Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Electron microscopy images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Rani A, Qureshi MB, Ud Din N. Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissuealvrhabdo.html. Accessed August 25th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Highly aggressive type of rhabdomyosarcoma characterized by uniform, primitive, round cells showing skeletal muscle differentiation (Cancer 1969;24:18)
Essential features
- High grade, cellular, round cell sarcoma with evidence of skeletal muscle differentiation
- Nests and sheets of monomorphic cells may have pseudoalveolar pattern (Curr Top Pathol 1995;89:273)
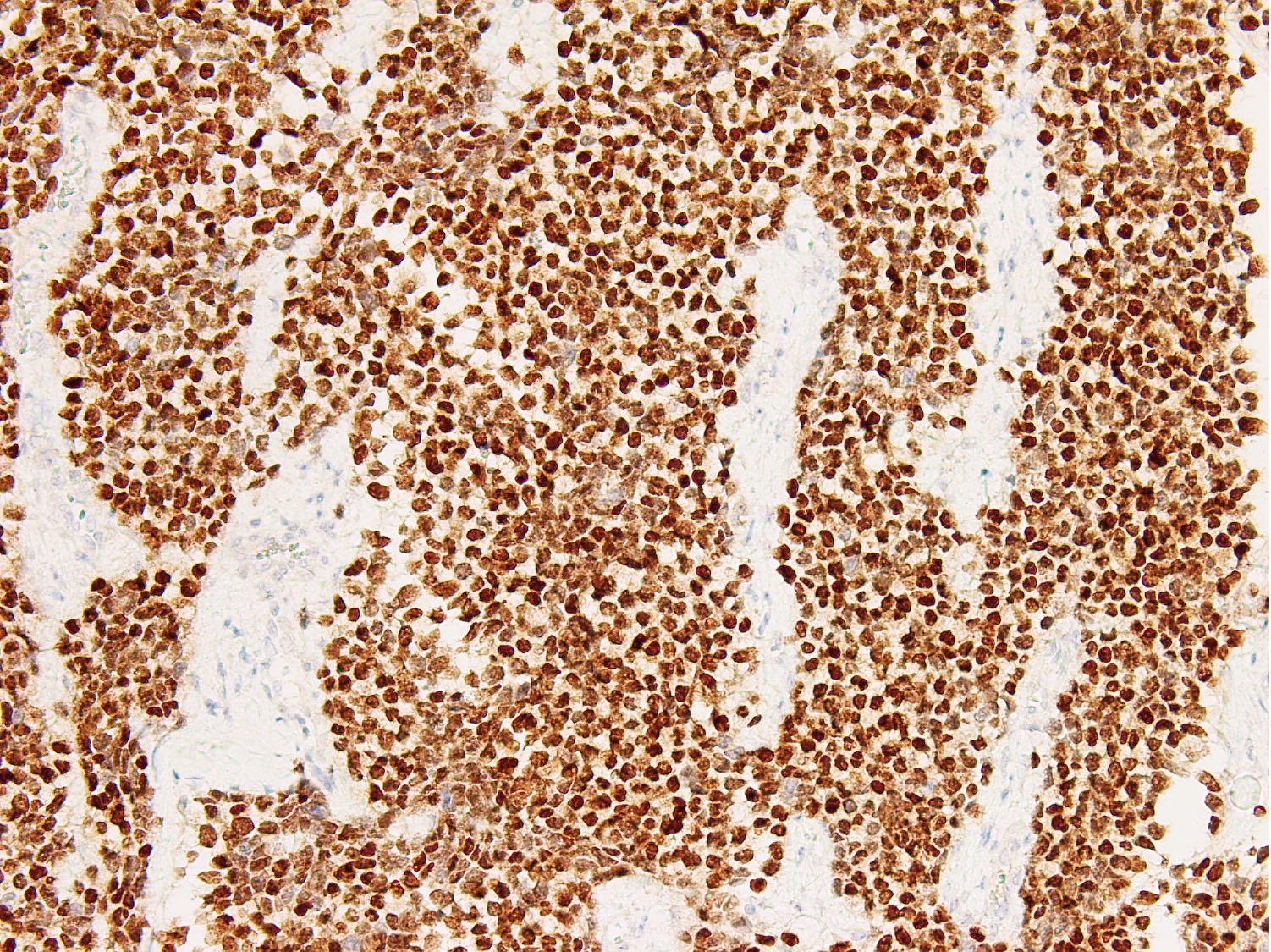
- Diffuse strong myogenin expression
- Detection of PAX3::FOXO1 (60%) or PAX7::FOXO1 (20%) gene fusions by molecular analysis (Oncogene 2001;20:5736)
- Predilection for deep soft tissue of lower extremities
- High stage at presentation with overall worse prognosis
Terminology
- Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma
- Preference towards switching to fusion positive and fusion negative rhabdomyosarcoma terminology among oncologists (Cancer Discov 2014;4:216)
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8920/3 - alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma
- ICD-10: C49.9 - malignant neoplasm of connective and soft tissue, unspecified
- ICD-11: 2B55.Z & XH7099 - rhabdomyosarcoma, unspecified primary site & alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma
Epidemiology
- Second most common type (25%) of rhabdomyosarcoma (Adv Anat Pathol 2013;20:387)
- Affects adolescents and young adults
