Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Kwon G, Nam G, Singh K. Tall cell carcinoma with reverse polarity. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastmalignantspcrp.html. Accessed October 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Rare subtype of papillary carcinoma of breast that histologically resembles tall cell variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma and frequently shows distinct IDH2 R172 hotspot mutations
Essential features
- Histologic subtype of papillary carcinoma of breast, first described in 2003 (Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:1114)
- Solid nodules of columnar epithelial cells, many with thin fibrovascular cores, leading to solid papillary architecture
- Epithelial cells contain abundant glassy eosinophilic cytoplasm and show abnormal apically located nucleus giving the impression of reverse nuclear polarity
- Frequent IDH2 R172 hotspot mutations
- Triple negative phenotype with presumed low malignant potential
Terminology
- Not recommended per WHO:
- Solid papillary carcinoma with reverse polarity (SPCRP)
- Breast tumor resembling tall cell variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Solid papillary breast carcinoma resembling tall cell variant of papillary thyroid neoplasm
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Rare tumor
- Women of postmenopausal age; median age of 64 (range: 39 - 89) (Am J Clin Pathol 2017;147:399, Histopathology 2018;73:339, Mod Pathol 2018;31:1367)
Sites
- Breast
Pathophysiology
- Pathophysiology still unclear
- The majority (84%) are characterized by IDH2 p.Arg172 hotspot mutations (Histopathology 2018;73:339, Int J Surg Pathol 2019;27:134)
Clinical features
- Typically presents as a mammographic or palpable breast mass
Diagnosis
- Tissue biopsy or surgical excision specimen showing the key histologic and immunohistochemical features
- Demonstration of IDH2 or TET2 mutation
- Exclusion of metastatic disease (i.e., thyroid carcinoma)
Radiology description
- Solid mass on mammogram or ultrasound (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:887)
- Ultrasonography can show a hypoechoic mass with or without posterior shadowing (Adv Anat Pathol 2012;19:108)
Prognostic factors
- Favorable prognosis with rare reports (2 cases) of metastases to lymph nodes and bone (Cancer Res 2016;76:7118, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:887)
