Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Immunofluorescence description | Immunofluorescence images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Electron microscopy images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Toklu A, Dehner C. Amyloidosis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skinnontumoramyloidosis.html. Accessed August 27th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Amyloidosis is characterized by extracellular deposition of amorphous material that has fibrillar morphology and is composed of insoluble misfolded autologous proteins
- Amyloid deposition can involve a solitary site or multiple organs
Essential features
- Characterized by extracellular deposition of misfolded autologous proteins arranged in a fibrillary form
- Amyloid deposits appear as amorphous eosinophilic material on H&E and show characteristic staining with Congo red yielding apple green birefringence under polarized light
- Amyloidoses with skin involvement are clinically classified into 2 main groups: systemic and localized; further subclassification is mainly based on the etiology, type of amyloid protein involved and pattern of deposition
- Systemic amyloidosis needs to be ruled out by clinical history and laboratory tests for diagnosis of primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Primary and myeloma associated systemic amyloidosis
- Cutaneous involvement in ~1/3 of patients (Int J Dermatol 2019;58:1062)
- Elderly population
- Secondary systemic amyloidosis
- Rare skin involvement
- Well documented in hemodialysis patients (Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 2023;11:e5039)
- Hereditary / familial amyloidosis
- Mainly associated with multisystemic diseases and autoinflammatory conditions (familial Mediterranean fever, Muckle-Wells syndrome, familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome, familial autoimmune polyneuropathy) (Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2003;17:929)
- Amyloid elastosis, very rare
- Macular amyloidosis, lichen amyloidosis and biphasic amyloidosis
- Adult population is affected, macular amyloidosis in a slightly younger population compared to lichen amyloidosis
- Macular amyloidosis affects female patients more than male patients (J Dermatol 1999;26:305)
- Lichen amyloidosis and macular amyloidosis are the most frequent types of primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis
- More common in Southeast Asia, South America and Middle East (skin phototype III - V); rare in Europe and North America (Clin Dermatol 1990;8:20, Australas J Dermatol 2023;64:e121)
- Nodular amyloidosis (NA)
- Rare
- Adult population, sixth decade is most common
- No clear gender predilection
- Familial primary cutaneous amyloidosis
- Very rare
- Autosomal dominant, shows genetic heterogeneity (Exp Dermatol 2010;19:416)
- Secondary localized cutaneous amyloidosis
- Associated with many cutaneous neoplasms such as squamous cell carcinoma in situ, melanocytic nevi, basal cell carcinoma
- Reference: Calonje: McKee’s Pathology of the Skin, 5th Edition, 2019
Sites
- Primary and myeloma associated systemic amyloidosis → head and neck, face, periorbital area, hands, flexural regions and rarely genitalia (Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2023;16:987)
- Hemodialysis associated amyloidosis → mostly on buttocks (Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 2023;11:e5039)
