Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Electron microscopy images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Pini GM, Colecchia M. Spermatocytic tumor. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/testisspermseminoma.html. Accessed September 15th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Spermatocytic tumor (ST) is a polymorphous triphasic germ cell neoplasm recapitulating spermatogonia development and unrelated to germ cell neoplasia in situ (GCNIS)
Essential features
- Does not arise from germ cell neoplasia in situ
- More common in older patients compared with patients with other germ cell tumors
- Classically characterized by tripartite tumor cells with 3 different cellular sizes (small, intermediate, giant)
- Immunohistochemical phenotype: CD117+, SALL4+, PLAP-, OCT3/4-, CD30-
- Excellent prognosis
Terminology
- Spermatocytic seminoma (not recommended by the WHO)
- Spermatocytoma (not recommended by the WHO)
- Spermatocytic variant of classic seminoma (not recommended by the WHO)
- Type III germ cell tumor (not recommended by the WHO)
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- ~1% of germ cell tumors
- Usually affects older men compared with germ cell neoplasia in situ derived tumors (mean age 52 years)
- Wide age range, including young patients (range 19 - 92 years)
- 30% of patients are 30 - 39 years; 35% are 40 - 59 years; 35% are ≥ 60 years (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1)
- No ethnic predisposition
Sites
- Testes
- 9% bilateral (synchronous or more frequently, metachronous)
- No primitive extragonadal cases reported so far
- Only 1 case of an ovarian spermatocytic tumor-like lesion reported in a gonadal mixed germ cell tumor (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:1290)
