in small cell type), glutamine synthetase
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Immature hepatocytes
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Gain of Xq in 60%, gain of Xp in 43%, also trisomy 2q (2q+) and trisomy 20, 1p-, 2q-, 4q-, 4q+
- Fetal type usually diploid, embryonal often aneuploid (Hum Pathol 2003;34:864)
- Deletion or translocation of 22q in small cell type (Front Biosci (Elite Ed) 2012;4:1287)
- Also FOXG1 overexpression (Hum Pathol 2007;38:400)
- Yin Yang 1 (YY1) protein (Virchows Arch 2011;458:453)
- SERPINB3 overexpression (Eur J Cancer 2012;48:1219)
Differential diagnosis
- Hepatocellular carcinoma:
- Resembles macrotrabecular variant of hepatoblastoma
- Uncommon in children
- Larger, more pleomorphic tumor cells
- No extramedullary hematopoiesis
- Metastatic tumors:
- More common than hepatoblastoma, primary tumor cells should not resemble hepatocytes
- Lymphoma
- Neuroblastoma
- Rhabdomyosarcoma
- Teratoma
- Undifferentiated sarcoma
- Wilms tumor
- Yolk sac tumor:
- Rare yolk sac cells may be present in hepatoblastoma
Diagnosis
- Usually by a combination of clinical, laboratory and radiology findings (Clin Liver Dis 2018;22:753)
- Biopsy / FNA may be necessary in some cases
Laboratory
- Serum AFP is significantly elevated in the majority of patients (about 90%)
Radiology description
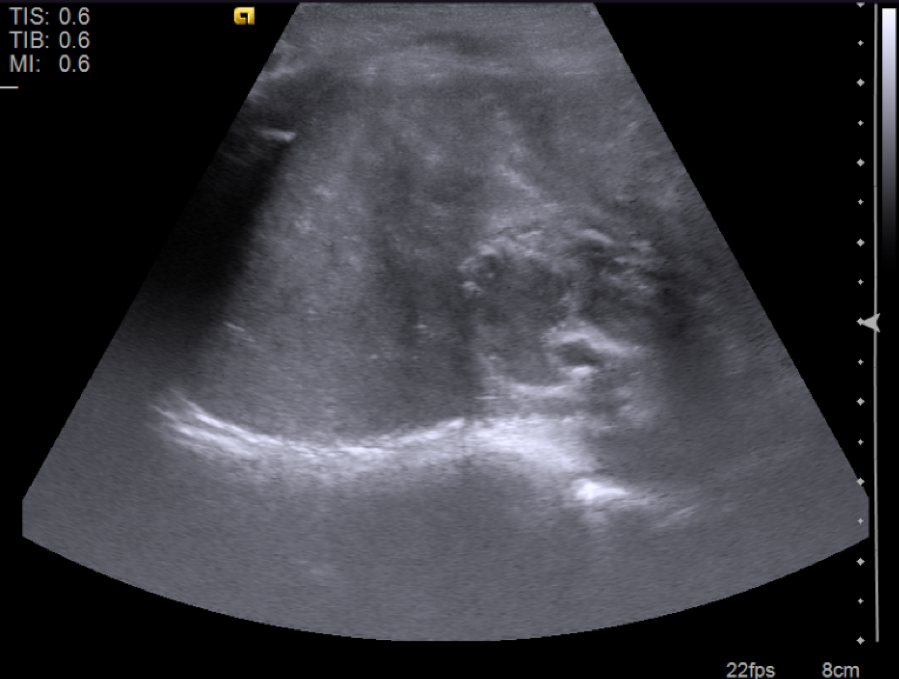
- Ultrasound
