Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Frozen section / intraoperative description | Frozen section images | Microscopic (histologic) description / diagnostic criteria | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2 | Practice question #3 | Practice answer #3 | Practice question #4 | Practice answer #4Cite this page: Asirvatham JR. Sentinel lymph nodes. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastmalignantsentinel.html. Accessed October 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
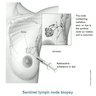
- Sentinel lymph nodes (SLN) are the first lymph nodes to receive lymphatic drainage and metastasis from a tumor
Essential features
- Blue dye (isosulphan blue or methylene blue) or radioactive isotope labeled colloid (technetium sulfur colloid) is injected to identify the draining SLN
- Entire breast largely drains to the same few SLN (Arch Surg 2004;139:614)
- SLN are usually axillary nodes (level I) but may be at level II or III; rarely intramammary, interpectoral (Rotter) or internal mammary node (Eur J Surg Oncol 2009;35:252)
- Intraoperative frozen section or intraoperative imprint cytology can be performed on the SLN (even after neoadjuvant chemotherapy) to determine need for axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) (Acad Radiol 2009;16:551)
Terminology
- At least 1 node with presence or absence of cancer as documented by pathologic examination is required for pathologic N classification in breast cancer staging
- Axillary lymph node metastases are classified into 3 groups: isolated tumor cell clusters, micrometastasis and macrometastasis
- AJCC sn modifier: when the number of sentinel and nonsentinel nodes removed is < 6
- AJCC f modifier: when nodal metastasis is confirmed by FNA or core biopsy only
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- 15 - 20% of clinically node negative patients will have a positive SLN (Breast Care (Basel) 2018;13:331)
- If SLN are negative, other axillary nodes are negative in > 95% of cases and axillary recurrence rate is only 0.3% at median 34 months (Eur J Surg Oncol 2008;34:1277)