Case reports
- 40 year old woman presented with a lump in the breast (Turk Patoloji Derg 2021;37:183)
- 55 year old woman with Lynch syndrome (J Clin Pathol 2018;71:1031)
- 60 year old woman with IDH2 and PIK3CA missense mutations (Mol Biol Rep 2020;47:4917)
- 63 year old woman with a finding of a nodular lesion during a screening mammogram (Cureus 2021;13:e16814)
- 65 year old woman with tall cell variant of papillary breast carcinoma (Pathologica 2017;109:162)
- 70 and 72 year old women with typical clinicopathological manifestations and hotspot mutations (Gland Surg 2021;10:3147)
- 71 year old woman with very rare breast tumor (Breast J 2021;27:369)
Treatment
- Surgical excision is mainstay treatment (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:887)
- Lack of evidence for sentinel lymph node procedure, radiation or systemic therapy
Gross description
- Usually a well circumscribed, firm, white-gray mass (Int J Surg Pathol 2007;15:14, Int J Surg Pathol 2015;23:217, Mod Pathol 2018;31:1367)
- Median size of 1.5 cm with a range of 0.6 - 5 cm (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:887, Mod Pathol 2018;31:1367, Histopathology 2018;73:339, Int J Surg Pathol 2019;27:134)
- Sometimes cystic with translucent, colloid-like area that resembles thyroid tissue (Int J Surg Pathol 2015;23:217)
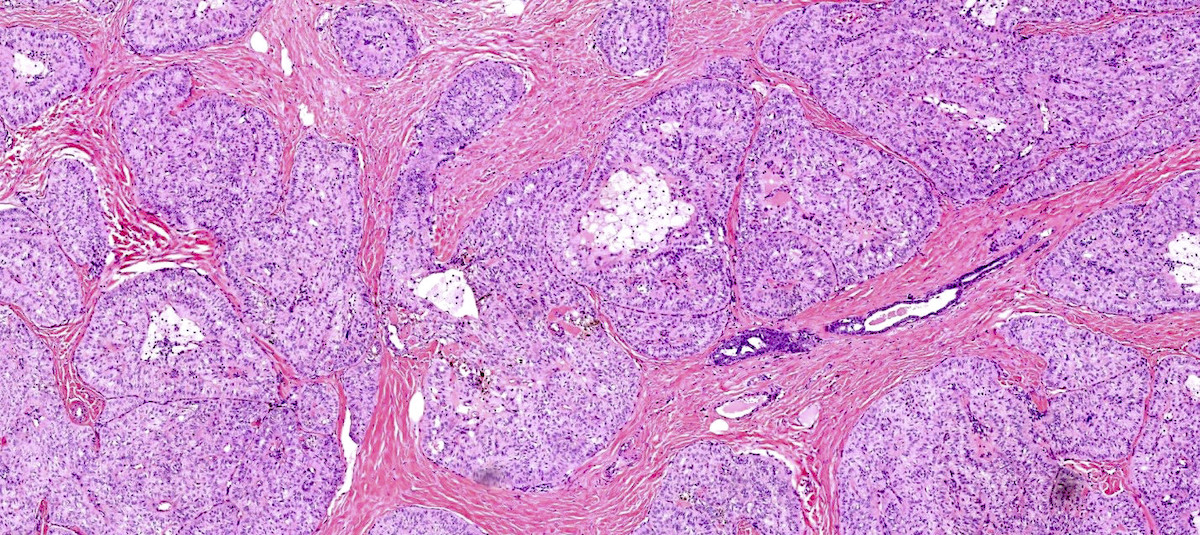
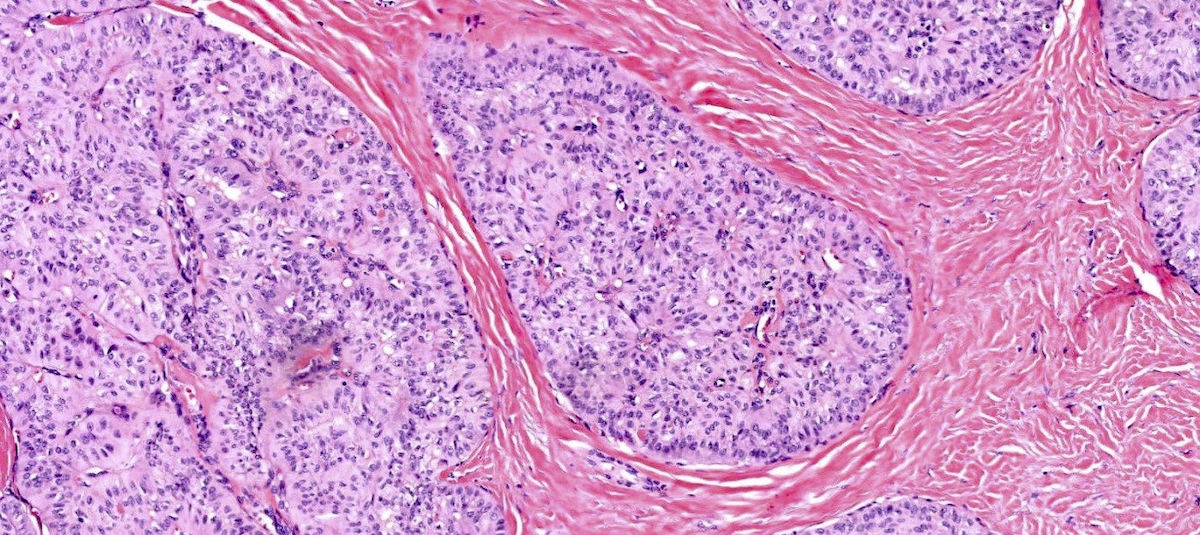
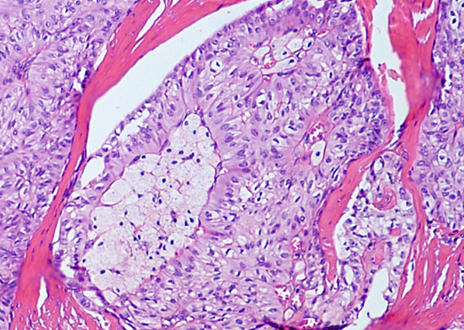
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Solid circumscribed nodules of epithelial cells with thin, petite papillae in a dense fibrous stroma (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:887)
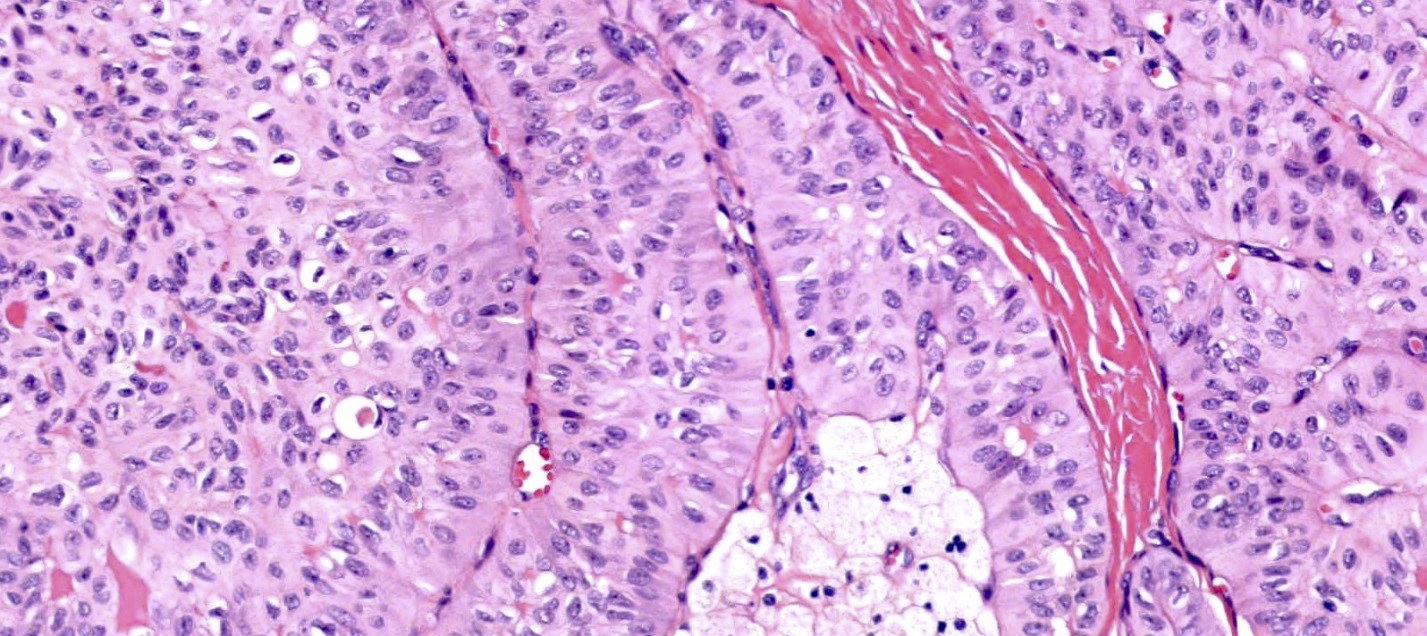
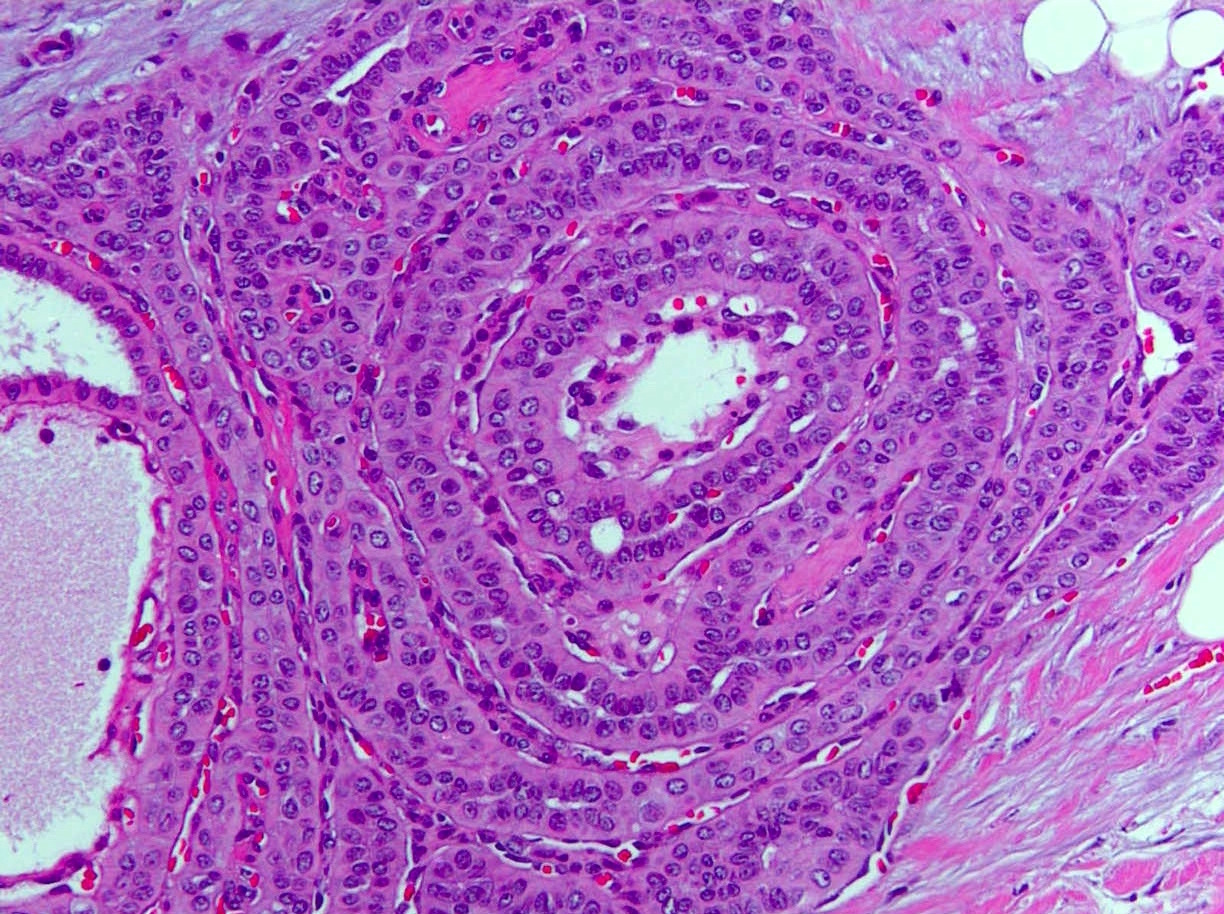
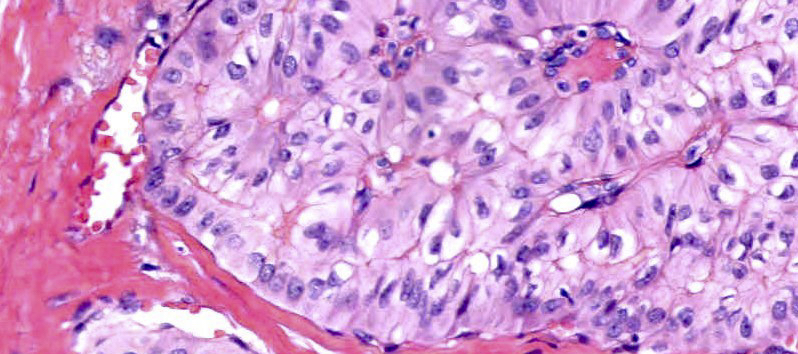
- Cuboidal, columnar or tall columnar tumor cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm; bland nuclear features with nuclei located at the apical pole rather than the basal pole, giving the impression of reverse nuclear polarity
- Variable presence of nuclear grooves with intranuclear pseudoinclusions
- True papillae and cystic spaces with amphophilic colloid-like secretions may be seen
- Foamy histiocyte aggregates often present within fibrovascular cores
- Mitotic figures rare
