Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Kao E, Belzarena C. Pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissuepleomorphicrhabdo.html. Accessed August 26th, 2025.
Definition / general
- High grade pleomorphic sarcoma composed of bizarre eosinophilic, round and spindle cells with skeletal muscle differentiation
- Exceedingly rare category of rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) in adults
- Highly aggressive tumor associated with poor prognosis (Anticancer Res 2015;35:6213)
Essential features
- High grade sarcoma composed of atypical cells that display skeletal muscle differentiation, confirmed with immunohistochemistry for myogenin or myoD1
Terminology
- Pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8901/3 - pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma, NOS
- ICD-11: 2B55 & XH5SX9 - rhabdomyosarcoma, primary site & pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma, NOS
Epidemiology
- Usually in the sixth to seventh decade
- Male predominance (1.8:1) (Anticancer Res 2015;35:6213)
Sites
- Deep soft tissues
- Most common in extremities (Anticancer Res 2015;35:6213)
- Less common locations include the pelvis, abdomen, thorax and head and neck (Anticancer Res 2015;35:6213)
Pathophysiology
- Complex karyotype but no signature genetic alteration
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Rapidly growing, painful deep mass, most commonly of lower extremity
- Nodal involvement uncommon (< 10%)
- Majority of patients (70%) with localized disease at presentation (Anticancer Res 2015;35:6213)
Diagnosis
- Pleomorphic cells with brightly eosinophilic cytoplasm (Mod Pathol 2001;14:595)
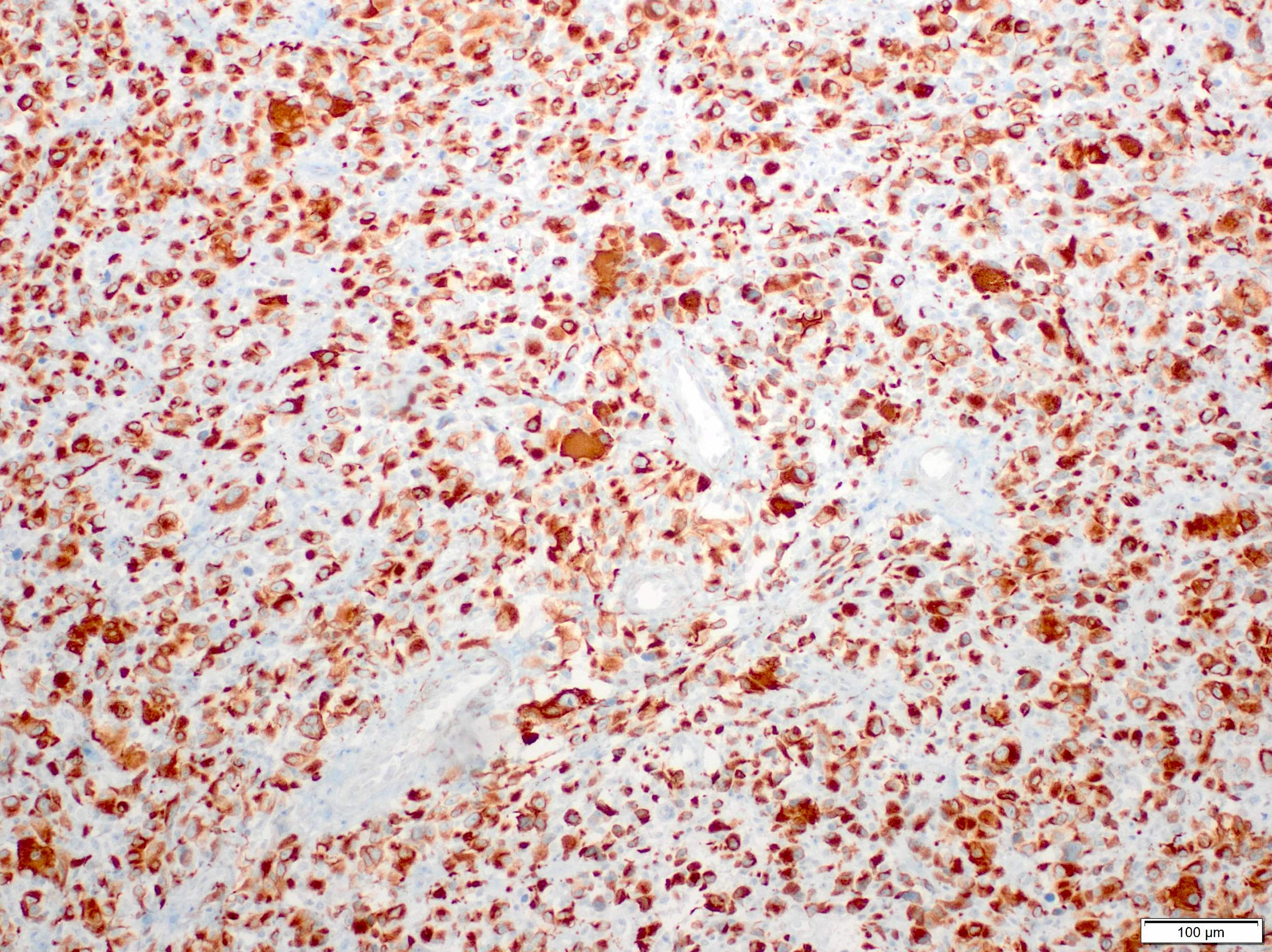
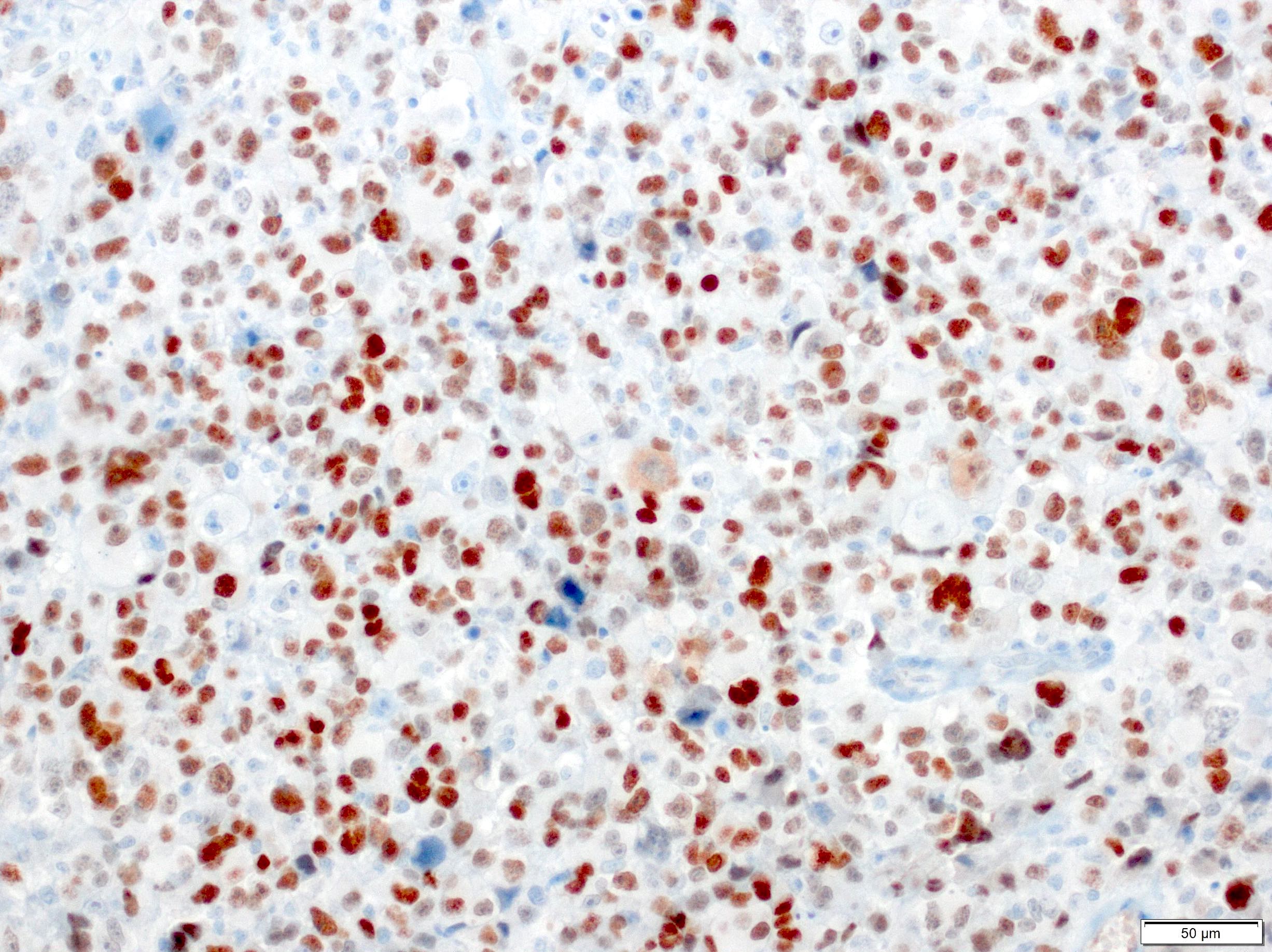
- Skeletal muscle differentiation as confirmed by desmin, myogenin or MyoD1 (Ann Diagn Pathol 2018;36:50)
- Thorough histologic sampling and evaluation are necessary for diagnostic confirmation
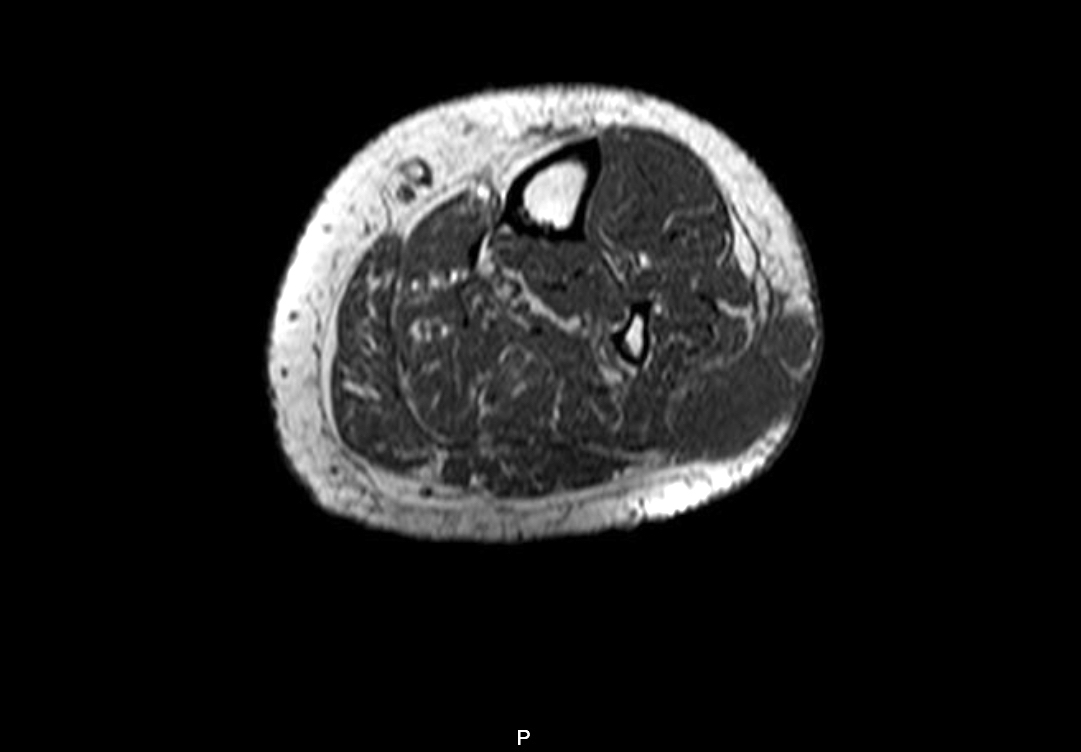
Radiology description
- In MRI T1 weighted sequences, the tumor appears iso or hypointense to muscle
- In T2 weighted and STIR sequences, the tumor is hyperintense with surrounding edema
- In postcontrast sequences, the mass shows heterogeneous enhancement; necrosis is usually present within
