Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Fielder T, Gupta R. Secretory carcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/salivaryglandssecretory.html. Accessed October 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Rare primary salivary gland tumor that harbors specific ETV6 genetic rearrangement, most commonly ETV6-NTRK3 translocation t(12;15)(q13;q25) (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:599)
- Similar morphological, immunohistochemical and molecular features as secretory carcinoma of the breast (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:599)
Essential features
- Rare primary salivary gland carcinoma characterized by ETV6 gene rearrangement (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:599, Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:1295, Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1121)
- Predominantly (76%) occurs in parotid, minor salivary glands of oral cavity and submandibular gland
- Also described in nasal cavity, skin and thyroid (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:1295)
- Predominantly adults, wide age range (5 - 87 years) (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:1295, Histopathology 2012;61:387)
- Various histological growth patterns, including cystic, solid, tubular, papillary cystic and lobular
- Cysts with intraluminal colloid-like secretions (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:599)
- Cells with bubbly cytoplasm and relatively monotonous round nuclei with small but distinct nucleoli (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:599, Histopathology 2012;61:387, Pathology 2015;47:659)
- Immunohistochemical expression of GATA3, S100, NTRK3, MUC4, mammaglobin (Pathology 2015;47:659, Head Neck Pathol 2013;7:311, Histopathology 2020;76:375)
- Generally low grade with indolent clinical behavior; however, local lymph node metastases may be seen in up to 22% (Histopathology 2012;61:387)
