Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Peripheral smear description | Peripheral smear images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Flow cytometry description | Flow cytometry images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Bidot S, Asakrah S. Burkitt lymphoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphomaburkitt.html. Accessed September 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Highly aggressive non-Hodgkin B cell lymphoma
- Association with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), especially endemic subtype
- Characteristic t(8;14) between c-MYC (8q24) and IGH (14q32) genes
Essential features
- Highly aggressive yet potentially curable, non-Hodgkin B cell lymphoma
- 3 subtypes
- Endemic subtype (Africa): affects children
- Sporadic subtype (Western countries): affects children and young adults
- Most common pediatric lymphoma in Western countries
- Immunodeficiency related subtype: affects HIV patients essentially
- Characteristic t(8;14) between c-MYC (8q24) and IGH (14q32) genes
- Association with EBV (~100% in endemic subtype, ~25 - 40% in other subtypes)
- Extranodal presentation often predominates
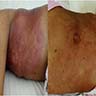
- Jaw / orbital mass in endemic subtype
- Abdominal mass in sporadic subtype
- Central nervous system and bone marrow involvement confer a poor prognosis
Terminology
- Burkitt tumor
- Malignant lymphoma, undifferentiated, Burkitt type
- Malignant lymphoma, small noncleaved, Burkitt type
Epidemiology
- 3 subtypes (endemic, sporadic, immunodeficiency related)
- All with a male predominance
- Endemic type (Lancet 2012;379:1234)
- Young children
- Distribution overlaps with that of holoendemic malaria (Burkitt lymphoma belt)
- Equatorial Africa, Papua New Guinea
- 50% of pediatric malignancies and 90% of pediatric lymphomas