- Reference: AJR Am J Roentgenol 2007;189:371
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- High propensity for metastatic spread
- Lungs are the most common site for metastases (77%)
- Positive margins associated with disease relapse (Anticancer Res 2015;35:6213)
- Tumors with superficial location (~20%) have a more favorable outcome
Case reports
- 28 year old man with pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma of the thigh (Oncol Lett 2016;12:1921)
- 50 year old man with pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma in subcutaneous tissue of the trunk (J Dermatol 2017;44:59)
- 53 year old woman with 3 synchronous lung metastasis from pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma (Cancer Treat Res Commun 2021;26:100282)
- 57 year old woman with pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma of the chest wall (Int J Surg Case Rep 2020;75:380)
- 60 year old man with pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma of the thigh (J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect 2020;10:287)
- 73 year old woman with pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma of the uterus (Anticancer Res 2017;37:2509)
Treatment
- Clinical behavior and responsiveness to chemotherapy are similar to adult high grade soft tissue sarcomas
- Poor prognosis with median survival of 7 months
- Surgical resection with wide margins is mainstay of treatment
- Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) has been used for lung oligometastases (Cancer Treat Res Commun 2021;26:100282)
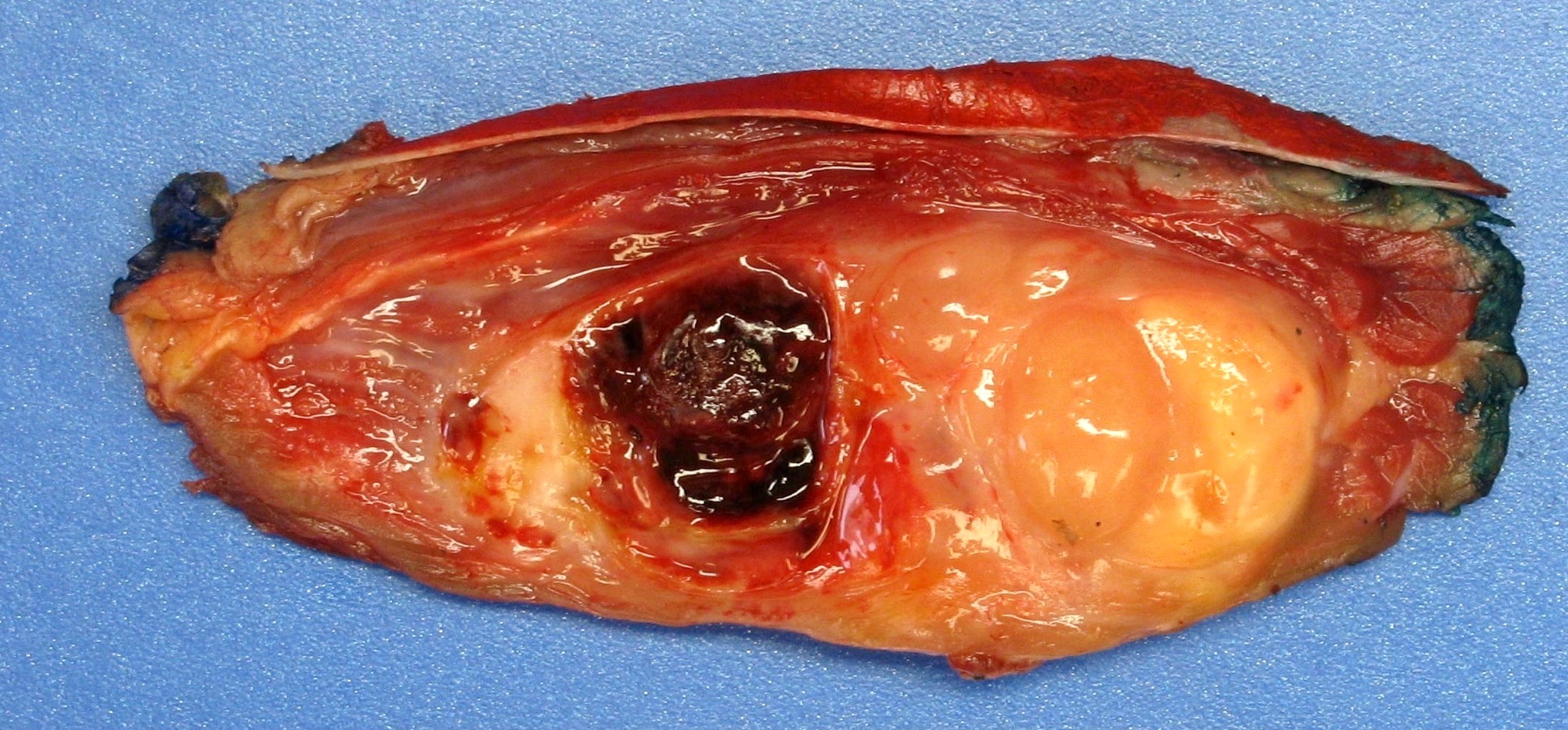
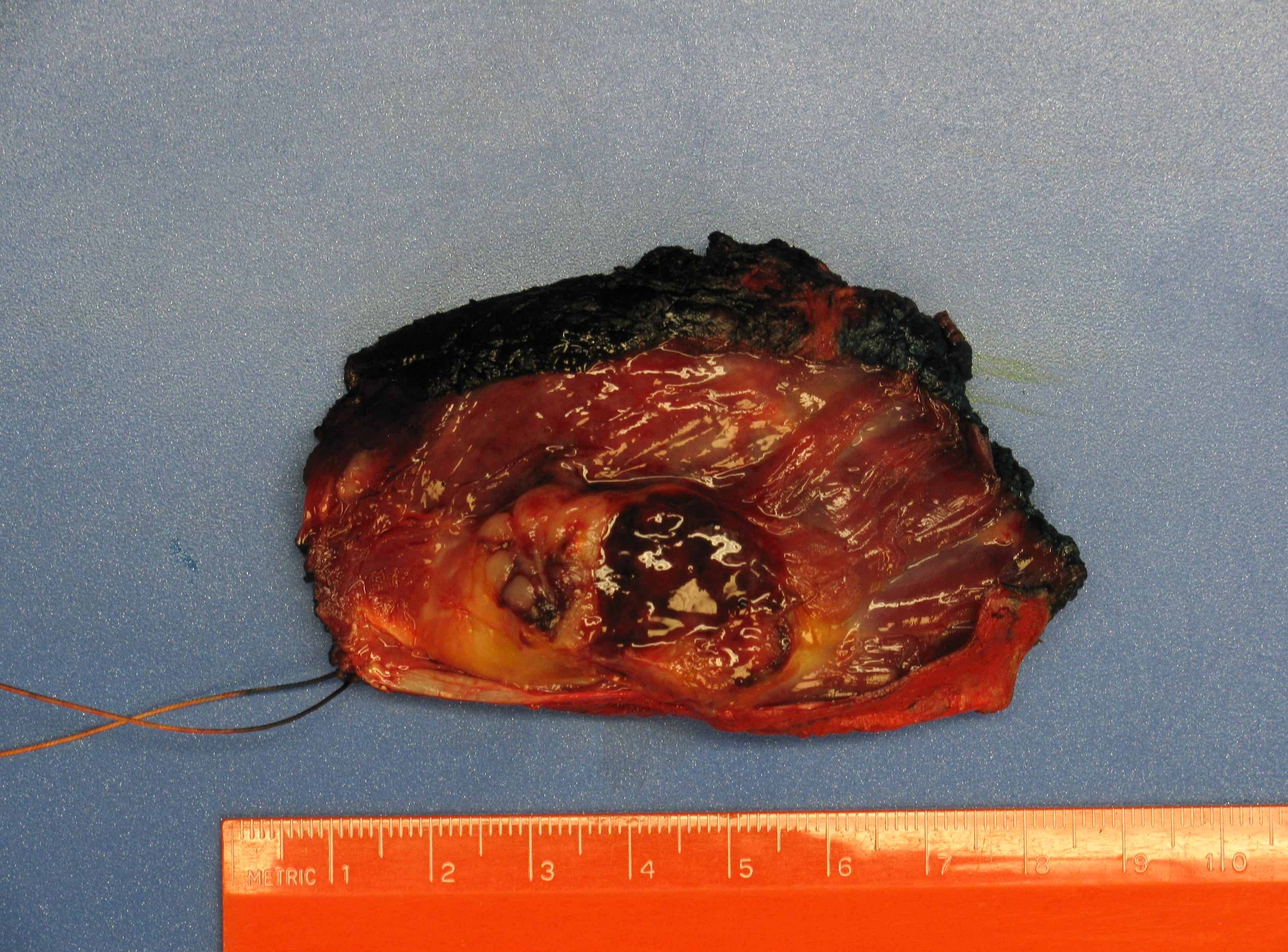
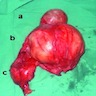
Gross description
- Can be variable in size (median 8 cm, range from 1 - 30 cm) (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1850)
- Cut surface with variable hemorrhage and necrosis
- Appears circumscribed, often in deep soft tissue and involving striated muscle (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1850)
Gross images
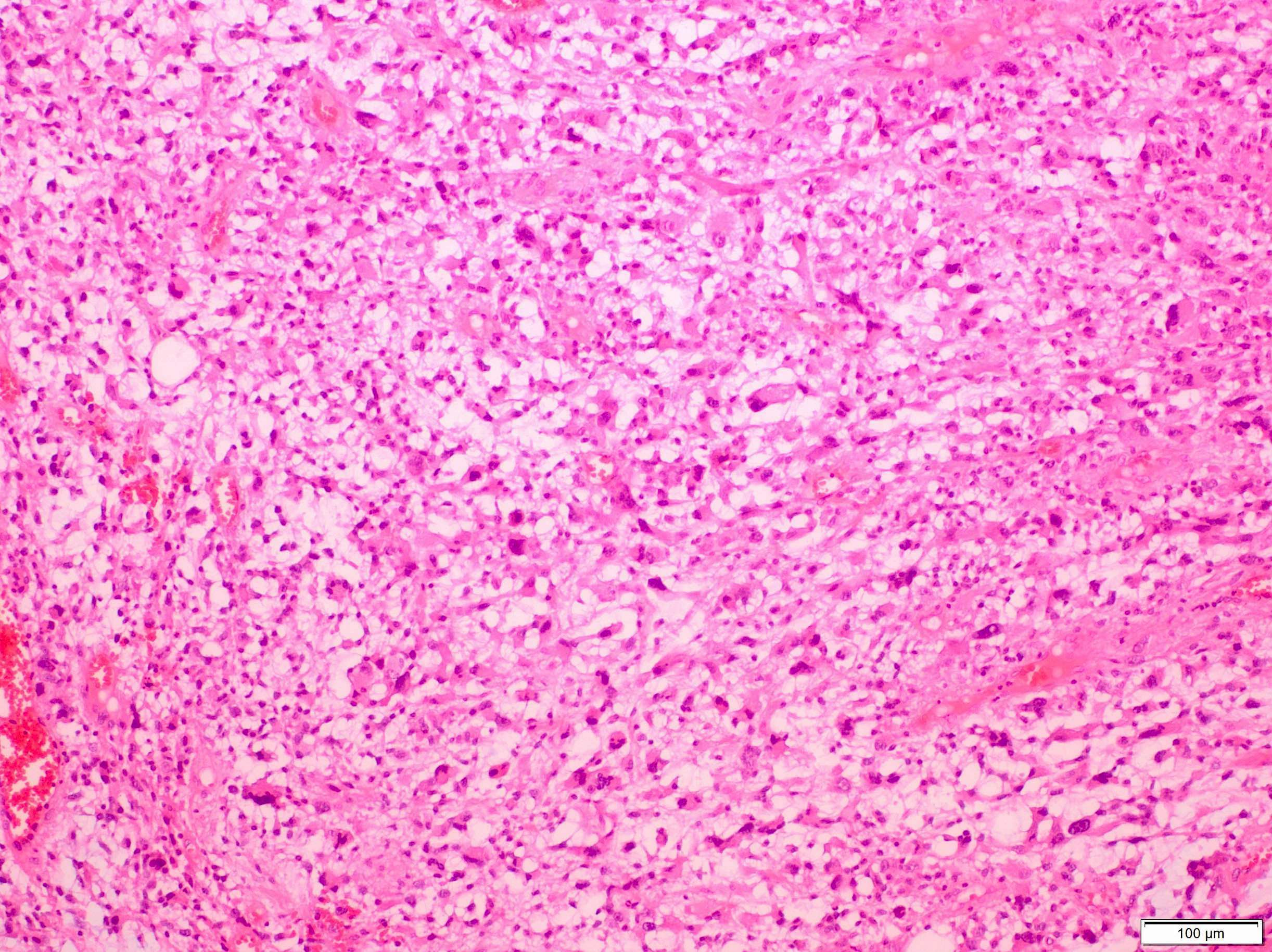
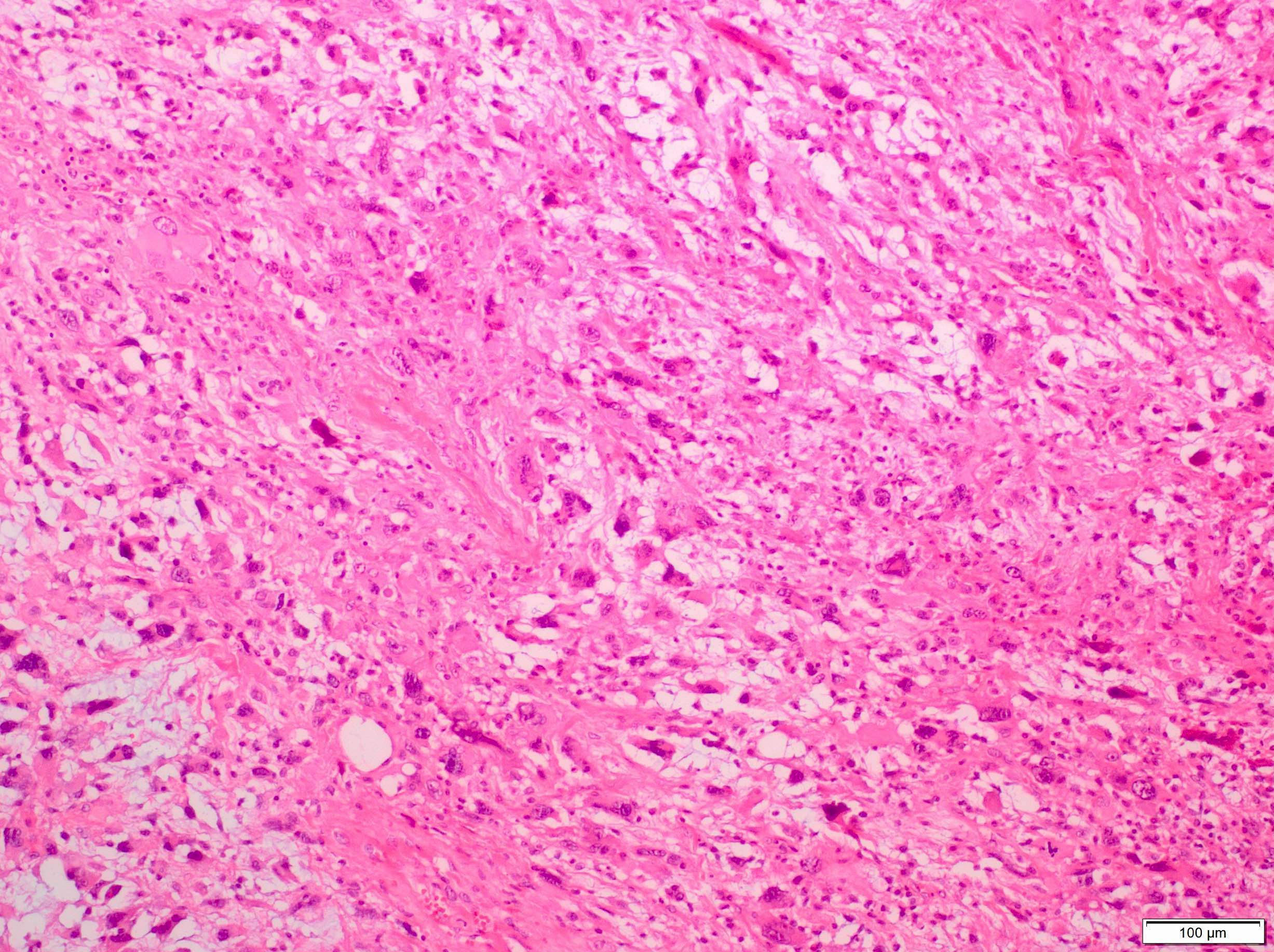
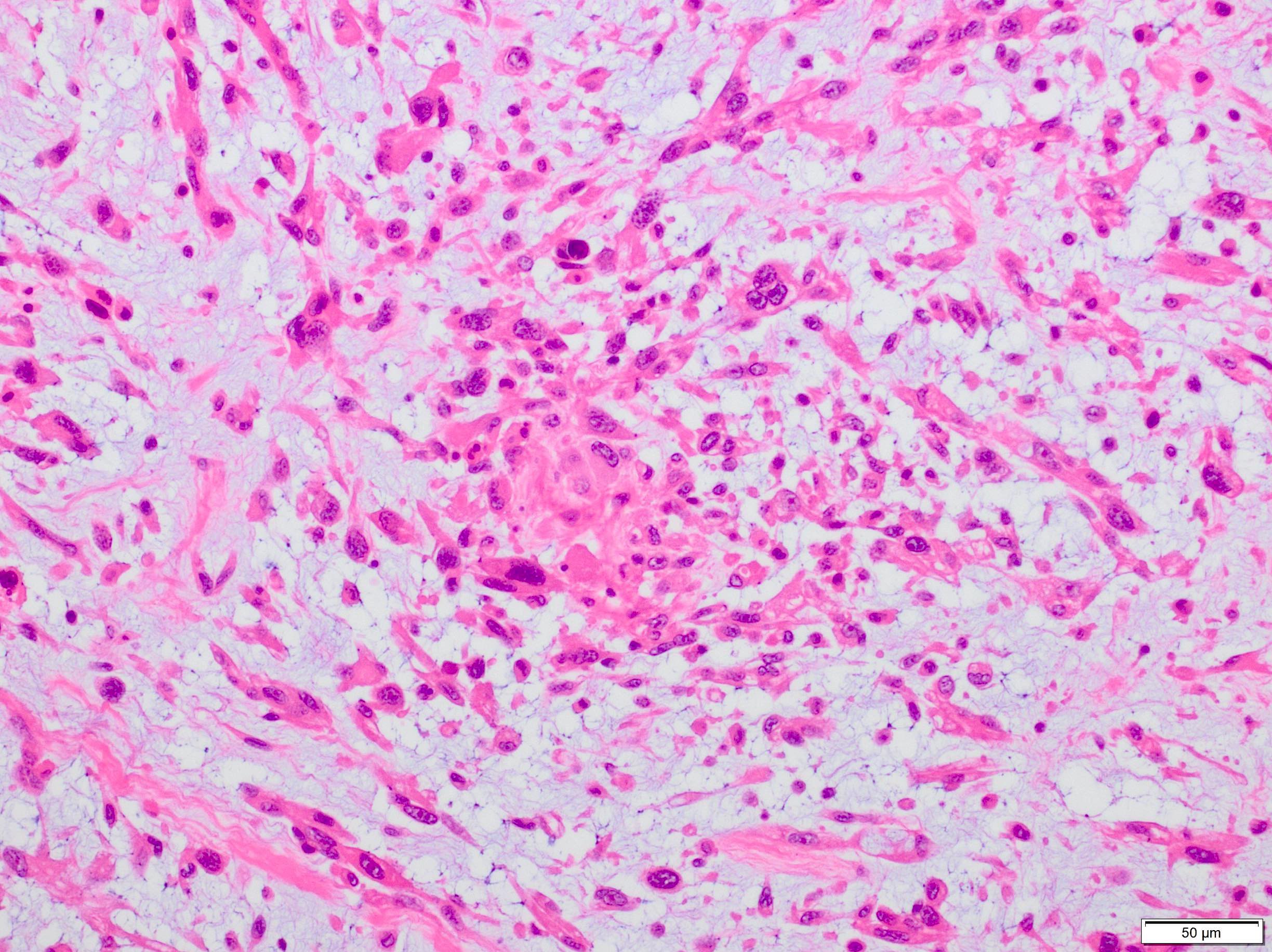
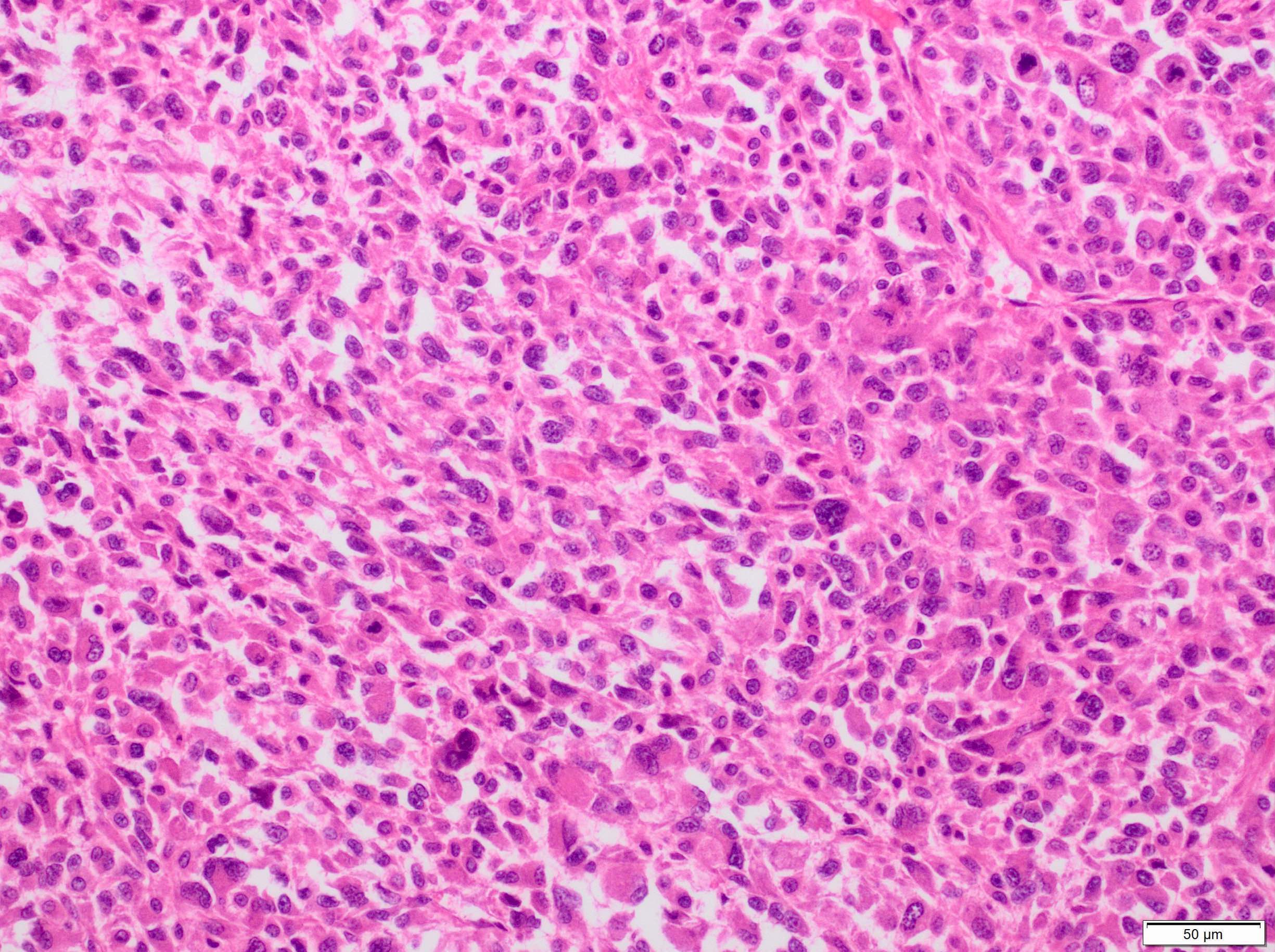