- Solid masses that are hyperechoic relative to the adjacent liver, although hypoechoic fibrotic septa can also be seen
- Epithelial hepatoblastomas may appear homogeneous
- Mixed epithelial / mesenchymal tumors exhibit heterogeneous imaging (due to osteoid, cartilaginous and fibrous tissue) and frequently have echogenic calcifications with acoustic shadowing and anechoic foci representing hemorrhage / necrosis (Radiol Bras 2017;50:68)
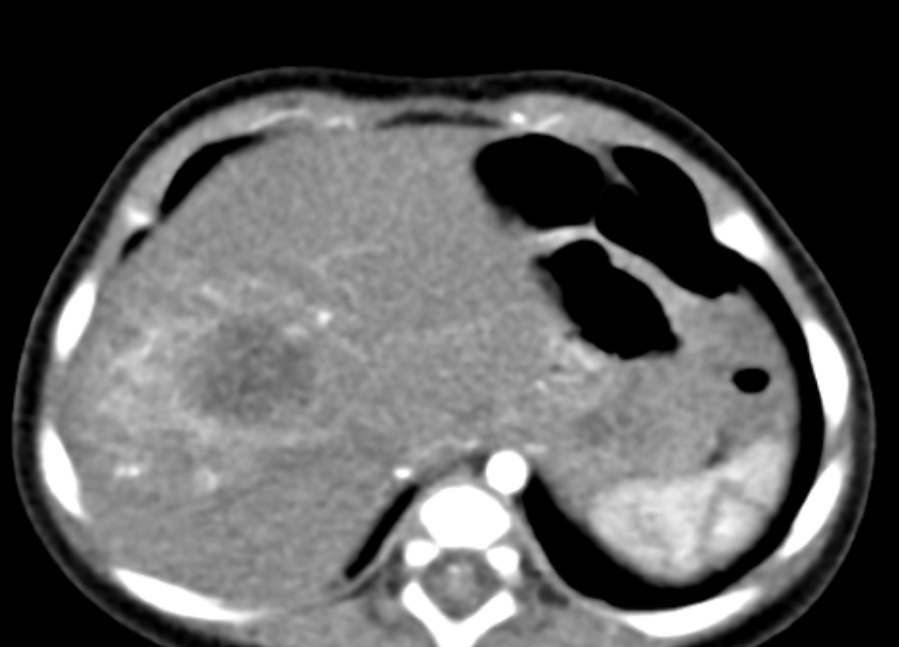
- Computed tomography
- Well defined mass with regular borders that is hypoattenuating in comparison with the adjacent hepatic parenchyma
- Common diffuse heterogeneous contrast enhancement
- Half of all hepatoblastomas appear lobulated or septated, especially on contrast enhanced images (Radiol Bras 2017;50:68)
Radiology images
Staging
- PRETEXT (PRE-Treatment EXTent of tumor) staging system is the recommended by the Pediatric Hepatic International Tumor Trial (PHITT) (Cancer Imaging 2016;16:21)
- Composed by:
- PRETEXT group describes the extent of tumor in the liver and therefore the amount that must be surgically removed
- Liver is divided into 4 sections: left lateral section (Couinaud segments 2 and 3), left medial section (Couinaud segments 4a and 4b), right anterior section (Couinaud segments 5 and 6) and right posterior section (Couinaud segments 6 and 7)
- PRETEXT I: 1 section is involved and the adjoining are free