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Highly cellular; cells dispersed, in nests and with papillary formation; nuclear grooves (Int J Surg Pathol 2006;14:79)
Positive stains
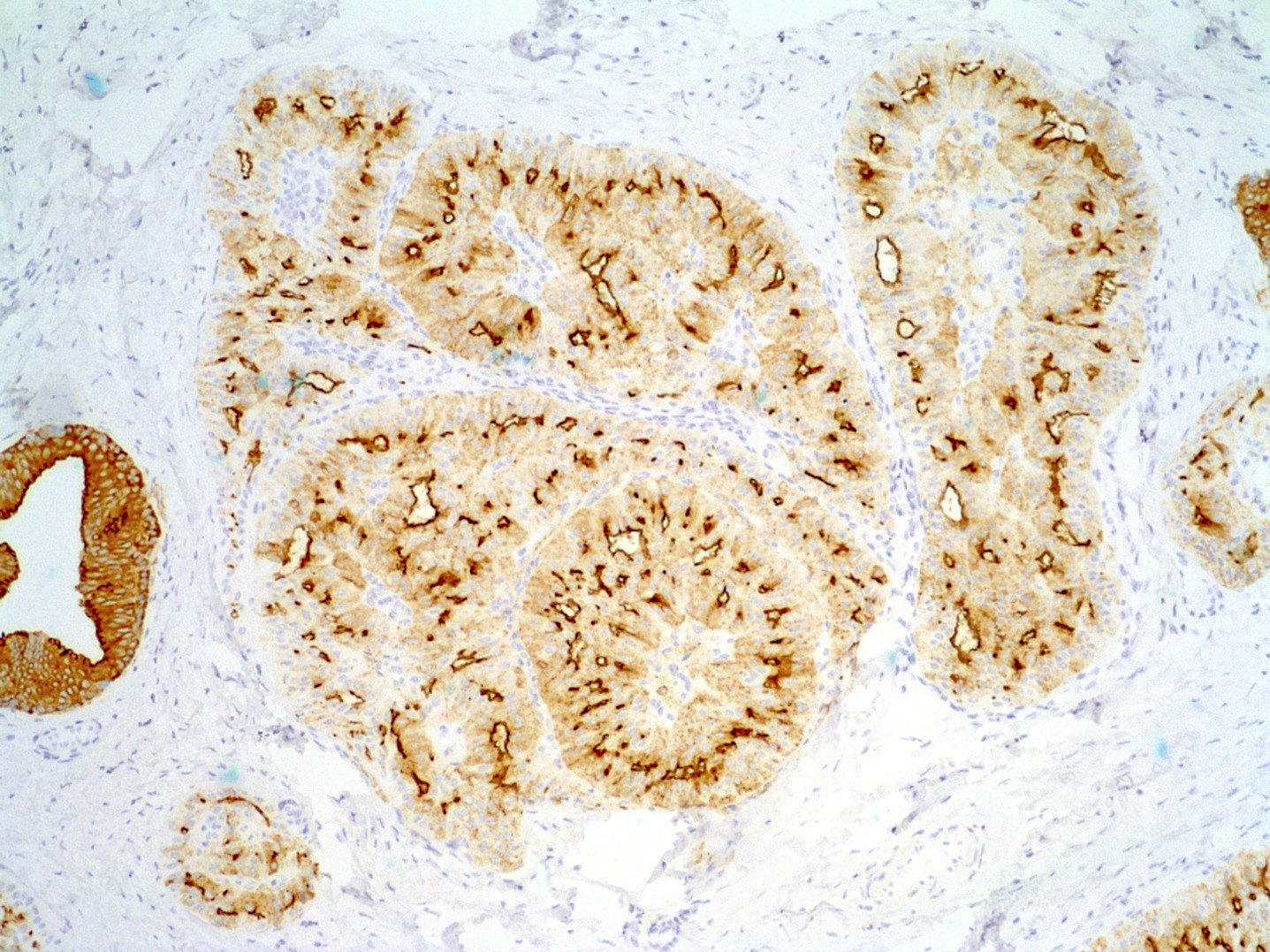
- CK5/6: mosaic cytoplasmic expression (similar to intraductal papilloma with usual ductal hyperplasia) (Mod Pathol 2018;31:1367)
- IDH1 / IDH2 mutant R132 / R172
- E-cadherin: strong lateral membrane expression with absent apical or basal expression
- MUC1: highlights the apical membranes of columnar epithelial cells (Cancer Res 2016;76:7118)
- Ki67 low < 5 % (Mod Pathol 2018;31:1367)
- Variable staining for GATA3, GCDFP-15, mammaglobin
- Characteristically express both low and high molecular weight cytokeratins as shown with CK7 and CK5/6 immunostaining
- Monoclonal antibody 11C8B1 sensitivity 93% and specificity 100% for IDH2 R172 hotspot mutations (Mod Pathol 2020;33:1056)
- Calretinin (Am J Clin Pathol 2017;147:399, Mod Pathol 2018;31:1367, Mod Pathol 2020;33:1056)
Negative stains
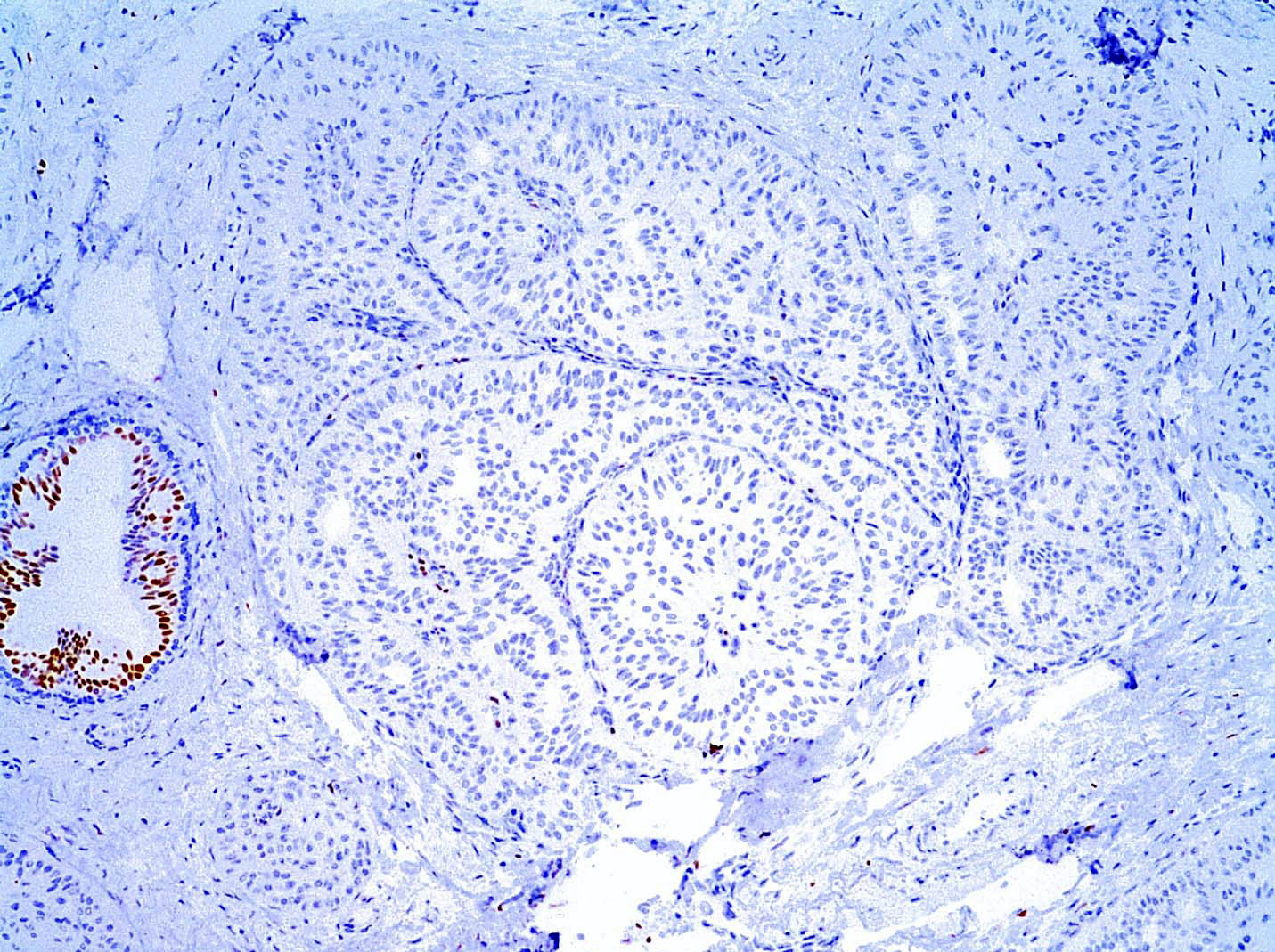
- Triple negative phenotype: hormone receptors and HER2 (ER, PR, HER2): generally negative; ER or PR can be focally positive (Int J Surg Pathol 2007;15:14, Mod Pathol 2018;31:1367, Pathobiology 2019;86:83, Int J Surg Pathol 2019;27:134)