Sites
- Breast lymphatic drainage (Am J Clin Pathol 2018;150:4):
- Superficial system: superficial breast and skin to axilla, independent
- Deep system: breast to axilla, anastomoses with perforating system
- Perforating system: traverses pectoralis muscles and drains into internal mammary node
- Axillary lymph nodes are divided into 3 levels:
- Low axilla: lateral to the lateral border of the pectoralis minor muscle
- Mid axilla: between the medial and lateral borders of the pectoralis minor muscle, plus the interpectoral (Rotter) lymph nodes
- Apical axilla or infraclavicular nodes: medial to the medial margin of the pectoralis minor muscle and inferior to the clavicle
- Intramammary nodes are most commonly present in the upper outer quadrant and are included with axillary nodes in AJCC N classification
- Internal mammary nodes, supraclavicular nodes and infraclavicular nodes are rarely removed for breast cancer staging
- If metastases are present in these nodes, there are specific AJCC N categories
- Medially located tumors are more likely to drain to internal mammary nodes (medial 28%; lateral 15%) (Am J Clin Pathol 2018;150:4)
- Tumor is more likely at the inflow junction of afferent lymphatic vessels (Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:385)
Clinical features
- SLN biopsy is successful in > 90% of eligible breast cancer patients
- False negative rate (FNR) in surgical practice (i.e. inability of the procedure to identify a positive draining lymph node): 5.5 - 16.7% (J Clin Oncol 2014;32:1365)
- Lowest FNR: if both blue dye and radioactive tracer are used, 6.7% (J Natl Cancer Inst 2006;98:599)
- Increased FNR when only a single SLN is removed (Lancet Oncol 2010;11:927)
- FNR in large multifocal / multicentric tumors appears to be similar to small unifocal tumors (systematic review of 26 studies, Eur J Surg Oncol 2011;37:371)
Diagnosis
- Gross sectioning of SLN at 2 mm intervals and histological examination of submitted tissue
Radiology description
- Axillary ultrasound (US) is the primary modality for evaluating axillary lymph node status prior to surgery
