Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2 | Board review style question #3 | Board review style answer #3Cite this page: Motanagh SA, Muller KE. Myofibroblastoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastmyofibroblastoma.html. Accessed April 26th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Benign spindle cell tumor of mammary stroma composed of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts with recurrent monoallelic loss of 13q14 region including RB1
- First recognized in 1981 and described by Wagotz in 1987 (Am J Surg Pathol 1987;11:493)
- When present in mesenchymal soft tissue, termed mammary type myofibroblastoma
- Rarely involves the lower genital tract, predominantly vagina (less commonly vulva and cervix)
Essential features
- Well circumscribed spindle cell tumor comprised of short fascicles of bland spindled cells and dense hyalinized collagen bundles
- Variants include collagenized / fibrous, cellular, infiltrative, myxoid, deciduoid, epithelioid, lipomatous and atypical
- Part of 13q / Rb family of tumors, as majority show deletion or rearrangement of 13q (13q14), which may result in loss of Rb expression by immunohistochemistry
- Benign and adequately treated by excision alone
Terminology
- Mammary type myofibroblastoma
- Benign stromal spindle cell tumor with predominant myofibroblastic differentiation
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8825/0 - myofibroblastoma
- ICD-10: D24.9 - benign neoplasm of unspecified breast
- ICD-11: 2F30 & XH3NQ0 - benign neoplasm of breast & myofibroblastoma
Epidemiology
- Breast: 25 - 87 years, F = M, predominantly seen in postmenopausal women and older men (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2008;132:1813)