Pathophysiology
- Does not arise from germ cell neoplasia in situ (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:e30)
- Derived from postpubertal type germ cells (spermatogonium / spermatocyte)
- Genetically features mainly chromosomal abnormalities
- Rate of genetic mutations increase with age
Etiology
- Cryptorchidism is not a risk factor
- Only 2 cases have been reported of coincidental incidence of spermatocytic tumor in an undescended testis (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1, Br J Urol 1993;72:657)
Clinical features
- Usually presents as a painless testicular nodule
- Rapid tumoral growth is associated with the presence of sarcomatous differentiation (Int J Surg Pathol 2017;25:559)
Diagnosis
- Spermatocytic tumor is diagnosed histologically (see Microscopic (histologic) description)
Laboratory
- Not associated with elevated lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), alpha fetoprotein (AFP) or beta human chorionic gonadotropin (beta hCG) blood concentration
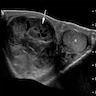
Radiology description
- Well circumscribed (Radiographics 2017;37:1085)
- Predominantly solid with heterogenous signal, including hyperechoic and hypoechoic components
- Multiple cystic areas
Prognostic factors
- Excellent prognosis overall
- ST with sarcomatous differentiation has a poor prognosis, a high risk of metastasis of the sarcomatous component to the lungs and a high mortality rate
- Some early reports of metastatic ST without sarcomatous differentiation have been reconsidered to be lymphomas (Cancer 1965;18:751, Cancer 1969;24:92)