- Lichen amyloidosis → predilection for extensor surfaces of the extremities, torso
- Macular amyloidosis → trunk; predilection for interscapular area (often overlying skin affected by notalgia parasthetica) (J Clin Med 2023;12:7672)
- Nodular amyloidosis → predilection for acral areas but can occur in any site including face, extremities, torso and genitalia (Arch Dermatol 2003;139:1157)
Pathophysiology
- Primary and myeloma associated systemic amyloidosis
- Amyloid derived from immunoglobulin light chains (AL), kappa or lambda
- Secondary systemic amyloidosis
- Amyloid A protein (AA), derived from a serum acute phase reactant (Rheum Dis Clin North Am 2018;44:585)
- Beta 2 microglobulin derived amyloid in dialysis related amyloidosis (J Dermatol 2005;32:410)
- Hereditary / familial amyloidosis
- AA amyloid or transthyretin depending on the associated disease (Ann Neurol 2017;82:44)
- Amyloid elastosis
- Considered to be a very rare variant of AL amyloidosis
- Elastin fibers covered by amyloid (Am J Dermatopathol 2022;44:43)
- Macular amyloidosis, lichen amyloidosis and biphasic amyloidosis
- Keratin derived amyloid, amyloid K (AK) resulting from degenerated keratinocytes
- Nodular amyloidosis
- Immunoglobulin light chain derived amyloid (AL), very rarely AK (Am J Dermatopathol 2015;37:e129)
- Risk of progression to systemic amyloidosis
Etiology
- Lichen amyloidosis and macular amyloidosis
- Keratinocyte theory: repeated minor trauma, friction, prolonged exfoliation and scratching cause damage to the epidermis, keratinocyte degeneration and release of keratin protein that subsequently gets phagocytosed by macrophages to be disposed; however, the disposal mechanism is disrupted for unclear reasons and keratin derived amyloid is formed
- Lichen amyloidosis is reported to be associated with autoimmune disorders, MEN2a syndrome (10% of lichen amyloidosis patients), chronic EBV infection and HIV infection have been documented (Thyroid 2002;12:1149, Acta Derm Venereol 1998;78:399, Ann Intern Med 1989;111:802)
- Nodular amyloidosis
- Has been associated with trauma and autoimmune disease but the exact mechanism is unknown (Int J Mol Sci 2023;24:7378)
- Results from local and usually clonal plasma cells producing immunoglobulin light chains
- Insulin injections may lead to secondary localized cutaneous amyloidosis (Indian J Endocrinol Metab 2015;19:174)
- Long term hemodialysis, infections and inflammation may lead to secondary systemic amyloidosis (J Dermatol 2005;32:410)
Clinical features
- Amyloidoses with skin involvement are clinically classified into 2 main groups: systemic and localized
- Systemic amyloidoses: primary, myeloma associated, secondary, hereditary / familial, amyloid elastosis
- Localized amyloidoses: lichen and macular amyloidosis, nodular, secondary, familial primary
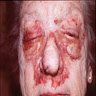
- Cutaneous involvement in primary systemic amyloidosis
- Most common symptom: hemorrhage due to vascular fragility caused by amyloid deposition in the vessel wall (Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2023;16:987)
- Waxy papules, nodules and plaques
- Hair loss may be present due to follicular atrophy caused by amyloid deposition surrounding the pilosebaceous units (Am J Dermatopathol 2019;41:799)
- Macular amyloidosis and lichen amyloidosis (Dermatology 2022;238:579)
- Most common symptom: pruritus (lichen amyloidosis > macular amyloidosis)
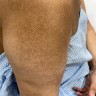