- Soft tissue: median age 55 years, 80% men
- No race predilection (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2008;132:1813)
- Limited cases reported in the setting of gynecomastia (Int J Surg Pathol 2001;9:331, Oncol Rep 1998;5:731)
Sites
- Breast, can also occur in extramammary sites including vagina, vulva, inguinal / groin, abdominal wall, perineum and paratesticular region (Oncol Rep 1998;5:731, Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:361, Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:1022, Ann Diagn Pathol 2010;14:358)
- Soft tissue: usually subcutis but may be deeper
Pathophysiology
- Arises from CD34+ mammary stromal fibroblasts and myofibroblasts capable of multidirectional mesenchymal differentiation (Ultrastruct Pathol 1999;23:249)
- Some debate exists over cells of origin and differentiation, myofibroblastic versus smooth muscle (Histopathology 2003;42:233, Ultrastruct Pathol 1999;23:249)
- Part of the so called 13q / Rb family of tumors, which have deletion or rearrangement of 13q14 resulting in loss of Rb expression by immunohistochemistry (J Pathol 2000;191:282, Hum Pathol 2012;43:1887, Mod Pathol 2011;24:82)
Etiology
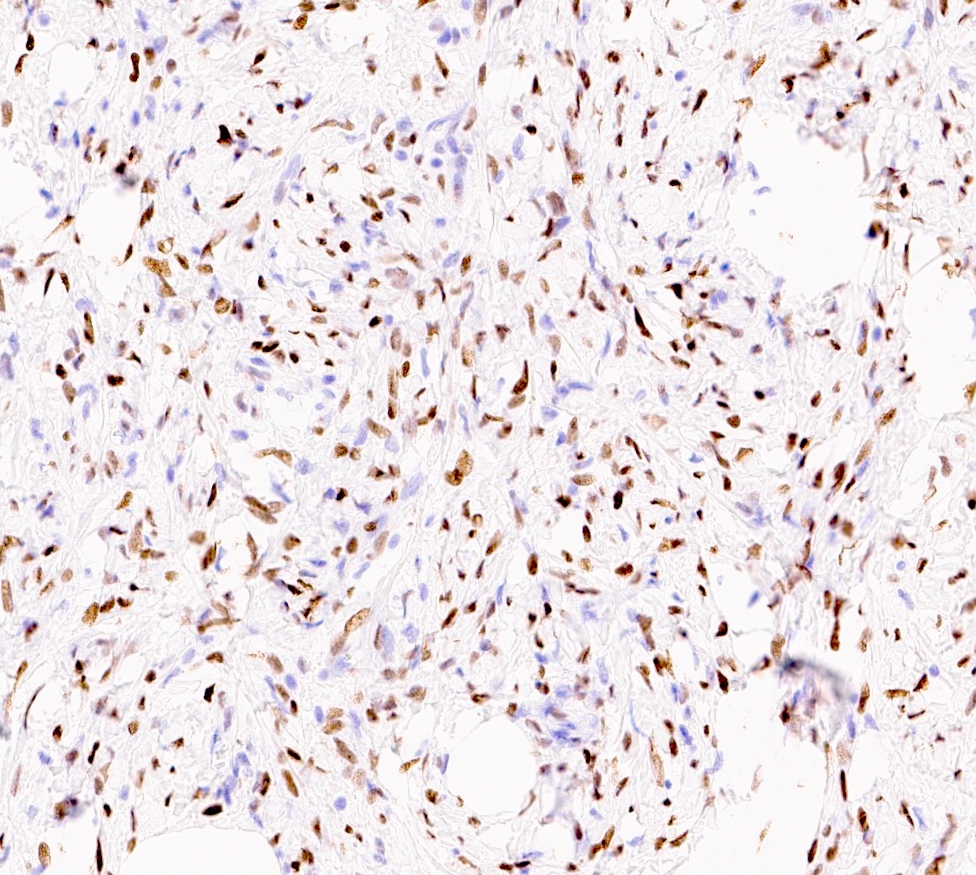
- Pathogenetic role of hormones has been suggested due to ER, PR and AR expression (Histopathology 2000;36:515, Hum Pathol 1998;29:347)
Clinical features
- Painless, nontender, slow growing, mobile mass
- Clinically mistaken for fibroadenoma
Diagnosis
- Imaging: ultrasound, mammogram, MRI
- Invasive procedure: biopsy, fine needle aspiration (FNA)
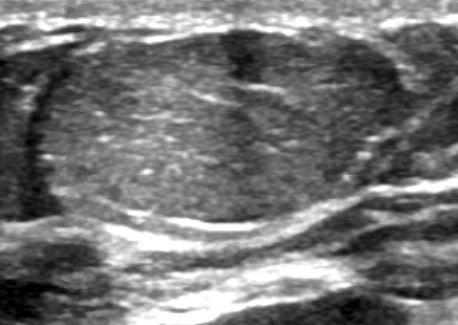
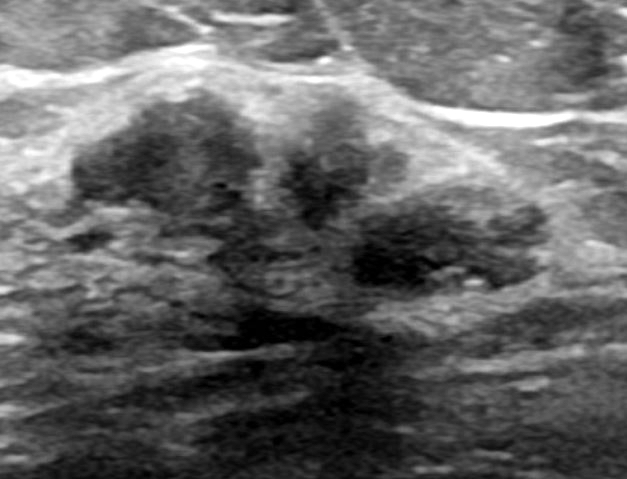
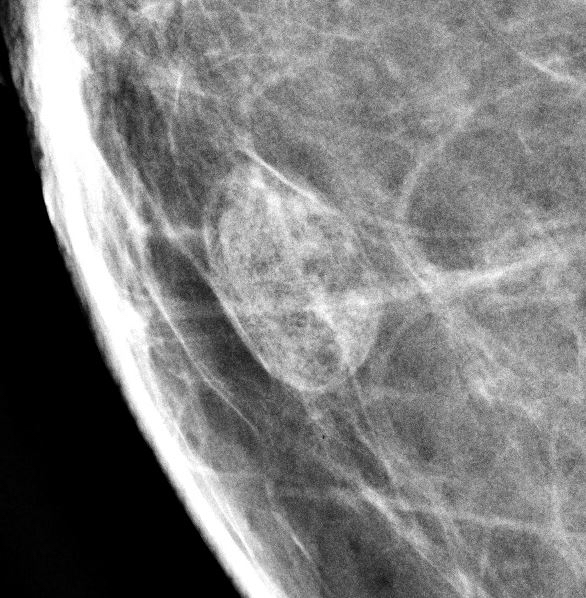
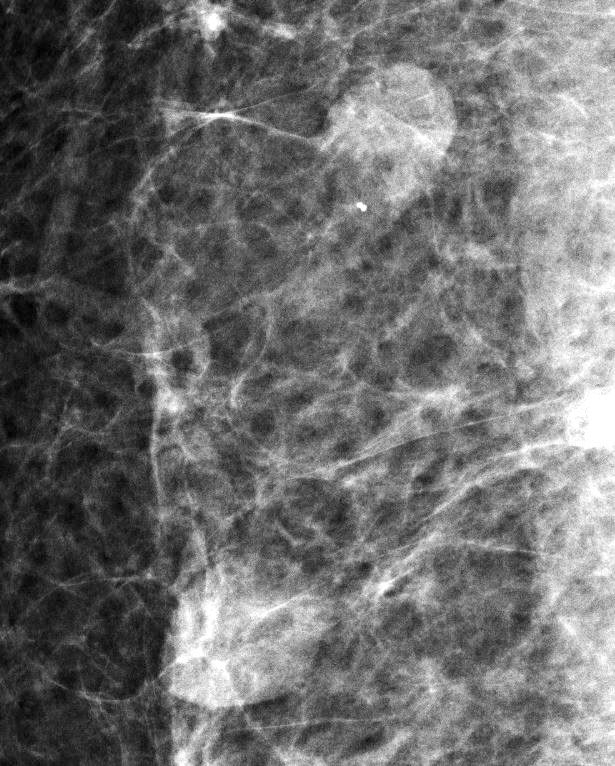