- Associated with EBV in ~100% of cases
- Sporadic type (Curr Oncol 2020;27:83)
- Bimodal distribution (young children and young adults)
- Found in low risk regions for malaria
- Eastern Europe, North America, East Asia
- 30 - 50% of pediatric lymphomas
- 1 - 2% of adult lymphomas
- Associated with EBV infection in 25 - 40% of cases
- Immunodeficiency related type (Lancet Haematol 2020;7:e594)
- Essentially HIV infected adults (40% of HIV associated lymphomas)
- Occurs early in the progression of the disease (high CD4 count)
- Associated with EBV infection in 25 - 40% of cases
Sites
- Extranodal involvement predominates
- All 3 types at risk for central nervous system involvement (poor prognosis)
- Endemic type
- Jaw, orbits, retroperitoneal area
- Bone marrow involvement is uncommon
- Sporadic type
- Gastrointestinal tract, especially the ileocecal junction
- Head and neck (lymph nodes, pharynx, tonsils, sinuses, except the jaw)
- Bone marrow involvement is common (20%)
- Immunodeficiency associated type
- Lymph nodes, gastrointestinal tract, bone marrow
- References: Lancet 2012;379:1234, Lancet Haematol 2020;7:e594
Pathophysiology
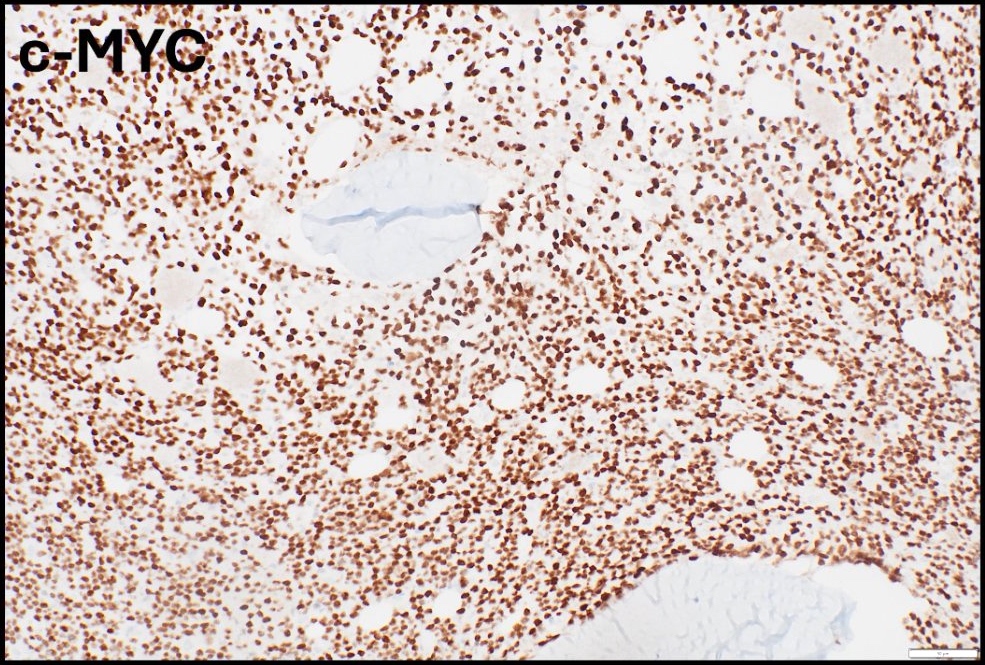
- c-MYC is a proto-oncogene on 8q24 involved the regulation of cell cycle progression (Curr Opin Hematol 2014;21:326)
- Rearrangement of c-MYC gene with the promoter sequence of either
- Ig heavy chain gene (IGH, 14q32)
- Ig light chain kappa (IGK, 2p12) or lambda (IGL, 22q11) genes
- Constitutive activation of c-MYC gene leading to unregulated germinal center derived B cell proliferation
- c-MYC dysregulation alone not likely sufficient to cause oncogenesis
- Other genetic factors have been identified
- Recurrent mutations, such as
- Cell cycle: ID3, TP53
- Nucleosome remodeling: SMARCS4
- Focal adhesion: GNA13