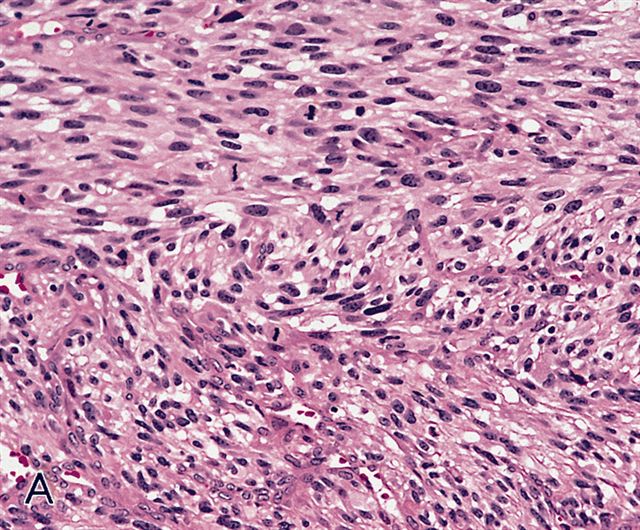
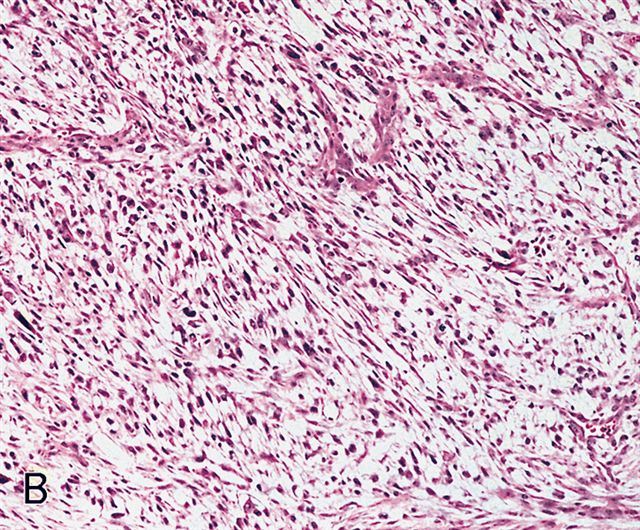
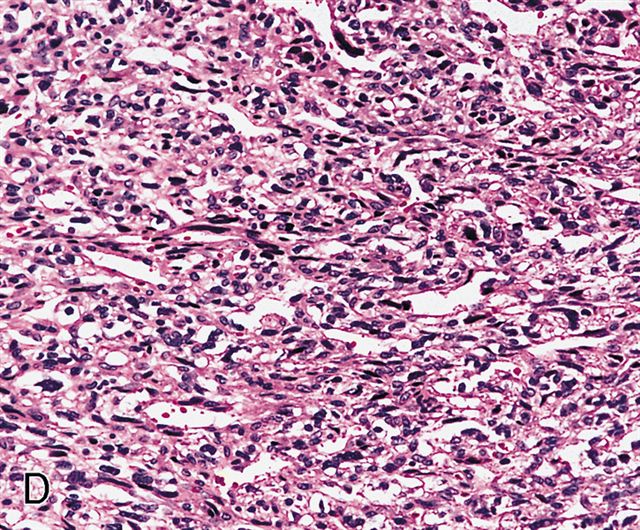
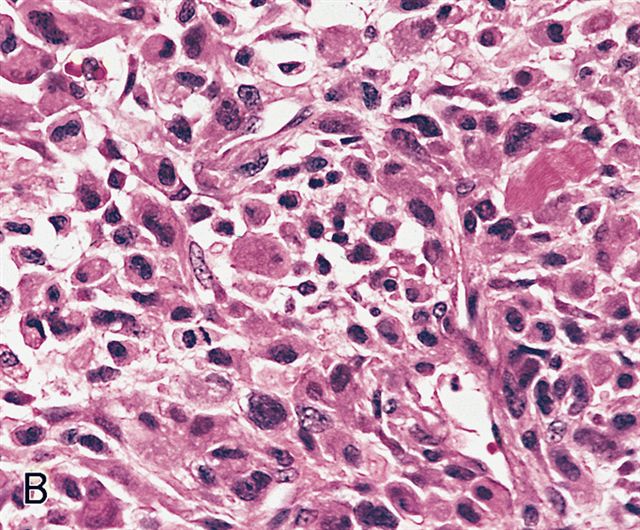
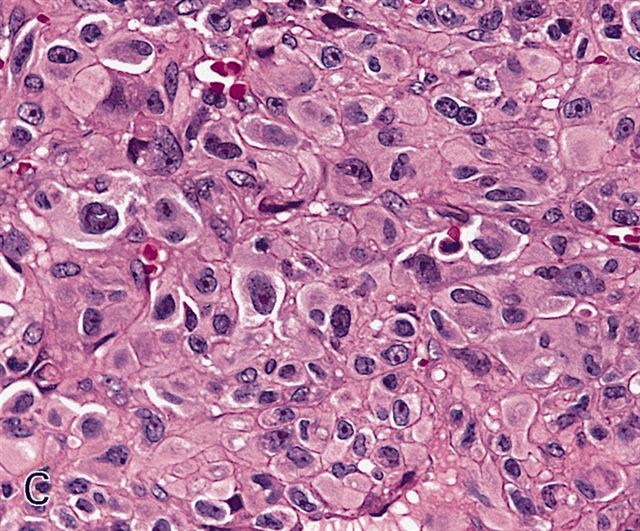
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Sheets of large, atypical and frequently multinucleated polygonal, spindled or rhabdoid eosinophilic cells (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1850)
- Cross striations are seldom detected
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Expresses desmin, MyoD1, skeletal muscle (fast) myosin and myogenin (Mod Pathol 2001;14:595)
- Variable SMA and may have focal keratin AE1 / AE3 and EMA positivity (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1850)
Electron microscopy description
- Skeletal muscle differentiation with rudimentary sarcomeres containing Z bands or Z band material with thick and thin filaments (Mod Pathol 2001;14:595)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Complex karyotype (Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2009;192:1)