- PRETEXT II: 1 or 2 sections are involved and 2 adjoining are free
- PRETEXT III: 2 or 3 sections are involved and no 2 adjoining sections are free
- PRETEXT IV: all sections are involved
- Annotation factors that describe additional risk factors
- Hepatic venous / inferior vena cava involvement
- Portal venous involvement
- Extrahepatic spread of disease
- Multifocal tumor
- Tumor rupture
- Caudate lobe involvement
- Lymph node metastases
- Distant metastases
Prognostic factors
- PRETEXT stages I and II are associated with good prognosis and PRETEXT stage IV is a predictor of bad prognosis
- Multifocal disease, extrahepatic and unresectable vascular involvement, tumor rupture and metastasis at diagnosis are factors of bad prognosis (in the pretreatment evaluation)
- After treatment, poor response to chemotherapy, disease progression under chemotherapy, positive surgical margins and tumor relapse are associated with unfavorable prognosis
- Age < 1 year (good prognosis) versus age > 6 years (worse prognosis) (Pediatr Blood Cancer 2020;67:e28350)
- Normal or low levels of alpha fetoprotein (AFP) are associated with aggressive course and small cell undifferentiated histological subtype
- Serum AFP reduction during treatment is a good prognosis and indicator of response to treatment (BMC Pediatr 2019;19:485)