- Rare high grade transformation with aggressive clinical behavior, including distant metastasis (Pathol Res Pract 2017;213:1112, Int J Surg Pathol 2017;25:613, Ann Oncol 2016;27:920)
Terminology
- Previously known as mammary analogue secretory carcinoma (MASC)
ICD coding
- ICD-10: C07 - Malignant neoplasm of parotid gland
Epidemiology
- Slight male predominance (M:F = 1.4:1) (Histopathology 2012;61:387)
- Wide age range (5 - 87 years) (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 2020 May 31 [Epub ahead of print])
- Mean age 49.9 (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:1295)
Sites
- Parotid (76%), minor salivary glands of oral cavity and submandibular gland (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:1295)
- Rare sites include
- Nasal cavity, skin and thyroid (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:1295)
- Lung (Hum Pathol 2018;74:109)
- Vulva (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2019;38:283)
- Lacrimal gland (Am J Ophthalmol 2018;193:178)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Slow growing painless mass; mean duration: 1 year (Head Neck 2019;41:1227, Oral Oncol 2018;82:29)
- Low T stage at diagnosis (almost always T1 or T2) (Oral Oncol 2018;82:29, Pathology 2015;47:659)
- Generally indolent clinical course with recurrence rates of < 10% and 10 year overall survival of 95% after macroscopically complete resection (Head Neck 2019;41:1227)
- Local lymph node involvement at diagnosis in a minority (5 - 22%) (JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2019;145:91, Histopathology 2012;61:387)
- Distant metastases in < 5% (JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2019;145:91, Head Neck 2019;41:1227)
- Locally aggressive behavior and poor outcomes have been reported if incompletely resected (Head Neck 2019;41:1227, Pathology 2015;47:659)
- High grade transformation with aggressive clinical behavior including distant metastasis has been reported (Pathol Res Pract 2017;213:1112, Int J Surg Pathol 2017;25:613)