- Comparative genomic in situ hybridization (CGH) reveals 8 highly amplified regions at 1p36.1-p36.2, 1p31-p32, 1q21-q31, 8q12-q21, 8q24-qter, 11q12-q13, 12q13-q14 and 18q12-q22 (Am J Cancer Res 2012;2:141)
Sample pathology report
- Soft tissue, biopsy:
- Pleomorphic sarcoma with rhabdomyoblastic differentiation (see comment)
- Comment: These findings may represent a pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma, although heterologous differentiation cannot be excluded.
Differential diagnosis
- Embryonal or alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma with anaplastic features:
- No evidence of embryonal or alveolar component which may have scattered pleomorphic cells or solid foci of pleomorphic cells (Am J Surg Pathol 1993;17:601)
- Embryonal RMS has ovoid to spindle cells, typically occurs in the pediatric population but can be in adults, and has a predilection for the head and neck and genitourinary system (Pediatr Blood Cancer 2021;68:e28798)
- Alveolar RMS tumor cells are arranged in nests separated by fibrovascular septa, which frequently exhibit loss of cellular cohesion in the center, conferring a pattern of irregular alveolar spaces; the presence of either a PAX3::FOXO1 or a PAX7::FOXO1 fusion gene is detected in the majority of alveolar RMS cases
