Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Rytych J, Krogh K, Yang GY, Escobar DJ. Mucinous pancreatic tumor overview. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/pancreasmucin.html. Accessed August 25th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Neoplasms within the pancreas characterized by predominant mucin production by the tumor cells
- Mucus: a substance that is 95 - 98% water and 2 - 5% solids, with > 60% of the solid component consisting of mucin (World J Gastroenterol 2011;17:4757)
- Mucin: a glycoprotein consisting of a polypeptide backbone with attached oligosaccharide conjugates
Essential features
- General term for benign, low or high grade dysplastic or malignant mucin producing epithelium within the pancreas
- 4 most prevalent types
- MCN and IPMN may harbor or develop into pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (small percentage); MCN may undergo transformation to cystadenocarcinoma as well (Pancreas 2017;46:745)
| Simple mucinous cyst / MNC | MCN | IPMN | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Age, decade | Sixth - seventh | Fourth - fifth | Sixth - seventh | Sixth - eighth |
| Location | Head = body = tail | Body / tail > head | Head > body / tail | Head > body / tail |
| Sex predilection | F > M | F >>> M | Main duct: M > F Branch duct: F > M |
M > F |
| CEA | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | N / A |
| Amylase | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ | N / A |
| Pancreatic duct communication | Rare | No | Yes | Yes |
| Precursor for invasive carcinoma | No | Yes | Yes | N / A |
| Cytologic atypia | No | Low grade / high grade | Low grade / high grade | N / A |
| Epithelium type | Flat | Flat or papillary | Papillary | Flat or papillary |
| Ovarian stroma | No | Yes | No | N / A |
| Molecular mutations | KMT2C, KRAS, BRAF, RNF43, CDKN2A, TP53, SMAD4 | KRAS, RNF43 (low grade); SMAD4, TP53 (high grade) | GNAS, KRAS, RNF43, TP53 | KRAS, TP53, CDKN2A, SMAD4, BRCA1/2 |
Terminology
- Simple mucinous cyst / mucinous nonneoplastic cyst
- Mucinous cystic neoplasm / mucinous cystadenoma
- Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm / carcinoma in situ
- Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma / duct cell adenocarcinoma / infiltrating duct carcinoma / tubular adenocarcinoma
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Simple mucinous cyst / mucinous nonneoplastic cyst (MNC)
- 2 - 7% of pancreatic cyst resections and 8 - 10% of mucinous cysts of the pancreas
- More common in women (F:M = 2.8:1), mean age of 64 years old (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330)
- Mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN)
- Comprises ~25% of resected pancreatic cystic neoplasms
- Almost exclusively in women (> 95%)
- Rare; 2 - 5% exocrine pancreatic tumors
- Most common in fourth through fifth decade (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330, Gut Liver 2015;9:571)
- Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN)
- May account for between 18 and 50% of resected cystic pancreatic lesions (Arch Surg 2009;144:448, Pancreas 2008;37:254, Pancreas 2011;40:779)