- Histological evaluation has impact: pure fetal pattern with low mitotic activity is related to good prognosis and small cell undifferentiated pattern is associated with bad prognosis
- Based on staging system, metastases and AFP levels, 5 prognostic groups have been established, with group 1 exhibiting the best prognosis and group 5 the worst (Lancet Oncol 2017;18:122)
Group |
|||
Case reports
- 8 day old girl underwent resection of a large hepatoblastoma (Jpn J Surg 1990;20:331)
- 20 month old boy underwent a biopsy which revealed hepatoblastoma, mixed epithelial and embryonal type without mesenchymal elements (Semin Diagn Pathol 2017;34:192)
- 11 year old boy with stage IV hepatoblastoma with lung and omental metastases at diagnosis (Medicine (Baltimore) 2017;96:e5858)
- 22 year old man with a rapidly expanding right hypochondrial mass (Int J Surg Case Rep 2013;4:204)
Treatment
- Chemotherapy and surgical intervention (Curr Opin Pediatr 2014;26:362)
- Complete surgical resection is essential
- Liver transplantation may be necessary (Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016;1:44)
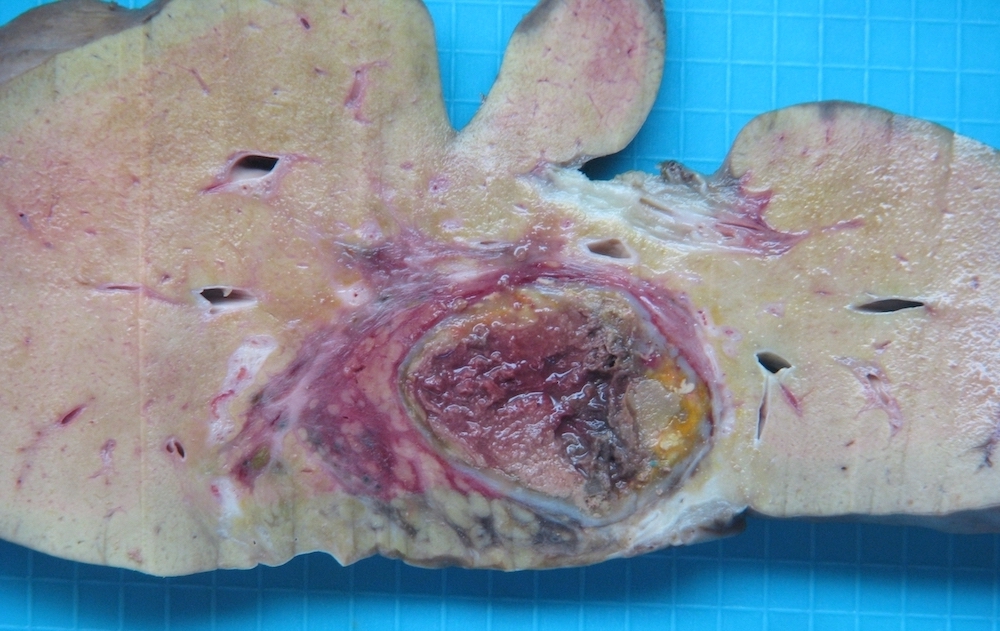
Gross description
- Single or multinodular tumor
- Well defined boundaries
- Tumors usually exhibit a tan-brown cut surface, especially in the fetal subtype (Medicine (Baltimore) 2018;97:e9647)
- Small cell undifferentiated subtypes have a variegated appearance
- Necrosis and hemorrhage are present in posttreatment specimens
