Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Epidemiology | Sites | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Case reports | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Bychkov A. Solid cell nests / ultimobranchial body remnants. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/thyroidsolidcellnests.html. Accessed September 14th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Small (< 1 mm) interfollicular clusters of epithelial cells resembling squamous / transitional epithelium
- First described by Getzowa in 1907 (Virchows Archiv 1907;188:181)
- Considered as normal thyroid gland components (J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997;82:4274, Acta Anat (Basel) 1992;143:79)
- Remnants of the ultimobranchial body derived from branchial apparatus (fourth / fifth pharyngeal pouch complexes) and giving rise to C cells (Am J Clin Pathol 1994;101:186, Lab Invest 2011;91:138)
Terminology
- Also known as ultimobranchial body remnants, ultimobranchial body nests
- Solid cell nests are the ultimobranchial body remnants in postnatal life
- Rarely called compact cell nests, solid cell rests
Epidemiology
- Adults: from 3% of routinely examined thyroids to 60% of the glands subjected to serial blocking (Acta Anat (Basel) 1986;127:262)
- 30% to 90% of serially sectioned fetal thyroids (J Pathol 1993;169:465, Arch Pathol Lab Med 1990;114:1049)
- Male predominance (Acta Anat (Basel) 1986;127:262, Acta Anat (Basel) 1992;143:79)
Sites
- Located in the middle or occasionally in the upper third of the thyroid lateral lobes and placed in a central to paracentral and slightly dorsal longitudinal axis (J Pathol 1988;155:191)
Clinical features
- May play a stem cell role in adult thyroid gland (Mod Pathol 2004;17:819, Endocr Pathol 2011;22:35)
- May be site of origin of CASTLE tumors (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:994, Thyroid 2013;23:511), primary thyroid mucoepidermoid carcinoma (Mod Pathol 2004;17:526)
- Histogenetic link to thyroid cancer is debated (Hum Pathol 2004;35:465, Hum Pathol 2005;36:590, Am J Clin Pathol 2012;137:612)
Diagnosis
- Usually an incidental microscopic finding
Case reports
- 47 year old man with ultimobranchial body remnants (J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2012;97:2209)