- Copy number variation
- Gain of 1q, 9q, 12q, 13q, 20q, 22q, Xq
- Loss of 4q, 13q, 17p
- Recurrent mutations, such as
- Cofactors (Lancet 2012;379:1234)
- EBV
- Blocks apoptosis in B cells with c-MYC rearrangement
- Promotes genetic instability
- Plasmodium species
- Unclear role
- Promotes EBV reactivation
- Decreases immune control of latently EBV infected B cells
- Induces c-MYC rearrangement
- HIV
- Pathophysiology is unclear
- No direct role of immunodeficiency (HIV patients have high CD4 count)
- Possible dysregulation of activated B cells
- HIV proteins might be directly involved in lymphomagenesis:
- Tat and p17 have been shown to promote DNA damage and c-MYC translocation (Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2016;113:13168, Lancet Haematol 2020;7:e594)
- Might explain the higher frequency of Burkitt lymphoma in HIV versus other forms of immunosuppression
- EBV
Etiology
- Primary event is likely c-MYC rearrangement arising in germinal center derived B cells
- However, c-MYC rearrangement is not sufficient and additional genetic events are required for lymphomagenesis (see Pathophysiology) (Nat Genet 2012;44:1321)
Clinical features
- Mass growing very quickly
- Fastest growing human tumor (doubling time = 24 - 48 hours)
- Patients have symptoms for only a few weeks prior to diagnosis
- Most common presenting signs and symptoms (Lancet 2012;379:1234):
- Endemic type
- Jaw mass, periorbital swelling (50 - 70%)
- Sporadic type
- Abdominal mass or pain, intussusception, gastrointestinal bleeding (60 - 80%)
- Immunodeficiency associated type
- Abdominal symptoms, cytopenia
- Endemic type
Diagnosis
- c-MYC translocation detected by karyotyping or FISH study usually confirms the diagnosis of Burkitt lymphoma; however, c-MYC translocation is not specific to Burkitt lymphoma and can be encountered in other lymphomas, including high grade B cell lymphoma (double / triple hit), diffuse large B cell lymphoma, plasmablastic lymphoma and others