- Only rare cases of bona fide metastatic ST without sarcomatous differentiation have been reported with spread to retroperitoneal lymph nodes, to the lungs and to the brain
- Intravascular space invasion or infiltration beyond testicular parenchyma were reported in metastatic ST without sarcomatous differentiation (Pathol Oncol Res 2017;23:223)
- Anaplastic ST is not currently considered to be a negative prognostic factor
Case reports
- 25 year old man with synchronous bilateral spermatocytic tumors (Scand J Urol 2017;51:78)
- 26 - 50 year old men with hybrid genetics in a metastatic spermatocytic tumor carrying 12p amplification (Pathology 2018;50:562)
- 30 year old man with a spermatocytic tumor (Med J Armed Forces India 2018;74:276)
- 77 year old man with cerebral metastasis of a spermatocytic tumor without sarcomatous differentiation (Pathol Oncol Res 2017;23:223)
- Chrondrosarcomatous differentiation in a spermatocytic tumor (Int J Surg Pathol 2017;25:559)
Treatment
- Orchiectomy
- Bleomycin, etoposide and cisplatin (BEP) chemotherapy has little effect on metastatic ST without sarcomatous differentiation (Med Oncol 2011;28:S423, Pathology 2018;50:562)
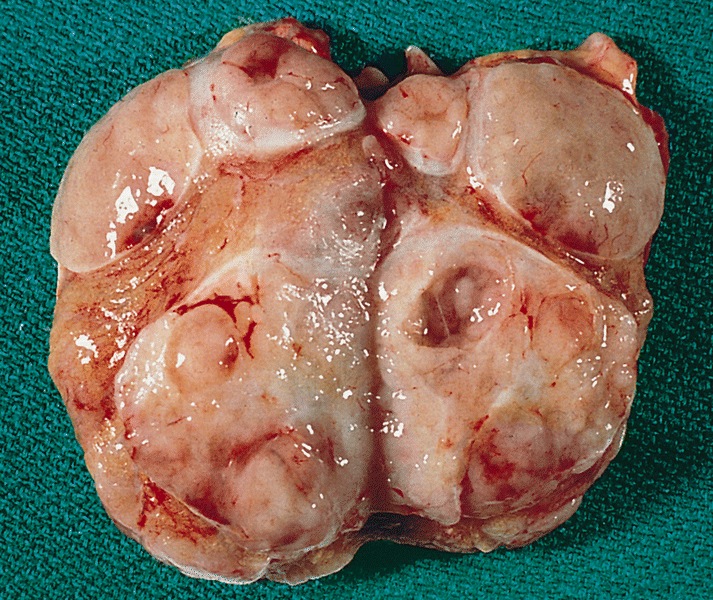
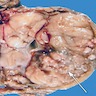
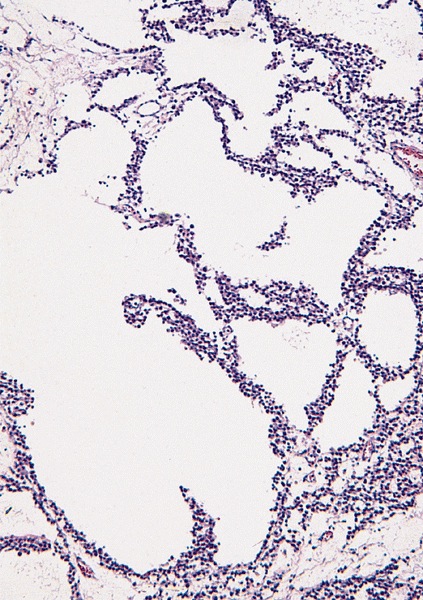
Gross description
- Variable size (mean 7 cm; range 1.4 - 28 cm)
- Homogenous or lobulated nodule
- Grayish white
- Edematous or mucoid
- Soft
- Necrosis and hemorrhage can be present
- Extension beyond the tunica albuginea might be present (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1)
- Fleshy and firm areas, with or without necrosis, might represent foci of sarcomatous differentiation
Gross images
Frozen section description