- 48 year old man with BRAF mutation in solid cell nest hyperplasia (Hum Pathol 2009;40:1029)
- 58 year old man with carcinoma showing thymus-like elements arising in close association with solid cell nests (Thyroid 2013;23:511)
- 65 year old man with branchial-like cysts of the thyroid associated with solid cell nests (Pathol Int 2006;56:150)
- 70 year old man with absence of the BRAF and GRIM-19 mutations in oncocytic solid cell nests (Am J Clin Pathol 2012;137:612)
- 70 year old man with thyroid tumor-in-tumor with basaloid differentiation and phenotype similar to solid cell nests (Int J Surg Pathol 2011;19:276)
- Giant solid cell rest of thyroid (Int J Surg Pathol 2009;17:268)
- Solid cell nest in fine needle aspiration of goiter (Diagn Cytopathol 2002;27:66)
- Thyroid type solid cell nests in struma ovarii (Int J Surg Pathol 2011;19:627)
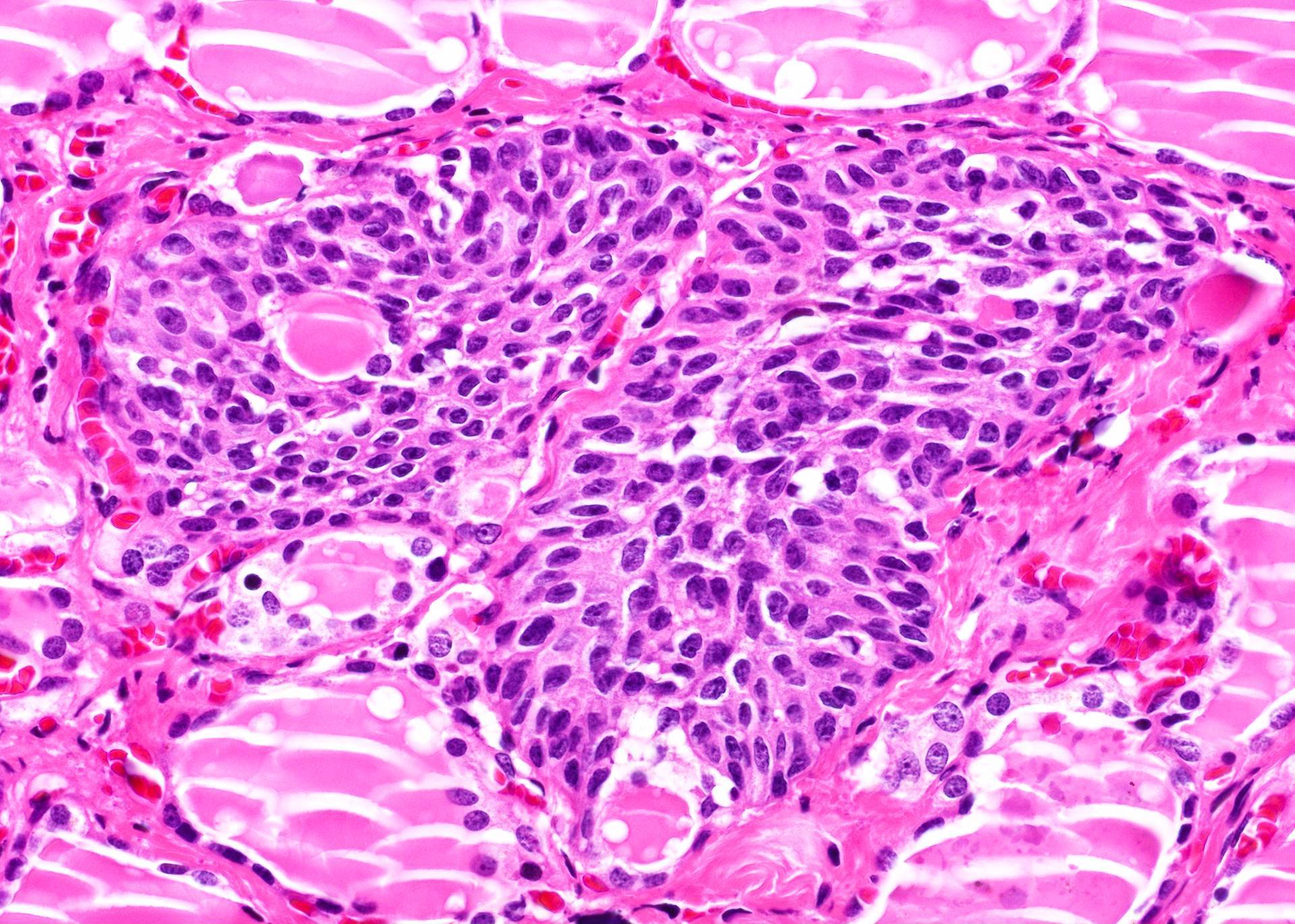
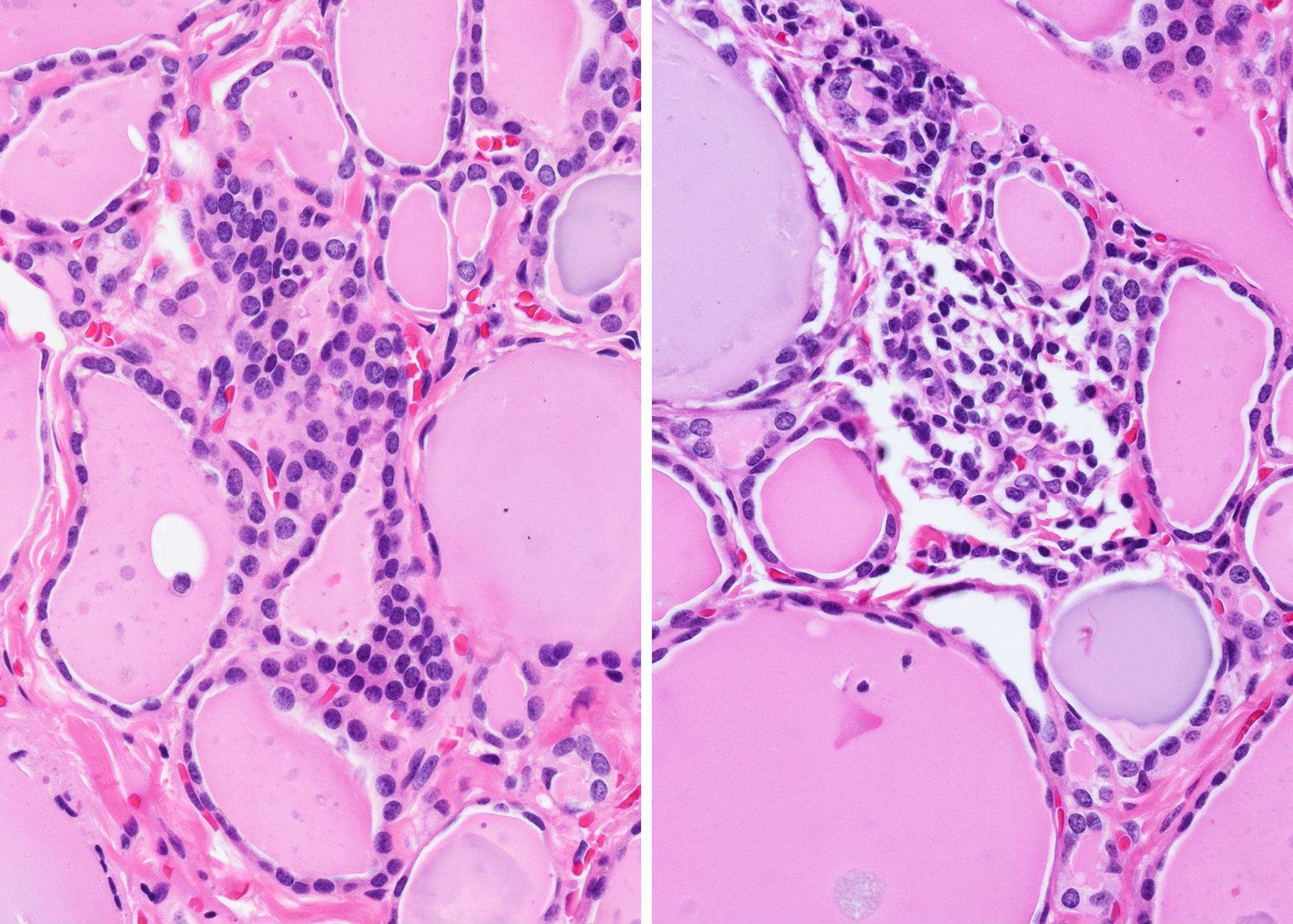
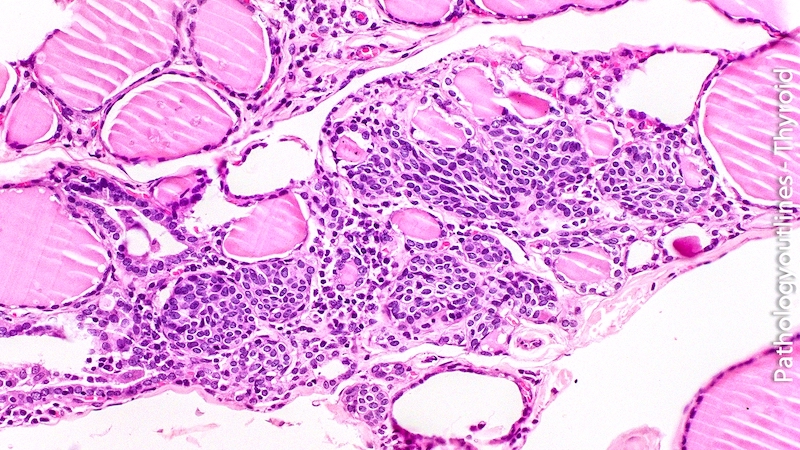
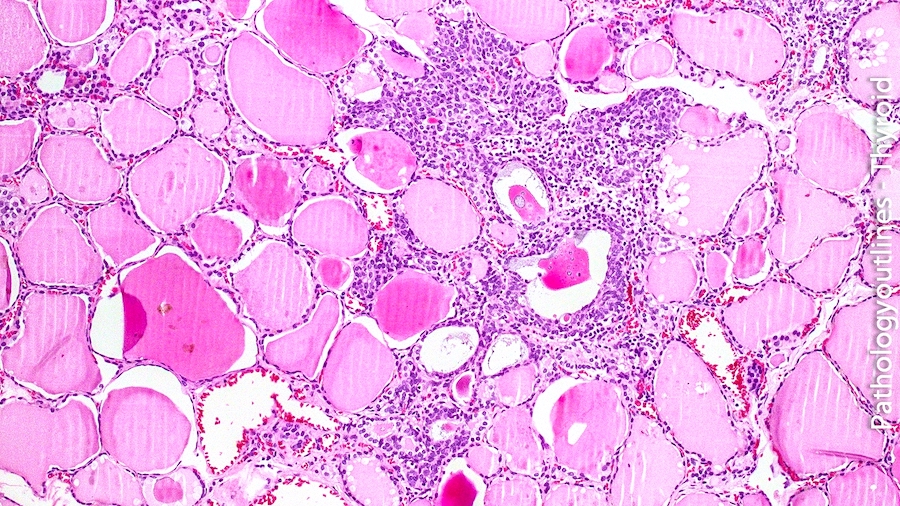
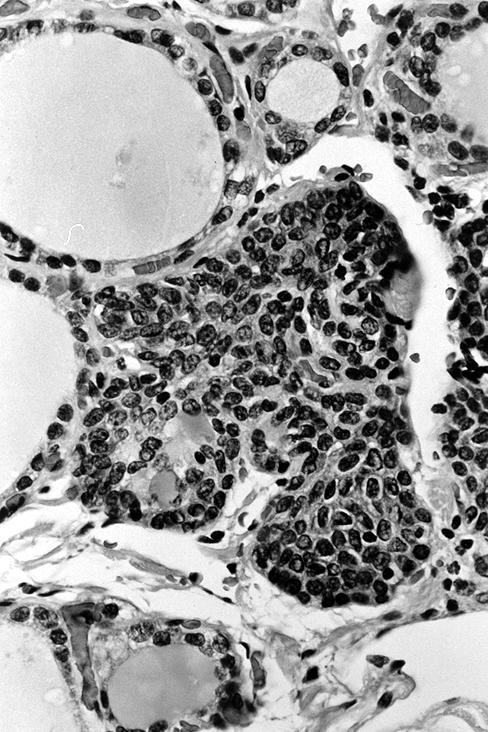
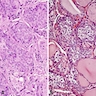