- Cortical thickening, hilar effacement and non-hilar cortical blood flow, are more important than size criteria (Radiographics 2013;33:1589)
- Preoperative axillary US and FNA cytology are routine at many breast units, with a sensitivity of 56% (confidence interval: 47 - 64%) and specificity of 90% (84 - 93%) for US alone and 76% (61 - 87%) and 100% (65 - 100%) when combined with FNA cytology (J BUON 2011;16:454)
- Standard breast MRI is comparable to dedicated axillary US in breast cancer patients; subsequent axillary US can be done on those with suspicious nodal findings (Eur J Radiol 2016;85:2288)
- CT and radionuclide imaging play a lesser role in imaging the axilla (Radiographics 2013;33:1589)
Prognostic factors
- High risk (60%) of tumor in nonsentinel nodes if sentinel node has macrometastatic tumor (≥ 2 mm) versus low risk (3%) if micrometastatic tumor (0.2 - 2 mm) (Mod Pathol 2005;18:762)
- Extranodal extension was a predictor of nonsentinel node involvement in a single institution study of 266 cases (Sci Rep 2020;10:14684)
Case reports
- Middle aged woman with subcapsular deposit of metastatic carcinoma and benign mammary inclusion (Breast J 2020;26:274)
- Perimenopausal patient underwent mastectomy which showed invasive lobular carcinoma (Case #548)
- 63 year old woman with intravascular nevus cell aggregate in axillary lymph node mimicking metastatic carcinoma (Breast J 2019;25:726)
- 86 year old woman with isolated tumor cells and benign Müllerian inclusions in axillary sentinel lymph node (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2016;24:144)
Treatment
- SLN biopsy (versus ALND) is standard of care in staging clinically node negative T1 / T2 tumors
- Notable exception per Choosing Wisely Society of Surgical Oncology recommendations: don't routinely use SLNB in clinically node negative women ≥ 70 years of age with early stage hormone receptor positive, HER2 negative invasive breast cancer
- Number of involved lymph nodes and size of deposit (micro / macrometastasis) are important for clinical decision making (Ann Oncol 2018;29:2153)