Diagnosis
- Imaging modalities for workup of salivary gland neoplasms include ultrasonography, CT and MRI (Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2021;164:27)
- Cytologic diagnosis requires awareness / high degree of suspicion and cell block for immunohistochemistry (Acta Cytol 2017;61:469)
Radiology description
- Imaging features are nonspecific; tumors often have a cystic component (Dentomaxillofac Radiol 2018;47:20170218)
Prognostic factors
- pT stage of 3 or 4 and high grade features appear most strongly associated with poor clinical outcomes (Head Neck 2019;41:1227, Pathology 2015;47:659)
- While definite thresholds are not yet described, nuclear pleomorphism, easily identified mitotic activity or presence of comedonecrosis have been described to confer poor prognosis (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7:9008)
- Rare high grade transformation with aggressive clinical behavior including distant metastasis has been reported (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:23, Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1121, Pathol Res Pract 2017;213:1112, Int J Surg Pathol 2017;25:613)
Case reports
- 15 year old girl with slow growing painless parotid mass (Am J Otolaryngol 2015;36:741)
- 44 year old man with painless buccal mass showing high grade transformation on histology developed pleural metastases within months of diagnosis (Int J Surg Pathol 2017;25:613)
- 59 year old woman with metastatic high grade secretory carcinoma with ETV6-RET rearrangement (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1121)
- 74 year old man with cervical lymph node involvement with no evident primary site of disease (Case Rep Oncol 2017;10:192)
Treatment
- Primary resection
- Neck dissection or adjuvant radiotherapy if adverse prognostic features or evidence of lymph node metastases present (JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2019;145:91, Pathol Res Pract 2017;213:1112, Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2021;164:27)