- Recognition of 3 cell types (small, intermediate, giant) is key to the correct diagnosis
- Intratubular ST in the surrounding parenchyma might be misinterpreted as germ cell neoplasia in situ
- No other types of germ cell neoplasia should be present
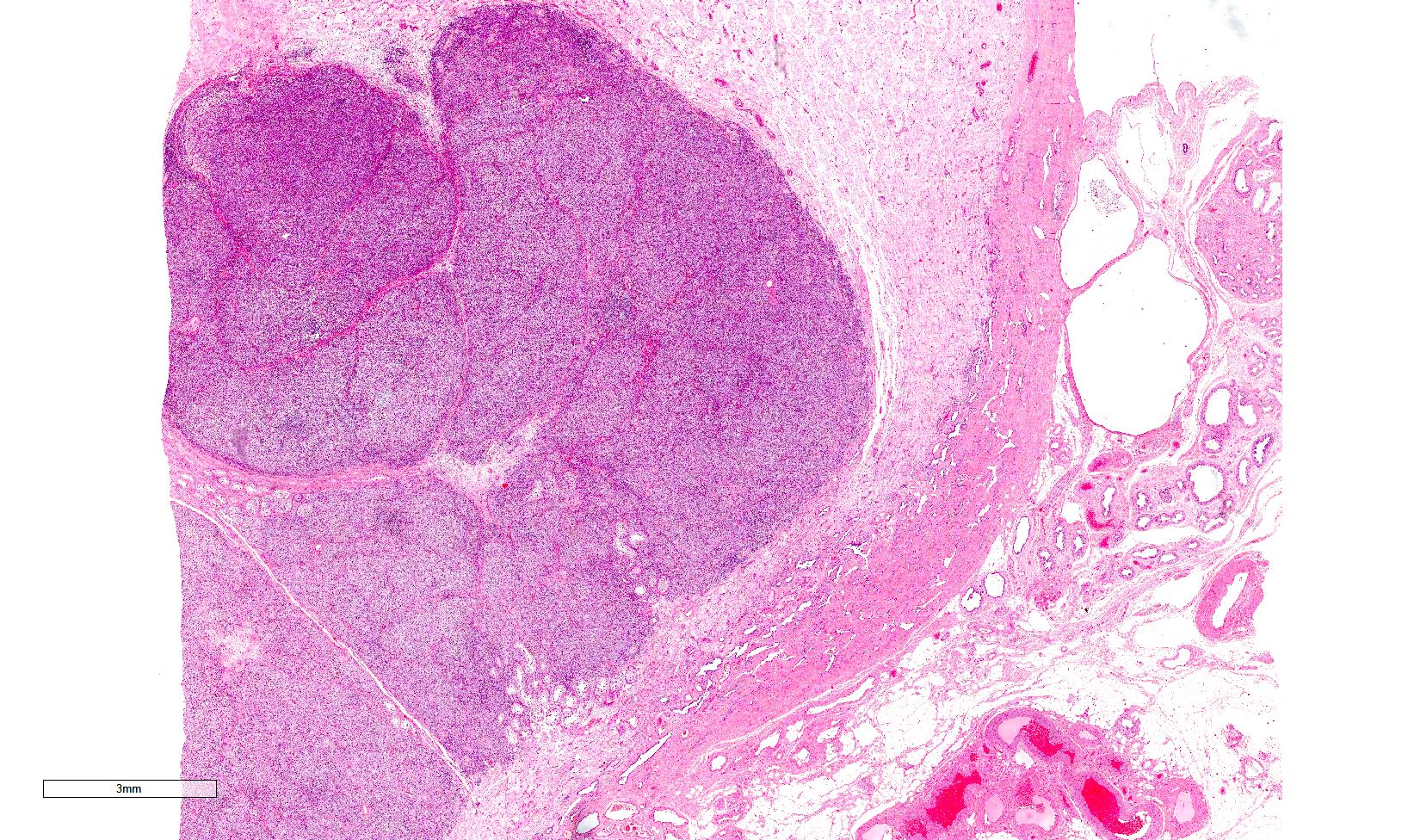
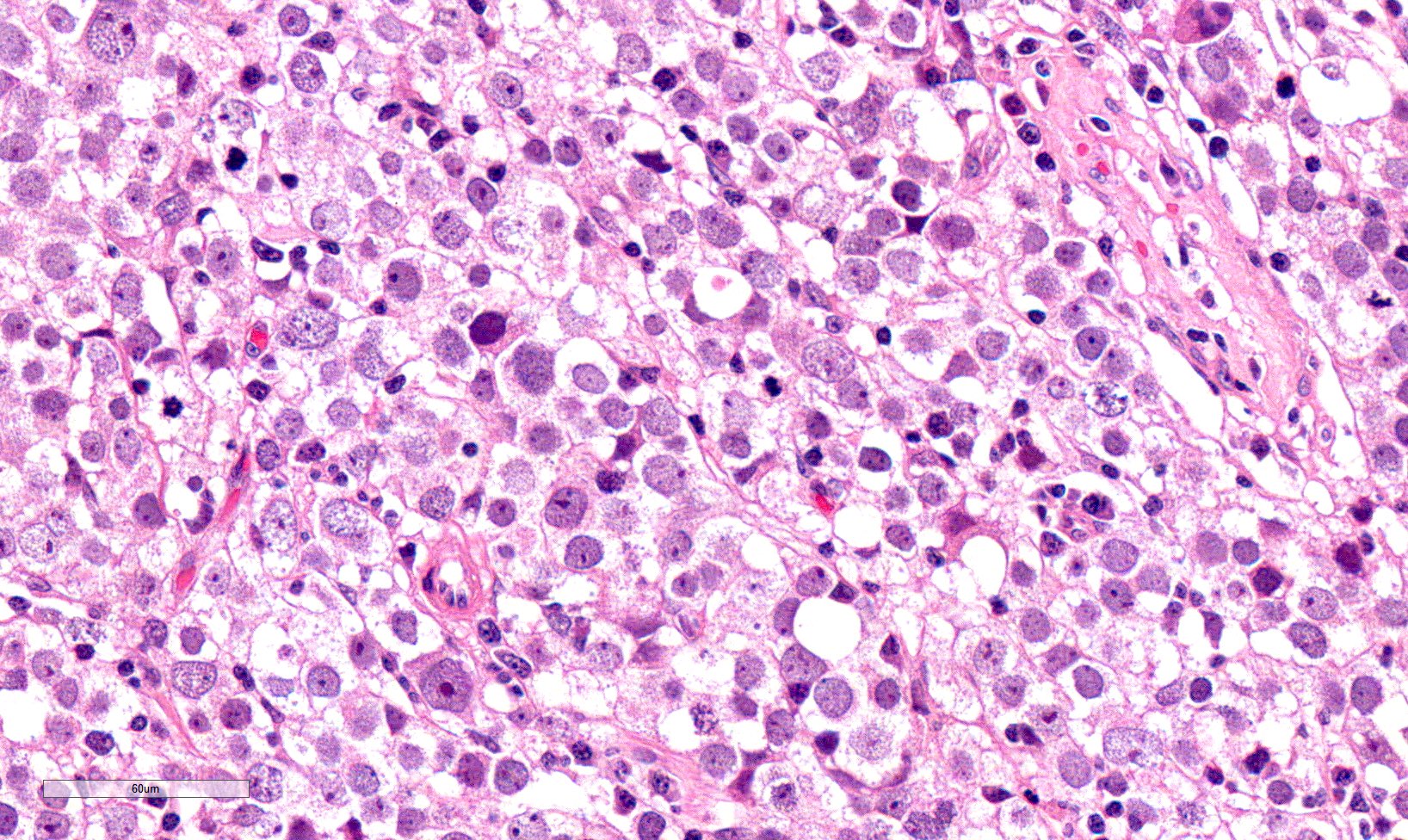
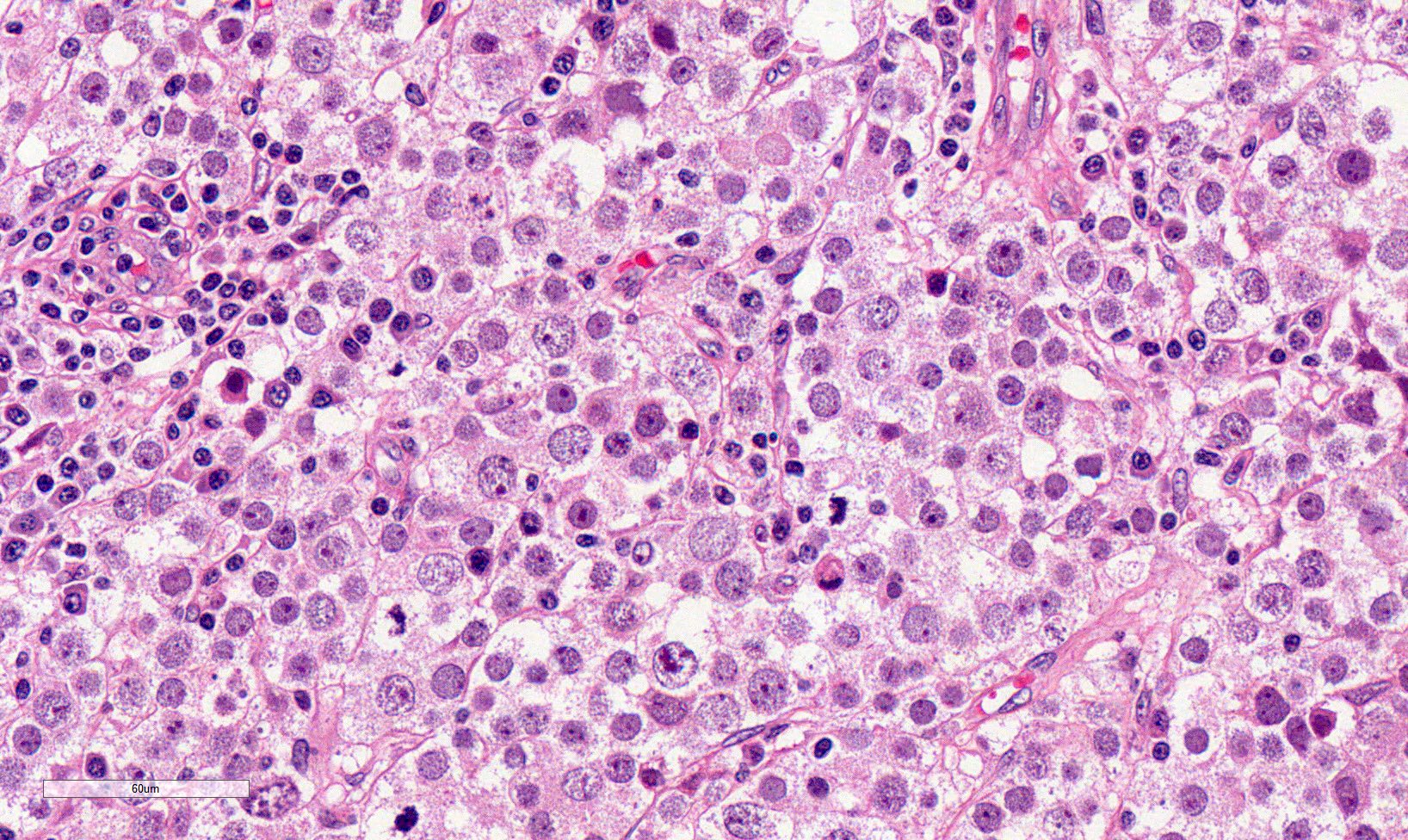
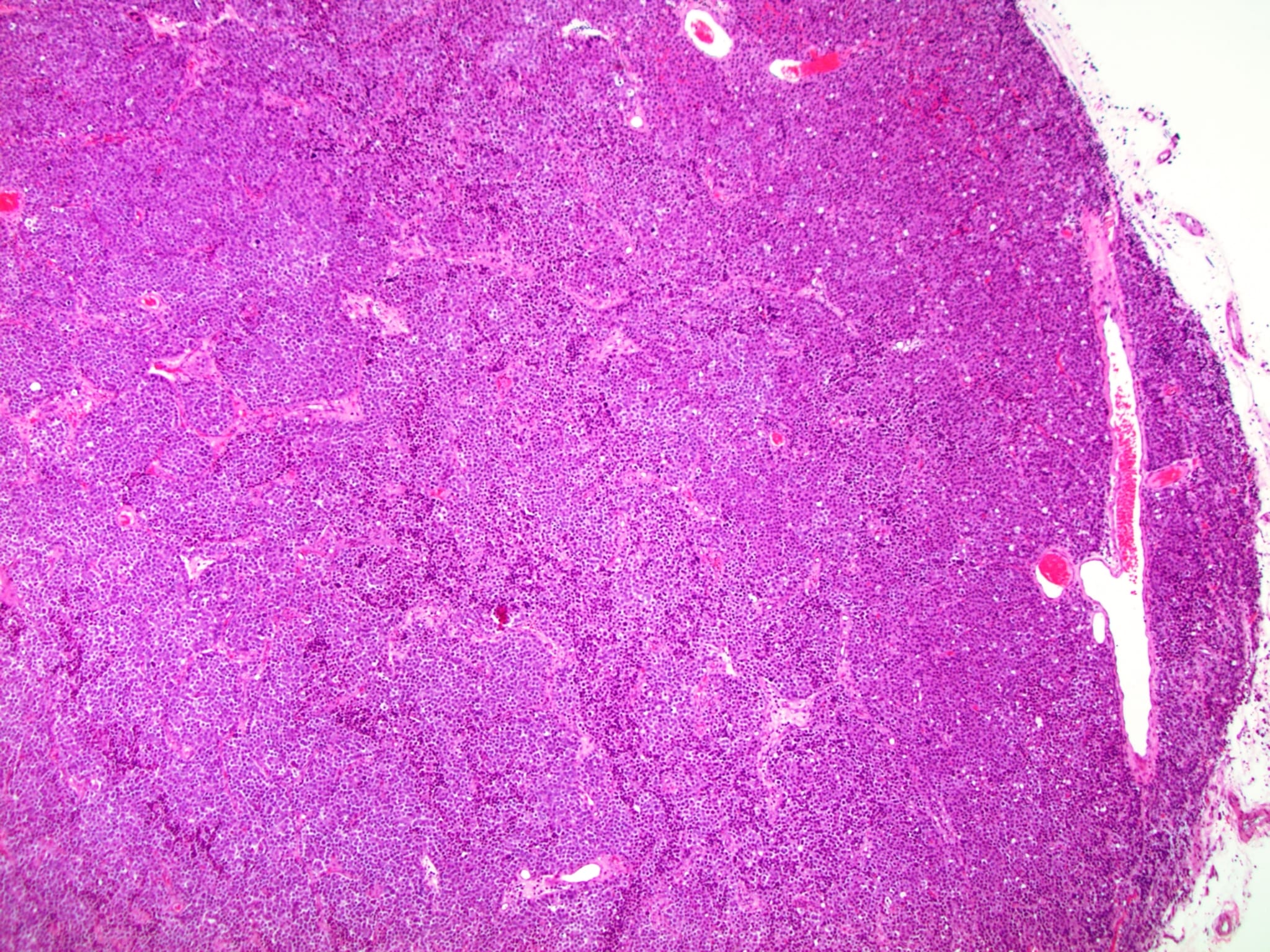
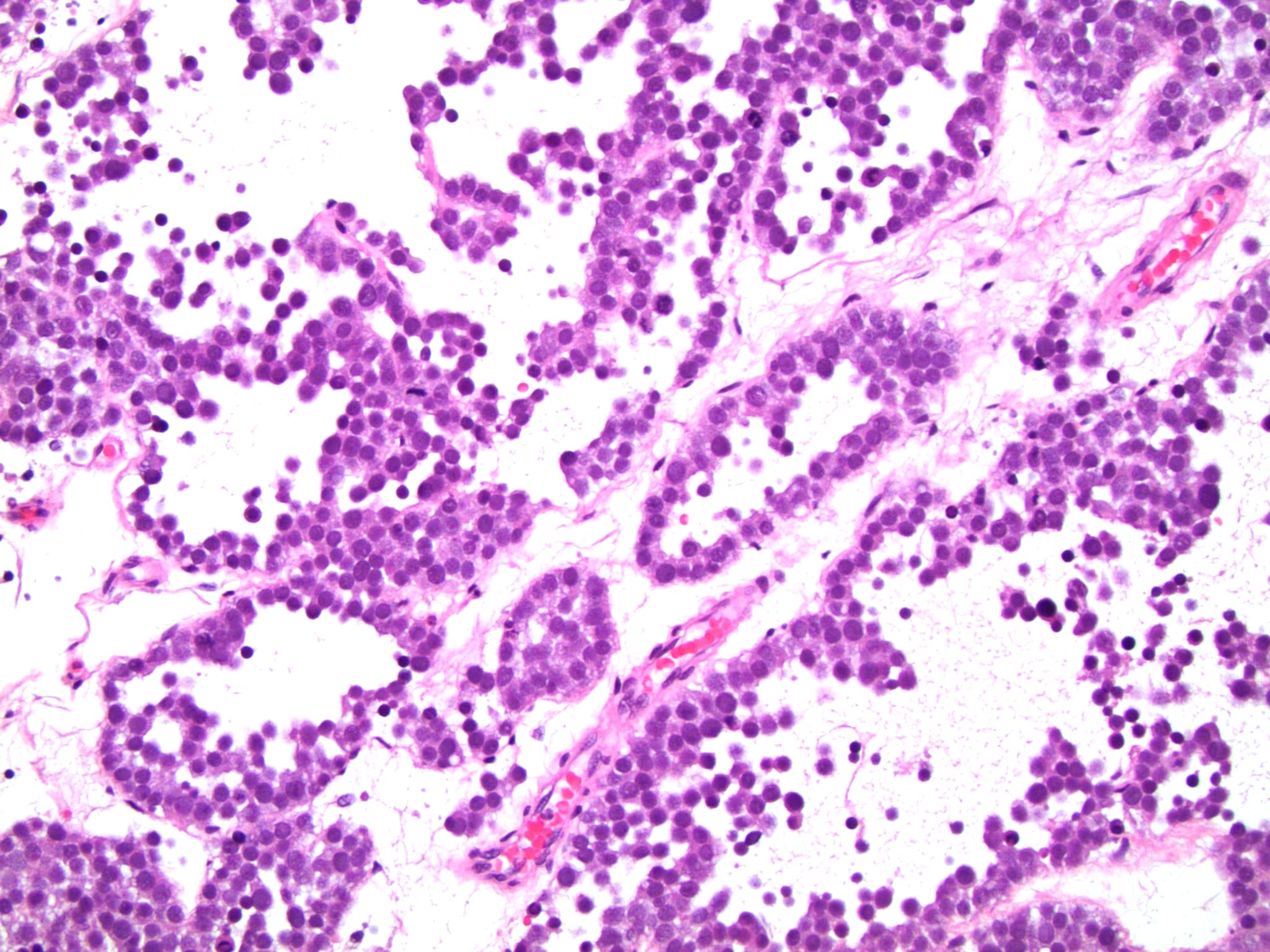
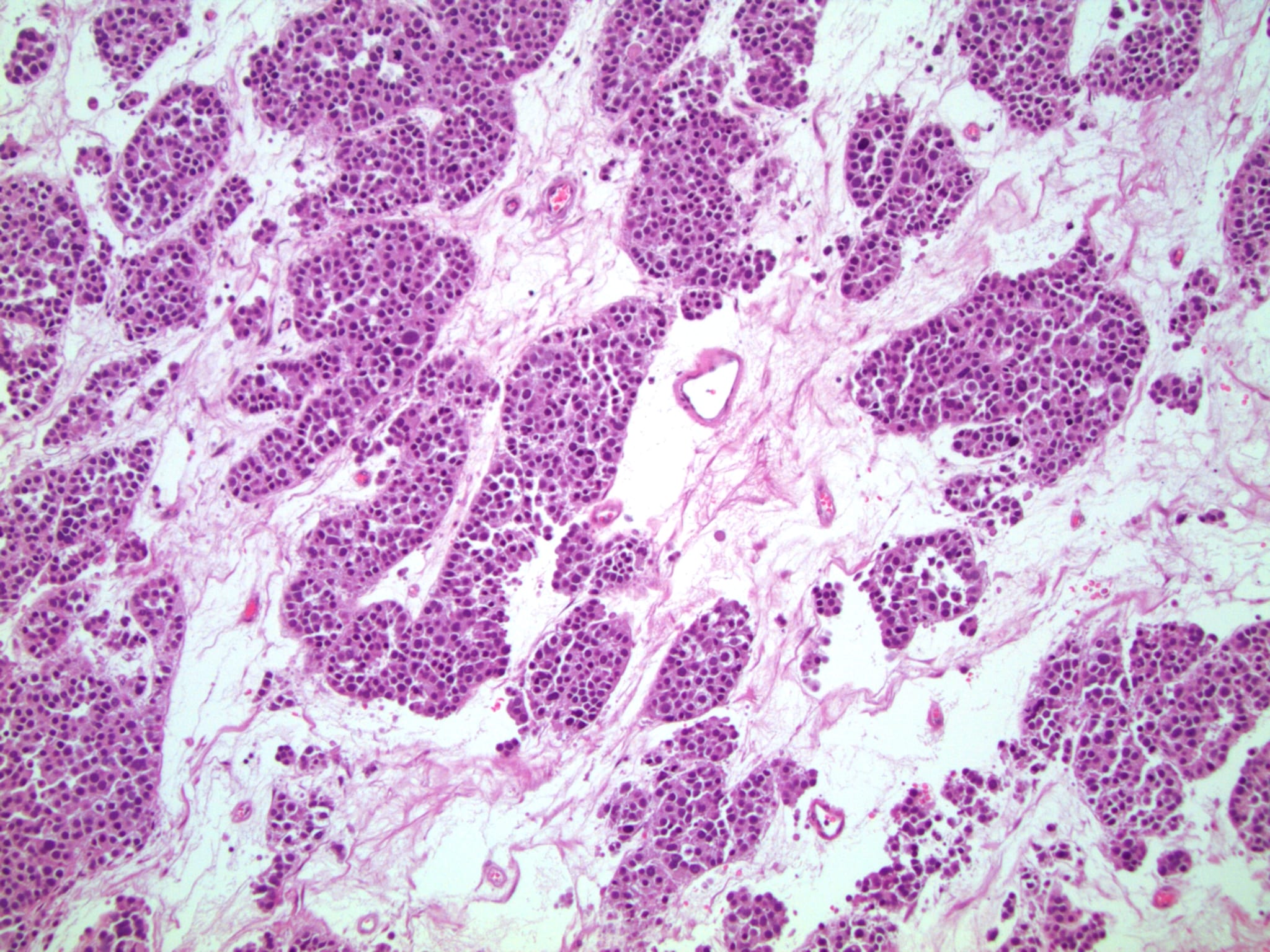
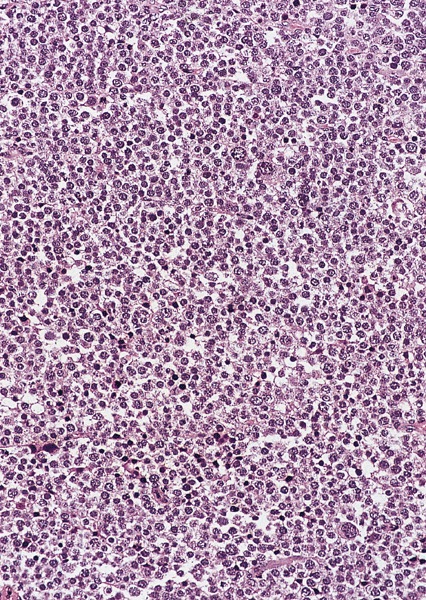
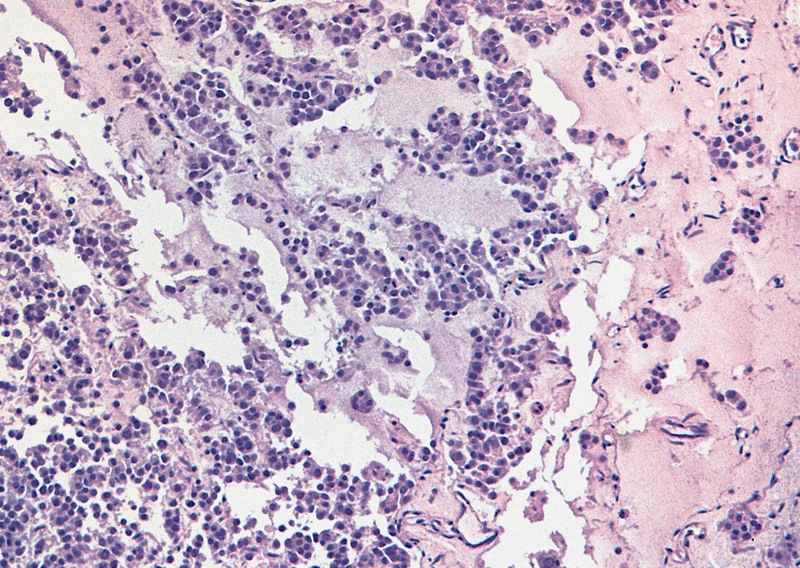
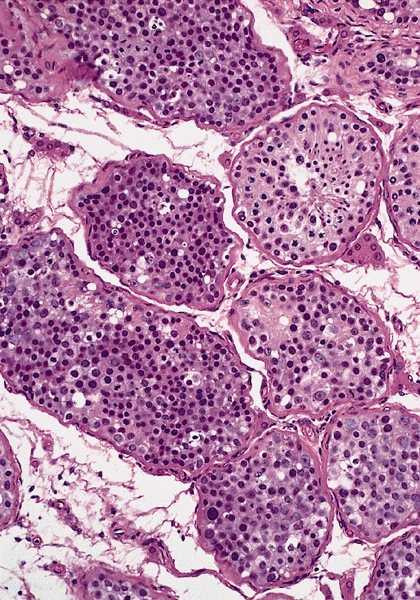
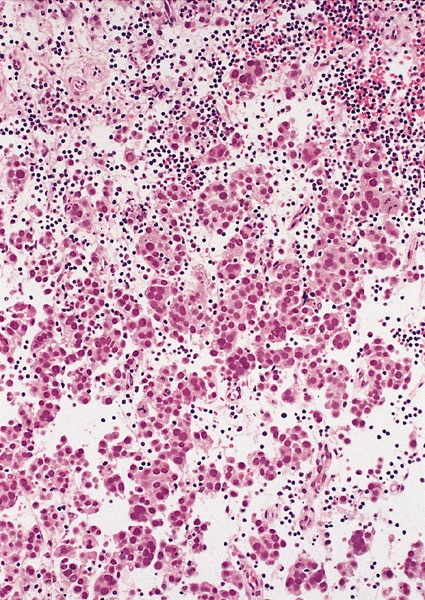
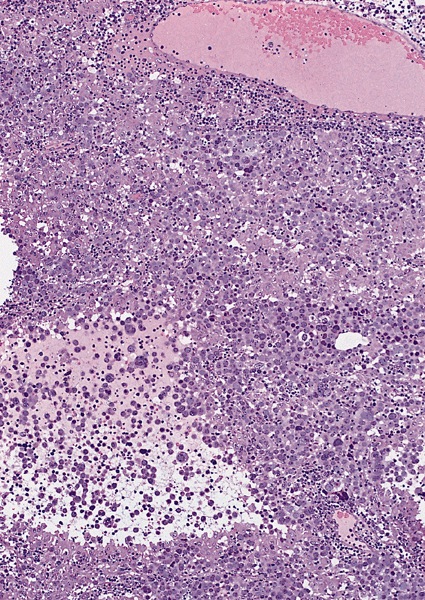
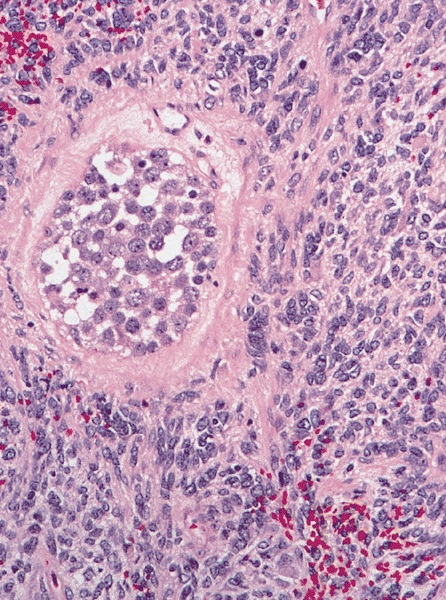
Microscopic (histologic) description
Low power magnification
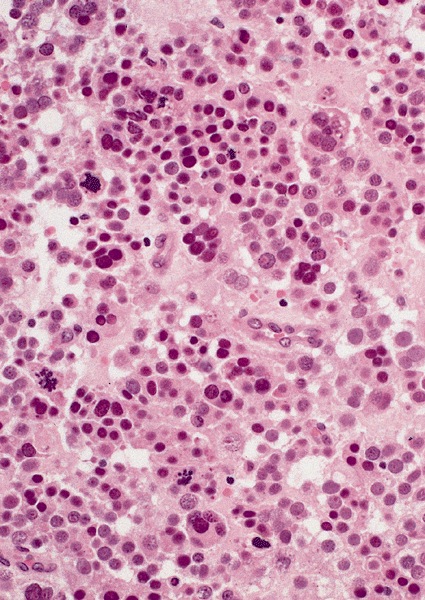
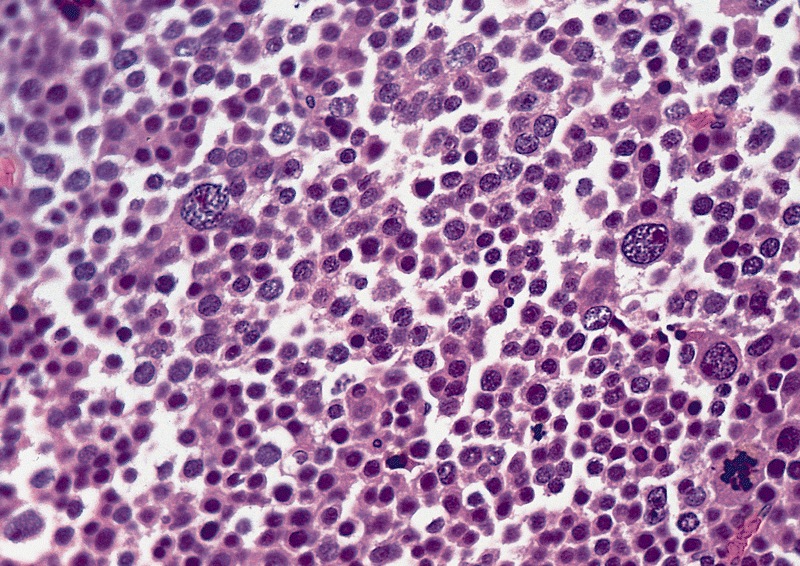
High power magnification
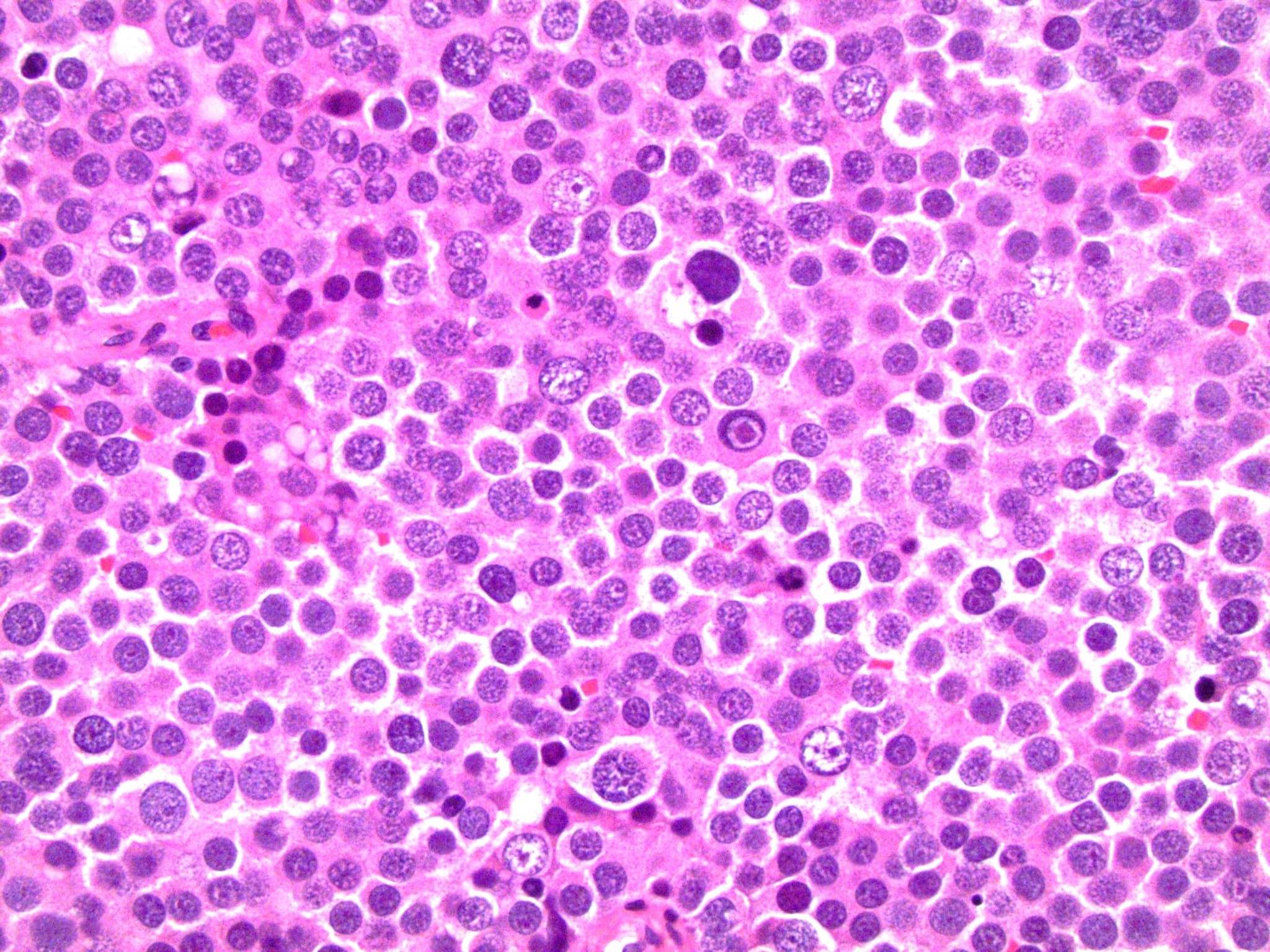
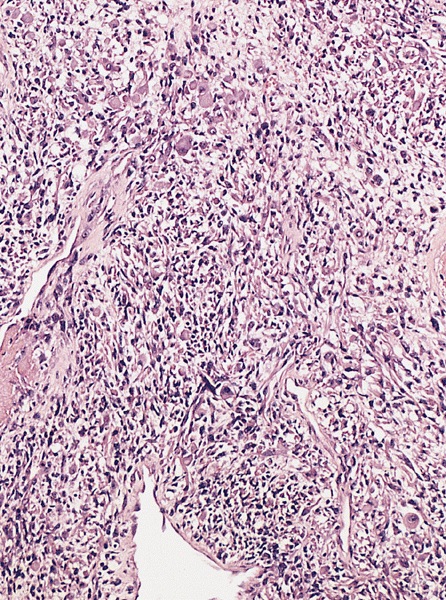
Spermatocytic tumor with sarcomatous differentiation
- Homogenous lesions show diffuse sheets of cells without evident fibrous septa and lymphocytic infiltrates
- Multinodular lesions show bands of loose fibrovascular tissue separating nodules (with or without lymphocytic infiltrates) and without remnants of testicular parenchyma between nodules
- Spaces filled with clear to pink fluid can be present and they can have different shapes:
- Irregular pseudocystic areas of variable size
- Pseudofollicular (roundish edematous areas surrounded by neoplastic cells)
- Microcystic spaces which separate ST into anastomosing islands with peripheral palisade of cells
- Usually expansive neoplastic profile, although corded pattern of growth with intertubular neoplastic cells can be present at the periphery of the lesion