- Lichen amyloidosis → small and waxy hyperpigmented papules
- Macular amyloidosis → hyperpigmented (or less commonly hypopigmented), ill defined macules coalescing into a patch or thin plaque
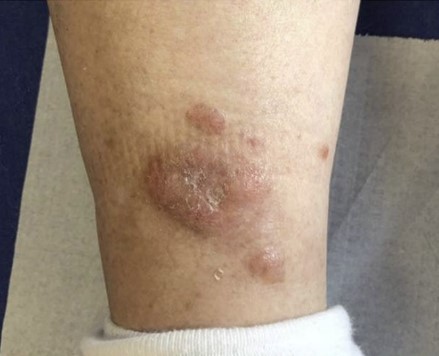
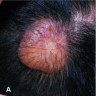
- Nodular amyloidosis
- Usually asymptomatic
- Single or multiple pink-brown waxy nodules that can coalesce, sometimes with atrophic or ulcerated surface
- Association with autoimmune conditions, primarily Sjögren syndrome (up to 25% of nodular amyloidosis patients) and CREST syndrome (J Dermatol 2005;32:120, Cutis 2008;82:55, J Clin Rheumatol 2011;17:368)
- Other rare, localized forms
- Poikilodermatous amyloidosis (includes amyloidosis cutis dyschromica) → reticulate hyperpigmentation with hypopigmented lesions all over the body (Dermatopathology (Basel) 2022;10:20)
- Anosacral amyloidosis, keratinic variant of bullous amyloidosis, incontinentia pigmenti-like amyloidosis, linear macular amyloidosis, keratinic variant of nodular amyloidosis
- Reference: Calonje: McKee’s Pathology of the Skin, 5th Edition, 2019
Diagnosis
- Essentially based on clinical findings and histopathologic evidence of amyloid deposition in tissues
- Requires sampling of the tissue, histopathological examination and confirmation by Congo red staining
- Electron microscopy is another confirmatory method but less frequently used due to limited availability and high cost
- Immunofluorescence
- Direct immunofluorescence using thioflavin T can be used as a complimentary method to Congo red staining in primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis (J Clin Diagn Res 2017;11:WC01)
- Examination of Congo red stained tissue by fluorescent microscopy can help to overcome the limitations of light microscopic examination (Hum Pathol 2014;45:1766)
- Immunohistochemistry
- Using antibodies against amyloidogenic proteins
- Helps discriminate between the amyloid proteins
- Lipid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry: definitive typing of amyloid (J Nippon Med Sch 2024;91:261)
- Systemic amyloidosis can be diagnosed by
- Blind abdominal fat pad aspiration biopsy (preferred method)
- Blind abdominal skin punch biopsy (J Cutan Pathol 2021;48:1342)
- Highly sensitive for diagnosis of AL (primary) amyloidosis (most common type of amyloid in systemic amyloidosis in developed countries)
- Specific for diagnosing AA (secondary) amyloidosis
- Sensitivity improved with adequate depth (> 10 mm) and diameter (> 6 mm) of biopsy (J Cutan Pathol 2021;48:1342)
Laboratory
- Diagnosing localized cutaneous amyloidosis requires absence of systemic involvement (Int J Mol Sci 2023;24:9409)
- Clinical work up to rule out primary systemic amyloidosis (Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2023;16:987)
- Complete blood count with differential
- Comprehensive metabolic panel (including ALP and cardiac biomarkers) allows assessment for organ involvement by systemic amyloidosis, such as heart, kidney and liver
- Urinalysis and urine protein electrophoresis (UPEP)
- Elevated urine free light chains, presence of clonal light chains on UPEP
- Proteinuria by 24 hour urine protein test and elevated albumin to creatinine ratio are suggestive of kidney involvement of systemic amyloidosis (Clin Chem Lab Med 2022;60:386)
- Serum protein electrophoresis (Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2023;16:987)