- Peak incidence is between 10 and 25 years (Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2015;16:757)
- Rare in older adults; very rare congenital occurrence (Hum Pathol 2009;40:341)
- M = F
Sites
- Commonly involves deep soft tissue of extremities, typically forearm
- Other sites include head and neck, trunk, paraspinal, pelvic, genitourinary regions and retroperitoneum
- Can present with widespread involvement, such as bone marrow infiltration (leukemia-like presentation) and lymphadenopathy (Diagn Pathol 2017;12:77)
- 25 - 30% of patients present with metastatic disease
- Most common metastatic sites include lung and lymph nodes (Int J Clin Oncol 2014;19:536)
- Can metastasize to other sites such as the bone; however, rare visceral metastases to brain, breast, kidney and pancreas have also been reported (Arch Argent Pediatr 2021;119:e349)
Pathophysiology
- Derived from cells with phenotypic and biologic features of myogenic lineage (undifferentiated mesodermal cells) (Cancer Lett 2009;279:126)
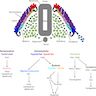
- Genetic fusion events including translocations t(2;13)(q36;q14) and t(1;13)(p36;q14) lead to expression of fusion proteins PAX3::FOXO1 and PAX7::FOXO1
- These proteins act as transcriptional activators, causing dysregulation of transcription affecting myogenesis
- PAX::FOXO1 proteins behave as oncoproteins and contribute to tumor development by alteration of cell growth pathways and apoptosis, modulation of myogenic differentiation and stimulation of motility and other downstream pathways (Skelet Muscle 2012;2:25)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Rapidly growing mass
- Tumor causes pressure symptoms depending upon site of origin, size and metastatic site (Case Rep Oncol 2022;15:783)