- Neoplastic nodules can be boarded by a rim of fibrin (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1)
- Usually confined to testicular parenchyma, although it may involve the rete testis, the epididymis or the tunica albuginea
- Nonneoplastic testicular parenchyma can have a mild degree of atrophy
High power magnification
- Landmark feature - tripartite cytology with cells of 3 different sizes:
- Small cells (6 - 8 microns)
- Round dark nuclei
- Narrow rim of eosinophilic cytoplasm
- They resemble lymphocytes
- Intermediate size cells (15 - 20 microns)
- Round nuclei with granular to filamentous chromatin (so called spireme-like chromatin, after the thread-like chromatin at the beginning of prophase)
- Usually no evident nucleoli, although they might be present
- Dense eosinophilic to amphophilic cytoplasm with no glycogen
- Poorly defined cytoplasmatic membranes
- Clearer cells with distinct membranes can be found close to edematous areas
- Giant cells (50 - 150 microns)
- 1 or more nuclei with the same features of medium cells
- Eosinophilic cytoplasm with the same features of medium cells
- Small cells (6 - 8 microns)
- Size distribution can vary among different cases (usually medium cells > small cells > giant cells)
- Mitoses (even atypical) and apoptotic bodies can be abundant
- Stroma is scant, with only small strips of connective tissue
- Lymphocytic infiltrates are scant to absent, both among neoplastic cells and within connective tissue strips
- Granulomas are usually not present and only rarely reported
- Intratubular extension of ST can be identified around the main lesion
- Germ cell neoplasia in situ is not present