- Presence of clonal immunoglobulins (M spike) in systemic disease
- Possibly bone marrow biopsy and aspirate - to rule out involvement by plasma cell neoplasm
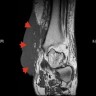
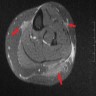
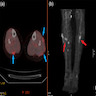
Radiology description
- Nodular amyloidosis may present as poorly defined subcutaneous soft tissue masses or nodules on imaging
- Post contrast enhancement on MRI (Amyloid 2006;13:135)
- Hypermetabolic on PET scan (J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep 2021;9:23247096211058488)
Prognostic factors
- Lichen amyloidosis: complete clinical remission is not usually achieved (World J Clin Cases 2023;11:2549)
- Nodular amyloidosis
- High rate of local recurrence even after excision, affected by the extent of the lesion
- Systemic work up and long term follow up are recommended due to increased risk of progression to systemic amyloidosis (in ~7 - 50% patients) (Br J Dermatol 2001;145:105)
Case reports
- 16 year old girl with hypopigmented and hyperpigmented macules on the legs (Dermatopathology (Basel) 2022;10:20)
- 23 year old woman with hyperpigmented patches on the upper back and extensor arms (Cureus 2024;16:e56248)
- 34 year old man with multiple dark brown papules on the scalp (Ann Dermatol 2023;35:S30)
- 60 year old man with a firm erythematous nodule on the nose (Ann Dermatol 2023;35:S376)
- 65 year old woman with multiple firm tender nodules on the lower extremities (QJM 2023;116:237)
- 74 year old woman with dark macules on the back, shoulders and dorsal upper arms (Cureus 2022;14:e29010)
Treatment
- Systemic amyloidosis
- Treatment of the underlying condition (e.g., plasma cell neoplasm, inflammatory condition, infection)
- Primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis
- Treatment not required, usually for cosmetic purposes and relief of associated symptoms
- Macular, lichen and biphasic amyloidosis
- Treatment for pruritus and cosmetic purposes topical or intralesional corticosteroids, antihistamines, emollients, topical tacrolimus, phototherapy, laser therapy, retinoids, cyclosporine, cyclophosphamide and thalidomide (Am J Clin Dermatol 2017;18:629)
- Nodular amyloidosis
- Surgical excision, dermabrasion, laser therapy, electrodesiccation and curettage, intralesional steroid injection and cryosurgery (Ann Dermatol 2023;35:S30)
Clinical images
Microscopic (histologic) description
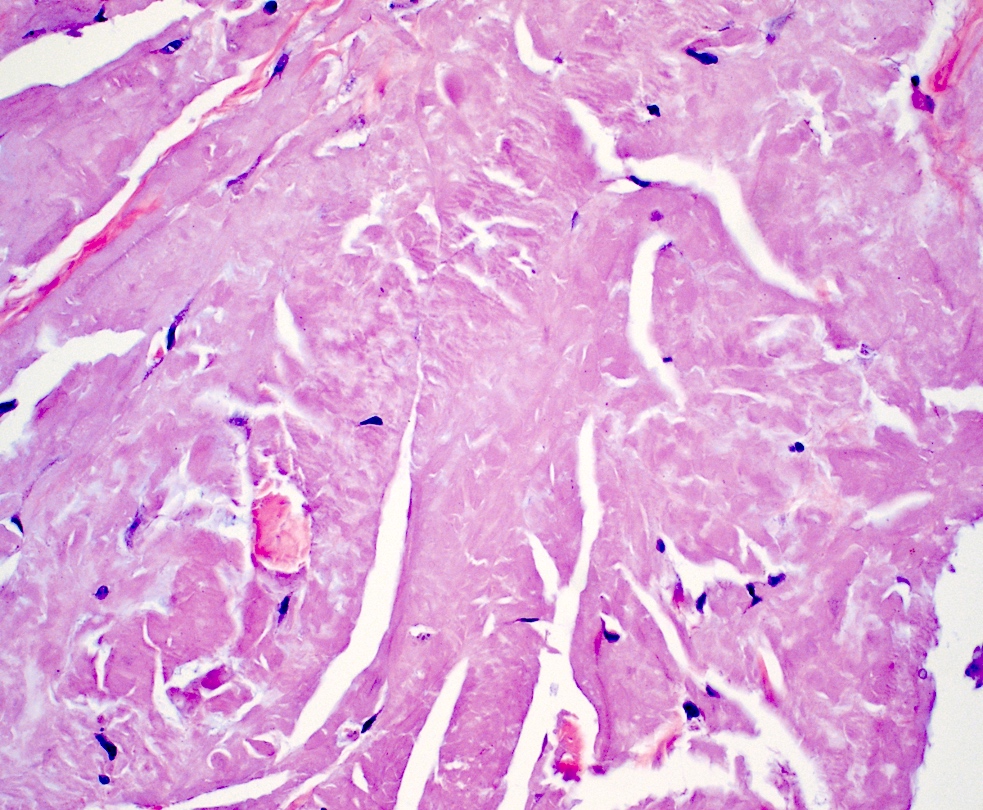
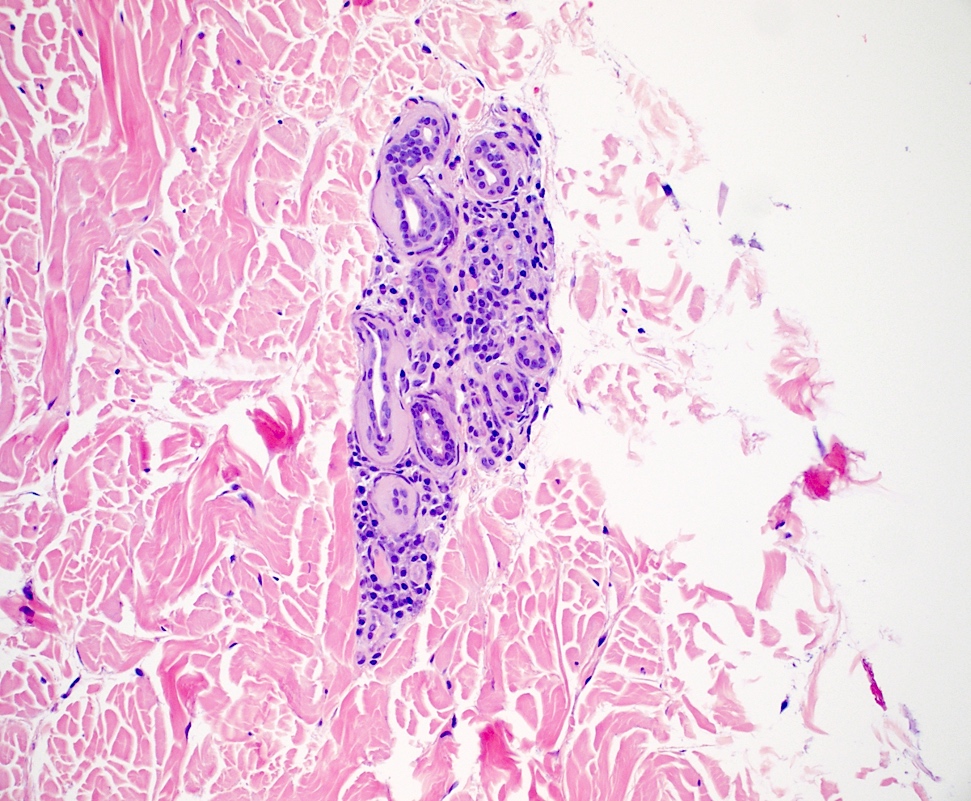
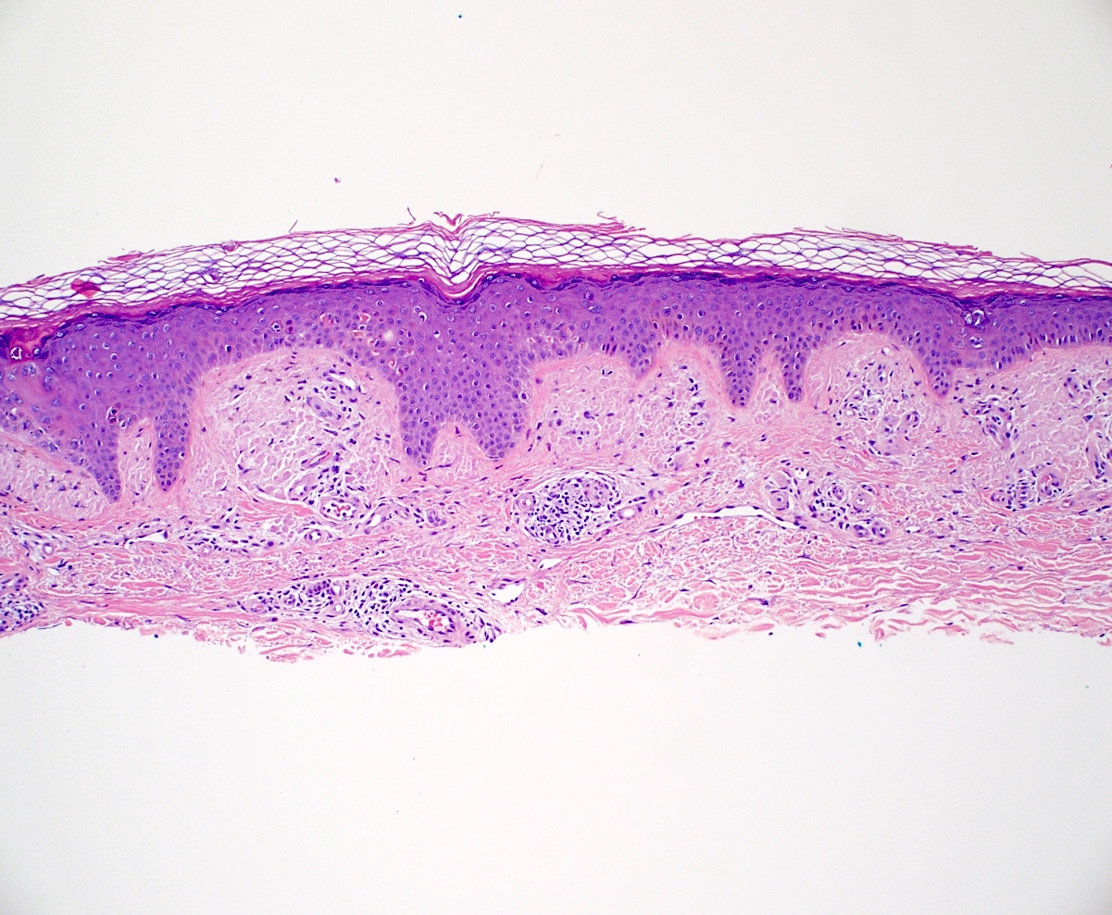
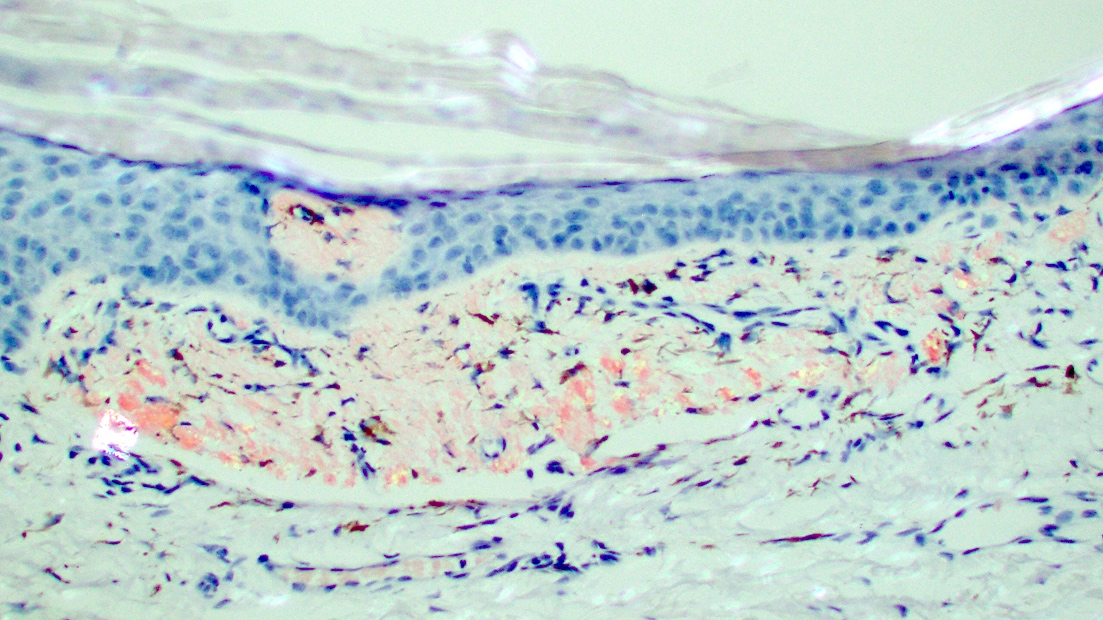
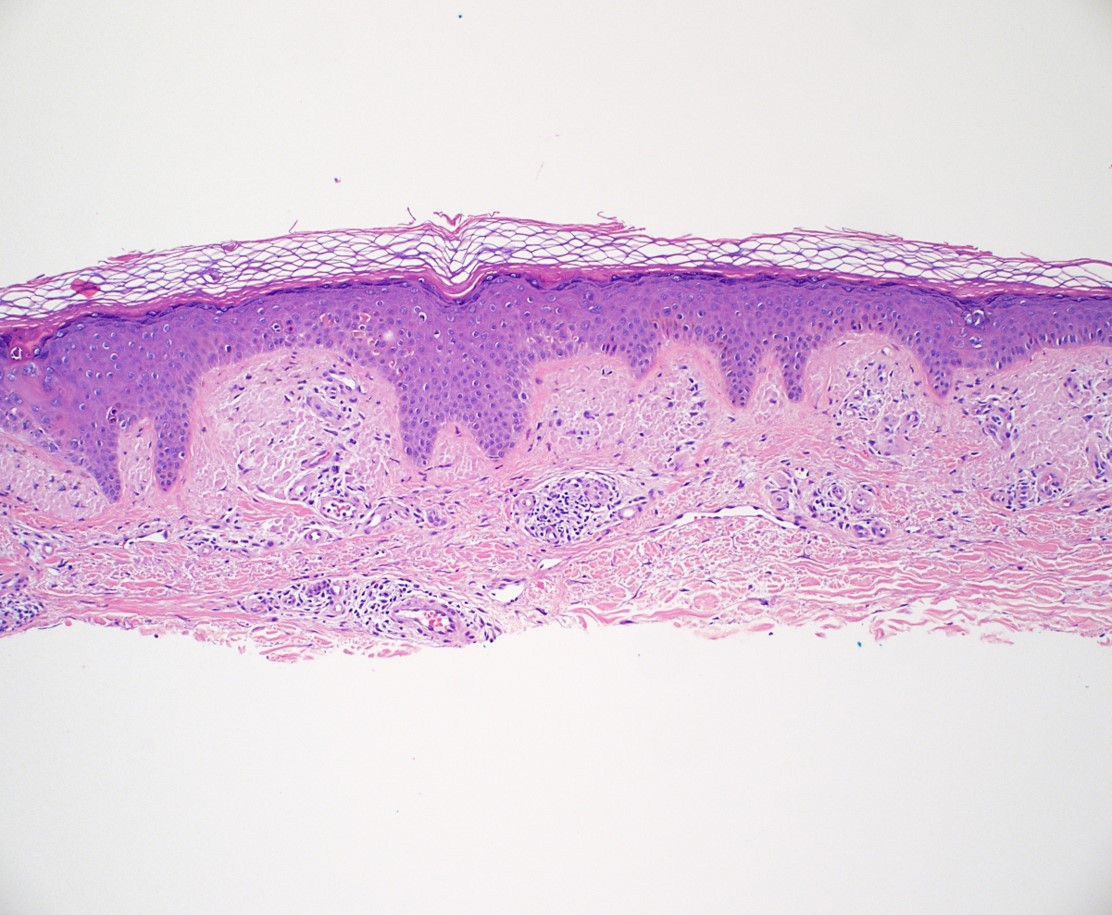
- Amyloid appears as eosinophilic amorphous material in all types of amyloidosis
- Systemic amyloidosis
- Large masses of fissured amyloid deposits in the dermis and subcutis
- Prominent perivascular amyloid deposition (Cureus 2023;15:e48346)
- Deposits are also seen in arrector pili muscles, adnexal structures and subcutaneous fat
- Flattened epidermis
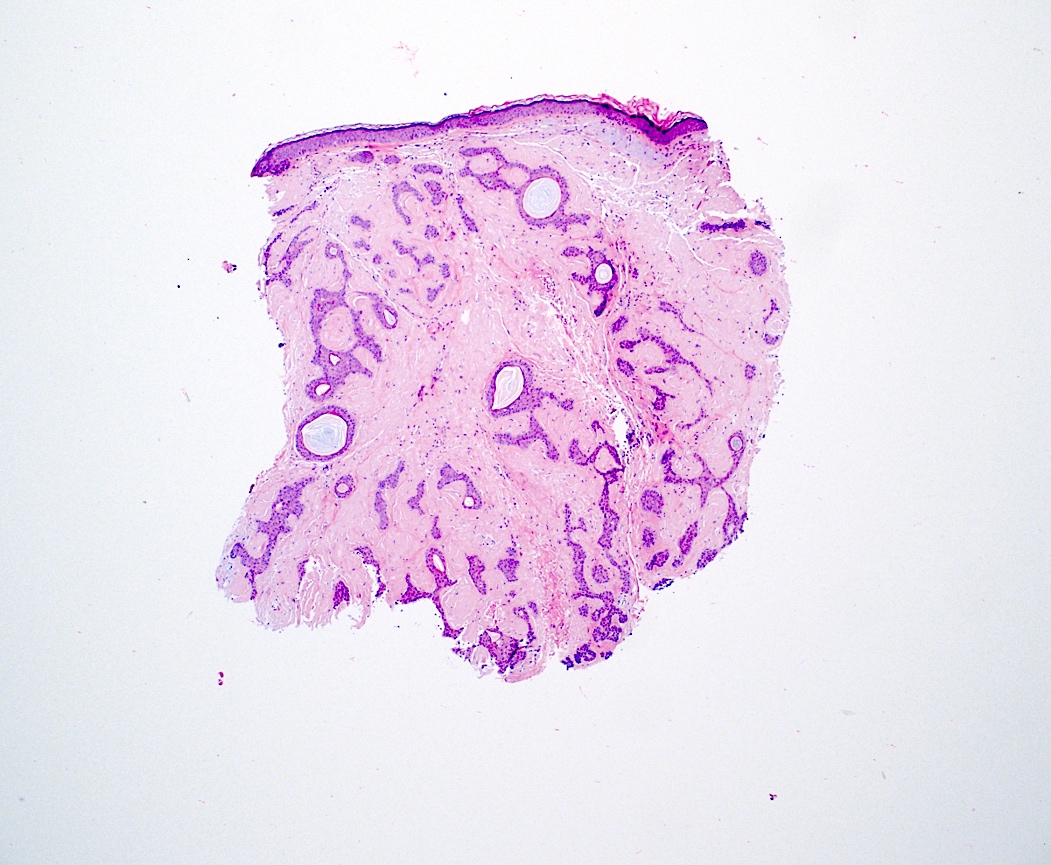
- Localized cutaneous amyloidosis
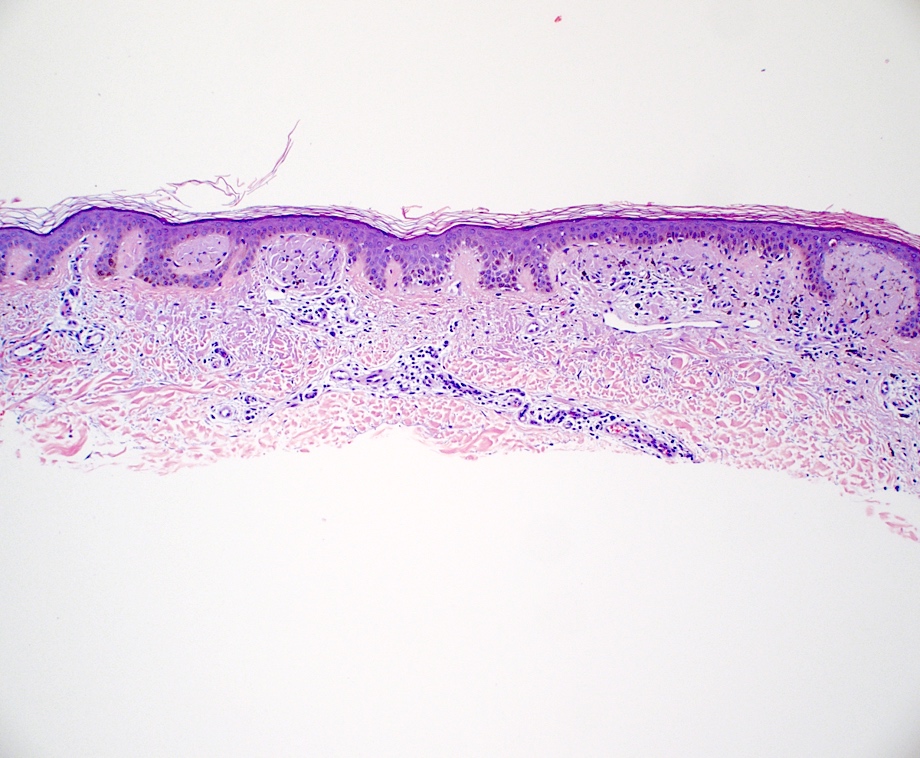
- Macular amyloidosis
- Limited quantity of small globular amyloid deposits in the papillary dermis with close proximity to the dermoepidermal junction (Australas J Dermatol 2001;42:176)
- Associated pigment incontinence and melanophages
- Mild chronic perivascular inflammatory infiltrate in the superficial dermis
- Epidermal changes are minimal and may include
- Hyperkeratosis