- Pleomorphic RMS prefers older adults and occurs in the extremities (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1850)
- No evidence of embryonal or alveolar component which may have scattered pleomorphic cells or solid foci of pleomorphic cells (Am J Surg Pathol 1993;17:601)
- Undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma:
- Diagnosis of exclusion
- No evidence of skeletal muscle differentiation
- Pleomorphic liposarcoma:
- No evidence of skeletal muscle differentiation
- Carcinomas with rhabdomyosarcomatous differentiation, such as malignant mixed Müllerian tumor:
- Carcinomatous component present
- Melanoma with rhabdomyosarcomatous dedifferentiation (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:181):
- Presence of BRAF mutation, history of melanoma with current presentation of tumor in a characteristic site of metastasis (lymph node, lung, etc.)
- Sarcomas with heterologous rhabdomyoblastic differentiation, such as dedifferentiated liposarcoma or MPNST (malignant Triton tumor):
- Histologic or molecular evidence of another tumor (i.e., MDM2 amplification present for dedifferentiated liposarcoma or a well differentiated liposarcoma component present), loss of H3K27me3 in MPNST or areas of more classic appearing MPNST arising from a nerve
Additional references
Practice question #1
Practice answer #1
A. A t(2;13)(q36;q14) translocation is found in the majority of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma
Comment Here
Reference: Pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma
Comment Here
Reference: Pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma
Practice question #2
Which rhabdomyosarcoma type is more predominant in adults in the sixth to seventh decades and is characterized by the presence of pleomorphic cells with a significant amount of bright eosinophilic cytoplasm?
- Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma
- Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma
- Pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma
- Spindle cell / sclerosing rhabdomyosarcoma
Practice answer #2