- If osteoid is present, the texture is firm and gritty
Gross images
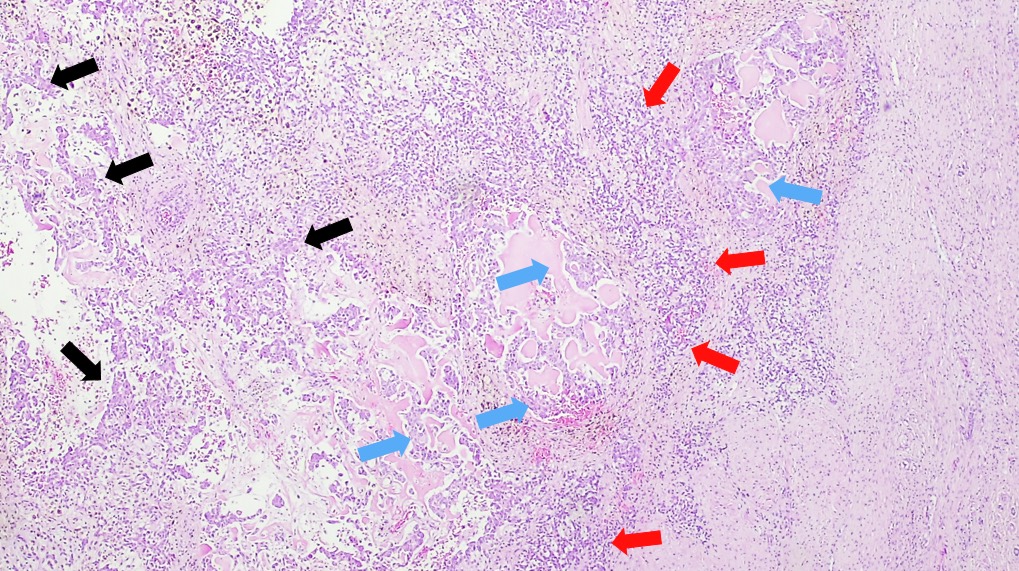
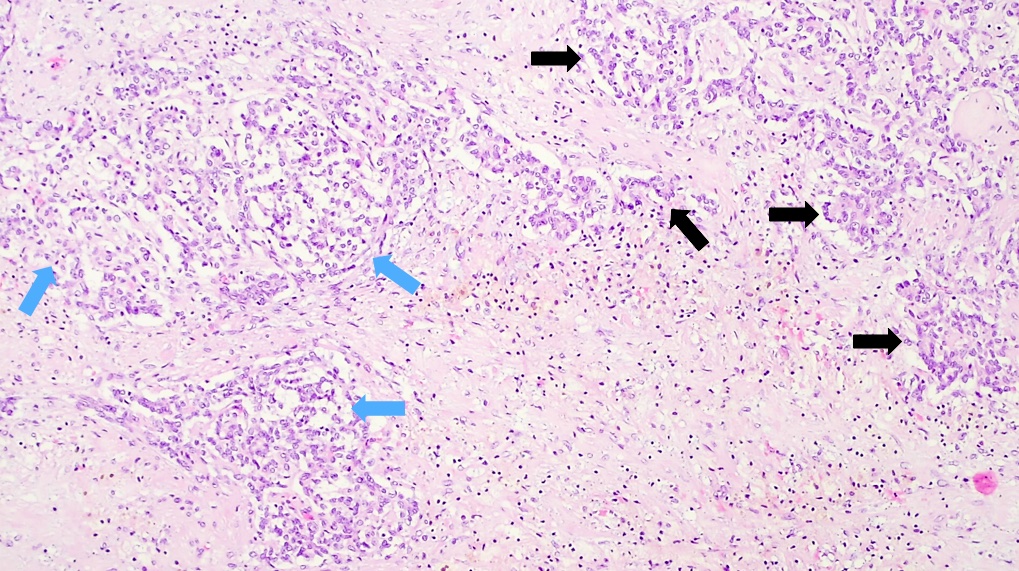
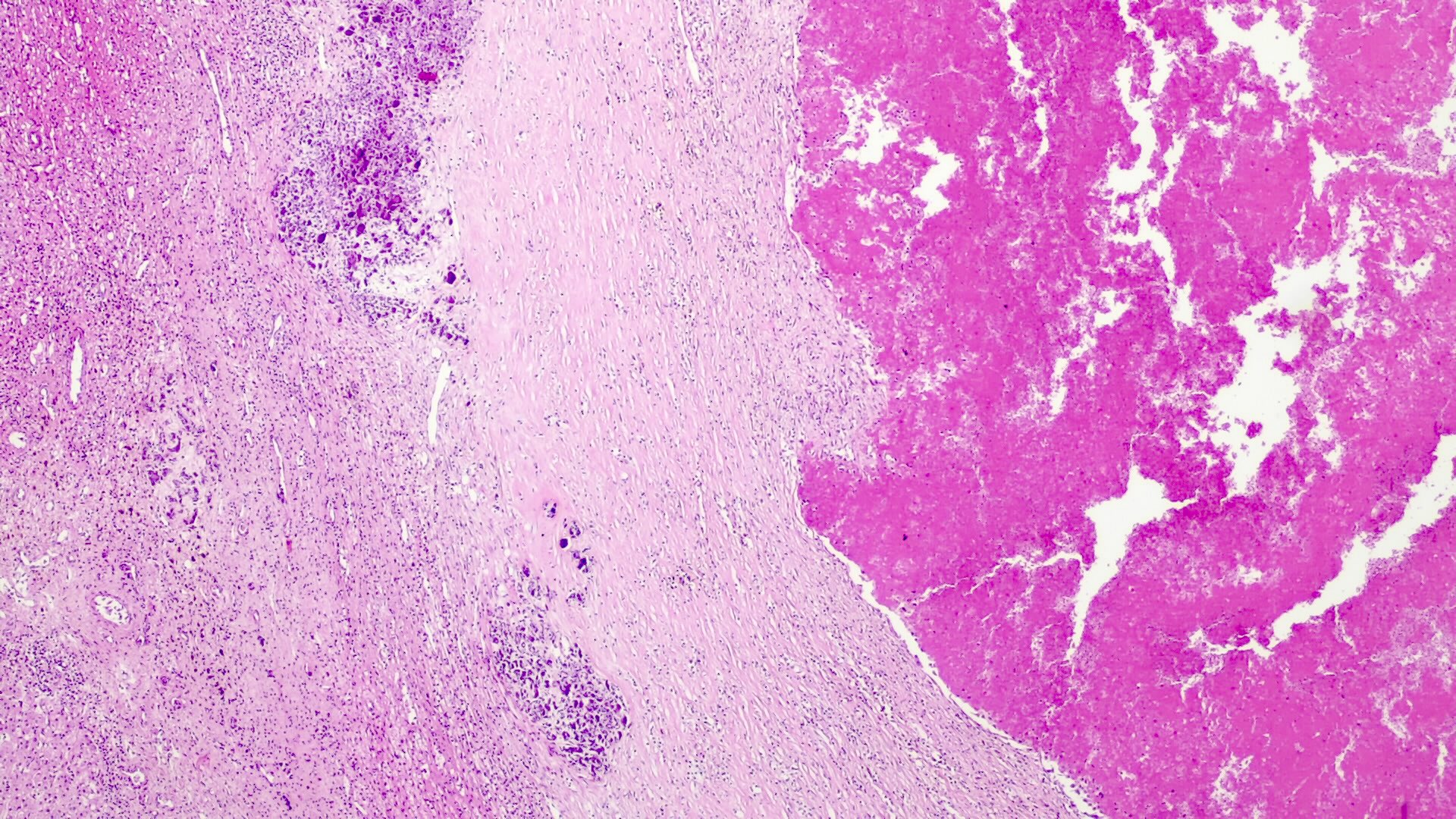
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Classified by the International Pediatric Liver Tumor Consensus Classification as epithelial or mixed epithelial and mesenchymal
- Epithelial hepatoblastoma may exhibit several patterns (alone or in combination): fetal, embryonal, small cell undifferentiated (SCUD), cholangioblastic and macrotrabecular (J Gastrointest Oncol 2018;9:326)
- Fetal pattern (Pediatr Dev Pathol 2020;23:79)
- Thin trabeculae or nests of small to medium sized cells resembling hepatocytes of the developing fetal liver
- Clear or finely granular cytoplasm with variable amount of glycogen and lipids
- Small round nucleus with indistinct nucleolus
- Foci of extramedullary hematopoiesis are usually present
- Typically has low mitotic activity, referred to as well differentiated hepatoblastoma
- A subset has increased mitotic activity, with decreased cytoplasmatic glycogen and pleomorphic nuclei, referred to as mitotically active hepatoblastoma
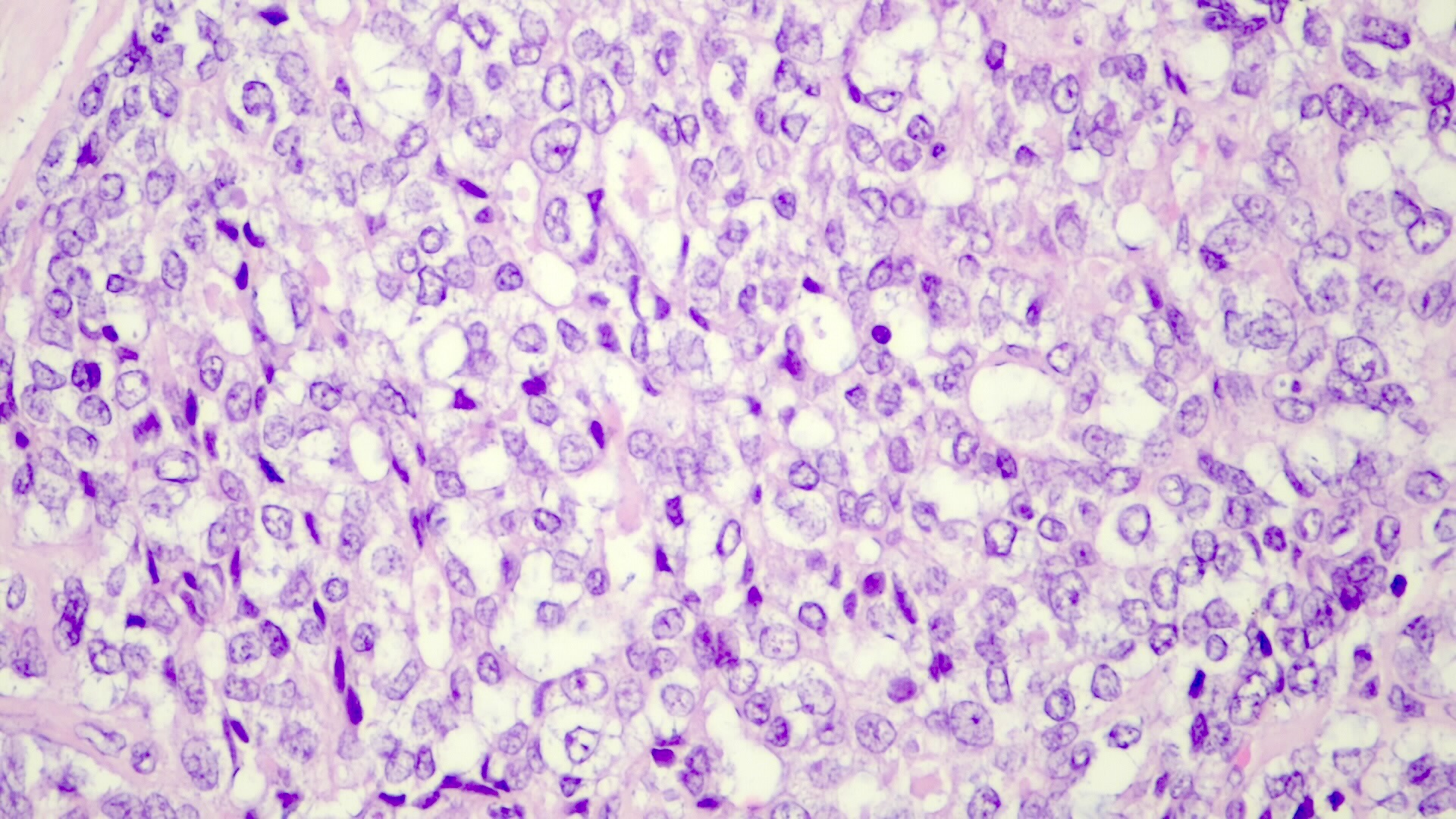
- Embryonal pattern (Pediatr Dev Pathol 2020;23:79)
- Resembles the developing liver at 6 - 8 weeks of gestation
- Solid nests or glandular / acinar morphology, with papillae and pseudorosettes