Radiology description
- Well circumscribed, homogenous, hyperdense or isodense, solid mass (Clin Imaging 2018;51:300)
- Typically devoid of calcifications
- Hypoechoic on ultrasound, may have posterior enhancement
- May be multilobulated
- Bilateral and multicentric tumors rare (Mod Pathol 1996;9:786, Int J Surg Pathol 2018;26:242)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Clinically benign behavior, local excision is curative
- No tendency for recurrence or distant metastasis (Virchows Arch 2002;440:249)
Case reports
- 37 year old woman with superficial myofibroblastoma in the vulva (Case Rep Pathol 2019;2019:1582714)
- 53 year old woman with epithelioid myofibroblastoma mimicking invasive lobular carcinoma (Int J Surg Pathol 2015;23:284)
- 55 year old postmenopausal woman with 2 cm mass (J Midlife Health 2018;9:47)
- 55 year old woman underwent a breast needle core biopsy after routine mammography that showed a slight interval size increase of a subcentimeter nodule (Case of the month #536)
- 61 year old man with 8 cm mass who presented first with shoulder pain (J Breast Health 2017;13:100)
- 62 year old man with giant myofibroblastoma arising in the background of gynecomastia (Malays J Med Sci 2012;19:74)
- 63 year old woman with vaginal superficial myofibroblastoma (Rom J Morphol Embryol 2007;48:165)
- 73 year old man with retroareolar mass on CT (Clin Imaging 2017;42:109)
- 74 year old man with bilateral multiple mammary myofibroblastomas (Int J Surg Pathol 2018;26:242)
- Myofibroblastoma with extensive myxoedematous stroma (Pathol Res Pract 2014;210:1106)
Treatment
- Surgical excision alone
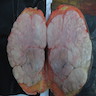
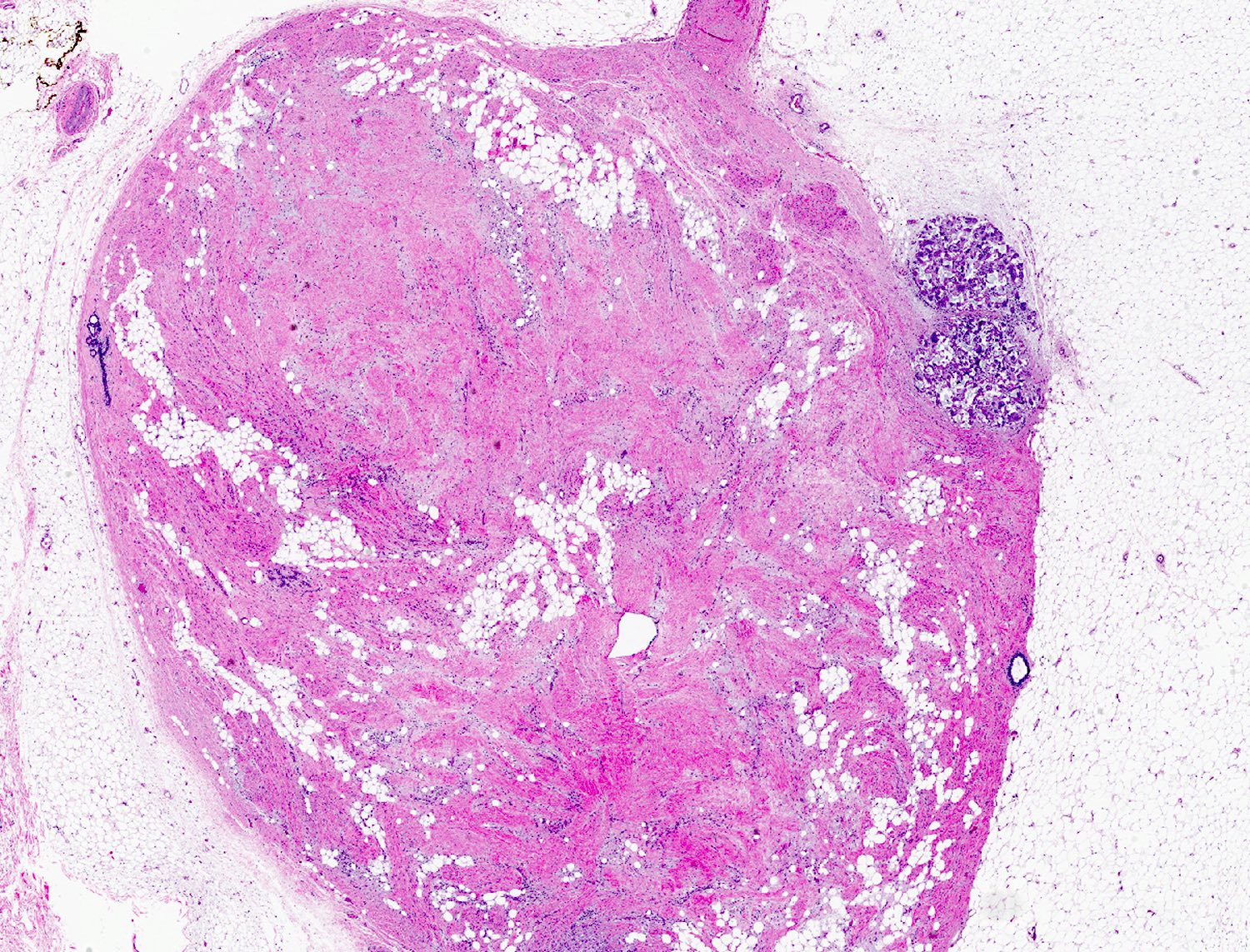
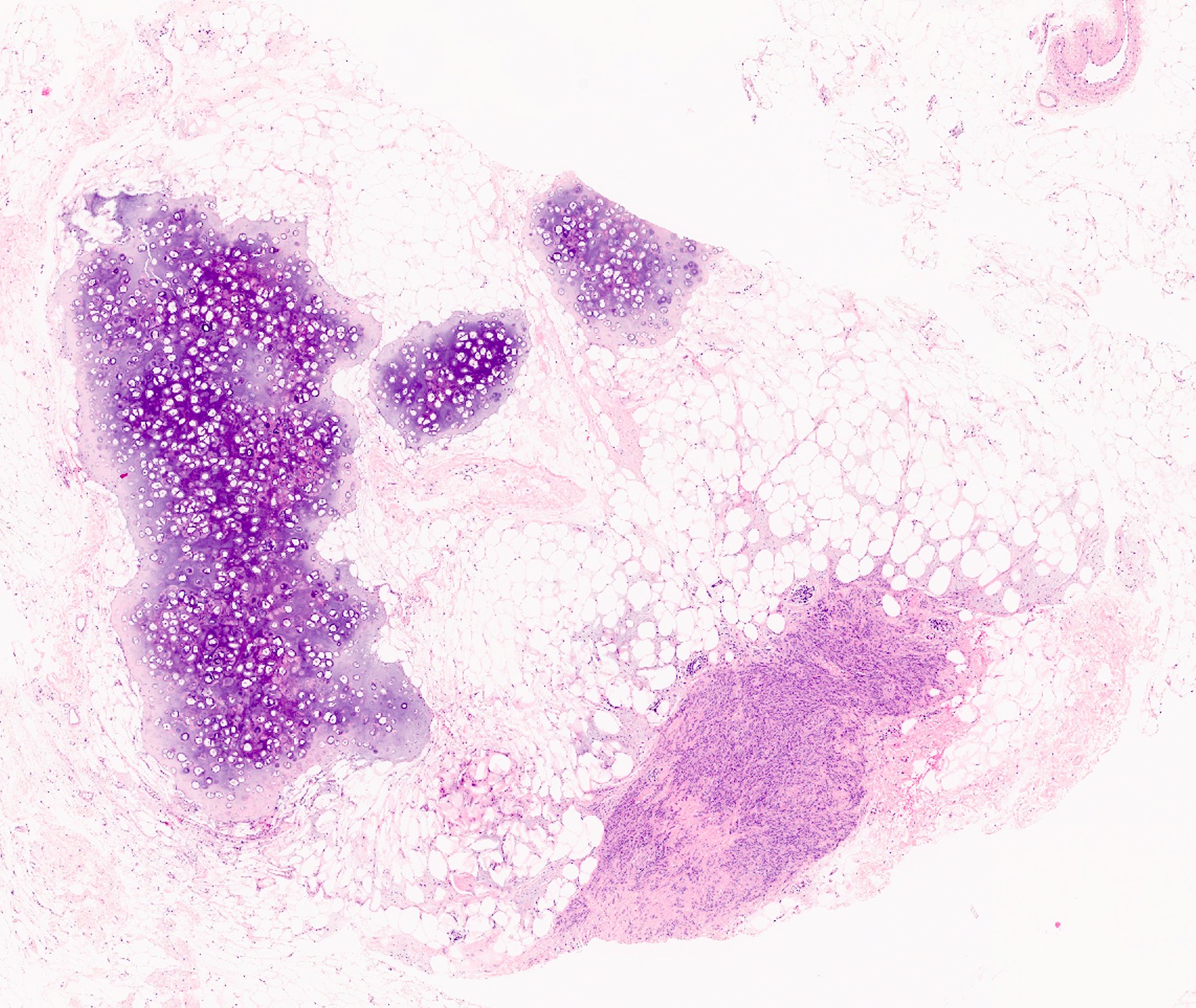