- Additionally, 5 - 10% of otherwise typical Burkitt lymphoma cases show no evidence of c-MYC translocation by cytogenetic study and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), which may be explained by either test failure due to detection limitations or mechanisms other than translocation being responsible for the elevated MYC protein and Burkitt lymphoma pathogenesis
- Reference: BMC Cancer 2015;15:668
Laboratory
- Elevated serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) (poor prognosis)
Prognostic factors
- Highly aggressive lymphoma but potentially curable
- Event free survival in high income countries
- In children ~ 90% at 5 years (Blood 2001;97:3370)
- In adults ~ 85% at 4 years (J Clin Oncol 2020;38:2519)
- Similar survival in well controlled HIV patient
- Lower survival in low income countries (e.g. ~ 45% at 4 years in Uganda) (Pediatr Blood Cancer 2019;66:e27813)
- Extent of disease is the main prognostic factor
- Common staging systems (StatPearls: Burkitt Lymphoma [Accessed 6 April 2021]
- St. Jude / Murphy system in children
- Murphy or Ann Arbor systems in adults
- Central nervous system or bone marrow involvement impart a poor prognosis
- Common staging systems (StatPearls: Burkitt Lymphoma [Accessed 6 April 2021]
- Other factors of poor prognosis
- Early relapse (within 6 months)
- High serum LDH level
Case reports
- 9 year old boy with Burkitt lymphoma involving the skin (Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther 2018;11:251)
- 11 year old boy with Burkitt lymphoma involving the jaw and the ileocecal junction simultaneously (Med J Malaysia 2019;74:90)
- 27 year old man with HIV and Burkitt lymphoma involving the right atrium (Am J Case Rep 2016;17:553)