- Head and neck tumors cause proptosis and cranial nerve deficits
- Paraspinal tumors of trunk cause paresthesia / paresis (Orbit 2022 Sep 21 [Epub ahead of print])
- Perineal tumors cause constipation
- Strong association of Nijmegen breakage syndrome with perianal primary site (Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2004;154:169)
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis is based on histologic features / immunomarkers expression in correlation with age, site and clinical findings (Mod Pathol 2001;14:506)
- Small, round, blue cell tumor with diffuse positivity for desmin and myogenin
- Molecular studies (PAX3::FOXO1 / PAX7::FOXO1 gene fusions) in morphologically challenging cases and cases with inconclusive immunohistochemistry (Skelet Muscle 2012;2:25)
- WHO essential and desirable diagnostic criteria
- Uniform round cells with or without alveolar growth pattern, diffuse homogenous expression of myogenin; heterogeneous expression for desmin or MyoD1; detection of PAX3::FOXO1 / PAX7::FOXO1 fusion by molecular analysis
Laboratory
- Nonspecific
Radiology description
- Radiological features are nonspecific in differentiating from other sarcomas (Clin Radiol 1978;29:53)
- Location and demographics are most useful in truncating differentials
- Plain radiograph: soft tissue density mass
- Ultrasound: well defined heterogeneous nonuniform mass of low to medium echogenicity
- CT: soft tissue density lesion with contrast enhancement
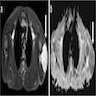
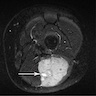
- MRI:
- T1: low to medium intensity lesion, isointense to adjacent muscle; prominent vascularity (Pediatr Radiol 2019;49:1516)