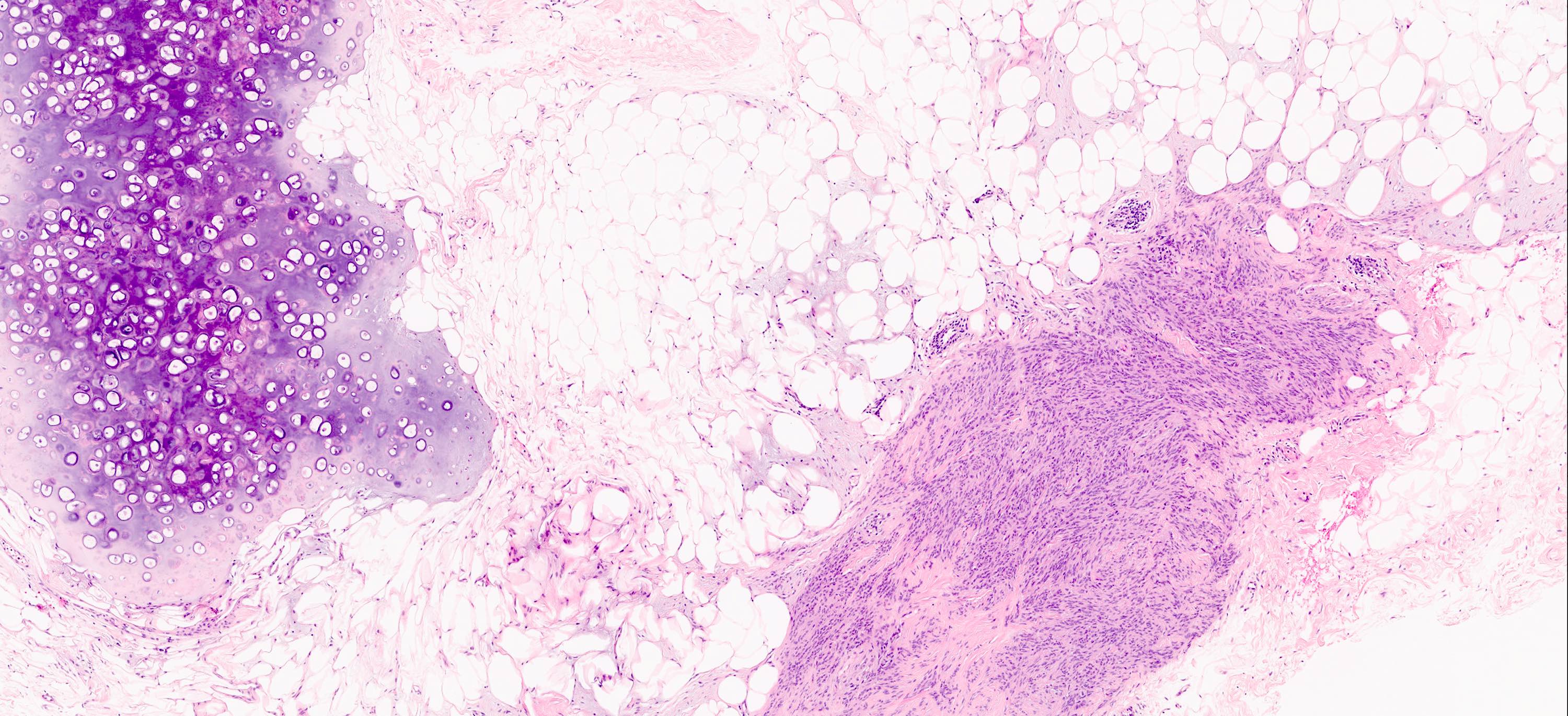
Gross description
- 2 mm to 15 cm, most cases not exceeding 3 cm (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2008;132:1813, Am J Surg Pathol 1994;18:1170)
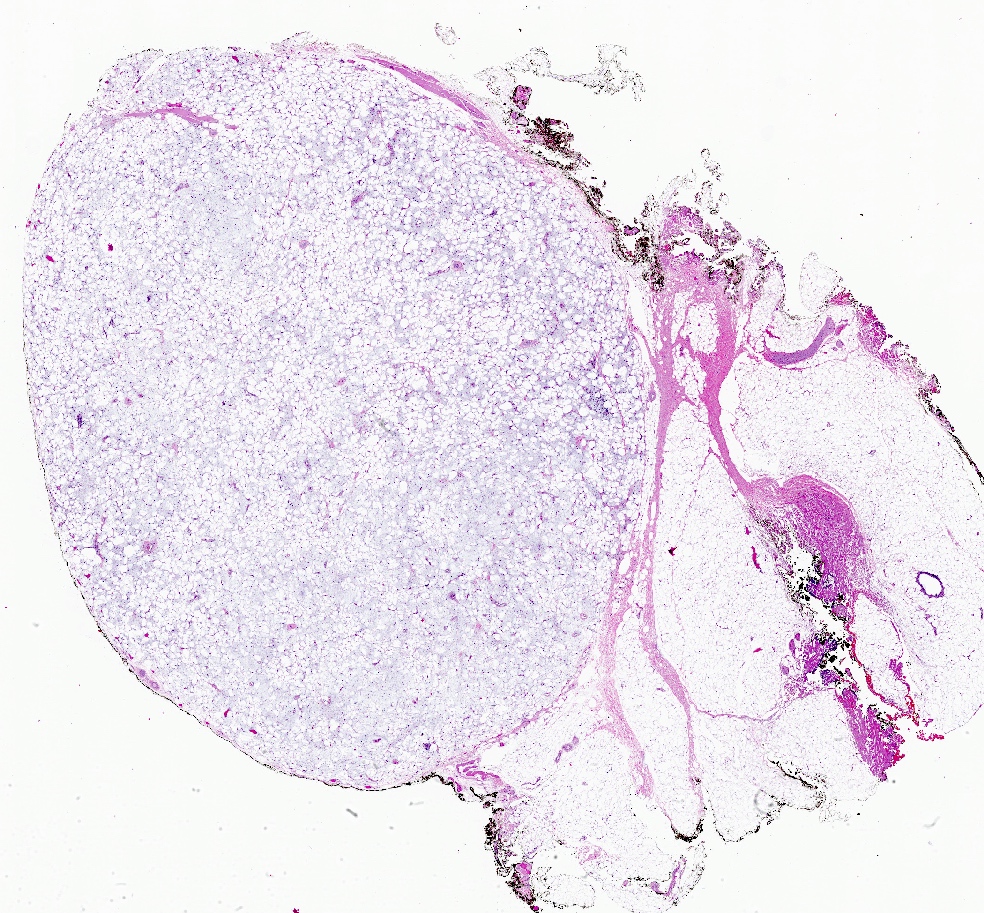
- Well circumscribed, unencapsulated solid mass
- Firm, rubbery to gelatinous, whitish gray to pink nodular or whorled cut surface
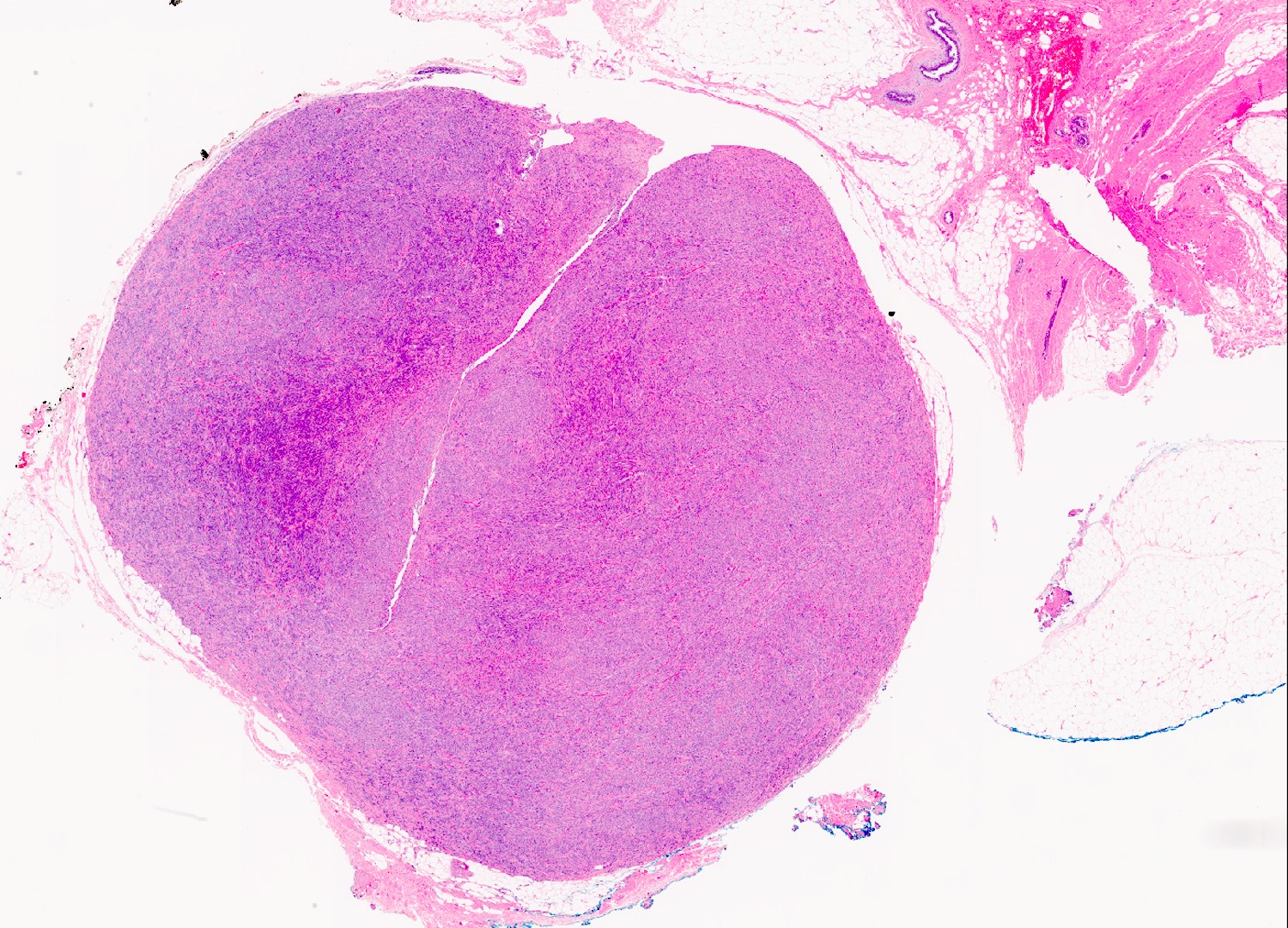
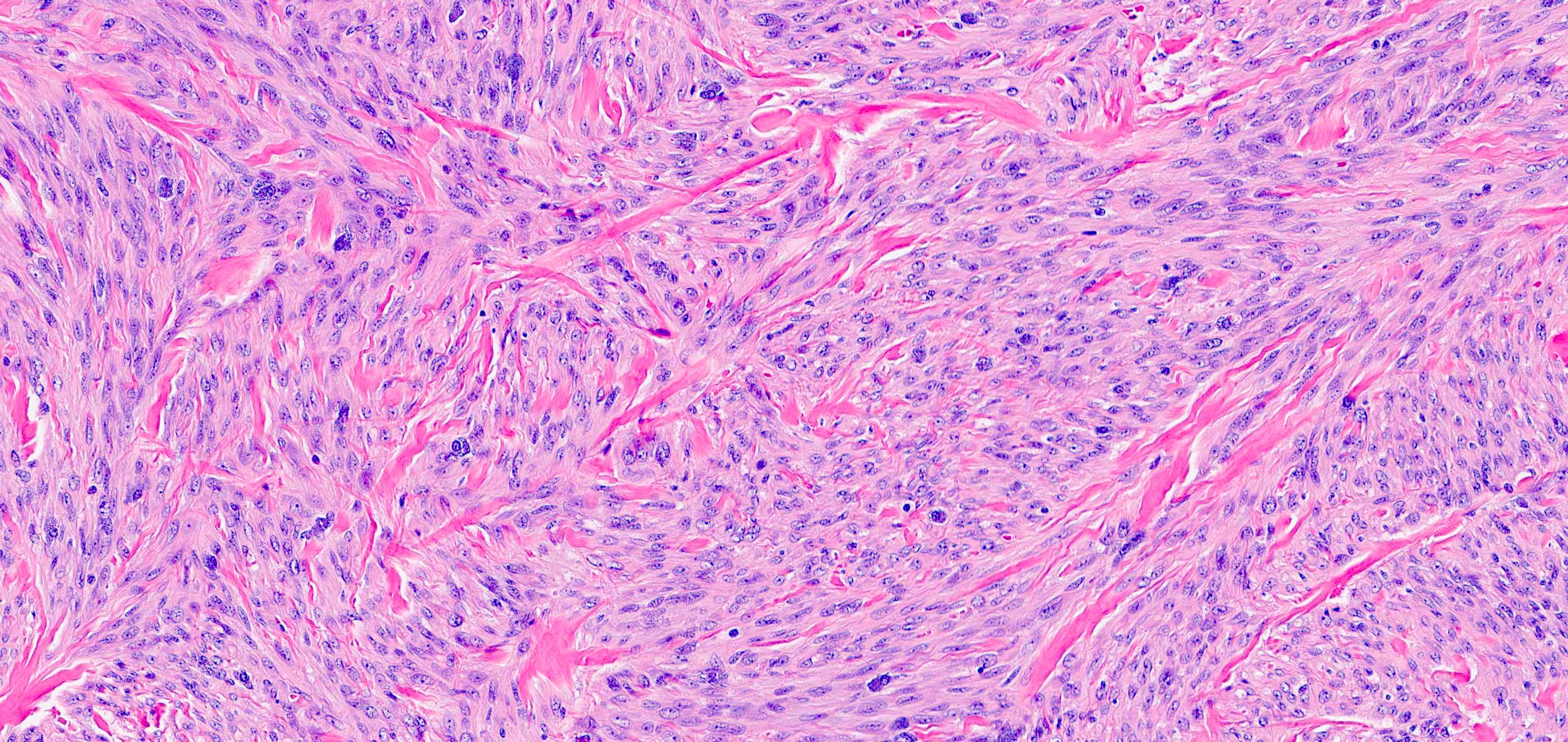
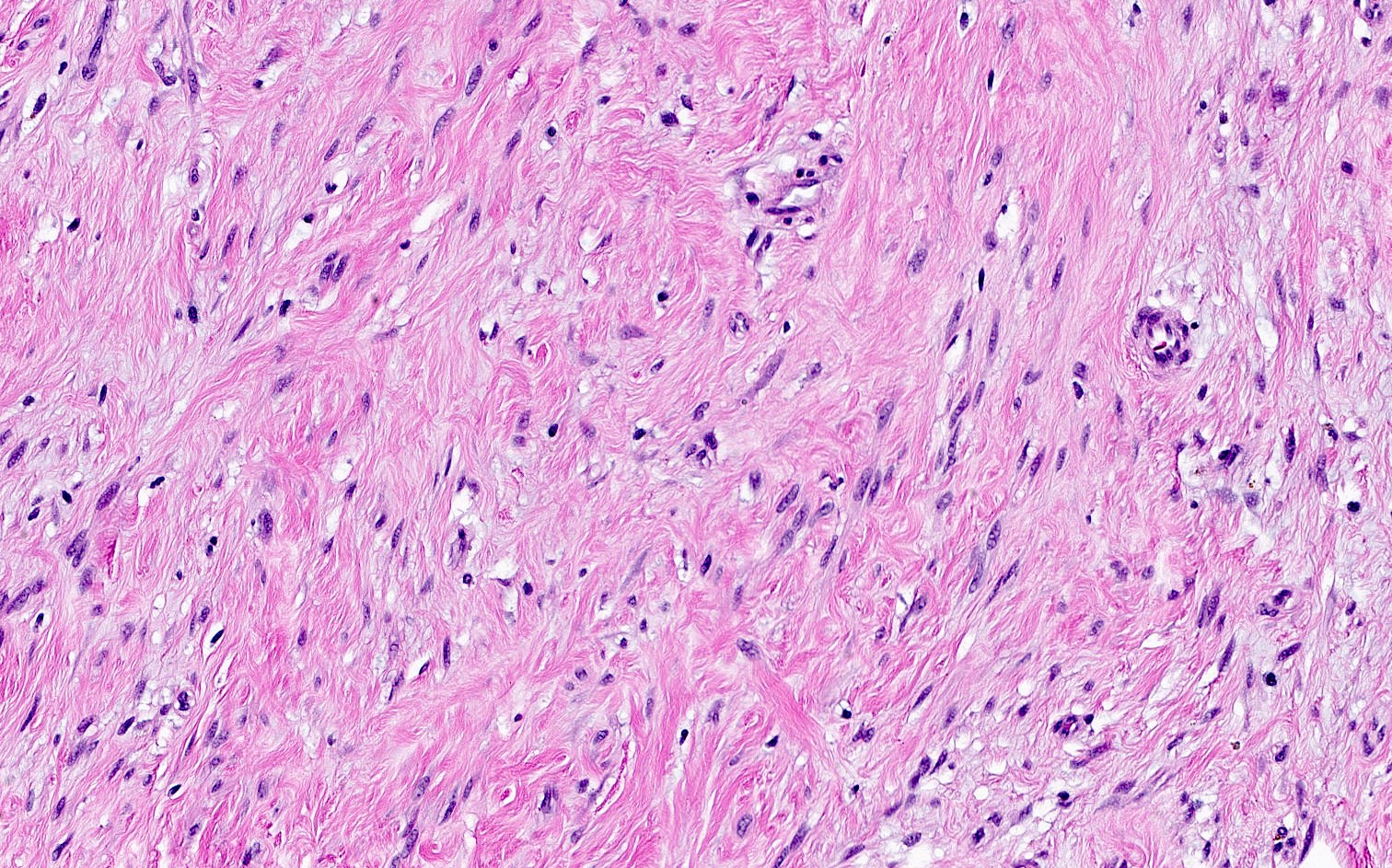
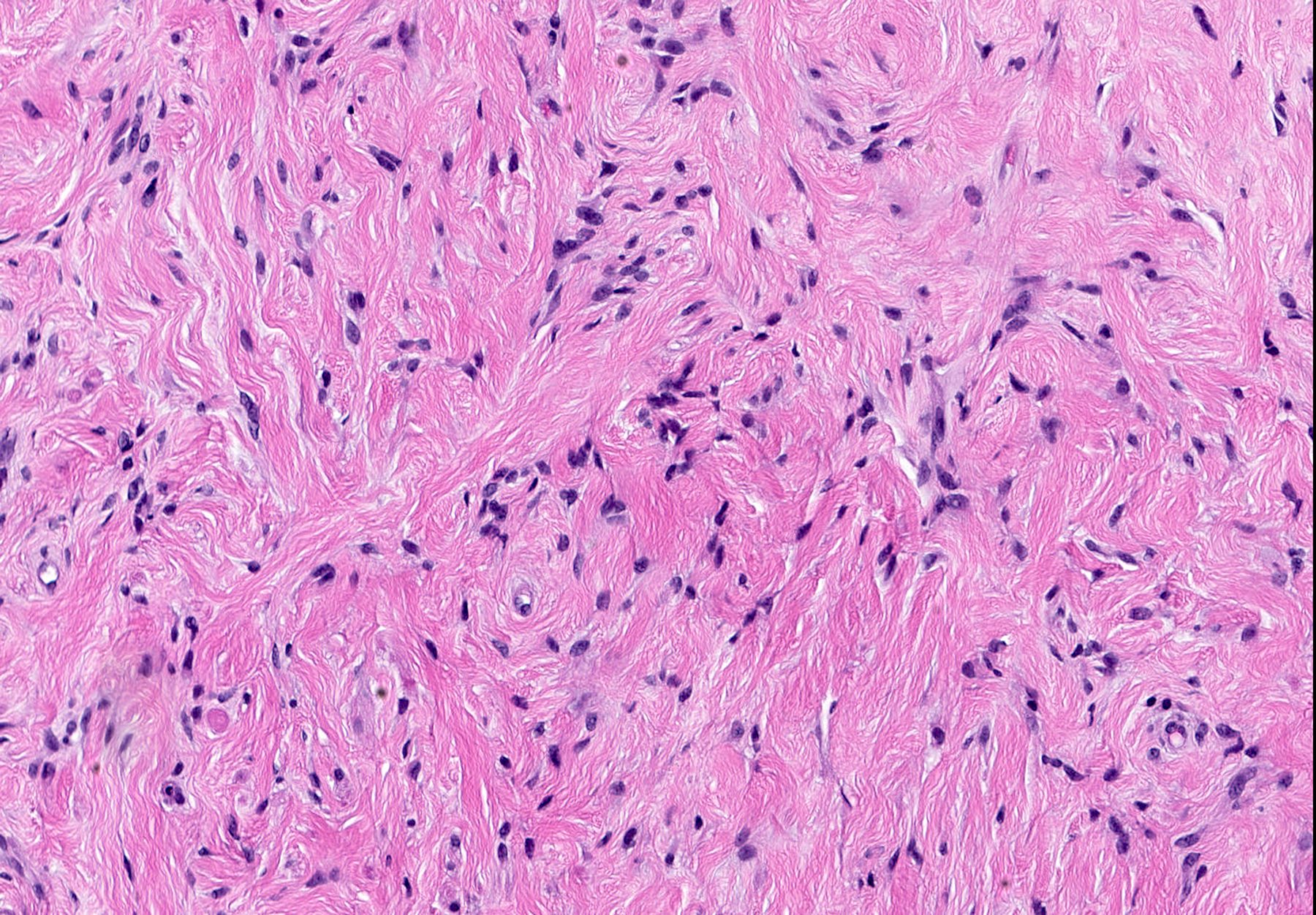
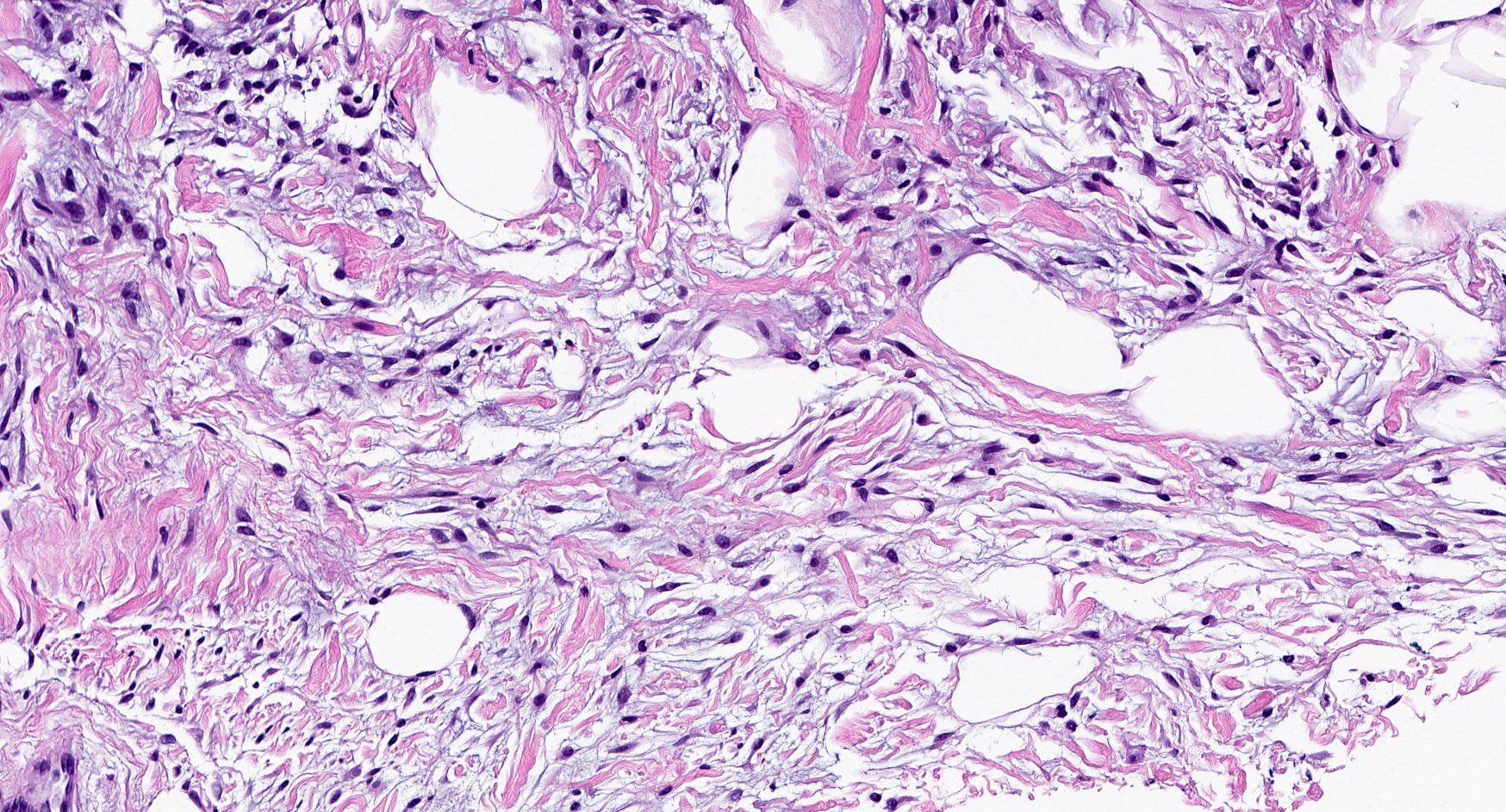
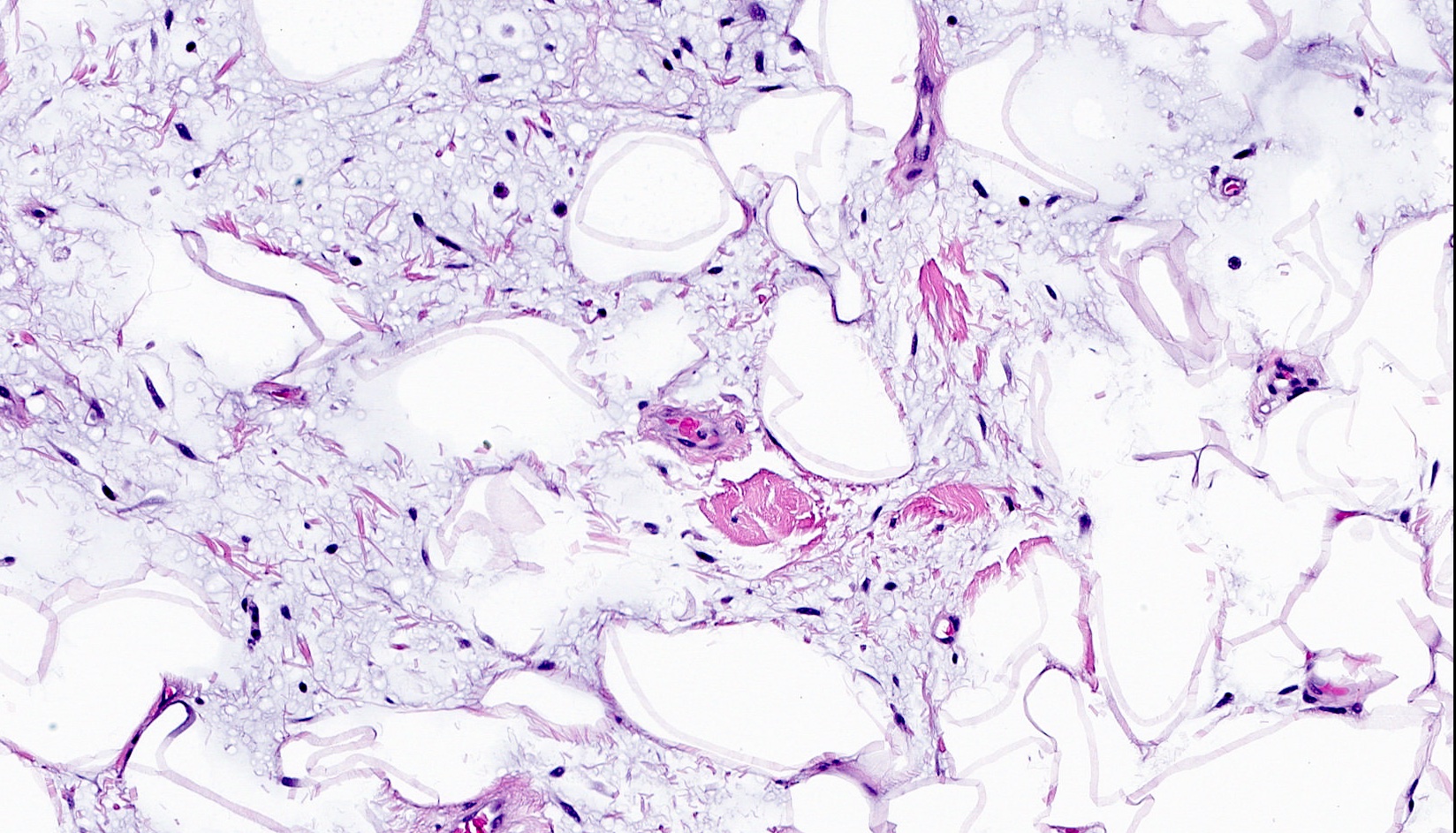
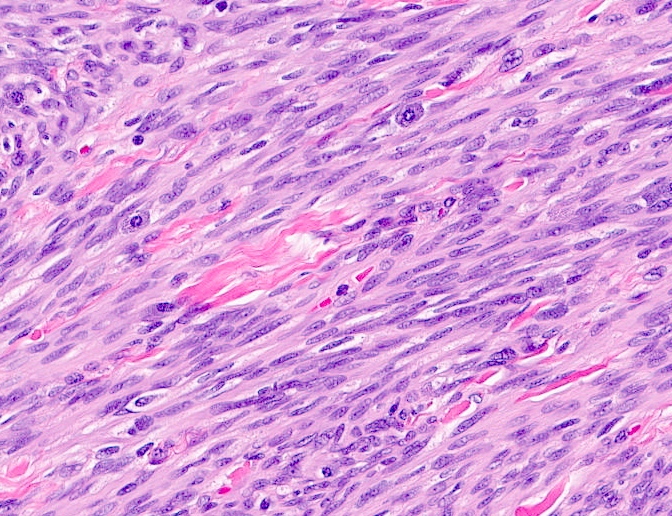
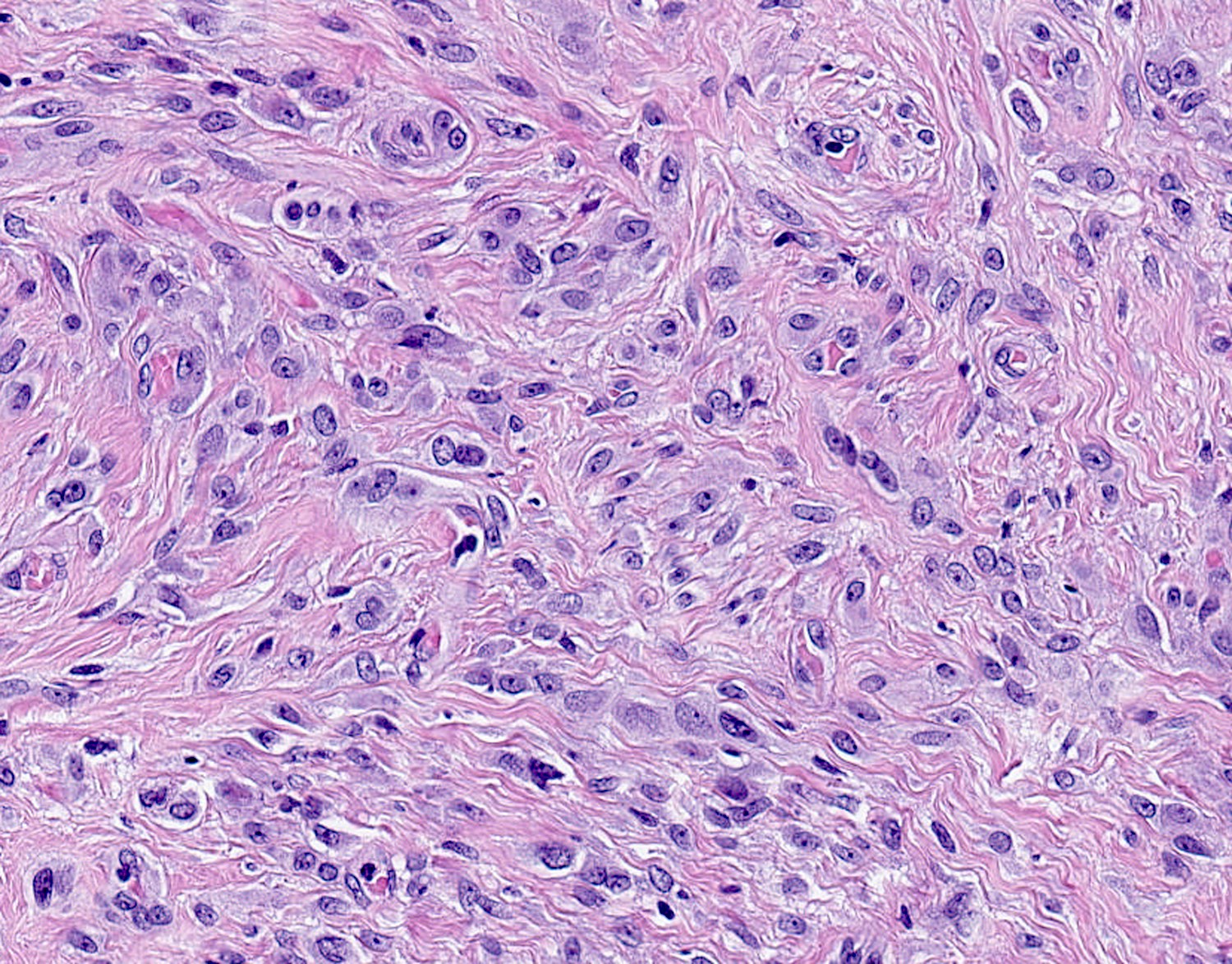
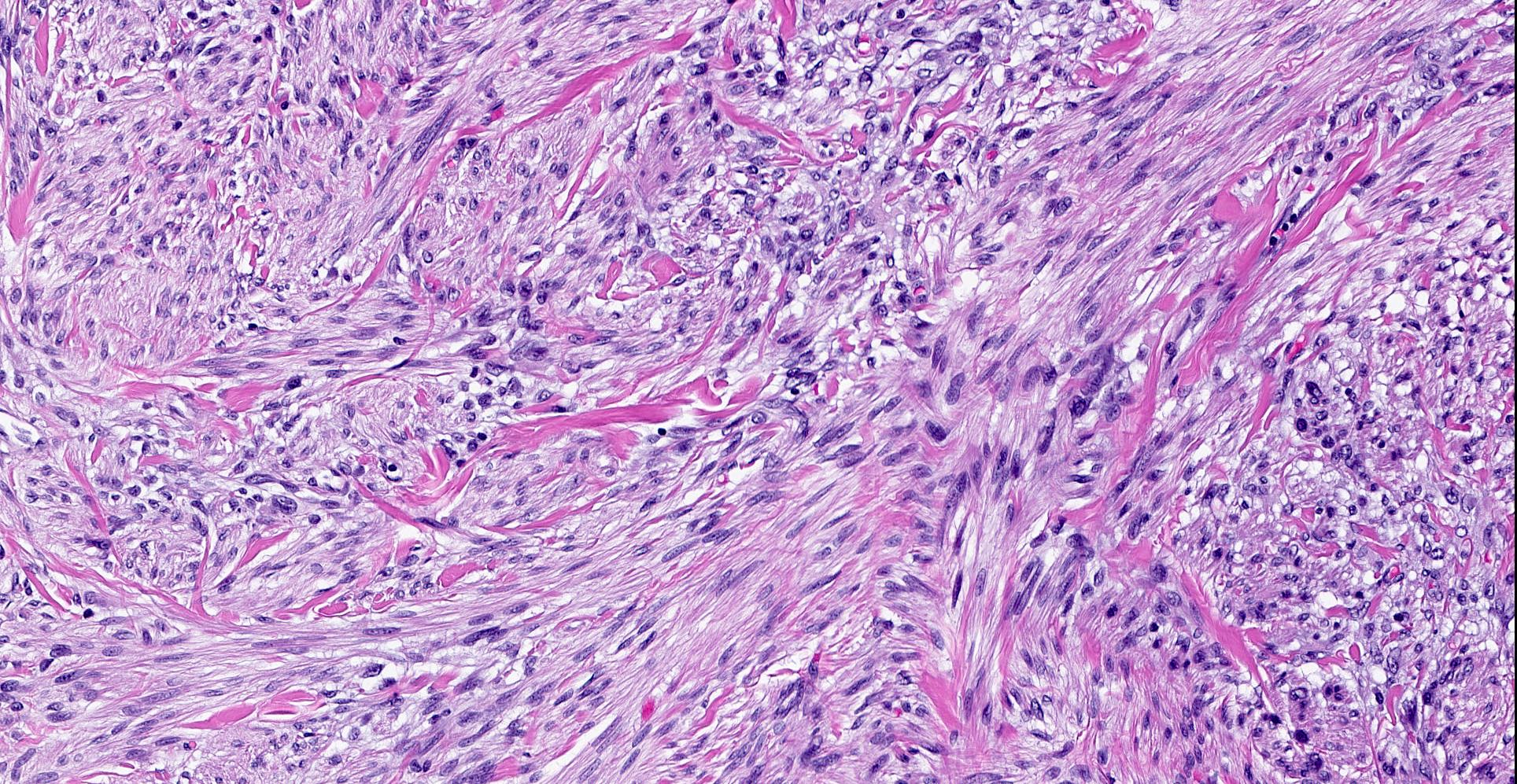
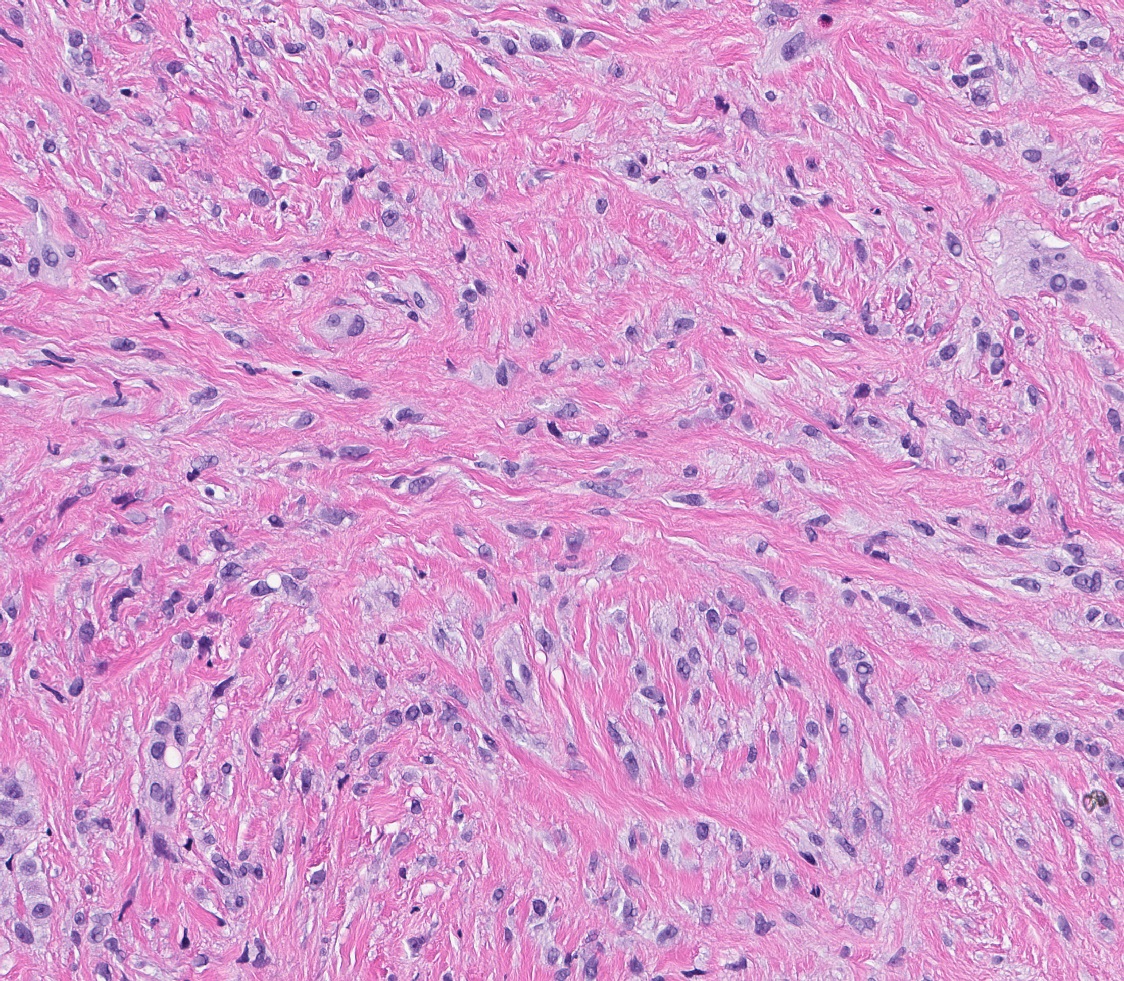
Microscopic (histologic) description
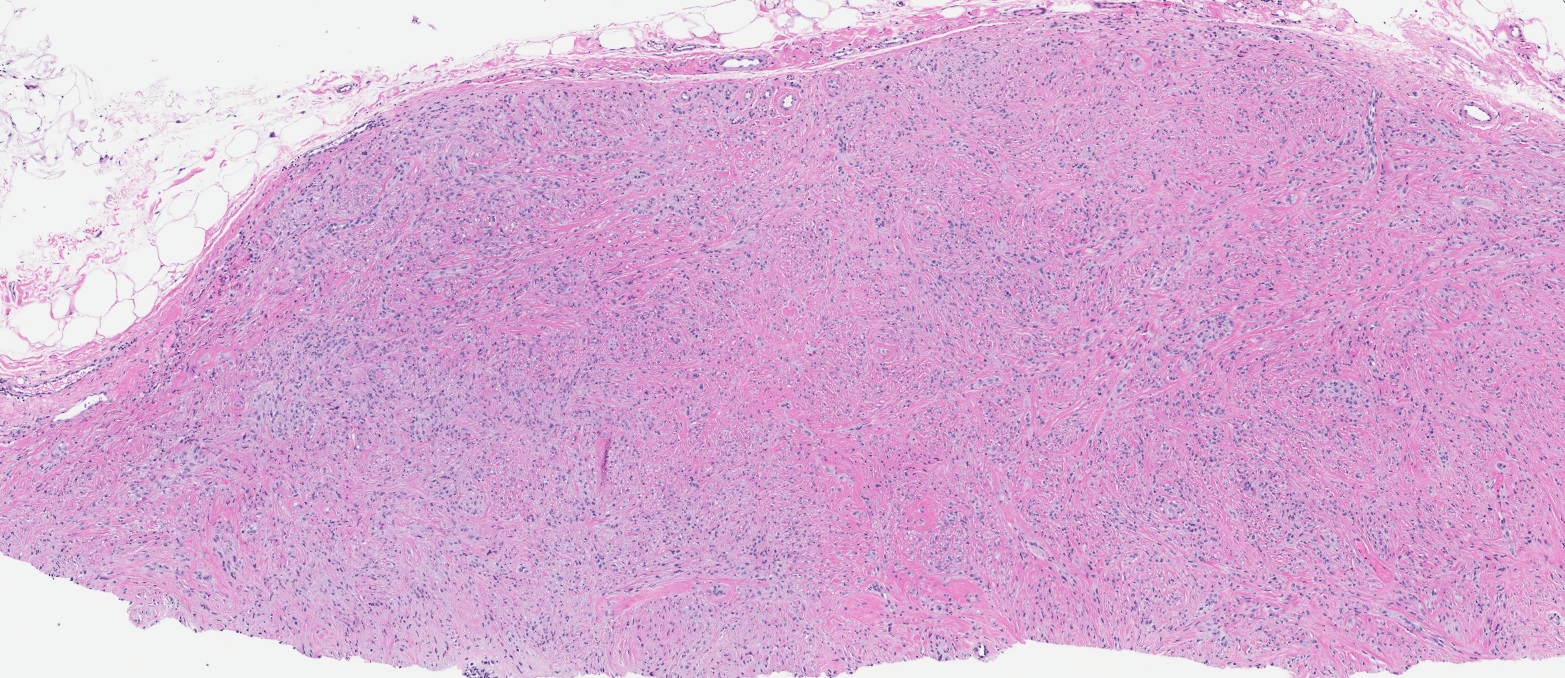
- Well circumscribed, lacks true capsule, rarely infiltrative
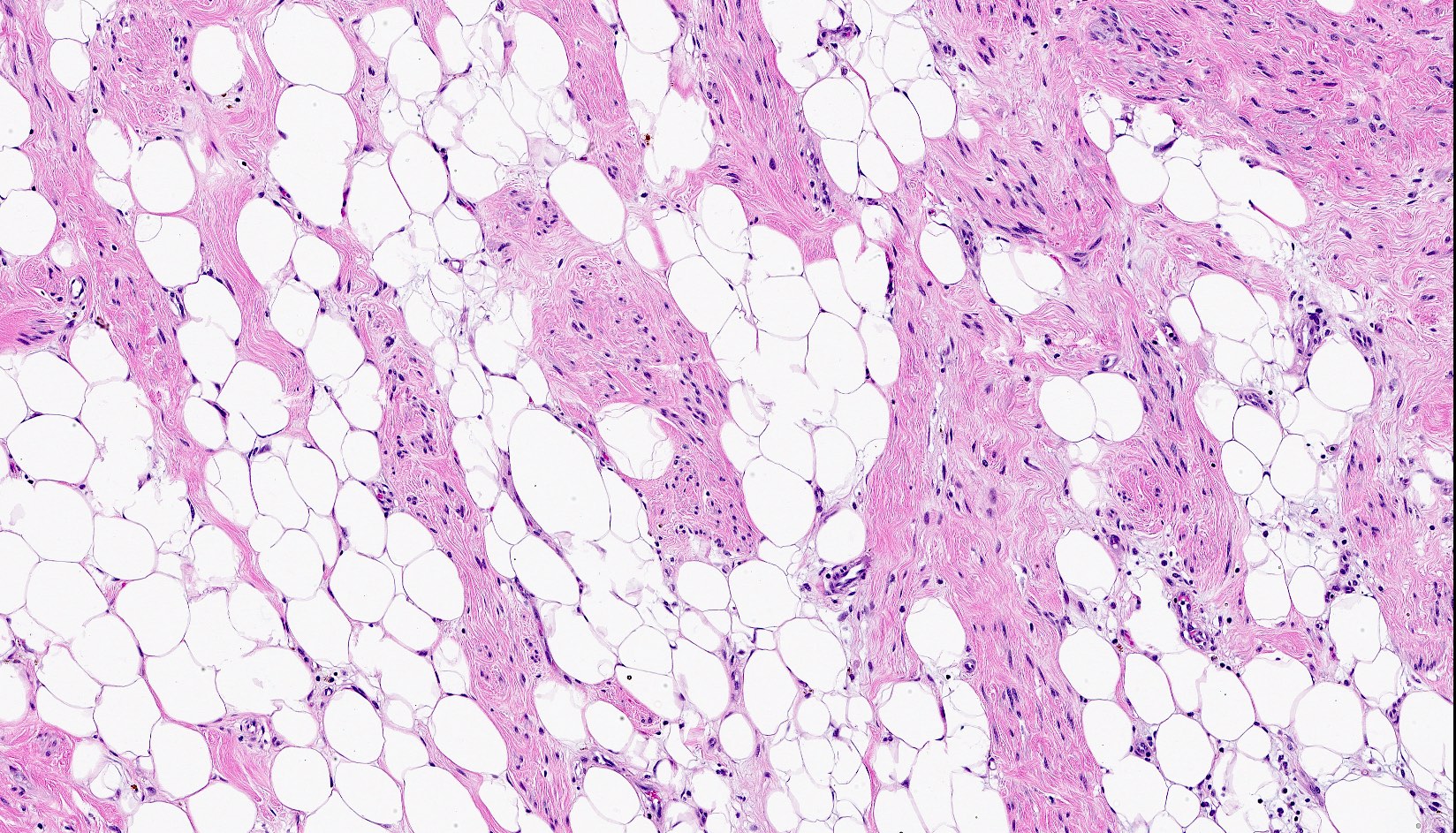
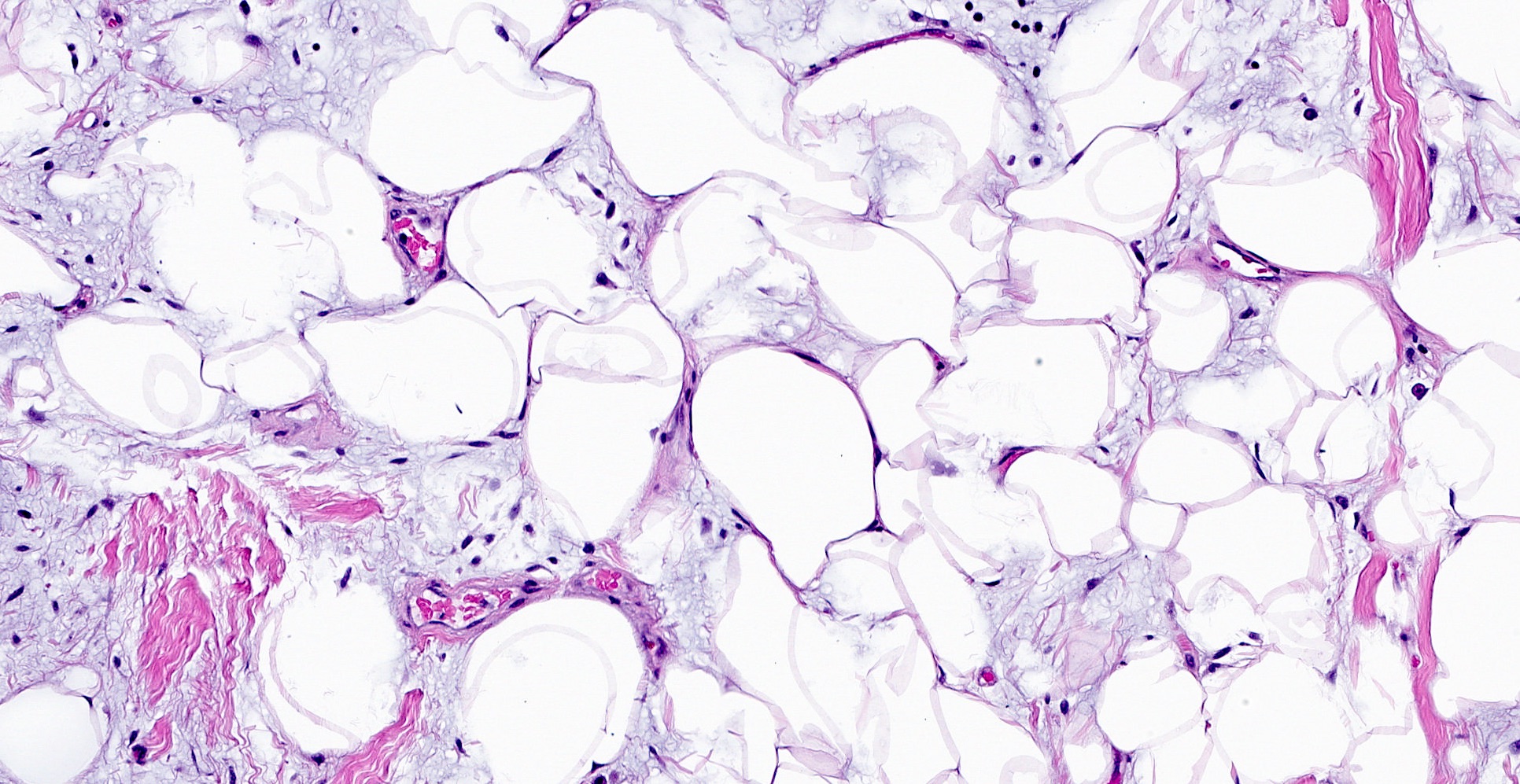
- Bland, uniform, short to elongated spindle cells arranged as short haphazard intersecting fascicles admixed with bands of hyalinized, brightly eosinophilic collagen and variable amounts of fat
- No more than mild nuclear atypia
- Mitoses usually absent, atypical mitoses and necrosis absent
- Mast cells common, perivascular lymphocytic infiltrates on occasion
- Focal myxoid stromal changes common
- May show smooth muscle leiomyomatous differentiation (elongated spindle cells with cigar shaped nuclei and pink cytoplasm)
- Rarely cartilaginous or osseous components
- Variants:
- Collagenized / fibrous: collagenous stroma predominates, may have hypocellular myofibroblastic spindle cell component