- Per current NCCN guidelines, clinically node negative patients with only micrometastasis or with macrometastasis meeting ACOSOG Z11 criteria (T1 / T2 tumor, ≤ 2 positive nodes, breast conserving surgery, whole breast RT planned, no preoperative chemotherapy) may be spared ALND
- ER+ / HER2- patients with limited involvement of axillary lymph nodes might be spared adjuvant chemotherapy if the tumor biology is favorable (Ann Oncol 2018;29:2153)
- Role of nodal radiation therapy in patients with 1 - 3 positive lymph nodes is unclear, though there is modest increase in disease free survival (JAMA Oncol 2016;2:991)
- Current NCCN guidelines recommend strongly considering radiation therapy
Gross description
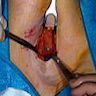
- Axillary SLN may be blue dyed, with or without surrounding adipose tissue
Frozen section / intraoperative description
- Axillary SLN are identified by the surgeon by determining uptake of radioisotope technetium 99 sulfur colloid, methylene blue dye or both
- Intraoperative frozen section or imprint cytology may be performed on the SLN to determine need for axillary lymph node dissection (World J Surg Oncol 2008;6:69, Eur J Surg Oncol 2009;35:16)
- Frozen section (FS) had an overall mean sensitivity of 73% (macrometastasis: 94%; micrometastasis 40%) and mean specificity of 100% (metaanalysis of 47 studies, Cancer 2011;117:250)
- SLN FS may be safely omitted in patients who meet ACOSOG Z11 criteria (Clin Breast Cancer 2018;18:276, J Clin Pathol 2016;146:57)
- FNR of intraoperative frozen section post neoadjuvant chemotherapy was 5.4% in a single institution study of 711 cases (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1377)
- Atypical cases on FS are usually negative on permanent sections (Mod Pathol 2005;18:58)
- In most cases, if metastases are present, the SLN will be involved; in rare cases, only nonsentinel nodes contain metastases
- Metastasis to nonsentinel lymph nodes can occur if the true SLN is completely replaced by tumor (and therefore is not detected by radioactive tracer or dye), if there is unusual lymphatic drainage or if there is failure of the technique to identify the node