- T2: hyperintense lesion; conspicuous vascularity (Radiographics 2020;40:791)
- Postcontrast sequences: heterogeneous enhancement; ring-like enhancement when necrosis
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Worse prognosis than embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (J Orthop Res 2019;37:2226)
- The Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study Group grouping system is predictive of outcome (risk stratification) (Pediatr Dev Pathol 1998;1:550)
- The group uses the parameters of surgical pathological staging and genetic fusion status
- Prognosis of FOXO1 fusion positive tumors is worse than fusion negative ones
- PAX3::FOXO1 fusion has a poorer outcome than PAX7::FOXO1 fusion (J Clin Oncol 2012;30:1670)
- Amplification of MYCN, CDK4 and miR-17-92 is associated with a poor outcome (J Clin Oncol 2005;23:880, Clin Cancer Res 2015;21:4947, Clin Cancer Res 2011;17:1463)
- Diffuse myogenin expression is an unfavorable prognostic factor (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:1513)
Case reports
- 11 year old boy presented with left upper arm mass (Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud 2021;7:a005983)
- 20 year old woman presented with a painless vulvar mass (J Int Med Res 2020;48:300060520905438)
- 22 year old man presented with acute neurological deterioration (BMJ Case Rep 2021;14:e240516)
- 30 year old woman presented with a painful nodule on mandibular gingiva (Oral Oncol 2023;137:106281)
- 51 year old woman presented with abdominal distention (Hum Pathol 2022;28:300637)
- 67 year old woman presented with epistaxis and generalized bone pain (Case Rep Oncol 2021;14:1505)