- Acanthosis
- Basal vacuolar change
- Colloid bodies
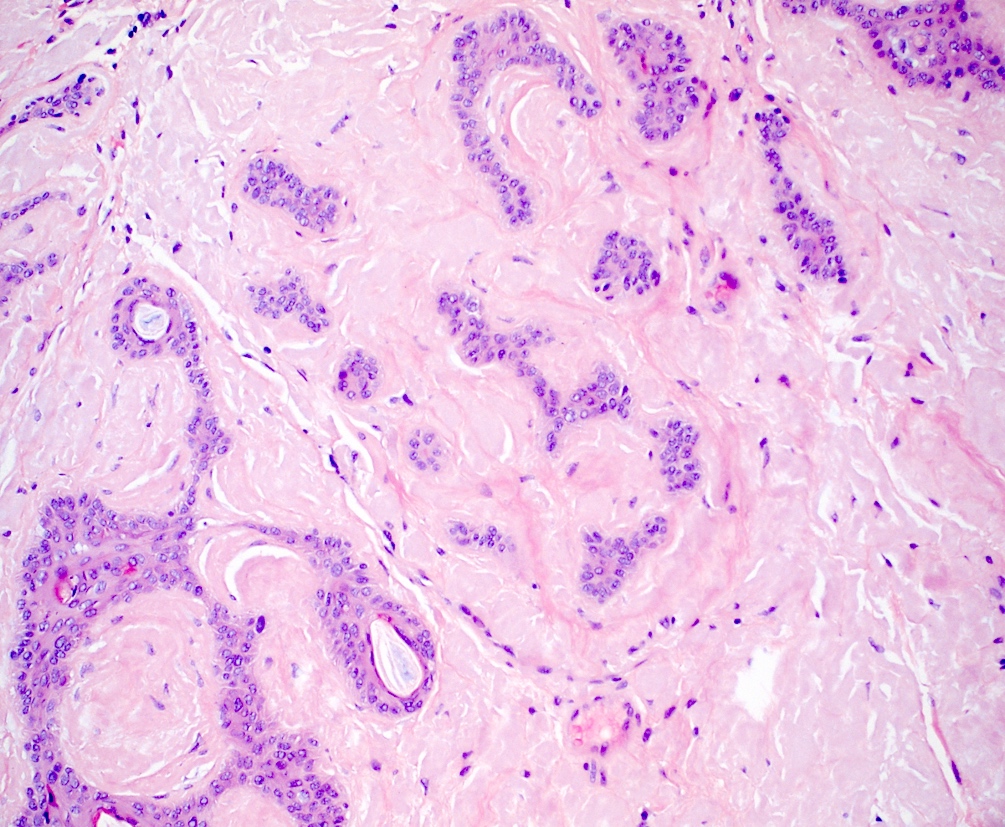
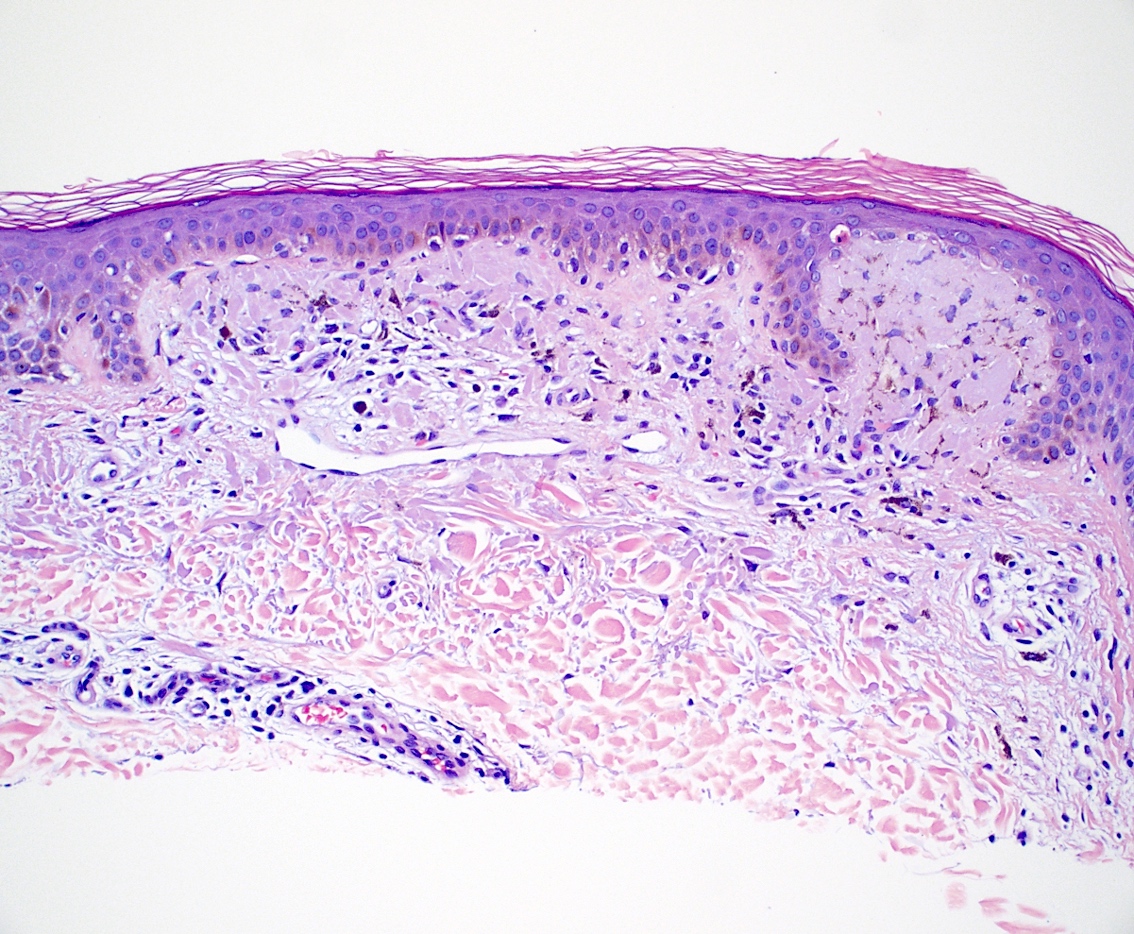
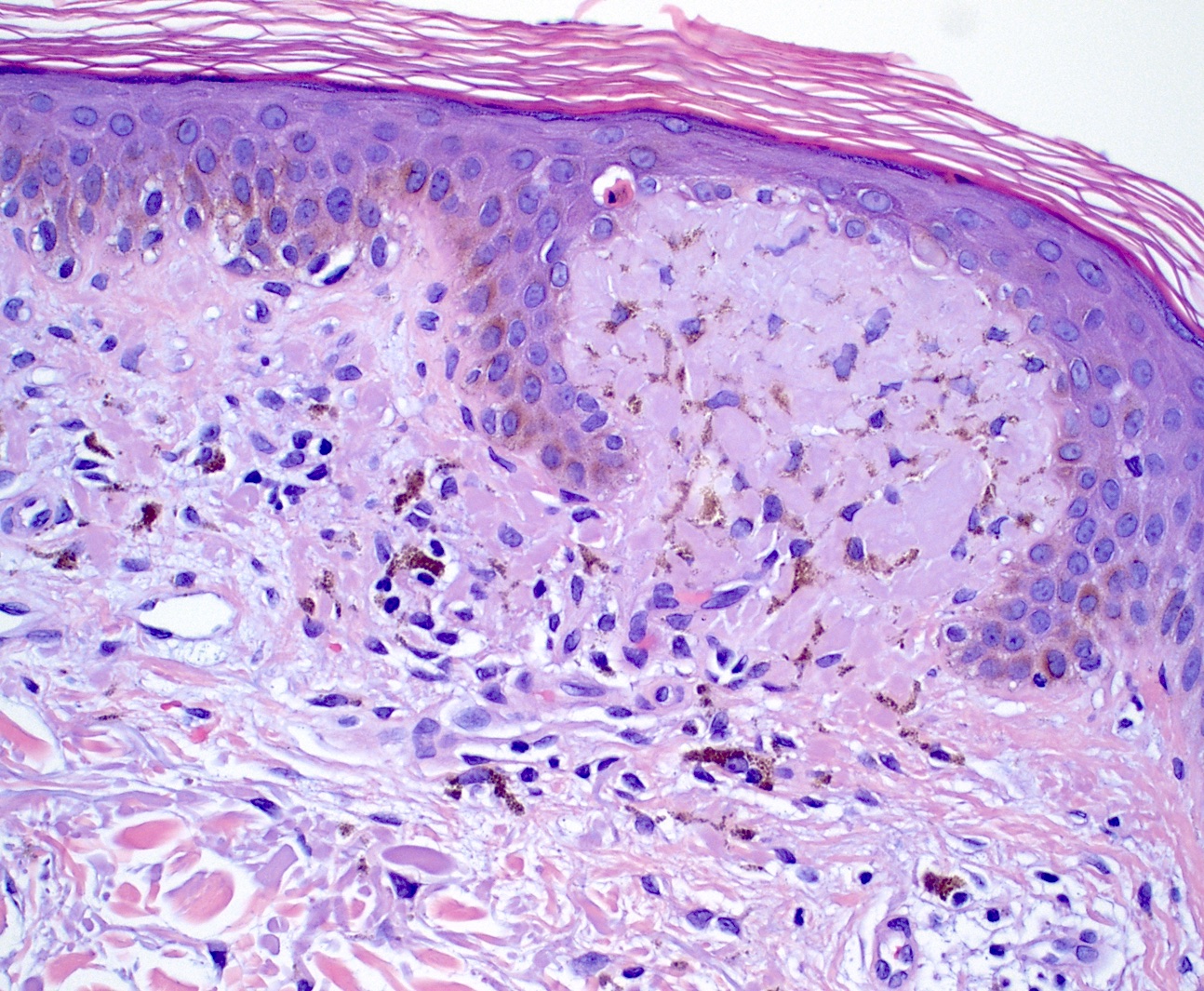
- Lichen amyloidosis
- Similar to macular amyloidosis; however
- Greater quantity of amyloid deposits in the papillary dermis with widened dermal papilla
- Pronounced epidermal changes, including
- Hyperkeratosis
- Acanthosis
- Hypergranulosis
- Basal vacuolar change
- Colloid bodies
- Associated pigment incontinence and melanophages (Clin Exp Dermatol 2023;48:261, J Clin Med 2023;12:7672)
- Similar to macular amyloidosis; however
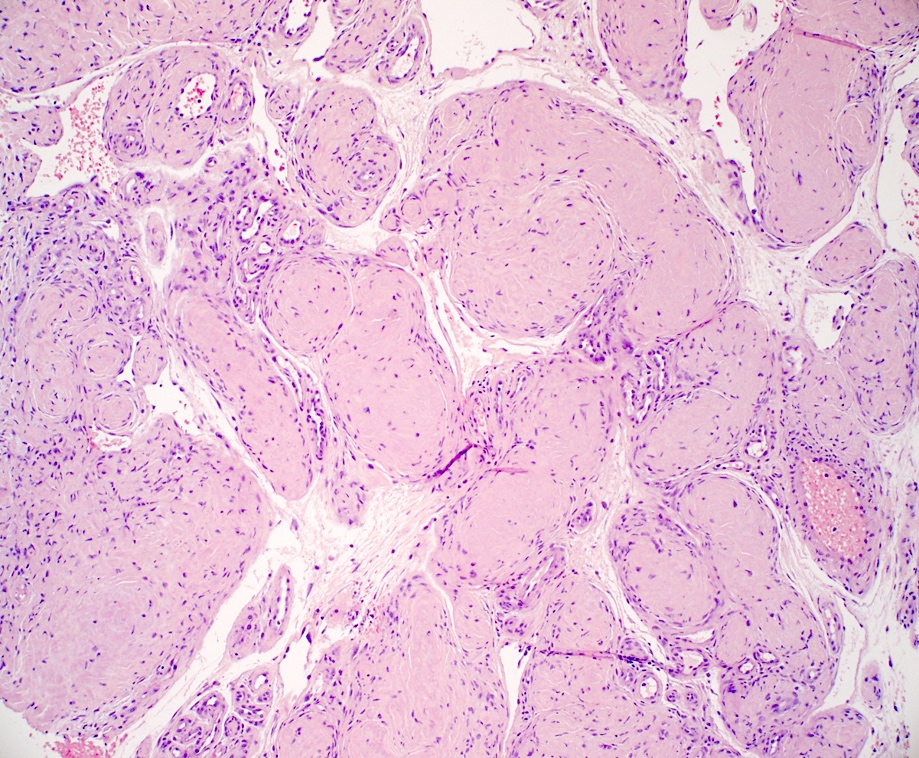
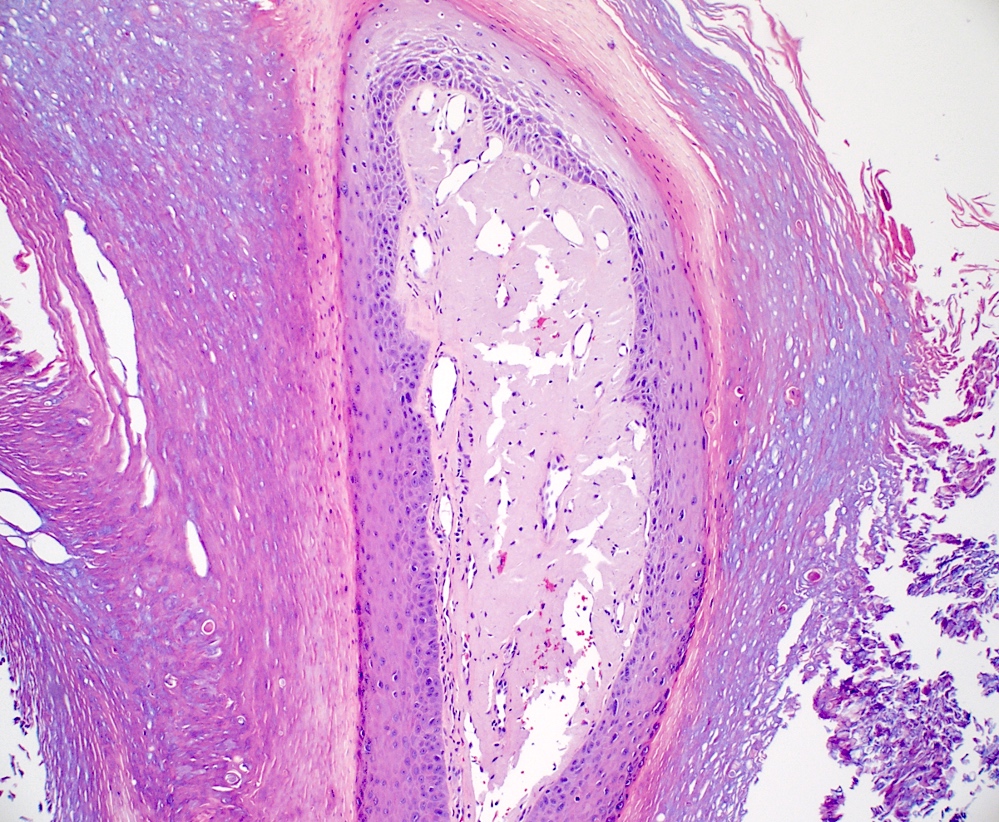
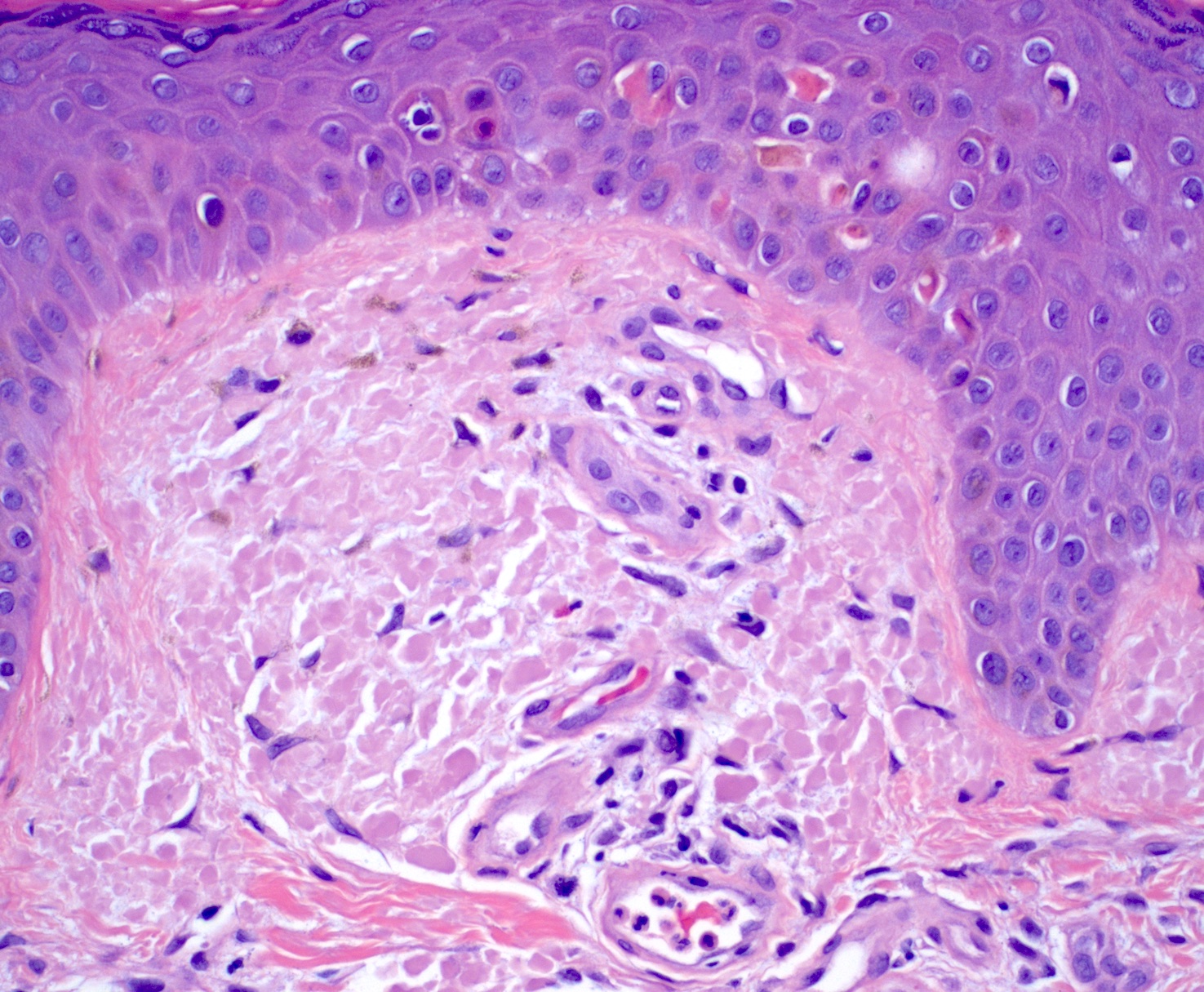
- Nodular amyloidosis
- Extensive deposition of amyloid in the dermis and subcutis (Ann Dermatol 2023;35:S30)
- Prominent in deep perivascular and periadnexal areas
- Associated plasma cell infiltrate
- Rare foreign body giant cells and calcifications
- Macular amyloidosis
- References: Calonje: McKee’s Pathology of the Skin, 5th Edition, 2019, Elston: Dermatopathology, 3rd Edition, 2018, Patterson: Weedon’s Skin Pathology, 5th Edition, 2020
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Ani Toklu, M.D. and Carina A. Dehner, M.D. Ph.D.
Virtual slides
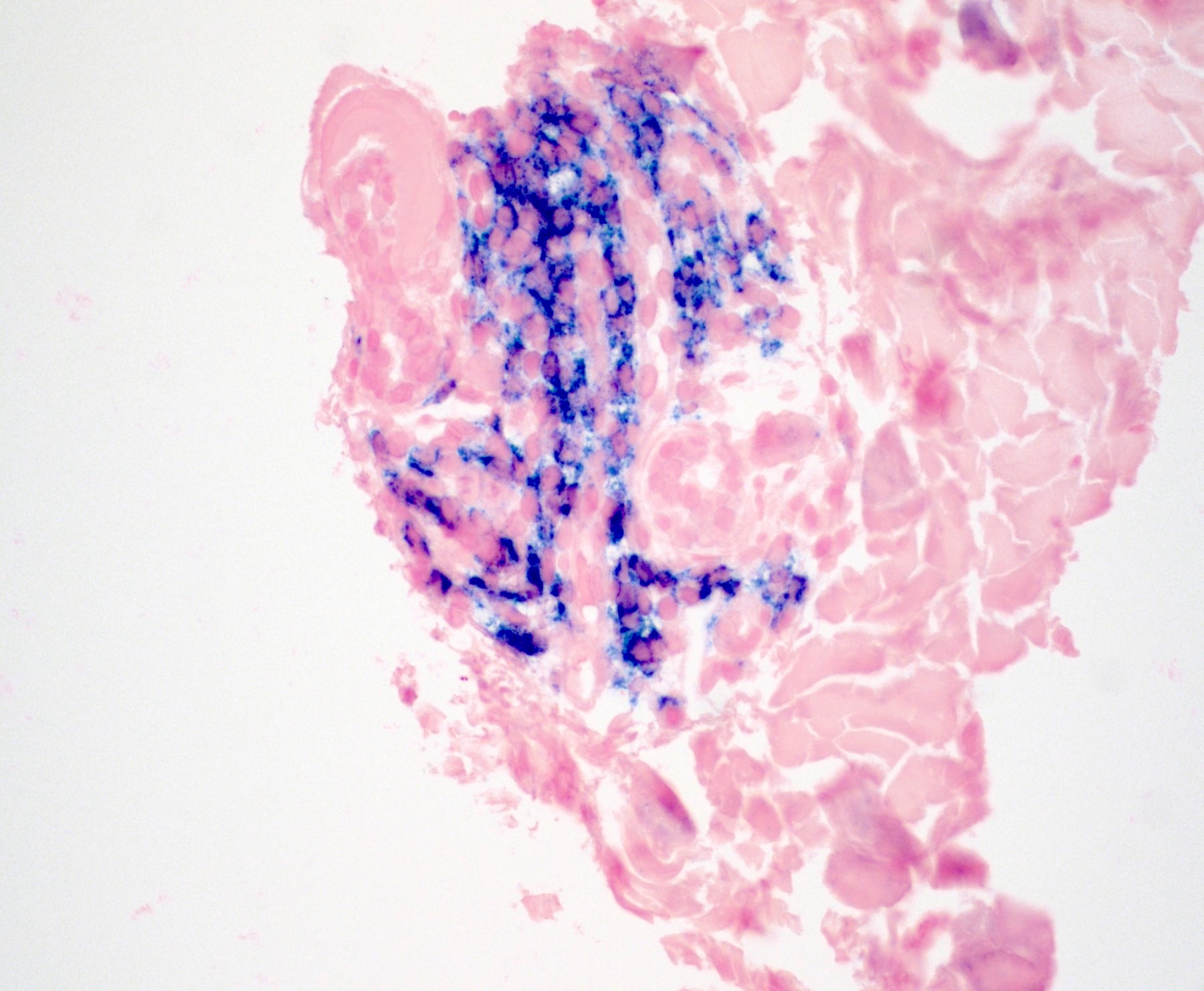
Cytology description
- Amyloid cytomorphology
- Diff-Quik stained smears: homogeneous clumps of dark blue to purple, slightly metachromatic material (Cancer Cytopathol 2024;132:179)
- Papanicolaou stained smears: pale, waxy, cyanophilic to orangophilic material (Acta Cytol 1999;43:746)
- ThinPrep preparation: more transparent, somewhat fibrillar, cyanophilic to amphophilic material (Diagn Cytopathol 2003;28:325)
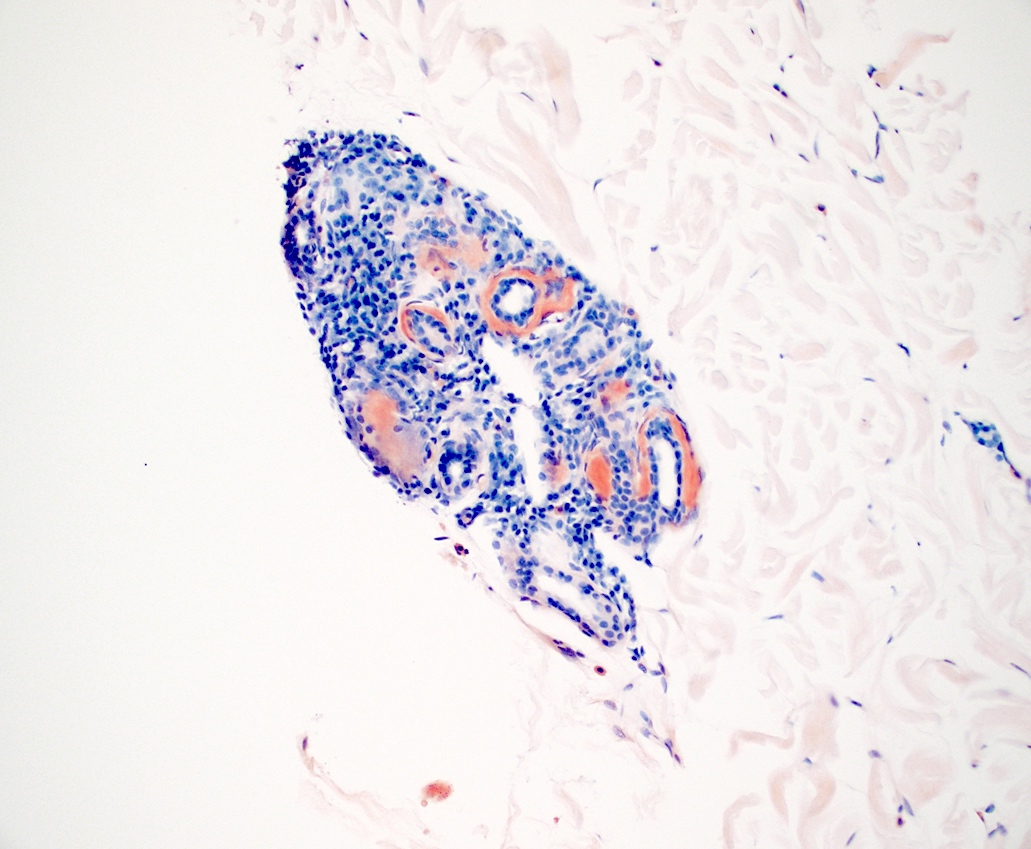
Immunofluorescence description
- Immunoglobulins and complements are found in the amyloid deposits due to nonspecific trapping
- Most frequent immunoreactants: IgM, IgA, C3 (Dermatologica 1980;160:240)
- Positivity along the basement membrane in lichen amyloidosis (J Clin Diagn Res 2017;11:WC01)
- Thioflavin T
- Very sensitive, binds to amyloid fibrils (binding sites are on the surfaces of cross β structures of the fibrils) and produces yellow-green fluorescence (Biochim Biophys Acta 2010;1804:1405)
- Type of amyloid fibril affects the intensity of fluorescence, can also bind to cholinesterase and human serum albumin (weaker fluorescence), lipomembranous change can lead to false positive results (Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2015;458:418, J Dermatol 2025;52:171)
Positive stains
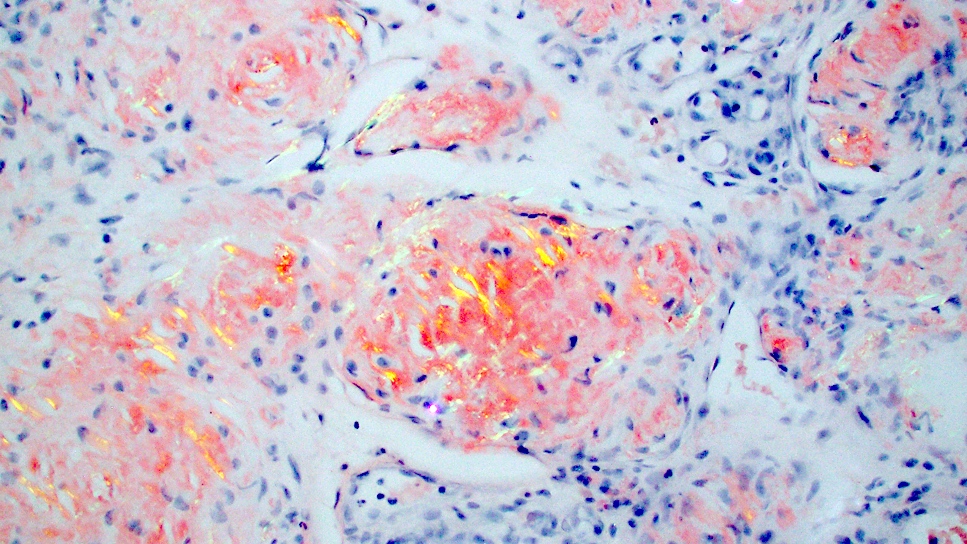
- Congo red
- Most commonly used special stain; considered gold standard
- Brick red staining, apple green birefringence with polarization
- Staining is not always strongly positive, false negative results due to limited presence of amyloids, thin tissue sections (ideal thickness: 8 - 10 μm) or technical variability (Biosci Rep 2019;39:BSR20181415)
- Positive staining is not specific for amyloid; can stain hyaline deposits in colloid milium and lipid proteinosis or elastin and collagen fibrils
- Lower sensitivity in macular amyloidosis (J Clin Diagn Res 2017;11:WC01)
- Higher sensitivity can be achieved in combination with alternative methods including immunohistochemistry, Congo red fluorescence and immunofluorescence (Hum Pathol 2014;45:1766)
- Thioflavin T