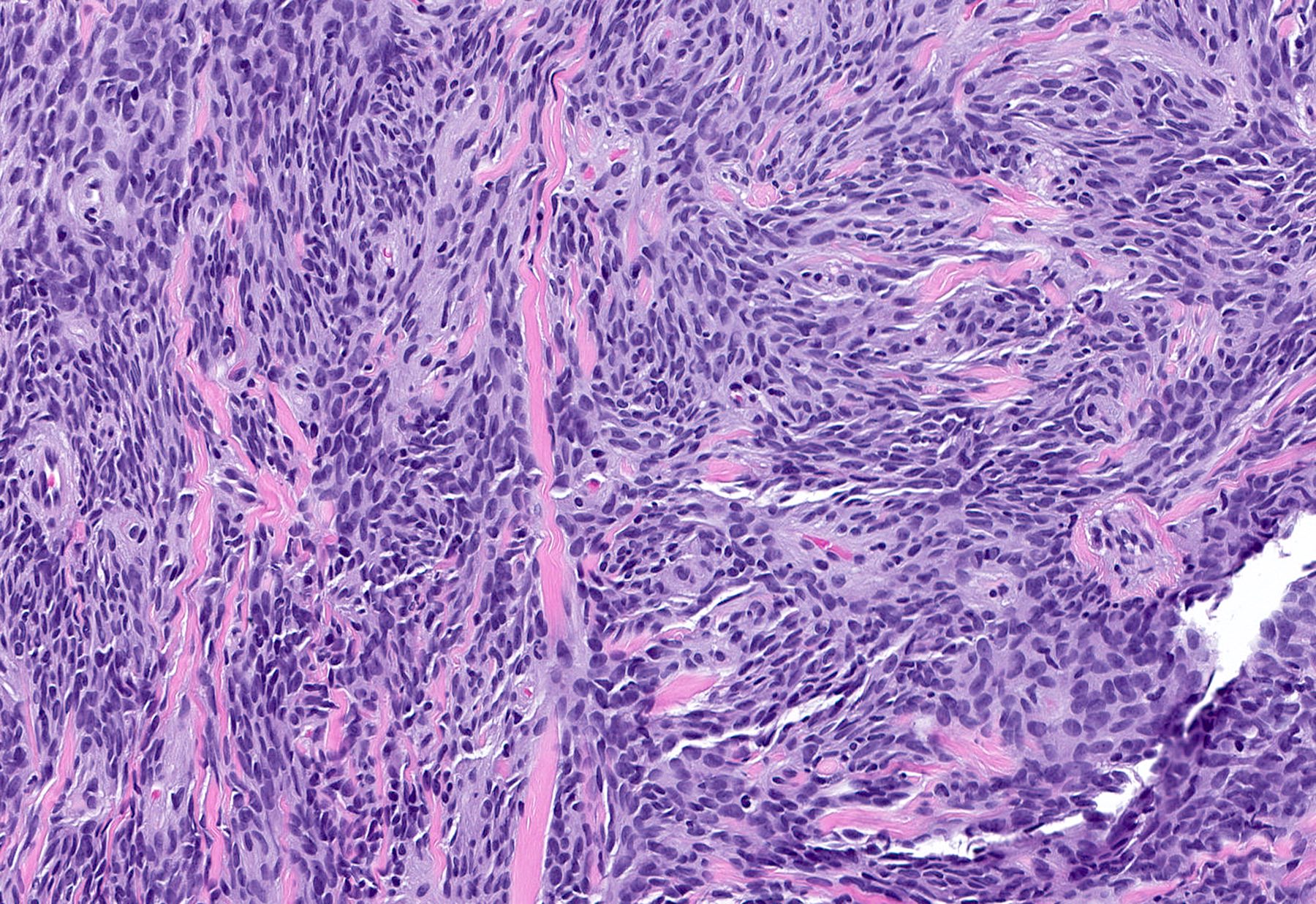
- Cellular: dense proliferation of myofibroblasts, ratio of spindle cells to collagen increased compared with classical variant, may have infiltrative borders, storiform or herringbone arrangement
- Infiltrative: irregular margins, grows into surrounding mammary parenchyma entrapping glandular tissue
- Myxoid: stellate and spindle cells in abundant myxoid stroma (Histol Histopathol 2016;31:1)
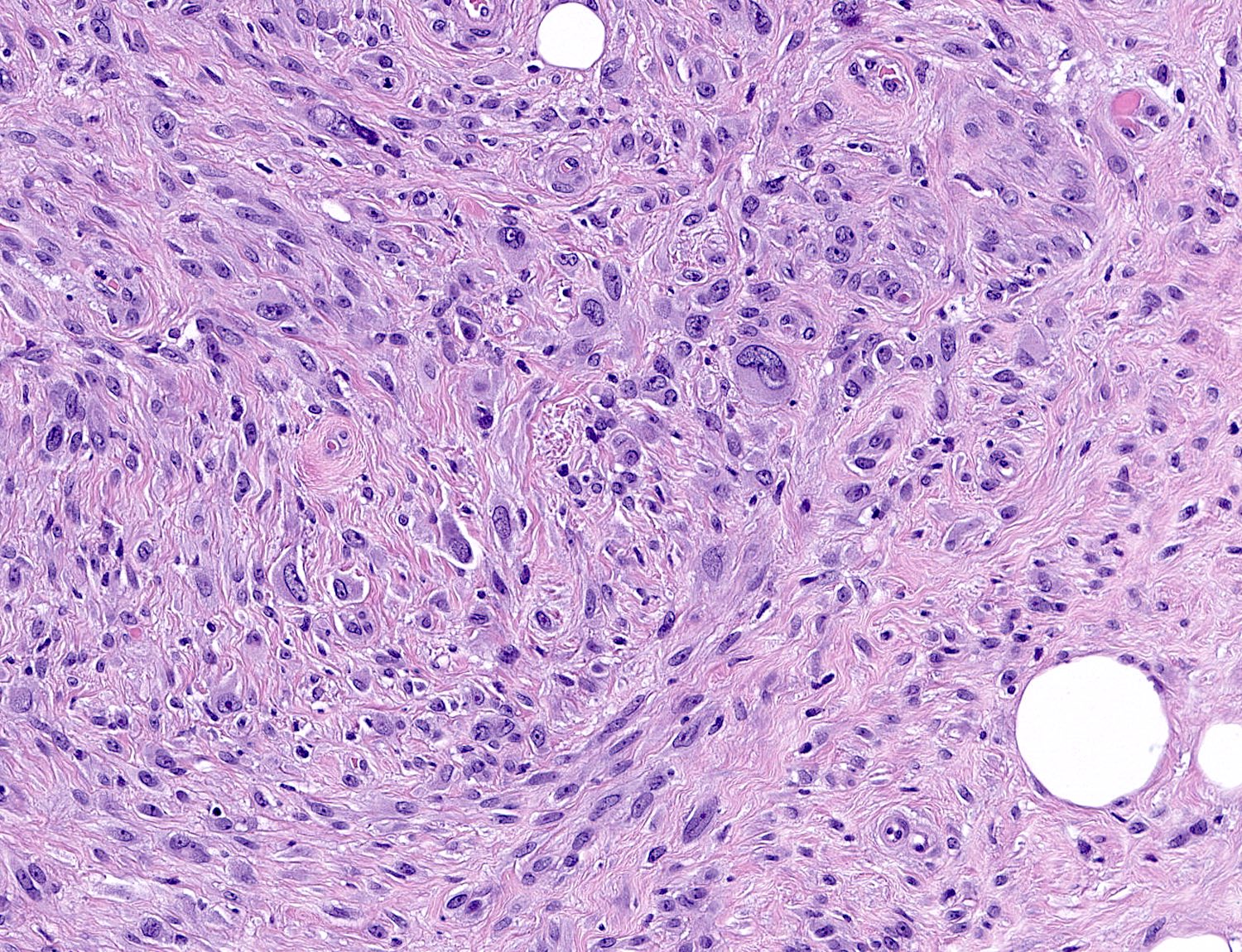
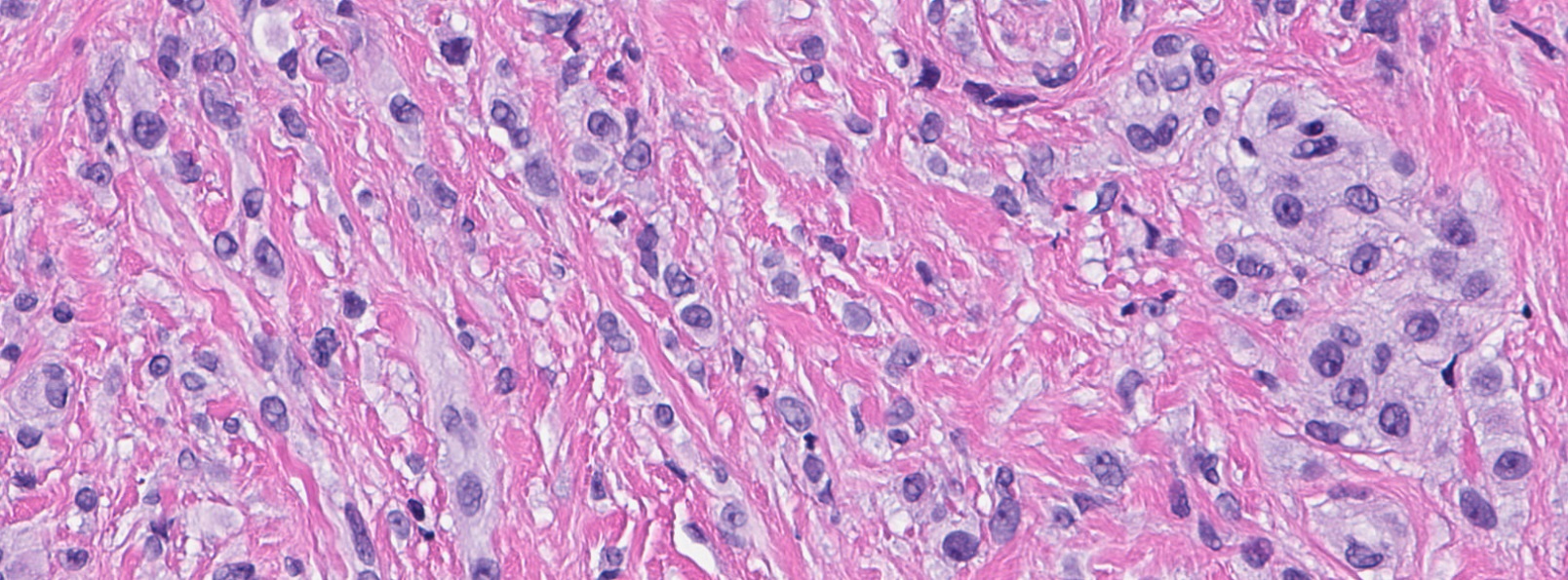
- Deciduoid: large round, polygonal cells with abundant eosinophilic glassy cytoplasm, single or multiple prominent nucleoli which may be eccentrically placed, binucleation, sharp cell borders, eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions (Histopathology 2008;52:652)
- Lipomatous: abundant adipocytic component
- Epithelioid: oval to polygonal cells arranged in clusters, cords, alveolar groups, linear strands, mono, bi or multinucleated, may have eccentrically placed nuclei with small nucleoli, well defined cell borders, single file arrangement may mimic invasive lobular carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1085)
- Atypical: single or scattered atypical mono or multinucleated cells with mild to severe nuclear pleomorphism, regarded as degenerative (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2008;132:1813)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Bland spindle to ovoid cells with scant cytoplasm dispersed as clusters and single cells (Acta Cytol 2012;56:501, Diagn Cytopathol 2016;44:1064)
- Intranuclear inclusions and mast cells may be present
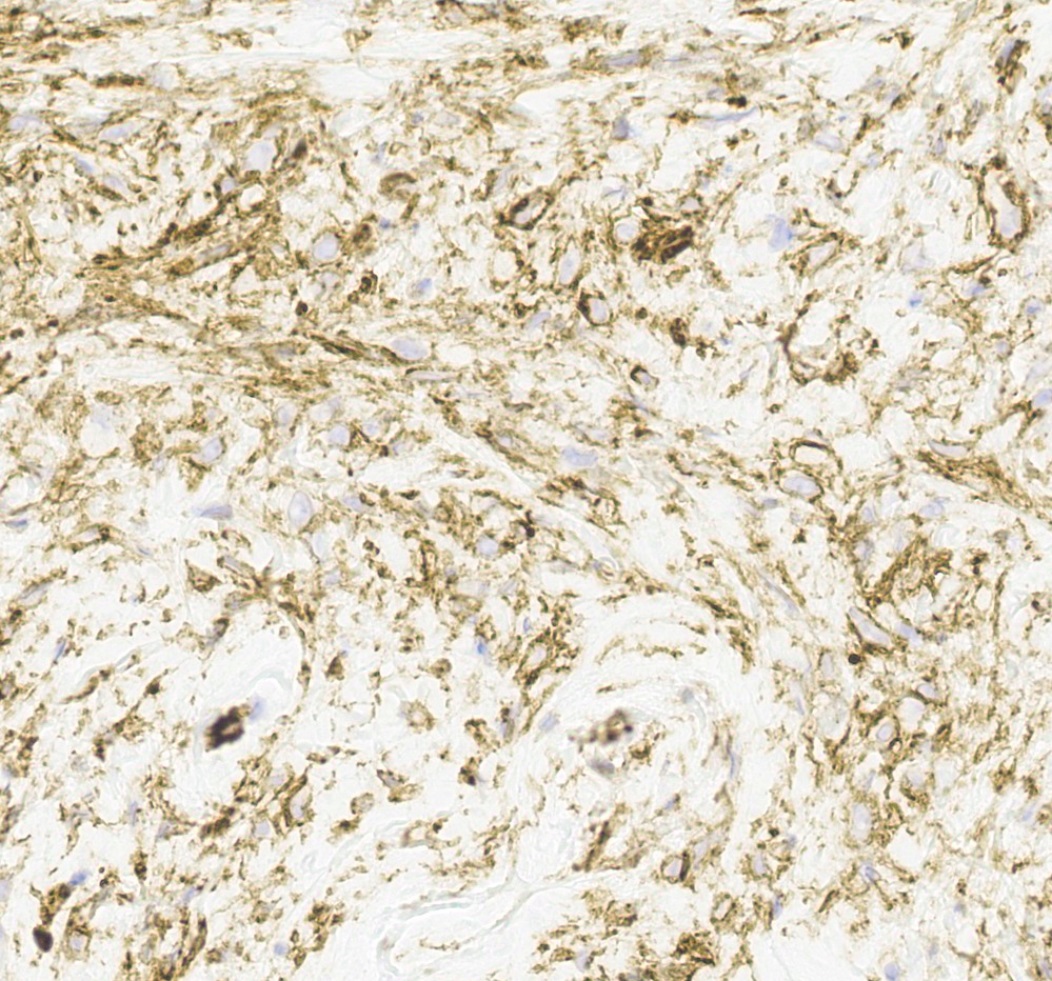
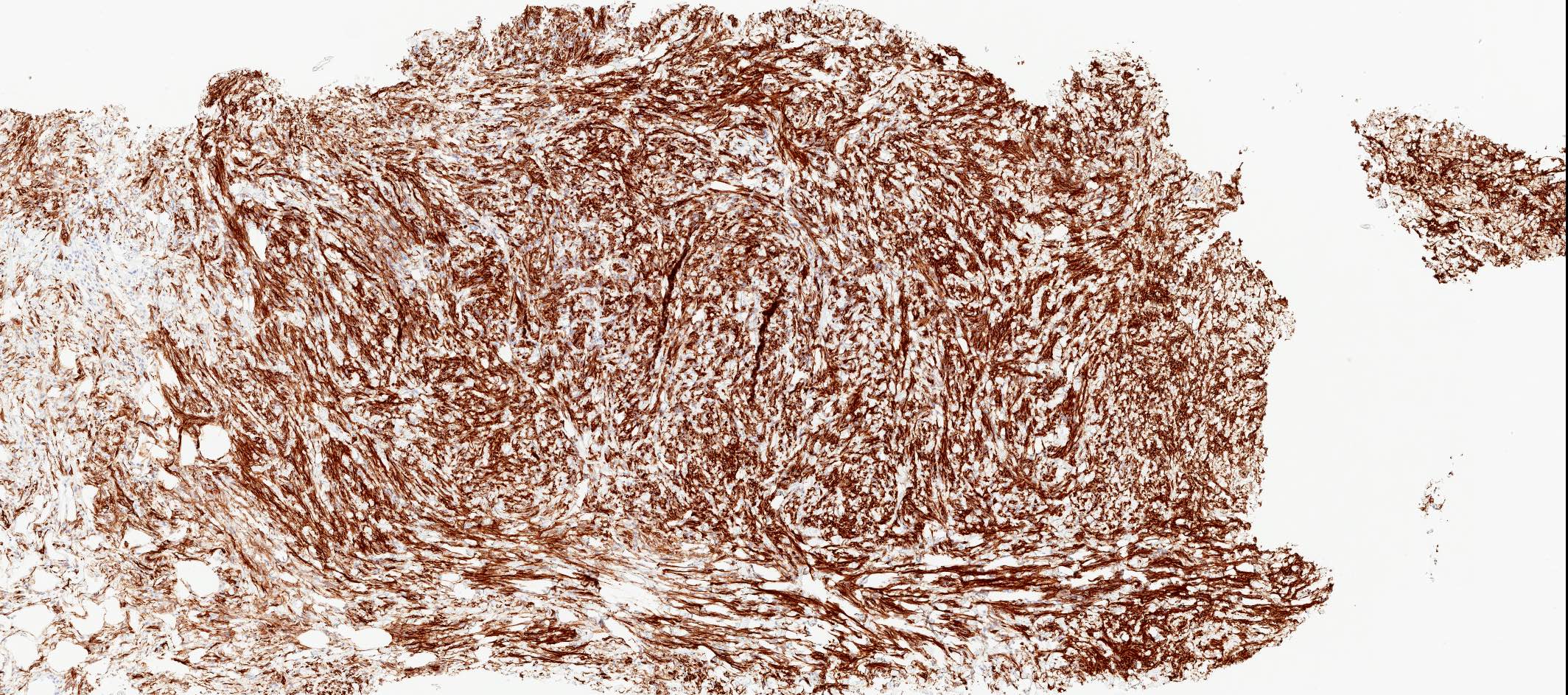
Positive stains
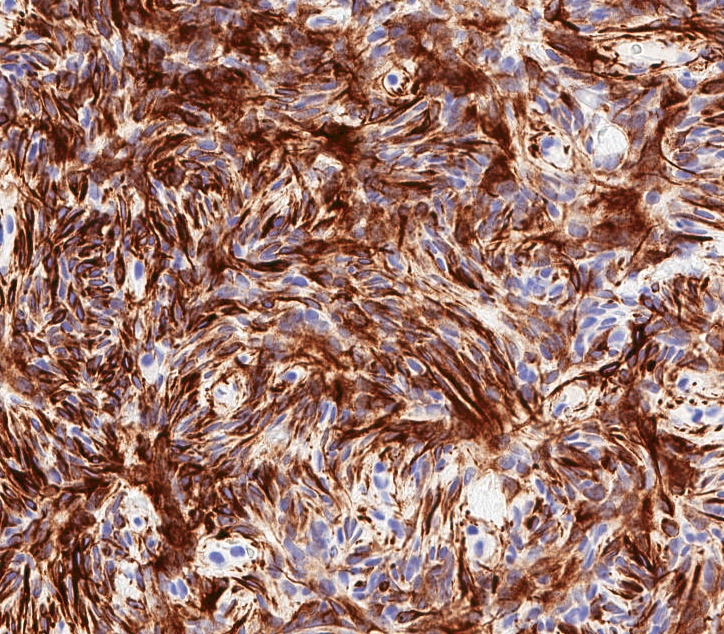