- Main duct IPMN is slightly more common in men (M:F = 1.1:1), while branch duct IPMN is more common in women (M:F = 0.76:1) (Diagnostics (Basel) 2022;13:65)
- Most common in sixth through seventh decade (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330)
- Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Most common pancreatic tumor (~90% of pancreatic cancer diagnoses)
- 80% occur in patients 60 - 80 years old
- Slightly more common in men (CA Cancer J Clin 2018;68:394)
- Colloid carcinoma / mucinous carcinoma is an uncommon variant with > 50% extracellular mucus production, accounting for 1 - 3%
Sites
- Simple mucinous cyst / mucinous nonneoplastic cyst (MNC)
- Occur equally in head / neck / uncinate and body / tail (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330)
- Mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN)
- > 95% arise in the distal pancreas as a single lesion (Gut Liver 2015;9:571)
- Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN)
- Can occur anywhere in the pancreas, most common in the head (~58%) (Am J Clin Pathol 2020;154:559)
- Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- 60 - 70% occur in pancreatic head
- Usually solitary, occasionally multifocal (Surg Pathol Clin 2016;9:547)
Pathophysiology
- Simple mucinous cyst / mucinous nonneoplastic cyst (MNC)
- Unknown pathogenesis but may develop from acinar ductal mucinous metaplasia (Hum Pathol 2010;41:513, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330)
- Mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN)
- Stromal component possibly derived from ovarian primordium / Müllerian type stroma or primary yolk cells implanted in the pancreas during embryogenesis (Am J Surg Pathol 1999;23:410, Dig Surg 2006;23:186)
- Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN)
- Histologically arising in the pancreatic main duct, branch duct or combined (Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2010;8:213)
- Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Arises from pancreatic duct epithelia
- Precursor lesions include intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN), mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN) and pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN)
Etiology
- Simple mucinous cyst / mucinous nonneoplastic cyst (MNC)
- Unclear etiology
- Mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN)
- No known etiology
- Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN)
- In one study, most patients with IPMN were cigarette smokers (Adv Anat Pathol 1999;6:65)
- Patients with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, familial adenomatous polyposis and McCune-Albright syndrome are at increased risk (Adv Anat Pathol 1999;6:65, Gut 2002;51:446, Virchows Arch 2017;470:391)
- Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Strongly associated with cigarette smoking (2 - 3x increased risk)
- History of pancreatitis (2 - 10 fold increased risk)
- Obesity / diet (risk increases with increasing body mass index [BMI])
- Hereditary pancreatic cancer syndrome (due to an underlying germline mutation)