- Intravascular invasion can be present
- Not associated with other forms of germ cell tumor
- Anaplastic spermatocytic tumor:
- Not currently considered a WHO subtype of ST
- No convincing clinical evidence of aggressive behavior
- Characterized by areas of relatively monomorphic intermediate sized cells with prominent nucleoli
- Areas of conventional ST can be found elsewhere in the tumor
Spermatocytic tumor with sarcomatous differentiation
- Considered a WHO subtype of ST
- Rare occurrence with poor prognosis
- Sarcomatous component usually features a high grade spindle cell morphology
- Other possible differentiations are rhabdomyosarcoma and chondrosarcoma
- Sarcoma cells can interdigitate with ST cells or grow juxtaposed to ST
- Sarcoma and ST can represent variable percentages of the lesion
- Cases with only a minor ST residual component can be difficult to recognize
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Maurizio Colecchia, M.D., Case #448 and AFIP images
Cytology description
- High cellularity
- Predominantly single cells
- Tripartite cytology with 3 different sizes of cells (small, intermediate and large), with a preponderance of intermediate sized cells
- Absence of tigroid background (foamy material attributed to the fragile glycogen rich cytoplasm of seminomas)
- No lymphocytes (Diagn Cytopathol 1999;20:233)
Positive stains
- CD117
- SALL4
- DMRT1
- NUT (specificity 100%, sensitivity 41% when positivity is present in ≥ 50% of neoplastic cells with equal intensity to spermatogonia internal control) (Histopathology 2014;65:35)
- OCT2
- SSX2
Negative stains
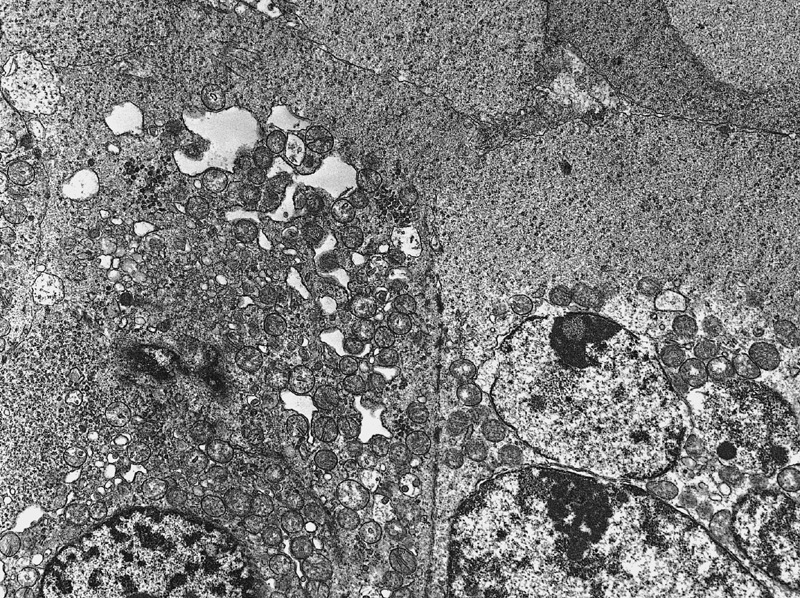
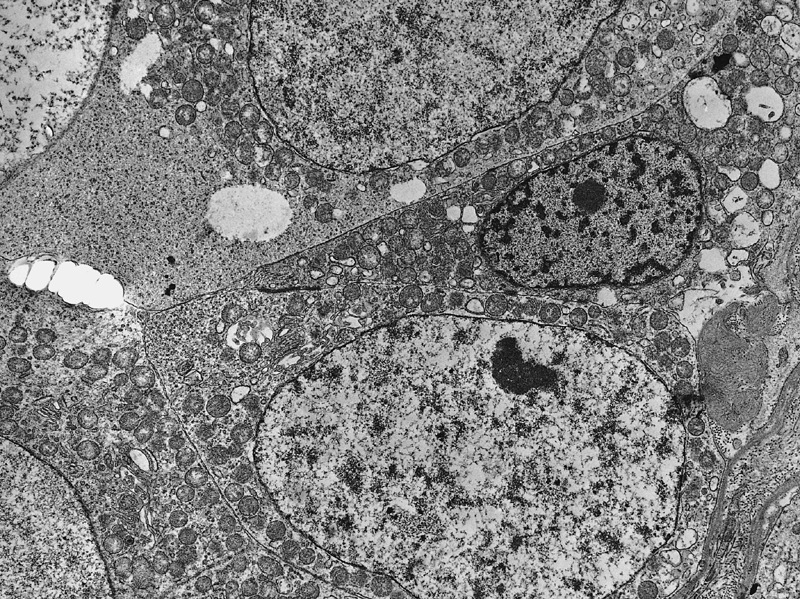
Electron microscopy description