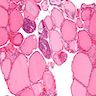
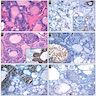
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Small cells in solid structures (50 - 1000 μm) interspersed between follicles
- Usually surrounded by stroma and demarcated by adjacent thyroid follicles
- Lobulated, nested or irregular shape on low power
- Multiple foci (2 - 8 per section) are common (Histopathology 2016;68:866)
- Composed of two cell populations - predominant main cells and a minority of C cells
- Sometimes with intermingled cystic structures containing mucin and mixed follicles
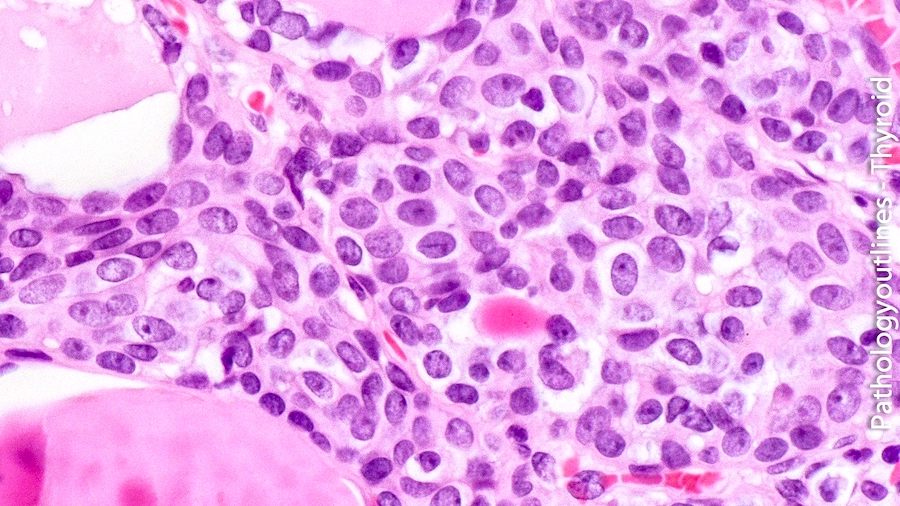
- Main cells:
- Polygonal / elongated to round to spindle cells
- Scant amphophilic or rarely deeply eosinophilic cytoplasm with squamoid features (but no intercellular bridges)
- Nuclei are centrally located, oval to fusiform, with finely granular chromatin, uneven nuclear membrane, occasional nuclear grooves
- C cells: minor population of cells with clear cytoplasm and centrally located, small compact nuclei
- May contain ciliated columnar cells
- May also contain cells with follicular lumen-like pattern (mixed follicles)