- Familial pancreatic cancer syndrome (defined as pancreatic cancer in at least 2 first degree relatives without an underlying germline mutation)
- Other possible factors: high alcohol consumption, previous gastric surgery and diabetes (Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016;1:298, Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016;1:226, Medicine (Baltimore) 2017;96:e5908)
Clinical features
- Simple mucinous cyst / mucinous nonneoplastic cyst (MNC)
- Half of patients are asymptomatic; others report abdominal pain or jaundice (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330)
- Mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN)
- More than half of patients are asymptomatic
- Causes compression of adjacent structures
- Symptoms include a palpable mass in the epigastric region and nonspecific abdominal pain or distension (World J Gastrointest Oncol 2020;12:642)
- Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN)
- Majority are asymptomatic; often incidental
- Symptoms present in 2 - 20% of patients and include epigastric pain, weight loss, diabetes and jaundice (Gut Liver 2015;9:571, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2022;146:298)
- Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Most commonly reported symptoms: loss of appetite (~45%), jaundice (~41%) and abdominal pain (40%)
- Other symptoms include weight loss, back pain, new onset diabetes, depression, migratory thrombophlebitis and acute pancreatitis (Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2004;2:510)
Diagnosis
- Overall, diagnosis of mucinous cysts and neoplasms of the pancreas relies on
- Cyst fluid analysis obtained from endoscopic ultrasound guided fine needle aspiration (EUS FNA)
- Cytology analysis (EUS FNA)
- Histologic analysis of surgical resection
- Reference: Front Physiol 2022;13:856803
Laboratory
- Simple mucinous cyst / mucinous nonneoplastic cyst (MNC)
- Cyst fluid often shows variably elevated carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and amylase
- Mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN)
- Serum tumor markers include CEA, CA 19-9, TAG-72, CA 15-3 or MCA and low levels of amylase
- Cyst fluid often shows elevated CEA, CA 19-9 and low amylase
- Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN)
- Serum amylase and lipase are elevated
- Cyst fluid shows elevated CEA and amylase
- Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Serum tumor markers include CA 19-9, CEA
- Cyst fluid has high levels of CA 19-9, DUPAN-2, CEA, Span-1 (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330, Front Physiol 2022;13:856803)
Radiology description
- Simple mucinous cyst / mucinous nonneoplastic cyst (MNC)
- Single unilocular or multilocular cyst (Front Physiol 2022;13:856803)
- Mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN)
- Well defined multilocular or unilocular thick walled cyst
- No connection with the main pancreatic duct (Front Physiol 2022;13:856803)
- Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN)
- Dilated main pancreatic duct in main duct type IPMN
- Branch duct IPMN typically produces a grape-like cyst
- Mural nodules may correspond to high grade dysplasia (Front Physiol 2022;13:856803)
- Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Irregular, solid hypodense mass
- Double duct sign (dilation of both the biliary and pancreatic ducts) is pathognomonic (Radiology 2011;260:446)
Prognostic factors
- Simple mucinous cyst / mucinous nonneoplastic cyst (MNC)
- Not associated with progression or invasive carcinoma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330)
- Mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN)
- 5 year survival rate of 96 - 100% after surgical resection (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:179, World J Surg Oncol 2020;18:287)
- No survival difference between MCNs with low grade or high grade dysplasia (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:578)
- Invasion limited to the ovarian type stroma, cystic septa or capsule has a favorable outcome (5 year survival 100%), while extracapsular invasion is associated with poor survival (J Pathol Clin Res 2021;7:507)
- Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN)
- Absence of invasive carcinoma is the most important prognostic factor (Hum Pathol 2012;43:1)
- Main duct type shows highest incidence of invasive adenocarcinoma (30 - 50%)
- Branch type without mural nodules are more commonly found with low grade dysplasia (~24% with invasion) (Dig Liver Dis 2012;44:257, Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:1372, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2022;146:298)
- Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Most ductal adenocarcinomas are fatal (5 year survival ~5%)
- Survival time is longer in patients with tumors confined to the pancreas or < 3 cm in diameter
- Tumors in the body or tail tend to present at a more advanced stage (Cancer Res 2014;74:2913, J Gastrointest Surg 2000;4:567)
- Colloid carcinomas have a better prognosis than conventional adenocarcinomas with a 5 year survival rate of > 55% (Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:571)
Case reports
- 32 year old woman with a large mucinous cystic neoplasm of the pancreas arising during pregnancy (J Surg Case Rep 2020;2020:rjaa085)
- 63 year old man with a 2 year history of abdominal pain without weight loss and a simple mucinous cyst (Virchows Arch 2021;479:179)
- 72 year old woman with pancreatic ductal carcinoma arising in pancreatic remnant 13 years after resected IPMN (Mol Clin Oncol 2018;8:417)
- 78 year old woman with a bowel obstruction and an intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (Radiol Case Rep 2023;18:1103)
- 91 year old woman with new onset diabetes mellitus and a pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (Cureus 2022;14:e31608)
Treatment
- Simple mucinous cyst / mucinous nonneoplastic cyst (MNC)
- Typically resected, may be treated conservatively with continued imaging follow up
- Mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN)
- Surgical resection is typical
- Can follow with close imaging surveillance for poor surgical candidates with MCN without high risk imaging findings (Gut Liver 2015;9:571)
- Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN)
- Surgical resection for main duct IPMNs
