Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology / etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Peevy J, Abdulfatah E, Ali-Fehmi R, Bandyopadhyay S, Shi DP. Adenomatoid tumor (peritoneum). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/pleuraperitoneumadenomatoid.html. Accessed August 15th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Benign lesion, often incidental finding on oophorectomy specimen
- More frequently these lesion are found in males (epididymis, spermatic cord and testicular membrane); however, in females lesions are seen more commonly in fallopian tubes, broad ligament and uterus
- Thought to arise from mesothelial serosal cells
- First described by Golden and Ash in 1945 (Am J Pathol 1945;21:63)
Essential features
- Rarely found within ovary
- Typically small with 0.5 - 3 cm incidental lesions near hilum
Terminology
- Previously known as benign mesothelioma of the genital tract
Epidemiology
- Usually occurs in the third and fourth decades (Int J Gynecol Pathol 1991;10:364)
- Most commonly adults females (23 - 79 years old)
- Average age 54 reported in literature (Int J Gynecol Pathol 1991;10:364)
Sites
- Ovarian and juxtaovarian sites are rare
- Occur predominantly at the ovarian hilum and may extend into and replace the ovarian parenchyma
- Most frequently unilateral, found within fallopian tube, broad ligament or on uterine serosal surface
Pathophysiology / etiology
- Mesothelial origin supported by ultrastructural and immunohistochemical features (Pathol Res Pract 1983;176:258)