- 60 year old woman with gastric Burkitt lymphoma (Medicine (Baltimore) 2017;96:e8954)
Treatment
- Paucity of randomized clinical trials (Int J Hematol 2019;110:265)
- Several chemotherapy regimens have been described
- Commonly recommended regimens:
- R-CODOX-M / R-IVAC (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, methotrexate, ifosfamide, etoposide, cytarabine)
- R-hyper-CVAD / R-MA (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, dexamethasone, methotrexate, cytarabine)
- For poor candidates for high intensity chemotherapy, DA-R-EPOCH (rituximab, etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, methotrexate)
- All the above regimens include central nervous system intrathecal prophylaxis (methotrexate with or without cytarabine)
- Superiority of 1 over the others is unknown
- If poor response or relapse, hematopoietic stem cell transplant might be considered
Gross description
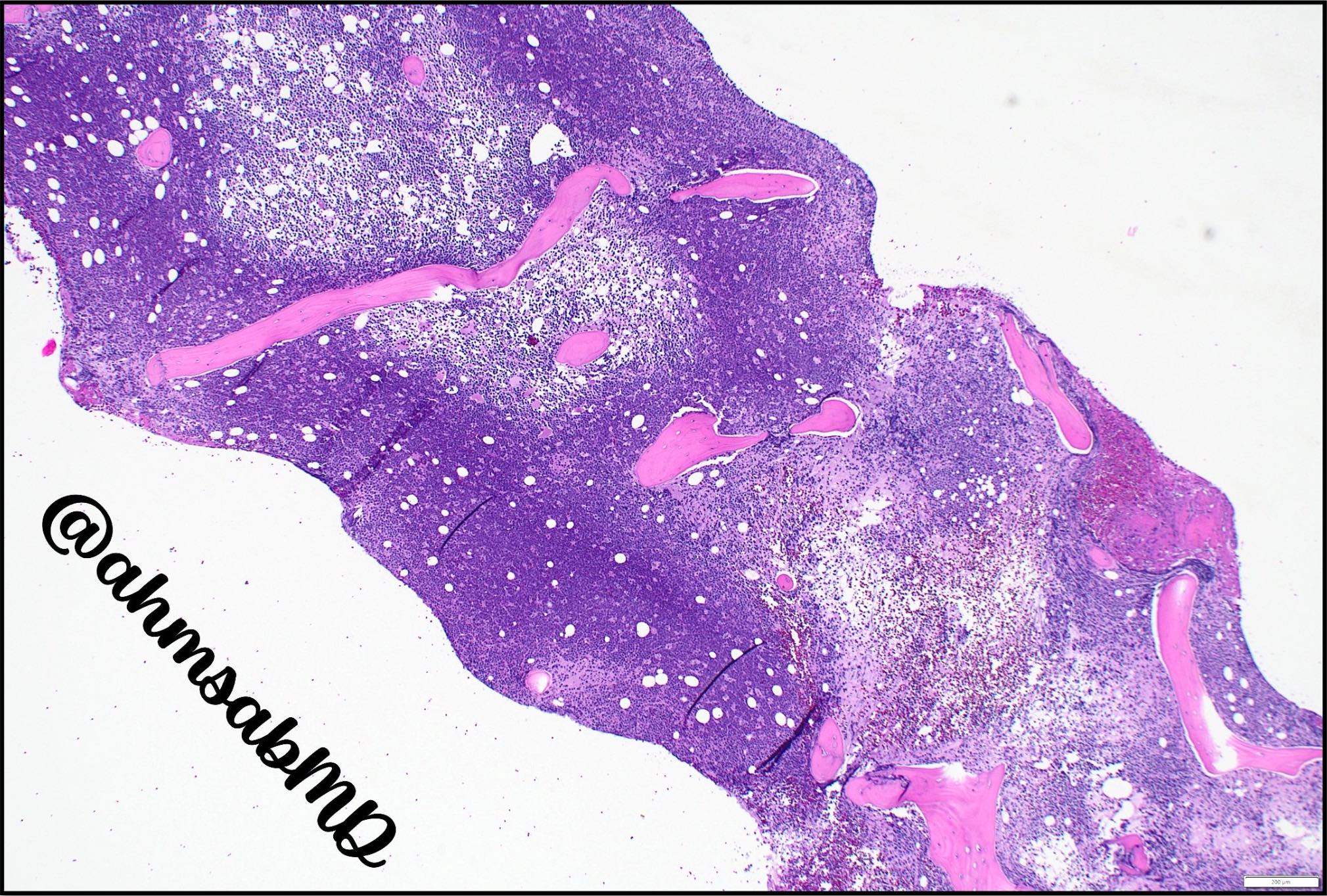
- Replacement of involved organs by fish flesh masses with hemorrhages and necrosis
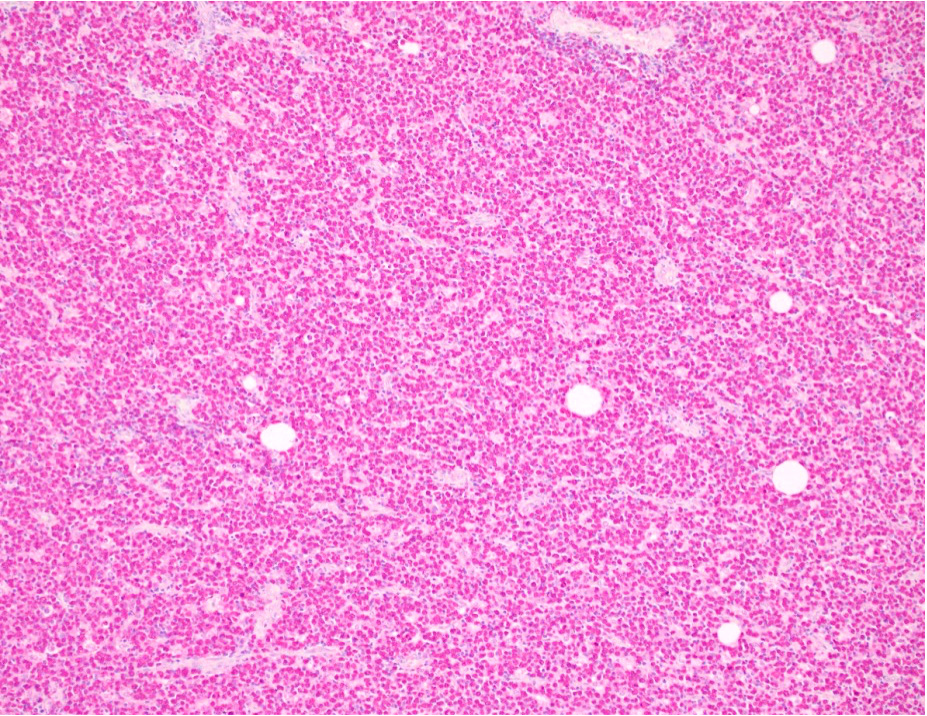
Microscopic (histologic) description
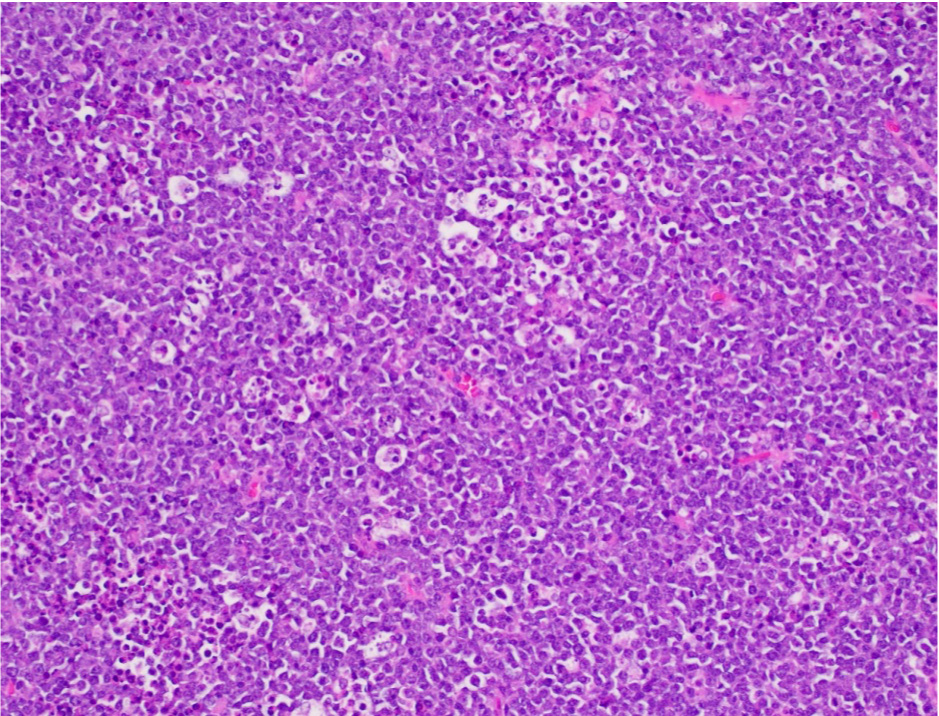
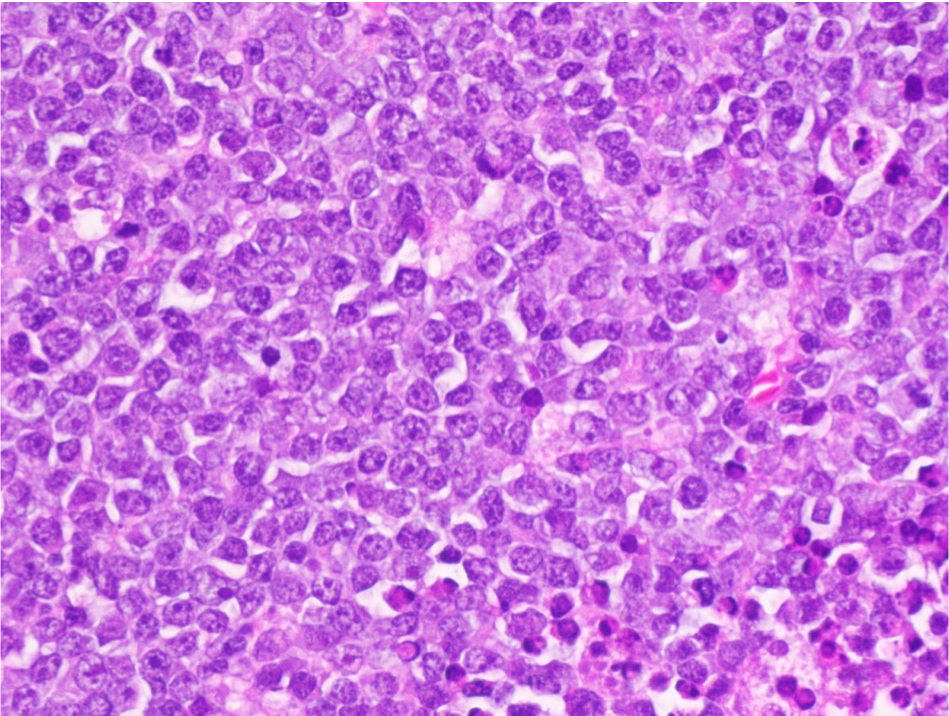
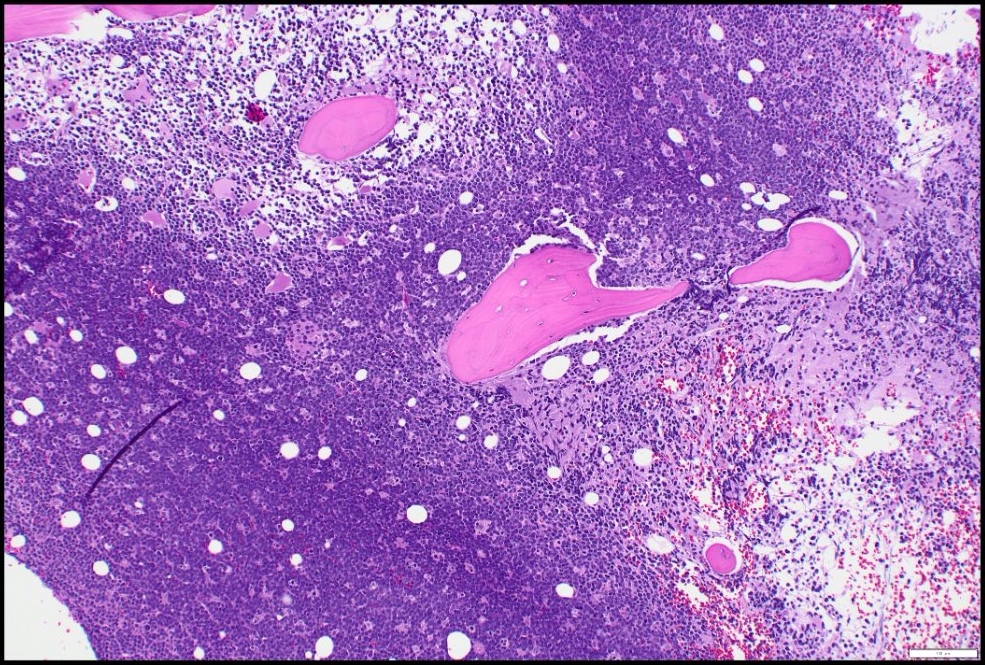
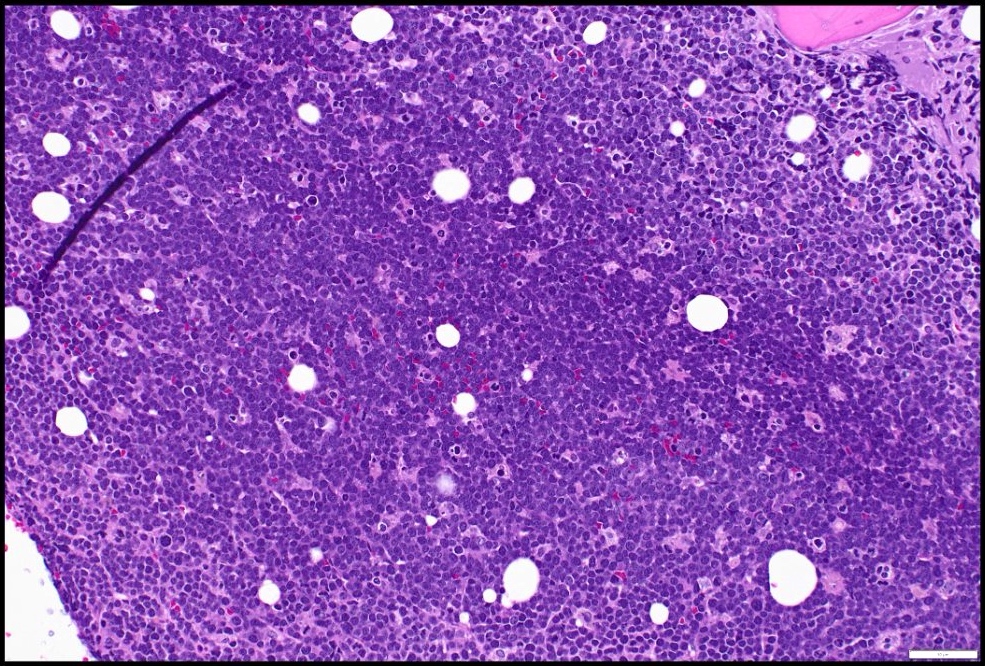
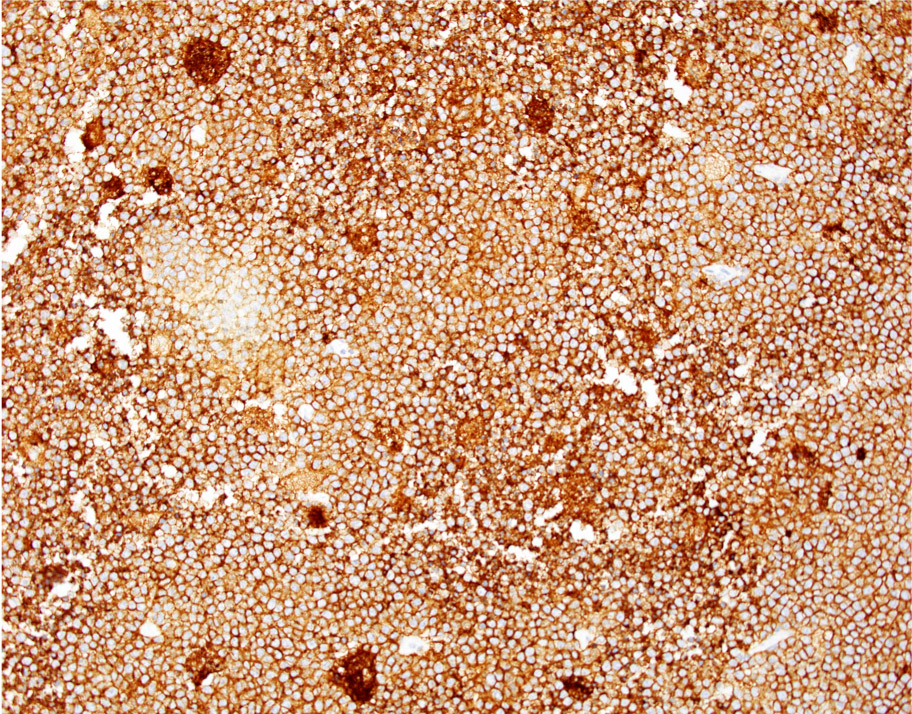
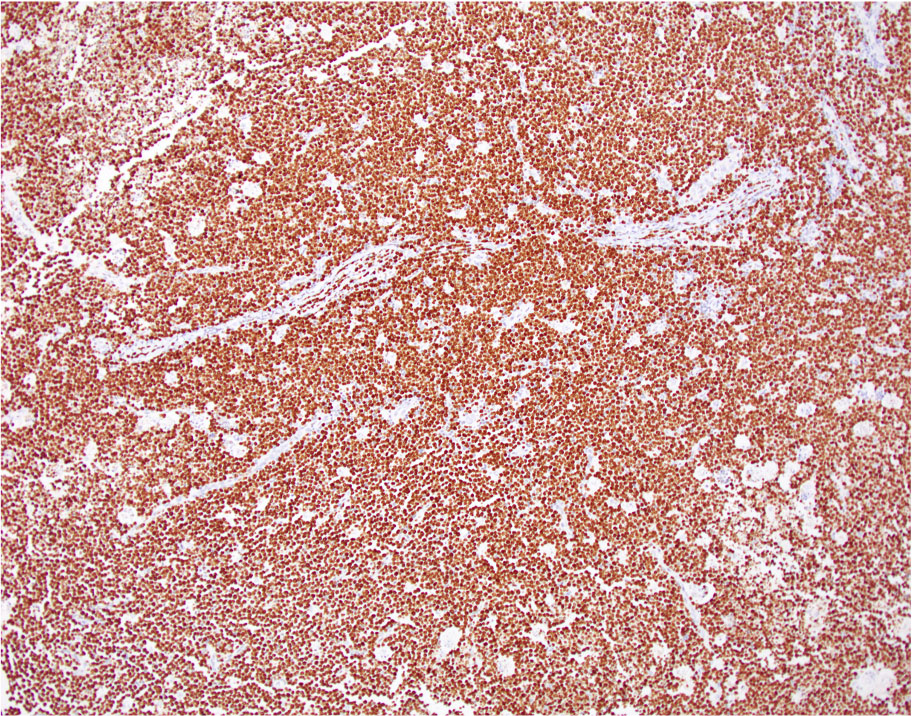
- Sheets of monotonous intermediate size cells with starry sky appearance (Lancet 2012;379:1234)
- Neoplastic cells
- Molded against each other (squared off borders)
- Gap between neoplastic cells secondary to retracted cytoplasm
- Round nuclei with finely clumped chromatin and several paracentral nucleoli
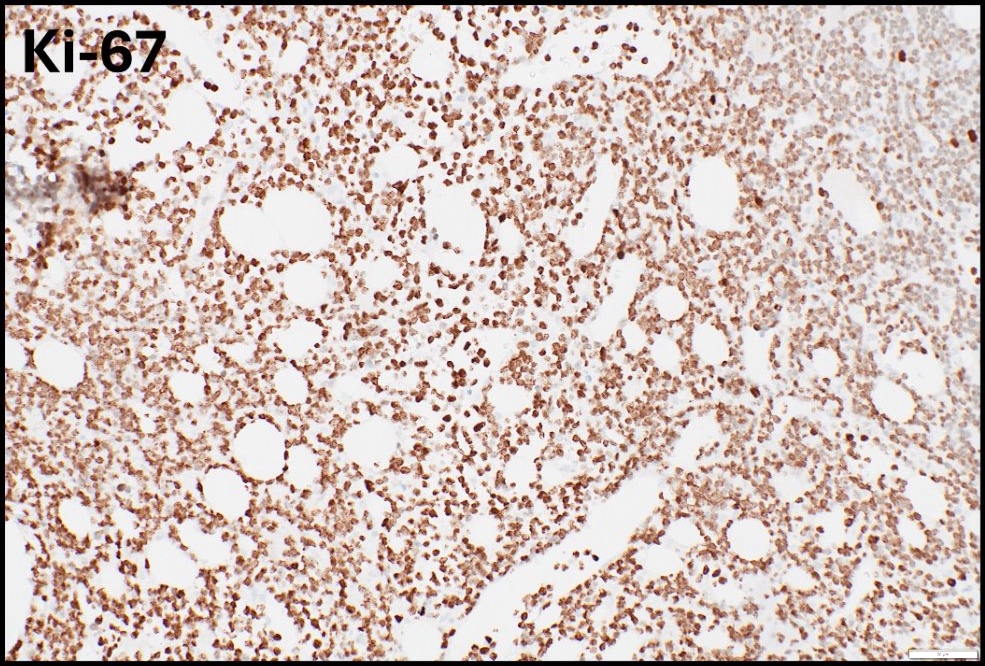
- High proliferation rate (numerous mitotic figures and apoptotic bodies)