- Very sensitive but requires fluorescence microscopy; yellow-green fluorescence (Biochim Biophys Acta 2010;1804:1405)
- Limited specificity; stains cartilage, elastic fibers and mucopolysaccharides
- Crystal violet, methyl violet
- Metachromatic staining (purple-red in a blue background) in amyloid and acid mucopolysaccharides
- Not commonly used due to overall low specificity and sensitivity compared to Congo red (Biosci Rep 2019;39:BSR20181415)
- Most sensitive for keratin derived amyloid
- Cotton dyes such as pagoda red, scarlet red, RIT cardinal red no. 9 (Arch Dermatol 1984;120:1184)
- Bright orange color
- Pagoda red most specific but rarely used
- PAS stains glycogen and mucopolysaccharides
- Not commonly used for amyloid detection due to lack of specificity
- Van Gieson stain can be used to differentiate colloid milium (stains yellow) from amyloidosis (stains pink)
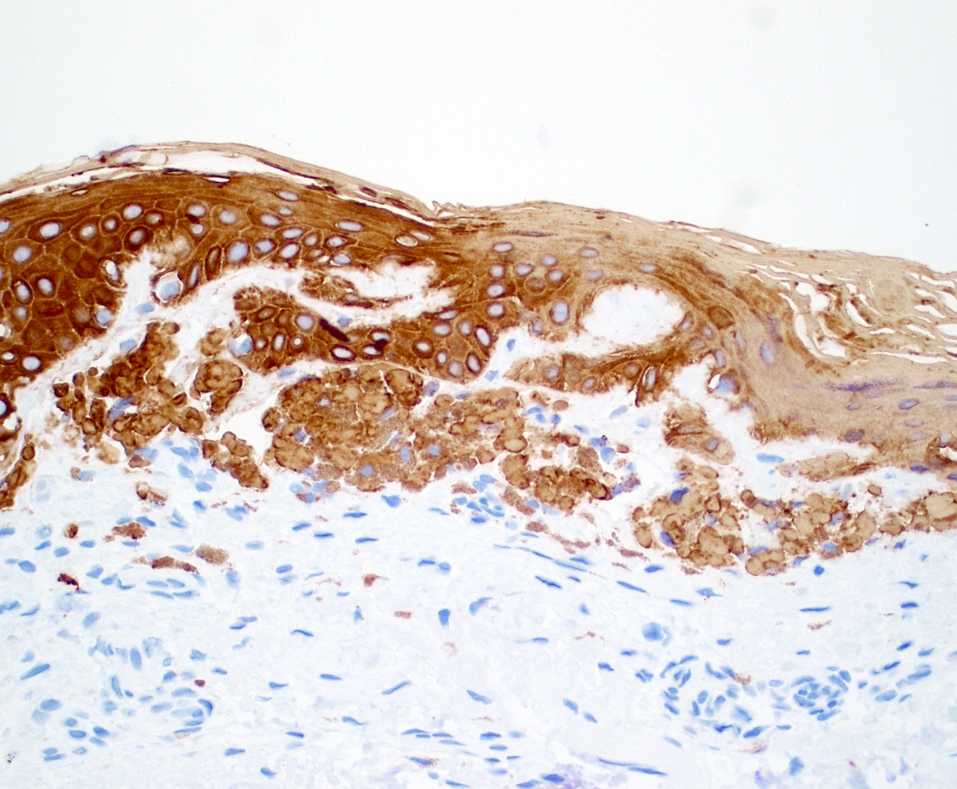
- Cytokeratin
- Positive staining in keratin derived amyloid deposits macular amyloidosis and lichen amyloidosis and less commonly nodular amyloidosis
- Most useful cytokeratins include high molecular weight (34 beta E12) and basic cytokeratins such as CK5 (J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2004;18:305)
- Immunoglobulin light chains
- Positive staining with either kappa or lambda (more often) light chains in the amyloid fibrils in nodular amyloidosis and cutaneous involvement of primary systemic amyloidosis
- Light chain restriction seen in the lesional plasma cells in nodular amyloidosis and systemic amyloidosis associated with plasma cell dyscrasia
- AA, A beta 2 microglobulin
- C4d
- Widely used in detecting amyloid in other organs such as kidney
- Sensitivity: 100% and specificity: 75.5% (Am J Dermatopathol 2022;44:28)
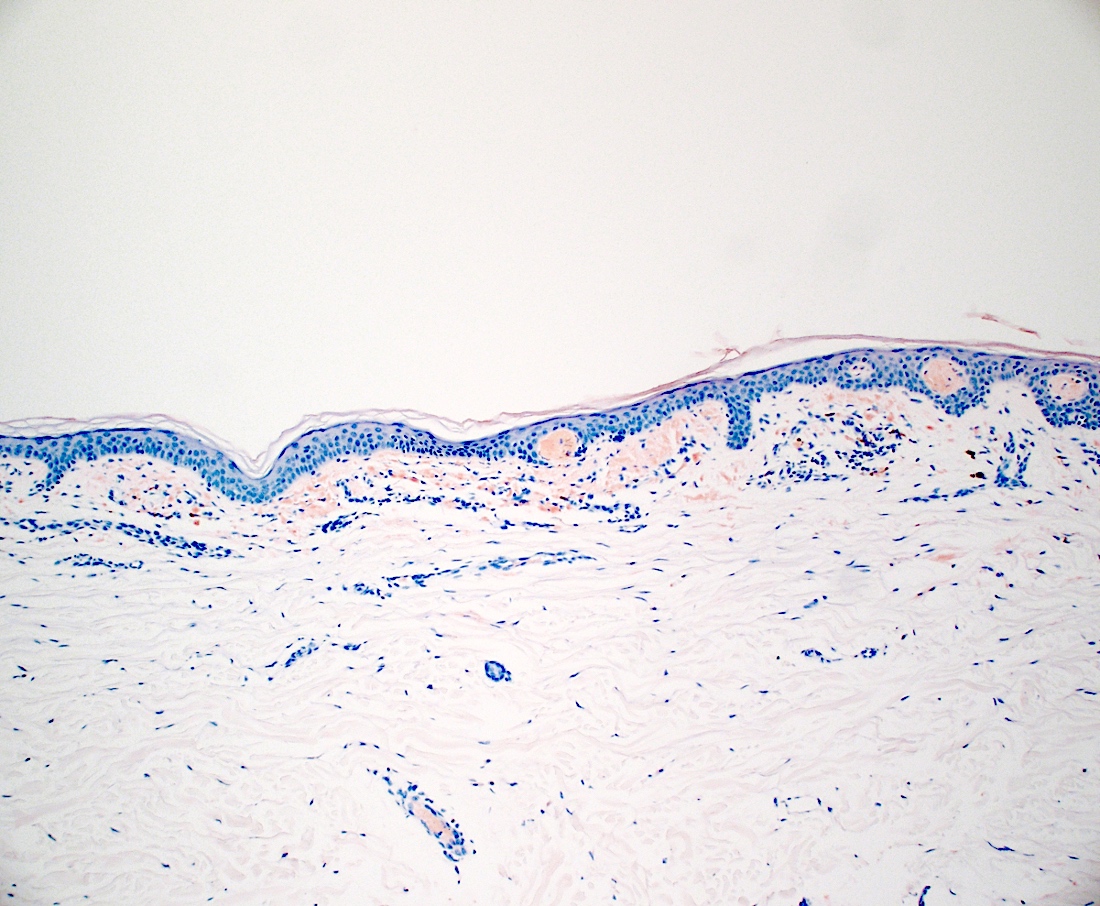
Negative stains
- Masson trichrome stains collagen blue (Methods Protoc 2022;5:13)
- Verhoeff van Gieson stains elastic fibers black (Biotech Histochem 2021;96:608)
- GMS
Electron microscopy description
- Long nonbranching straight rod shaped filaments with variable length, a diameter of 6 - 10 nm and random arrangement without bundle formation (Ann Dermatol 2023;35:S376)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- In situ hybridization (ISH) for immunoglobulin light chains kappa and lambda as an alternative method to IHC to demonstrate light chain restriction in plasma cells
- Light chain restriction is expected in nodular amyloidosis or cutaneous involvement by systemic amyloidosis associated with plasma cell dyscrasia
- Polymerase chain reaction and gene rearrangement studies can confirm clonality of the plasma cells in nodular amyloidosis (Br J Dermatol 1996;135:630)
- Not required for diagnosis, infrequently used for diagnostic purposes
Videos
Lichen amyloidosis
Macular amyloidosis
Nodular amyloidosis
Sample pathology report
- Skin, abdomen, biopsy:
- Amyloid deposits in papillary dermis and around eccrine glands, consistent with cutaneous amyloidosis (see comment)
- Comment: There are amorphous, pink deposits with clefting in the papillary dermis and around eccrine glands. The deposits are strongly positive with Congo red and negative for cytokeratin 34 beta E12. The kappa in situ hybridization was negative while lambda in situ hybridization identified a clonal infiltrate of plasma cells. Further studies (mass spectrophotometry) are pending.