- Usually have a tropism to lymphocytes because of the common embryologic derivation of SCNs and the thymus (Pathol Int 2006;56:150, Hum Pathol 2009;40:1029)
- C cells in small clusters are common in the vicinity of solid cell nests
- Cartilage and adipose tissue are rarely seen (Hum Pathol 1994;25:684)
- Asioli et al classified SCN based on the solid (types 1 - 2) or cystic (types 3 - 4) patterns (Endocr Pathol 2009;20:197):
- Type 1 (floret-like) is composed of main cells, characterized by round to oval or elongated cells with scant cytoplasm, centrally located oval to fusiform nuclei, and occasional nuclear grooves
- The cells form round to oval groups, surrounded by lymphocytes
- Type 2 SCN (epidermoid-like) are made of larger, polygonal cells with an epidermoid appearance
- Type 3 has cystic architecture lined by flattened or polygonal cells
- Type 4 SCNs (mixed follicles) have a follicular appearance and contain both follicular epithelium and small main cells
- Type 1 (floret-like) is composed of main cells, characterized by round to oval or elongated cells with scant cytoplasm, centrally located oval to fusiform nuclei, and occasional nuclear grooves
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Andrey Bychkov, M.D., Ph.D. and AFIP
Images hosted on other servers:
Cytology description
- Cohesive cellular group consisting of polygonal squamoid cells with lightly eosinophilic cytoplasm (no intercellular bridges), elongated to columnar shaped cells with clear cytoplasm, and scattered lymphocytes
- Nucleus is large and centrally located, slightly irregular with evenly distributed chromatin and chromocenter (Hum Pathol 2004;35:465)
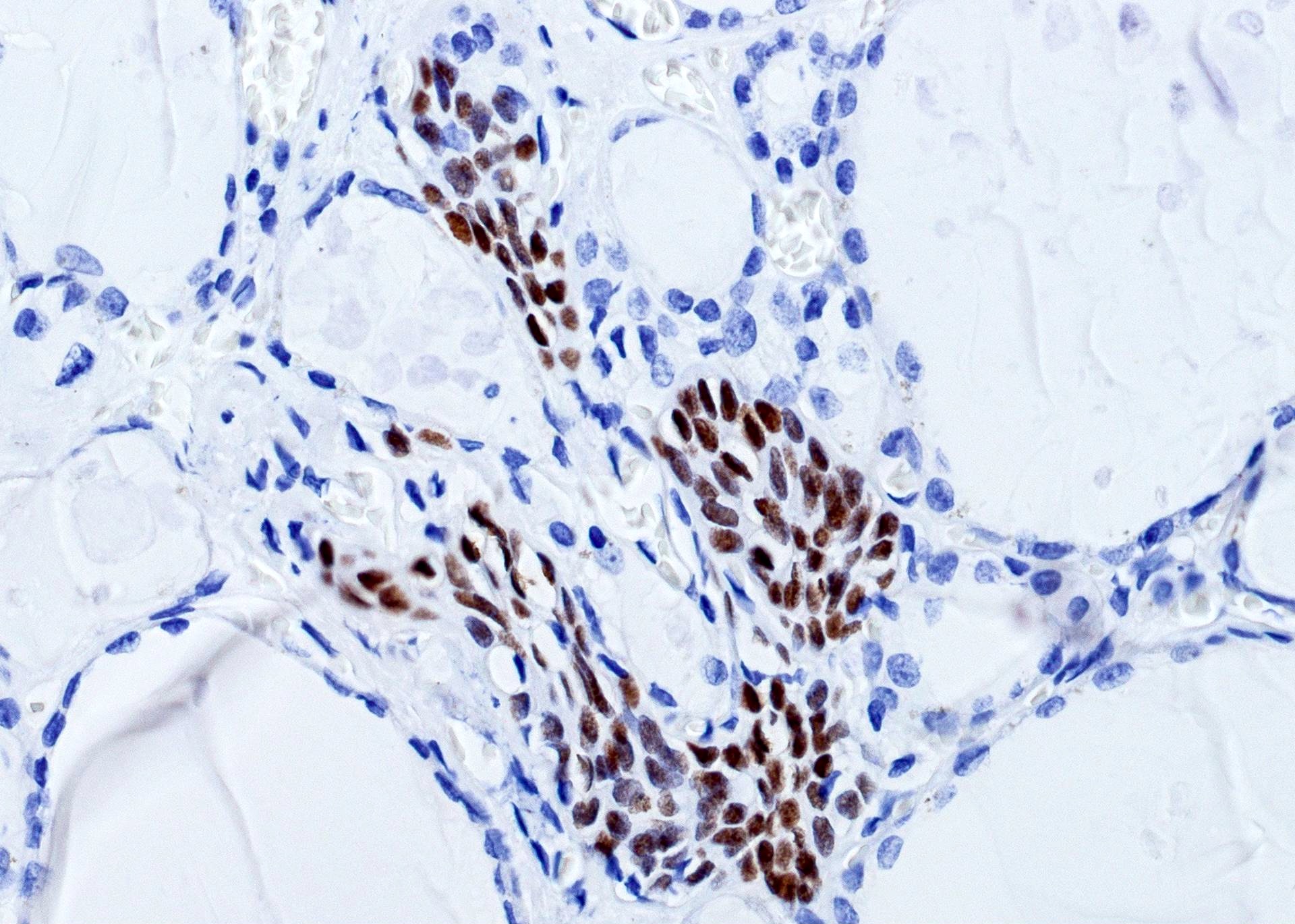
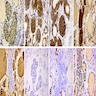
Positive stains
- Main cells:
- p63 (Mod Pathol 2003;16:43, Hum Pathol 2004;35:465), p40 (Histopathology 2016;68:866)
- CEA (variable)
- bcl2
- Cytokeratins (AE1 / AE3, CK7, CK19, CAM5.2, 34βE12)
- Galectin 3 (J Clin Pathol 2003;56:142)
- C cells:
- Calcitonin (may leak into adjacent cells), calcitonin gene related peptide, chromogranin
- TTF1
- Lumina: PAS+ colloid
Negative stains
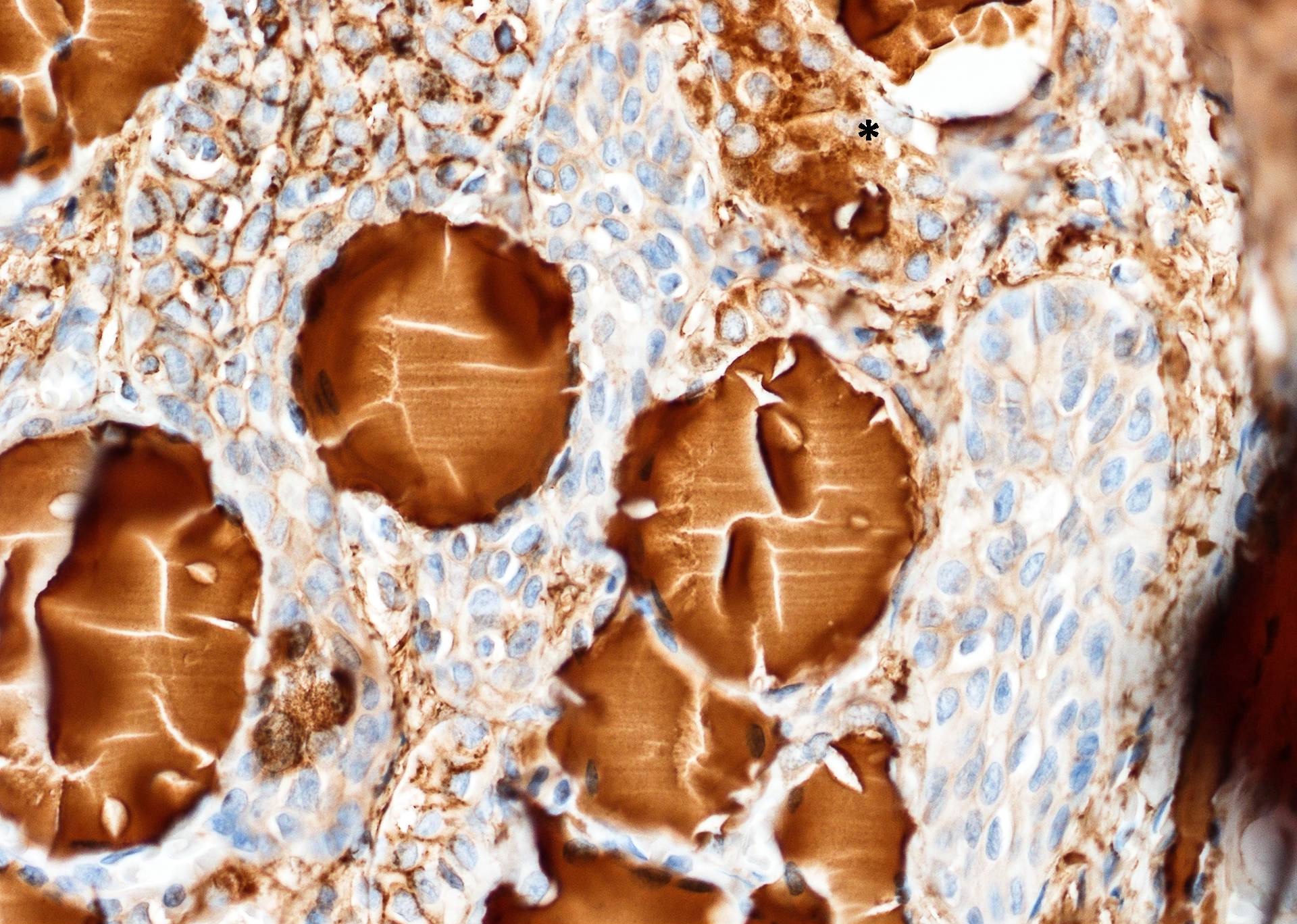
- Main cells:
- TTF1, thyroglobulin
- CK20
- HBME1 (inconsistent across different studies, e.g. Am J Clin Pathol 2010;134:169, Histopathology 2016;68:866)
- C cells: p63
Electron microscopy description
- Main cells: desmosomes, intermediate filaments, intracytoplasmic vacuoles and projections (Acta Anat (Basel) 1987;129:289)
- C cells: neurosecretory granules; also ciliated cells, lymphocytes (Ultrastruct Pathol 2000;24:1)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- No BRAF mutations found (Am J Clin Pathol 2012;137:612, Histopathology 2016;68:866)
Differential diagnosis
- C cell hyperplasia and medullary microcarcinoma: uniformly positive for calcitonin; p63 negative
- Intrathyroidal thymic remnants: Hassall corpuscles
- Papillary microcarcinoma: TTF1 and thyroglobulin positive, p63 negative
- Not recommended to rely on CK19 / galectin 3 (positive in both SCN and papillary microcarcinoma)
- Primary or metastatic squamous carcinoma: cellular atypia, mitotic activity, stromal desmoplasia
- Squamous metaplasia in Hashimoto thyroiditis: associated with chronic inflammation (p63 positive and TTF1 positive)
- Tangential sections of normal follicles
- Thyroglossal duct cyst: midline location (e.g. thyroid isthmus)