- Desmin (91%), vimentin, ER, PR, AR, BCL2, CD10, CD99 (Histopathology 2000;36:515, Virchows Arch 2007;450:727)
- CD34 (89%) diffuse and strong characteristic but may uncommonly show absent / focal expression (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:361, Breast J 2018;24:55)
- H-caldesmon if smooth muscle differentiation / leiomyomatous variant (Hum Pathol 2016;58:54, Histopathology 2003;42:233)
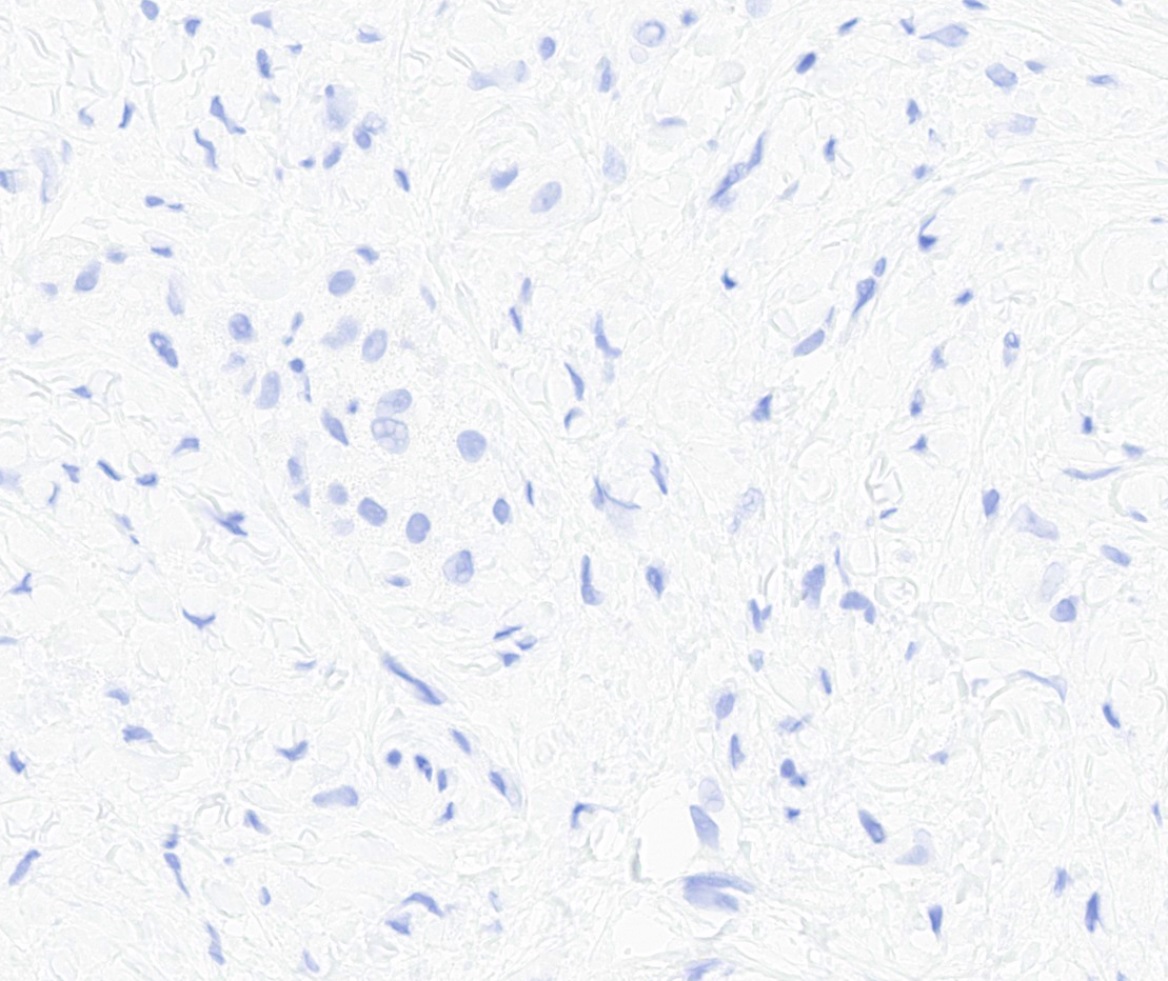
Negative stains
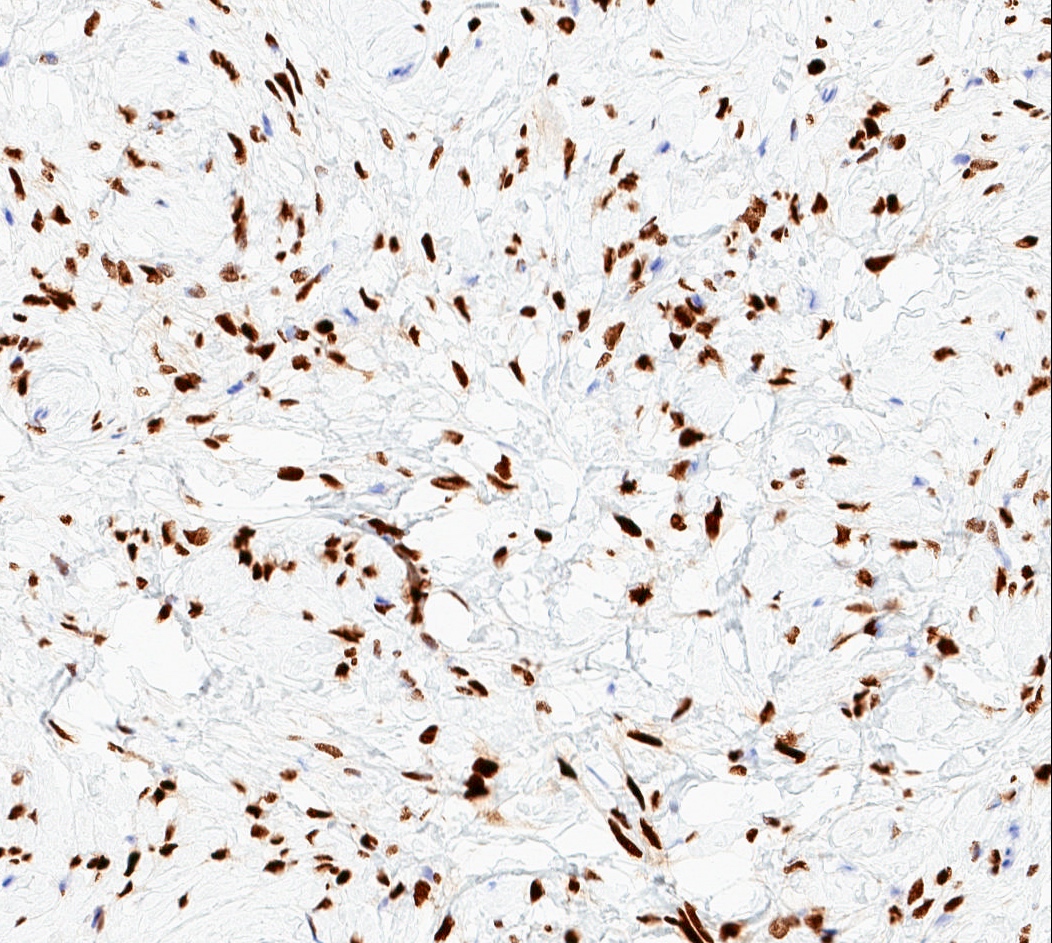
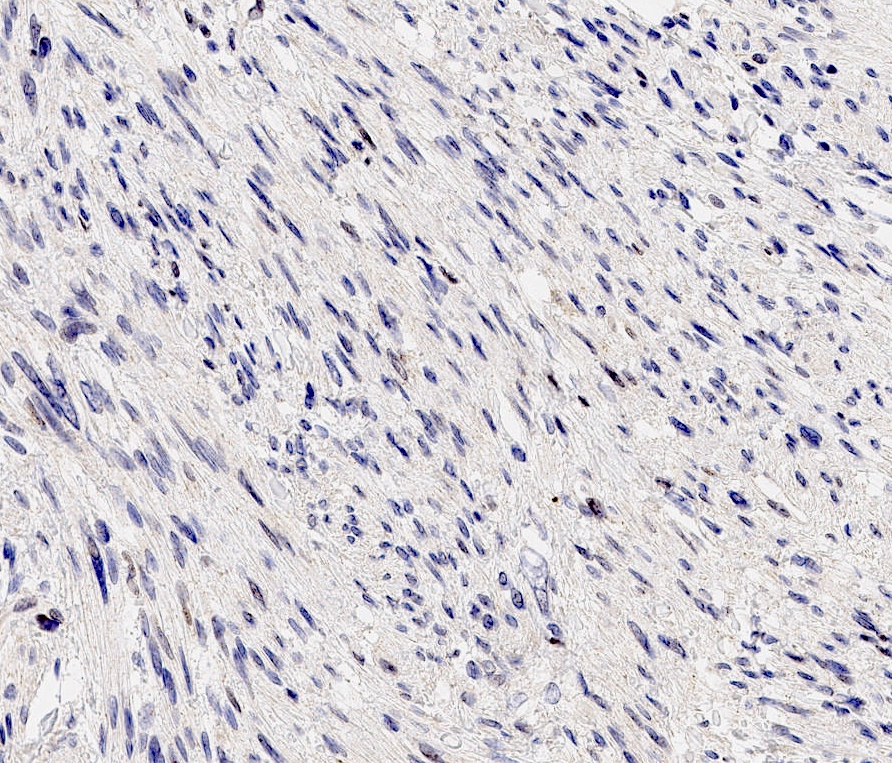
- Rb (negative in 89 - 92%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:361, Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1119)
- Actin (negative in 63%)
- Cytokeratins, S100, p63
Electron microscopy description
- Features of smooth muscle and myofibroblasts: rough endoplasmic reticulum, bundles of myofilaments with focal densities, intermediate filaments and attachment plaques (Pathol Res Pract 1999;195:1, Ultrastruct Pathol 1999;23:249)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Recurrent monoallelic loss of 13q14 region, including RB1 and FOXO1 loci (J Pathol 2000;191:282, Hum Pathol 2012;43:1887)
- Related to multiple CD34 positive neoplasms with similar morphology and deletion of 13q14: spindle cell lipoma, extramammary myofibroblastoma, cellular angiofibroma and superficial acral fibromyxoma (J Pathol 2000;191:282, Hum Pathol 2017;60:192)
Sample pathology report
- Left breast, mass, needle core biopsy:
- Bland spindle cell lesion consistent with myofibroblastoma (see comment)