- TRK inhibitors have shown promise in phase 1 and 2 trials for ETV6-NTRK3 rearranged tumors but efficacy is not established (N Engl J Med 2018;378:731)
- Cases of initial response followed by acquired resistance have been reported in advanced disease (Ann Oncol 2016;27:920, Int J Surg Pathol 2017;25:613)
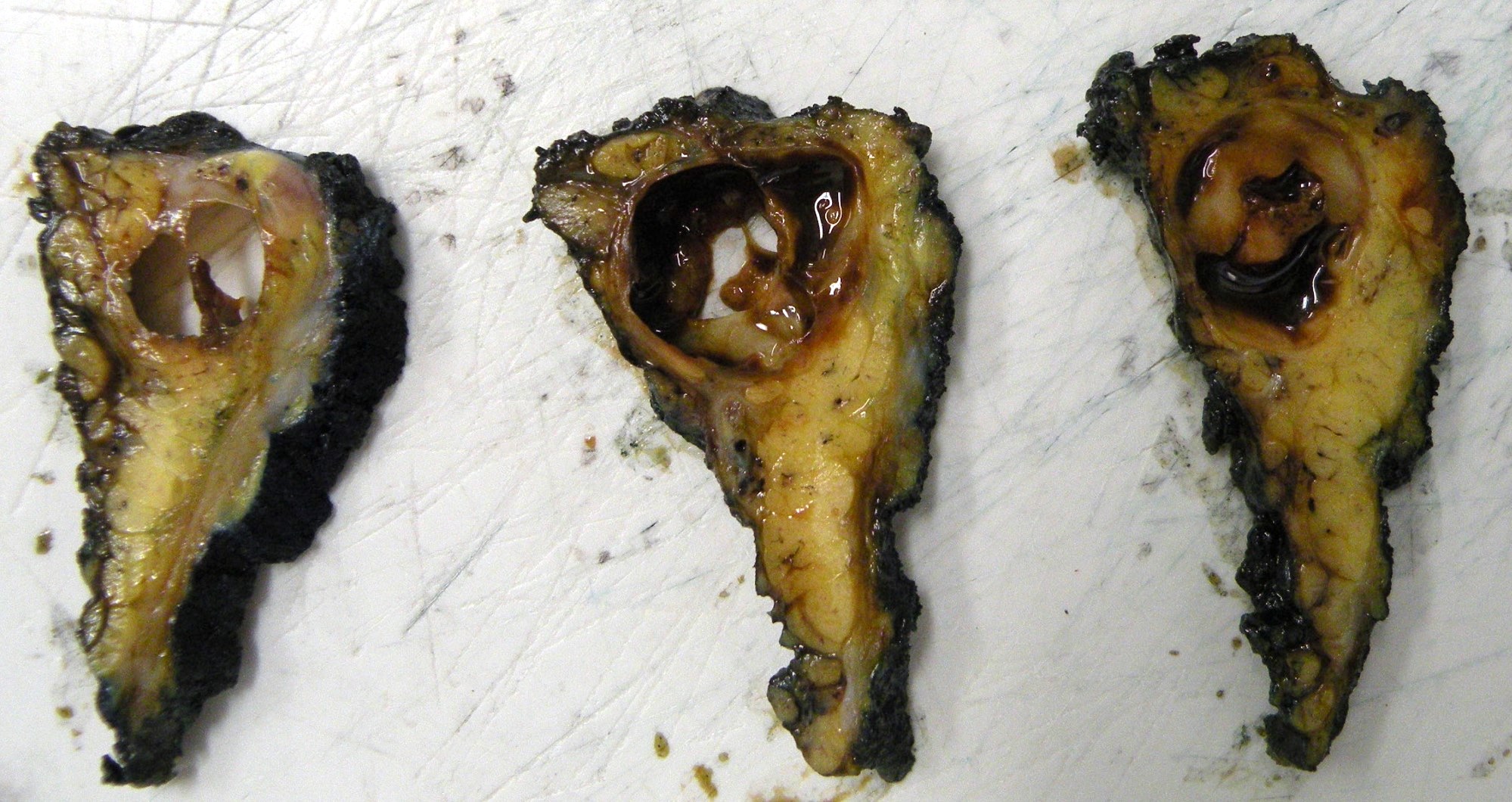
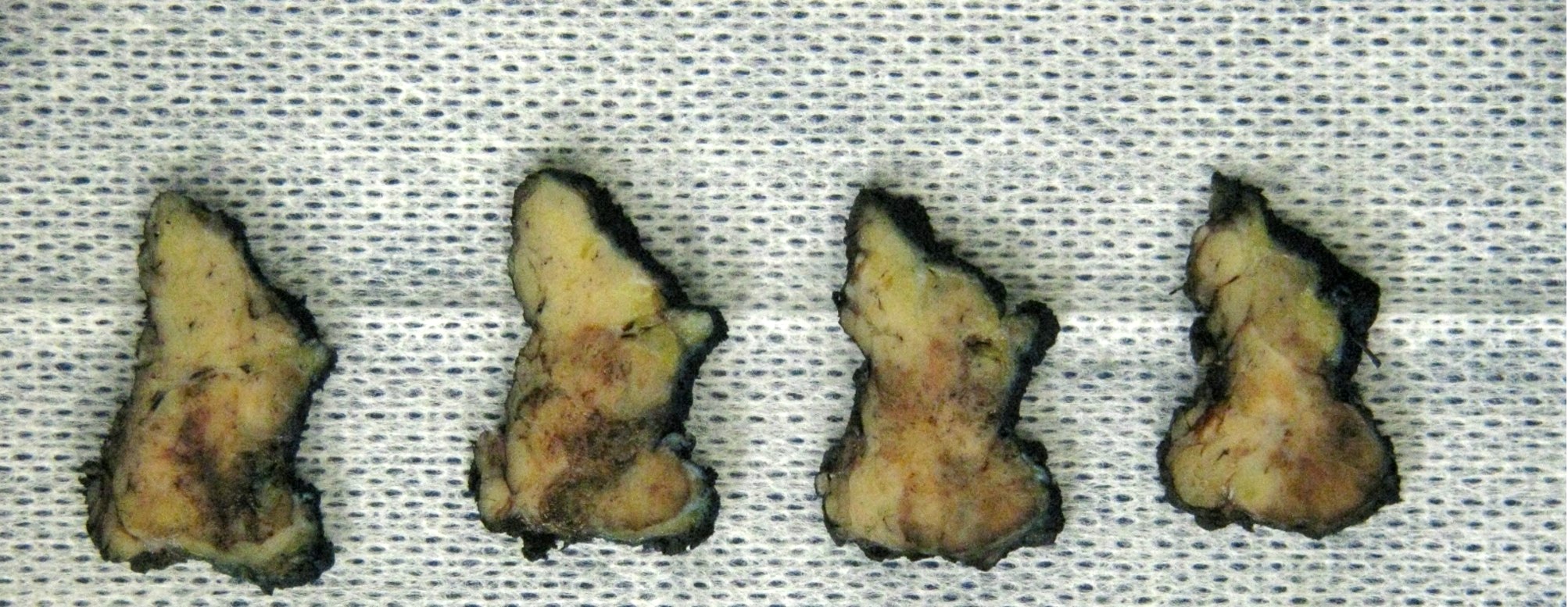
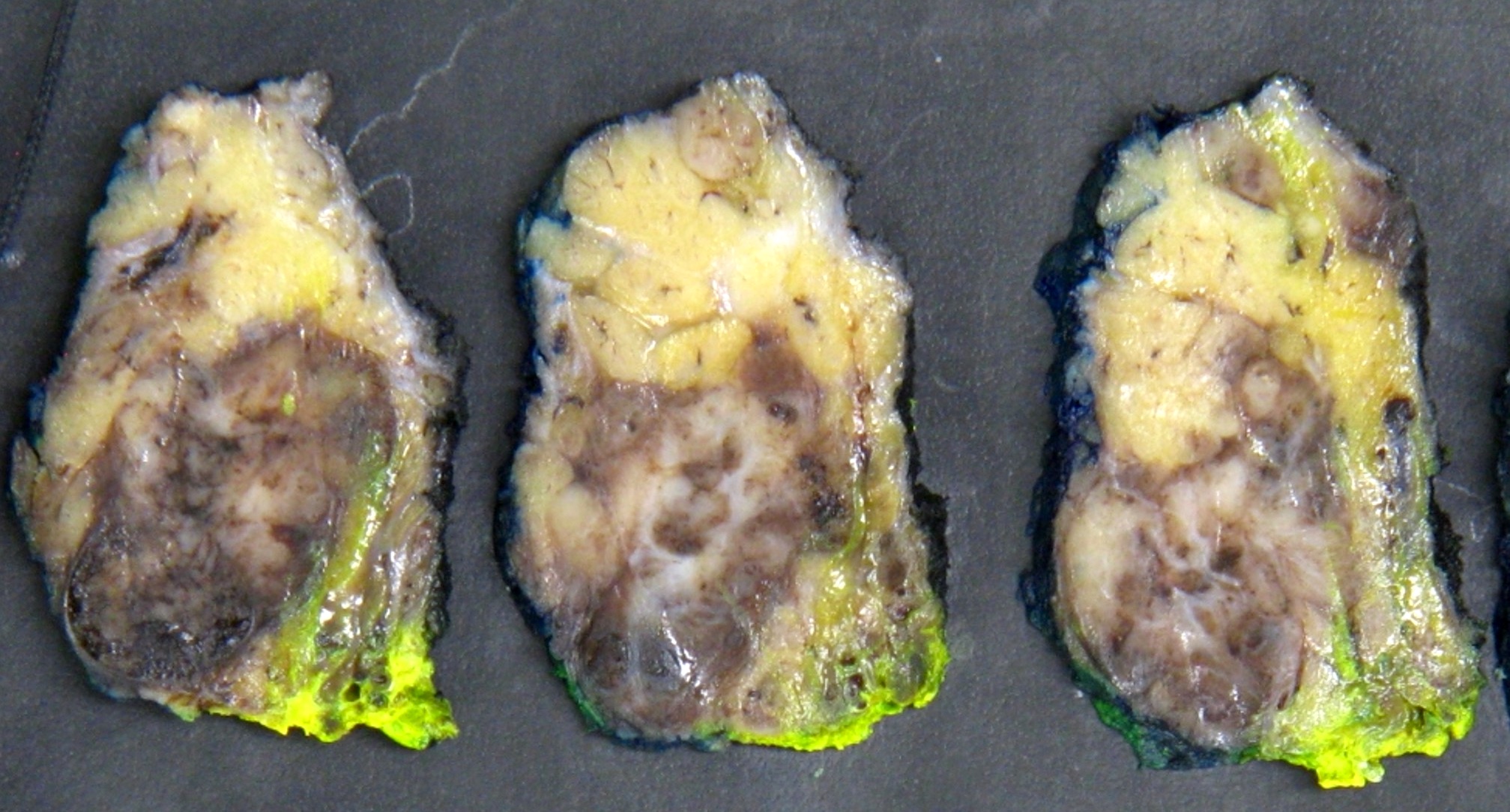
Gross description
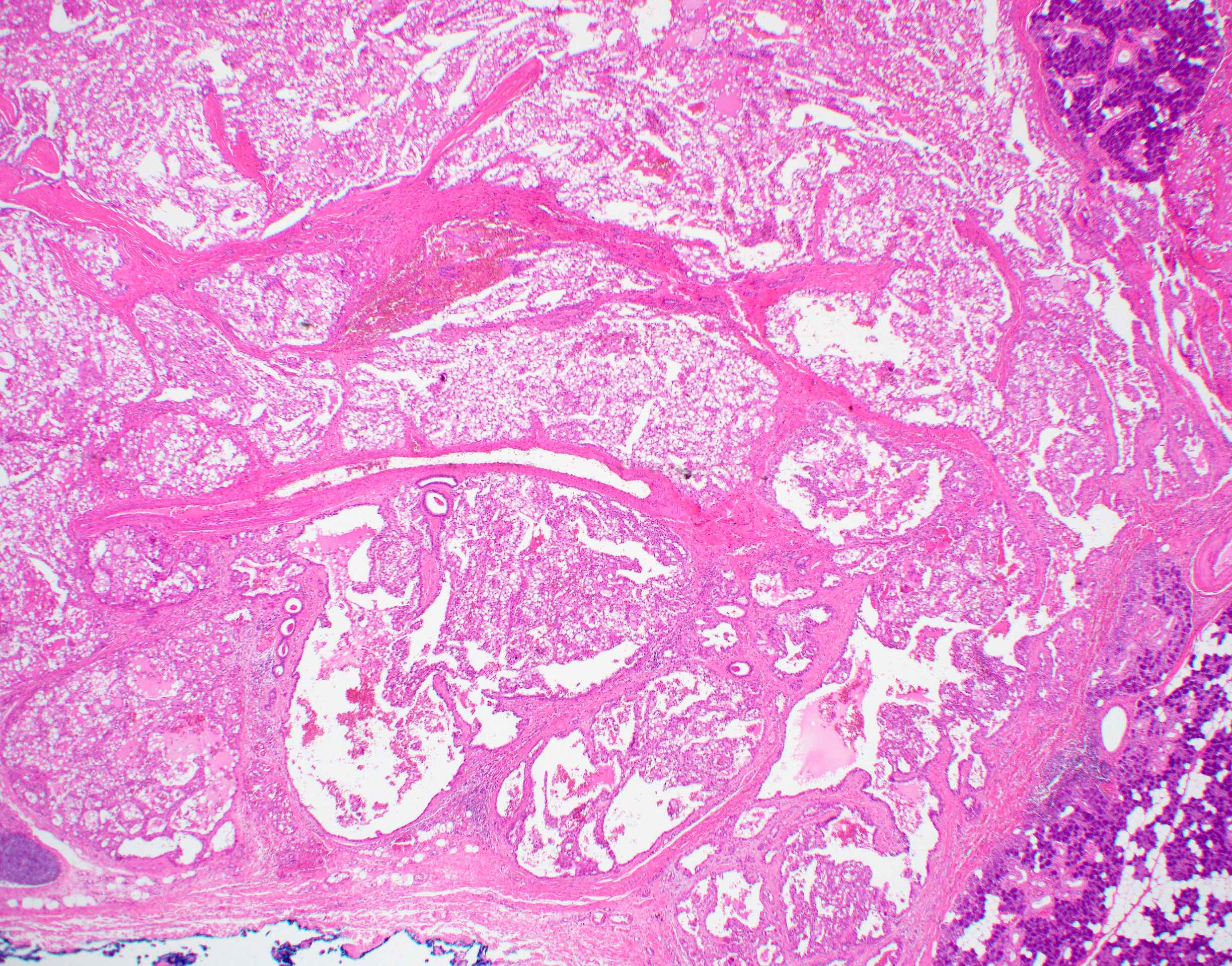
- Generally well circumscribed unencapsulated lesions, solid or cystic (Pathology 2015;47:659)
- Size range 6 - 30 mm, median 20 mm in a series of 22 cases (Head Neck 2019;41:1227)
- Tumors as large as 70 mm have been reported (Pathol Res Pract 2017;213:1112)
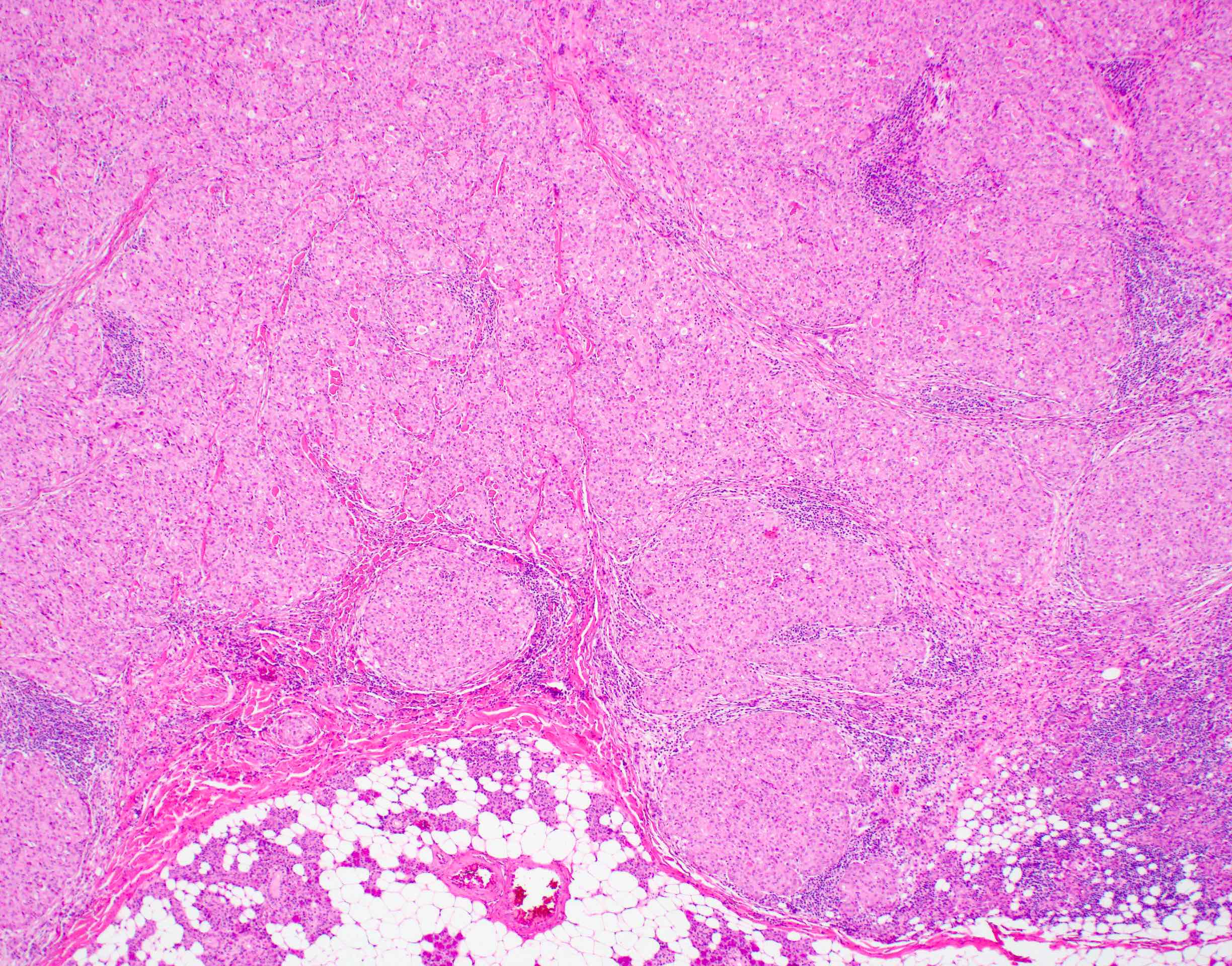
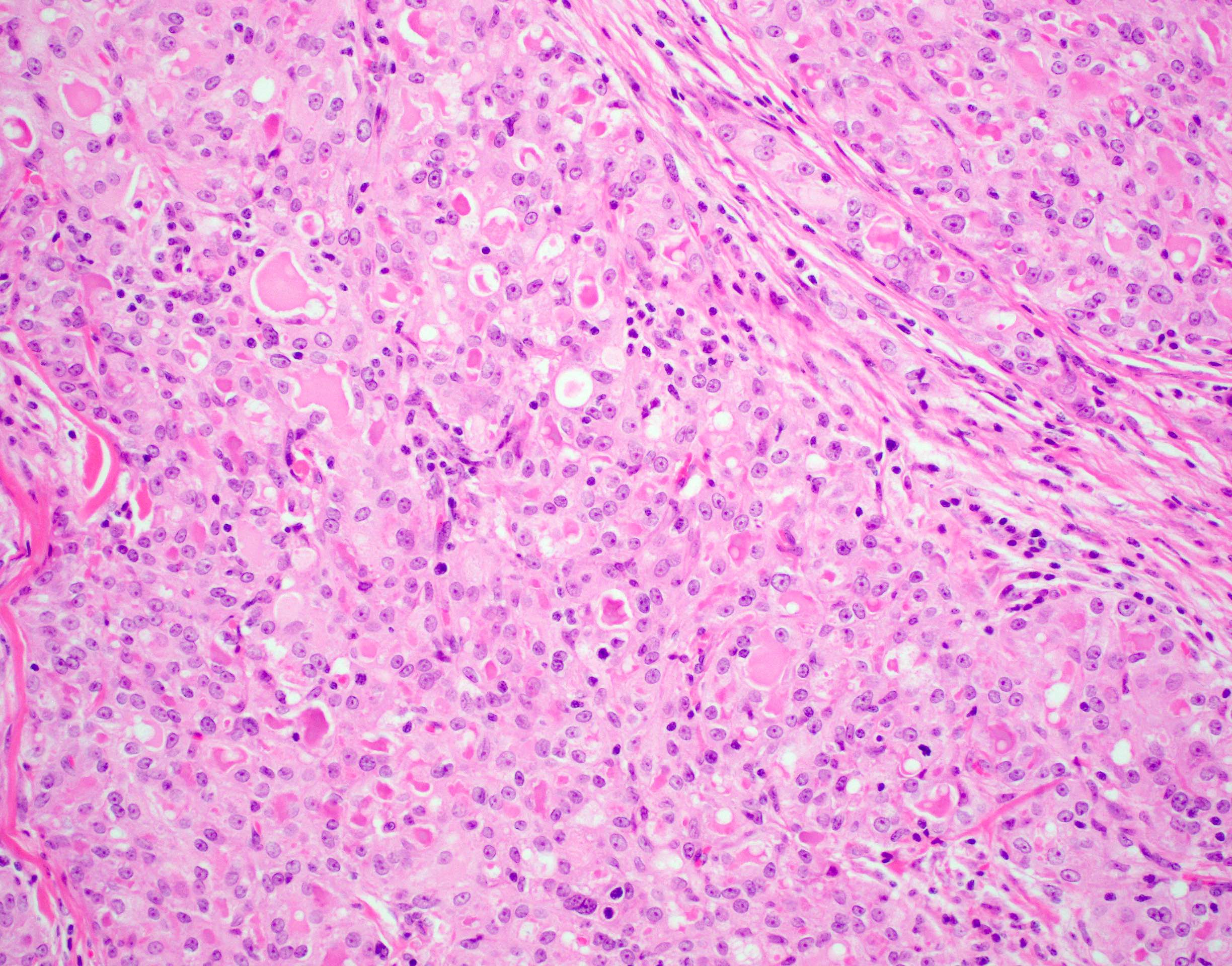
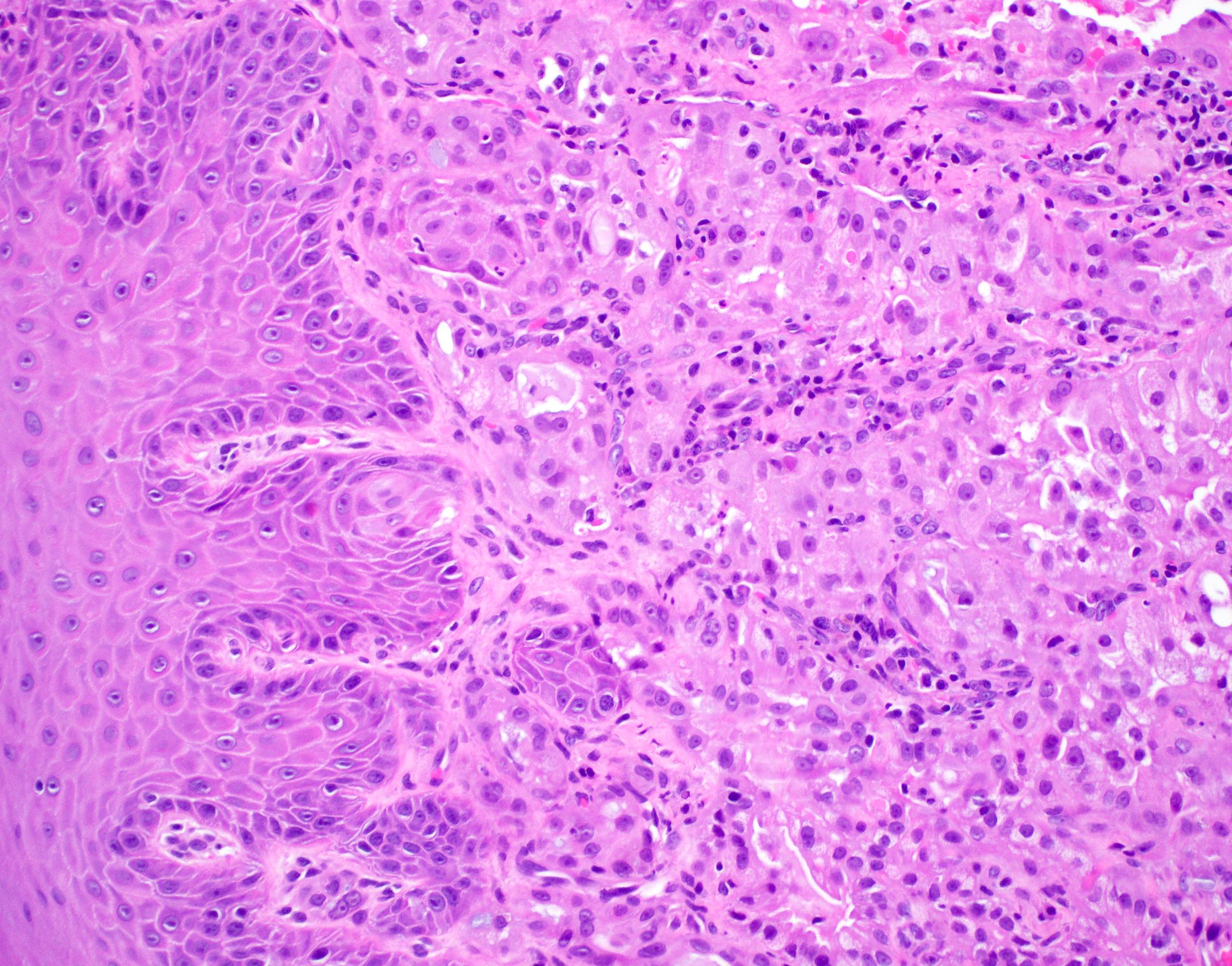
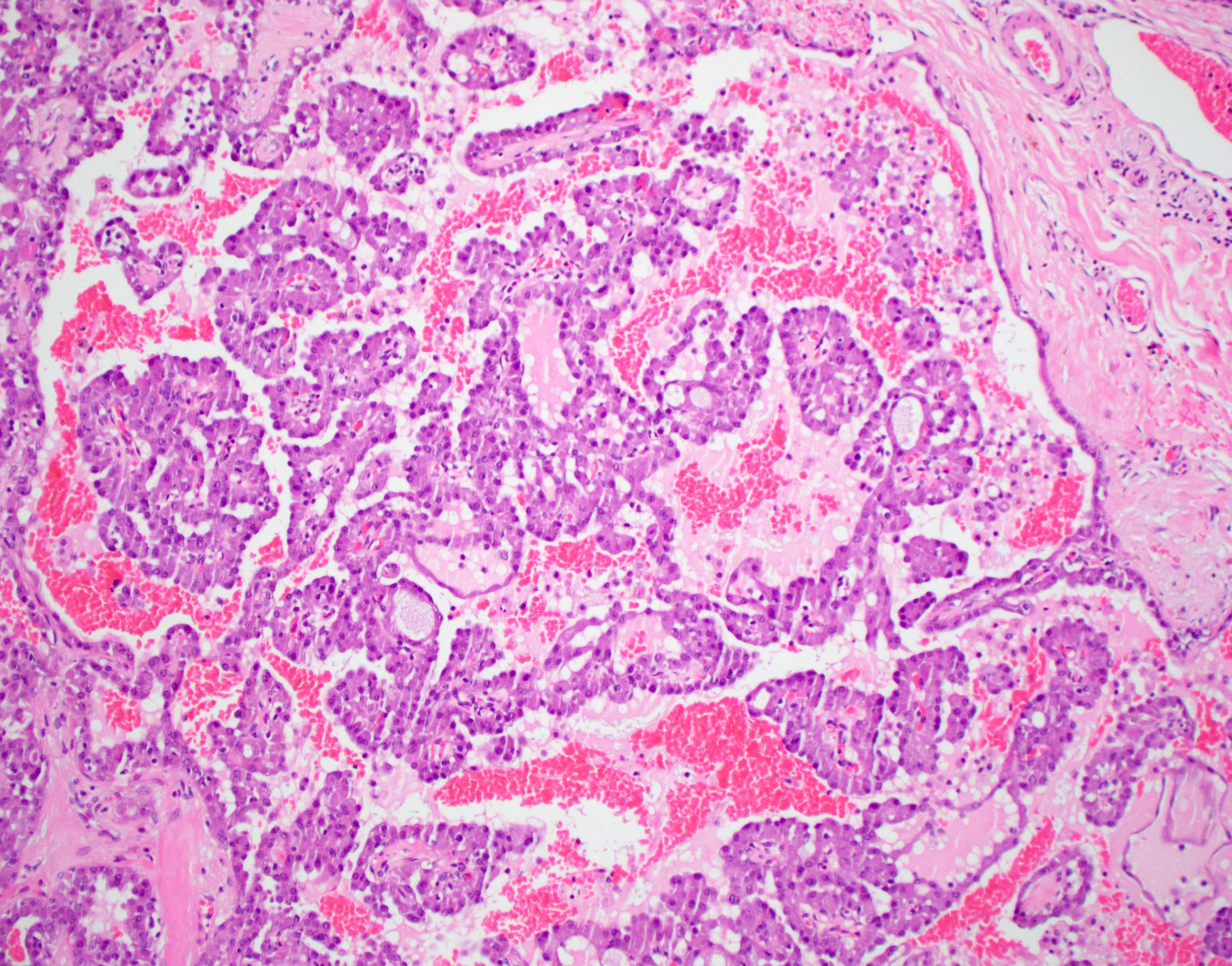
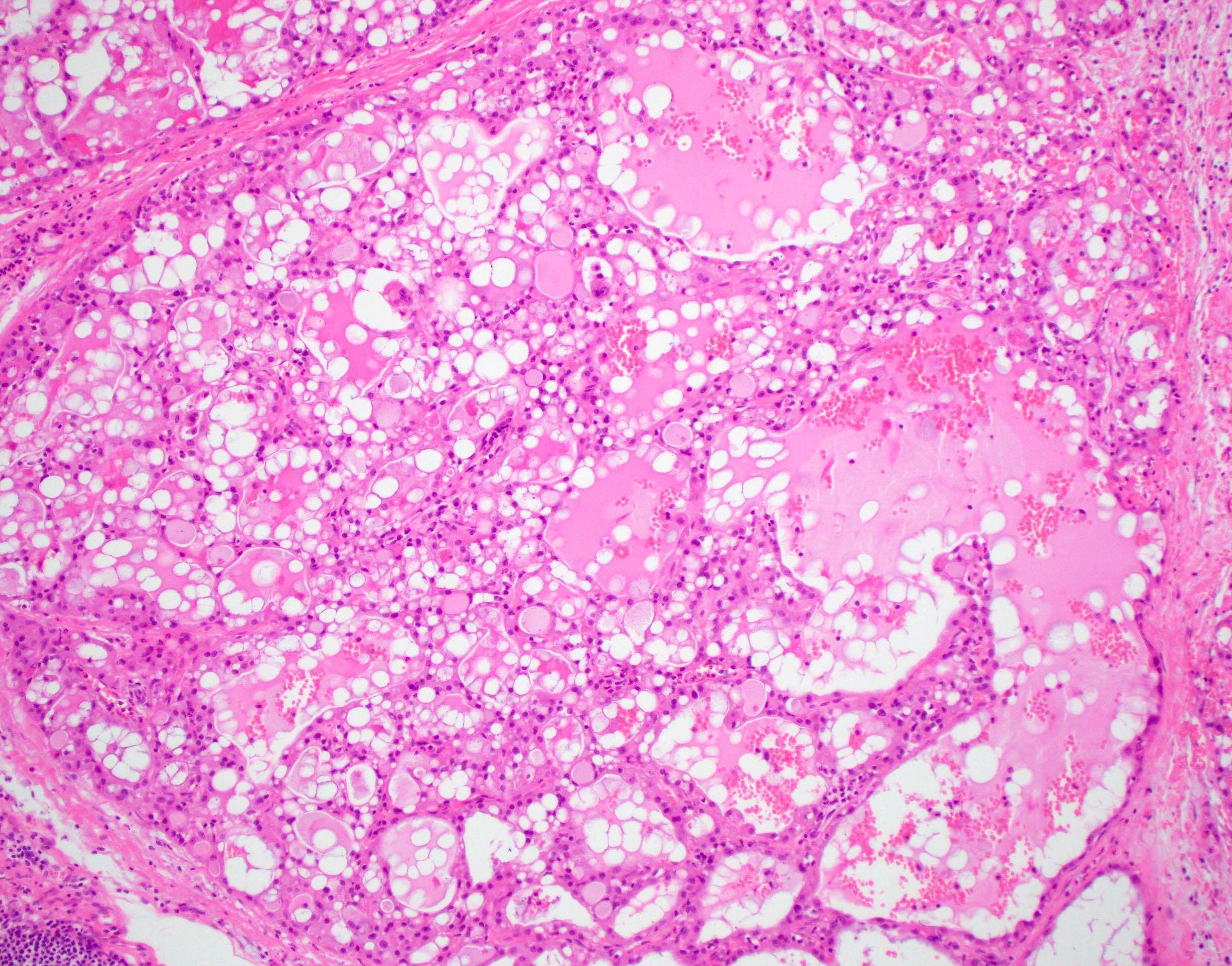
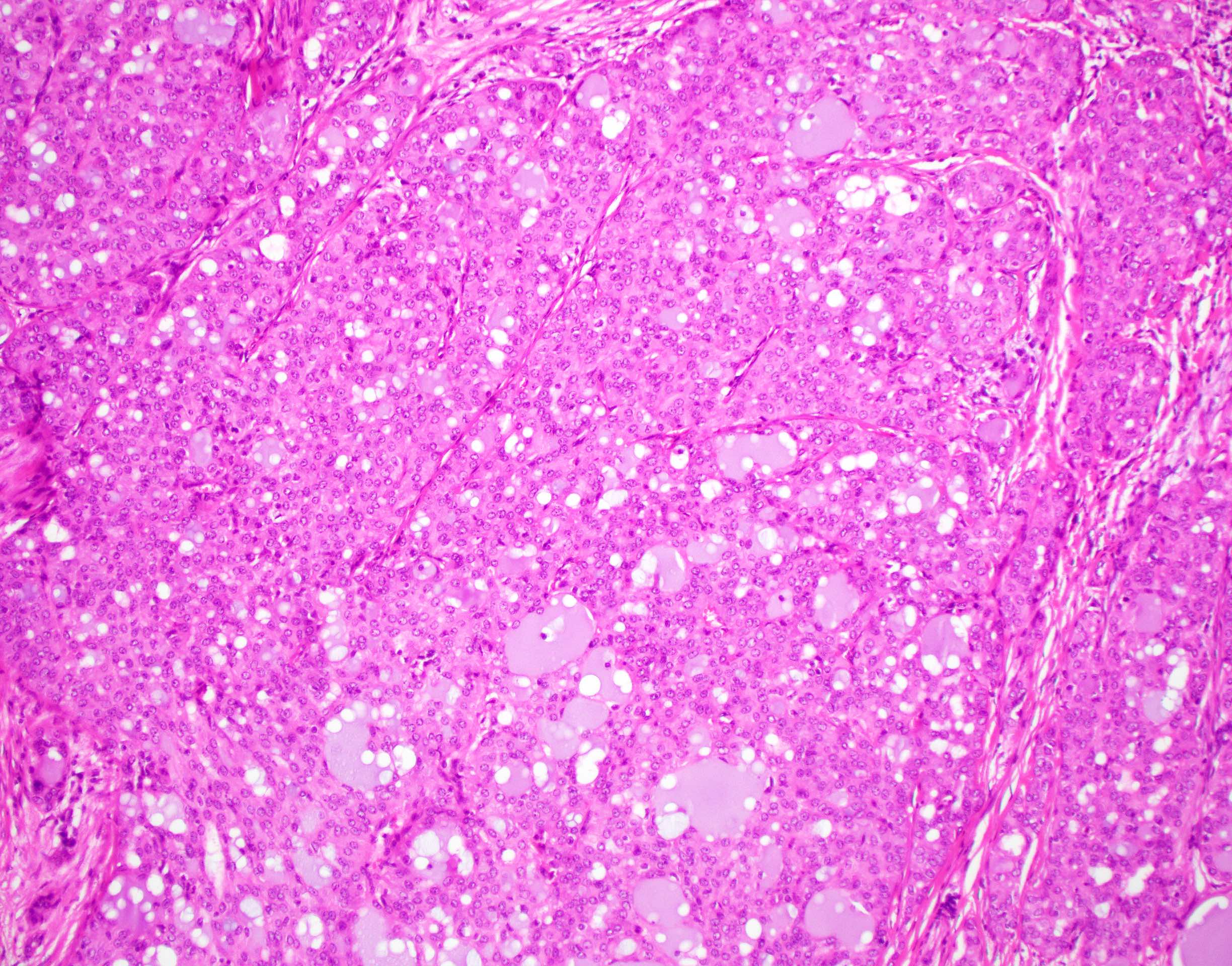
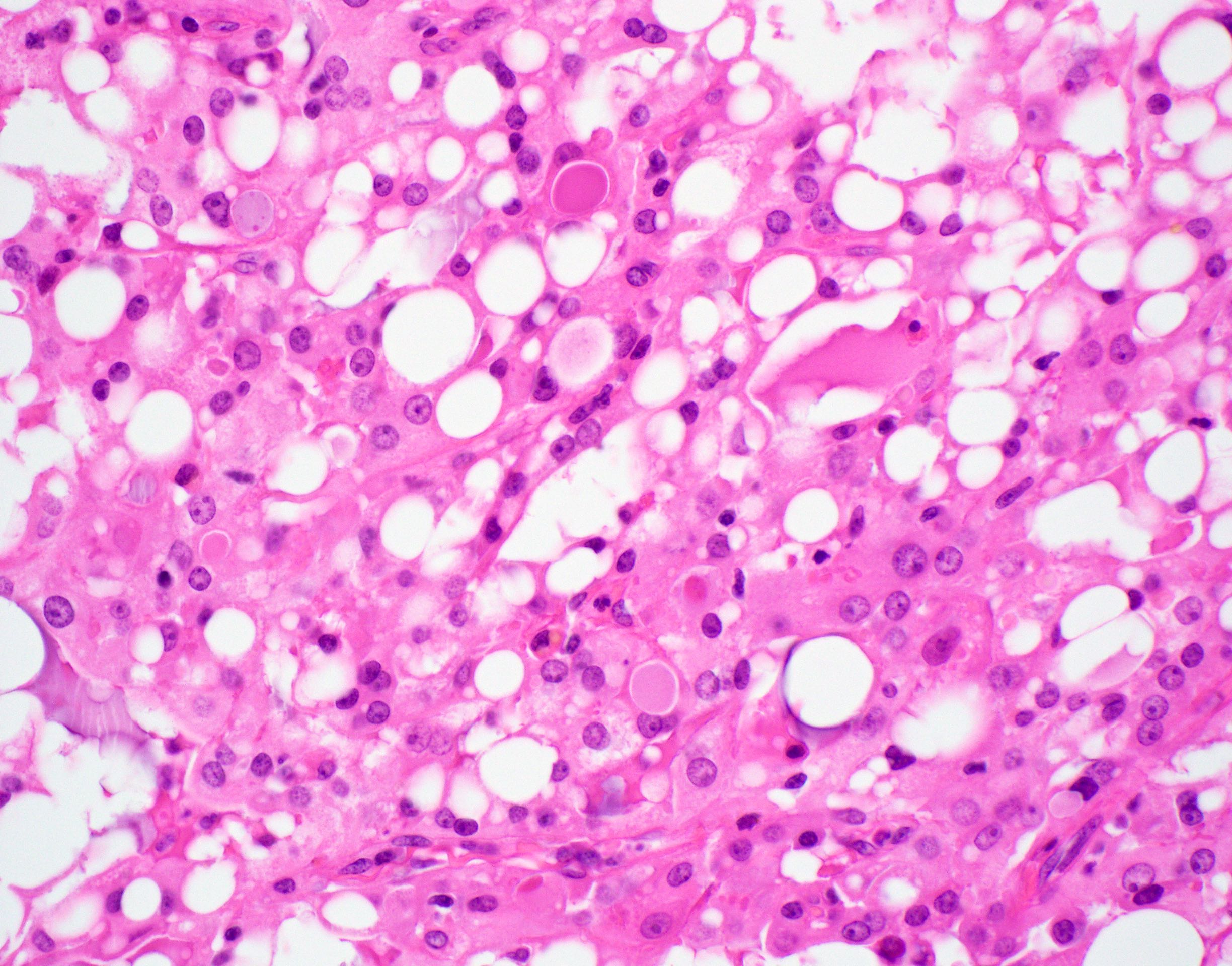
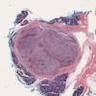
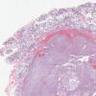
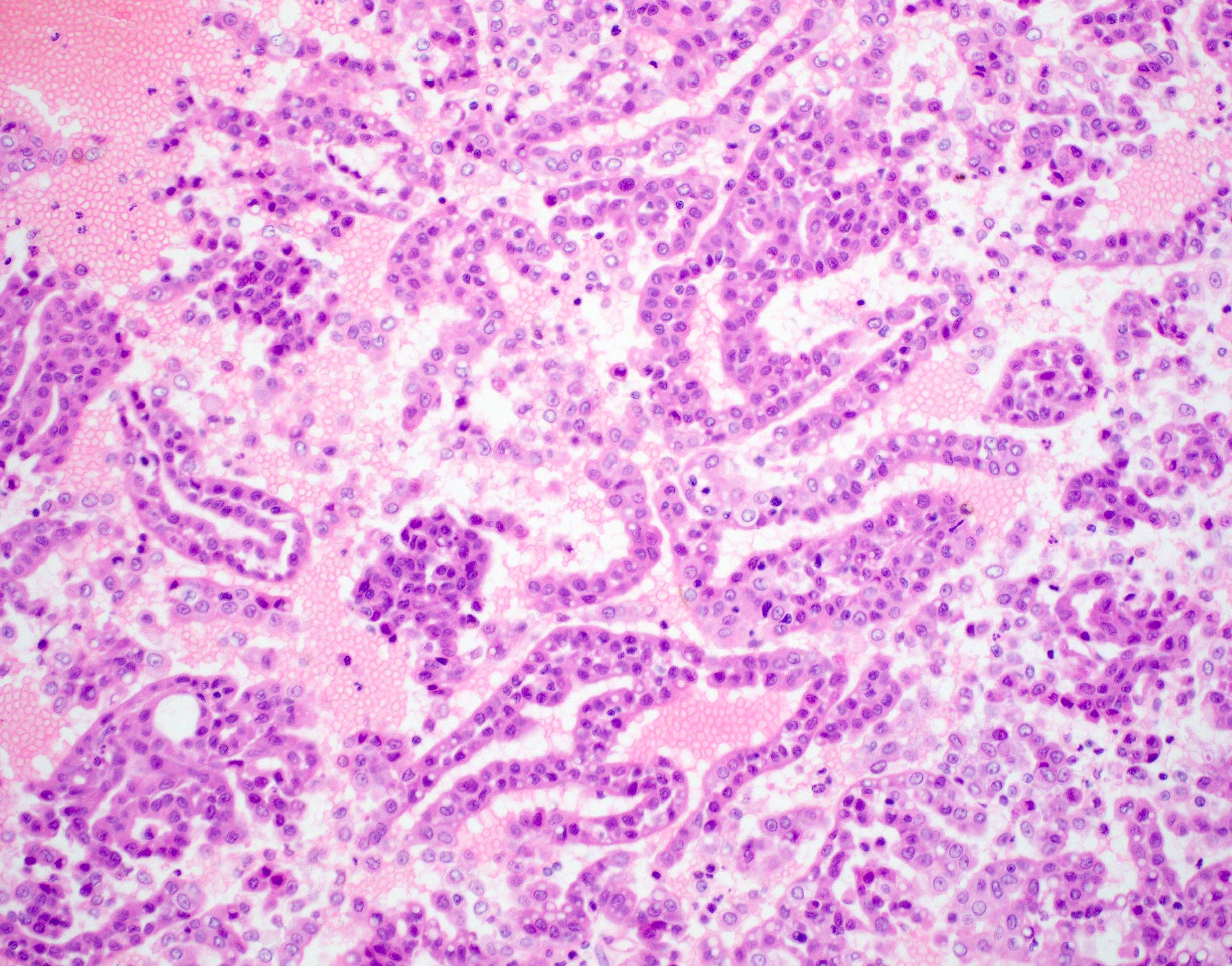
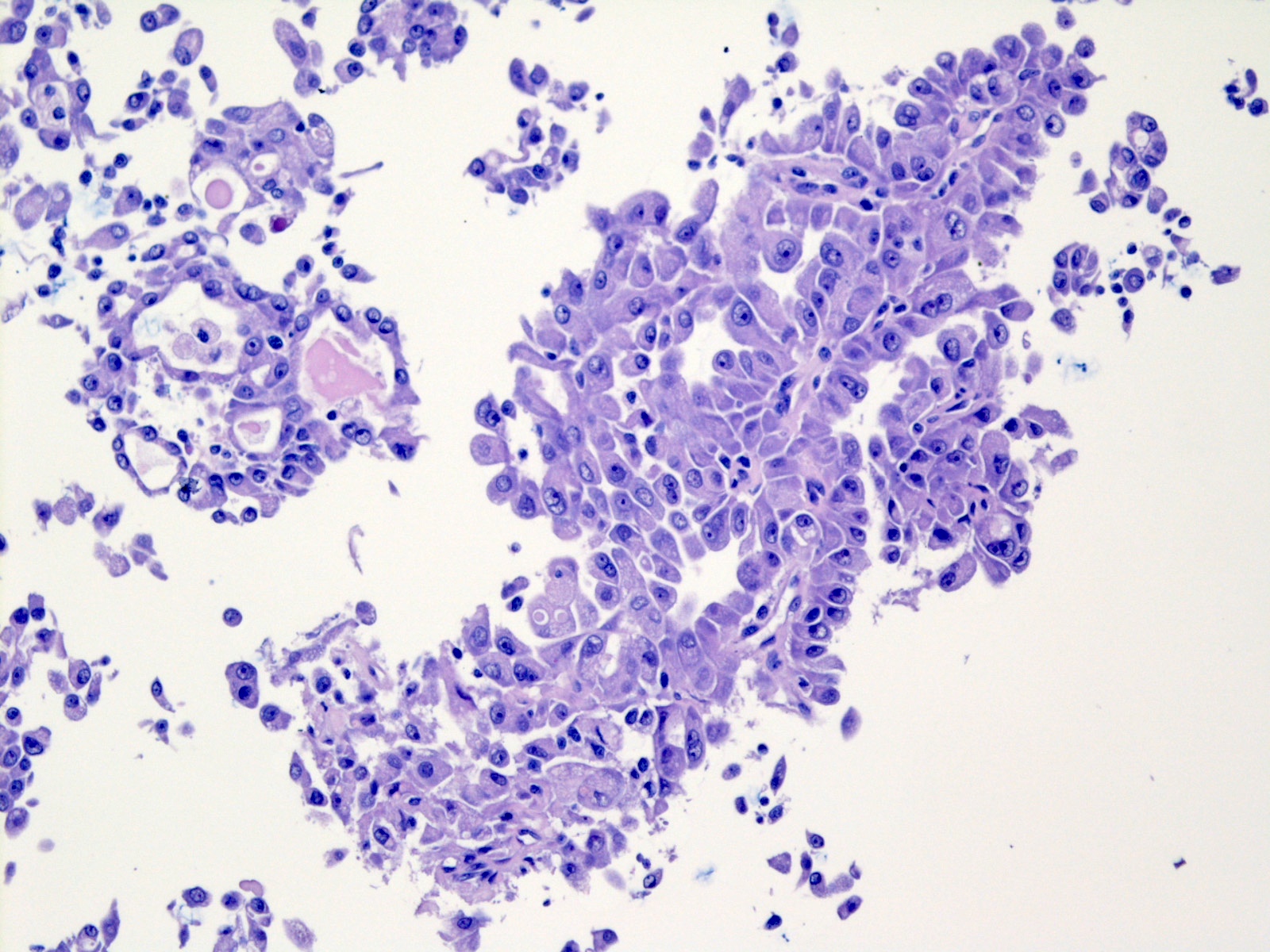
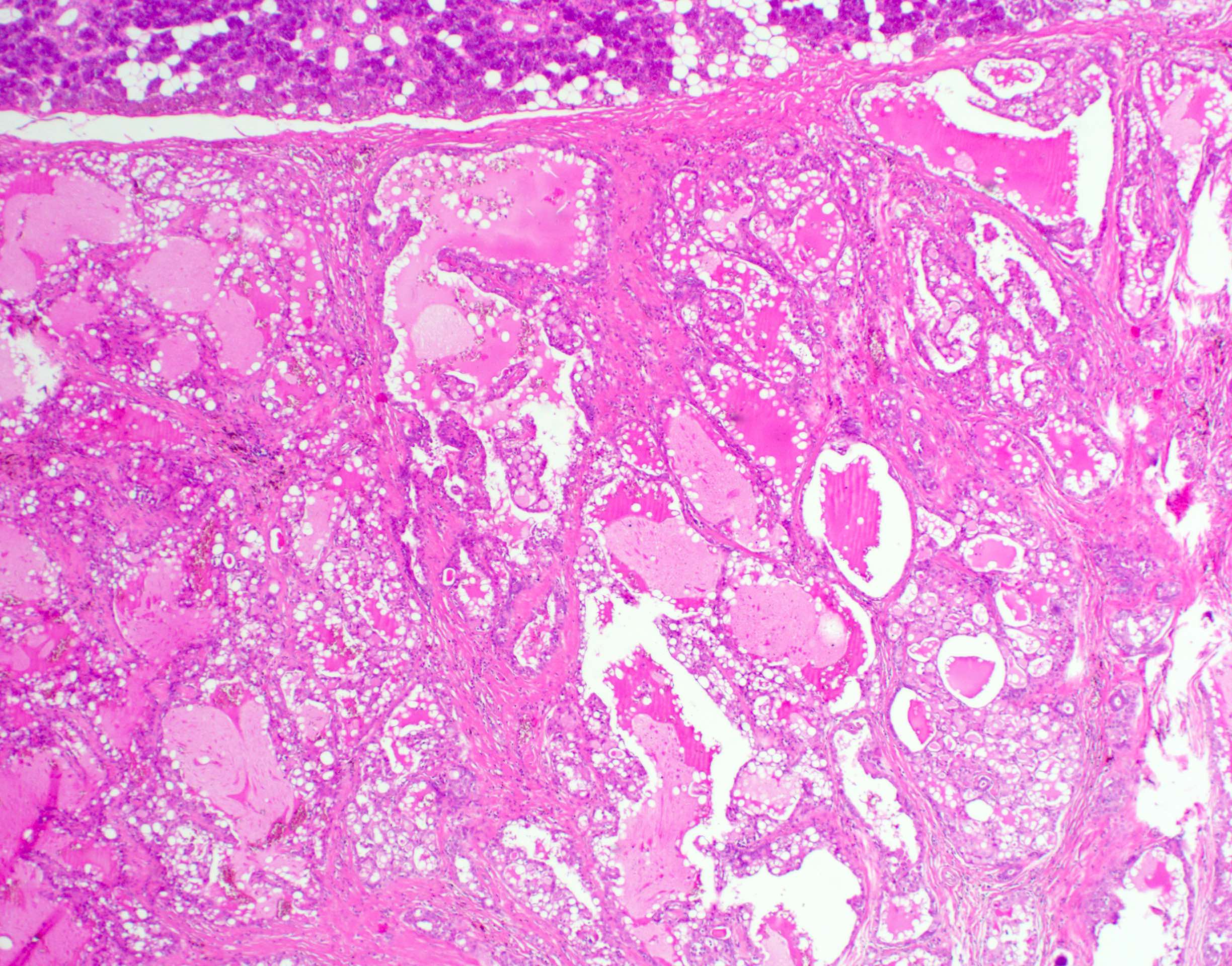
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Circumscribed or infiltrative edge
- Lobulated architecture
- Variable arrangements, including macrocystic, microcystic, solid, tubular, follicular and papillary cystic patterns (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:599, Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1483)
- Pale eosinophilic colloid-like intraluminal secretions; secretions are periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) reagent positive and diastase resistant (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:599)
- Tumor cells have eosinophilic or vacuolated cytoplasm and monomorphic round vesicular nuclei with small but distinctive nucleoli