- Derivation from differentiated mesothelial cells by inclusion or embolization has been postulated (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2000;124:609)
- An origin from pluripotent Müllerian mesencyhmal stem cells has been suggested (Cancer 1958;11:337)
Clinical features
- Asymptomatic, discovered as an incidental finding
- Usually 0.5 - 3.0 cm, rarely larger and symptomatic
Diagnosis
- Histologic recognition, confirmed by immunophenotype
- Often incidental
Laboratory
- Nondiagnostic
- Rare reports have describe slightly elevated CEA with normal CA-125 (J Clin Ultrasound 2005;33:233)
- Other reports have described normal serum markers (Eur J Gynaecol Oncol 2014;35:91)
Radiology description
- Not routinely performed for primary diagnosis
- Case reports describe incidental lesions on transvaginal ultrasound displaying multilocular cystic mass often with vascularized central / solid portion
- Radiographic differential diagnosis, if provided, may include epithelial tumors, inclusion peritoneal cysts, and multiple large follicles
- CT imaging seldom describes lesion (J Clin Ultrasound 2005;33:233)
Prognostic factors
- Benign behavior, no reports of recurrence or malignant transformation
Case reports
- 26 year old woman with adenomatoid tumors involving uterus, ovary and appendix (J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2003;29:234)
- 52 year old woman with oxyphilic adenomatoid tumor of the ovary (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2007;26:16)