- Can follow with close imaging surveillance for branch duct IPMN < 3 cm without high risk imaging findings (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2022;146:298)
- Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Radical resection with or without chemotherapy
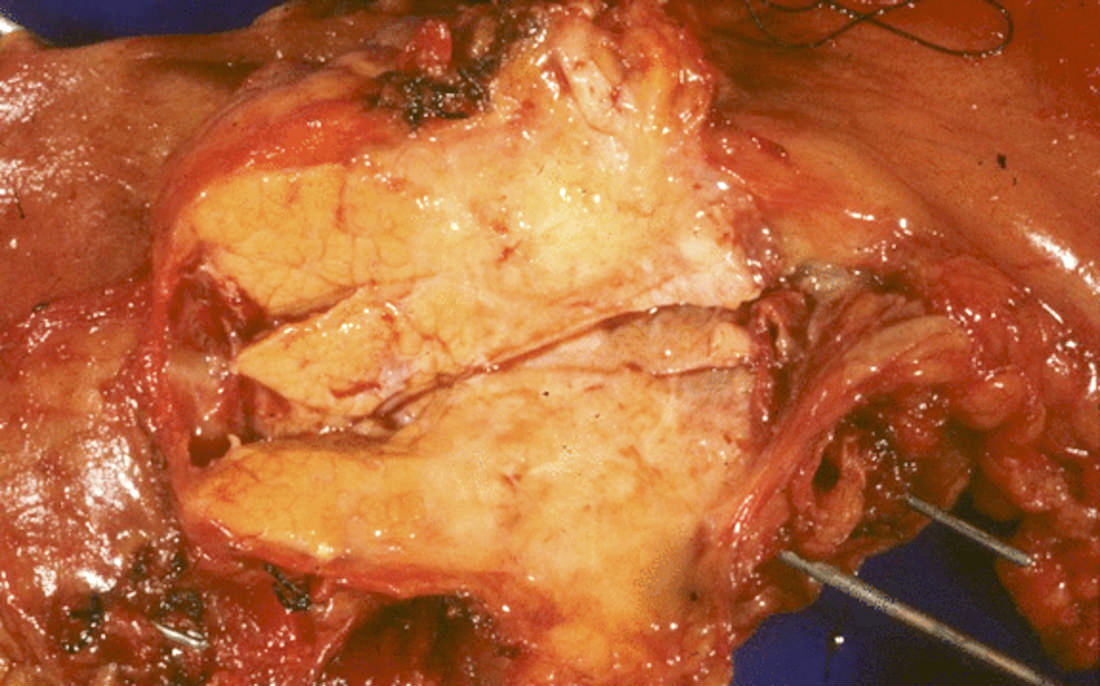
Gross description
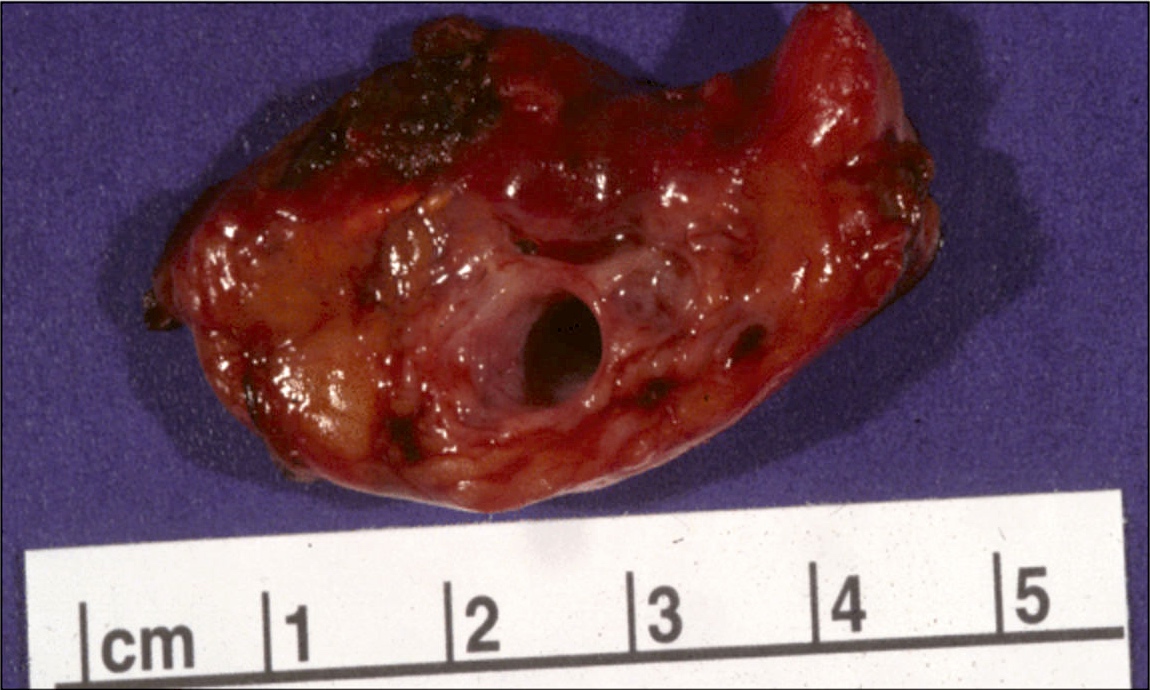
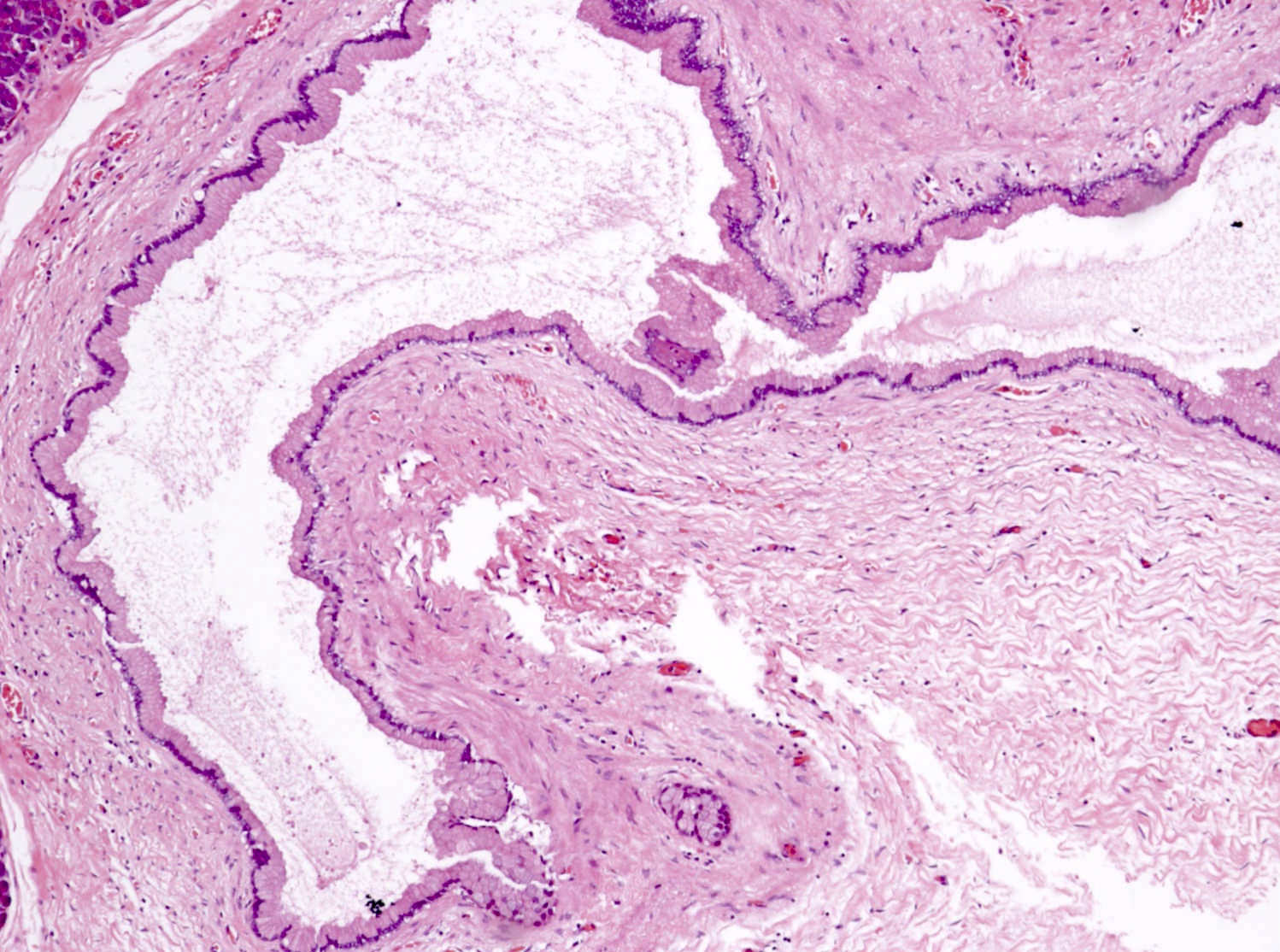
- Simple mucinous cyst / mucinous nonneoplastic cyst (MNC)
- Macroscopic cyst > 1 cm, usually 3 - 12 cm
- Unilocular or multilocular
- May contain clear, serous or mucinous fluid (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330)
- Mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN)
- 2 - 35 cm in greatest dimension
- Unilocular or multilocular, thick walls
- Round mass with smooth surface and fibrous pseudocapsule, can have papillary projections in higher grade lesions
- Calcifications may be present
- May contain thick mucin, hemorrhage or necrotic debris (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:179)
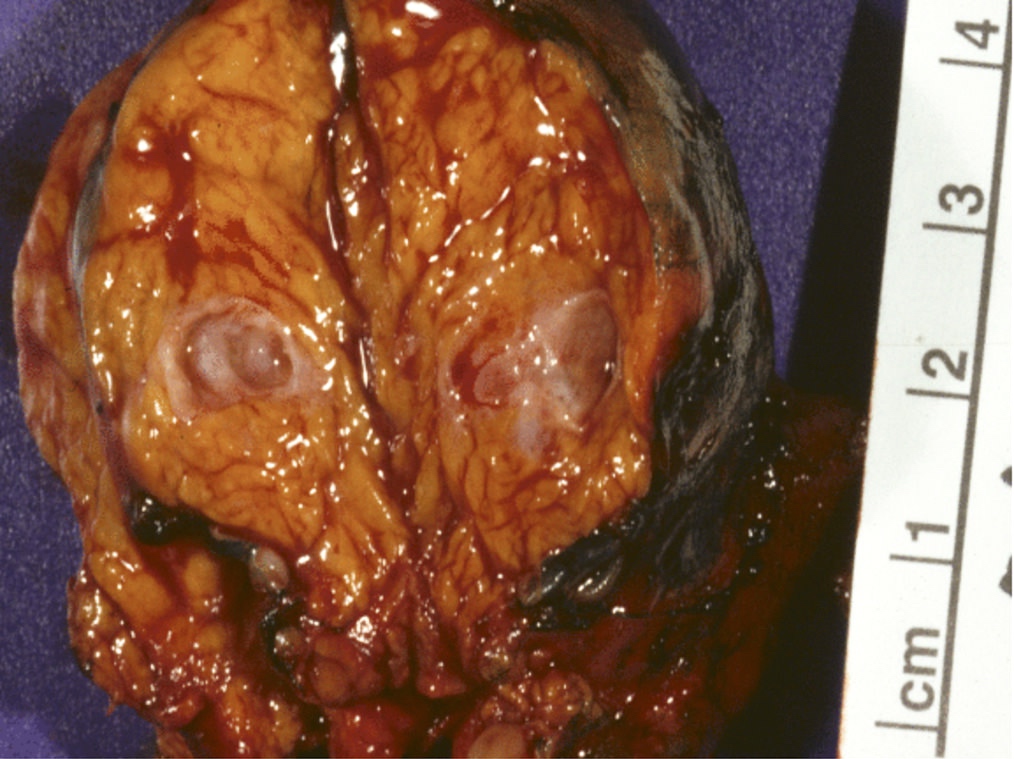
- Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN)
- 1 - 8 cm in greatest dimension
- Cystic, multiloculated
- Grape-like clusters in branch type
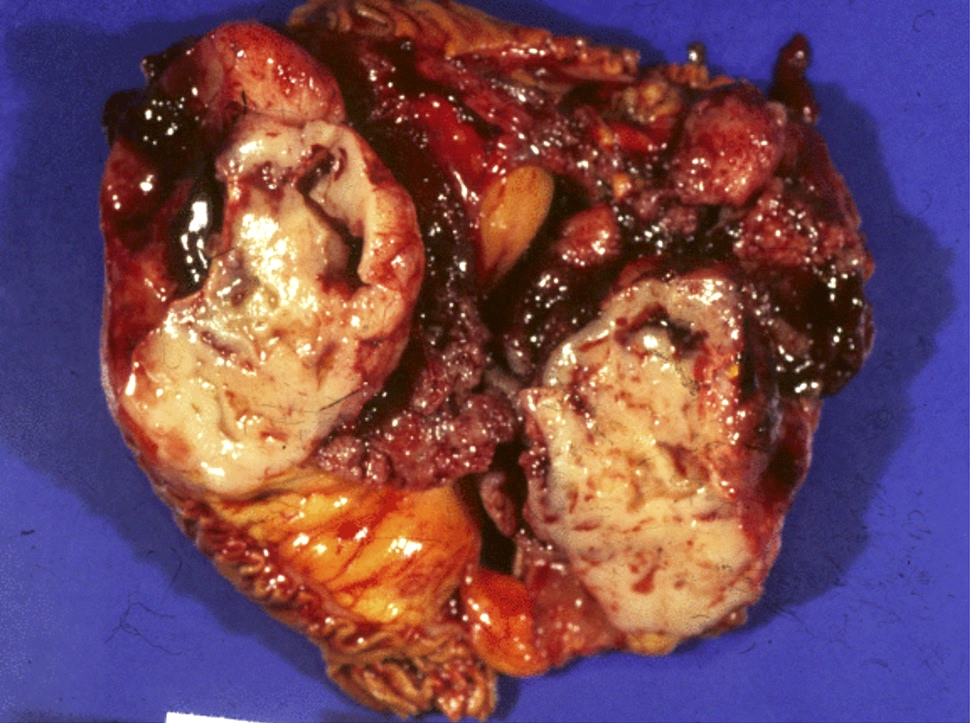
- Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Firm, poorly defined mass, with yellow to white cut surface
- Can be difficult to differentiate from background pancreatitis (HPB (Oxford) 2014;16:83)
Gross images
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Simple mucinous cyst / mucinous nonneoplastic cyst (MNC)
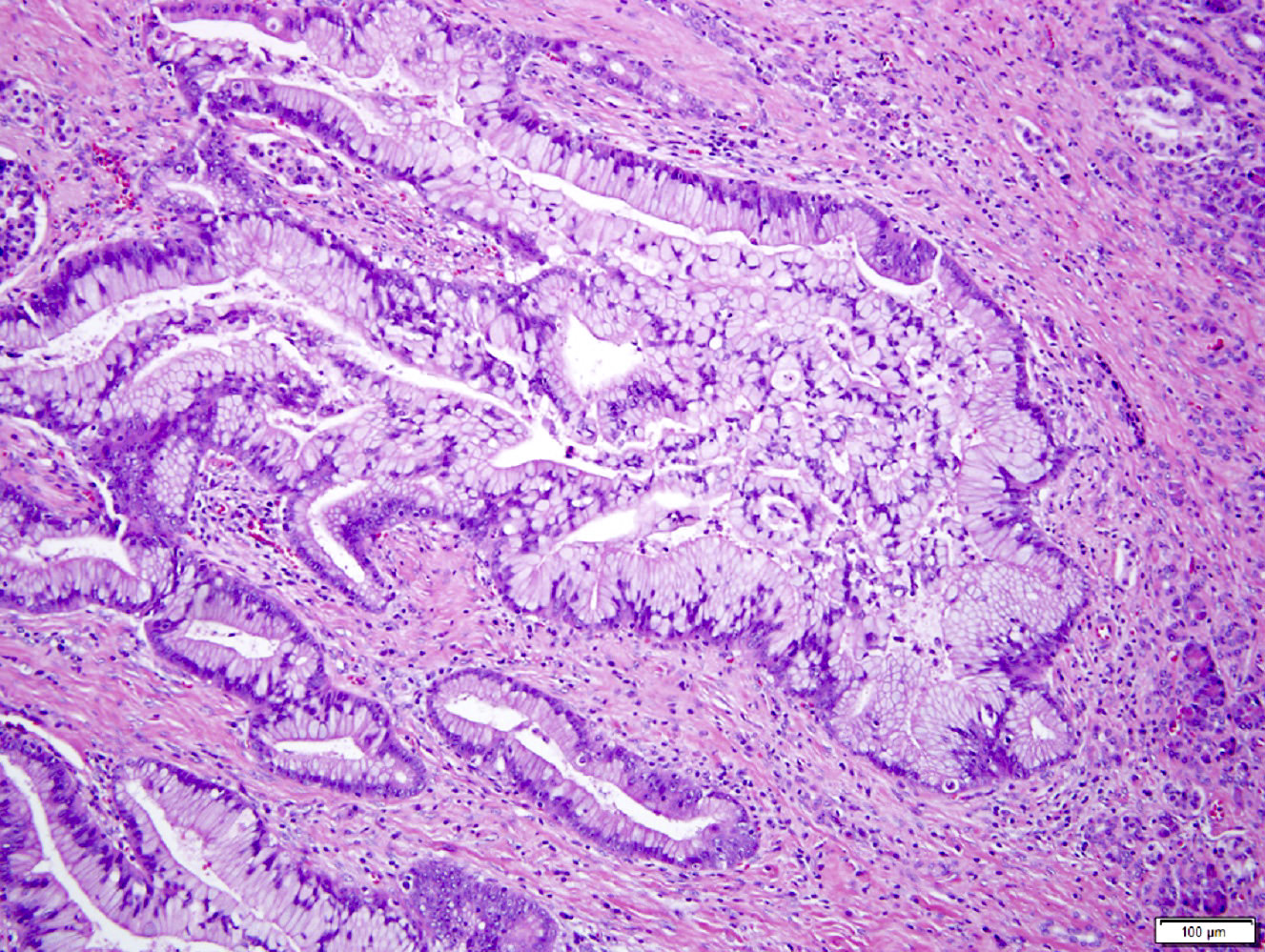
- Cyst lined by monolayer of cuboidal to columnar mucinous epithelium
- Usually has gastric phenotype
- No ovarian type stroma present
- Little to no cytologic atypia and no / minimal papillary excrescences in epithelial lining
- No malignant potential
- Rare cases of focal high grade dysplasia reported (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330)
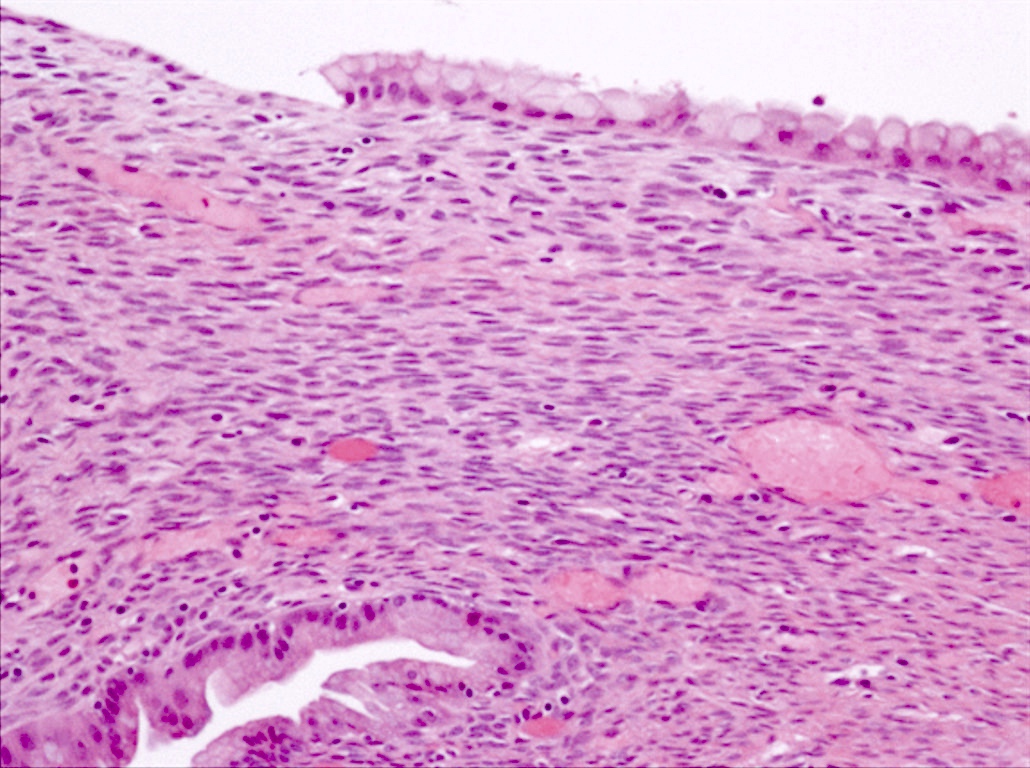
- Mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN)
- Cyst lined by 2 components
- Inner epithelial layer composed predominantly of mucin producing cells
- Outer densely cellular Müllerian / ovarian type stroma
- No connection to ducts
- Stroma can undergo luteinization, can have hilar-like cells and immunophenotypic sex cord stromal differentiation
- 2 tiered grading system
- Low grade: mild moderate atypia, mitoses and papillary projections uncommon
- High grade: severe atypia, papillae formation with irregular branching, loss of nuclear polarity, frequent mitoses
- Invasion seen in ~16% of MCN (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2022;146:298)
- Cyst lined by 2 components
- Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN)
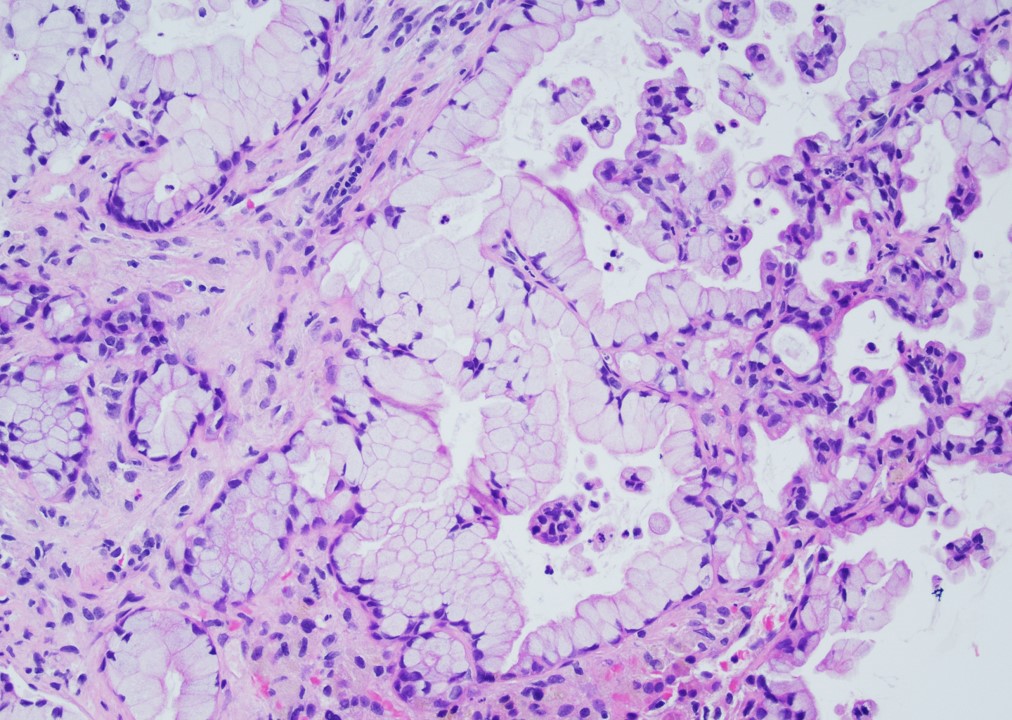
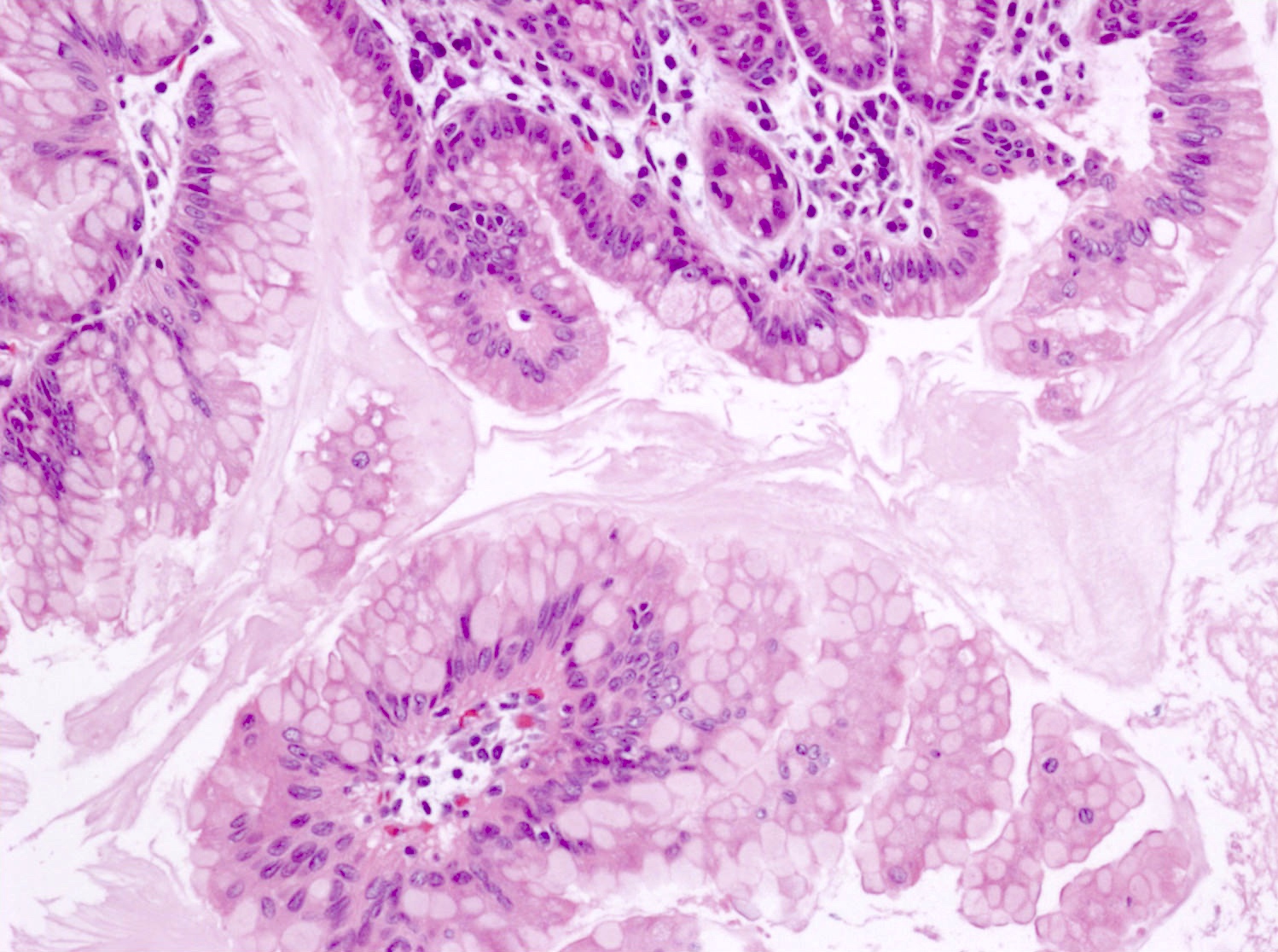
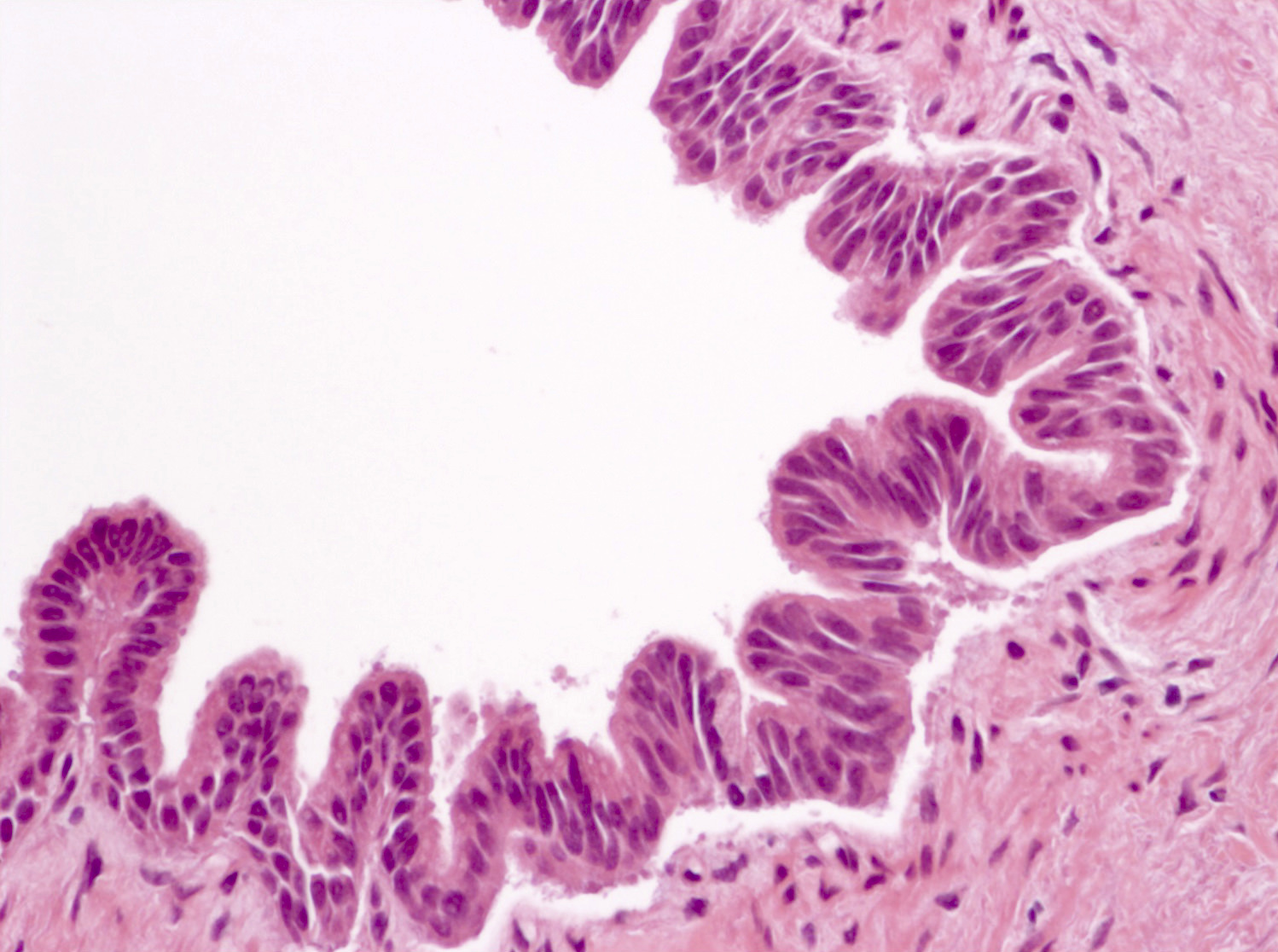
- Cyst lined by neoplastic columnar / mucinous epithelium that can be flat or form papillae
- 3 types of epithelium
- Intestinal type (~20%): resembles villous adenomas of the gastrointestinal tract; often contains high grade dysplasia