- Comment: Sections show bland spindle cells arranged in short fascicles admixed with hyalinized collagen bundles and adipose tissue. The lesional cells express CD34, desmin, smooth muscle actin, BCL2 and PR, are negative for cytokeratins and show a loss of Rb1 by immunohistochemistry. Overall, the morphologic and immunohistochemical findings are compatible with mammary type myofibroblastoma.
Differential diagnosis
- Invasive lobular carcinoma:
- Cytologic atypia, mitoses
- Presence of in situ carcinoma supports malignant process
- Cytokeratin positive, CD34 negative, desmin negative
- Both may be ER and PR positive
- Metaplastic spindle cell carcinoma:
- More cytologic atypia, mitoses, infiltrative borders
- May have areas with glandular morphology or squamous metaplasia
- Presence of in situ carcinoma supports malignant process
- Cytokeratin and p63 positive, CD34 negative
- Fibromatosis:
- Long, sweeping fascicles
- Stellate or infiltrative appearing
- CD34 negative, nuclear expression of beta catenin
- CTNNB1 mutations
- Nodular fasciitis:
- Loose storiform proliferation of bland spindle cells; mitoses may be present and conspicuous
- Extravasated erythrocytes often present
- Scattered inflammatory cells (lymphocytes, histiocytes) present
- CD34 and desmin negative
- MYH9-USP6 fusion or other USP6 rearrangement by FISH, PCR or RNA sequencing
- May spontaneously regress
- Pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia (PASH):
- Solitary fibrous tumor:
- STAT6 positive (Pathol Res Pract 2018;214:1544)
- No loss of RB1 (13q14) by FISH (Am J Clin Pathol 2012;137:963)
- Spindle cell lipoma:
- Fat component usually predominates
- Focal or absent myogenic marker expression
- In the lower female genital tract:
- Cellular angiofibroma:
- Morphologic overlap with similar genetics
- Thicker, hyalinized vessels, focal to absent myogenic marker expression