- Dark and granular cytoplasm without glycogen or lipids
- Enlarged nuclei with coarse chromatin, resembling blastemal cells
- Extramedullary hematopoiesis is usually absent
- Increased mitotic activity
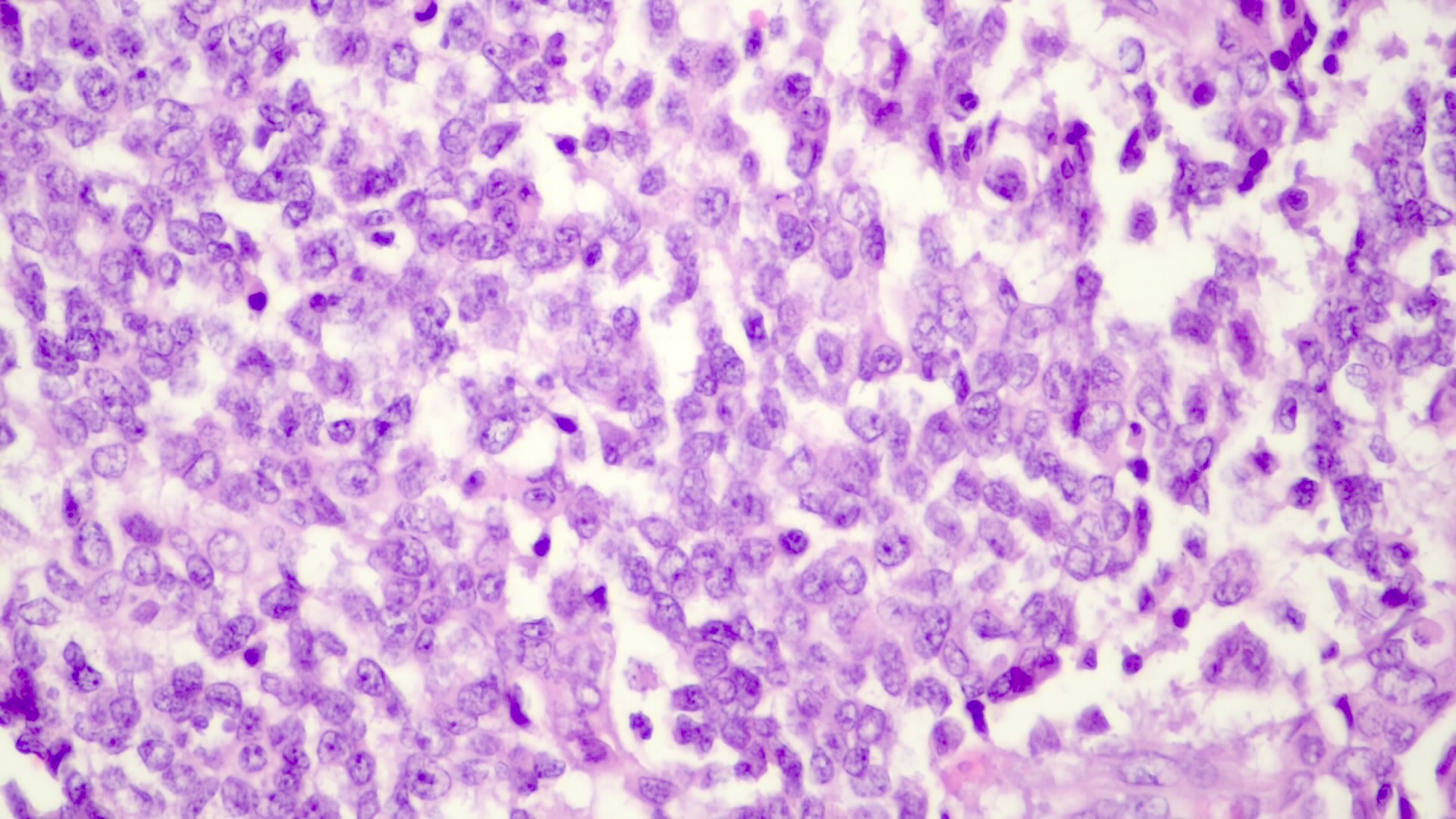
- Small cell undifferentiated pattern (Pediatr Dev Pathol 2020;23:79)
- Solid sheets of discohesive small cells (small, round blue tumor)
- Abundant mitoses, apoptosis and necrosis
- Macrotrabecular pattern
- Thick trabeculae (5 - 12 cells thick)
- Trabeculae may be composed of fetal, embryonal, pleomorphic or hepatocellular carcinoma-like cells
- Cholangioblastic pattern
- Small ducts within or around hepatocellular components
- Mesenchymal pattern (Pediatr Dev Pathol 2020;23:79)
- Mature and immature fibrous tissue
- Osteoid or osteoid-like tissue (more abundant after chemotherapy)
- Hyaline cartilage
- Small subset may exhibit teratoid features: endodermal, neuroectodermal (neuronal cells, glial tissue, melanin producing cells) and complex tissue (striated muscle)
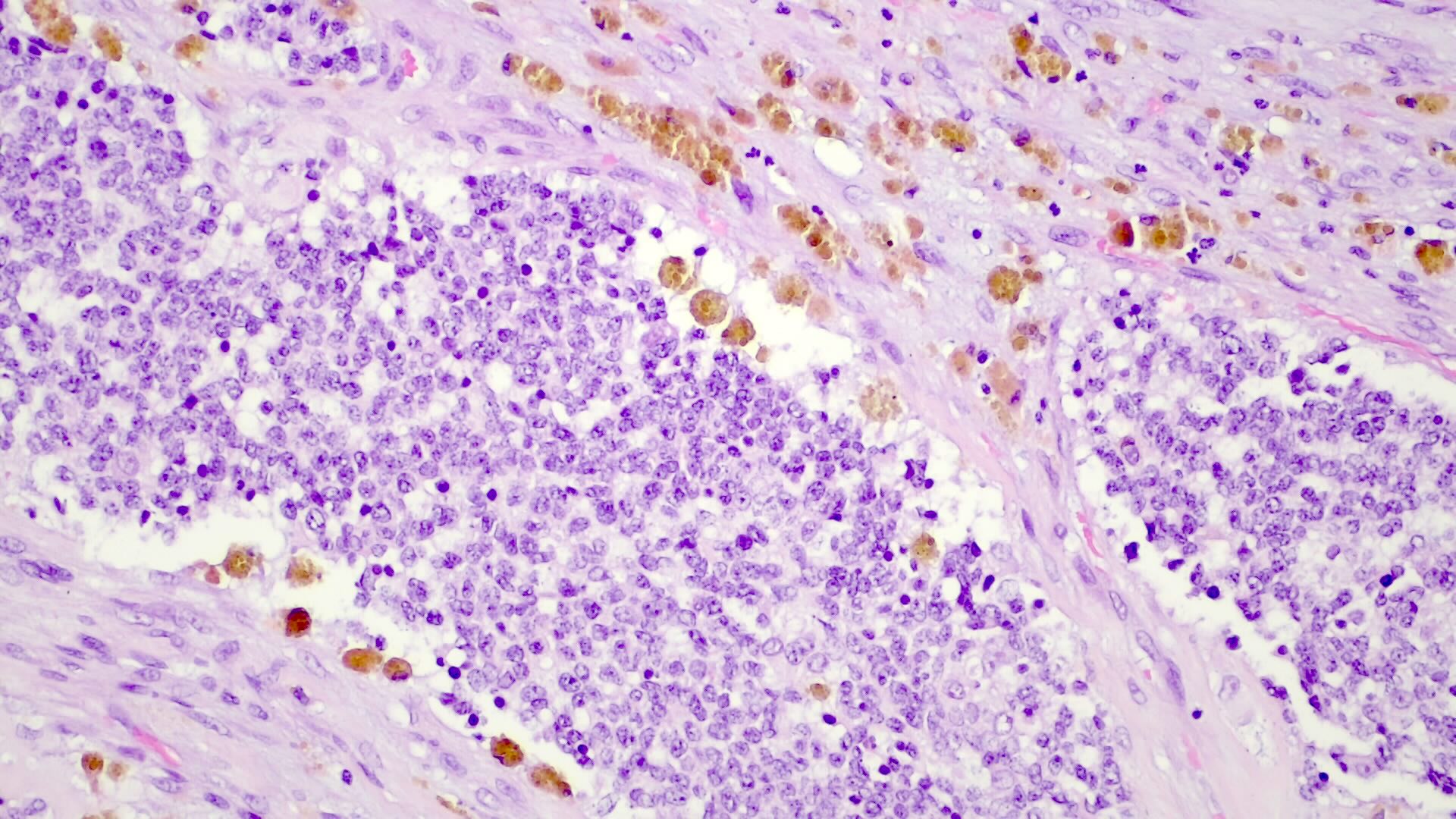
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Relies on clinical correlation of a hepatic mass in children, with elevated serum AFP
- Supported by immunohistochemistry
- High grade elements and a mesenchymal component can be identified (Acta Cytol 2005;49:355, Indian J Pathol Microbiol 2005;48:331)