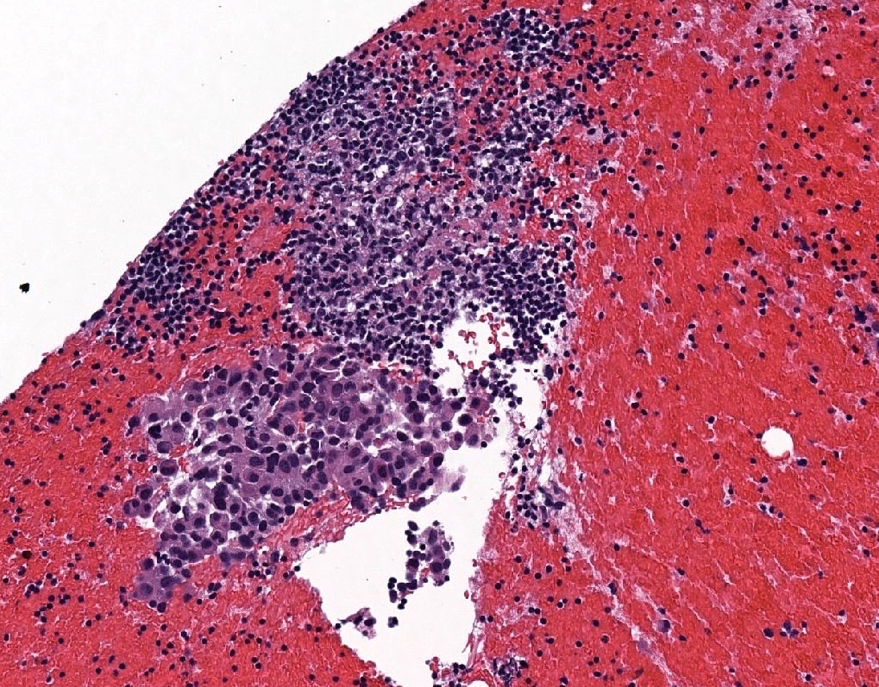
Microscopic (histologic) description / diagnostic criteria
- See Staging of breast carcinoma
- Size of the metastatic focus is measured from the largest contiguous cluster of tumor cells
- Direct extension of primary tumor into a regional node is classified as node positive
- Tumor nodule with a smooth contour in a regional node area is classified as a positive node
- Size of the metastasis, not the size of the node, is used for the criterion for the N category
- Cases with isolated tumor cells only in lymph nodes are classified as pN0(i+)
- Dispersed pattern of lymph node metastasis can be difficult to categorize
- Particularly lobular carcinomas metastasize as single cells and do not form cohesive clusters
- If > 200 tumor cells are present in 1 cross section of the node, then the category isolated tumor cells should not be used
- If there is difficulty in assigning the N classification, it is recommended that the reason be provided in a note
- The area of extracapsular extension is included in the overall size of the lymph node metastasis if contiguous
- Size of the metastasis includes the tumor cells and the desmoplastic response in treatment naïve patients (i.e. the cells do not need to be contiguous but the cells plus fibrosis should be contiguous)
- Finding of extranodal invasion is also reported
- Areas of carcinoma invading into the stroma in axillary adipose tissue, without residual nodal tissue, are considered to be positive lymph nodes
- However, if there is surrounding breast tissue or ductal carcinoma in situ, then the focus should be classified as an invasive carcinoma and not as a lymph node metastasis (CAP: Protocol for the Examination of Specimens from Patients with Invasive Carcinoma of the Breast [Accessed 20 August 2021])
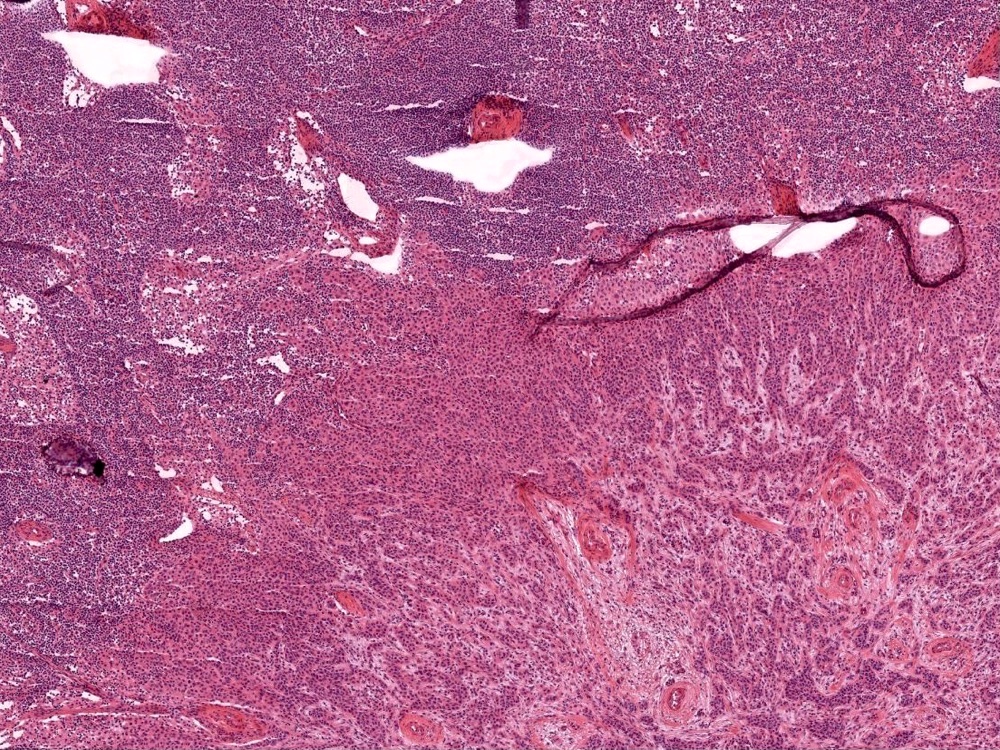
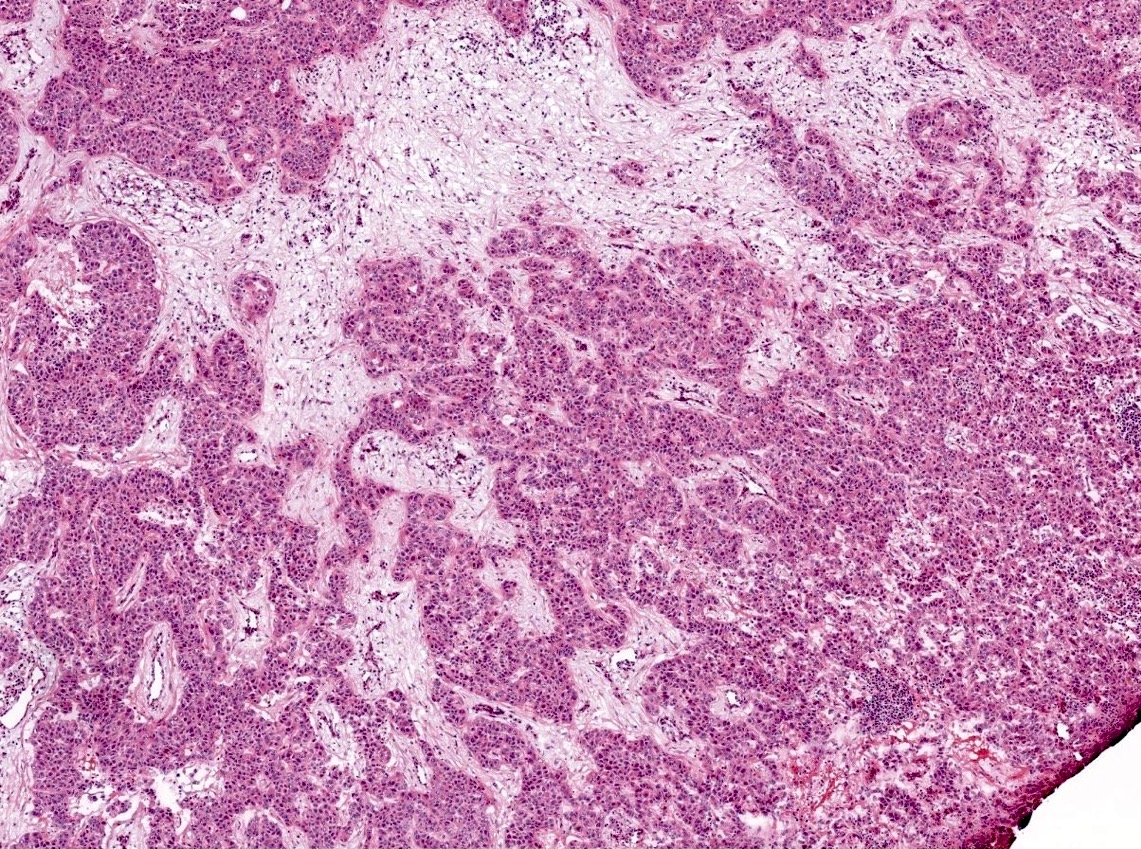
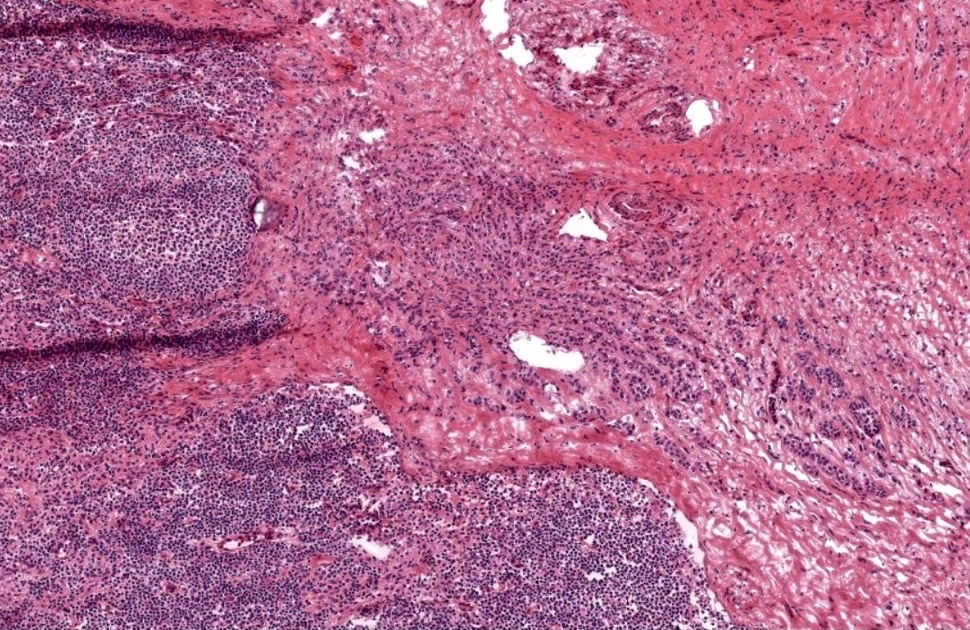
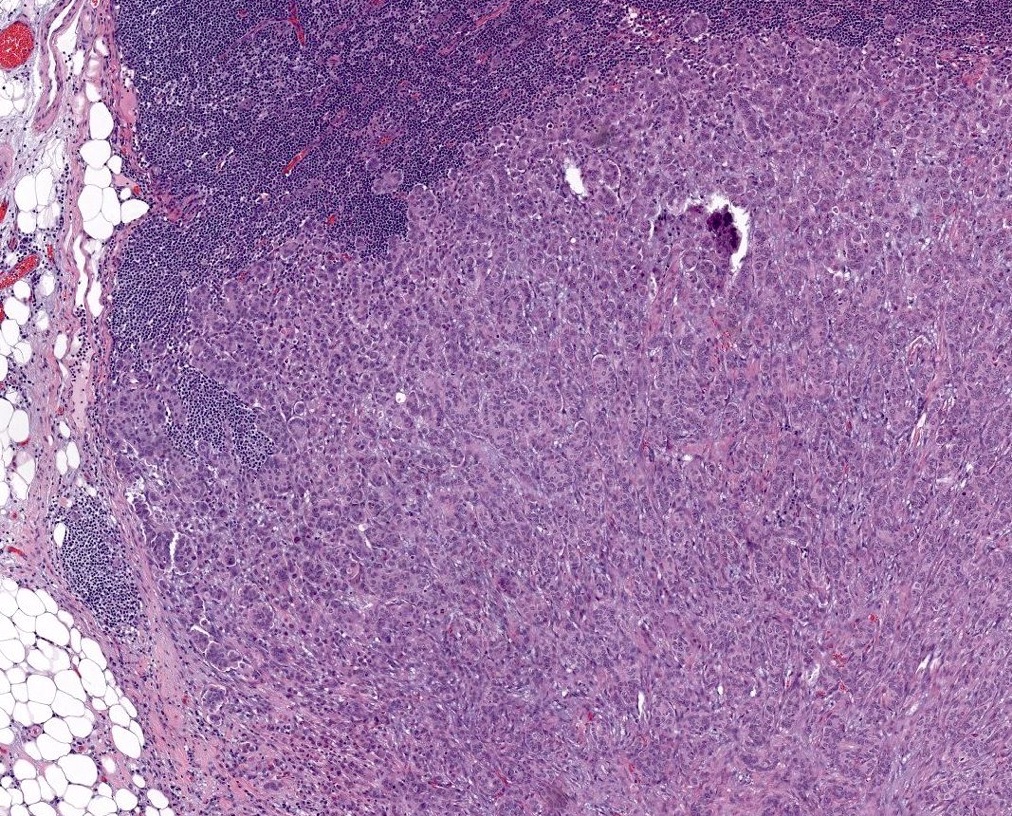
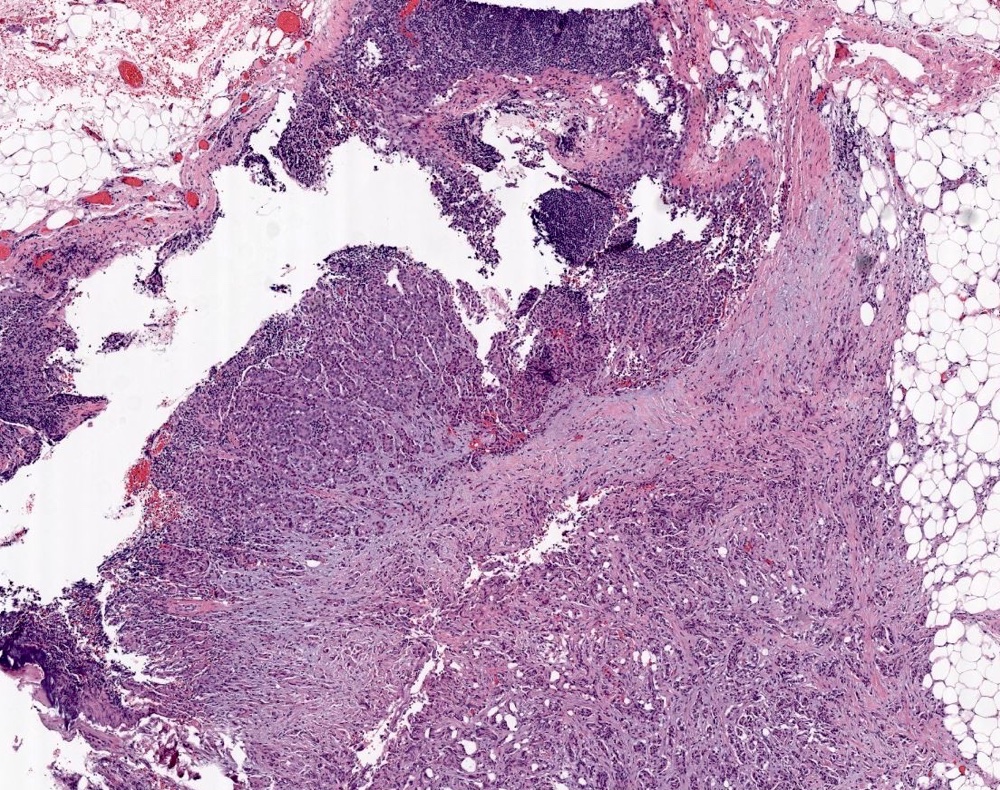
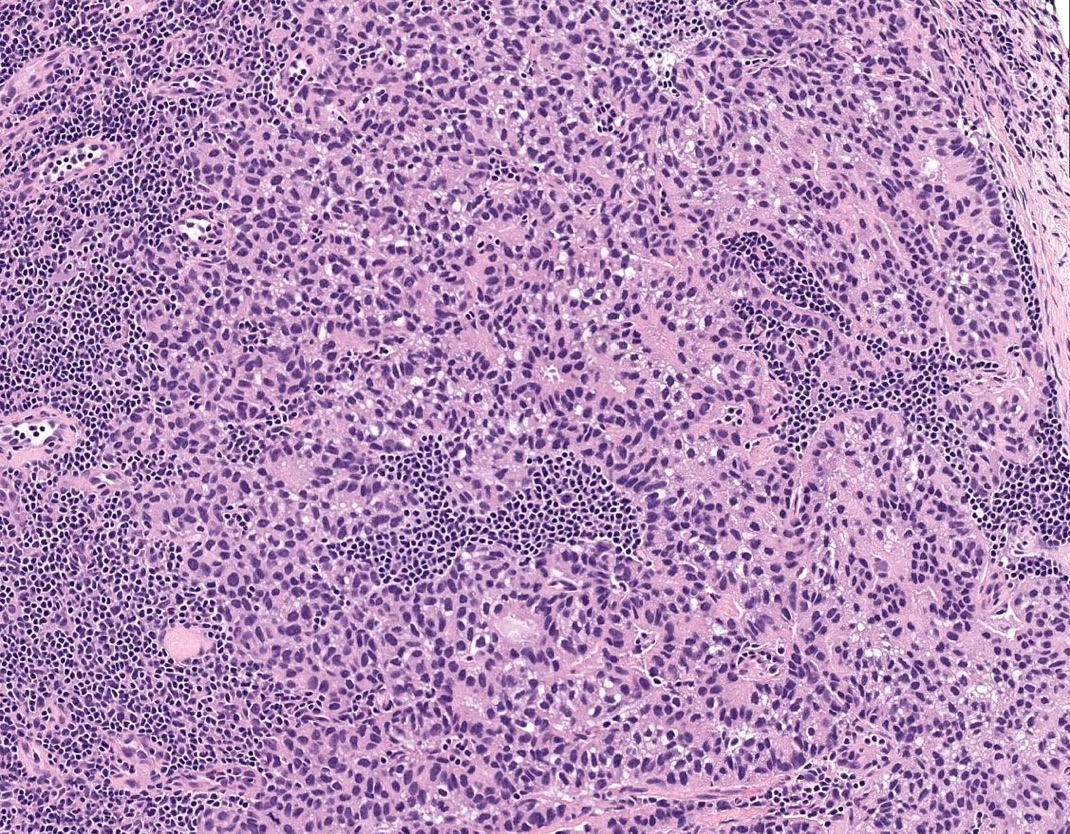
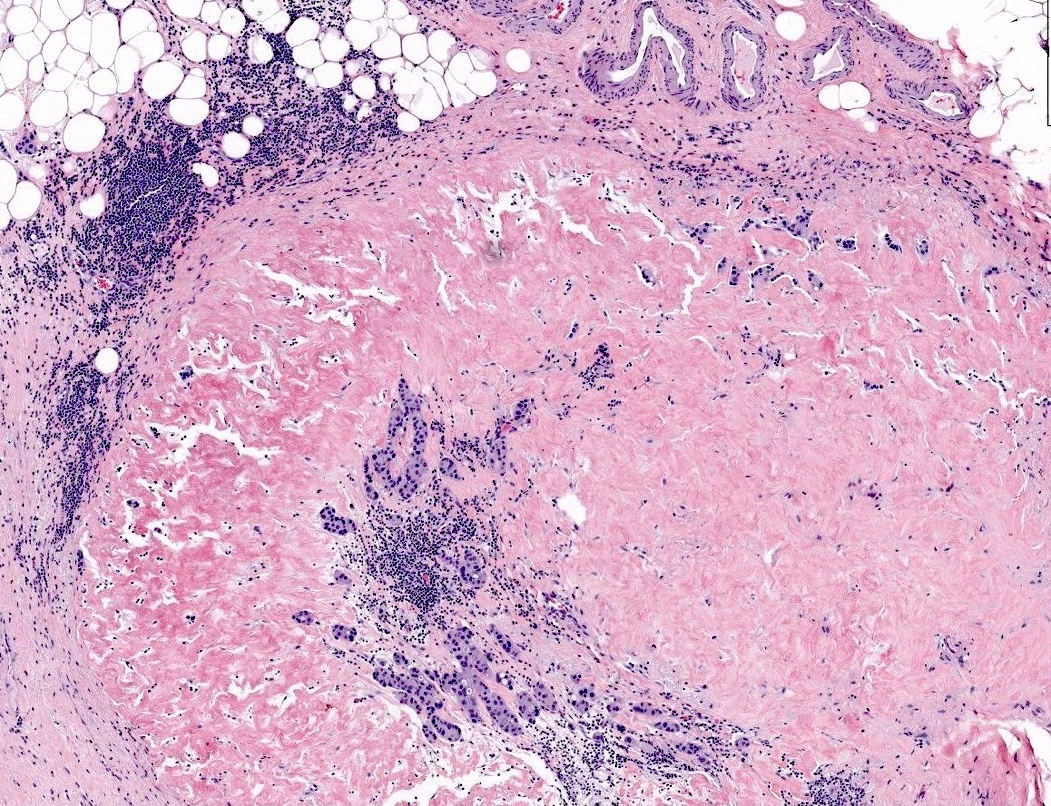
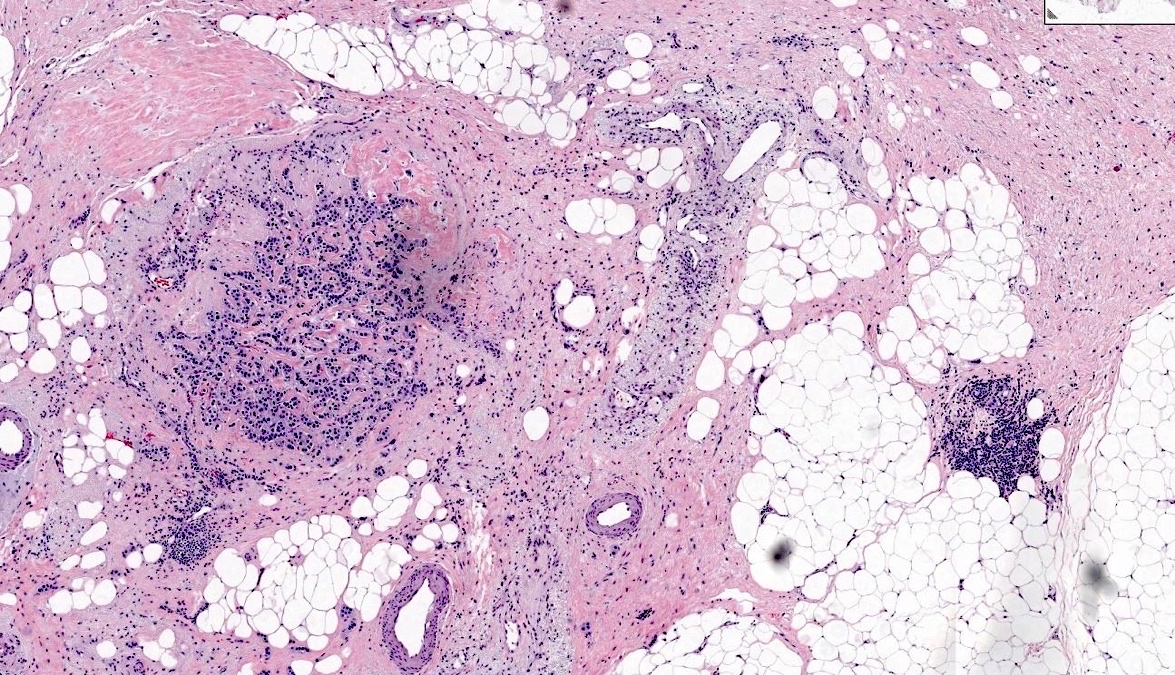