- Intercellular bridges between tumor cells identical to those between spermatocytes and between spermatids (Cancer 1969;24:103)
- Syncytial formation
- Scanty or absent cytoplasmatic glycogen and lipids
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Aneuploid
- Classically without 12p abnormalities
- Presence of 12p amplification (hybrid genetics) might be linked to the development of metastases or anaplastic morphology (Pathology 2018;50:562, Hum Pathol 2022;124:85)
- Amplification of chromosome 9p is the most frequent genetic abnormality, with a consequent amplification of the DMRT1 gene locus (Cancer Res 2006;66:290, Hum Pathol 2022;124:85)
- Other gains include chromosome 1 and 20
- Partial loss of chromosome 22 can be present
- Mutations are infrequent
- Activating mutations of HRAS and FGFR3 can be present, especially in elderly patients (PLoS One 2017;12:e0178169)
- Epigenetics: loss of biparental imprinting with re-establishment of paternal imprinting
Sample pathology report
- Testicle, partial / radical orchiectomy:
- Spermatocytic tumor
- Immunohistochemistry (supporting the above diagnosis): neoplastic cells are CD117+, SALL4+, OCT3/4-
- Infiltration of rete testis present / absent; infiltration of epididymis present / absent; infiltration of hilar fat present / absent; infiltration of spermatic cord present / absent; infiltration of rete testis present / absent; infiltration of tunica vaginalis / scrotal wall testis present / absent
- Lymphovascular invasion present / absent
- Surgical margin involved / not involved by neoplasia
Differential diagnosis
- Diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) of the testis:
- DLBCL is the most common testicular neoplasia in the elderly