- Necrosis, mitoses and apoptosis may indicate the diagnosis of embryonal and small cell undifferentiated pattern (Acta Cytol 2005;49:355)
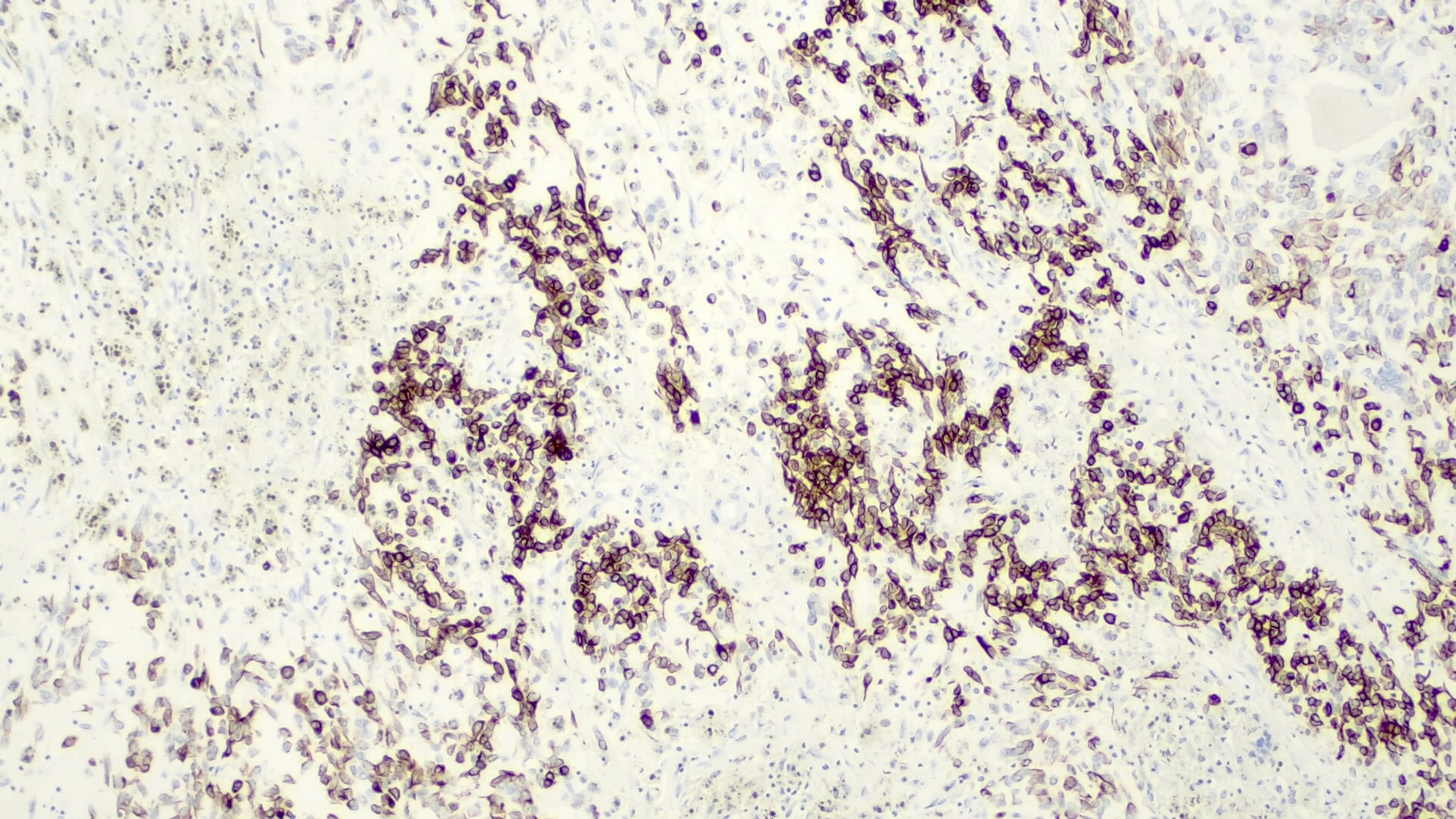
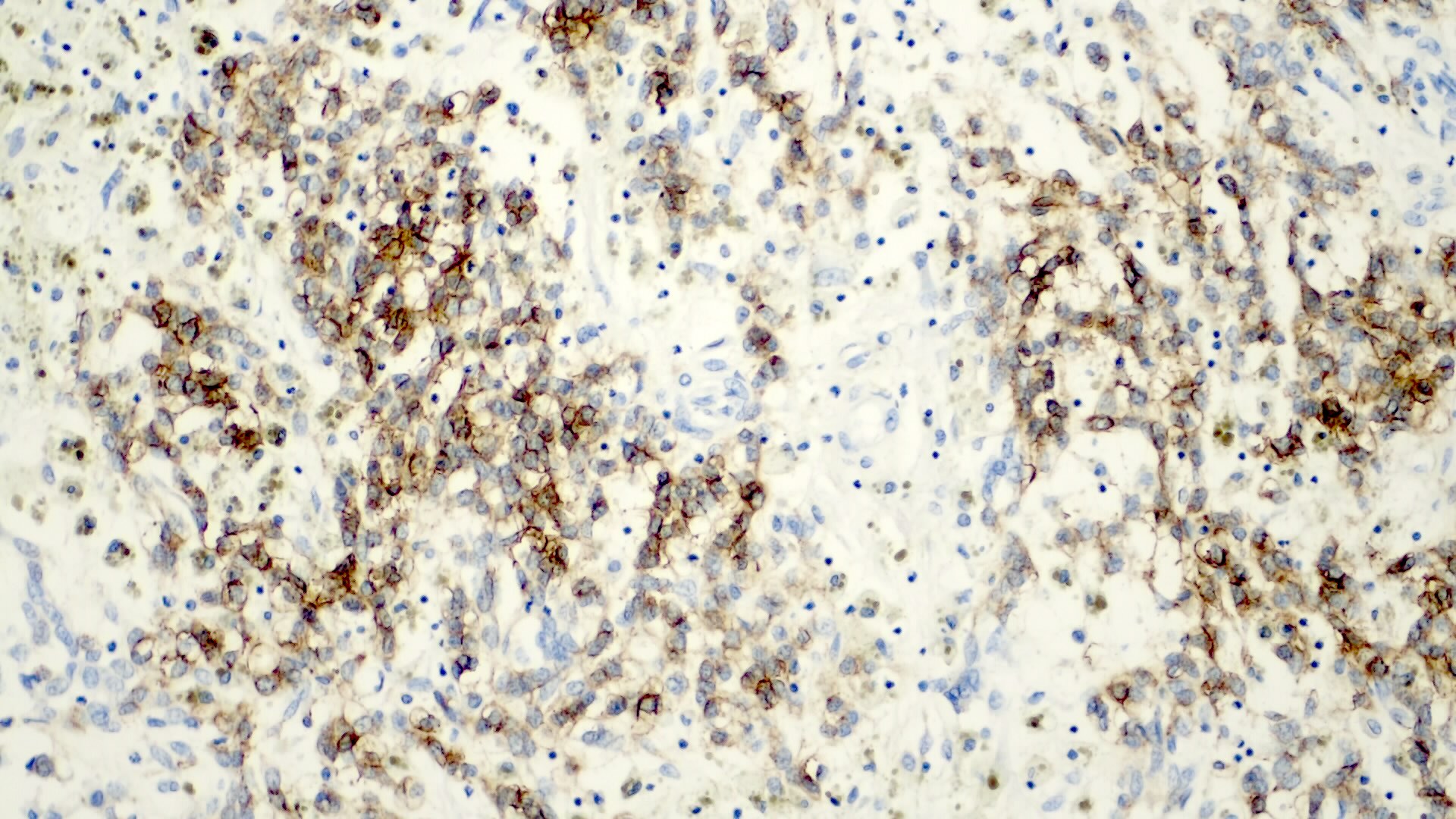
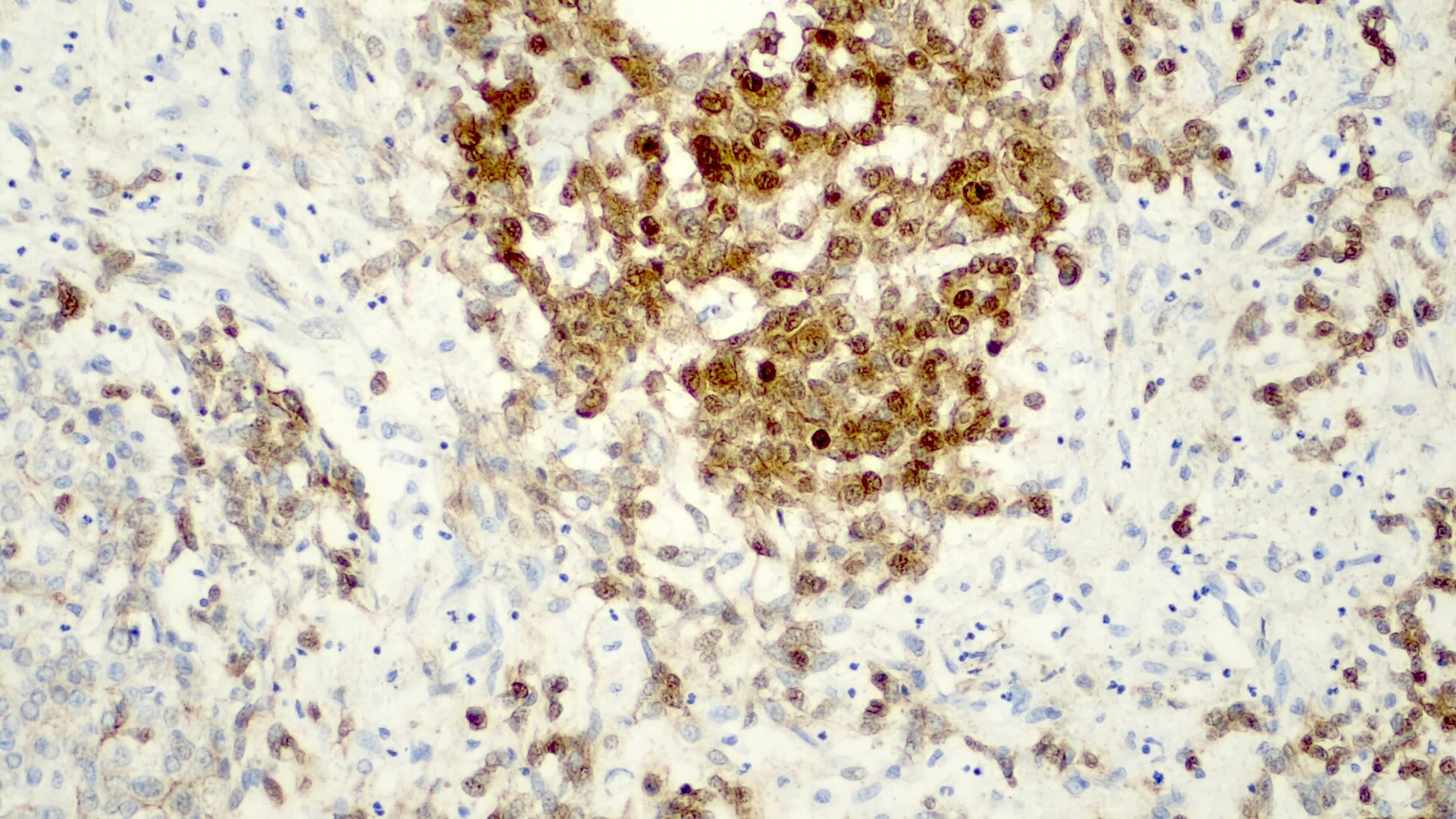
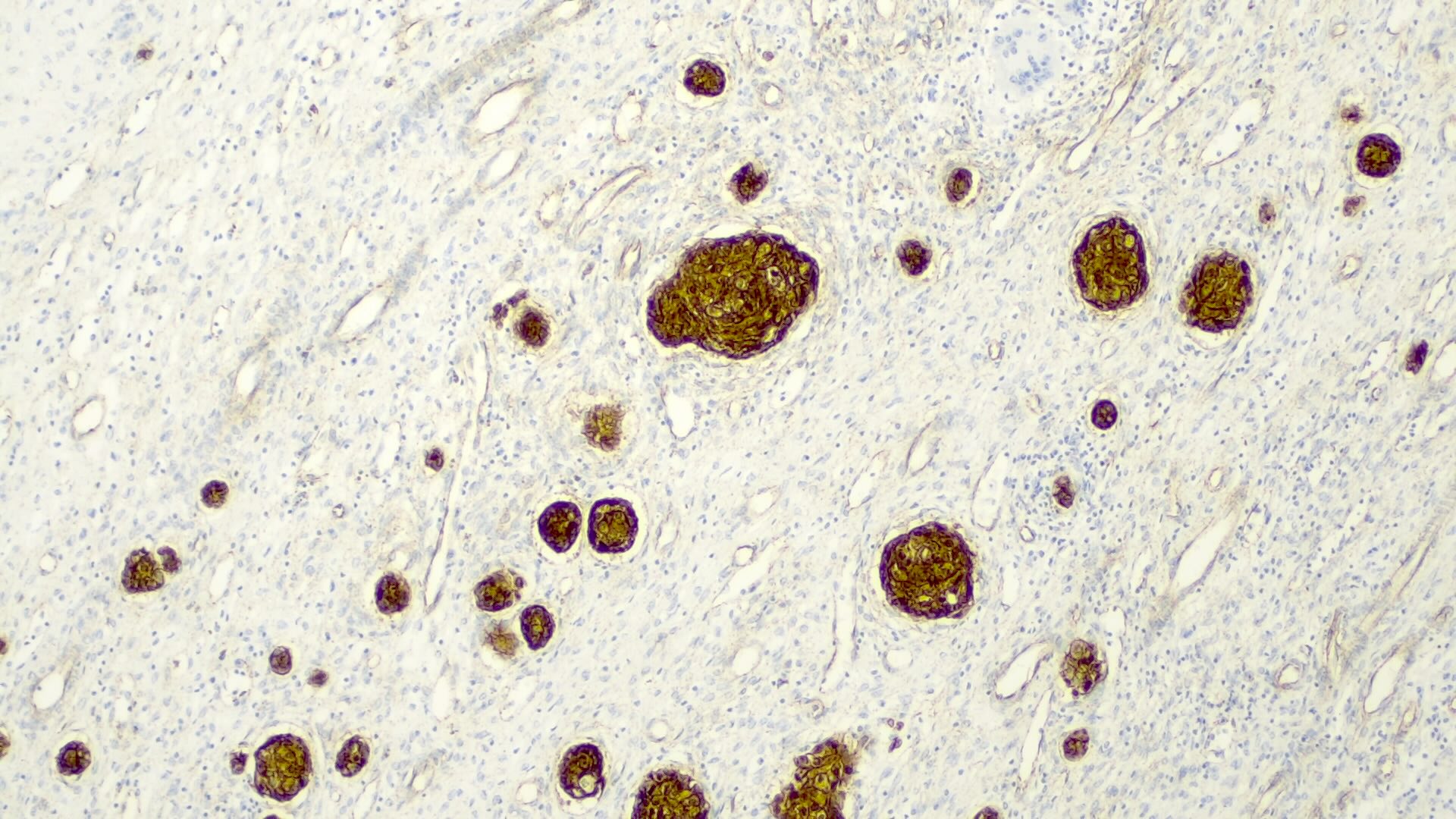
Positive stains
- Frequent beta catenin and glutamine synthetase in the epithelial fetal (except the well differentiated and low mitotic subtype) and mesenchymal patterns (Pediatr Dev Pathol 2020;23:79, Biosci Rep 2019;39:BSR20192466)
- AFP in the less differentiated epithelial components
- HepPar1 in the fetal pattern
- Polyclonal CEA
- Glypican 3 in the fetal and embryonal pattern
- Pancytokeratins have variable expression (J Gastrointest Oncol 2018;9:326)
- CK7 and CK19 in the cholangioblastic pattern (J Gastrointest Oncol 2018;9:326)
- INI1 / SMARCB1 usually retained
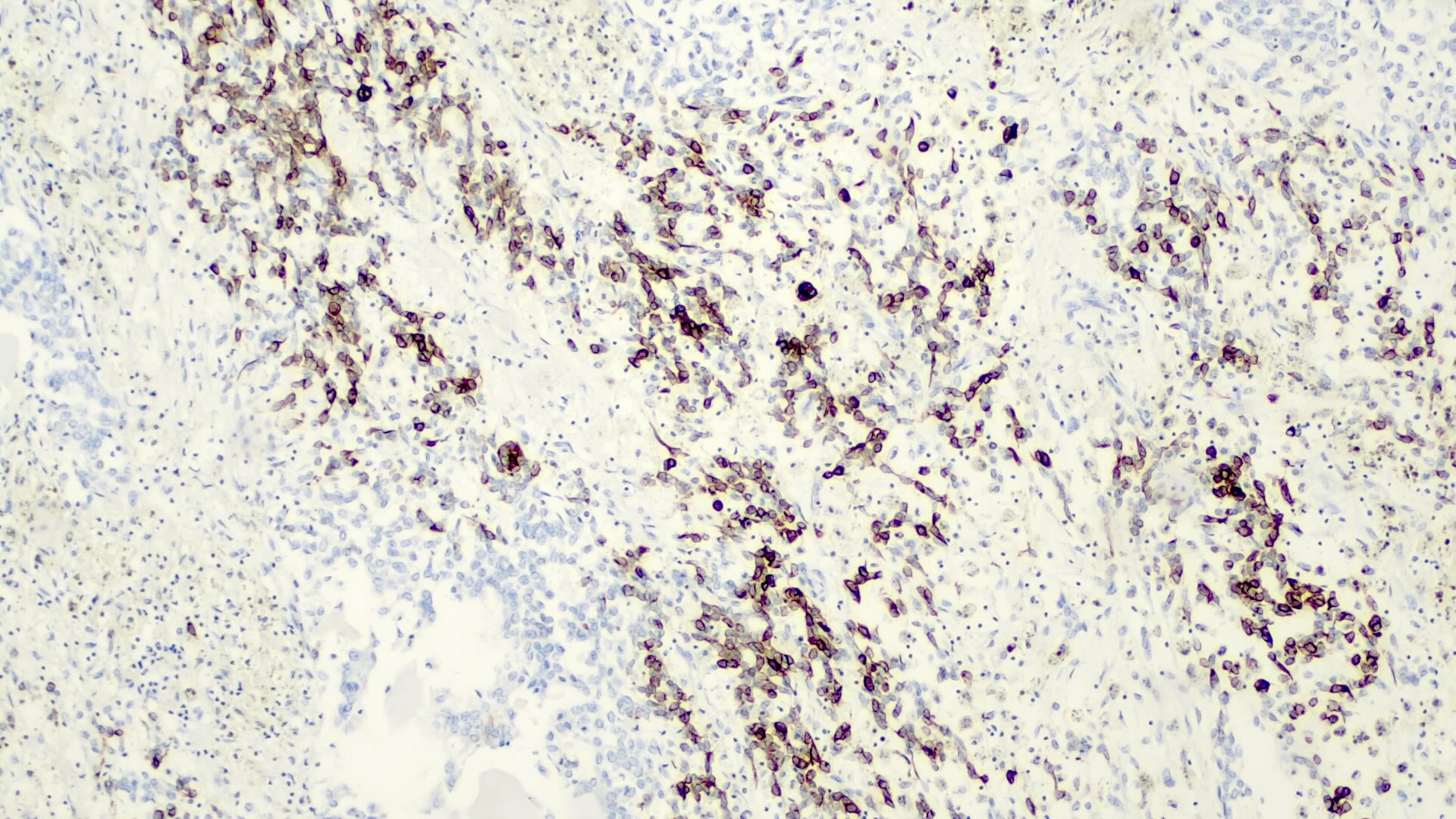
Negative stains
- INI1 / SMARCB1 is lost in a subset of small cell undifferentiated pattern, which has worse prognosis; some authors believe that this represents a malignant rhabdoid tumor rather than hepatoblastoma (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2016;55:925)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Gene expression profile may be helpful in stratifying patients:
- High risk tumors have upregulation of NFE2L2 activity, high LIN28B, HMGA2, SALL4 and AFP expression and high coordinated expression of oncofetal proteins and stem cell markers