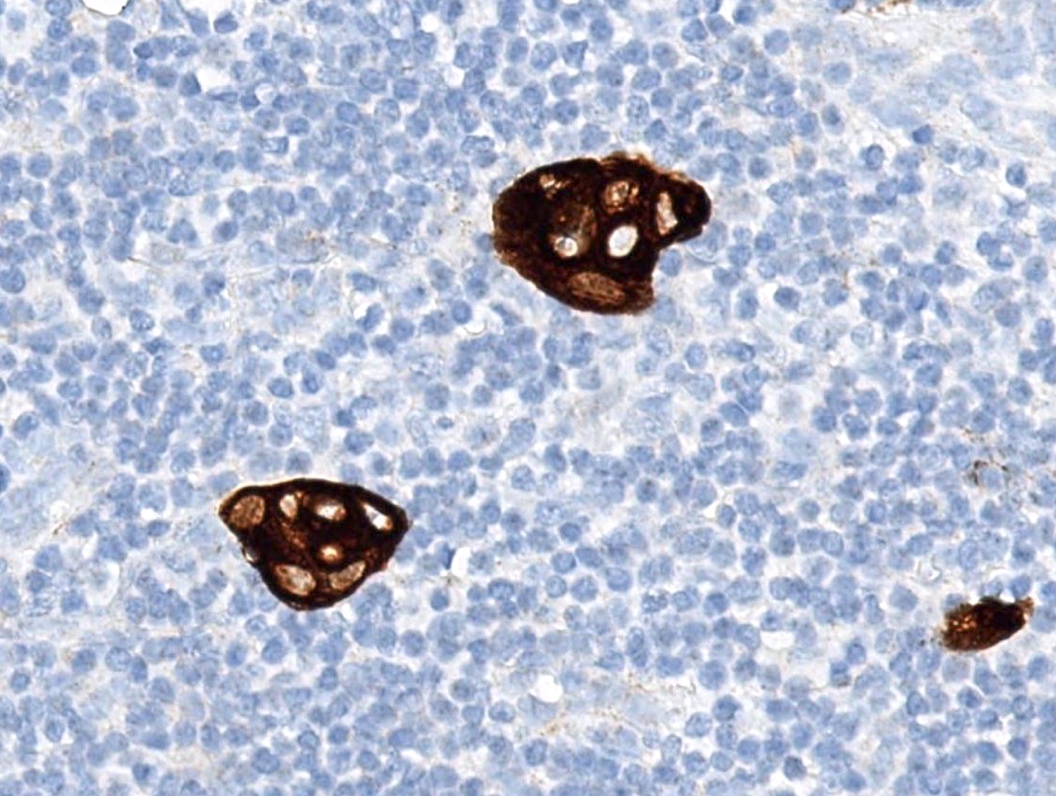
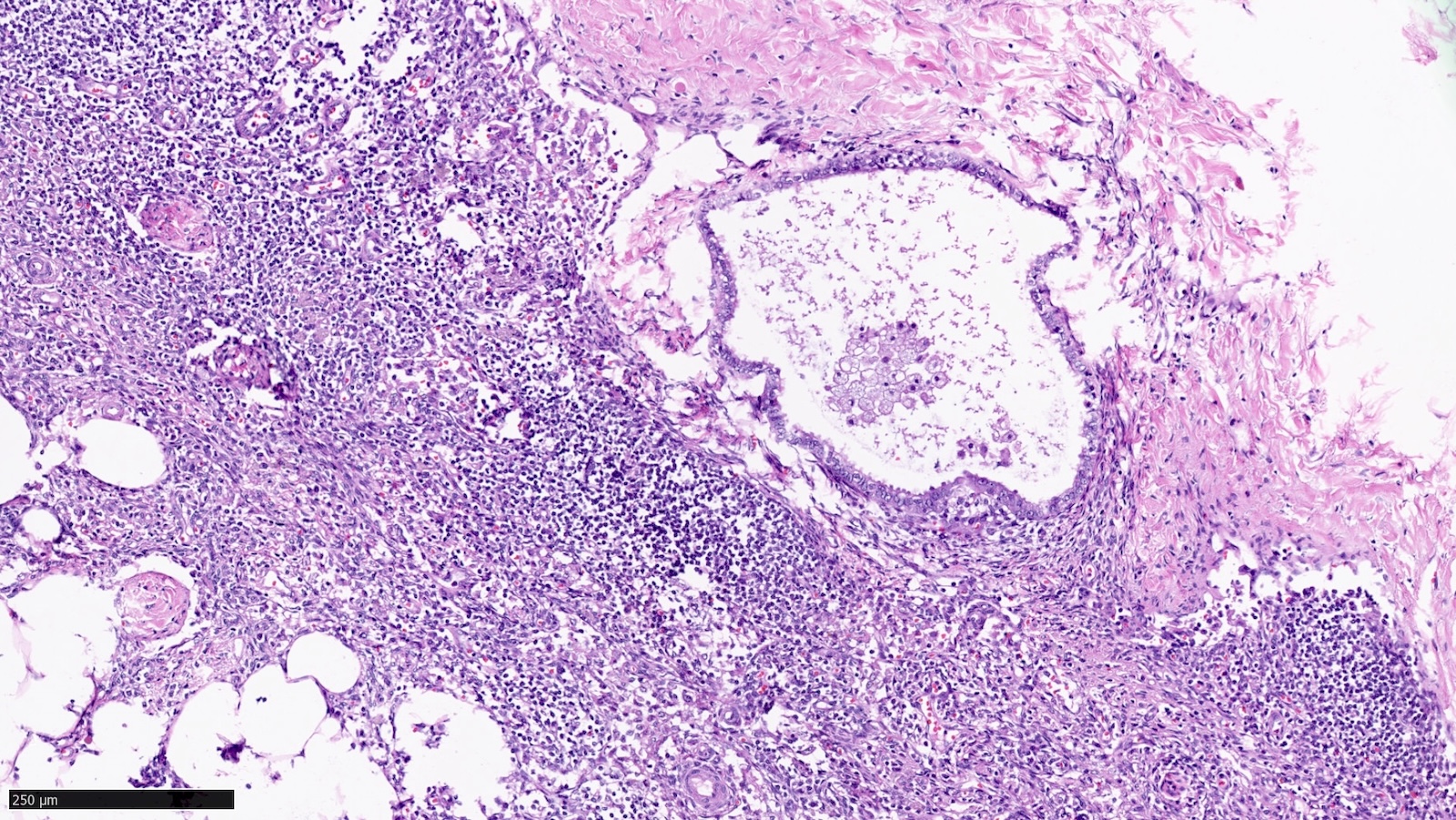
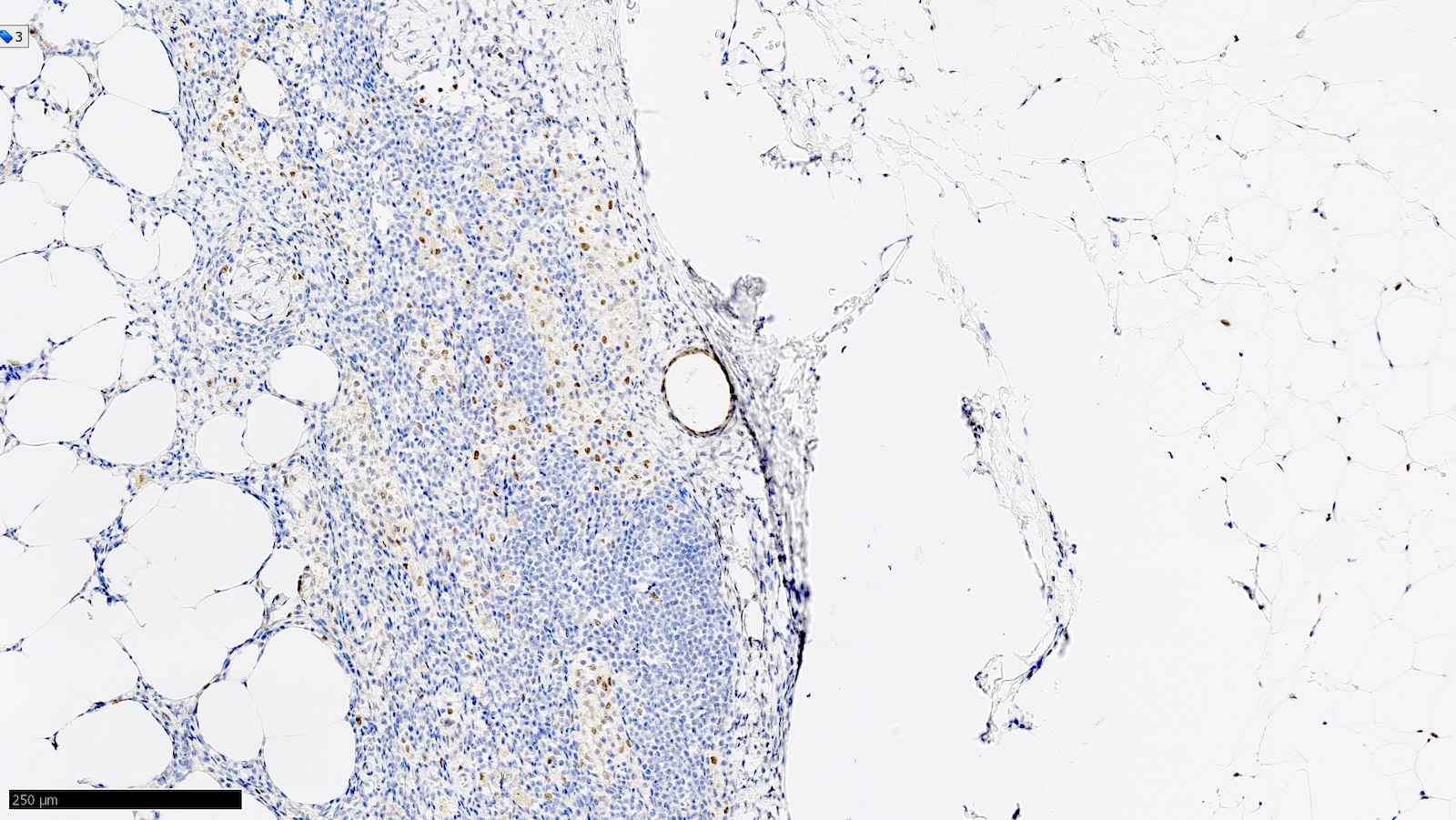
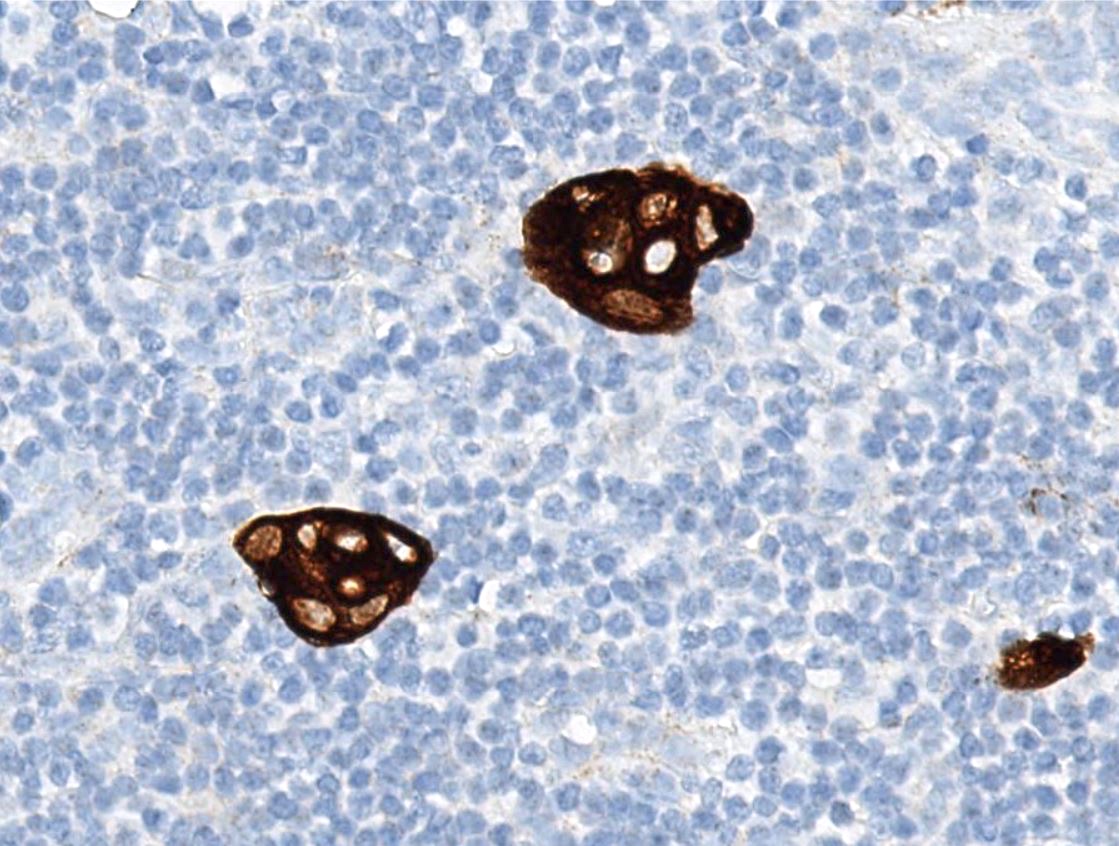
Microscopic (histologic) images
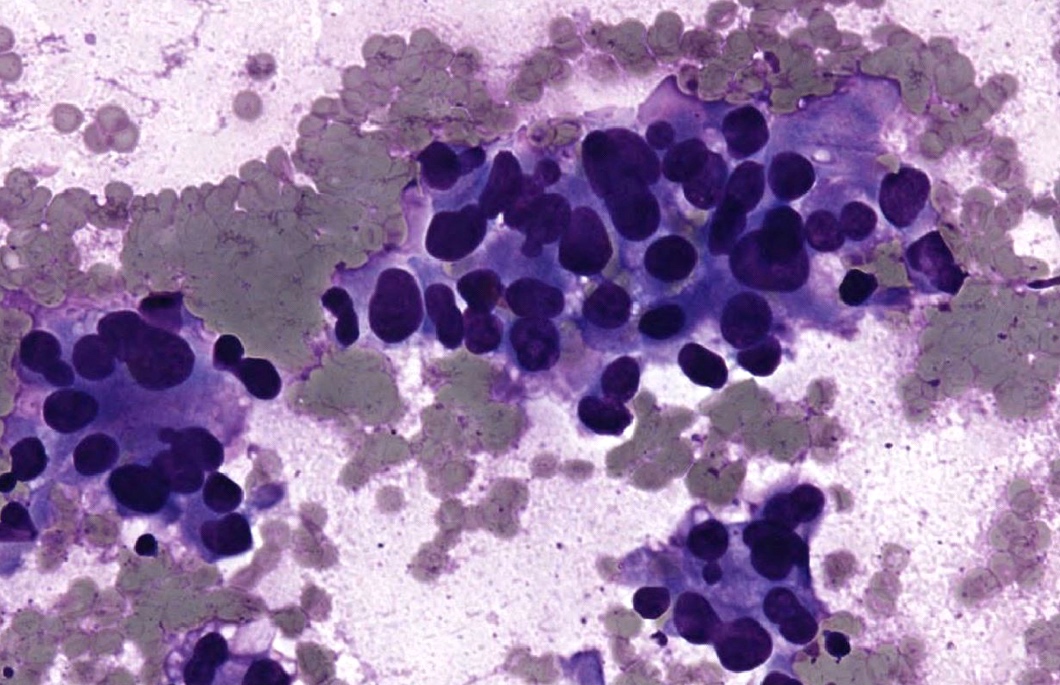
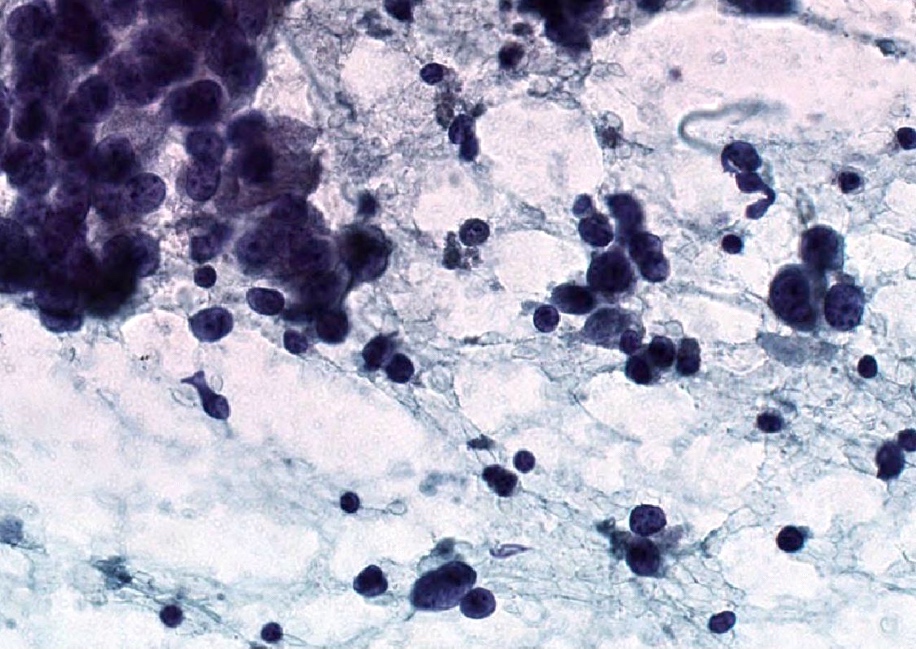
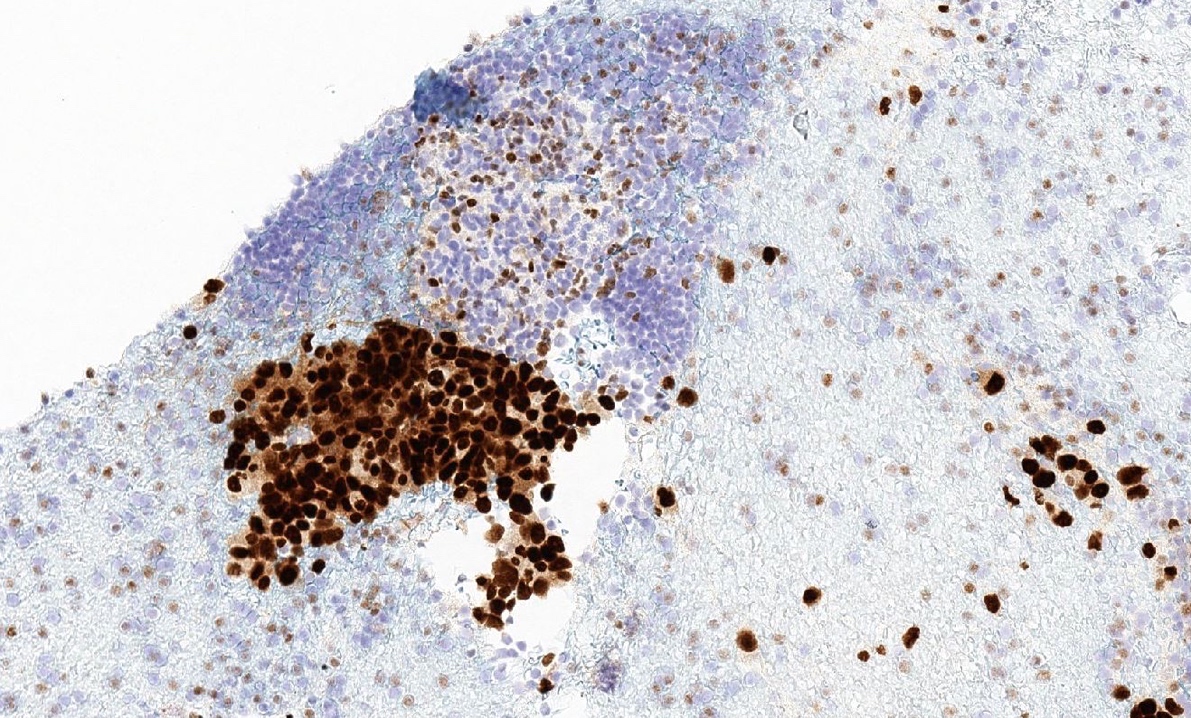
Contributed by Sucheta Srivastava, M.D., Jaya Ruth Asirvatham, M.B.B.S., Rahul Koshy, D.O. and Julie M. Jorns, M.D. (Case #548)
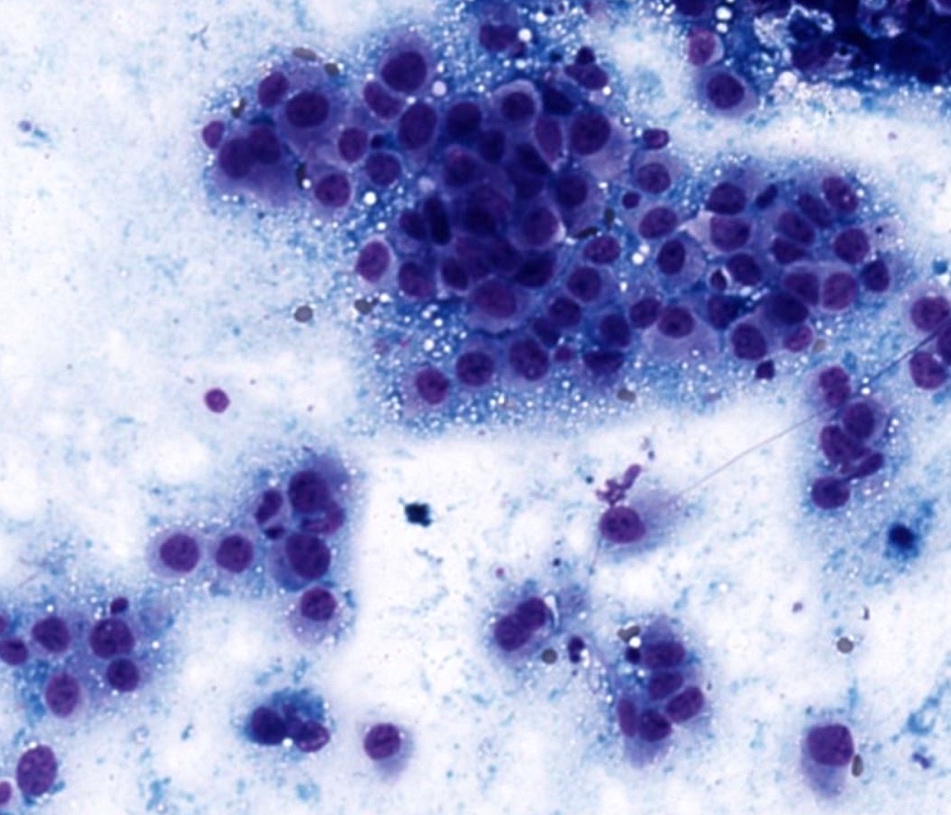
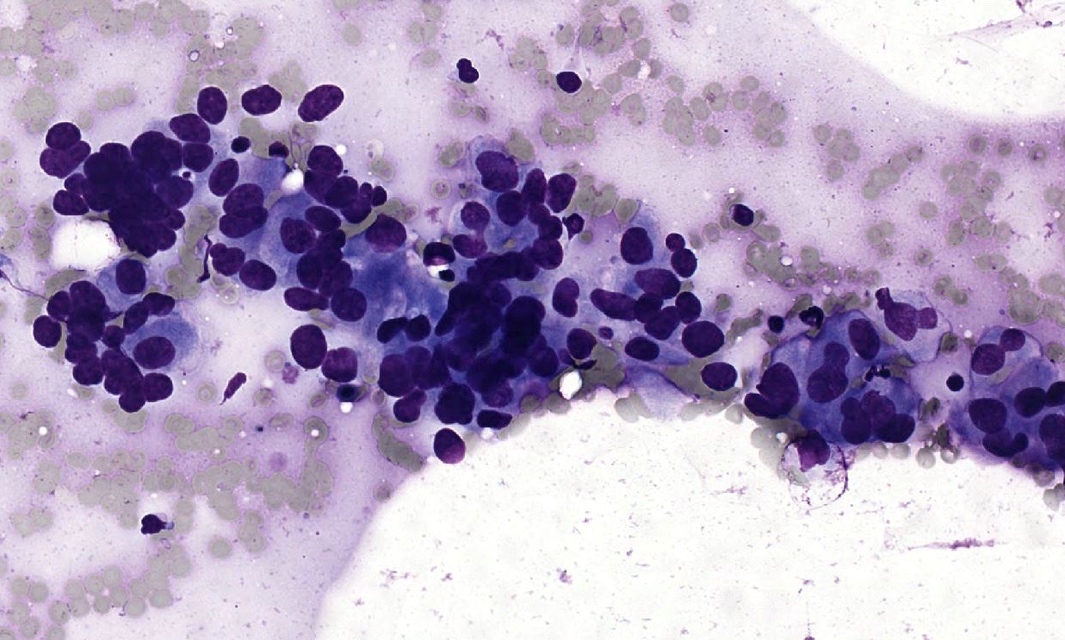
Cytology description
- Fine needle aspiration smears of positive axillary lymph node are characterized by crowded, disorganized groups of cells with enlarged nuclei, nuclear pleomorphism, irregular nuclear membranes and intracytoplasmic vacuoles with or without mucin
- Necrosis or mucin in the background and single intact malignant cells may be present
- Imprint cytology had an overall sensitivity of 63% (macrometastasis: 81%, micrometastasis: 22%) and specificity of 99% (meta analysis of 31 studies, Br J Surg 2005;92:1068)
- Factors that can affect the outcome of fine needle aspiration are size of the metastasis in the lymph node, experience of the person performing image guided fine needle aspiration and pathologist evaluation of the sample for adequacy (at the time of fine needle aspiration)
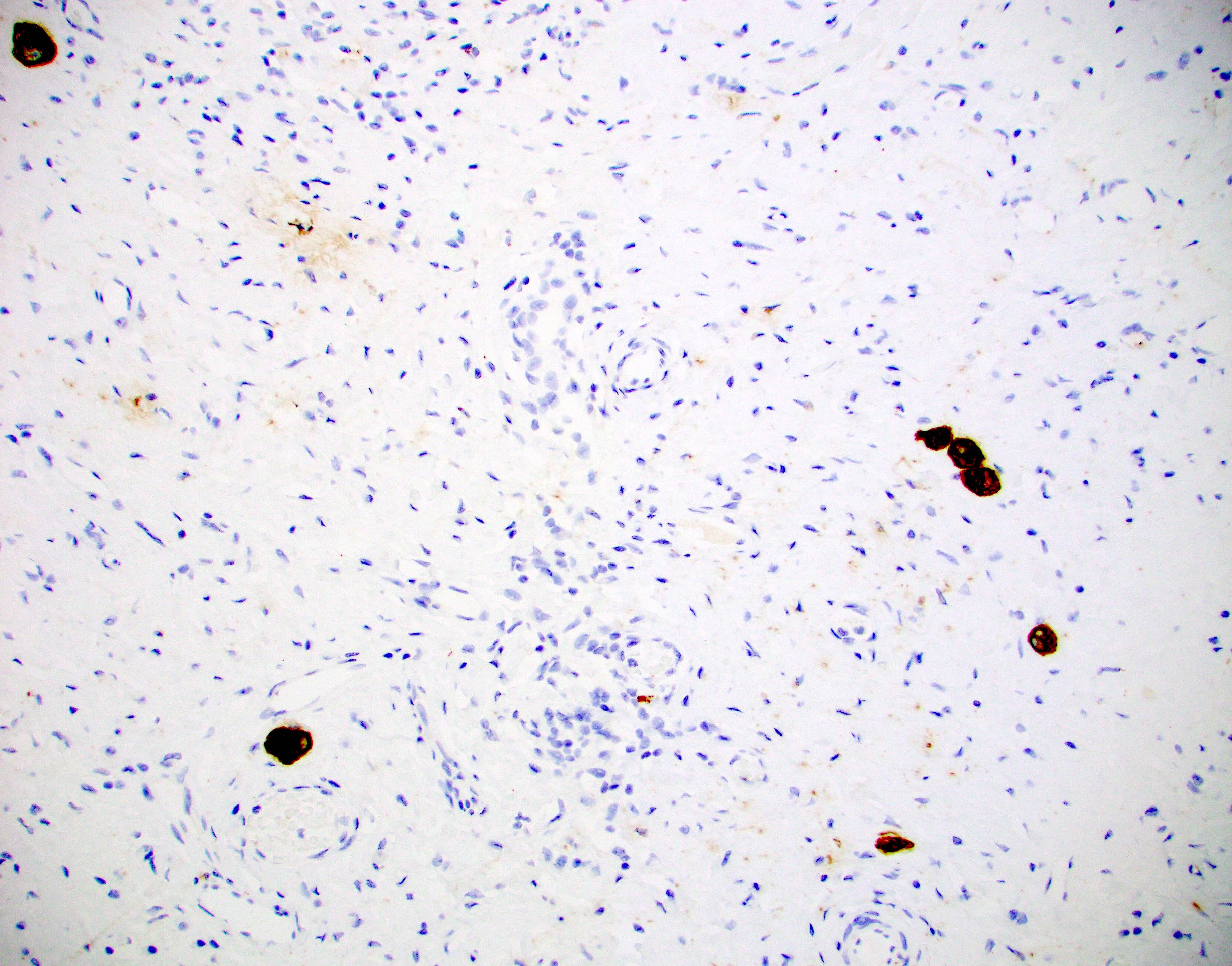
Positive stains
- Note: "enhanced methods" of SLN metastasis detection, including routine immunohistochemistry, are not recommended (i.e. should be used on a case by case basis / when necessary for diagnosis) (J Clin Oncol 2014;32:1365)
- AE1 / AE3, CK7, GATA3
- Estrogen receptor / ER (depends on biomarker status)
- Reference: Semin Diagn Pathol 2018;35:143
Negative stains
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Some studies have reported usefulness of molecular assays, usually reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) (J Clin Oncol 2008;26:3338)
- False positive and false negative results can occur with RT-PCR
- Significance of a positive RT-PCR result for a histologically negative lymph node is unknown (J Clin Oncol 2008;26:3338)
- Current AJCC cancer staging manual (8th edition) includes positive molecular findings by RT-PCR; no isolated tumor cell clusters detected as pN0 (mol+)
Sample pathology report
- Right axilla, sentinel lymph node #1, excision:
- One lymph node negative for metastatic carcinoma (0/1)
- Right axilla, sentinel lymph node #1, excision:
- One lymph node with macrometastatic carcinoma (12 mm deposit) with extranodal extension (measuring 2 mm) (1/1)
Differential diagnosis
- Benign epithelial inclusions in axillary lymph node (Int J Surg Pathol 2018;26:564, Breast J 2020;26:274):
- These inclusions can be glandular (most common) or squamous epithelium lining cystic lumina
- Glandular inclusions often have a luminal and myoepithelial cell layer
- In some cases, the glandular epithelium shows proliferative changes like usual ductal hyperplasia in the breast
- Immunoreactivity for myoepithelial cell markers (p63, calponin, SMMHC / smooth muscle myosin heavy chain, actin - alpha smooth muscle) is often demonstrable but it may be variable or absent in morphologically benign inclusions
- Endosalpingiosis of axillary lymph nodes (Case Rep Pathol 2016;2016:2856358, Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:1211, Breast J 2020;26:274):
- Müllerian type glandular inclusions lined by cytologically bland cuboid to columnar epithelial cells that are reminiscent of fallopian tube type lining or coelomic type lining
- Cilia, when present, is a reassuring feature to confirm a benign diagnosis
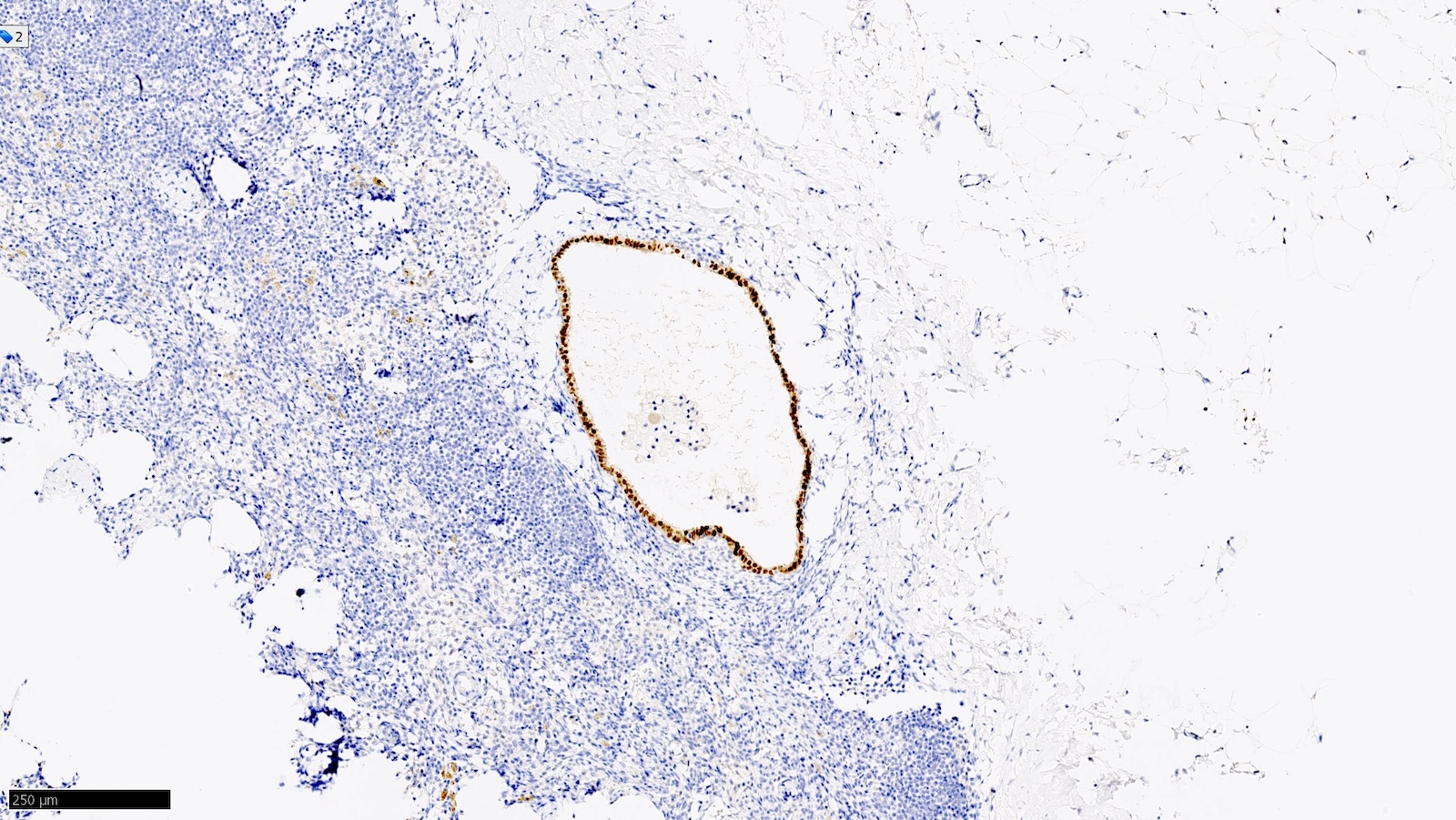
- Positive for PAX8 and WT1 (good markers of Müllerian origin) and negative for GATA3
- Nevus cell clusters:
- Positive for MelanA and HMB45
- Negative for estrogen receptor / ER, GATA3
- Nevus cells may rarely be intravascular (Breast J 2019;25:726)
Additional references
Practice question #1
Practice answer #1
A. pN0(i+): isolated tumor cell clusters (malignant cell clusters ≤ 0.2 mm)
Comment Here
Reference: Sentinel lymph nodes
Comment Here
Reference: Sentinel lymph nodes
Practice question #2
Which of the following is true for axillary sentinel lymph nodes?
- Evaluation requires grossing at 2 mm intervals and routine use of immunohistochemistry
- Isolated tumor cell clusters are clusters of cells ≤ 0.2 mm and ≤ 200 cells in a single cross section
- Most commonly, sentinel lymph node is in level II
- Only the first excised lymph node is a sentinel lymph node
Practice answer #2
B. Isolated tumor cell clusters are clusters of cells ≤ 0.2 mm and ≤ 200 cells in a single cross section
Comment Here
Reference: Sentinel lymph nodes
Comment Here
Reference: Sentinel lymph nodes
Practice question #3
Which of the following supports a diagnosis of metastatic carcinoma in sentinel lymph nodes?
- Bland nests located within lymph node capsule that are positive for MelanA
- Cell clusters within lymph node parenchyma with significant nuclear atypia
- Glands with ciliated cells that are positive for PAX8
- Glandular structures with peripheral myoepithelial cells
Practice answer #3
B. Cell clusters within lymph node parenchyma with significant nuclear atypia
Comment Here
Reference: Sentinel lymph nodes
Comment Here
Reference: Sentinel lymph nodes
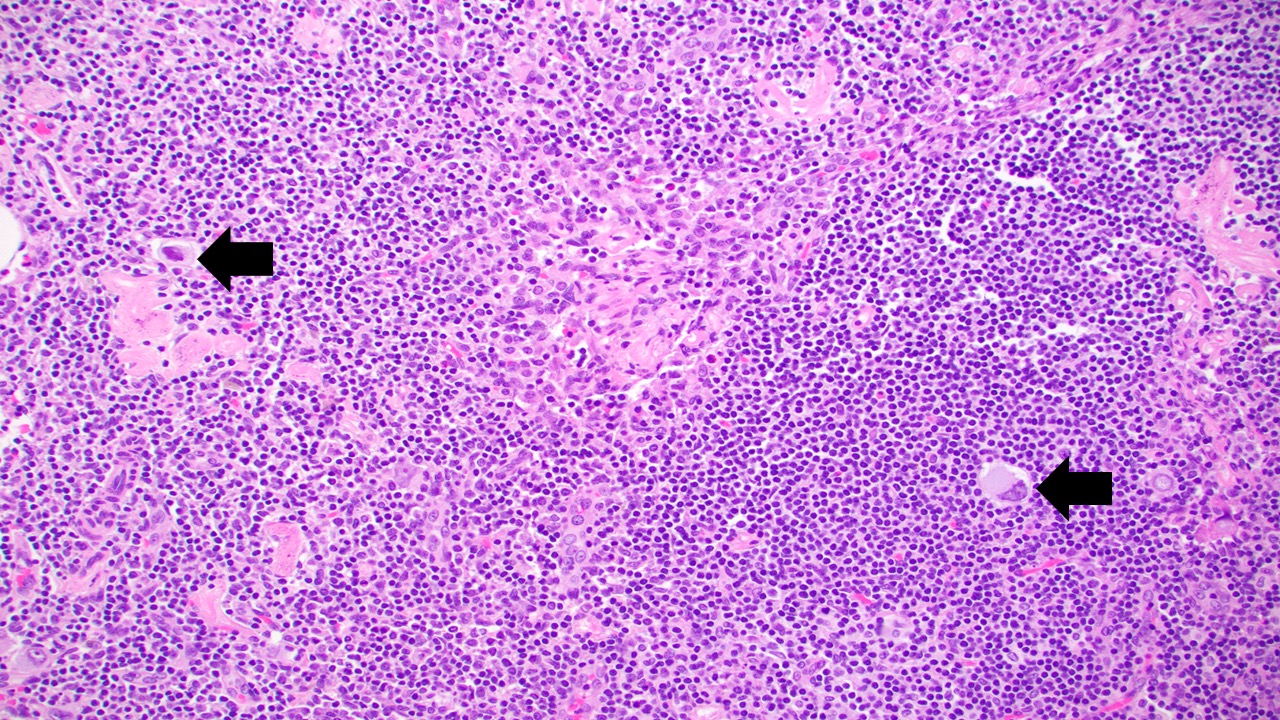
Practice question #4
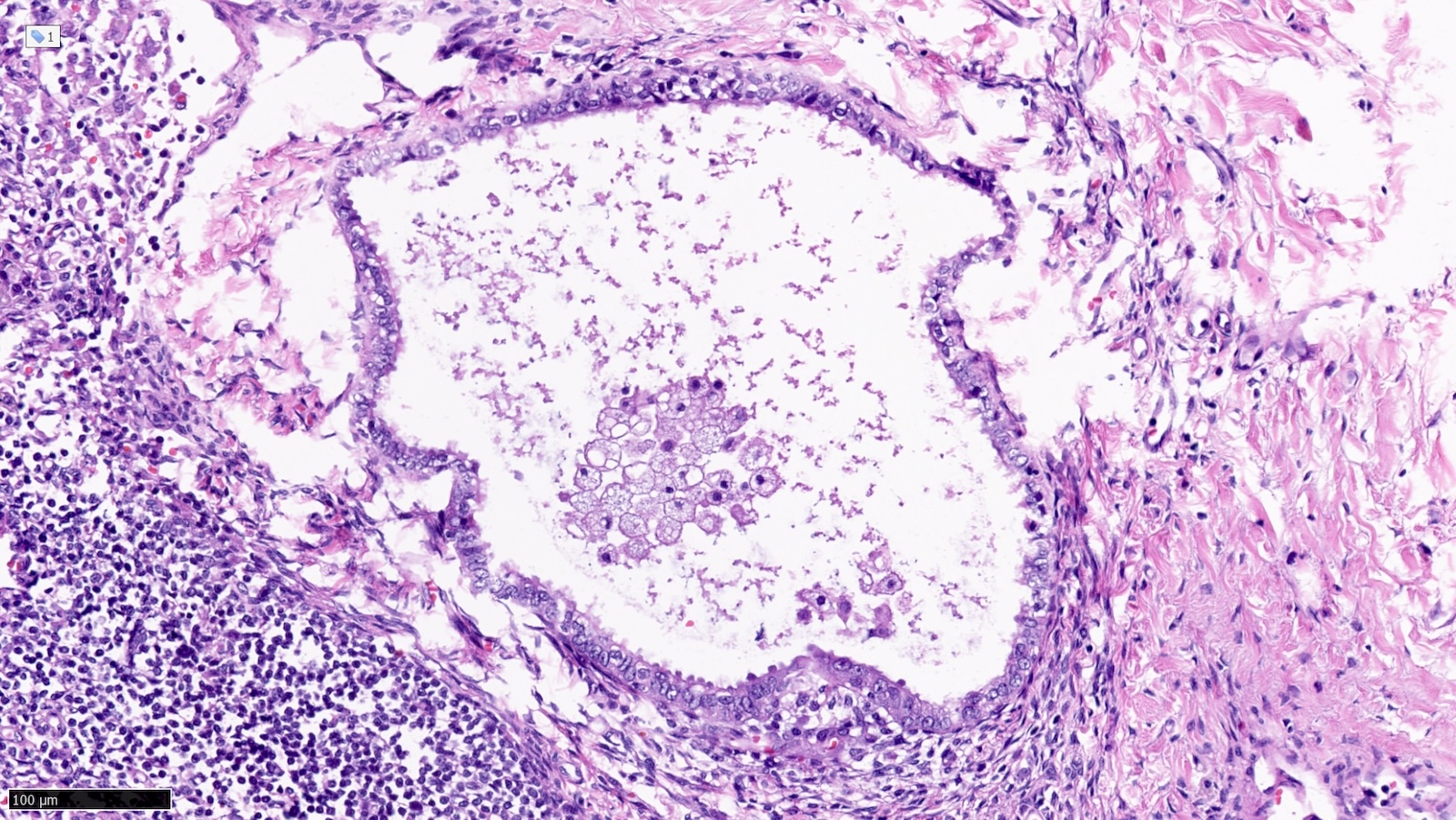
A patient with breast cancer undergoes sentinel lymph node excision. What is the next step based on the histologic findings shown above?
- Assign axillary nodal stage (AJCC 8th edition) as pN1mi(sn)
- Confirm epithelial subtype by immunohistochemistry
- Recommend axillary lymph node dissection
- Recommend nodal basin radiation therapy
Practice answer #4
B. Confirm epithelial subtype by immunohistochemistry. The histology of the glandular epithelial structure in the lymph node capsule resembles fallopian tube epithelium. PAX8 (positive) and TRPS1 (negative) immunohistochemical stains would further support Müllerian origin and the diagnosis of endosalpingiosis in an axillary sentinel lymph node. Answers A, C and D are incorrect because the patient should not be staged as pN1mi(sn) or receive additional surgery or radiation therapy to the axilla, respectively.
Comment Here
Reference: Sentinel lymph nodes
Comment Here
Reference: Sentinel lymph nodes