- 61 year old woman (Jpn J Clin Oncol 1988;18:159)
Treatment
- Excision results in complete cure
- Recurrence after excision is rare
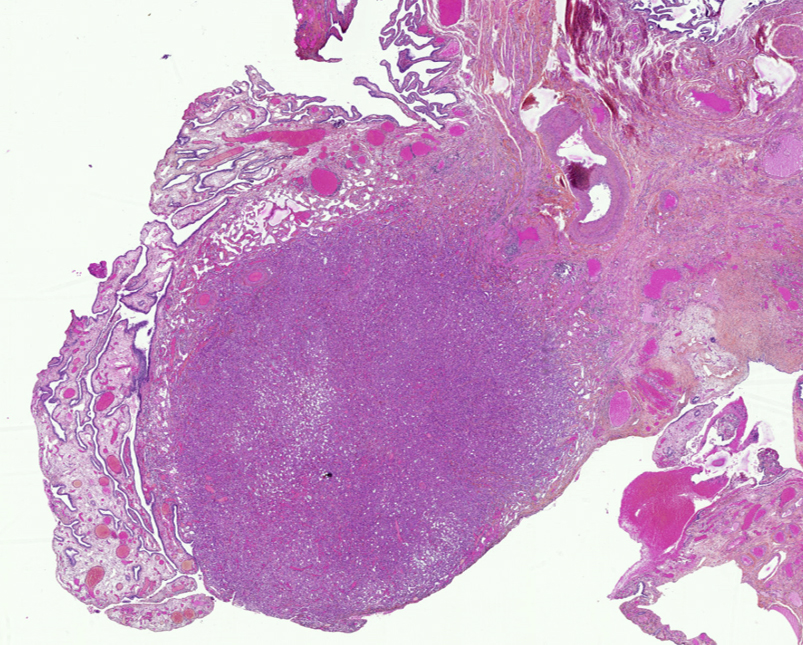
Gross description
- Small, round to oval, well circumscribed tumor
- Cut surface may have small cystic spaces
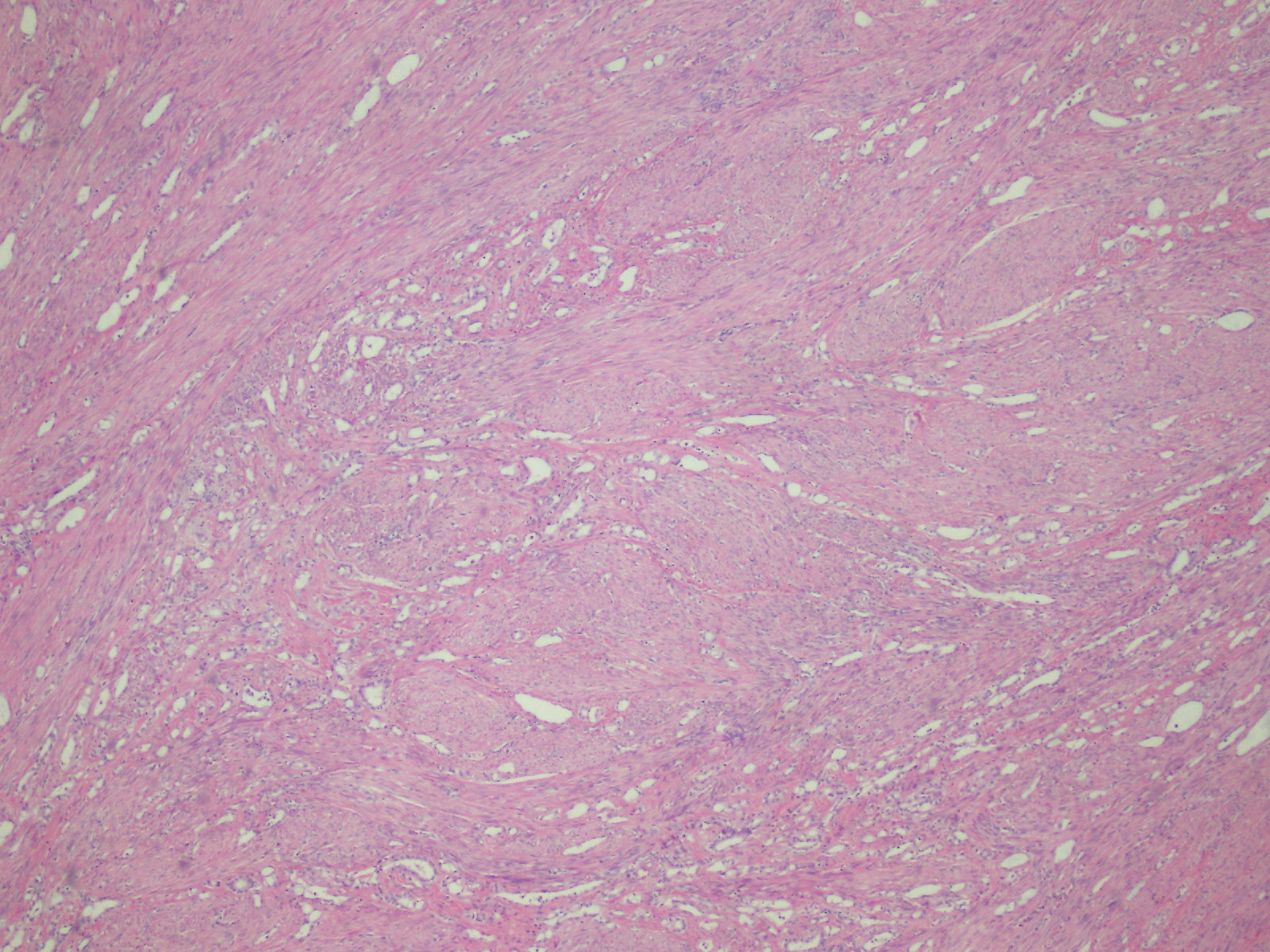
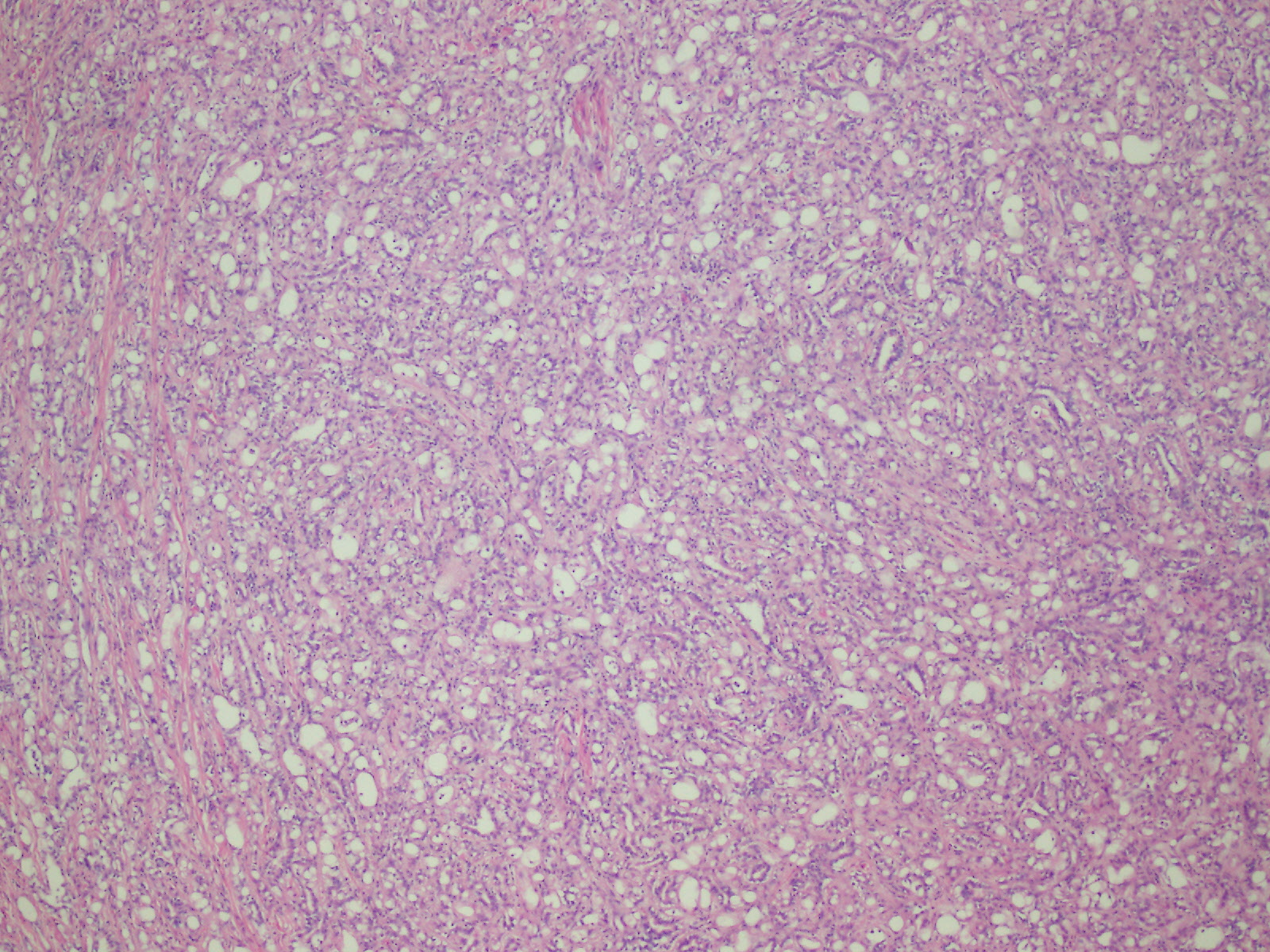
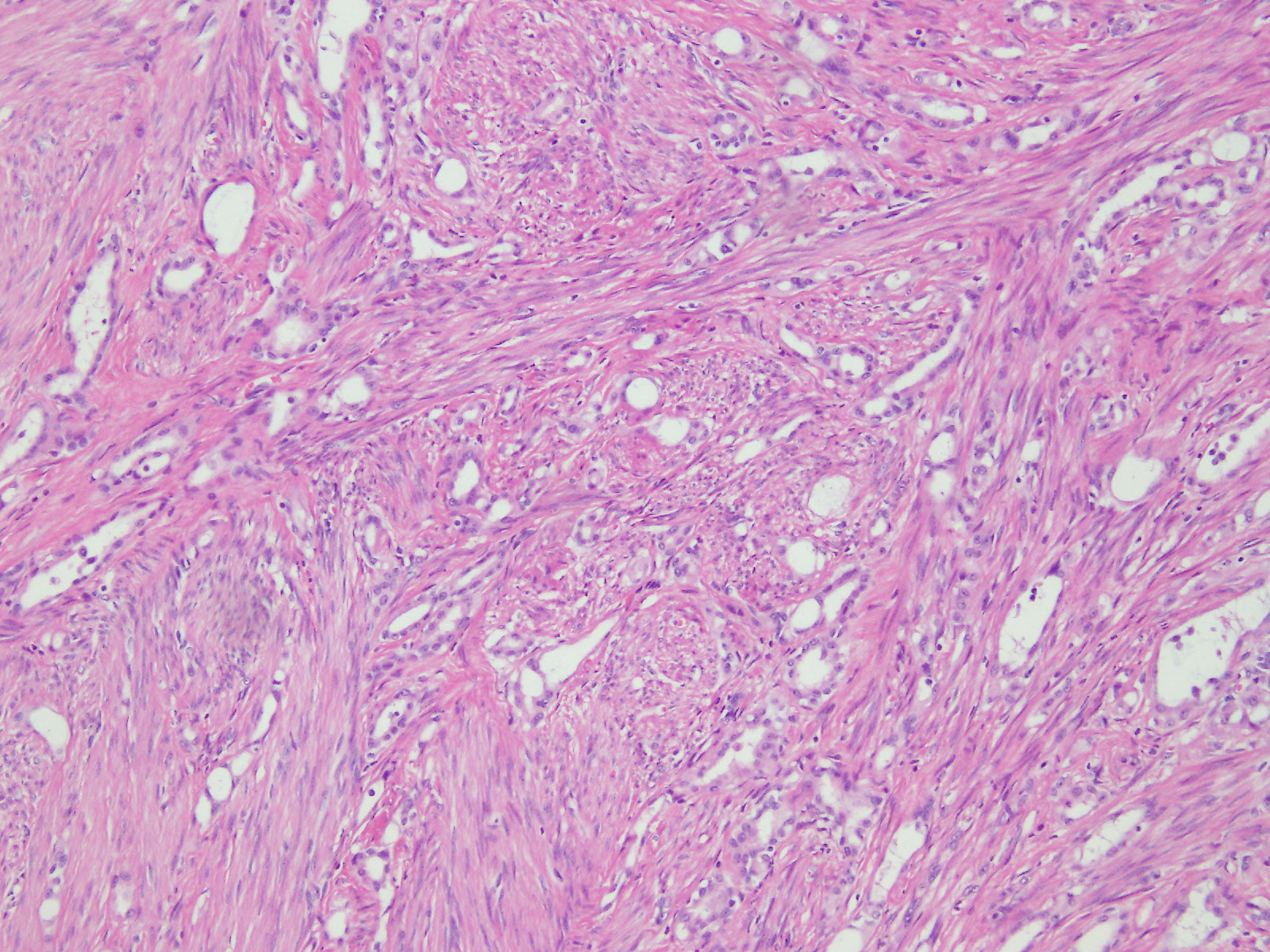
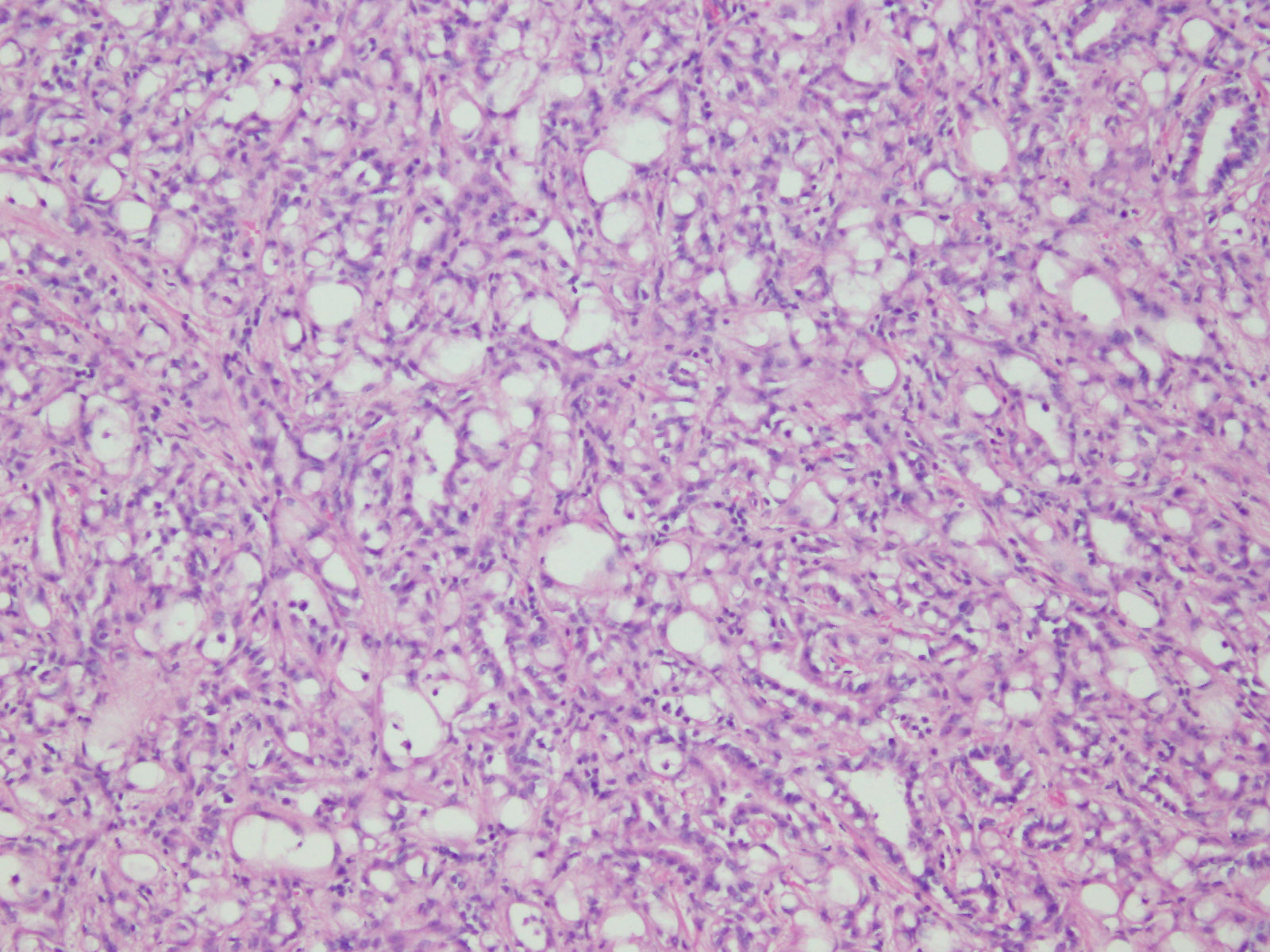
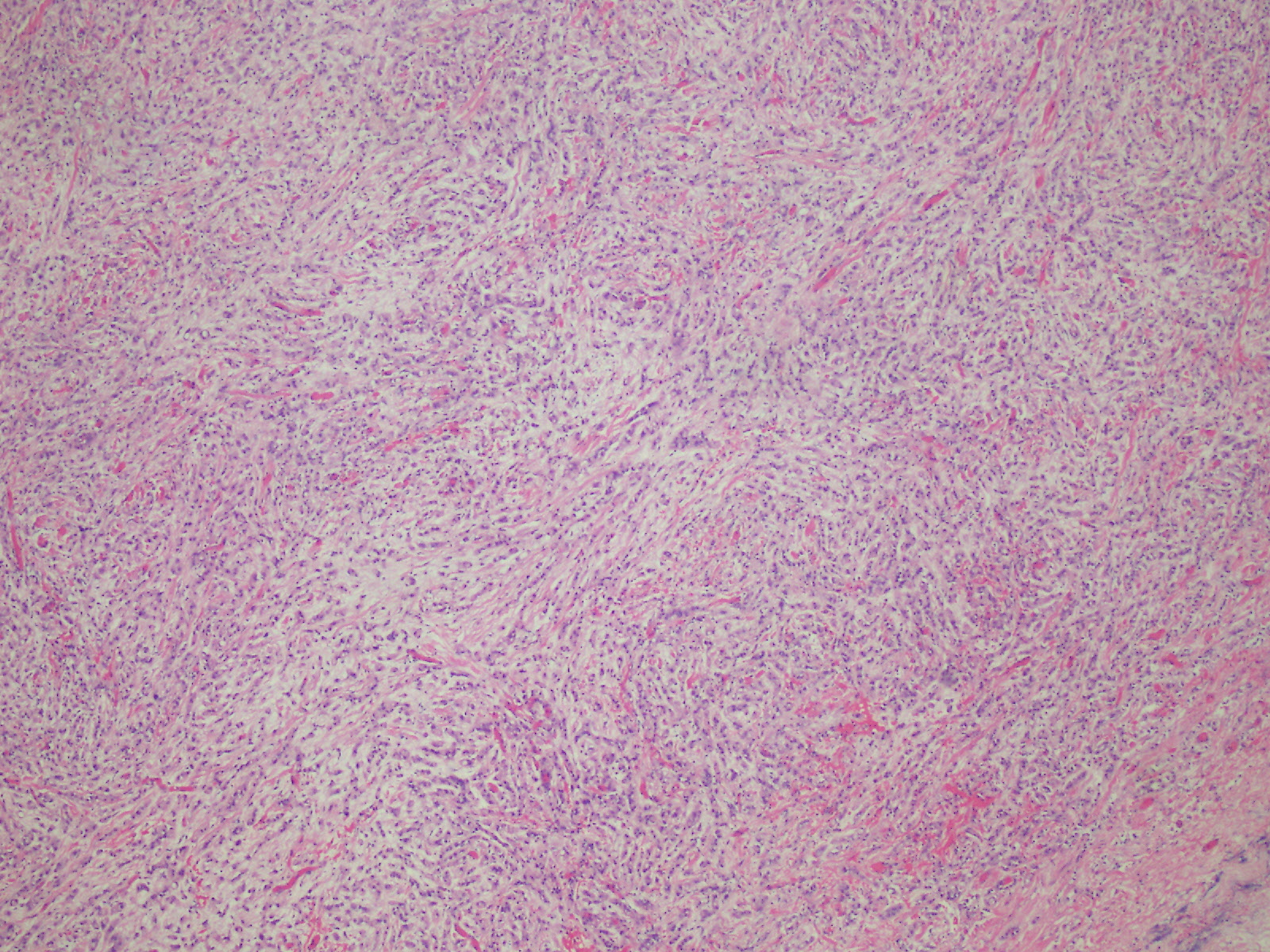
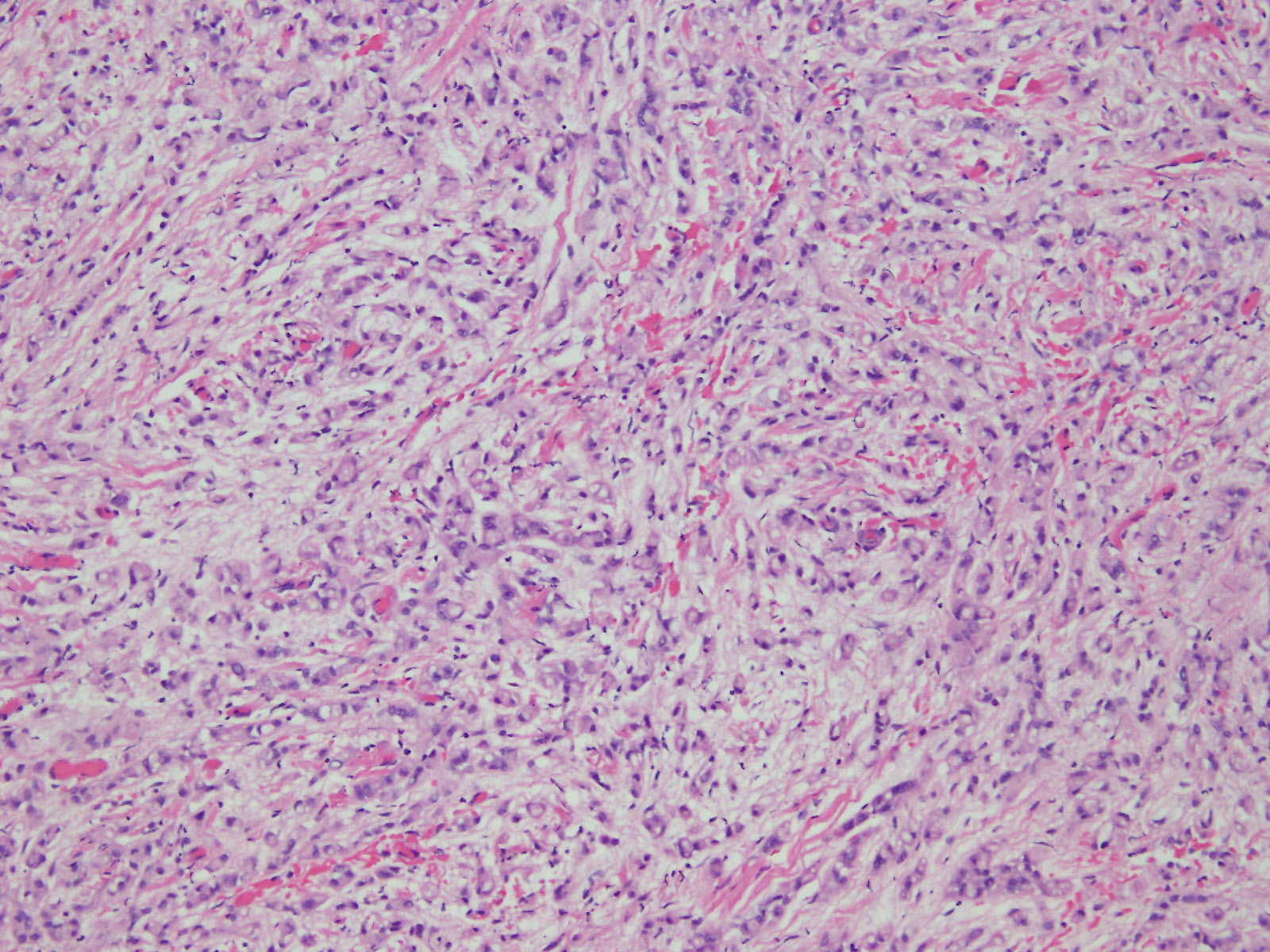
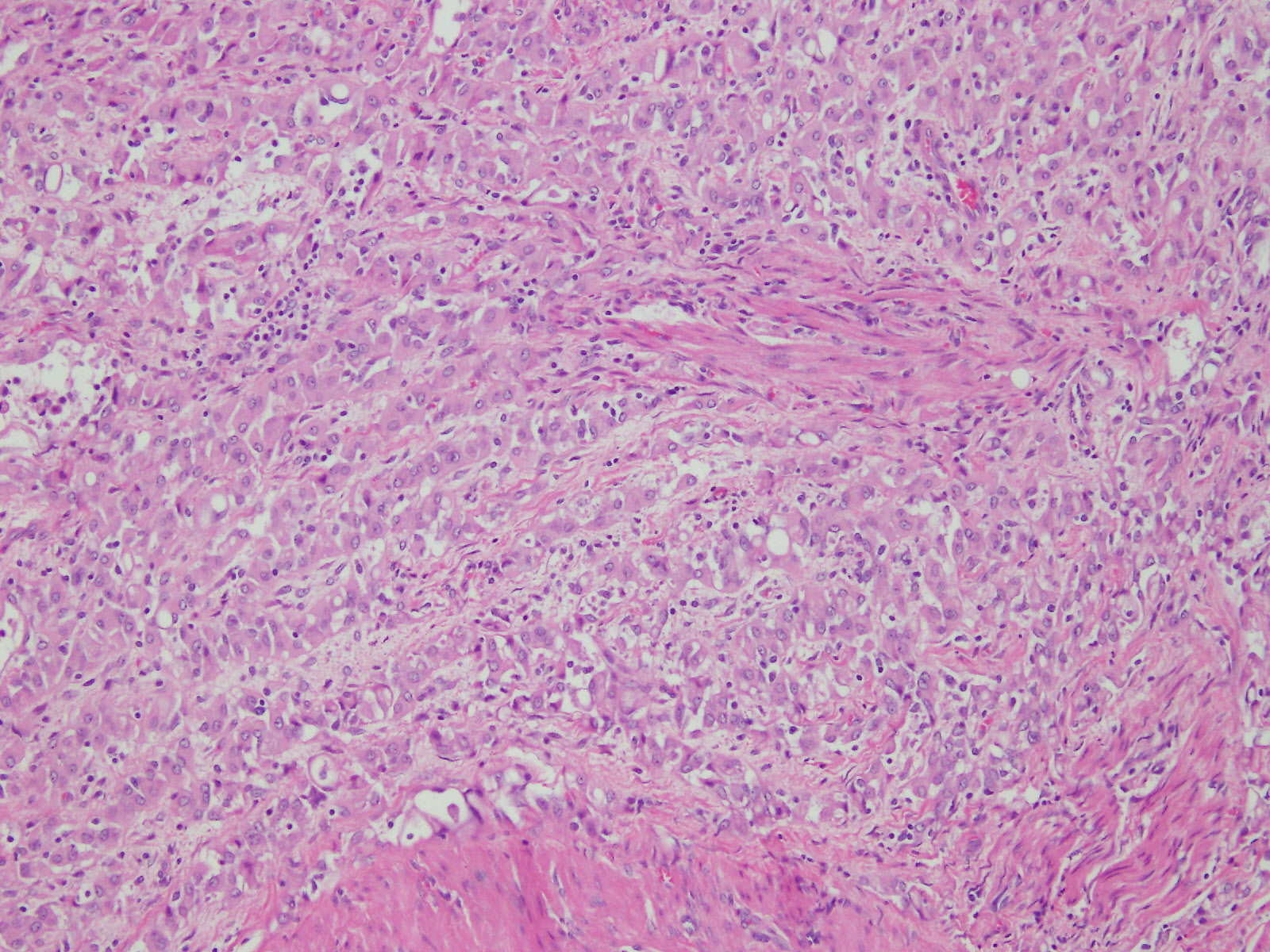
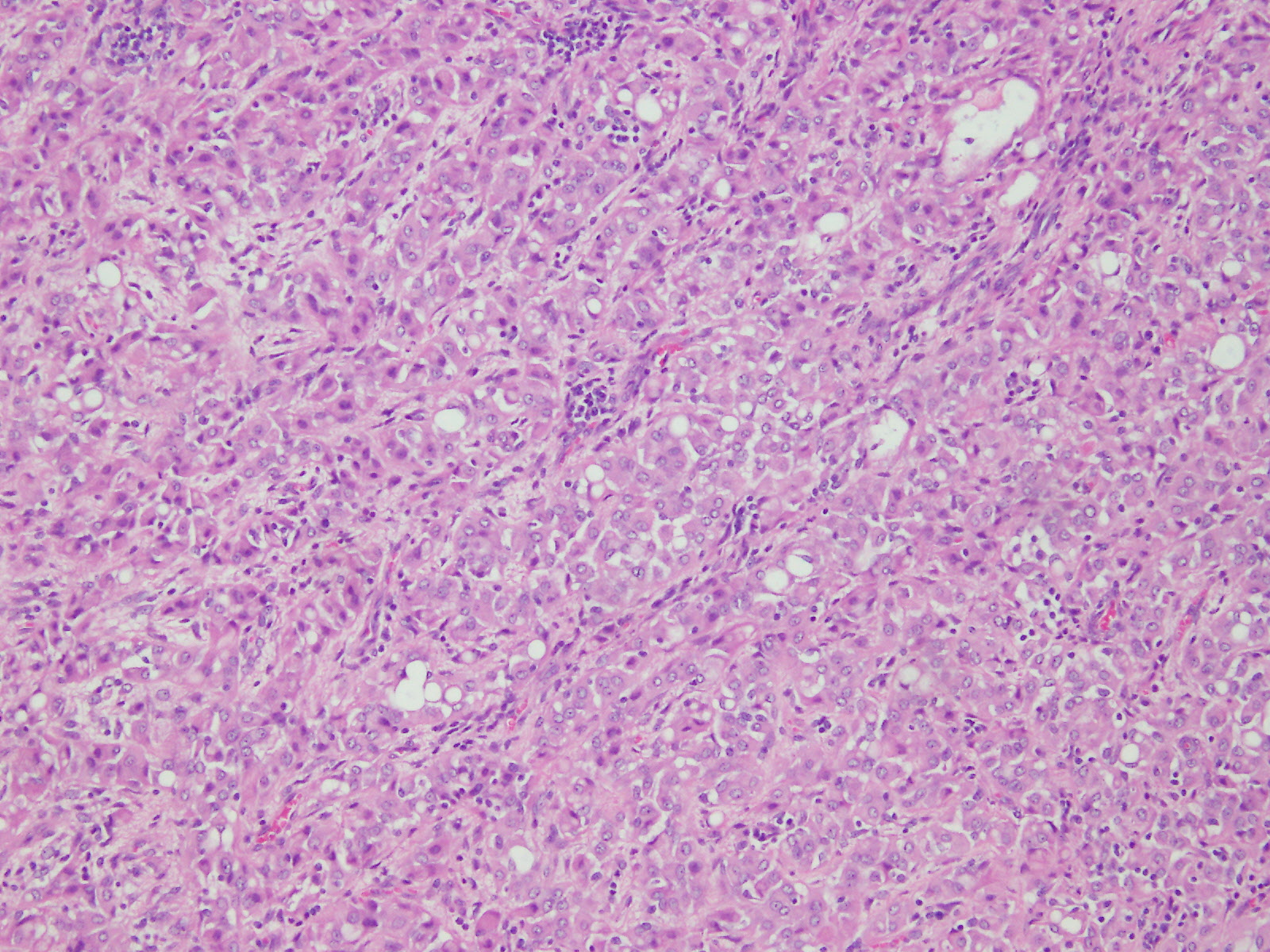
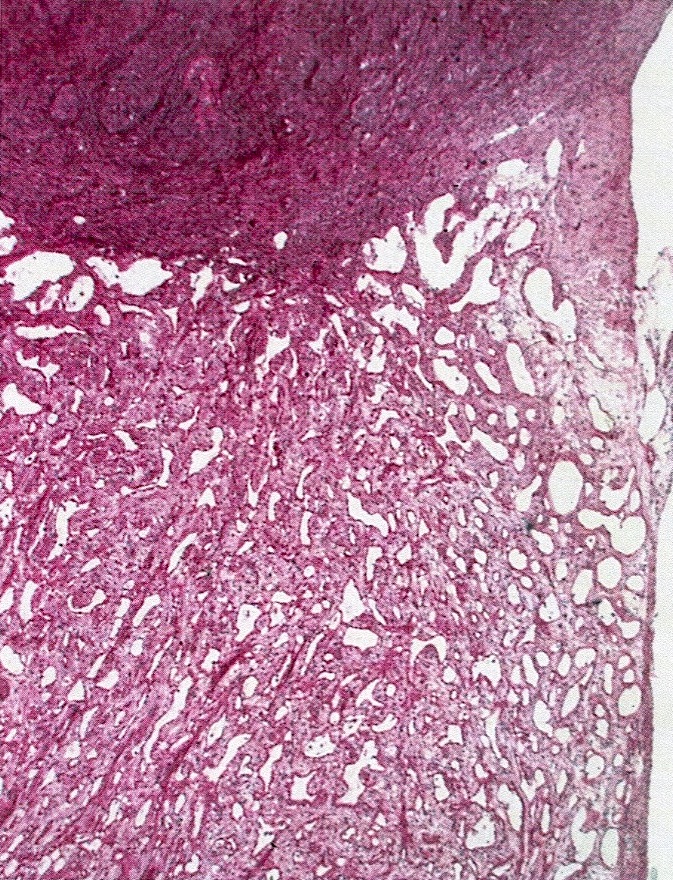
Microscopic (histologic) description
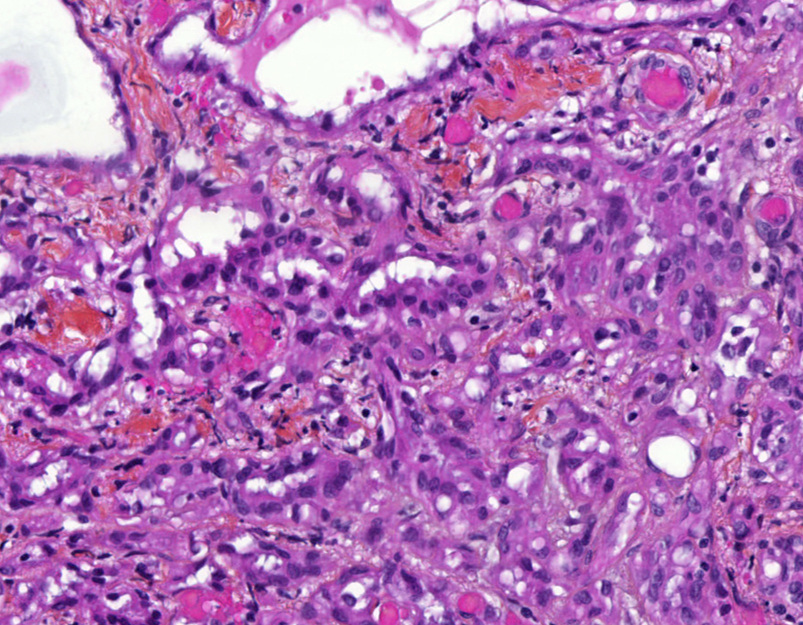