- Low risk tumors have LIN28B and let-7 expression and high HNF1A activity (Hepatology 2017;65:104)
Sample pathology report
- Liver, hepatectomy:
- Hepatoblastoma (see comment)
- Comment: There is a neoplasia with well defined boundaries, composed of small to medium sized cells resembling hepatocytes of the developing fetal liver, arranged in trabeculae and with foci of extramedullary hematopoiesis. The tumor exhibits mostly a fetal pattern, with some areas with a cholangioblastic pattern and a small cell undifferentiated pattern in the periphery of the lesion. There is fibrosis, hemosiderin pigment and osteoid-like tissue in the center, with probable association with neoadjuvant chemotherapy, comprising circa 30% of the lesion volume. No vascular invasion was seen. Nontumoral parenchyma without changes.
Differential diagnosis
- Rhabdoid tumor:
- Positive for desmin
- Rhabdoid morphology, without the diversity of patterns
- Well differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma:
- Positive only for hepatocellular markers
- Usually in a cirrhotic liver background
- No mesenchymal or fetal components
Additional references
Practice question #1
Regarding evaluation of hepatoblastoma, which staging system has the best prognostic value?
- AJCC
- LI-RADS
- PRETEXT
- TNM
Practice answer #1
Practice question #2
Practice answer #2