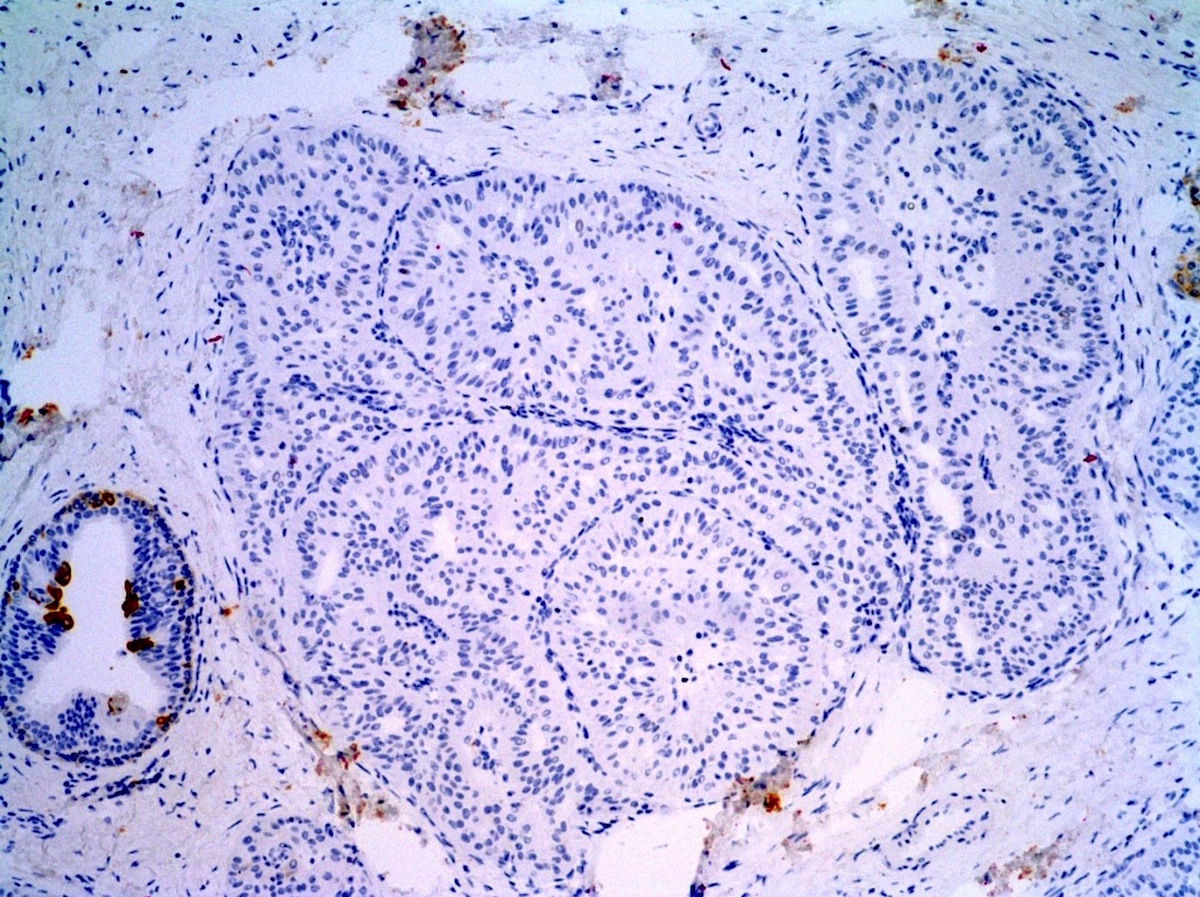
- Myoepithelial markers (p63, SMMHC, calponin)
- TTF1, thyroglobulin
- Chromogranin A and synaptophysin
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- IDH2 R172 hotspot mutations in 77 - 100% (Cancer Res 2016;76:7118)
- PIK3CA hotspot mutations in 67% (Histopathology 2018;73:339)
- TET2 truncating mutation
- PRUNE2 mutation (Mod Pathol 2018;31:1367)
- ATM, KIT and MET alterations (Am J Clin Pathol 2017;147:399)
- BRAF mutations and RET / PTC rearrangement is negative in studied cases (positive in PTC)
Sample pathology report
- Right breast, 9 o'clock, excisional biopsy:
- Tall cell carcinoma with reverse polarity (see comment)
- Comment: Sections show circumscribed nests of a solid, papillary and partially cystic neoplasm comprised of low to intermediate nuclear grade columnar epithelial cells with abundant cytoplasm, irregular nuclear contours and scattered nuclear grooves. The columnar cells appear to show apical localization, so called reverse polarization. Myoepithelial immunostains are negative. The lesional