- Occasional lymphovascular invasion and perineural invasion are seen (Head Neck 2019;41:1227)
- High grade transformation has been reported with a distinct population of tumor cells exhibiting solid or trabecular growth, infiltrative margins, desmoplastic stromal reaction, comedo-like necrosis, nuclear pleomorphism, increased mitotic rate, loss of secretory activity and perineural invasion
- A distinct low grade (conventional) carcinomatous component is also present (Pathol Res Pract 2017;213:1112)
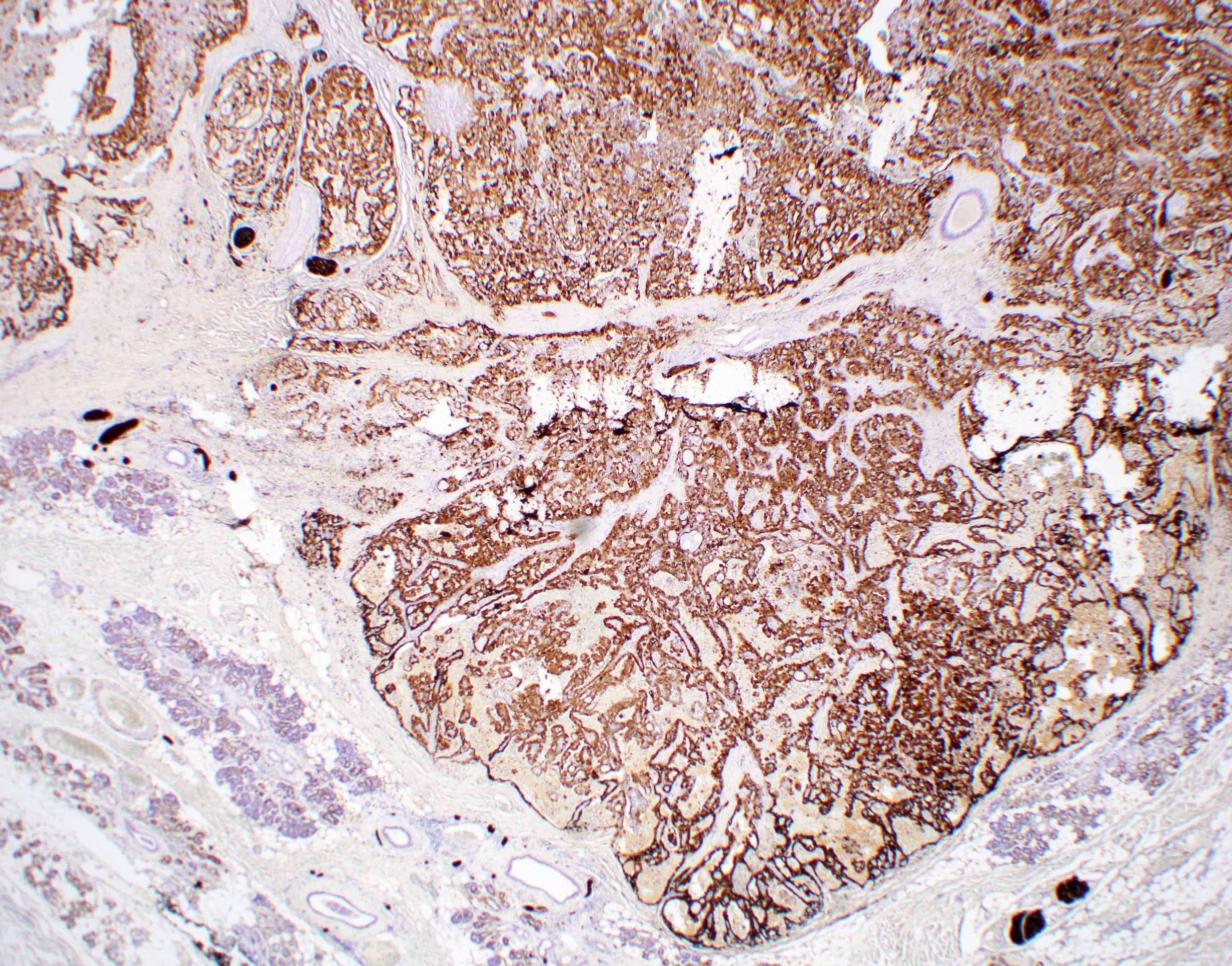
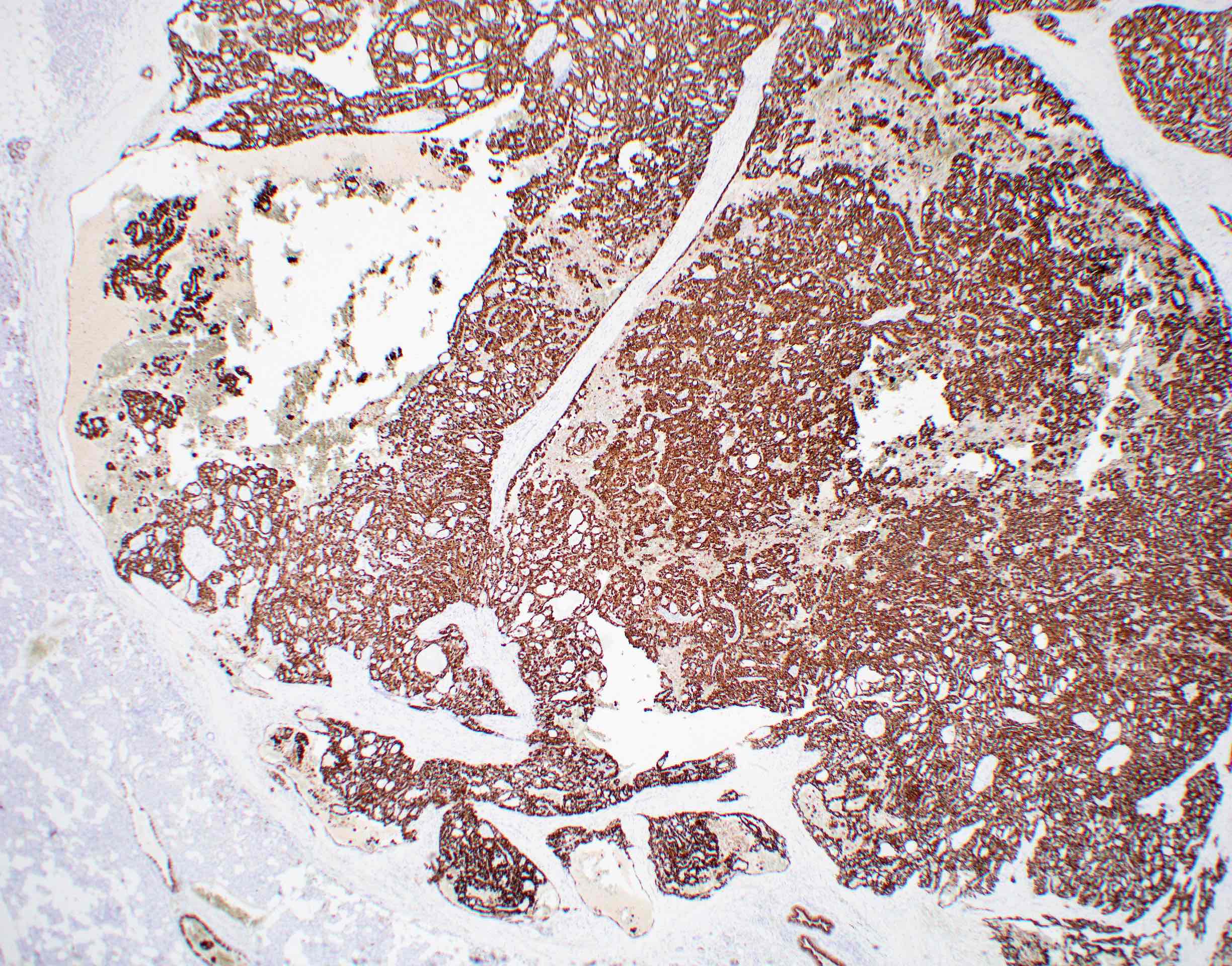
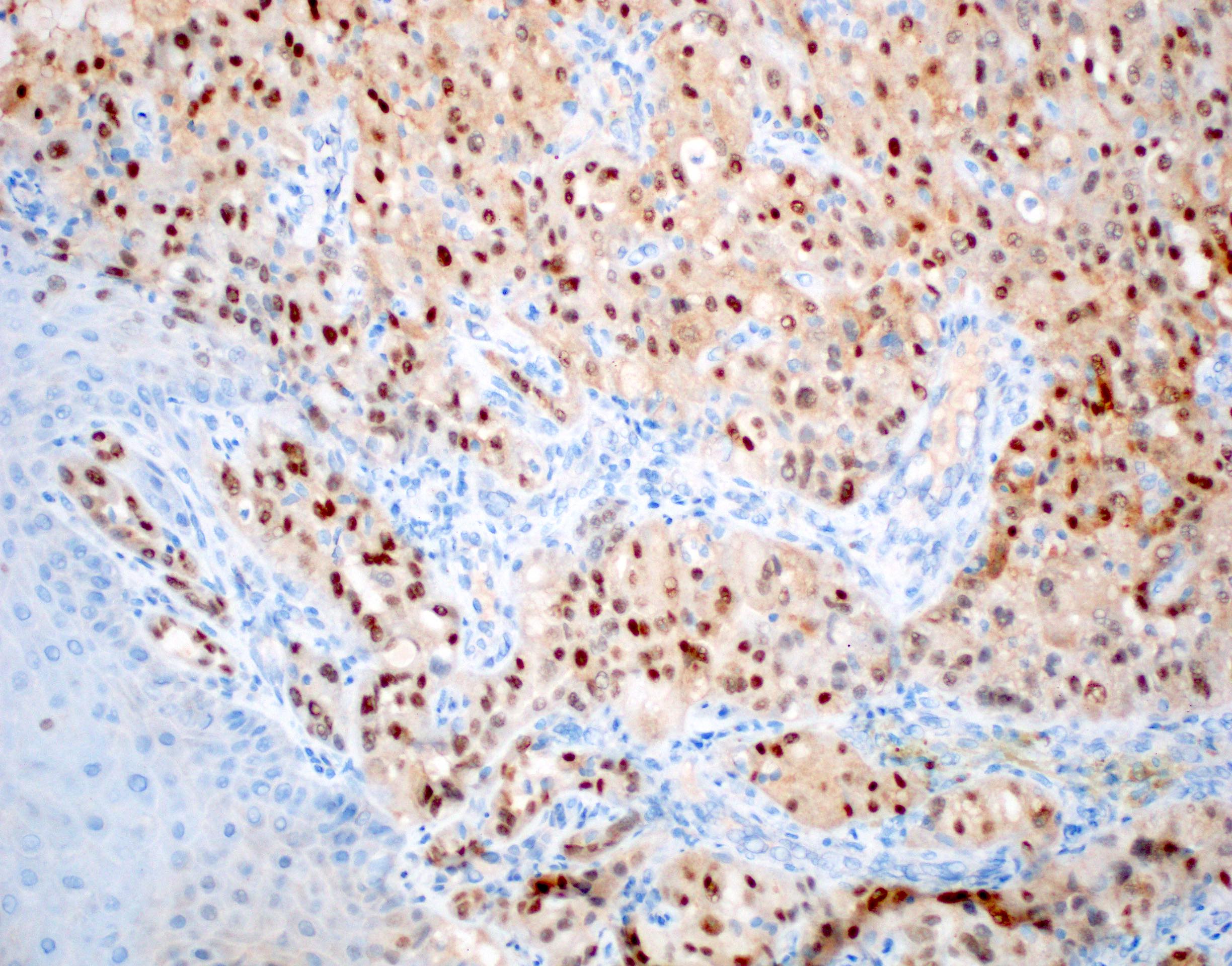
Microscopic (histologic) images
Virtual slides
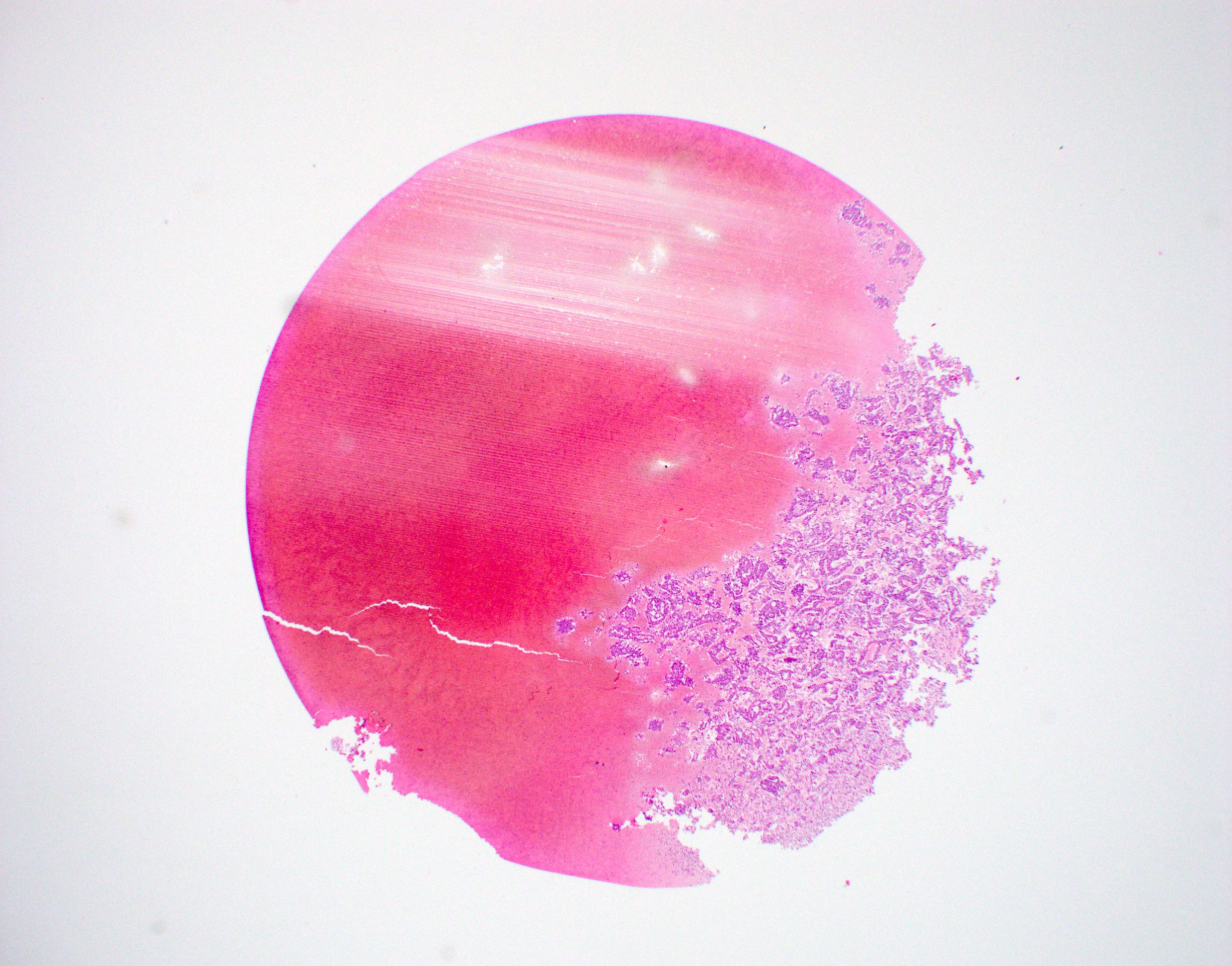
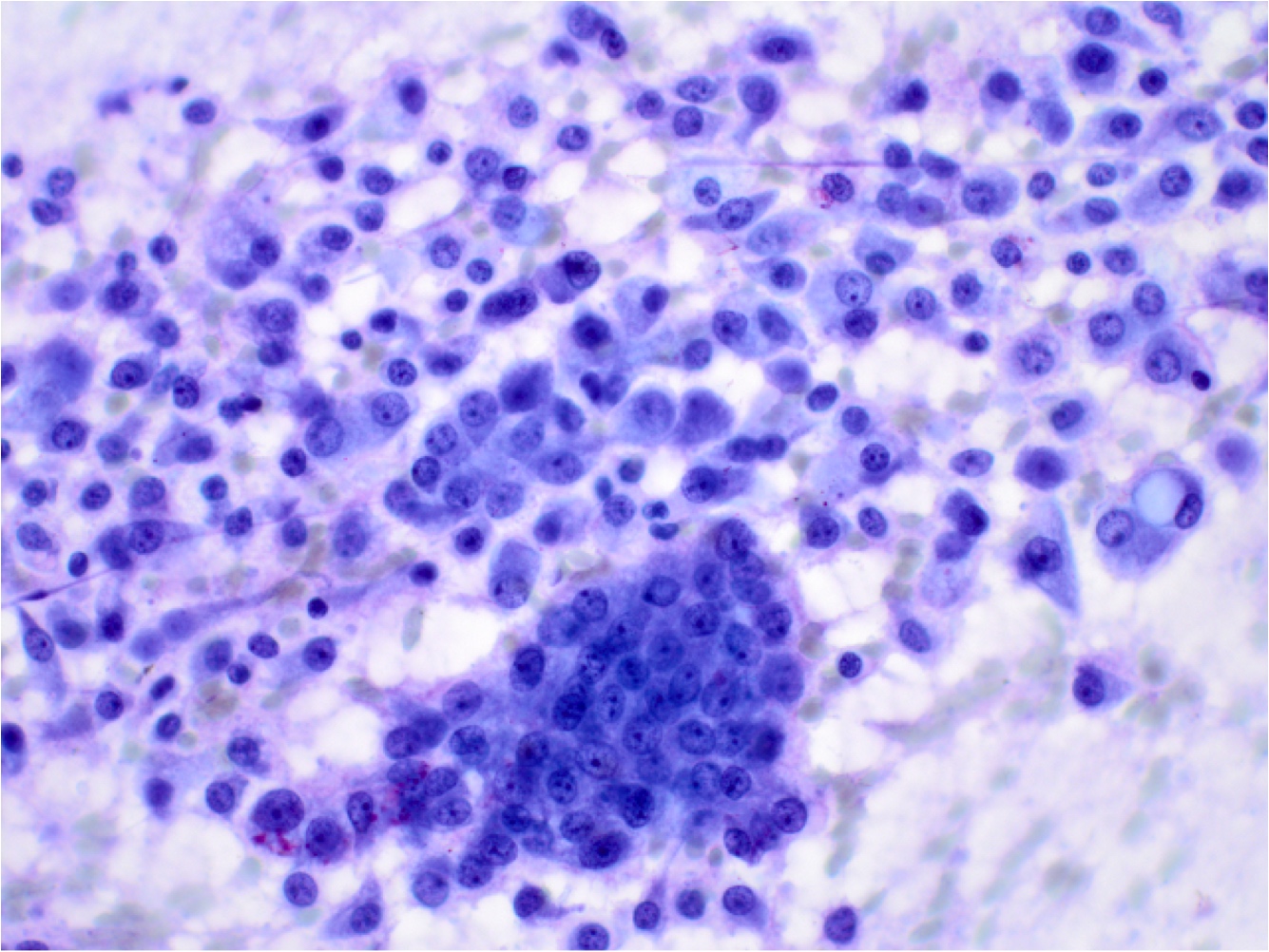
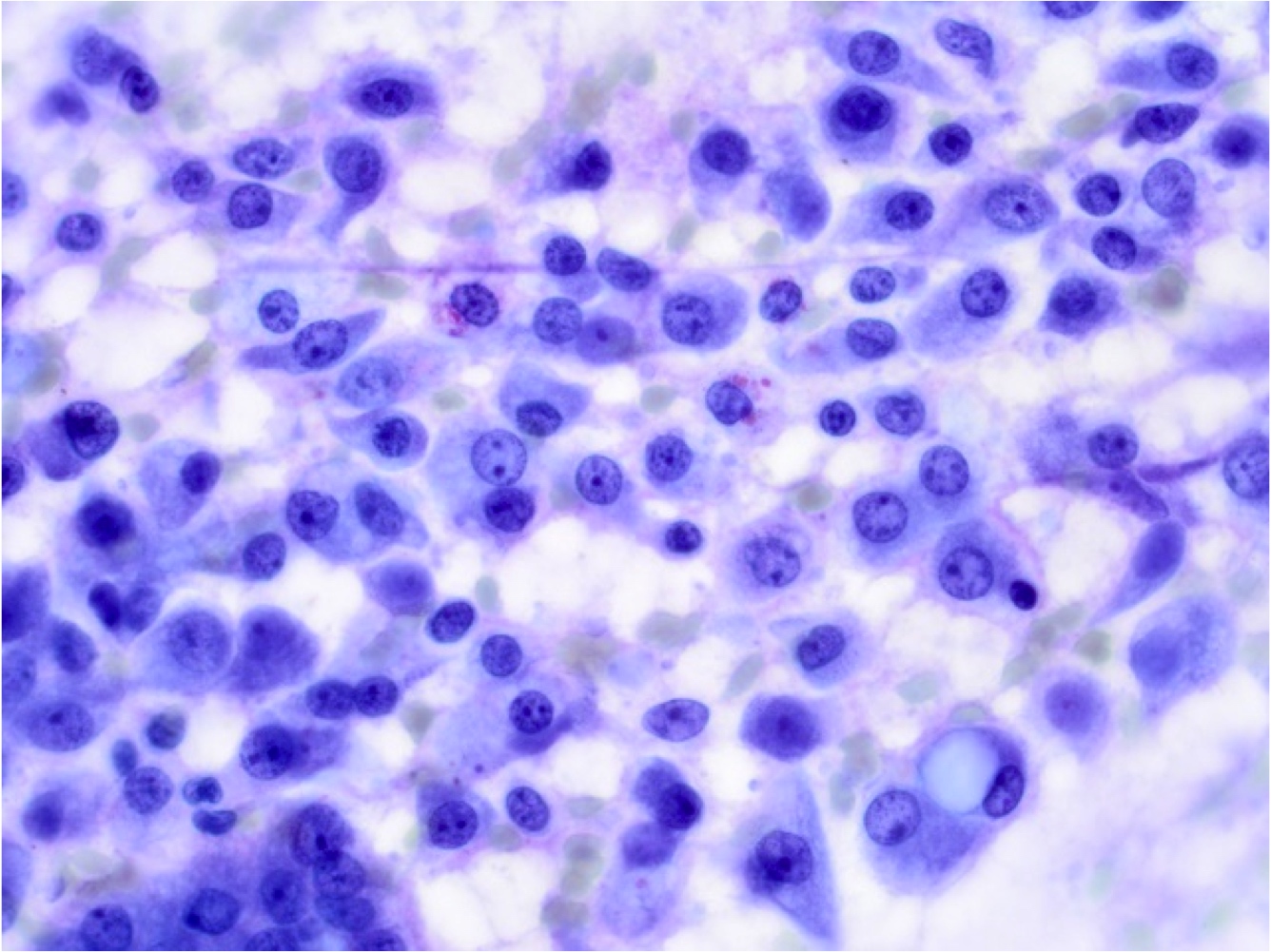
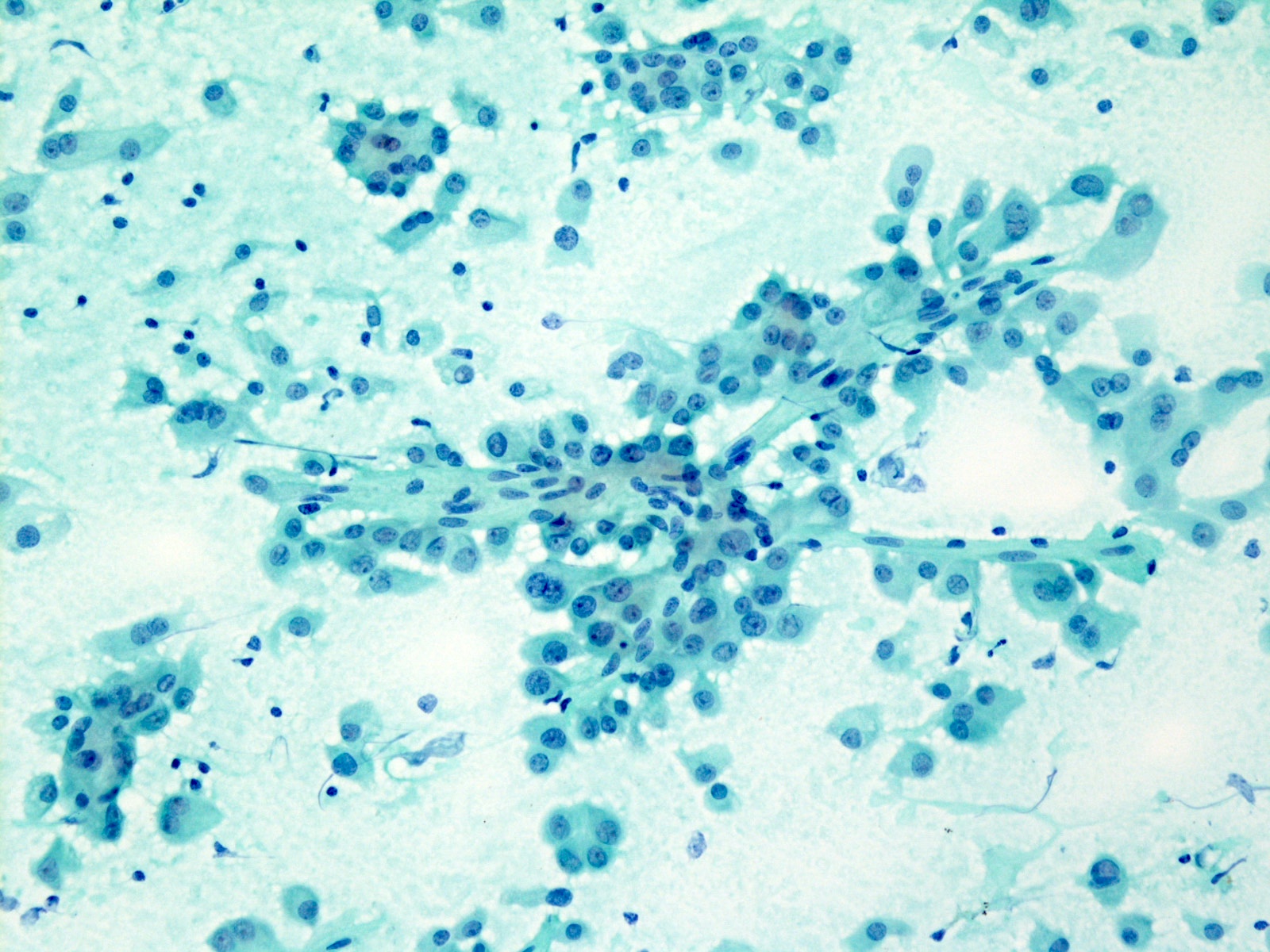
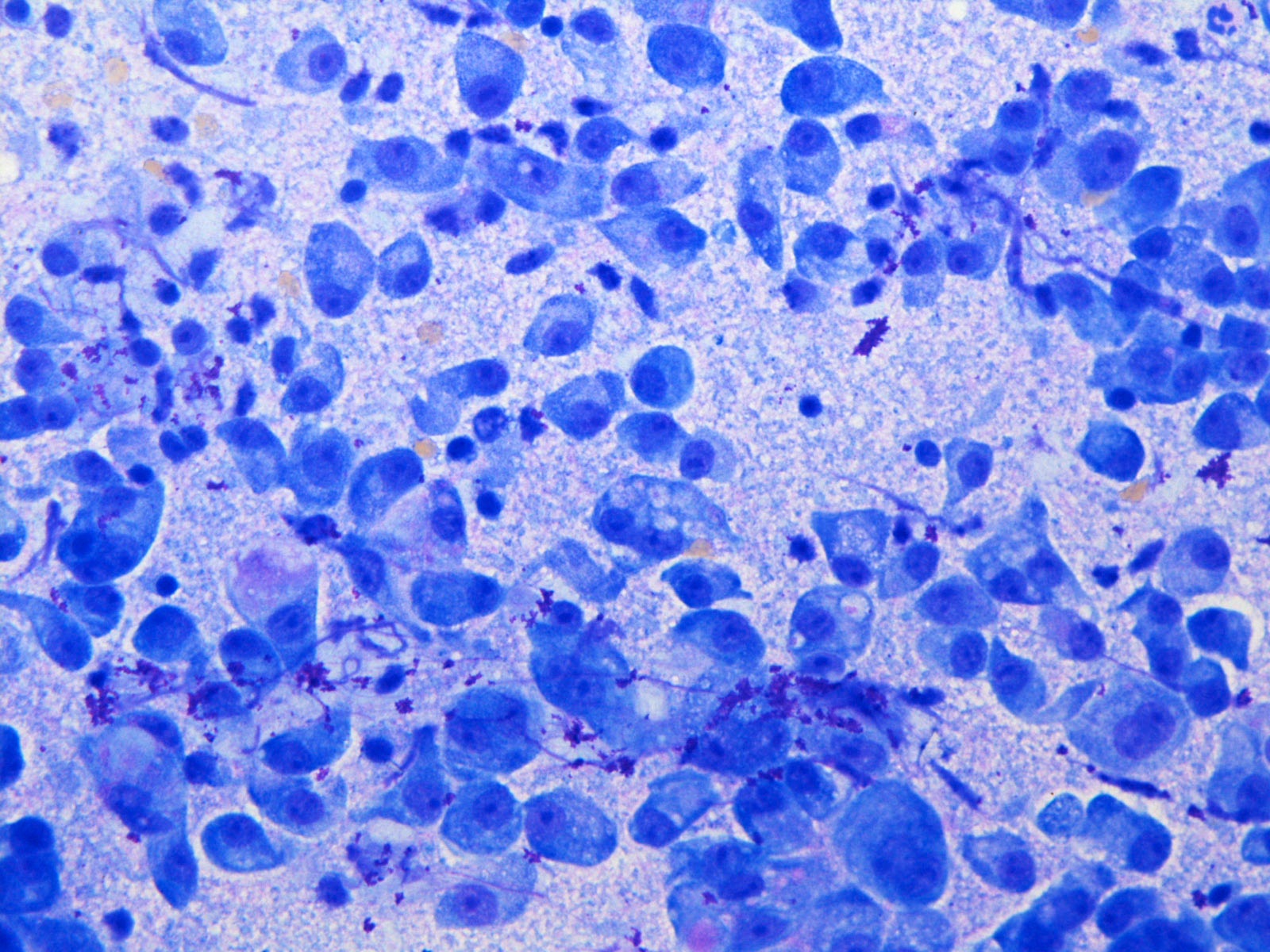
Cytology description
- Cytology is variable and nonspecific and requires high index of suspicion / awareness and cell block preparation
- Difficult to distinguish from benign entities and other low grade malignancies (APMIS 2019;127:491, Acta Cytol 2017;61:469)
- Cohesive clusters or sheets of epithelial cells with variable eosinophilic, granular to vacuolated cytoplasm and uniform nuclei with single nucleoli (APMIS 2019;127:491)
- Papillary fragments and acinar arrangements commonly seen; cystic lesions may show cystic debris in the background (APMIS 2019;127:491, Diagn Cytopathol 2015;43:287)
- Cell block preparation for immunohistochemistry with S100, GATA3, pan-TRK is useful (APMIS 2019;127:491, Cancer Cytopathol 2018;126:627)
Cytology images
Positive stains
- CK7: 100% sensitive, nonspecific when compared with acinic cell carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:599)
- GATA3: 100% sensitive; useful to distinguish from histologic mimic acinic cell carcinoma but nonspecific (53%) when the differential diagnoses include a variety of other salivary gland neoplasms (Head Neck Pathol 2013;7:311)