- Gastric type (~70%): resembles gastric foveolar epithelium; often low grade dysplasia
- Pancreatobiliary type (~10%): frequently involves the main duct, shows complex branching of papillae and often contains high grade dysplasia
- 2 tiered grading system
- Low grade: mild moderate atypia, mitoses are uncommon
- High grade: severe atypia, irregular branching and budding of papillae, loss of nuclear polarity, frequent mitoses (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2022;146:298)
- Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Classically shows well developed neoplastic glands that imitate normal pancreatic ducts in the background of desmoplastic stroma
- Neoplastic glands show an irregular and haphazard distribution with irregular contours and frequently contain neutrophils and necrotic debris
- Nuclear pleomorphism, prominent nucleoli and mitoses are typically frequent
- Mucin containing glands may be ruptured or poorly formed
- Most are well to moderately differentiated
- Grade (College of American Pathologists) based on extent of glandular differentiation
- Well differentiated (> 95% of tumor composed of glands)
- Moderately differentiated (50 - 95% of tumor composed of glands)
- Poorly differentiated (≤ 49% of tumor composed of glands)
- Colloid carcinoma is a subtype that contains ≥ 80% of neoplastic cells suspended in pools of mucin
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Simple mucinous cyst / mucinous nonneoplastic cyst (MNC)
- Cuboidal or columnar cells in strips or honeycomb sheets without significant atypia
- Background mucin and macrophages are frequently present (Pancreas 2013;42:27)
- Mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN)
- Cannot be distinguished from IPMN on cytology
- Low grade MCN will have low cellularity with a variable amount of mucin with histiocytes and bland epithelial cells
- High grade MCN will have low to moderate cellularity, variable amount of mucin, pleomorphic, atypical cells with a high nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio and frequent necrosis
- Ovarian type stroma is not typically present (Cancer Cytopathol 2017;125:169)
- Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN)
- Cannot be distinguished from MCN on cytology
- Low grade IPMN will have low cellularity with minimal nuclear atypia in epithelial cells and no background necrosis
- High grade IPMN will be more cellular with small epithelial cells with hyperchromatic, irregular nuclei and prominent background inflammation and necrosis in most cases (Cancer Cytopathol 2014;122:40)
- Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Typically highly cellular, often with background necrosis
- Tissue fragments are composed of cells with irregular nuclear spacing (drunken honeycomb), hyperchromatic nuclei with irregular contours and occasional atypical mitotic figures (Cancer 2003;99:44)
Positive stains
Negative stains
- Simple mucinous cyst / mucinous nonneoplastic cyst (MNC)
- Trypsin, CEA, synaptophysin, chromogranin A, calretinin, alpha inhibin, MUC1 (35% positive), MUC2 (1% positive), PR (8% positive)
- CDX2 (can be focally positive) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:121, Virchows Arch 2021;479:179)
- Mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN)
- MUC1 (can be aberrantly expressed in invasion), MUC2, pVHL (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2015;139:24)
- Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN)
- MUC2 (in biliary and gastric types)
- MUC1 (in gastric and intestinal types) (Front Physiol 2022;13:856803)
- Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- CK20, vimentin, synaptophysin, chromogranin, MUC2
- pVHL (positive in reactive ducts) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012;136:601, Hum Pathol 2013;44:503)
- SMAD4 / DPC4 loss seen in 55%; specific for malignancy (Am J Clin Pathol 2001;116:831)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Simple mucinous cyst / mucinous nonneoplastic cyst (MNC)
- KMT2C (62%), KRAS (15%), TP53 (15%), BRAF (8%), RNF43 (8%), CDKN2A (8%), SMAD4 (8%)
- No mutations detected in 31% of cases (Hum Pathol 2020;101:1)
- Mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN)
- KRAS (21 - 46%) and RNF43 (~50%) mutations in low grade lesions
- Inactivating and TP53 mutations in more advanced MCN
- No GNAS mutations (Gut Liver 2015;9:571, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011;108:21188, J Gastrointest Surg 2020;24:1201, Virchows Arch 2022;480:1189)
- Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN)
- Commonly mutated: KRAS (90%), GNAS (40 - 60%), RNF43 (25%), TP53 (10%)
- Lower frequency: CDKN2A, CTNNB1, IDH1, STK11, PTEN (World J Gastroenterol 2021;27:2710)
- Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Key drivers
- TP53 is inactivated in 50 - 75%
- KRAS: 70 - 95%, early event
- CDKN2A (p16): > 95%
- SMAD4: ~50 - 55%
- BRCA1 / BRCA2: 5 - 10%
- Other less common alterations: microsatellite instability (MSI), BRAF mutations, MGMT promotor hypermethylation (Cancer Cell 2017;32:185, World J Gastroenterol 2021;27:2710)
- Key drivers
Sample pathology report
- Distal pancreas and spleen, distal pancreatectomy and splenectomy:
- Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) (3.0 cm), low grade, involving branch ducts (see comment)
- Comment: Pancreatic resection margin, negative for dysplasia. No high grade dysplasia or invasive component was identified. 13 lymph nodes with reactive changes (0/13).
Differential diagnosis
Additional references
Practice question #1
A 55 year old woman presents with a pancreatic cyst incidentally detected on abdominal imaging. The cyst is located in the head of the pancreas and measures ~3 cm in size. Endoscopic ultrasound guided fine needle aspiration (EUS FNA) is performed and analysis of the cyst fluid reveals the following laboratory values: high CEA level, elevated amylase and low viscosity. A picture of the resection specimen is shown above. Which of the following statements is true about the most likely diagnosis?
- This lesion can display multiple histologic subtypes that resemble gastric, intestinal or pancreatobiliary epithelium
- This lesion does not commonly connect with the pancreatic duct system
- This lesion is not a precursor for invasive ductal adenocarcinoma
- VHL is the most commonly mutated gene in this lesion