Treatment
- Multimodal approach with surgery and chemotherapy (Pediatr Blood Cancer 2023;70:e28608)
- Second line chemotherapy or radiotherapy in tumors with poor initial response
- Therapeutic target inhibitors: ATR, KDM4B and PDGFRA inhibitors (Nat Commun 2022;13:4297, Sci Transl Med 2022;14:eabq2096, Oncogene 2008;27:6550)
- Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study Postsurgical Clinical Grouping System is recommended to plan treatment in pediatric cases (J Pediatr Surg 2000;35:317)
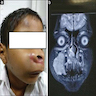
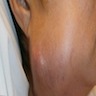
Clinical images
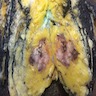
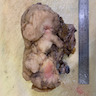
Gross description
- Soft, fleshy, friable tumor with irregular margins (StatPearls: Rhabdomyosarcoma [Accessed 27 February 2023])
- Gray-white cut surface with variable fibrous tissue
- Areas of necrosis and hemorrhage may be present
- Deep tumors may show infiltrative margins
Gross images
Frozen section description
- Sensitive but not very specific (Turk Patoloji Derg 2015;31:16)
- Clusters and single tumor cells with variable fibrous component
- Dense cytoplasm with cytoplasmic vacuolation
- Irregular, hyperchromatic nuclei with conspicuous nucleoli
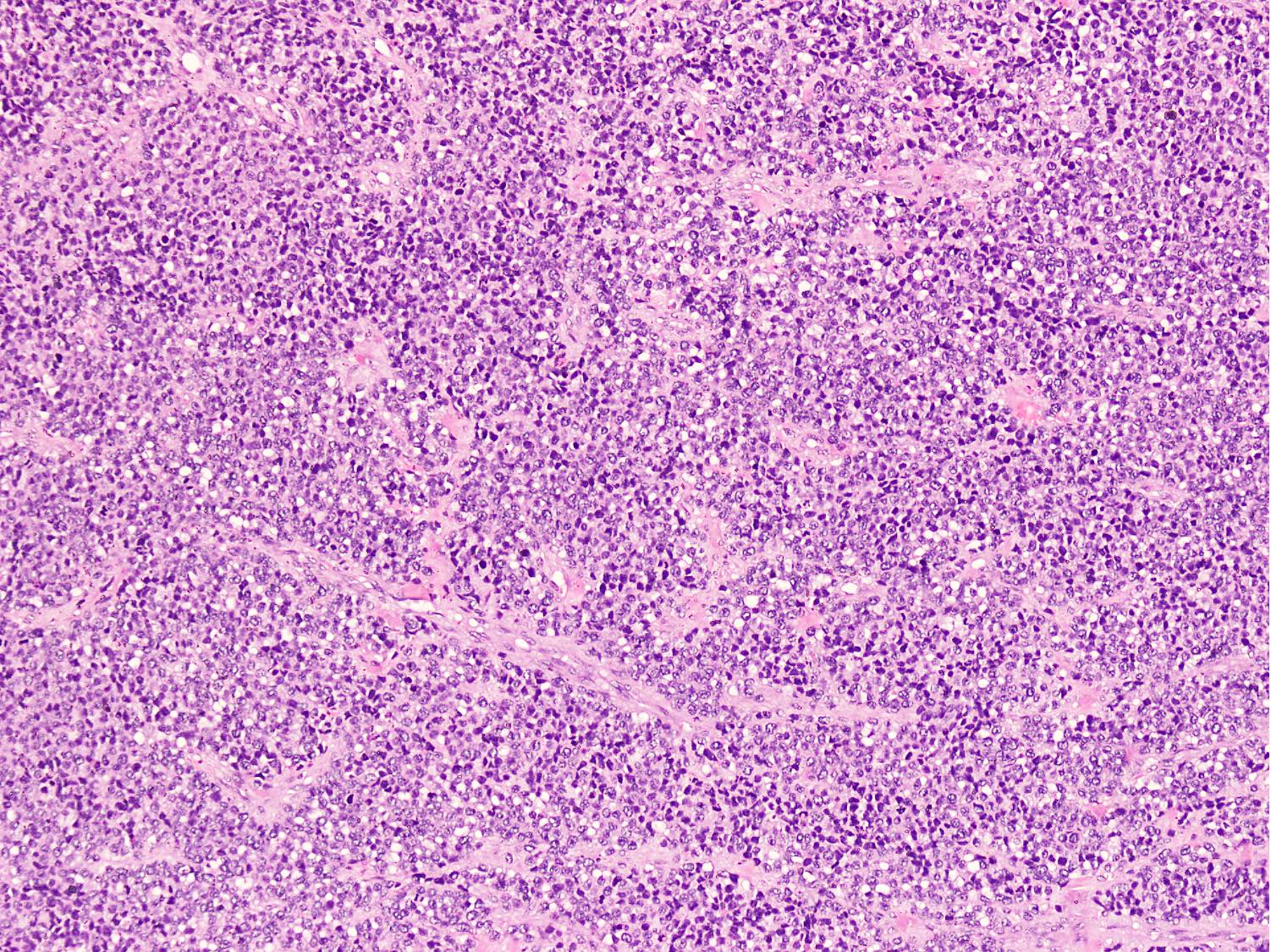
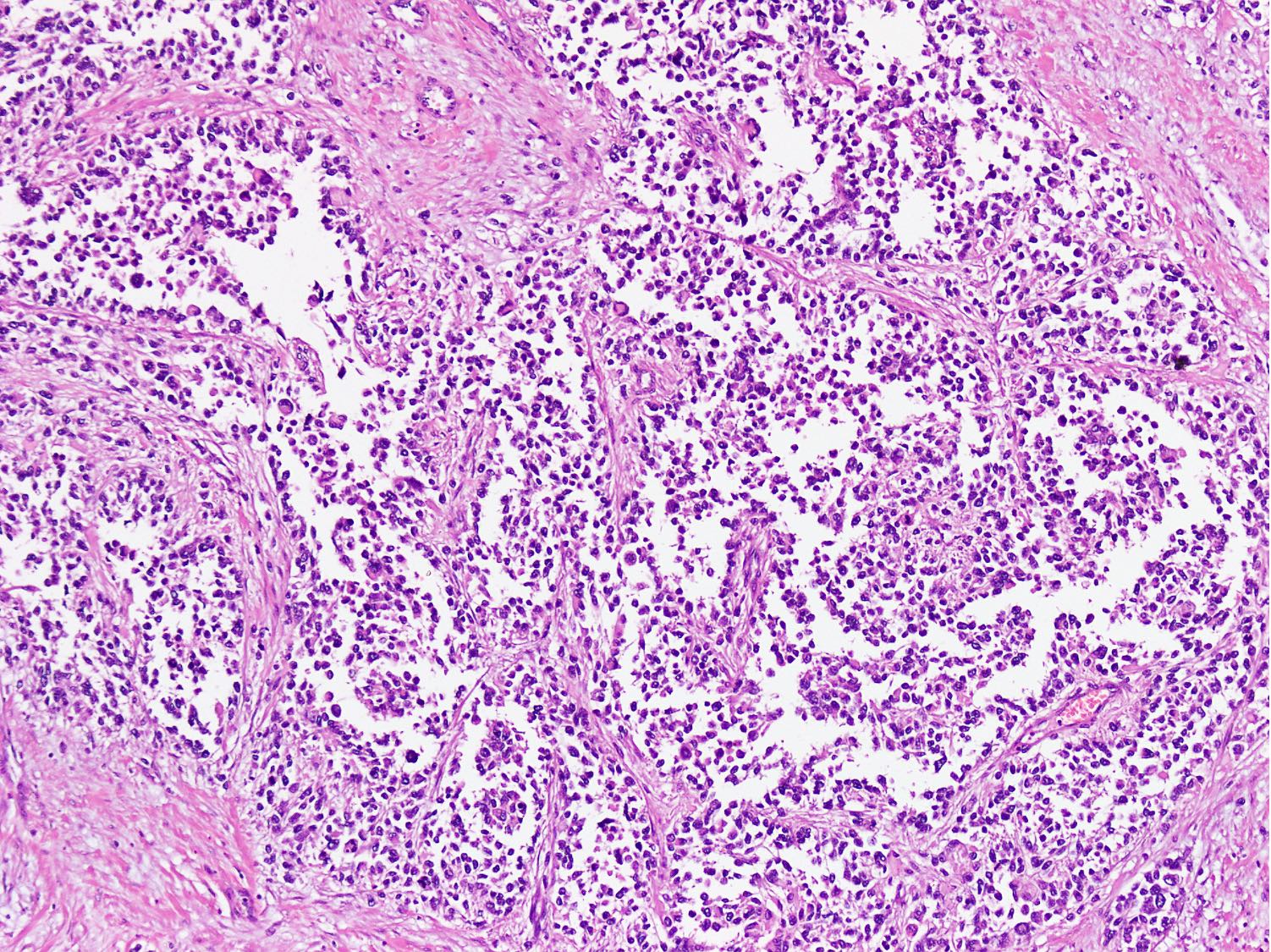
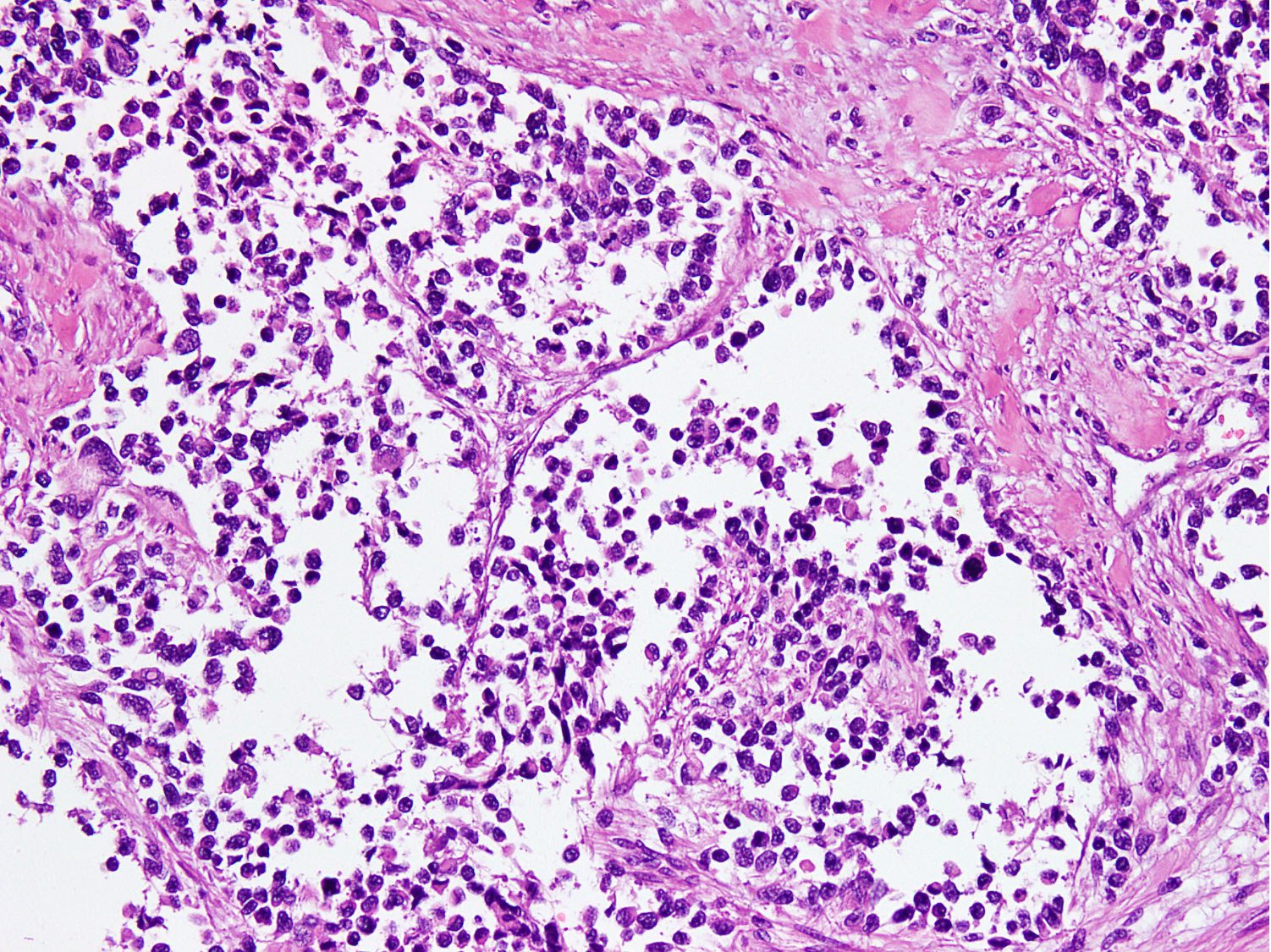
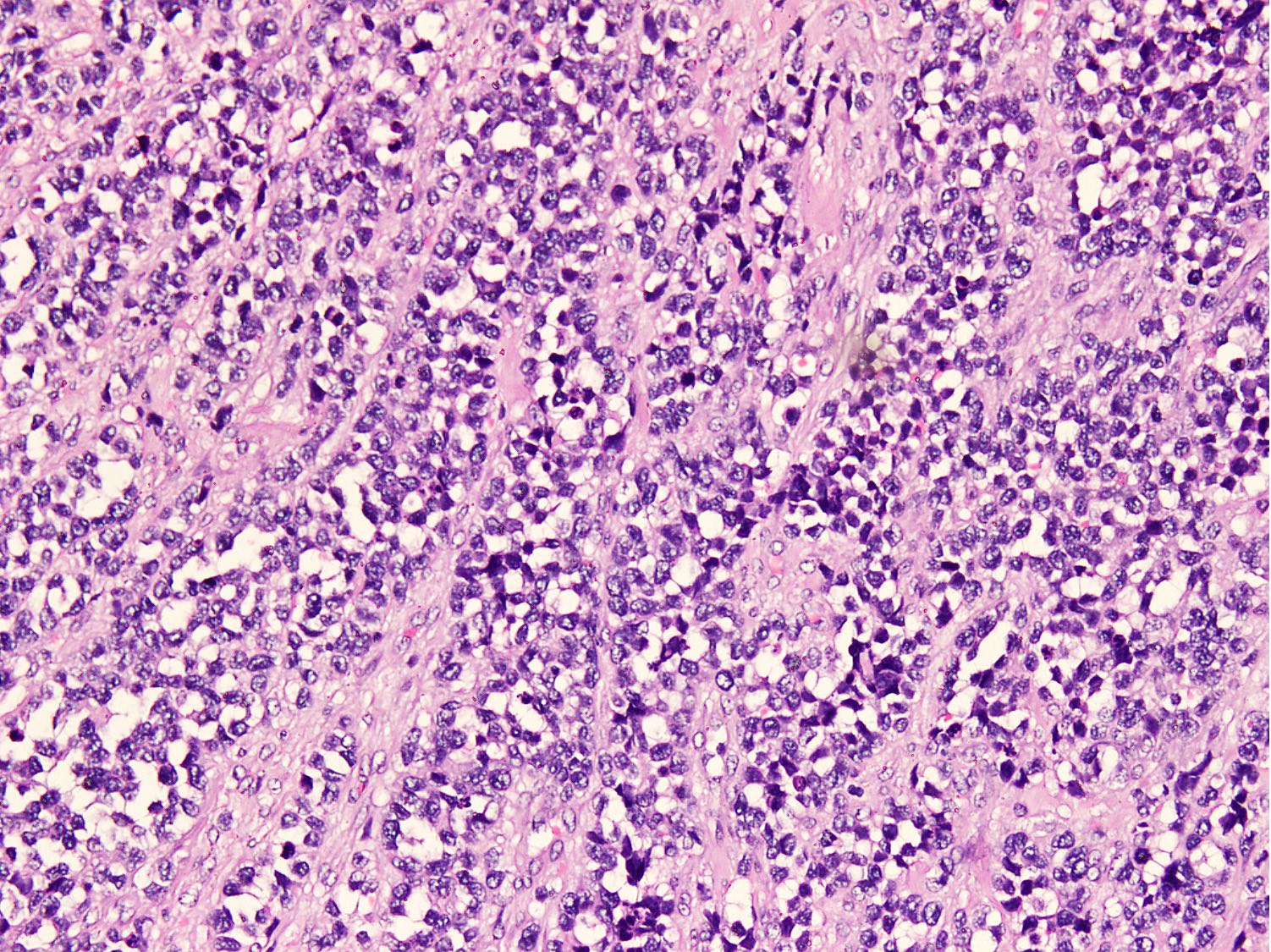
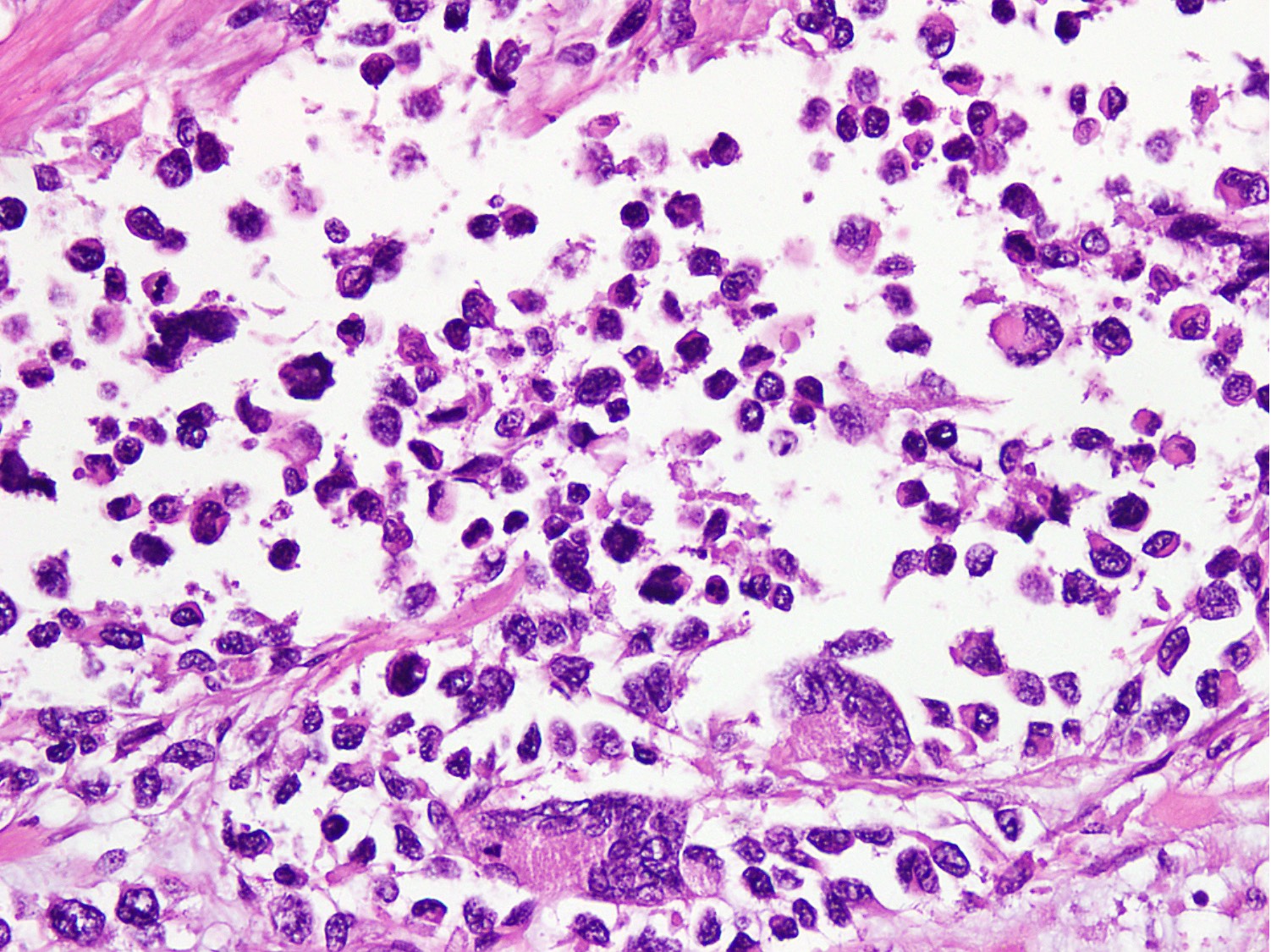
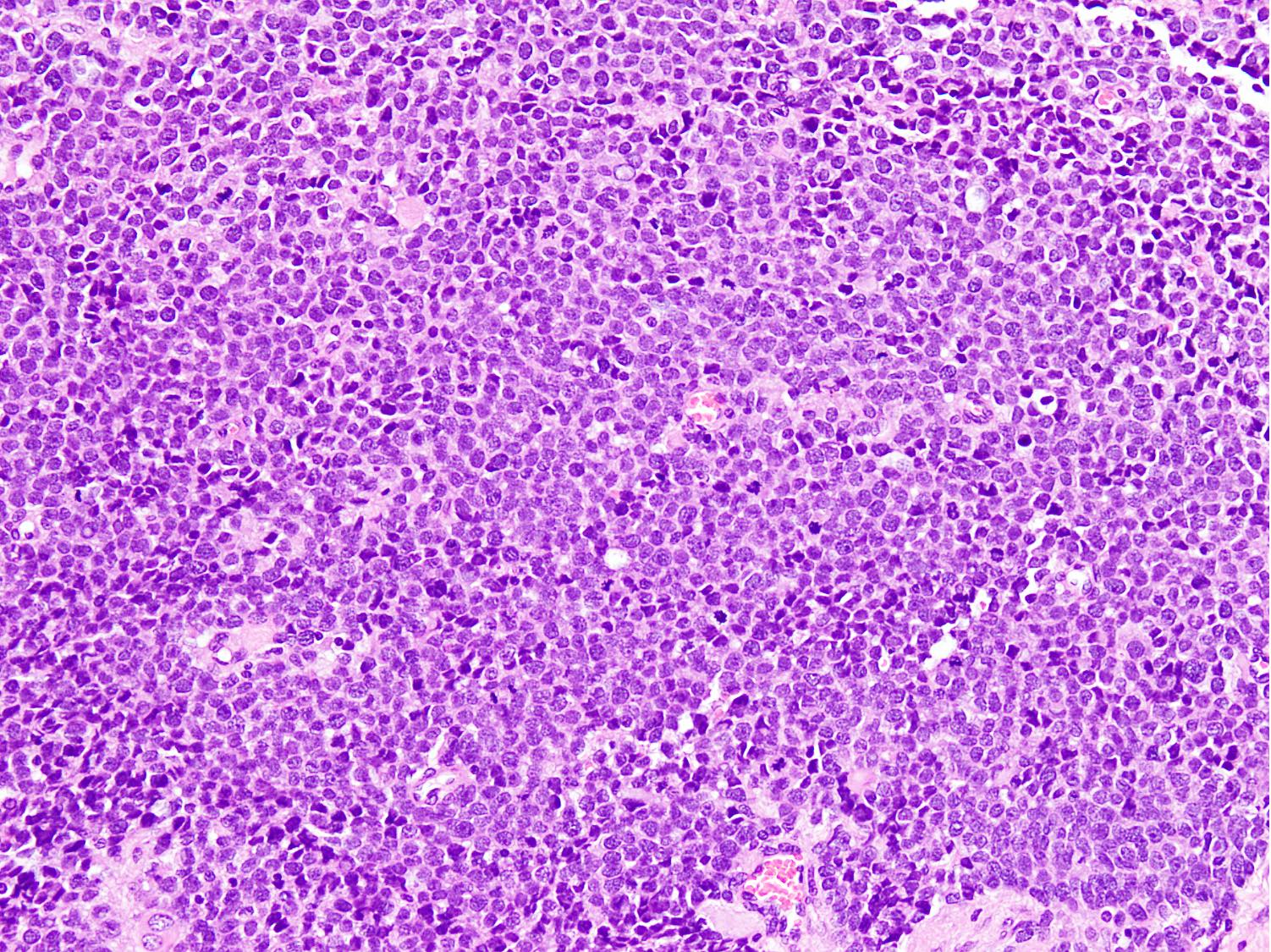
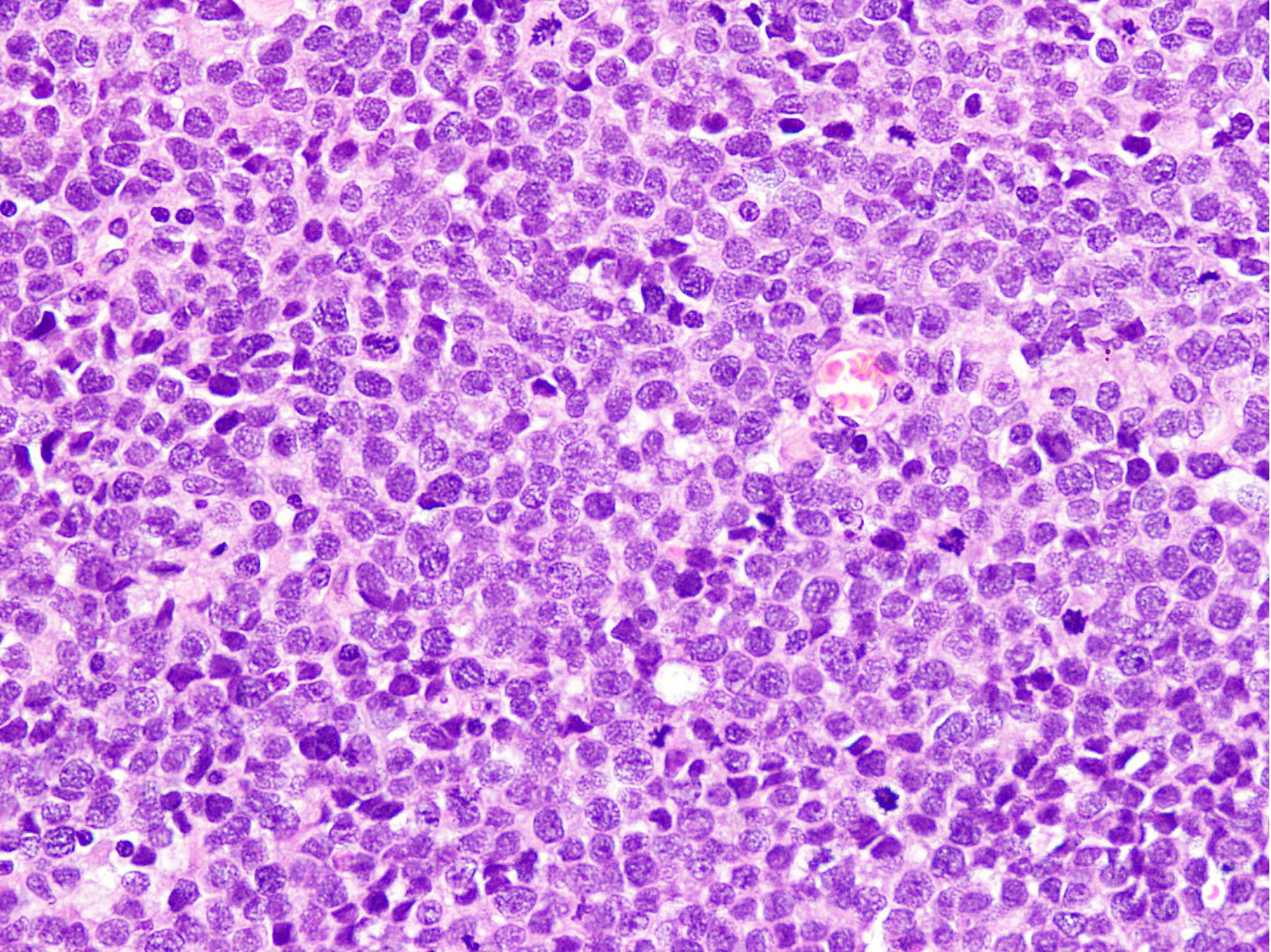
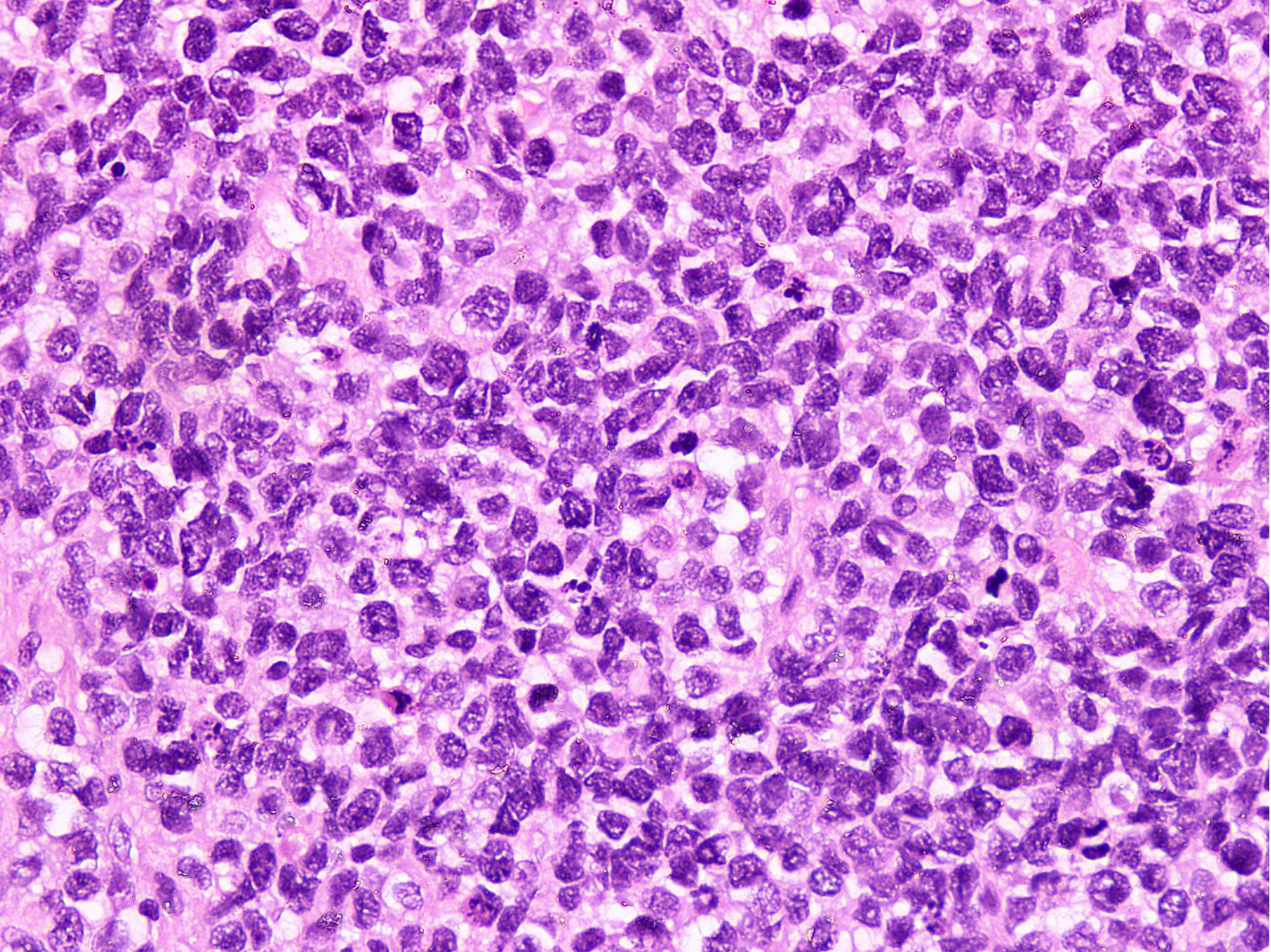
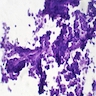
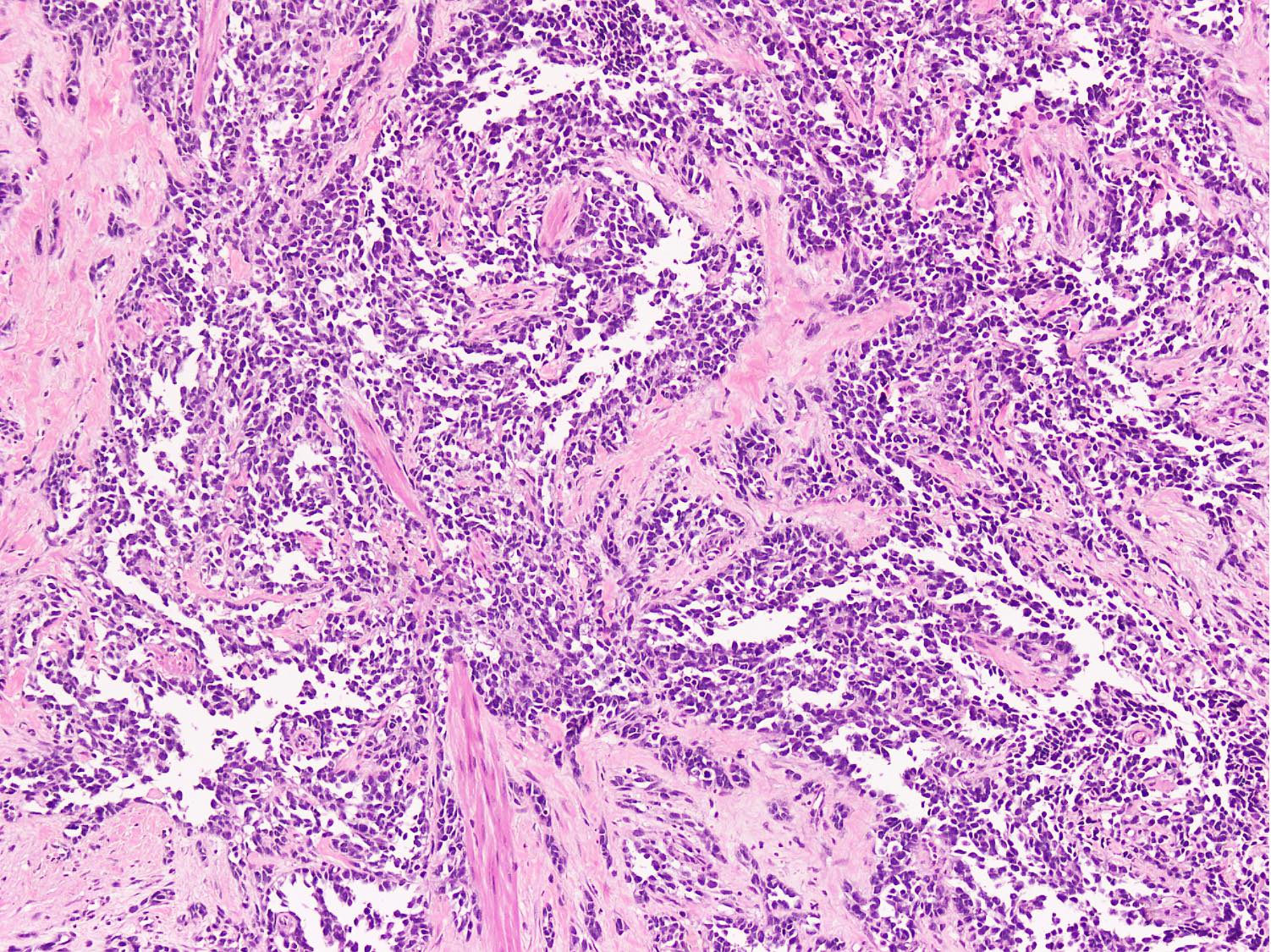