- Plasmacytoid differentiation and mild pleomorphism possible in immunodeficiency related Burkitt lymphoma
- Tingible body macrophages phagocyting apoptotic debris (tingible bodies)
- Are the "stars" scattered in the sheet of neoplastic cells (the "dark sky")
- No histologic grading
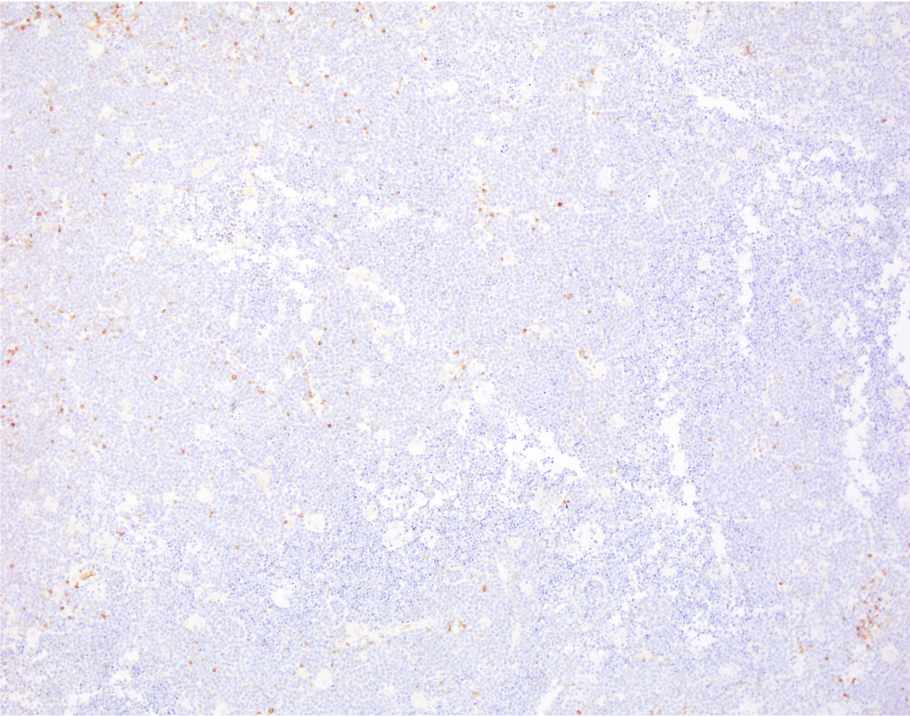
Microscopic (histologic) images
Virtual slides
Cytology description
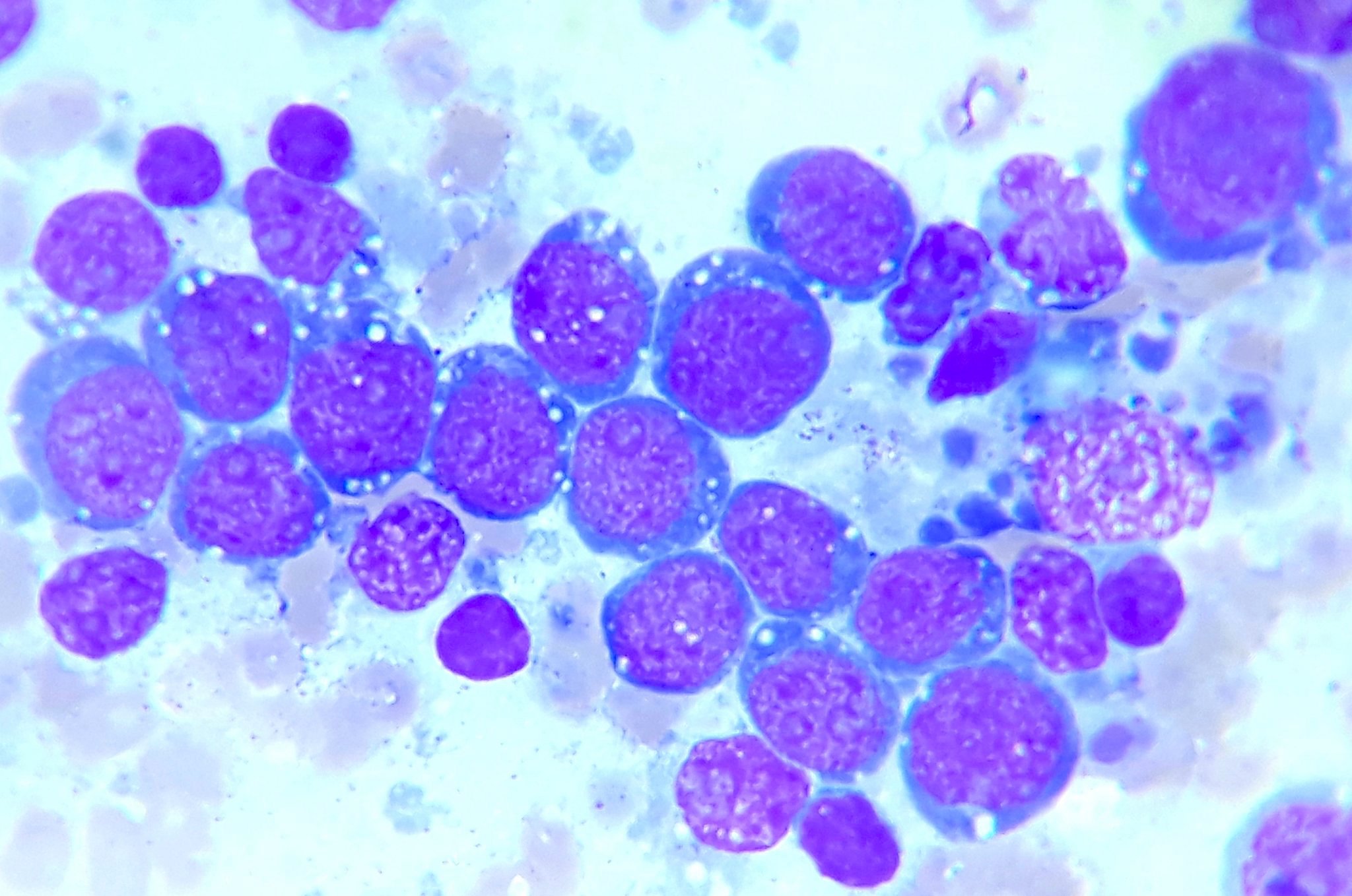
- Hypercellular smear (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2004;128:1459)
- Monotonous neoplastic cells with
- Round or oval nuclei
- Several small nucleoli
- Thin rim of basophilic cytoplasm, often containing lipid vacuoles
- Dirty background (numerous apoptotic bodies)
- Scattered tingible body macrophages
Cytology images
Peripheral smear description
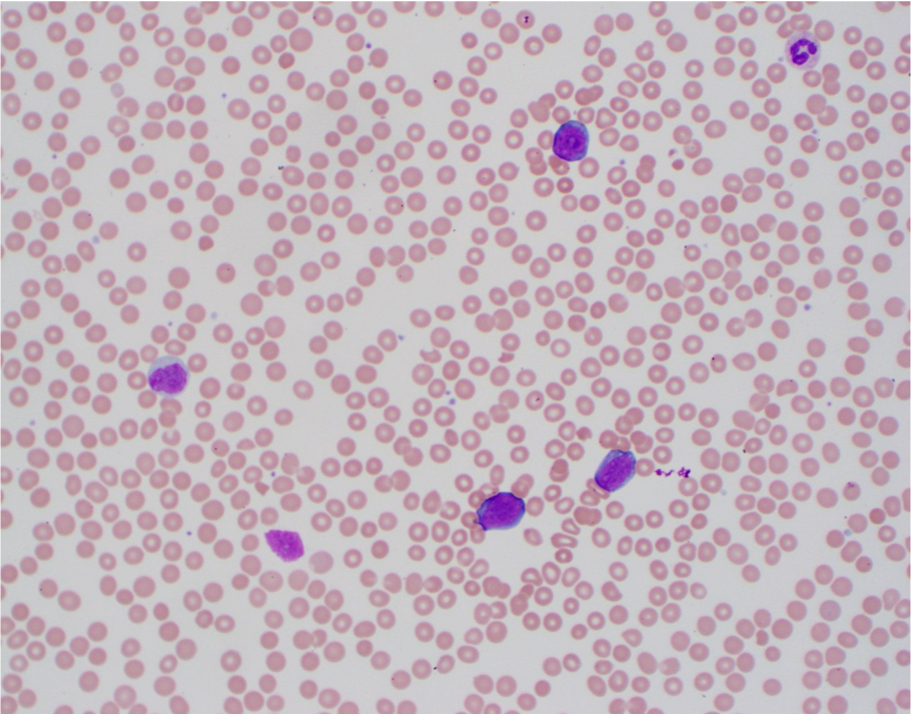
- Neoplastic cells with round or oval nuclei and a thin rim of basophilic cytoplasm, often containing lipid vacuoles
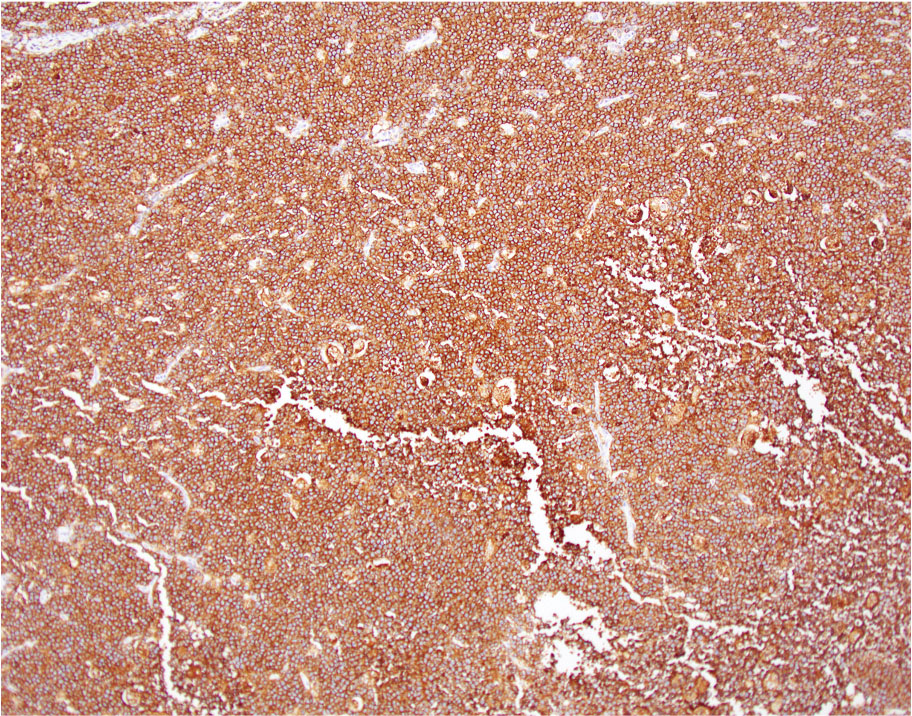
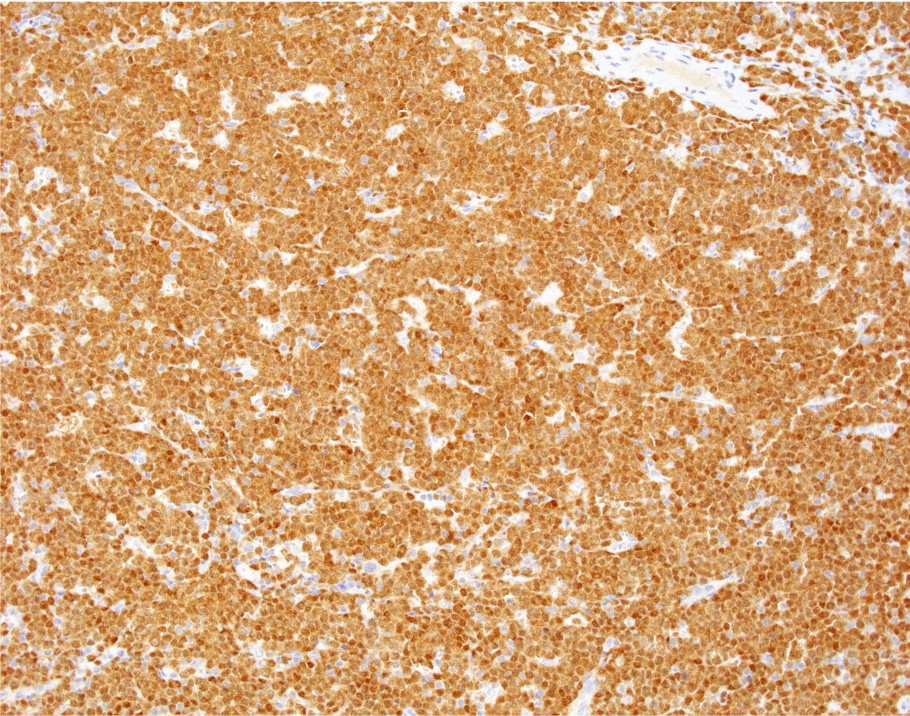
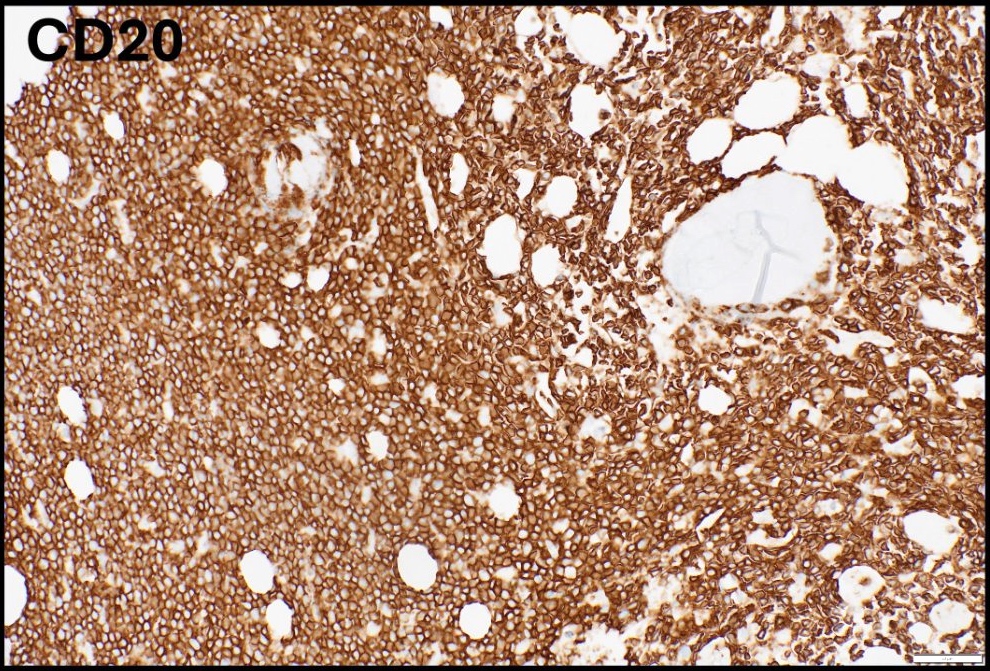
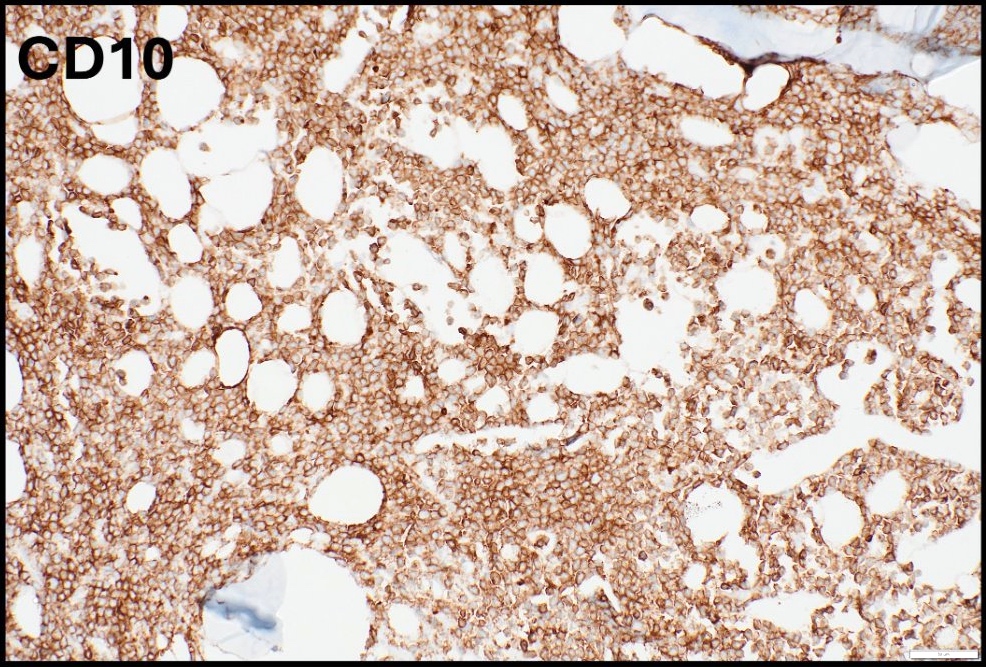
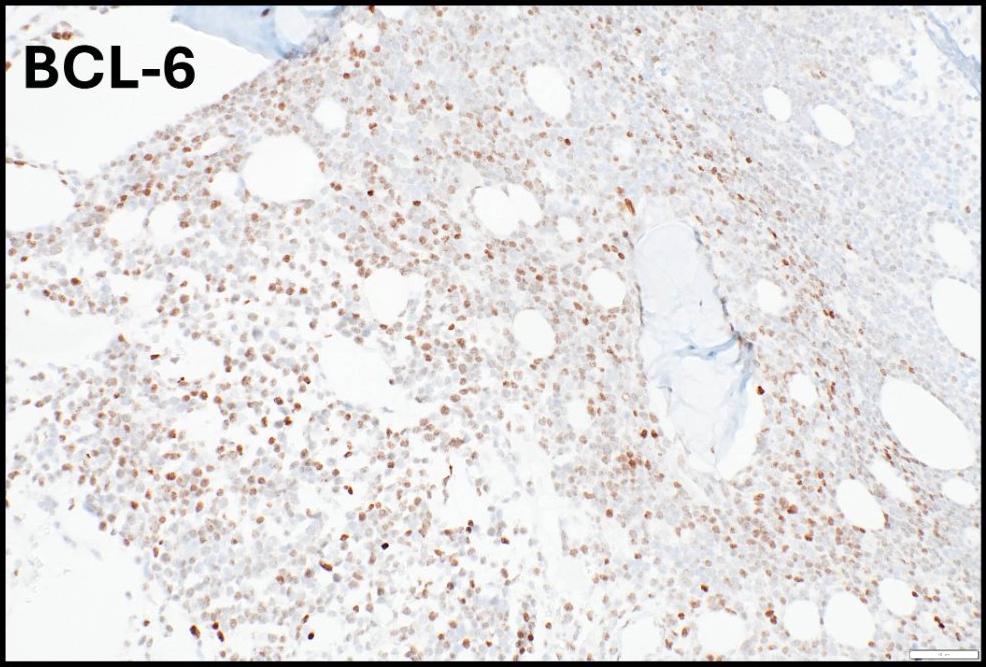
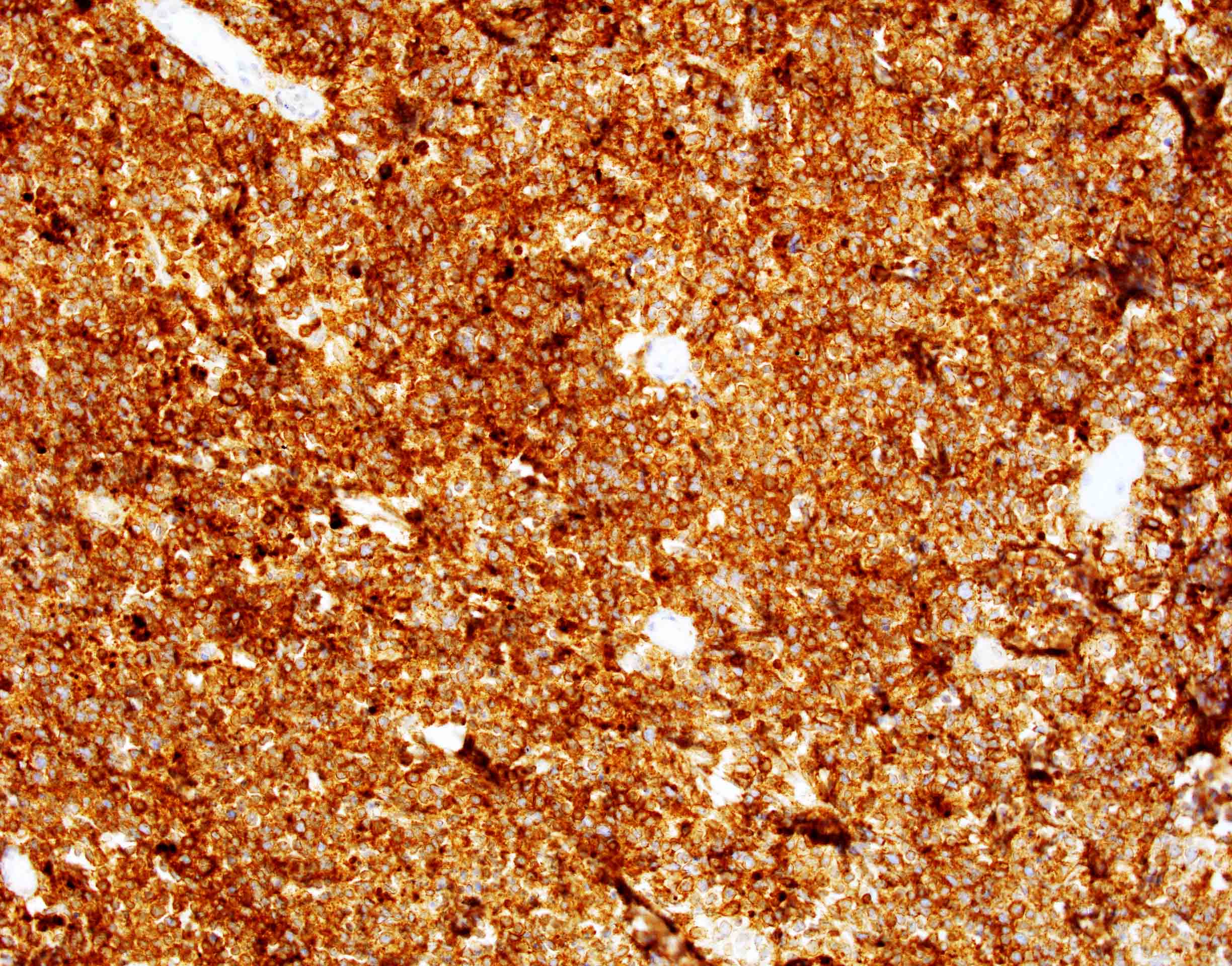
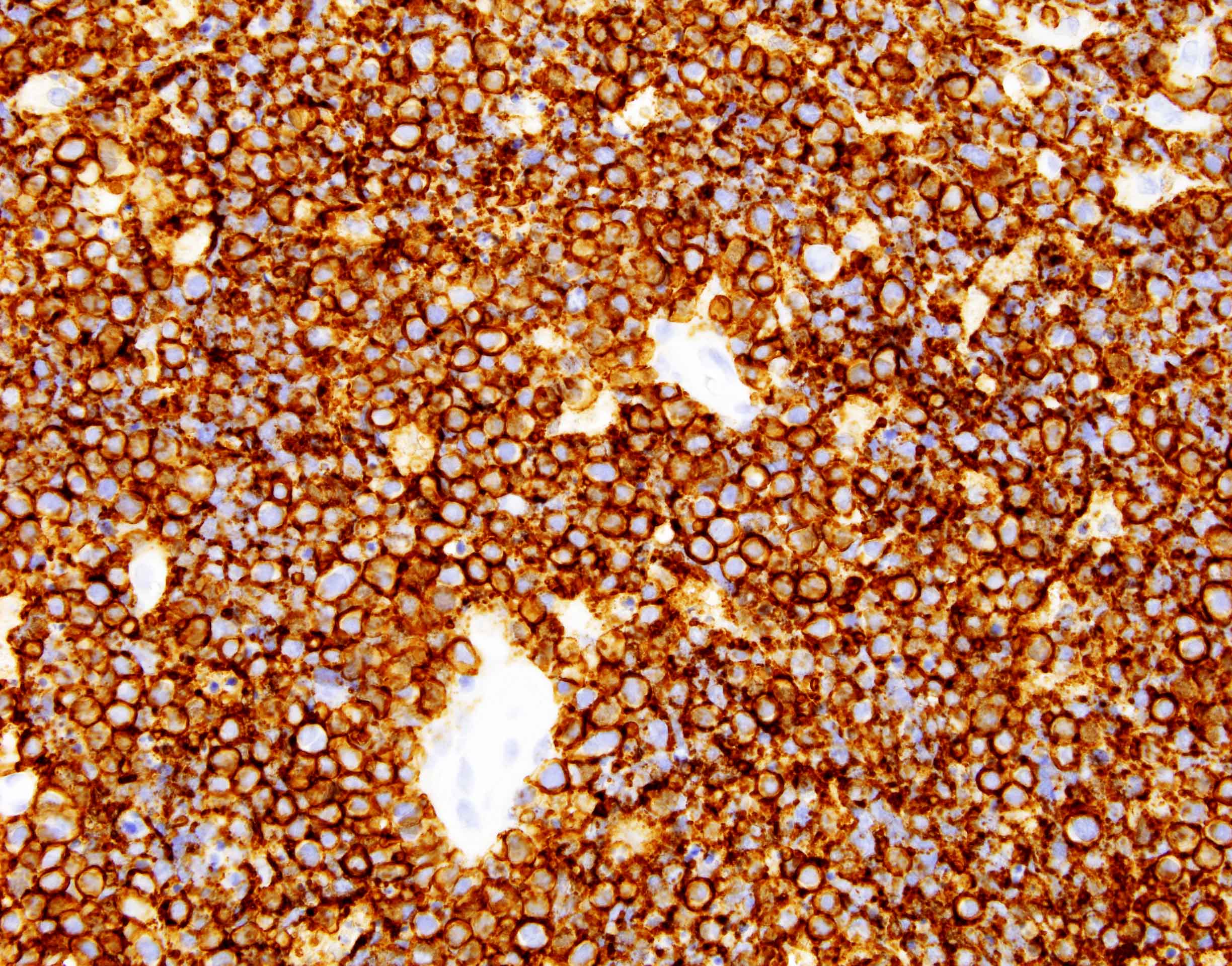
Positive stains
Negative stains
- T cell markers: CD2, CD3, CD5, CD7 (Lancet 2012;379:1234, Front Oncol 2017;7:209)
- BCL2
- TdT
Flow cytometry description
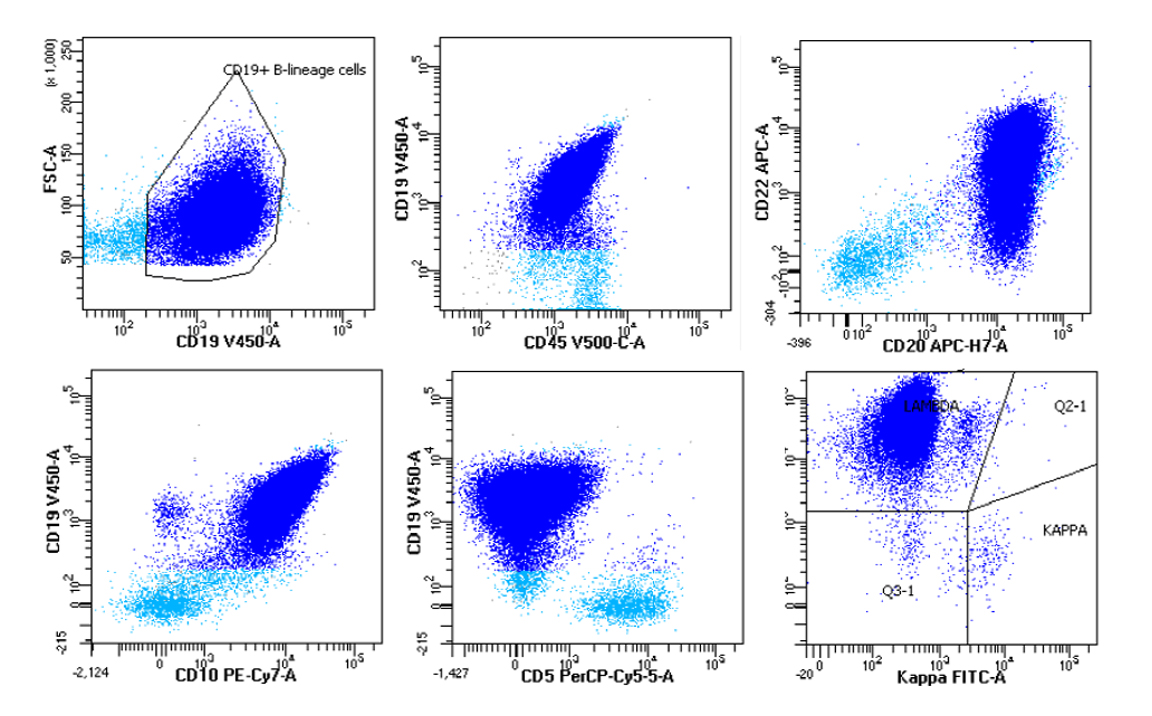
- Nonspecific pattern
- Medium sized monoclonal cells positive for CD10 and pan B markers
- Can also be seen in follicular lymphoma and a subset of large B cell lymphoma
- Bright CD38 expression that can be seen by flow cytometry in MYC rearranged B cell lymphomas (Leuk Lymphoma 2014;55:2592, Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2020;98:412)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Cytogenetics (Curr Opin Hematol 2014;21:326)