- Often bilateral
- Diffuse growth of monomorphic cells
- Scant stroma
- LCA (CD45)+, CD20+, PLAP-, OCT3/4-
- Seminoma:
- Seminoma is more frequent than ST in the elderly
- Seminoma cells are monomorphic with squared off nuclei
- Fibrous stroma with more prominent lymphocytic infiltrates and often granulomatous reaction
- Germ cell neoplasia in situ present; either pure or mixed with other types of germ cell neoplasia
- PAS+, PLAP+, SALL4+, CD117+, OCT3/4+, D2-40+
- Embryonal carcinoma:
- Yolk sac tumor with microcystic edema:
- Usually in young patients
- Elevated AFP blood levels
- Schiller-Duval bodies
- Uniform cells with clear or vacuolated to lightly eosinophilic cytoplasm
- Germ cell neoplasia in situ present; rarely pure, usually mixed with other types of germ cell neoplasia
- Glypican 3+, AFP+, SALL4+, AE1 / AE3+
- Germ cell neoplasia in situ (GCNIS):
- Intratubular spread of ST can be mistaken for GCNIS
- GCNIS features thickened basement membrane (versus nonthickened in intratubular ST), single layer of monomorphic neoplastic cells above the basement membrane (versus tubules at least partially filled with tripartite cytology in intratubular ST), lack of spermatogenesis (versus spermatogenesis partially retained in some tubules in intratubular ST)
- PLAP+, SALL4+, CD117+, OCT3/4+, D2-40+
Additional references
Practice question #1
Which of the following answers is correct about spermatocytic tumor?
- It can be either pure or mixed with postpubertal teratoma
- It does not derive from germ cell neoplasia in situ
- It often presents as an extragonadal neoplasia
- The most frequent location is the mediastinum
Practice answer #1
Practice question #2
Practice answer #2