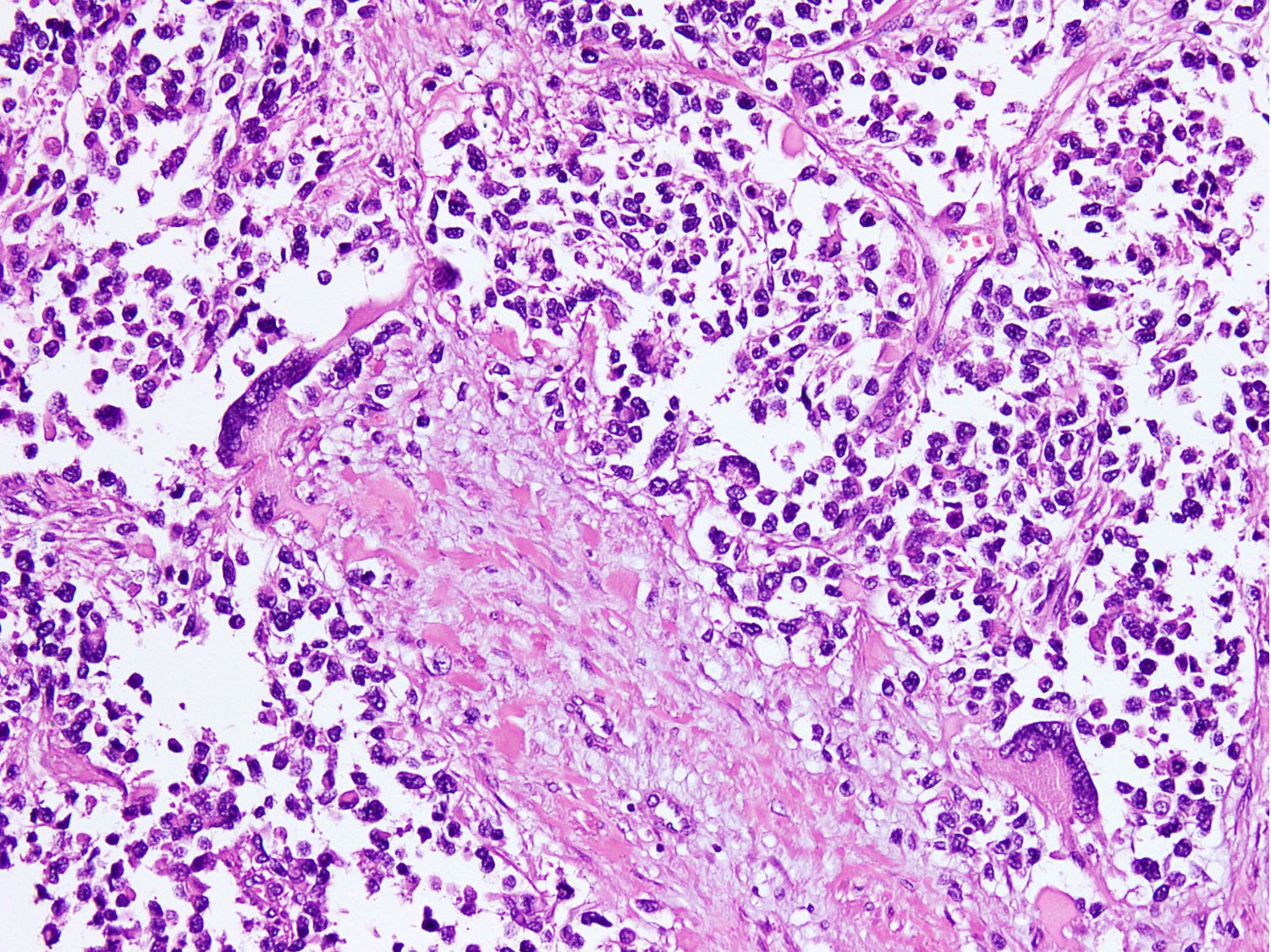
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Cellular round cell tumor
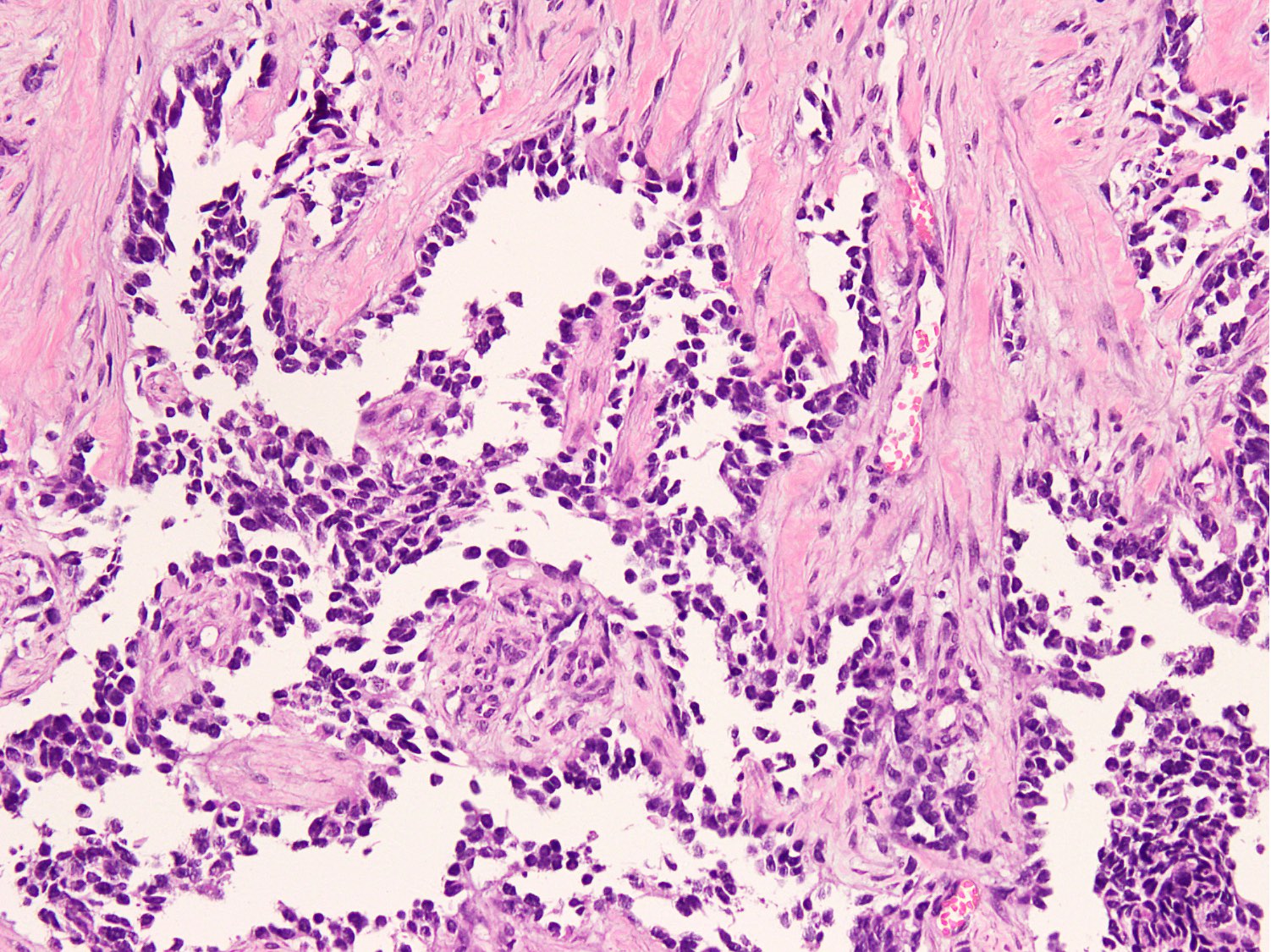
- Large clusters, nests, cords and trabeculae of primitive round cells, separated by variably thick fibrovascular septa
- Loss of cellular cohesion in the center forms alveolar-like, cystic and vague papillary appearance (Histopathology 2022;80:98)
- Layer of cells adheres to the periphery of the spaces and fibrous septa
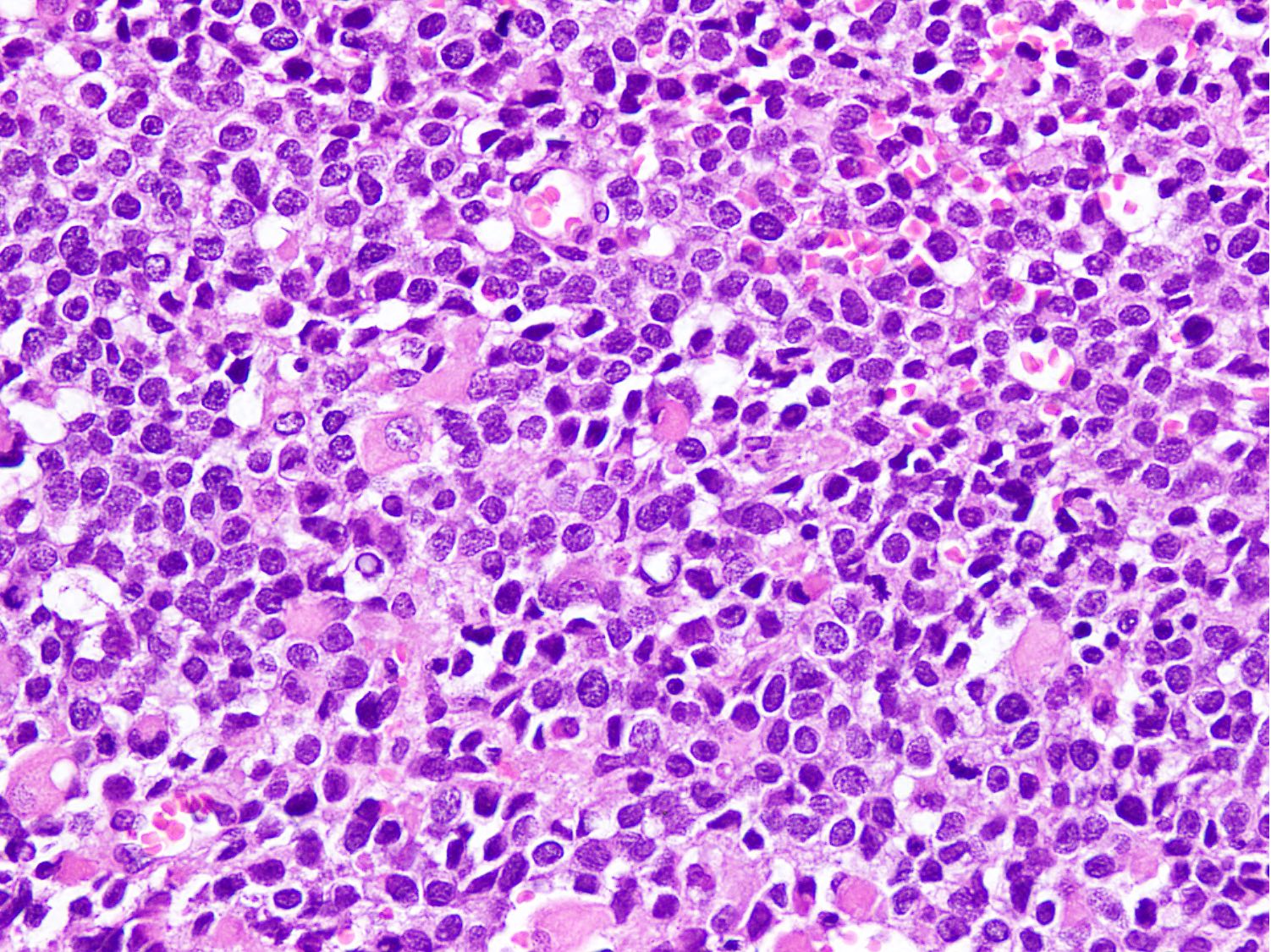
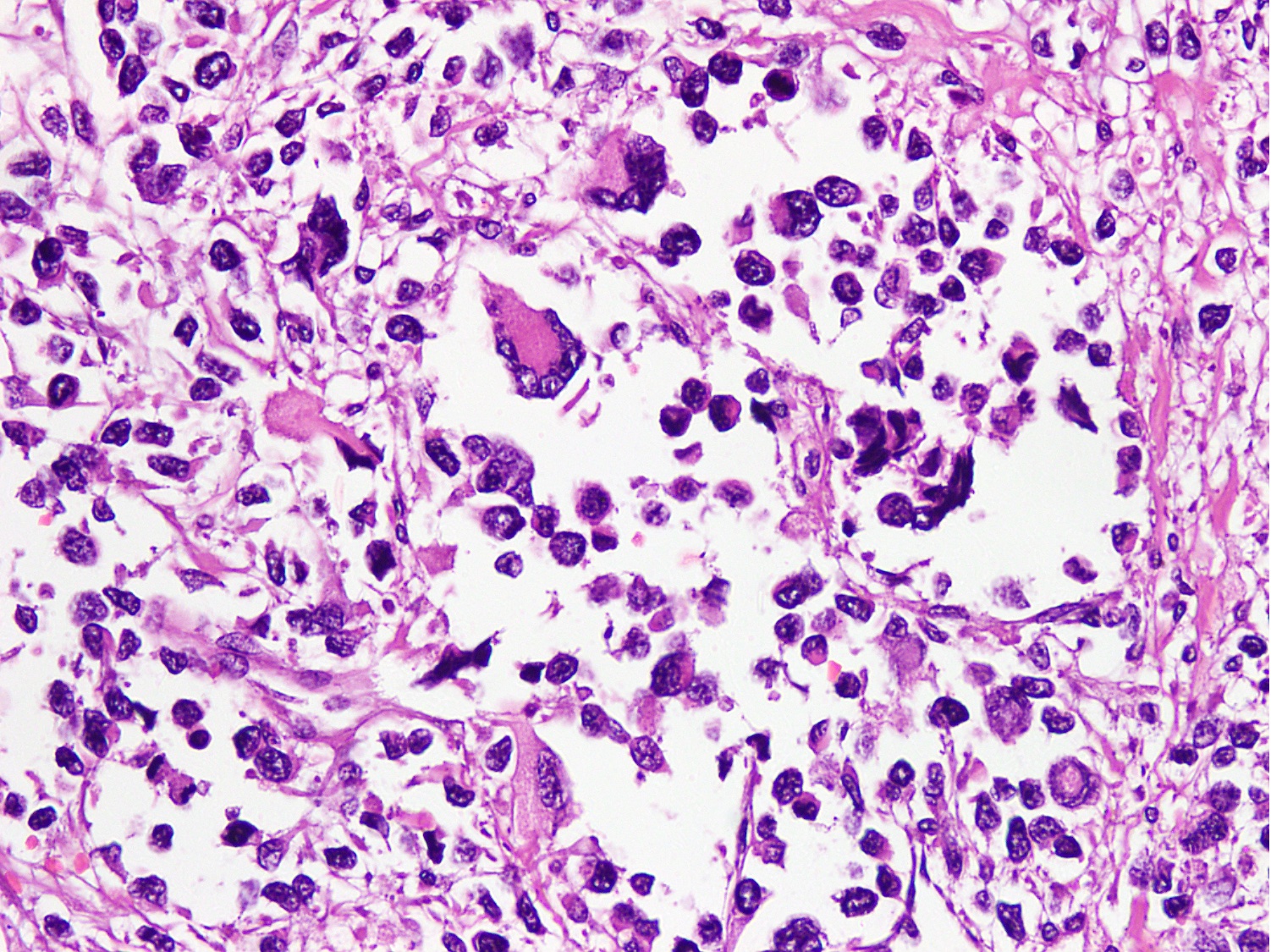
- Small to intermediate sized monomorphic cells with scant cytoplasm
- Hyperchromatic nuclei with variable conspicuous small nucleoli
- Cells in the center have poor preservation and are necrotic; may appear floating
- Multinucleated tumor giant cells with wreath-like lineup of nuclei are common (Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand A 1982;90:345)
- Round to oval rhabdomyoblasts with abundant acidophilic cytoplasm may be present
- Brisk mitosis and variable tumor necrosis
- Occasional cases may show clear cell morphology with pale, glycogenated cytoplasm
- Rare anaplasia
- Some cases may show histologic features of embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma; molecular studies are essential to characterize such cases (Am J Clin Pathol 2013;140:82)
- Solid variant:
- Sheets of neoplastic cells
- Lack fibrovascular septa, pseudoalveolar spaces and dyscohesion (Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2005;163:138)
- May show rhabdomyoblastic differentiation
- Abundant mitotic activity
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Nasir Ud Din, M.B.B.S.