- S100: 100% sensitive, 67% specific when compared with acinic cell carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:599)
- SOX10: 100% sensitive (Hum Pathol 2016;56:134)
- Not specific, as a variety of salivary gland tumors including acinic cell carcinoma can show staining
- MUC4: 91% sensitivity, 100% specificity (Histopathology 2020 Sep 15 [Epub ahead of print])
- May also be seen in mucoepidermoid carcinoma
- Mammaglobin: 83% sensitive but lacks specificity in diagnostic context as it is expressed in intraductal carcinoma (86%) and polymorphous adenocarcinoma (37%) (Histopathology 2020 Sep 15 [Epub ahead of print])
- Pan-TRK: nuclear staining is 64% sensitive and reported specificities range from 92% to 100% (Histopathology 2020;76:375, Histopathology 2019;75:54)
- NB: cytoplasmic pan-TRK staining is extremely nonspecific and should be disregarded (Histopathology 2019;75:54)
- Pan-TRK will not stain tumors with other fusion partners for ETV6 (Histopathology 2019;75:54, Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:962)
Negative stains
- DOG1 (Med Mol Morphol 2021;54:23)
- NR4A3 (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1264)
- p63 negative or focal (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:599, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2016;24:501, Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1483)
- p40 (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2016;24:501)
- CK5/6 (Pathology 2015;47:659)
- Calponin (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:599)
- SMA (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:599)
- Androgen receptor (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:599)
- ER / PR (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:599)
- TTF1 (Head Neck Pathol 2017;11:124)
Electron microscopy description
- Not used in routine practice