- Addendum: Mass spectrophotometry detected a peptide profile consistent with AL (lambda) type amyloid. These findings support amyloid deposition associated with plasma cell proliferation. Correlation with clinical and laboratory findings is recommended to distinguish systemic from localized AL amyloidosis.
- Skin, left pretibial region, biopsy:
- Lichen amyloidosis (see comment)
- Comment: H&E sections reveal hyperkeratosis, slight epidermal hyperplasia and dyskeratotic cells in the epidermis. There are melanophages in the papillary dermis, a sparse perivascular lymphocytic inflammatory infiltrate and small, discrete globules of amorphous material in the papillary dermis. The material is positive for cytokeratin AE1 / AE3 and Congo red stain with apple green birefringence under polarized light. These findings support the above diagnosis.
- Skin, right lateral heel, biopsy:
- Squamous cell carcinoma in situ with papillary dermal amyloid deposition (see comment)
- Comment: Extensive, pink, amorphous deposits in the papillary dermis underlying squamous cell carcinoma in situ is highlighted by Congo red staining. This likely represents secondary localized cutaneous amyloidosis; however, another form of cutaneous amyloidosis could also be considered. Clinical correlation is recommended.
Differential diagnosis
- Colloid milium (adult form):
- Deposition of amorphous eosinophilic material with clefts in the superficial dermis
- Grenz zone with solar elastosis
- No periadnexal involvement
- Positive staining with Congo red, crystal violet, PAS and thioflavin S fluorescence, cytokeratins and light chains are negative on IHC; no immunoglobulins or complement on direct immunofluorescence (DIF)
- Small, dome shaped, yellow papules on sun exposed skin of fair skinned individuals
- Lipoid proteinosis:
- Concentric layers of diffuse perivascular and perieccrine hyaline material in the dermis
- PAS, crystal violet and Congo red (weak) positive, negative for pagoda red no. 9 staining
- Also positive for colloidal iron and lipid stains, such as Sudan black and oil red O
- Thickened skin with lesions varying in appearance
- Erythropoietic protoporphyria:
- Elevated erythrocyte and plasma protoporphyrins
- Prominent perivascular and intramural PAS+ hyaline material deposition in the dermis
- Subepidermal blistering (not always)
- Scant inflammation
- IgG, C3, fibrin deposition around vessels on DIF
- Lichen sclerosus et atrophicus:
- White to light pink plaques, most commonly in anogenital region
- Well developed lesions may show basal keratinocyte degeneration, lichenoid lymphocytic inflammation and hyalinization in the upper dermis
- Absence of amyloid unlike lichen amyloidosis
- Primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoproliferative disorder, plasmacytic variant:
- Mature appearing light chain restricted plasma cell infiltrate and neoplastic B lymphocytes in the dermis
- Similar phenotype may be encountered in nodular amyloidosis recurrence (Curr Oncol 2022;29:3026)
- Waldenström macroglobulinemia:
- Skin involvement accompanied by systemic findings
- Rarely, amorphous eosinophilic material is seen in the dermis positive for PAS but negative for amyloid stains
- Strong immunoreaction with IgM
- Systemic sclerosis:
- Increased collagen bundles extending to deep reticular dermis and subcutis
- Perivascular and periadnexal predominantly chronic inflammatory infiltrate
- Atrophy of pilosebaceous units and loss of interstitial fibroblasts
- Collagenoma:
- Increased collagen bundles in the dermis, negative for Congo red and other amyloid stains
- Clinical and histologic differentials also include the following entities:
- Lichen simplex chronicus, lichen planus pigmentosus, dermatophyte infection, eczematous dermatitis, postinflammatory hyperpigmentation for lichen amyloidosis
- Seborrheic dermatitis, scleredema, lupus, guttate psoriasis, dermatophyte infection, urticaria pigmentosa, guttate morphea and vitiligo for macular amyloidosis
- Granulomatous lesions and skin lymphomas for nodular amyloidosis
Practice question #1
A 56 year old woman presents with persistent pruritic and hyperpigmented papules on her shins. A skin biopsy is performed and histopathologic examination reveals deposits in the papillary dermis that are positive for Congo red staining. What is the primary component of the deposits observed in this type of amyloidosis?
- β2 microglobulin
- Immunoglobulin light chains
- Keratin derived amyloid
- Serum amyloid A protein
- Transthyretin
Practice answer #1
C. Keratin derived amyloid. The patient's diagnosis is most consistent with lichen amyloidosis based on the given clinical and histopathologic findings. In lichen amyloidosis, the amyloid deposits are derived from degenerated keratinocytes.
Answer A is incorrect because β2 microglobulin derived amyloid is associated with dialysis related amyloidosis.
Answer B is incorrect because immunoglobulin light chains are associated with AL amyloidosis that may be seen in primary systemic amyloidosis, nodular amyloidosis or in association with plasma cell dyscrasia.
Answer D is incorrect because serum amyloid A protein is related to AA amyloidosis, commonly related to systemic inflammatory conditions.
Answer E is incorrect because transthyretin is associated with ATTR amyloidosis, which rarely affects skin.
Comment Here
Reference: Amyloidosis
Comment Here
Reference: Amyloidosis
Practice question #2
A 77 year old woman with multiple, waxy, translucent papules on her periorbital region complains of fatigue and easy bruising. Physical examination is remarkable for macroglossia. A skin biopsy is performed, showing perivascular amyloid deposits in the dermis. Which of the following findings would be most consistent with primary systemic amyloidosis associated with plasma cell dyscrasia?
- Elevated serum amyloid A levels
- History of Sjögren syndrome
- Low serum complement levels
- Monoclonal spike on serum protein electrophoresis
- Positive antinuclear antibody (ANA) test
Practice answer #2
D. Monoclonal spike on serum protein electrophoresis. The presence of a monoclonal spike (M spike) on serum protein electrophoresis is indicative of a monoclonal immunoglobulin seen in plasma cell dyscrasias. This is expected to be seen in primary systemic amyloidosis (AL amyloidosis) where the amyloid deposits are composed of immunoglobulin light chains.
Answer A is incorrect because elevated serum amyloid A levels are associated with AA amyloidosis, resulting from chronic inflammation.
Answer B is incorrect because Sjögren syndrome has been reported to be associated with nodular amyloidosis.
Answers C and E are incorrect because positive ANA test and low serum complement levels are commonly seen in autoimmune conditions and are not related to primary systemic amyloidosis associated with plasma cell dyscrasia (Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2023;16:987).
Comment Here
Reference: Amyloidosis
Comment Here
Reference: Amyloidosis