Cytology description
- Cellular smear with dyscohesive loose clusters of small to intermediate sized monotonous cells; may show pseudoalveolar pattern (Diagn Cytopathol 2014;42:1069)
- Cells have scant cytoplasm, round to irregular hyperchromatic nuclei (Diagn Cytopathol 1992;8:465)
- Variable fibrous tissue, wreath-like multinucleated cells and rhabdomyoblastic differentiation
Cytology images
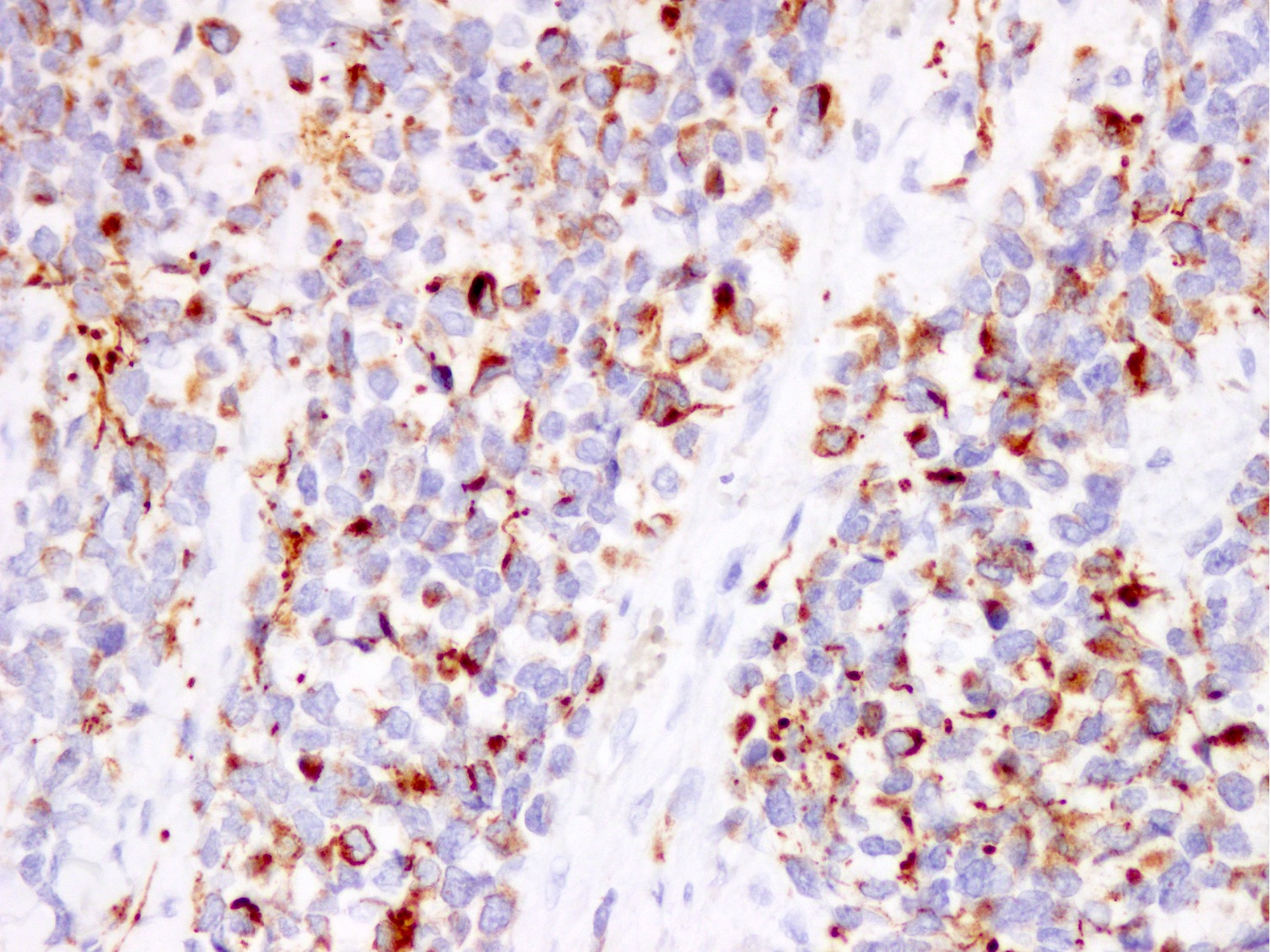
Positive stains
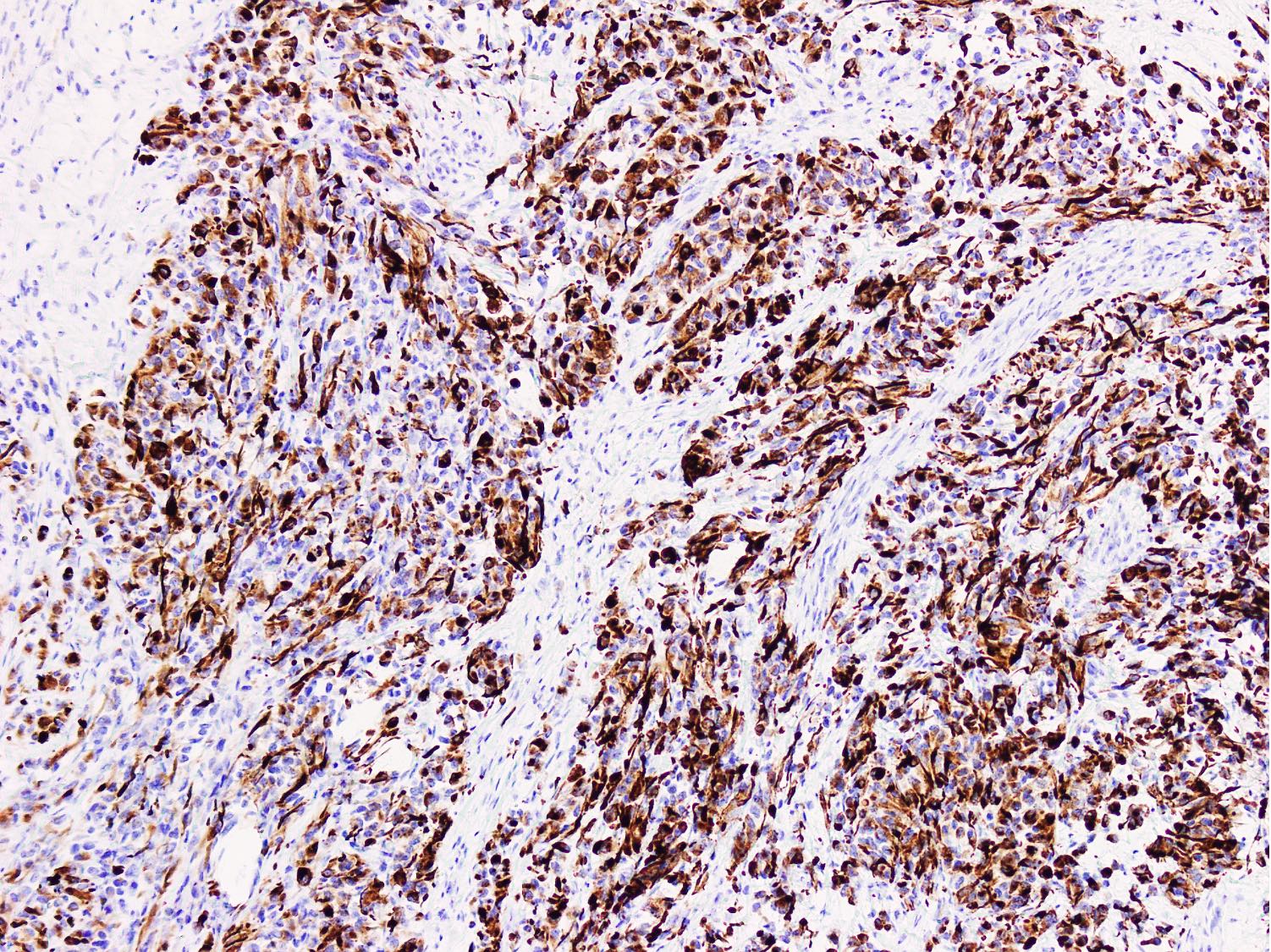
- Stains for myogenic differentiation:
- Desmin
- Myogenin (strong and diffuse) (Ann Diagn Pathol 2018;36:50)
- MyoD1 (variable)
- Muscle specific actin (variable)
- PAX3::FOXO1 / PAX7::FOXO1 fusion specific antibodies (Mod Pathol 2021;34:748, Histopathology 2023 Mar 1 [Epub ahead of print])
- Stains with variable expression:
- PAX5
- MUC4 (Histopathology 2021;78:905)
- ALK1 (cytoplasmic)
- PAX7 (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1305)
- AP2β
- Cytokeratin
- Synaptophysin
- CD56
- Chromogranin (Mod Pathol 2008;21:795)
- CD99
- P-cadherin
- p80
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Sarcomere related structures such as thick and thin filaments (Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 1972;70:131)
Electron microscopy images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- PAX3::FOXO1 / PAX7::FOXO1 fusion (85% of cases):
- t(2;13)(q36;q14): PAX3::FOXO1 in 70 - 90% (Curr Mol Med 2007;7:47)
- Amplification of MYCN and CDK4 in PAX3::FOXO1 positive cases
- t(1;13)(p36;q14): PAX7::FOXO1 in 10 - 30%
- Amplification of PAX7 and MIR17HG in PAX7::FOXO1 positive cases
- Other fusions:
- PAX3::FOXO4 fusion
- PAX3::NCOA1 fusion
- PAX3::INO80D fusion
- FOXO1::FGFR1 fusion
- Inactivating mutation of TP53 and CDKN2 (J Clin Oncol 2021;39:2859)
- Activating mutation of FGFR4
- Overexpression of ALK protein (Pediatr Dev Pathol 2009;12:275)
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Videos
Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma
Sample pathology report
- Forearm, wide margin excision:
- Features are consistent with alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma (see comment)
- Tumor size: 6 x 5 x 4.5 cm
- Margins: superior margin: 1.8 cm
- Inferior margin: 2.1 cm
- Medial margin: 2 cm
- Lateral margin: 2.2 cm
- Anterior margin: 1.9 cm
- Posterior margin: 2.2 cm
- Comment: Histology shows an infiltrative cellular tumor composed of large clusters and nests of primitive round cells, separated by variably thick fibrovascular septa. Irregular pseudoalveolar spaces and cystic change are present within the nests. Scattered wreath-like multinucleated giant cells and rhabdomyoblasts are present along with brisk mitosis and necrosis. Tumor cells show strong and diffuse desmin and myogenin expression, focal MyoD1 and alpha smooth muscle actin positivity, whereas CD34, S100, CK AE1 / AE3, CD99, SALL4, LCA, TdT and synaptophysin are negative. Morphological features and immunoprofile strongly support the diagnosis of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. It is a malignant high grade soft tissue sarcoma with myogenic differentiation and an overall worse prognosis.
Differential diagnosis
- Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma:
- Most common type of rhabdomyosarcoma
- More common in head and neck and genitourinary system
- Rarely involves extremities
- Younger age group
- Slightly M > F
- Alternate areas of dense and loose cellularity
- Morphologic heterogeneity
- Spindle to stellate to tadpole-like cells with rhabdomyoblasts in different stages of differentiation (Histopathology 2022;80:98)
- May show poorly differentiated round cells
- Variable positivity for desmin, myogenin and MyoD1
- Lacks FOXO1 gene fusions
- Sclerosing rhabdomyosarcoma:
- Affects infants, children and adults
- More common in paratesticular area and head and neck in children (Surg Pathol Clin 2020;13:729)
- Cords and trabeculae of round to ovoid cells in a sclerotic collagenous background
- Diffuse to focal desmin and MyoD1, focal myogenin
- Lacks FOXO1 gene mutations
- Alveolar soft part sarcoma:
- Wide age range of 1 - 78 years
- Commonly affects deep soft tissue of extremities and trunk
- Organoid, nested and pseudoalveolar pattern of arrangement (Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi 2020;49:134)
- Large polygonal cells with abundant eosinophilic granular cytoplasm
- Intracytoplasmic rhomboid crystals and granules
- Sinusoidal capillary vasculature
- Pleomorphism, giant cells, mitoses and necrosis are uncommon
- TFE3 positive, desmin focal positive (50%), myogenin negative
- TFE3 gene rearrangement or ASPSCR1::TFE3 fusion
- Lacks FOXO1 gene mutations
Alveolar soft part sarcoma versus alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma
- Ewing sarcoma:
- Similar age group
- Involves extremities and trunk
- Nests and sheets of monotonous small, round, blue cells (Semin Diagn Pathol 2014;31:39)
- Typically lacks giant cells
- CD99 diffuse strong membranous positive, NKX2.2 positive
- Desmin and myogenin negative
- EWSR1 translocations