- c-MYC reciprocal translocation is characteristic but nonspecific
- Partner genes (DNA Repair (Amst) 2006;5:1213):
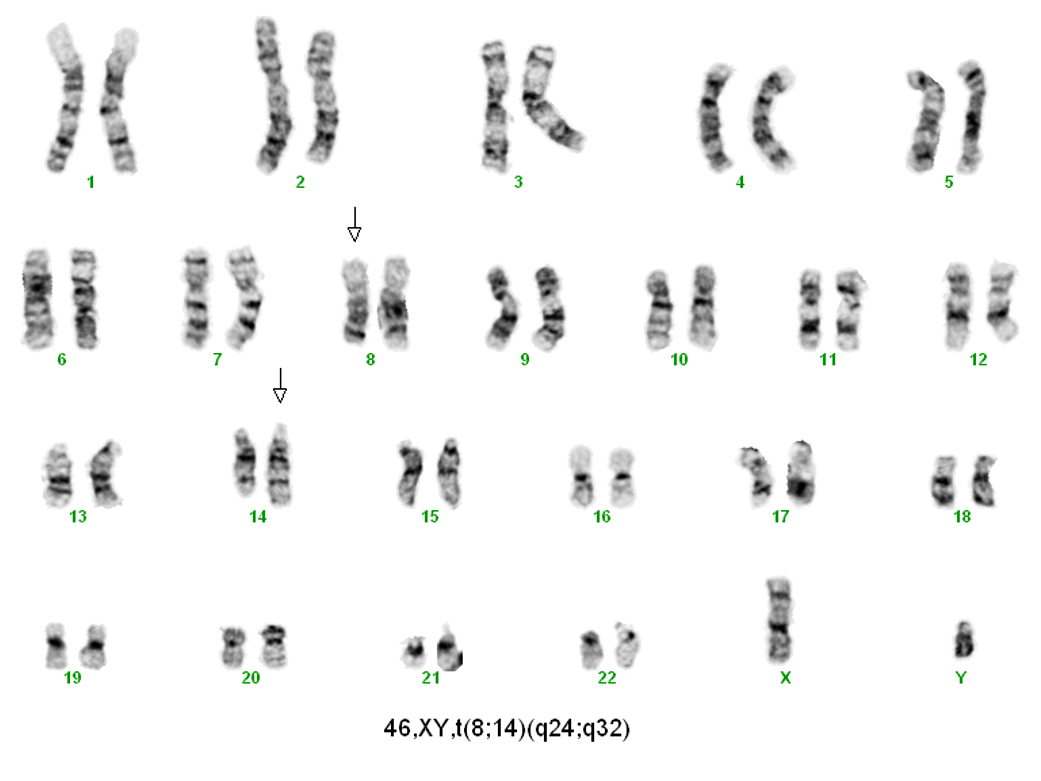
- t(8;14)(q24;q32) c-MYC-IGH (~ 80%)
- t(8;22)(q24;q11) c-MYC-IGL (~ 15%)
- t(2;8)(p11;q24) c-MYC-IGK (~ 5%)
- Additional chromosomal abnormalities possible (see Pathophysiology)
- Karyotype overall simpler than that of other aggressive B cell lymphomas
- In situ hybridization
- EBER+ in EBV positive Burkitt lymphoma
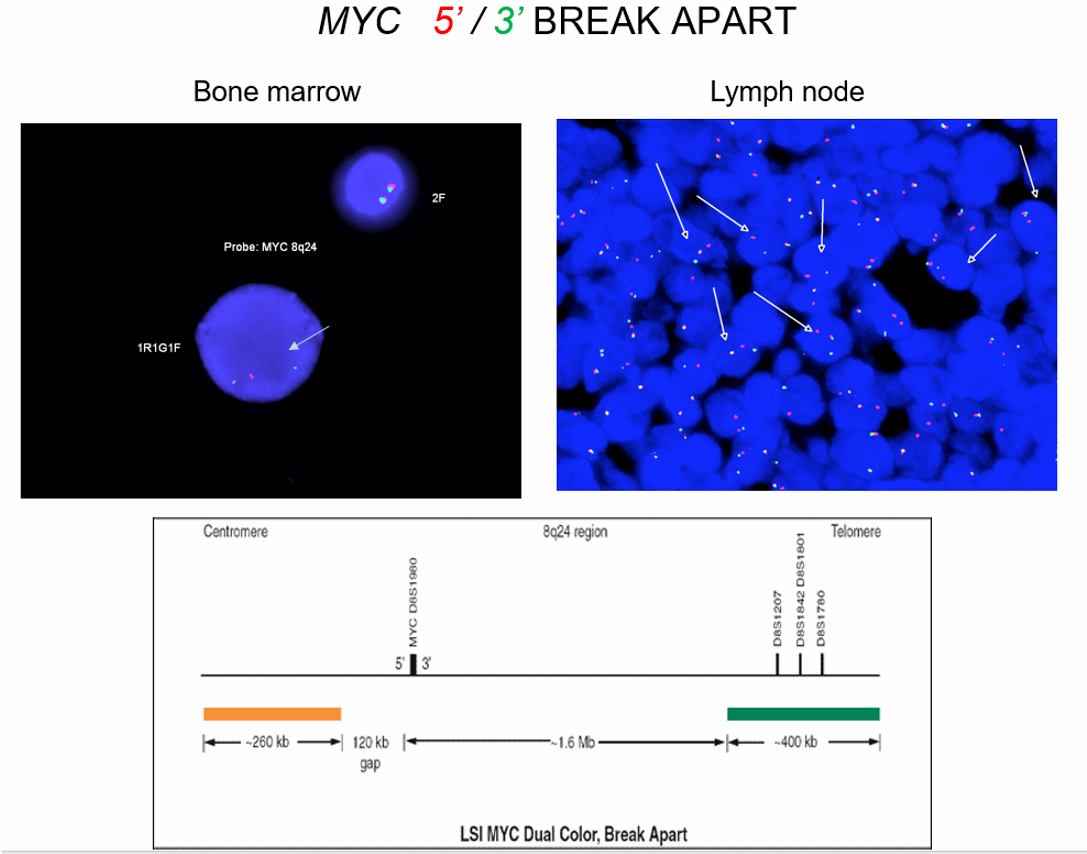
- FISH for c-MYC translocation
- PCR
- Positive for monoclonal immunoglobulin gene rearrangement
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Sample pathology report
- Colon, cecal mass, biopsy:
- Burkitt lymphoma (see comment)
- Comment: Sections show colonic mucosa with diffuse atypical lymphoid infiltrate composes of medium sized monotonous cells with frequent mitosis, apoptotic bodies and scattered tingible body macrophages, creating a starry sky appearance at low microscopic power.
- Corresponding flow cytometry analysis identified a monotypic CD10 positive B cell population with lambda light chain restriction.
- By immunohistochemistry, the atypical lymphocytes express B cell markers including CD20 and PAX5, co-express germinal center markers CD10 and BCL6 and are negative for BCL2, cyclin D1, SOX11, CD5, TdT and CD34. Ki67 proliferation fraction is markedly high and approaching 100%. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) encoded RNA (EBER) in situ hybridization is positive within the vast majority of the atypical lymphocytes.
- Fluorescence in situ hybridization, identified MYC rearrangement in 95% of cells. BCL2-IGH and BCL6 rearrangements are not detected. Karyotype analysis detected t(8;14) in 20 of the analyzed metaphase cells.