- Cells show features of intercalated / striated duct cell differentiation (Head Neck Pathol 2017;11:419)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
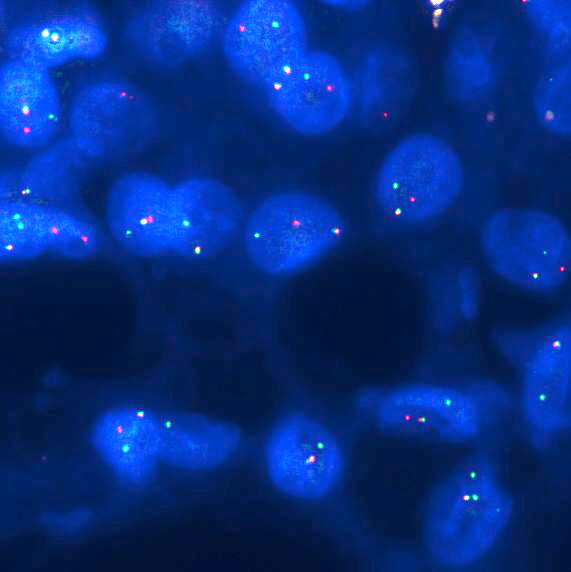
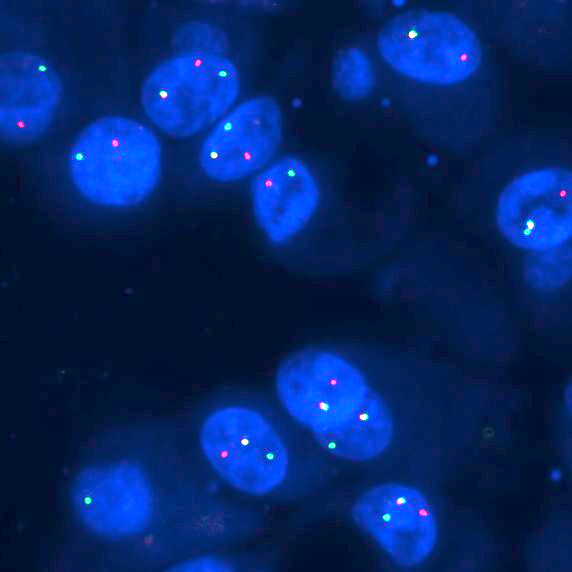
- Recurrent translocation t(12;15)(p13;q24), resulting in fusion of ETV6 on chromosome 12 and NTRK3 on chromosome 15 (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:599)
- Alternate fusion partners have been identified, including ETV6-RET and ETV6-MET (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:1295, Hum Pathol 2019;83:50, Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1121)
- Potential role of other non-ETV6 translocations according to recent reports: VIM-RET and CTNNA1-ALK (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:1295, Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:962)
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Videos
Salivary gland neoplasms characterized by gene fusions
Case presentations of various salivary gland pathologies
Sample pathology report
- Left parotid, excision:
- Secretory carcinoma (see comment)
- Comment: There is a well demarcated but focally infiltrative parotid neoplasm with lobulated growth, macrocystic and microcystic areas. The cysts are lined by relatively monomorphic epithelioid cells with moderate amounts of vacuolated eosinophilic cytoplasm and a central round nucleus with a small but distinctive nucleolus. The microcysts contain colloid-like eosinophilic secretions. Immunohistochemistry shows tumor cells to be positive for S100, MUC4, pan-TRK and GATA3 and negative for DOG1. The combined morphological and immunohistochemical features strongly support the diagnosis of secretory carcinoma, a primary salivary gland malignancy. This is further confirmed by fluorescent in situ hybridization using ETV6 break apart probe demonstrating ETV6 rearrangement. Lymphovascular or perineural involvement is not seen. The tumor is 2 mm from the closest margin of resection.