- Composed of clefts and spaces lined by cuboidal, low columnar or flattened epithelial-like cells
- Surrounded by connective tissue that varies from loose and edematous to dense and hyalinized
- The epithelial-like cells may exhibit marked vacoulation, which in some cases may contain weakly basophilic material
- A spotty lymphoid aggregate may be a low power clue to the diagnosis
- Distinctive thread-like bridging strands crossing the tubular spaces are useful diagnostic features
- Morphologic patterns:
- Adenoid
- Angiomatoid
- Cystic
- Glandular
- Solid
- Tubular
- Plexiform
- Canalicular
- Similar appearance to appearance found within other locations
- Relatively well demarcated, nonencapsulated solid aggregates of cells forming cleft-like spaces lined by low columnar to cuboidal flattened epithelial-like cells
- Cells often surrounded by stroma that ranges from dense / fibrotic to loose / edematous
- Epithelial-like cells may display marked vacuolization, signet ring cell-like appearance or oxyphilic cytoplasm
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Smears are moderately cellular with sheets of monotonous round to oval cells showing indistinct cell borders and moderate to abundant pale cytoplasm with vacuolations
- Nuclei are eccentric in location, but regular with inconspicuous nucleoli
Positive stains
- Low molecular weight cytokeratin
- CK 5/6
- Calretinin
- WT1
- D240
- Alcian Blue (epithelial cells and within cleft-like spaces)
- Weak PAS
Electron microscopy description
- No microvilli, no bundles of cytoplasmic filaments, no tight junctional complexes, no intercellular spaces
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- No specific genetic abnormality has been identified
Differential diagnosis
- Epithelioid hemagioendothelioma: positive for CD34 and factor VIII
- Leiomyoma
- Lymphangioma: positive for CD31, CD34 and factor VIII
- Malignant mesothelioma / adenomatoid-like mesothelioma: rare, marked cytologic atypia with features of invasion
- Metastatic adenocarcinoma: most likely from GYN origin
- Mucinous carcinoids: positive for neuroendocrine markers
- Signet ring cell carcinoma (Krukenberg tumor): positive for mucicarmine, EMA, BerEP4, cytological atypia, brisk mitosis
- Yolk sac tumor: AFP+, nuclei larger with prominent nucleoli and brisk mitotic activity