Practice answer #1
A. This lesion can display multiple histologic subtypes that resemble gastric, intestinal or pancreatobiliary epithelium. This lesion in the head of the pancreas with elevated CEA and amylase levels in the cyst fluid is an intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN). The epithelium in IPMNs most commonly resembles gastric epithelium, with intestinal and pancreatobiliary types being less common.
Answer B is incorrect because IPMNs connect with the pancreatic duct system, which causes an increase in amylase levels in the cyst fluid. Other pancreatic cysts such as mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN) and simple mucinous cysts do not typically connect with the pancreatic duct system.
Answer C is incorrect because invasive carcinomas are found in ~30 - 50% of main duct IPMNs and ~24% of branch duct IPMNs.
Answer D is incorrect because VHL is commonly mutated in serous cystadenomas, not IPMNs.
Comment Here
Reference: Mucinous pancreatic tumor overview
Comment Here
Reference: Mucinous pancreatic tumor overview
Practice question #2
A 45 year old woman presents with abdominal discomfort and a large cystic lesion in the tail of the pancreas on abdominal imaging. Endoscopic ultrasound guided fine needle aspiration (EUS FNA) is performed and analysis of the cyst fluid reveals elevated levels of CEA, CA 19-9 and low amylase. A picture of the resection specimen is shown above. Which of the following statements about this pancreatic lesion is true?
- This lesion contains ovarian type stroma and is most commonly seen in females
- This lesion is most commonly seen in older men with a history of chronic pancreatitis
- This lesion is typically a benign cystic tumor that contains serous fluid
- These lesions are typically associated with elevated levels of amylase and CEA in the cyst fluid
Practice answer #2
A. This lesion contains ovarian type stroma and is most commonly seen in females. This female patient with a cystic lesion in the tail of the pancreas with elevated CEA, CA 19-9 and low amylase has a mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN). MCNs are characterized by the presence of ovarian type stroma and are seen almost exclusively in females (> 95%).
Answer B is incorrect because pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas are more commonly associated with older men with a history of chronic pancreatitis. MCNs are seen in female patients and are not associated with chronic pancreatitis.
Answer C is incorrect because serous cystadenomas are benign cystic tumors that contain serous fluid. MCNs contain mucin and are characterized as low grade or high grade lesions with ~16% associated with invasive carcinoma.
Answer D is incorrect because the cyst fluid of MCNs typically has elevated CEA and CA 19-9 but has low amylase levels because they do not connect to the pancreatic duct system. The presence of elevated amylase and CEA levels in pancreatic cyst fluid is most often associated with an intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN).
Comment Here
Reference: Mucinous pancreatic tumor overview
Comment Here
Reference: Mucinous pancreatic tumor overview