- Lacks FOXO1 gene mutations
- Lymphoblastic lymphoma / leukemia:
- Small round cell tumor in sheets
- TdT positive, LCA variable
- Desmin and myogenin negative
- IgH gene rearrangement / T cell receptor gene rearrangement (Clin Lab Med 2021;41:405)
- Lacks FOXO1 gene mutations
- Neuroblastoma:
- Younger age group of 1 - 4 years (J Pediatr Surg 2019;54:383)
- M > F
- Occurs anywhere along sympathoadrenal neuroendocrine system
- Small, round, blue cell tumor with rosettes in a neurofibrillary background
- Synaptophysin, NSE, CD56 positive
- Desmin and myogenin negative
- Lacks FOXO1 gene mutations
- Metastatic neuroendocrine carcinoma:
- Known primary
- Older age group
- Small, round, blue cells with high N:C ratio
- Finely dispersed chromatin (salt and pepper) (World Neurosurg 2017;104:1047.e1)
- Keratin, EMA, neuroendocrine markers positive
- Desmin and myogenin negative
- Lacks FOXO1 gene mutations
- Germ cell tumors (yolk sac tumor / embryonal carcinoma):
- Variable morphologic patterns
- SALL4 positive
- Yolk sac tumor: glypican 3 positive
- Embryonal carcinoma: CK AE1 / AE3, CD30, OCT 3/4 positive
- Desmoplastic round cell tumor:
- Affects children and young adults
- M > F
- Majority arise in abdominal cavity
- Nests of small, round, blue cells in a prominent desmoplastic stroma (Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:823)
- May show cytoplasmic eosinophilic rhabdoid inclusions
- May have pleomorphic large cells
- CK AE1 / AE3, EMA, WT1 and desmin (perinuclear dot-like) positive
- Myogenin and MyoD1 negative
- EWSR1::WT1 gene fusion
- Lacks FOXO1 gene mutations
- Poorly differentiated synovial sarcoma:
- Affects adolescents, young and elder adults
- Majority arise in extremities
- Small, round, blue cell morphology with thin fibrovascular septa (Histopathology 2003;43:220)
- Branching vasculature
- Frequent mitoses and necrosis
- May have conventional synovial sarcoma areas
- TLE1, SS18::SSX positive
- Desmin and myogenin negative
- SS18::SSX1 / SS18::SSX2 / SS18::SSX4 fusion present
- Lacks FOXO1 gene mutations
- Small cell osteosarcoma:
Additional references
Practice question #1
An 18 year old boy presented with a rapidly growing mass in the right forearm, which was resected. Gross examination showed a skin covered fibromuscular tissue with an infiltrative, soft, fleshy gray-white tumor of 6 x 5 x 4.5 cm. Histology showed a small, round, blue cell tumor arranged in nests and aggregates separated by fibrous septa. Pseudoalveolar spaces with cystic change were present along with frequent mitoses and focal necrosis. Immunostains desmin and myogenin were diffuse strong positive. CD34, S100, CK AE1 / AE3, CD99, SALL4, LCA, TdT and synaptophysin were negative. Focal muscle specific actin and MyoD1 expression was present. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma
- Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma
- Pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma
- Sclerosing rhabdomyosarcoma
- Spindle cell rhabdomyosarcoma
Practice answer #1
A. Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma shows small, round, blue cell morphology with pseudoalveolar change, diffuse desmin and myogenin expression and focal MyoD1. Answer B is incorrect because embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma has round and spindle cell morphology with scattered differentiated rhabdomyoblasts as well as desmin positivity and heterogeneous nuclear staining for myogenin and MyoD1. Answer C is incorrect because pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma has sheets of large, atypical pleomorphic and frequently multinucleated polygonal, spindle or rhabdoid eosinophilic cells as well as diffuse strong desmin positivity with focal myogenin and MyoD1. Answer D is incorrect because sclerosing rhabdomyosarcoma has cords and trabeculae of round to ovoid cells in a sclerotic collagenous background as well as diffuse MyoD1 positivity, focal desmin and myogenin. Answer E is incorrect because spindle cell rhabdomyosarcoma has fascicles of spindle cells as well as diffuse MyoD1, focal desmin and myogenin.
Comment Here
Reference: Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma
Comment Here
Reference: Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma
Practice question #2
Practice answer #2
E. Wreath-like giant cells. Wreath-like giant cells are seen in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma and clear cell sarcoma. Answer A is incorrect because floret-like giant cells are present in spindle cell / pleomorphic lipoma, neurofibroma and giant cell fibroblastoma. Answer B is incorrect because Langhans giant cells are seen in tuberculosis and sarcoidosis. Answer C is incorrect because osteoclast-like giant cells are seen in giant cell tumor and tenosynovial giant cell tumor. Answer D is incorrect because Touton type giant cells are seen in xanthoma, xanthelasma and myxofibrosarcoma.
Comment Here
Reference: Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma
Comment Here
Reference: Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma