Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Alexiev BA. Sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissuesclerosingepithelioidfibrosarcoma.html. Accessed May 13th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma (SEF) is a rare, malignant mesenchymal tumor with unique architectural features consisting of cords, nests or sheets of monotonous epithelioid cells within a dense collagenous background (Virchows Arch 2020 Oct 21 [Epub ahead of print])
- A subset is related morphologically and molecularly to low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma (LGFMS) (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:801)
Essential features
- Rare aggressive fibroblastic neoplasm composed of cords, nests or sheets of uniform epithelioid cells embedded in a dense collagenous stroma
- Some cases show morphologic and molecular overlap with low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1444)
- MUC4 expression (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1444)
- Recurrent EWSR1-CREB3L1 gene fusions (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:801)
- A minority of cases show FUS-CREB3L2 fusions (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2015;54:28)
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- M:F = 1.3:1 with a median age of 45 years (Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19:979)
Sites
- Tumors are deep seated and arise most often in the lower extremities and limb girdles, followed by the trunk, upper limb girdles and the head and neck (Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19:979)
- Rarely, tumors arise in the kidneys, intestinal tract, mesentery and bone (Diagn Pathol 2015;10:186, Int J Surg Pathol 2020 Sep 23 [Epub ahead of print], Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2017;56:695, Virchows Arch 2020 Oct 21 [Epub ahead of print])
Pathophysiology
- Most cases are driven by fusion genes (see Molecular description)
Etiology
- Tumors appear to be sporadic and of unknown etiology
Clinical features
- Most patients present with a mass of variable duration, with 33% reporting recent enlargement or pain (Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19:979)
Diagnosis
- Tissue sampling is the gold standard for a definitive diagnosis
- MUC4 expression (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1444)
- EWSR1-CREB3L1 gene fusions (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:801)
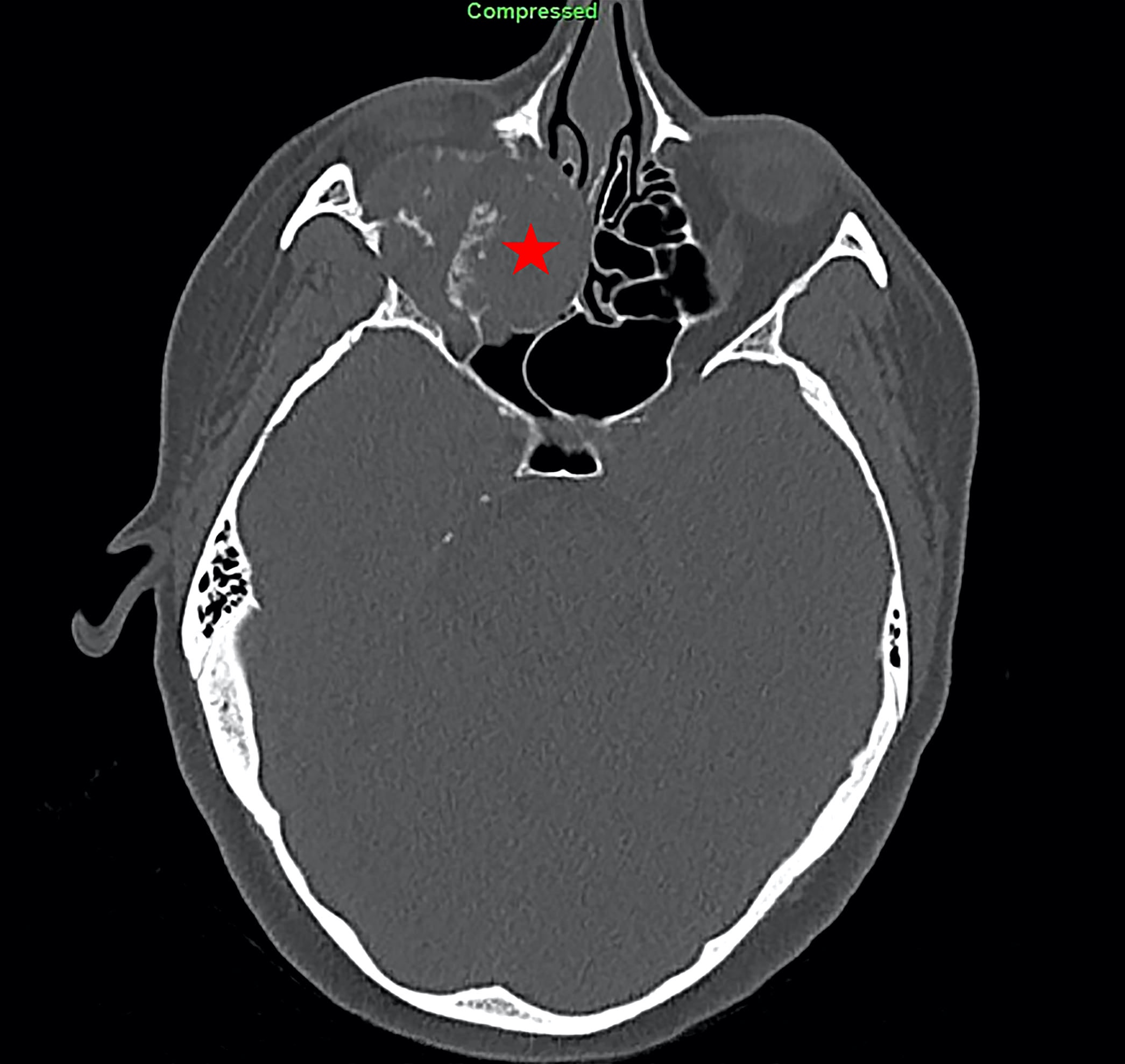
Radiology description
- Zonal architecture on MRI, with a central core of very low signal intensity and a peripheral rim of intermediate to high signal intensity on T1 and T2 weighted images (Skeletal Radiol 1997;26:619, Virchows Arch 2015;467:339)
- Radiographs of bone tumor show osteolytic lesion associated with destruction of the cortex and soft tissue extension (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2020;59:217)
- Positron emission tomography (PET) show increased uptake (Virchows Arch 2015;467:339)
Prognostic factors
- Distinct sarcoma that behaves more aggressively than low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma with a shorter survival, higher metastatic rate and greater propensity to involve deep soft tissue and bone (Am J Surg Pathol 2020 Aug 4 [Epub ahead of print])
- Poor prognostic features include proximal location and large tumor size (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:699, Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19:979)
- Recurrences and metastases, mainly to lung and bone, are common, occurring in about 50% of cases (Am J Surg Pathol 2020 Aug 4 [Epub ahead of print])
Case reports
- 16 year old girl and 57 year old woman with renal mass (Diagn Pathol 2015;10:186)
- 18 year old man with intraabdominal tumor (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2017;56:695)
- 35 year old woman with gastric mass (Int J Surg Pathol 2020 Sep 23 [Epub ahead of print])
- 55 year old woman with right mandible mass (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:594)
- 55 year old woman with a mass in the soft tissue of the thigh (Wien Med Wochenschr 2017;167:120)
Treatment
- Radical resection for localized disease (Med Oncol 2018;35:138)
- Pre or postoperative radiotherapy for optimal local disease control (Med Oncol 2018;35:138)
- Limited responsiveness to conventional chemotherapy (Med Oncol 2018;35:138)
- Recurrent genomic alterations (CD24 and DMD) constitute potential therapeutic targets (Clin Cancer Res 2017;23:7426)
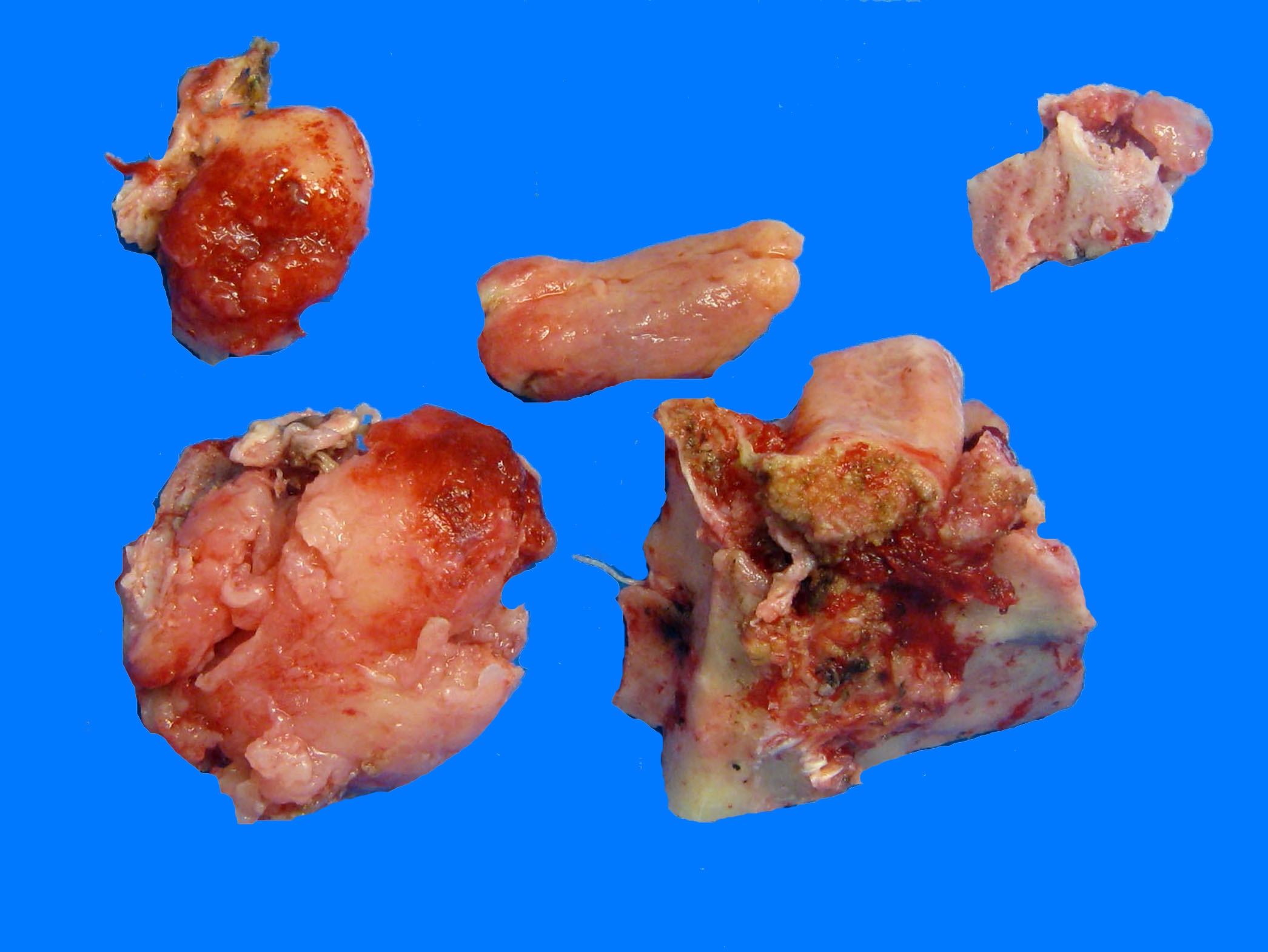
Gross description
- Most lesions are grossly circumscribed (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:699)
- Cut surface is typically homogeneously white or white-tan, lobulated and very hard (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:699, Virchows Arch 2020 Oct 21 [Epub ahead of print])
Frozen section description
- Cords, nests or sheets of monotonous epithelioid cells within a dense collagenous background (Virchows Arch 2020 Oct 21 [Epub ahead of print])
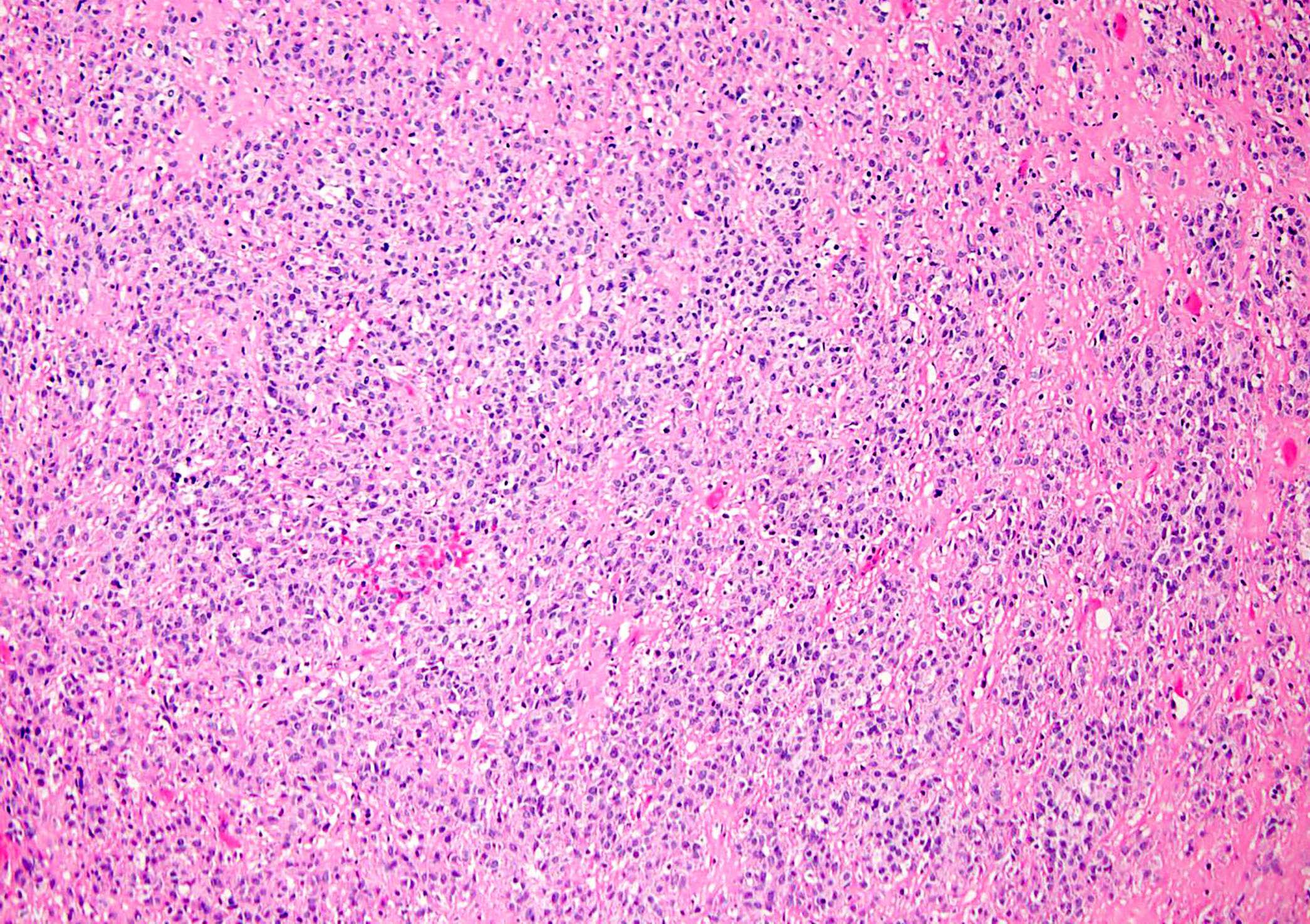
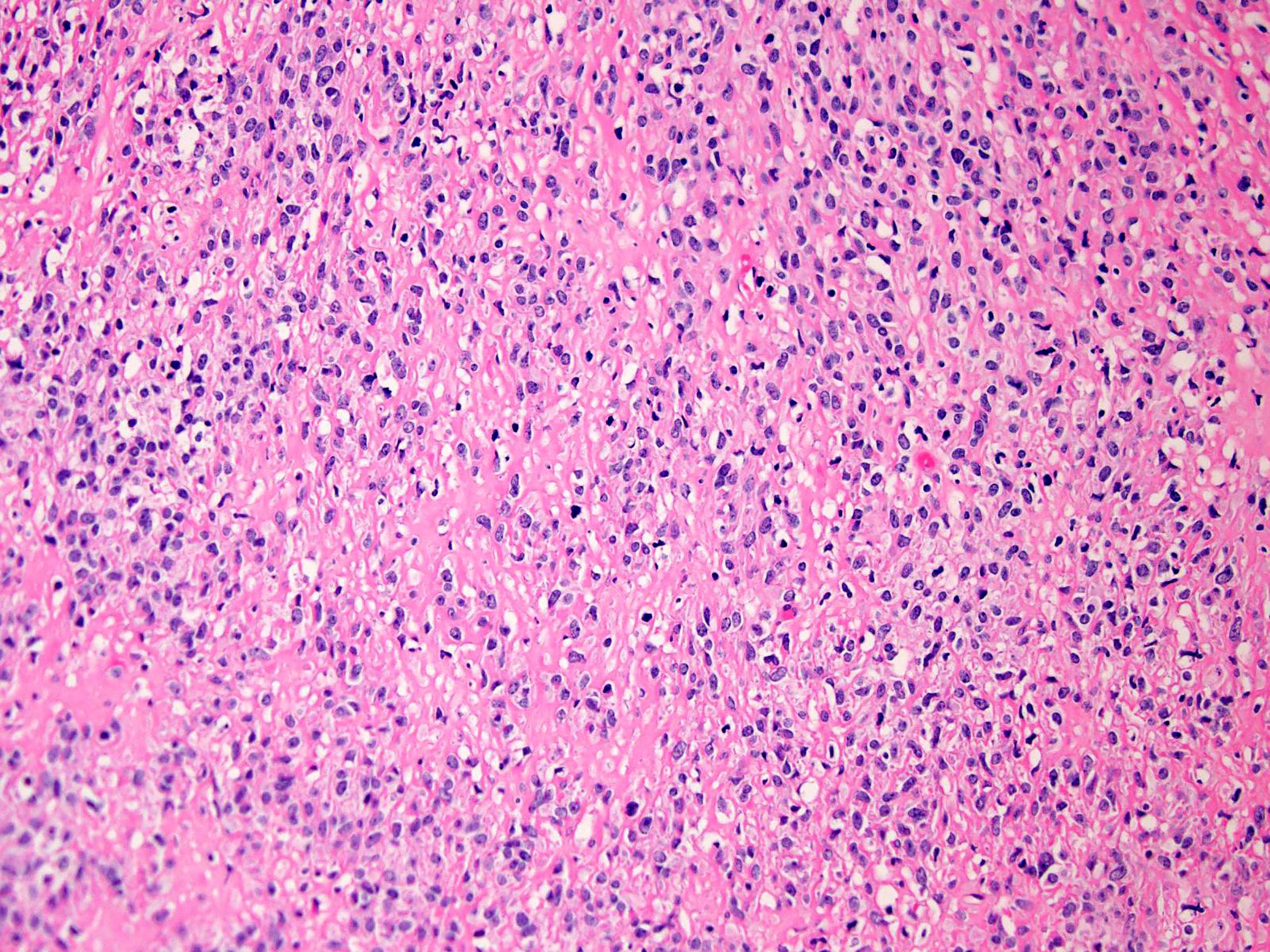
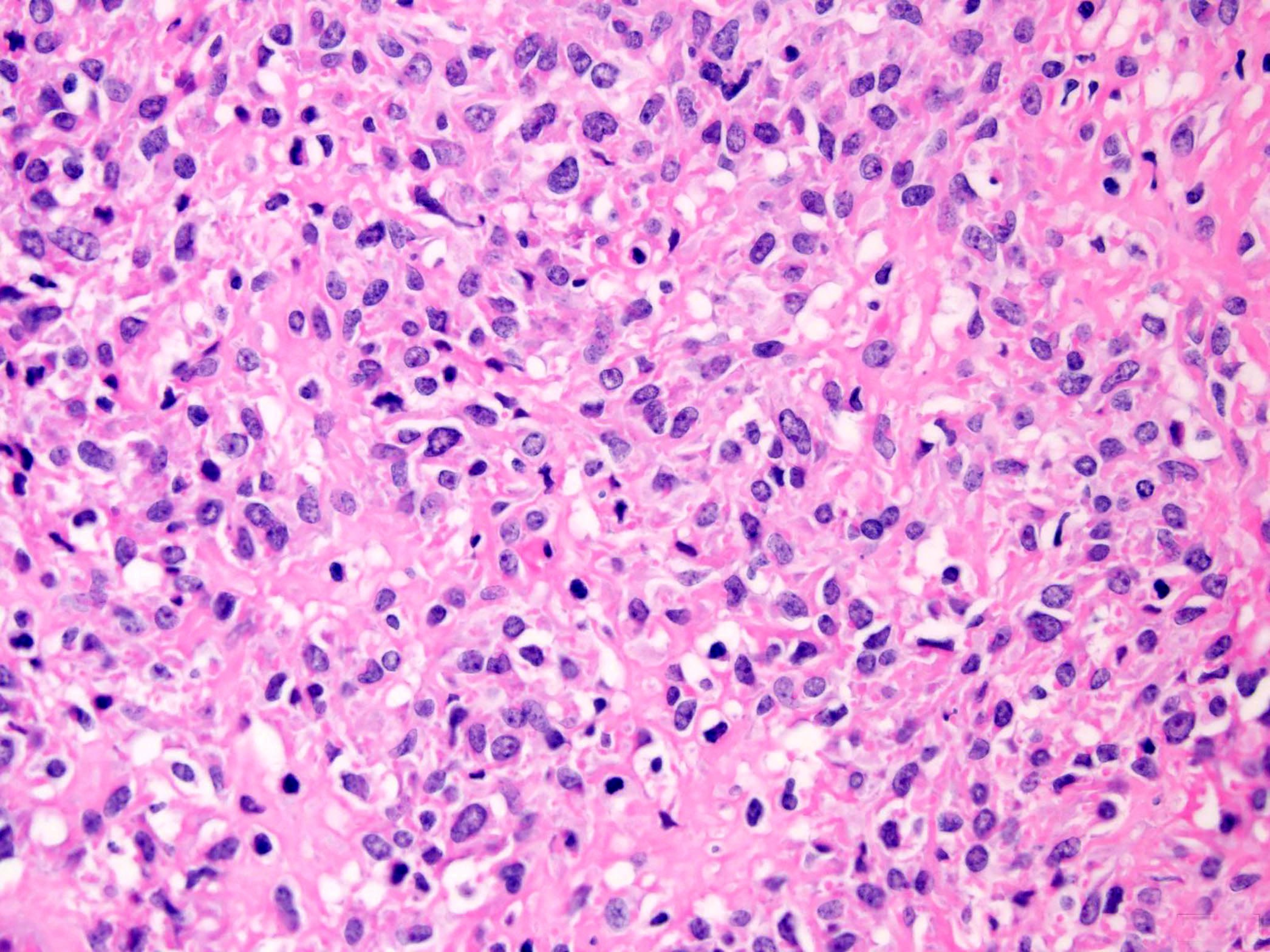
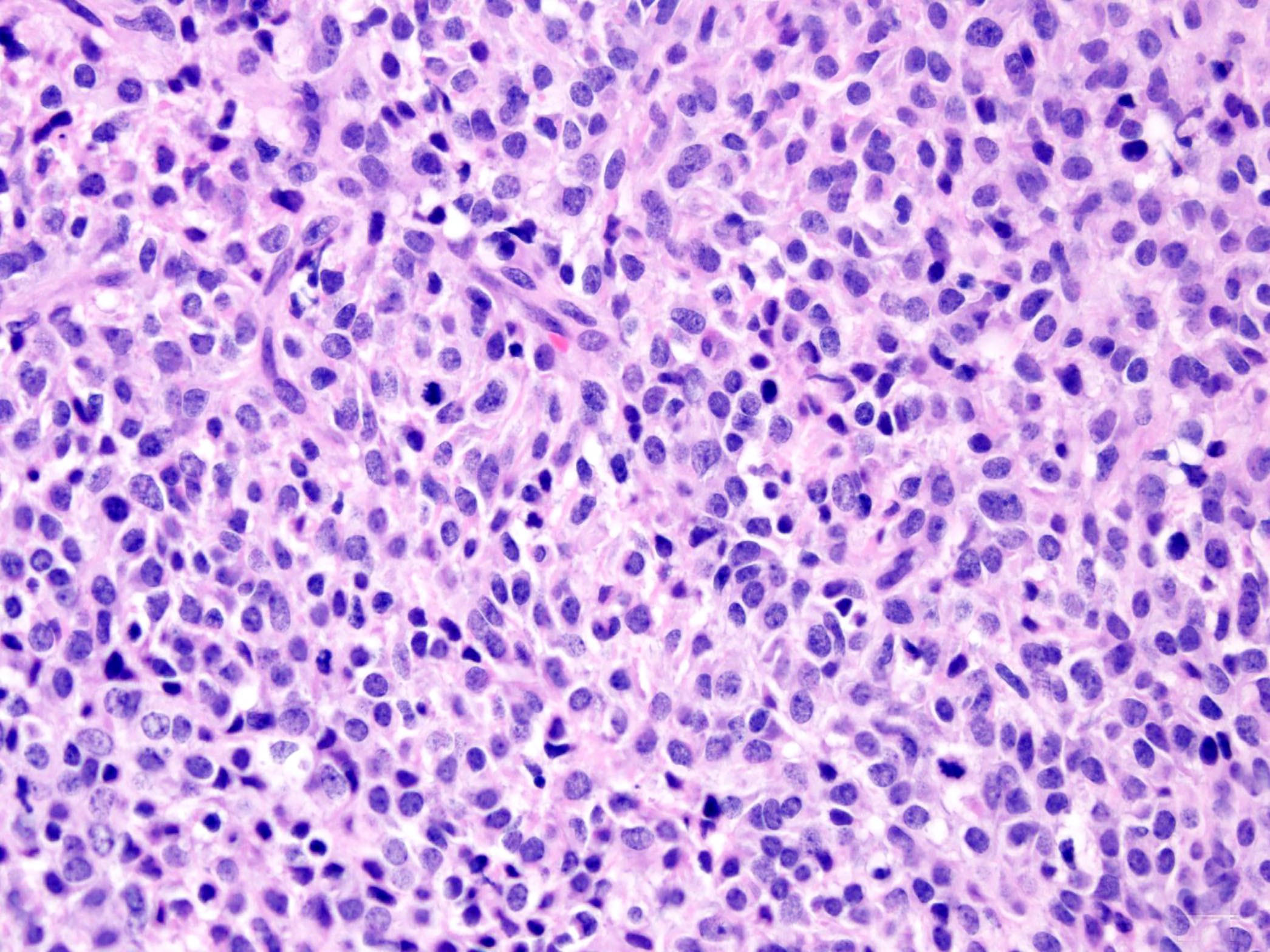
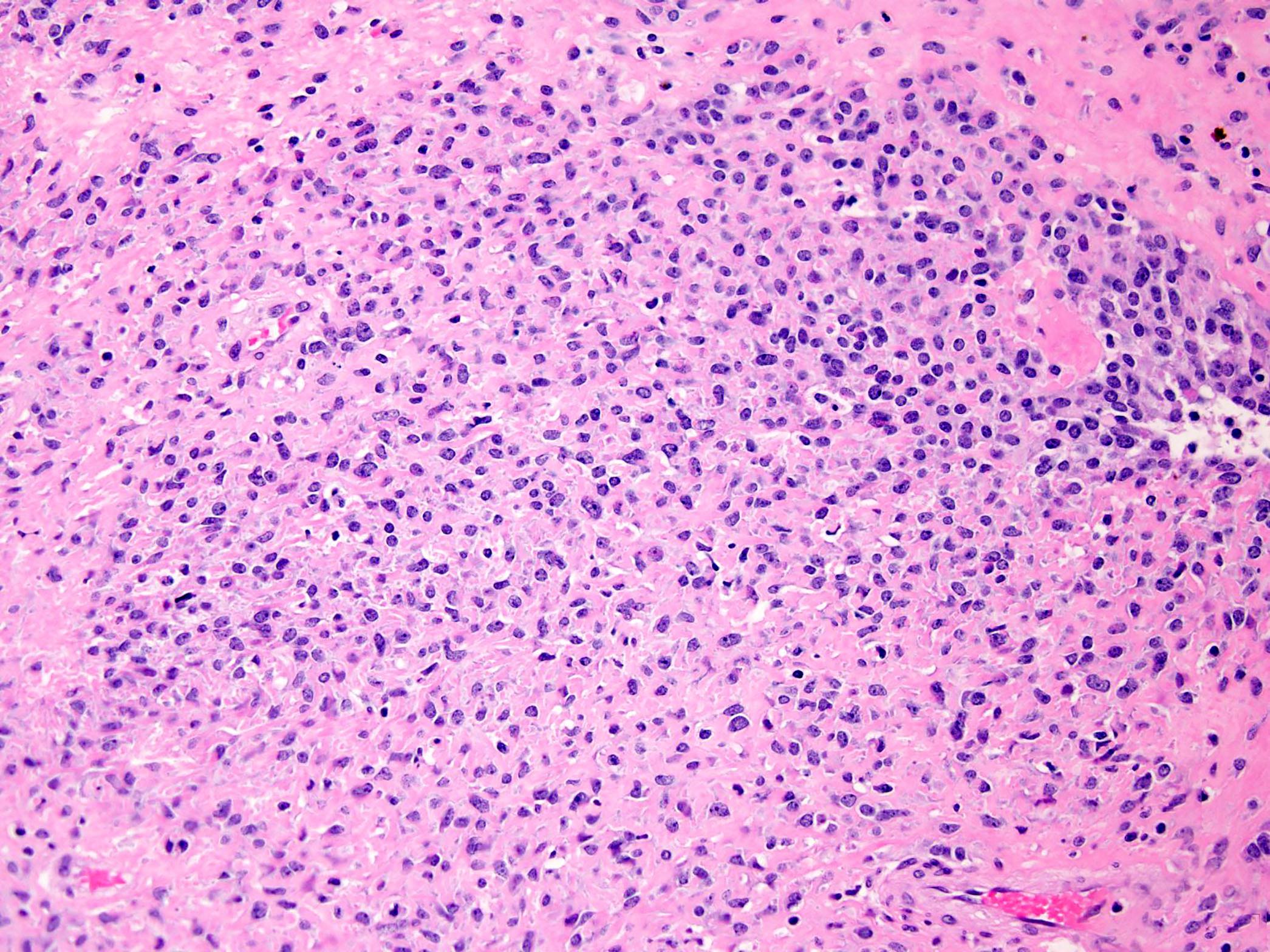
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Proliferation of uniform, small, round to ovoid epithelioid cells with sparse, often clear cytoplasm and round to oval nuclei with inconspicuous nucleoli (Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19:979, Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2020;59:217)
- Tumor cells are arranged in nests, cords or sheets (Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19:979, Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2020;59:217)
- Areas with pseudoalveolar pattern may be present
- Prominent hyalinized sclerotic collagenous stroma, sometimes reminiscent of osteoid or cartilage (Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19:979, Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2020;59:217)
- Occasional myxoid zones with cyst formation and foci of hyaline cartilage, calcification and metaplastic bone (Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19:979)
- Focal ectatic staghorn vasculature
- Mitotic figures are generally scarce (Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19:979)
- Necrosis is uncommon
- Variant morphology:
- Complete absence of the defining collagen (nonfibrosing variant) (Histopathology 2016;68:760)
- Areas of increased cellularity, reminiscent of a round to undifferentiated neoplasm (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2020;59:217)
- Fibroma-like and conventional fibrosarcoma-like areas (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:699)
- Low grade fibromixoid sarcoma-like areas (so called hybrid LGFMS / SEF) (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1444, Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:801, Pediatr Dev Pathol 2018;21:574)
- Tumor cells with eccentric nuclei and eosinophilic cytoplasm (plasma cell-like) (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2020;59:217)
- Foci of increased nuclear pleomorphism and atypia
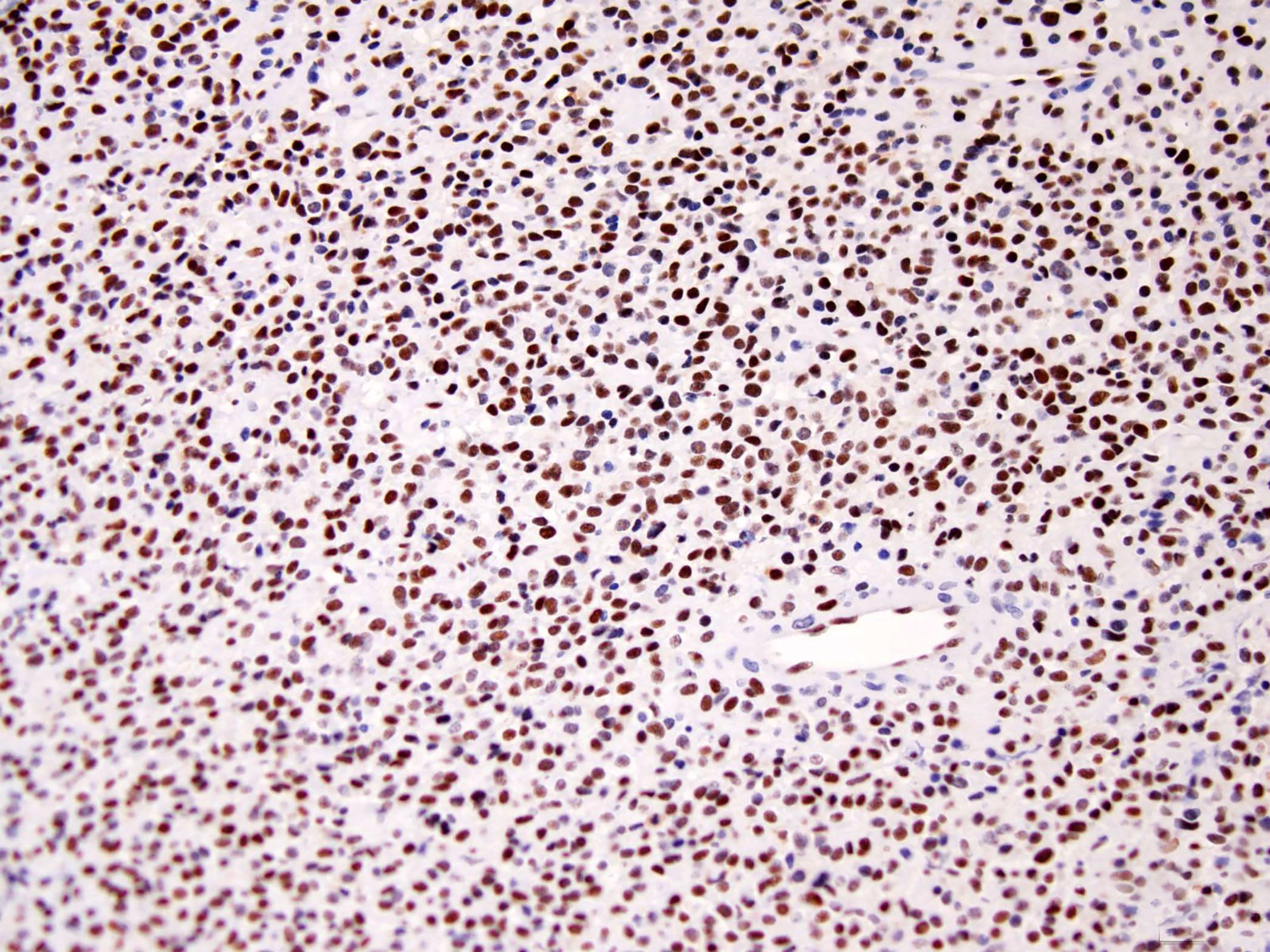
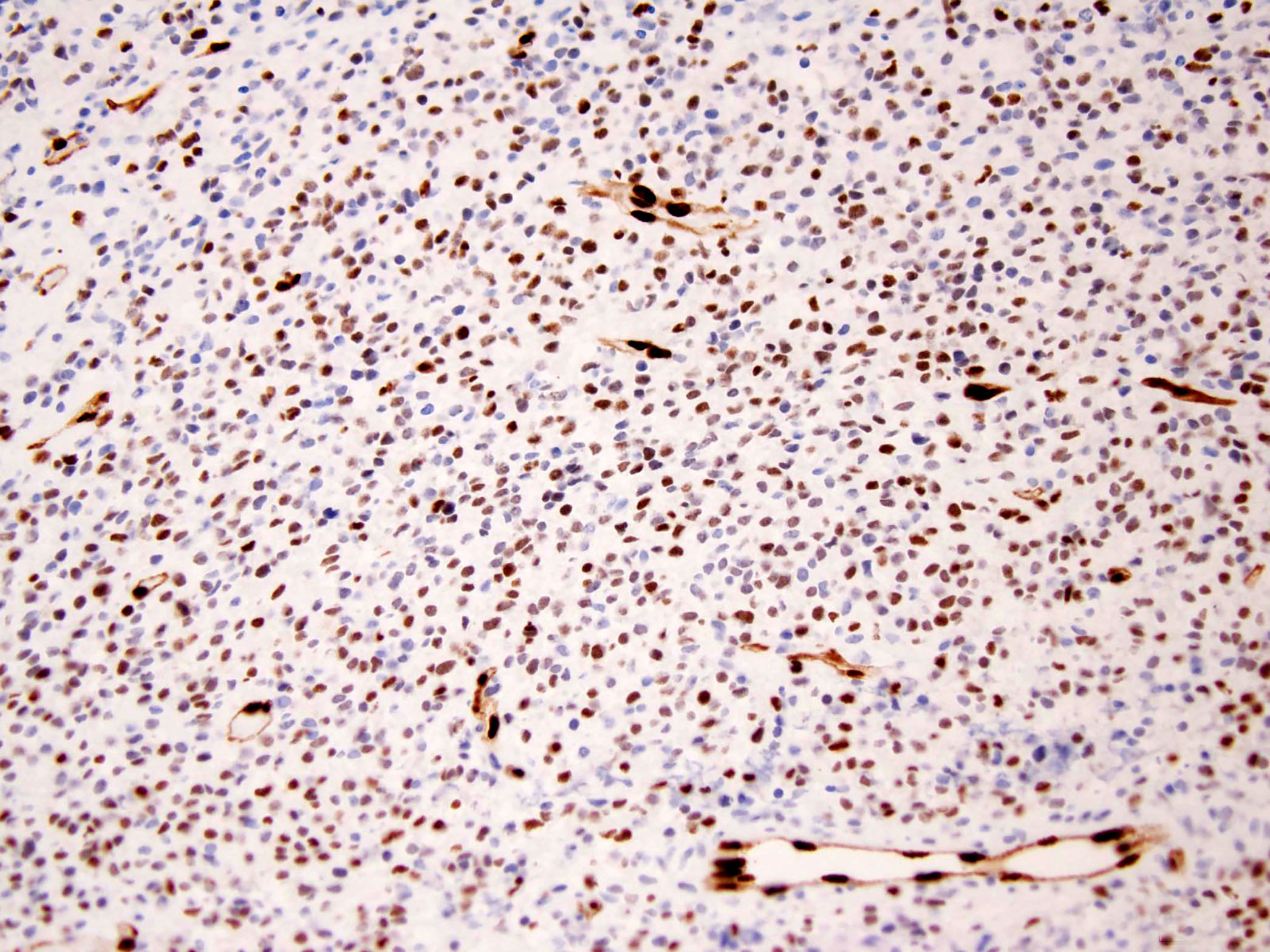
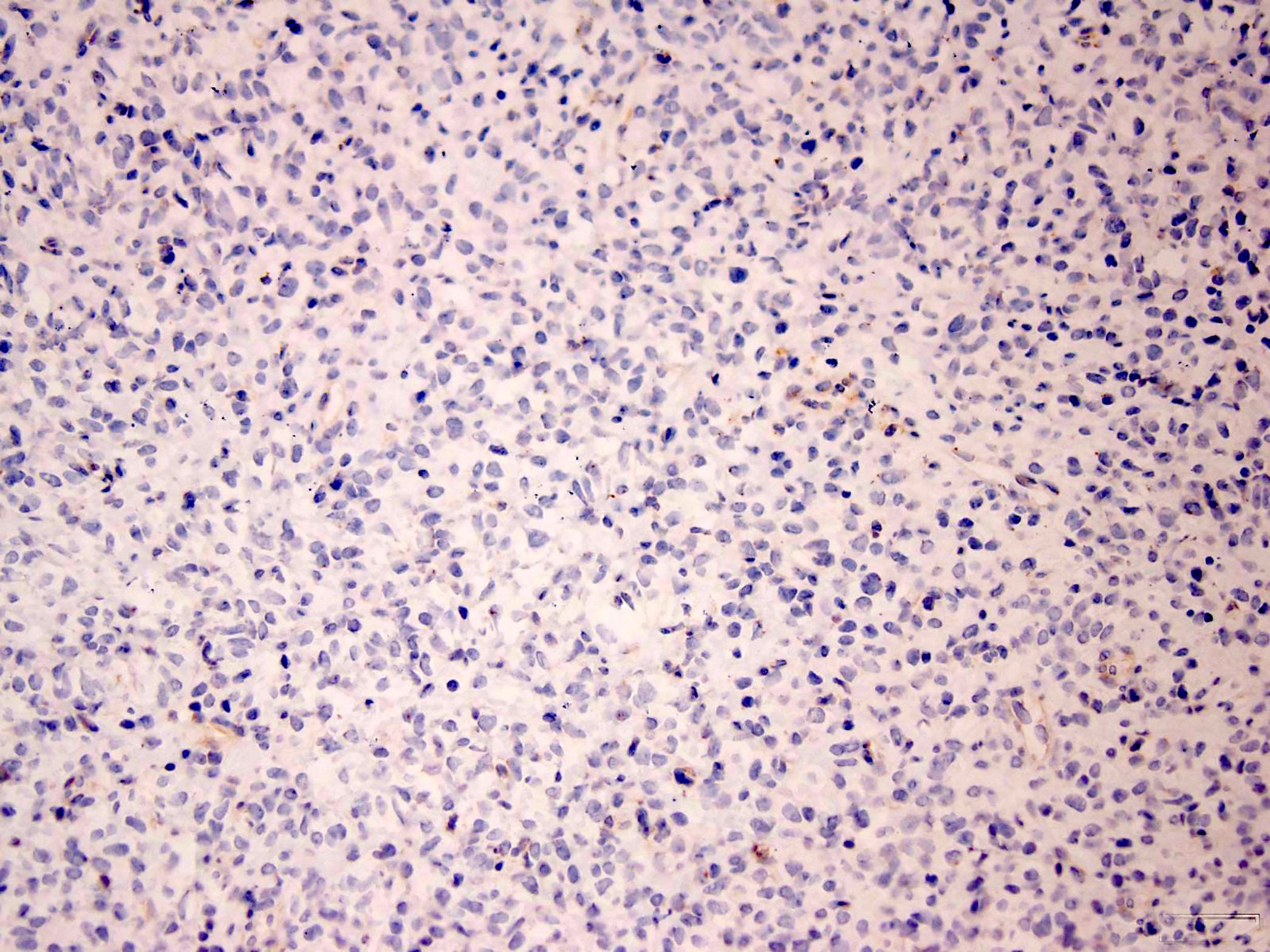
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Diagnosis based solely upon cytologic features remains challenging (J Am Soc Cytopathol 2020;9:513)
- Tumor cells range from small round, medium sized ovoid / short spindle, to epithelioid / plasmacytoid cells
- Sclerotic, fibrous to myxoid stroma
- Cellular variants can mimic plasmacytoma / myeloma and myoepithelioma (Int J Surg Case Rep 2020;68:228)
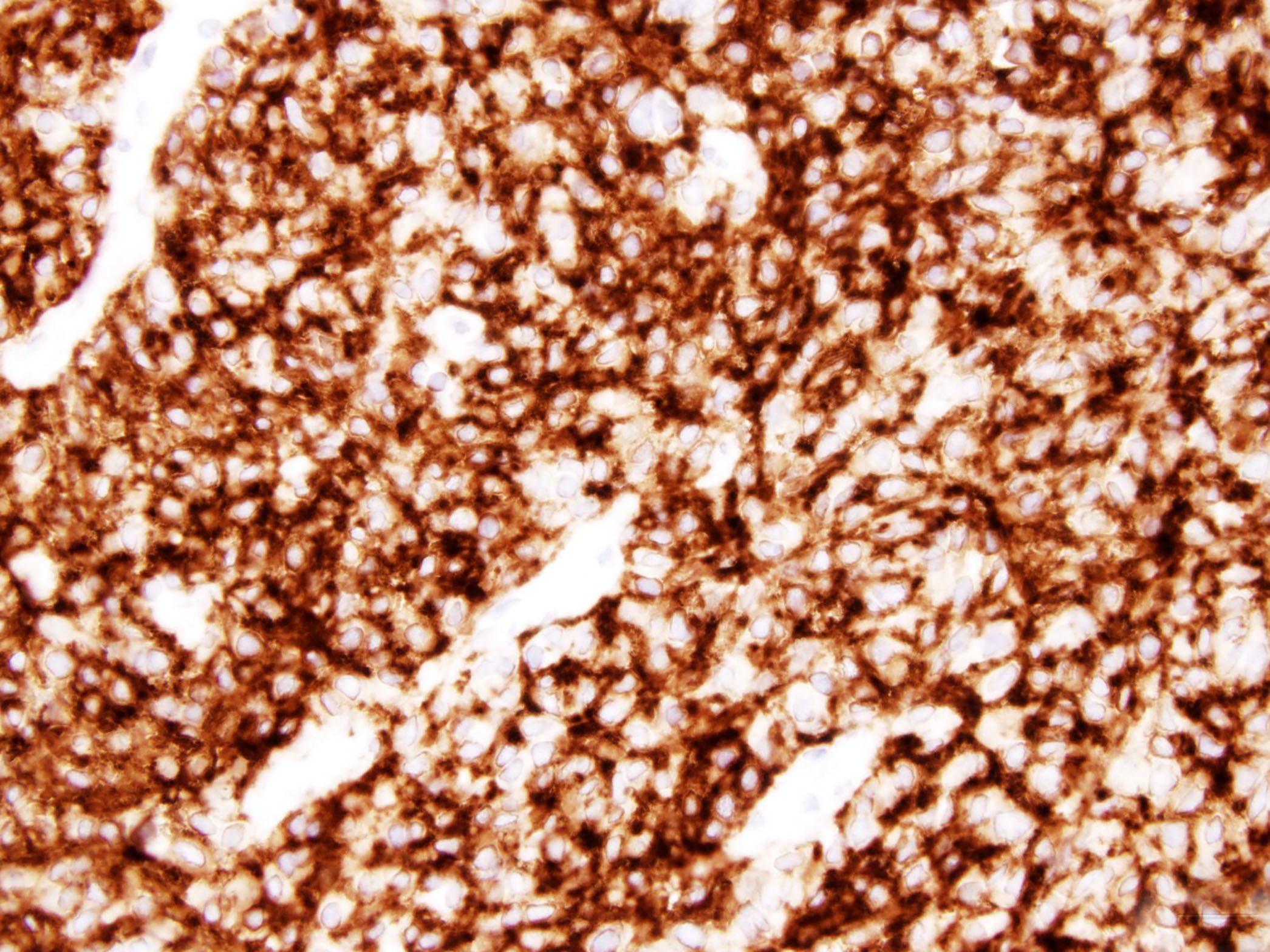
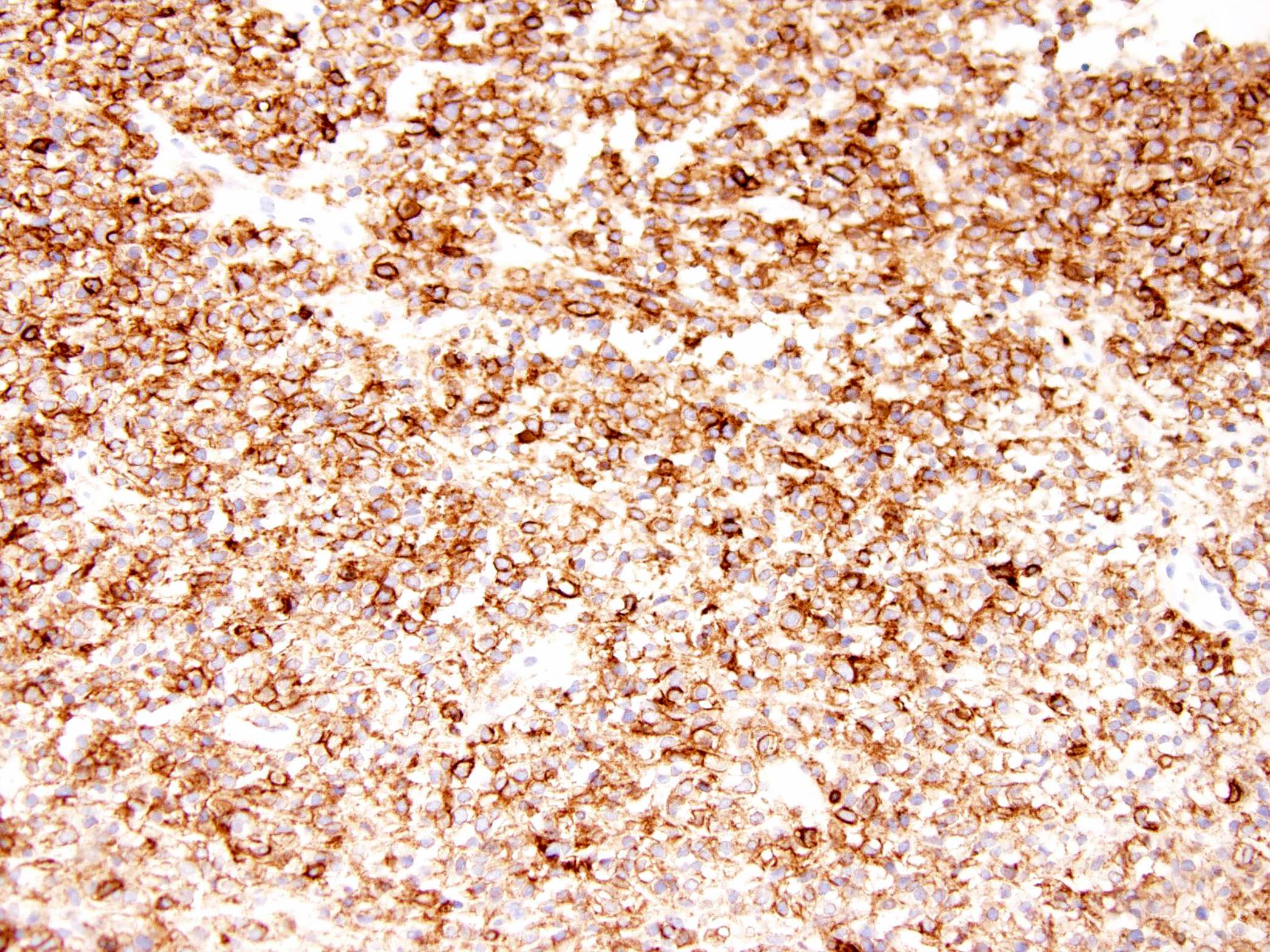
Positive stains
- MUC4 (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1444)
- Vimentin (Diagn Pathol 2015;10:186)
- BCL2 (Diagn Pathol 2015;10:186)
- CD99 in 50% of cases (Diagn Pathol 2015;10:186)
- EMA (focal and weak) (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:699)
- CD56, ERG and FLI1 in SEF with EWSR1-CREB3L1 fusion (personal communication)
Negative stains
- Keratins (AE1 / AE3, CAM5.2) (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:699)
- SATB2, see comment (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2020;59:217)
- S100 (Diagn Pathol 2015;10:186)
- CD34 (Diagn Pathol 2015;10:186, Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:699)
- Desmin (Diagn Pathol 2015;10:186)
- SMA (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:699)
- Comment: A recent study demonstrated SATB2 expression in primary SEF of bone (5/8 cases) (Virchows Arch 2020 Oct 21 [Epub ahead of print])
Electron microscopy description
- Features of fibroblasts, with an abundant, rough endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria and a well developed Golgi apparatus with dense bodies and collagen secretion granules (Pathol Int 2002;52:135, Histopathology 1998;33:354)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Predominantly EWSR1-CREB3L1 fusion and complex secondary genomic alterations (Am J Surg Pathol 2020 Aug 4 [Epub ahead of print])
- A subset of SEF with composite histologic features of SEF and low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma (hybrid tumors) is more likely to harbor the FUS-CREB3L2 fusion, which is also seen in most low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:594)
- Recurrent YAP1 and KMT2A gene rearrangements in a subset of MUC4 negative, EWSR1 / FUS fusion negative SEF (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:594, Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:368)
- Rare cases with FUS-CREM fusion (Int J Surg Pathol 2020 Sep 23 [Epub ahead of print])
Sample pathology report
- Right maxillary mass, biopsy:
- Sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma (see comment)
- Comment: The neoplasm is composed of cords and strands of uniform epithelioid cells with scant pale cytoplasm and round to oval nuclei in a dense sclerotic stroma. Occasional mitotic figures are identified (2 mitoses/10 high power fields). Immunohistochemical stains for MUC4, CD56, FLI1, ERG and EMA (focal) are positive in tumor cells while all of the following are negative: pankeratin AE1 / AE3, S100, CD34, SMA, desmin and p63. SMARCB1 / INI1 expression is preserved. Next generation sequencing is positive for EWSR1-CREB3L1 fusion. The findings support the above diagnosis. Sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma behaves more aggressively than the related low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma with a shorter survival, higher metastatic rate and greater propensity to involve deep soft tissue and bone. Recurrences and metastases, mainly to lung and bone, are common, occurring in about 50% of cases.
Differential diagnosis
- Low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma (LGFMS):
- May contain areas resembling SEF, either in the primary tumor (so called hybrid LGFMS / SEF) or in recurrences
- Classic admixture of hypocellular fibrous zones and cellular myxoid areas (Head Neck Pathol 2016;10:161)
- Majority of cases characterized by t(7;16)(q33;p11) resulting in FUS-CREB3L2 fusion (Ann Diagn Pathol 2017;28:60)
- Ossifying fibromyxoid tumor (OFMT):
- Most cases show a peripheral shell of lamellar bone (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2014;53:183)
- CD10 expression (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:996)
- S100 expression (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:996, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1751)
- Desmin expression in 70% of cases (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2014;53:183)
- PHF1 gene rearrangement in 80% of cases, including benign, atypical and malignant subtypes, with fusion to EP400 in 44% of cases (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2016;140:371, Hum Pathol 2013;44:2603)
- ZC3H7B-BCOR and MEAF6-PHF1 fusions occur predominantly in S100 negative and malignant OFMT (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2014;53:183)
- Metastatic carcinoma:
- Cord, nests and chains of small to medium sized epithelial cells in some breast and gastric carcinomas
- Densely sclerotic stroma uncommon
- Clinical evidence of primary tumor
- Strong keratin expression (AE1 / AE3, OSCAR, CAM 5.2) (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2020)
- No EWSR1 and CREB3L1 rearrangements
- Sclerosing rhabdomyosarcoma:
- Occasional rhabdomyoblasts
- Strong MyoD1 expression (Surg Pathol Clin 2020;13:729, Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2014;53:779)
- Variable desmin and myogenin expression (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2014;53:779)
- Negative for MUC4
- MyoD1 mutations (Surg Pathol Clin 2020;13:729, Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2014;53:779)
- No EWSR1 and CREB3L1 rearrangements
- Osteosarcoma:
- Identification of malignant osteoid matrix formation and the integration of clinical and radiological data remain the cornerstone of osteosarcoma diagnosis (Pathol Res Pract 2016;212:811)
- Significant nuclear atypia
- Mitoses common and often abnormal
- SATB2 expression in > 90% of osteosarcomas (Pathol Res Pract 2016;212:811)
- However, a recent study demonstrated SATB2 positivity in SEFs of bone (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2020;59:217)
- KPNA2 expression (Diagn Pathol 2020;15:135)
- Negative for MUC4
- No EWSR1 and CREB3L1 rearrangements
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
A 47 year old man presented with a mass in the soft tissue of the thigh. Hematoxylin eosin stains show a tumor composed of uniform, small, round to ovoid epithelioid cells with sparse, often clear cytoplasm and round to oval nuclei with inconspicuous nucleoli. The tumor cells are arranged in small nests and cords in a dense sclerotic stroma. Occasional mitotic figures are identified (2 mitoses/10 high power fields). The margins of the tumor are infiltrative into muscle and periosteum.
Immunohistochemical stains for MUC4, vimentin and EMA (focal) are positive in tumor cells while all of the following are negative: CD34, SOX10, S100, GFAP, desmin, p63, MyoD1, CD10 and AE1 / AE3.
Which of the following is most likely the correct diagnosis?
- Epithelioid sarcoma
- Metastatic carcinoma
- Ossifying fibromyxoid tumor
- Sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma
- Spindle cell / sclerosing rhabdomyosarcoma
Board review style answer #2