cells are strongly and diffusely immunoreactive for cytokeratin 5 and negative for ER, PR and HER2. Concurrent molecular analysis revealed IDH2 and PIK3CA mutations. Overall, the morphologic, immunohistochemical and molecular findings are compatible with a tall cell carcinoma with reverse polarity.
Differential diagnosis
- Solid papillary carcinoma:
- Lack of reverse polarity of nuclei
- Strongly ER positive, variable CK5/6
- Plasmacytoid cells with neuroendocrine differentiation may be present (chromogranin and synaptophysin positive)
- Intracellular mucin may be present
- Encapsulated papillary carcinoma:
- Intraductal papilloma with usual ductal hyperplasia:
- Metastatic thyroid carcinoma:
- Psammoma bodies, giant cells and optically clear Orphan Annie nuclei
- TTF1 and thyroglobulin positive
- BRAF and RET / PTC molecular alterations
Additional references
Practice question #1
A 59 year old woman had a 1.0 cm spiculated breast mass, represented above. Tumor cells express GCDFP-15 and mammaglobin. The tumor cells are negative for ER, PR and HER2. Myoepithelial markers (p63 and SMMHC) are also negative. Other negative markers include TTF1 and thyroglobulin. What is the most common molecular alteration seen in these tumors?
- BRAF mutation
- CDH1 mutation
- IDH2 R172 hotspot mutations
- RET mutation
- TET2 truncating mutation
Practice answer #1
Practice question #2
Which of the following IHC panels would differentiate solid papillary carcinoma from recently described tall cell carcinoma with reverse polarity?
- CK5/6 and ER
- CK7, CK18 and KIT
- E-cadherin and p120
- ER, PR and HER2
- GATA3 and TTF1
Practice answer #2
A. CK5/6 and ER. Tall cell carcinoma with reverse polarity is usually ER negative and may show variable loss of keratin 5/6. In contrast, solid papillary carcinoma shows negative CK5/6 and strong ER staining. Both tumors show loss of myoepithelial cells by p63 and smooth muscle myosin heavy chain. ER, PR and HER2 (biomarkers), E-cadherin and p120 (ductal versus lobular), GATA3 and TTF1 (primary breast versus metastasis), and CK4, CK14, CK18 and KIT (adenoid cystic carcinoma) do not help in distinguishing solid papillary carcinoma and tall cell carcinoma with reverse polarity.
Comment here
Reference: Tall cell carcinoma with reverse polarity
Comment here
Reference: Tall cell carcinoma with reverse polarity