- Lacks thick hyalinized collagen bundles
- Angiomyofibroblastoma:
- Alternating zones of hypo and hypercellularity
- More prominent vascular component (delicate capillary sized vessels)
- Usually CD34 negative
- Aggressive angiomyxoma:
- Infiltrative, not circumscribed, involves deep soft tissues
- Hypocellular with abundant myxoid matrix
- Medium to large sized hyalinized vessels
- Cellular angiofibroma:
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is true regarding mammary type myofibroblastomas?
- The cellular and epithelioid variants are positive for cytokeratins
- They are always CD34 positive
- They are genetically related to spindle cell lipoma and cellular angiofibroma and cytogenetically show monoallelic loss of 13q14 region
- They are related to solitary fibrous tumors and are STAT6 positive by immunohistochemistry
- They may have aggressive behavior if cytologic atypia is present
Board review style answer #2
C. They are genetically related to spindle cell lipoma and cellular angiofibroma and cytogenetically show monoallelic loss of 13q14 region
Comment Here
Reference: Myofibroblastoma
Comment Here
Reference: Myofibroblastoma
Board review style question #3
Which immunoprofile is most suggestive of mammary type myofibroblastoma?
- CD34 negative, desmin positive, smooth muscle actin positive, Rb1 positive
- CD34 negative, desmin negative, cytokeratin positive, Rb1 negative
- CD34 positive, desmin positive, CD10 negative, Rb1 positive
- CD34 positive, desmin positive, STAT6 negative, Rb1 negative
- CD34 positive, STAT6 positive, Rb1 positive
Board review style answer #3
D. CD34 positive, desmin positive, STAT6 negative, Rb1 negative
Comment Here
Reference: Myofibroblastoma
Comment Here
Reference: Myofibroblastoma