- The constellation of the above findings are consistent with the diagnosis of Burkitt lymphoma.
Differential diagnosis
- High grade B cell lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 or BCL6 rearrangement (i.e. double / triple hit):
- Older patient
- Morphologic features overlaps between Burkitt lymphoma and diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- MYC and BCL2 rearrangement in double hit lymphoma; MYC, BCL2 and BCL6 rearrangement in triple hit lymphoma
- Complex karyotype
- High grade B cell lymphoma, NOS:
- Morphologic features overlap between Burkitt lymphoma, diffuse large B cell lymphoma and lymphoblastic lymphoma (blastoid morphology)
- Immunophenotype is not typical for Burkitt lymphoma
- c-MYC rearrangement can be positive
- Usually associated with a more complex karyotype
- Mantle cell lymphoma, blastoid variant:
- Diffuse large B cell lymphoma, NOS:
- Older patient
- Starry sky appearance uncommon
- Larger neoplastic cells with vesicular nuclear chromatin
- Ki67 might be high but usually < 90%
- c-MYC rearrangement (when present) associated with complex karyotype
- B lymphoblastic lymphoma:
- Burkitt-like lymphoma with 11q alteration:
- Resembles Burkitt lymphoma morphologically
- Lacks c-MYC rearrangement
- Associated with chromosome 11q alterations, particularly gain or amplification of 11q12/q13-q23/q24 and loss of the rest of the chromosome
- Plasmablastic lymphoma:
- Strongly associated with HIV
- Starry sky appearance is common
- Plasmacytoid differentiation
- Positive for plasma cell markers (CD38, CD138, IRF4 / MUM1) and negative for pan B markers
- EBV is positive in the majority of cases
- c-MYC rearrangement is positive in approximately 50% of cases
Additional references
Practice question #1
Practice answer #1
B. BCL2 negativity
The section shows a sheet of monotonous medium to large size CD20 positive cells with squared off borders and a starry sky appearance, raising concern for an aggressive B cell lymphoma. These cells are positive for CD10 and BCL6, suggesting a germinal center origin. Ki67 reactivity in almost 100% of the cells is suspicious for Burkitt lymphoma. Unlike diffuse large B cell lymphoma and high grade B cell lymphoma, BCL2 would be negative in Burkitt lymphoma.
Diffuse and strong CD30 positivity would be suggestive of anaplastic large T cell lymphoma. ALK positivity would be seen in ALK positive anaplastic large T cell lymphoma and ALK positive diffuse large B cell lymphoma. MYC is positive in Burkitt lymphoma, mirroring MYC overexpression. Finally, although GFAP would indeed be negative in Burkitt lymphoma, this immunostain would not be helpful as a glioma would not be in the differential.
Comment Here
Reference: Burkitt lymphoma
The section shows a sheet of monotonous medium to large size CD20 positive cells with squared off borders and a starry sky appearance, raising concern for an aggressive B cell lymphoma. These cells are positive for CD10 and BCL6, suggesting a germinal center origin. Ki67 reactivity in almost 100% of the cells is suspicious for Burkitt lymphoma. Unlike diffuse large B cell lymphoma and high grade B cell lymphoma, BCL2 would be negative in Burkitt lymphoma.
Diffuse and strong CD30 positivity would be suggestive of anaplastic large T cell lymphoma. ALK positivity would be seen in ALK positive anaplastic large T cell lymphoma and ALK positive diffuse large B cell lymphoma. MYC is positive in Burkitt lymphoma, mirroring MYC overexpression. Finally, although GFAP would indeed be negative in Burkitt lymphoma, this immunostain would not be helpful as a glioma would not be in the differential.
Comment Here
Reference: Burkitt lymphoma
Practice question #2
This specimen is a touch imprint obtained from an axillary lymph node of a 35 year old white man with HIV. Which of the following viruses is associated with this disease and with what frequency?
- Epstein-Barr virus in 30% of cases
- Epstein-Barr virus in > 95% of cases
- Human herpesvirus 8 in 50% of cases
- Human herpesvirus 8 in > 95% of cases
- Human T cell leukemia virus type 1 in > 95% of cases
Practice answer #2
A. Epstein-Barr virus in 30% of cases
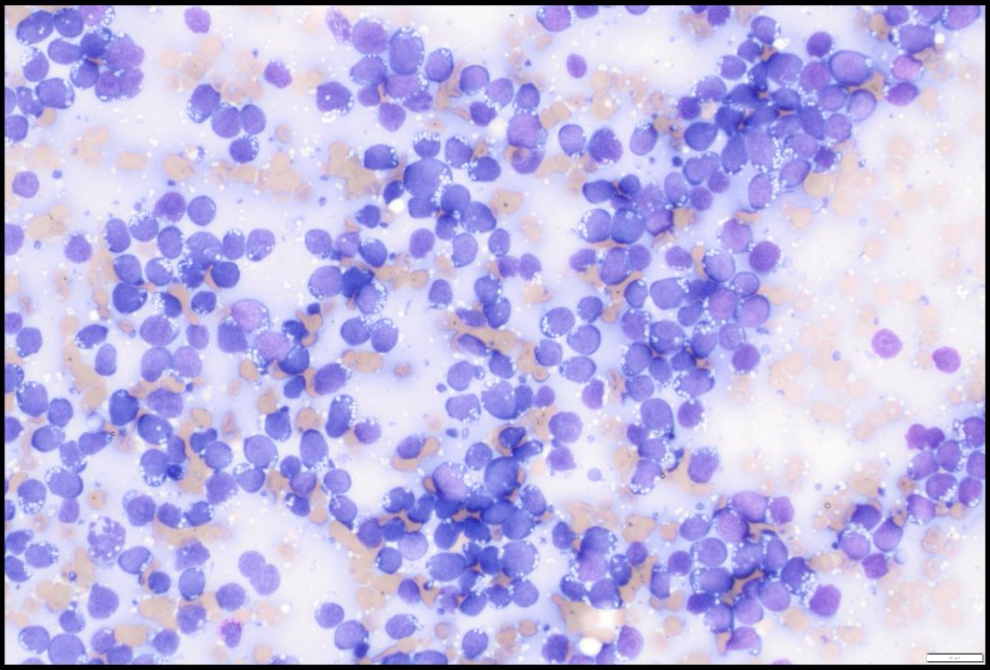
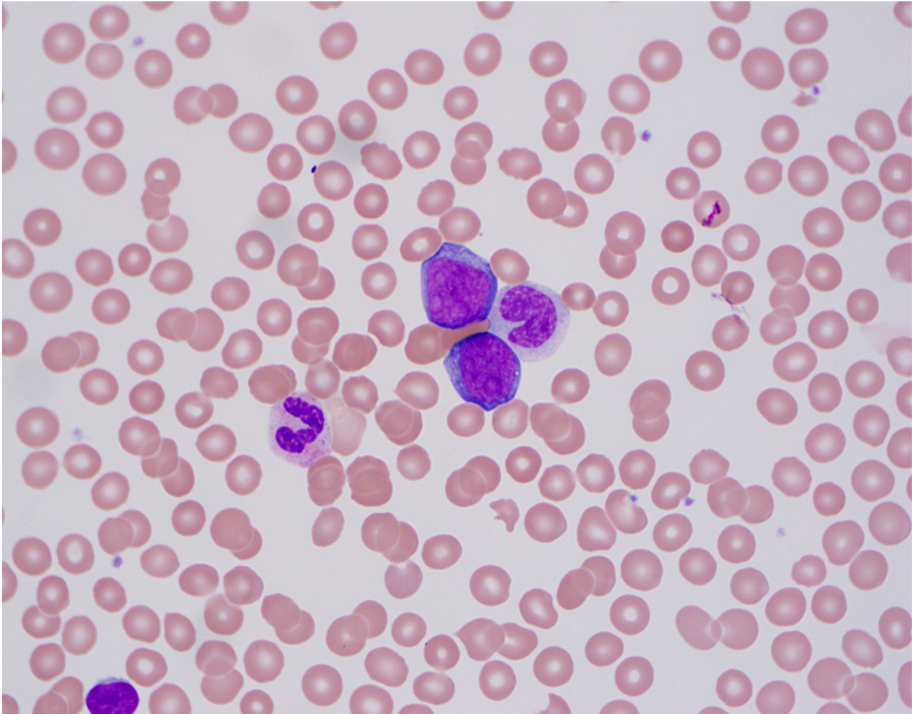
The touch imprint shows a sheet of monotonous cells with nuclei containing fine chromatin and prominent nucleoli, surrounded by a thin rim of deeply basophilic cytoplasm containing vacuoles; this raises concern for Burkitt lymphoma. A tingible body macrophage is present in the upper center.
Unlike the endemic variant of Burkitt lymphoma seen in Equatorial Africa and Papua New Guinea, where Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is present in almost 100% of cases, the immunodeficiency associated variant is mainly seen in HIV patients and is associated with EBV in 25 - 40% of cases. Human herpesvirus 8 (HHV8) is associated with primary effusion lymphoma, multicentric Castleman disease, Kaposi sarcoma and HHV8 associated diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Human T cell leukemia virus type 1 is associated with adult T cell lymphoma.
Comment Here
Reference: Burkitt lymphoma
The touch imprint shows a sheet of monotonous cells with nuclei containing fine chromatin and prominent nucleoli, surrounded by a thin rim of deeply basophilic cytoplasm containing vacuoles; this raises concern for Burkitt lymphoma. A tingible body macrophage is present in the upper center.
Unlike the endemic variant of Burkitt lymphoma seen in Equatorial Africa and Papua New Guinea, where Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is present in almost 100% of cases, the immunodeficiency associated variant is mainly seen in HIV patients and is associated with EBV in 25 - 40% of cases. Human herpesvirus 8 (HHV8) is associated with primary effusion lymphoma, multicentric Castleman disease, Kaposi sarcoma and HHV8 associated diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Human T cell leukemia virus type 1 is associated with adult T cell lymphoma.
Comment Here
Reference: Burkitt lymphoma