- Secretory carcinoma generally demonstrates indolent behavior. However, it has a propensity to recur unless completely excised. Local lymph node metastasis occurs in up to 22% of patients and distant metastasis, while rare, has been reported in a subset of cases
Differential diagnosis
- Acinic cell carcinoma:
- Rare in nonparotid locations
- Cytoplasmic PAS diastase resistant zymogen granules
- NR4A3+, DOG1+ (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1264, Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2016;273:3511)
- GATA3-, MUC4-, mammaglobin-, pan-TRK- (Histopathology 2020 Sep 15 [Epub ahead of print], Head Neck Pathol 2013;7:311, Histopathology 2019;75:54)
- Intraductal carcinoma:
- Cystic structures with intracystic epithelial proliferation resembling ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast, including Roman bridge formations
- Similar immunohistochemical profile but myoepithelial markers positive in the peripheral myoepithelial cell layer and MUC4- in tumor cells (Histopathology 2020 Sep 15 [Epub ahead of print], APMIS 2020;128:191)
- RET rearrangements in the majority of tumors (APMIS 2020;128:191)
- Polymorphous adenocarcinoma:
- Tumor of minor salivary glands, rare in major salivary glands
- Multiple varying architectural patterns, lacking secretions
- p63+, SMA+ (Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2018;275:1681)
- GATA3-, pan-TRK- nuclear (may have cytoplasmic staining), mammaglobin variable (Histopathology 2020 Sep 15 [Epub ahead of print], Head Neck Pathol 2013;7:311 Histopathology 2020;76:375)
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma:
- Goblet cells with intracytoplasmic mucin among squamoid intermediate cells
- p63+, CK5/6+ (Head Neck Pathol 2014;8:133)
- S100-, mammaglobin-
- MAML2-CRTC1 translocations in the majority of tumors (Ann Surg Oncol 2002;9:688)
Practice question #1
A 48 year old man has a parotid nodule for 9 - 12 months. Which of the following is true?
- It is characterized by PAS diastase resistant cytoplasmic zymogenic granules and immunohistochemically by positivity for DOG1 and S100
- It is characterized by PAS diastase resistant cytoplasmic zymogenic granules and immunohistochemically by positivity for ER and PR
- It is characterized histologically by PAS diastase resistant intraluminal secretions and immunohistochemically by positivity for androgen receptor and p63
- It is characterized histologically by PAS diastase resistant intraluminal secretions and immunohistochemically by positivity for pan-TRK, S100 and mammaglobin
- It is generally a highly aggressive malignancy with most patients showing distant solid organ metastases at presentation
Practice answer #1
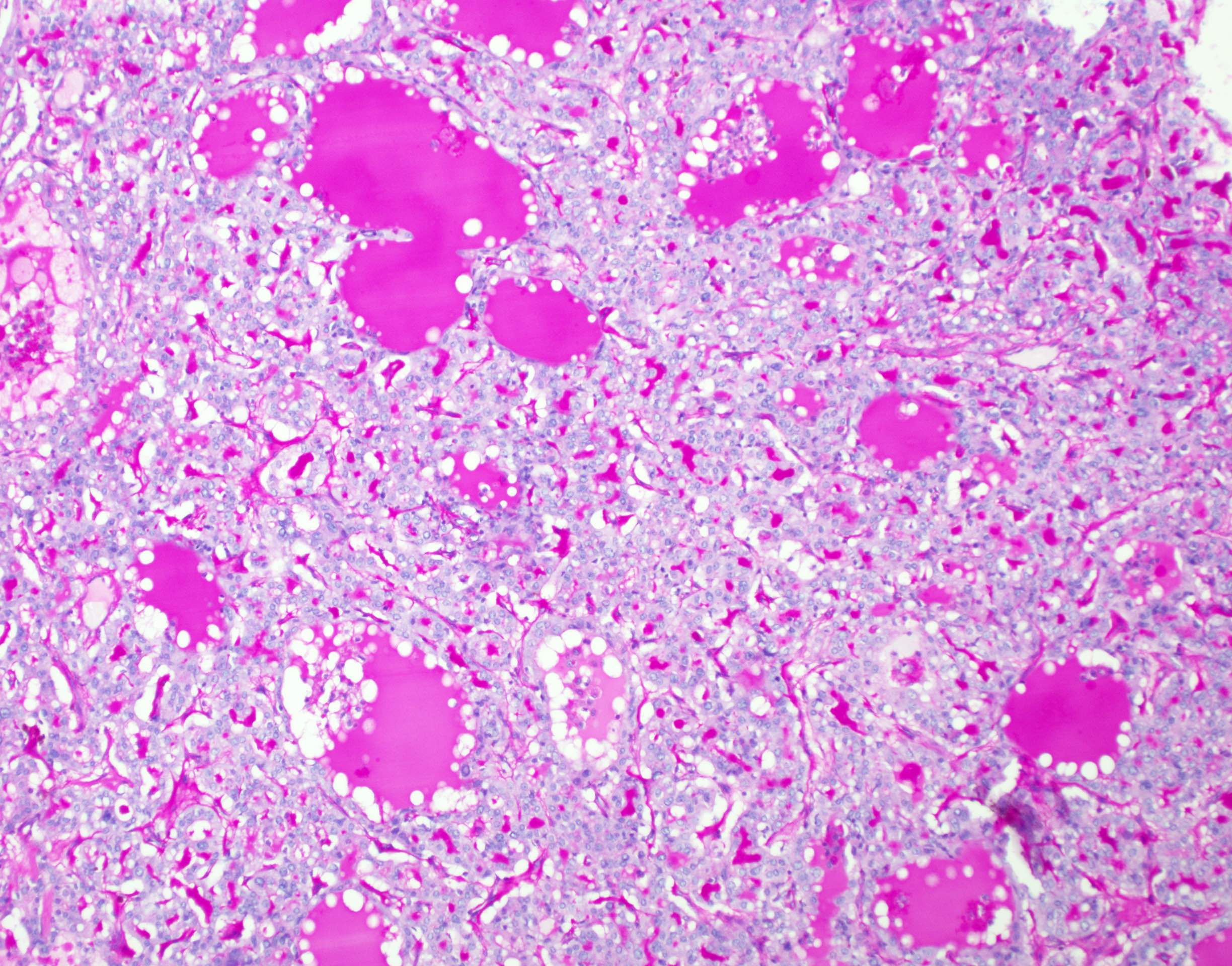
D. It is characterized histologically by PAS diastase resistant intraluminal secretions and immunohistochemically by positivity for pan-TRK, S100 and mammaglobin. The image shows a secretory carcinoma with abundant secretions.
Comment Here
Reference: Secretory carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Secretory carcinoma
Practice question #2
A 49 year old woman has a lesion on the floor of the mouth with metastases to lymph nodes. The tumor cells show strong staining with S100 and MUC4. Which of the following genetic changes are likely to be found in this tumor?
- ETV6-NTRK3 translocation
- HER2 amplification
- MAML2-CRTC1 translocation
- MYB-NFIB translocation
- PLAG1 translocation
Practice answer #2
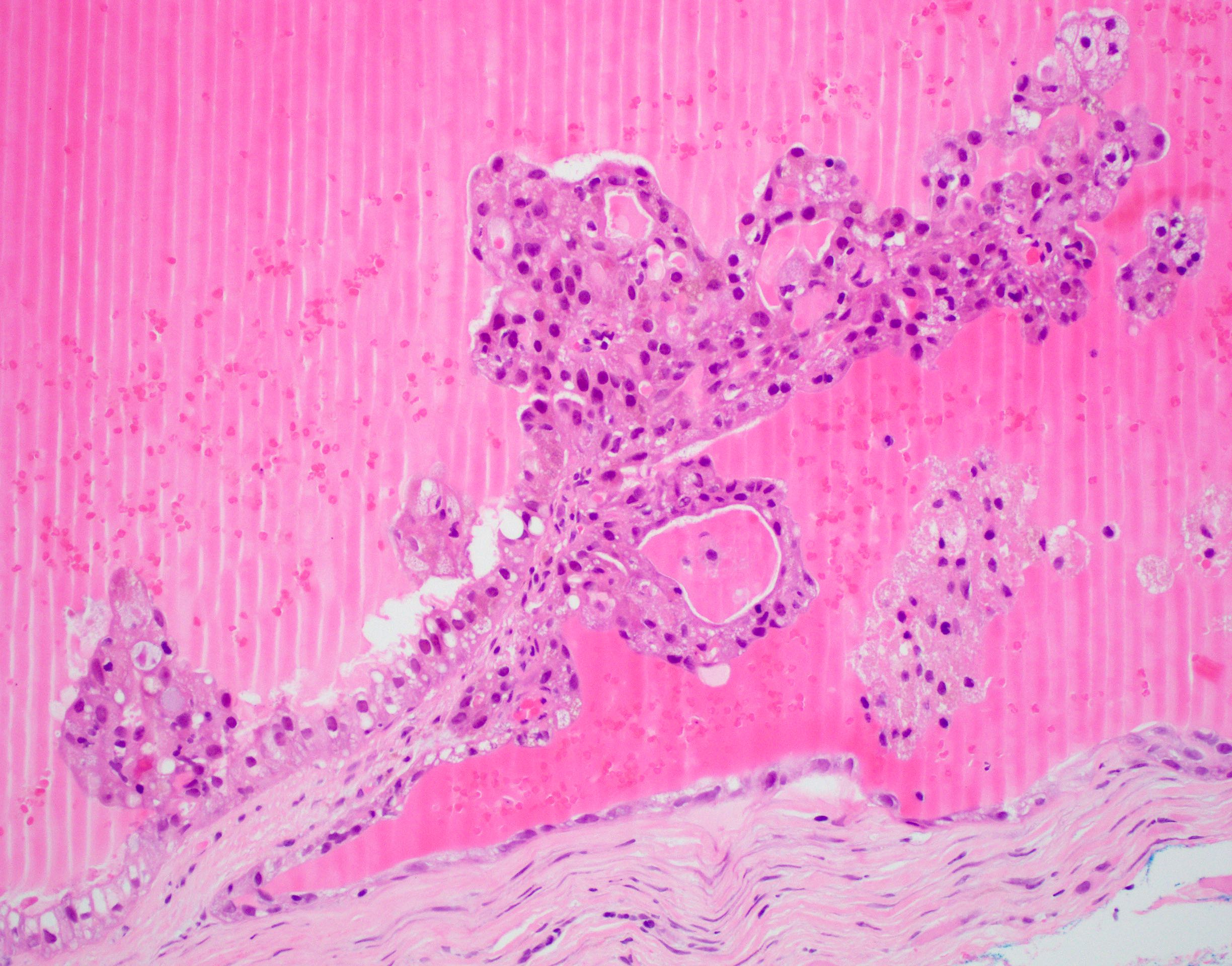
A. ETV6-NTRK3 translocation. The image shows a secretory carcinoma with papilliform architecture.
Comment Here
Reference: Secretory carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Secretory carcinoma