Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Electron microscopy images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Chen IY, Agostini-Vulaj D. Gastroblastoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stomachgastroblastoma.html. Accessed May 14th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Rare, biphasic tumor of the stomach (only 13 cases currently reported) (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2021;60:640)
Essential features
- Rare, biphasic epitheliomesenchymal neoplasm of the stomach
- Majority of cases have characteristic fusion gene, MALAT1::GLI1
- Novel EWSR1::CTBP1 fusion was recently identified
- Mostly seen in young adults
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8976/3 - gastroblastoma
- ICD-11: 2F70.1 & XH4VQ1 - neoplasms of uncertain behavior of stomach & gastroblastoma
Epidemiology
- Young adults, most < 30 years of age but also seen in older adults; M > F (Histopathology 2019;75:778, Mod Pathol 2017;30:1443)
Sites
- Stomach (intramural), antrum > body (Histopathology 2019;75:778)
Pathophysiology
- MALAT1::GLI1 fusion drives the oncogenic properties of GLI1 and activates hedgehog pathway (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2022;61:285)
- EWSR1::CTBP1 fusion drives the NOTCH and FGFR pathway activation (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2022;61:285)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Nonspecific symptoms at presentation (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1370)
Diagnosis
- Imaging followed by tissue diagnosis
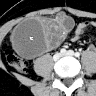
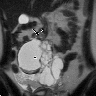
Radiology description
- CT: solid and cystic heterogenous mass centered in gastric wall or exophytic (Radiographics 2014;34:1929)
Prognostic factors
- Unknown at this time
Case reports
- 17 year old boy with Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome and allogeneic bone marrow transplants presented with bright red hematemesis and melena (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2021;60:640)
- 43 year old woman with gastrointestinal bleed (Case Rep Pathol 2019;2019:4084196)
- 79 year old man with weight loss and dysphagia (Histopathology 2019;75:778)
Treatment
- Surgical resection; some reported cases received adjuvant radiation treatment as well (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1370, J Clin Pathol 2010;63:270)
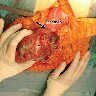
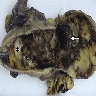
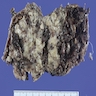
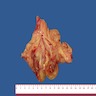
Gross description
- Size range: 2.3 - 15 cm (Case Rep Pathol 2019;2019:4084196)
- Solid or solid / cystic mass originating from gastric wall with variable hemorrhage and necrosis (Int J Surg Case Rep 2017;39:72)
- Can be ulcerated, polypoidal, intramural or exophytic (Int J Surg Case Rep 2017;39:72)
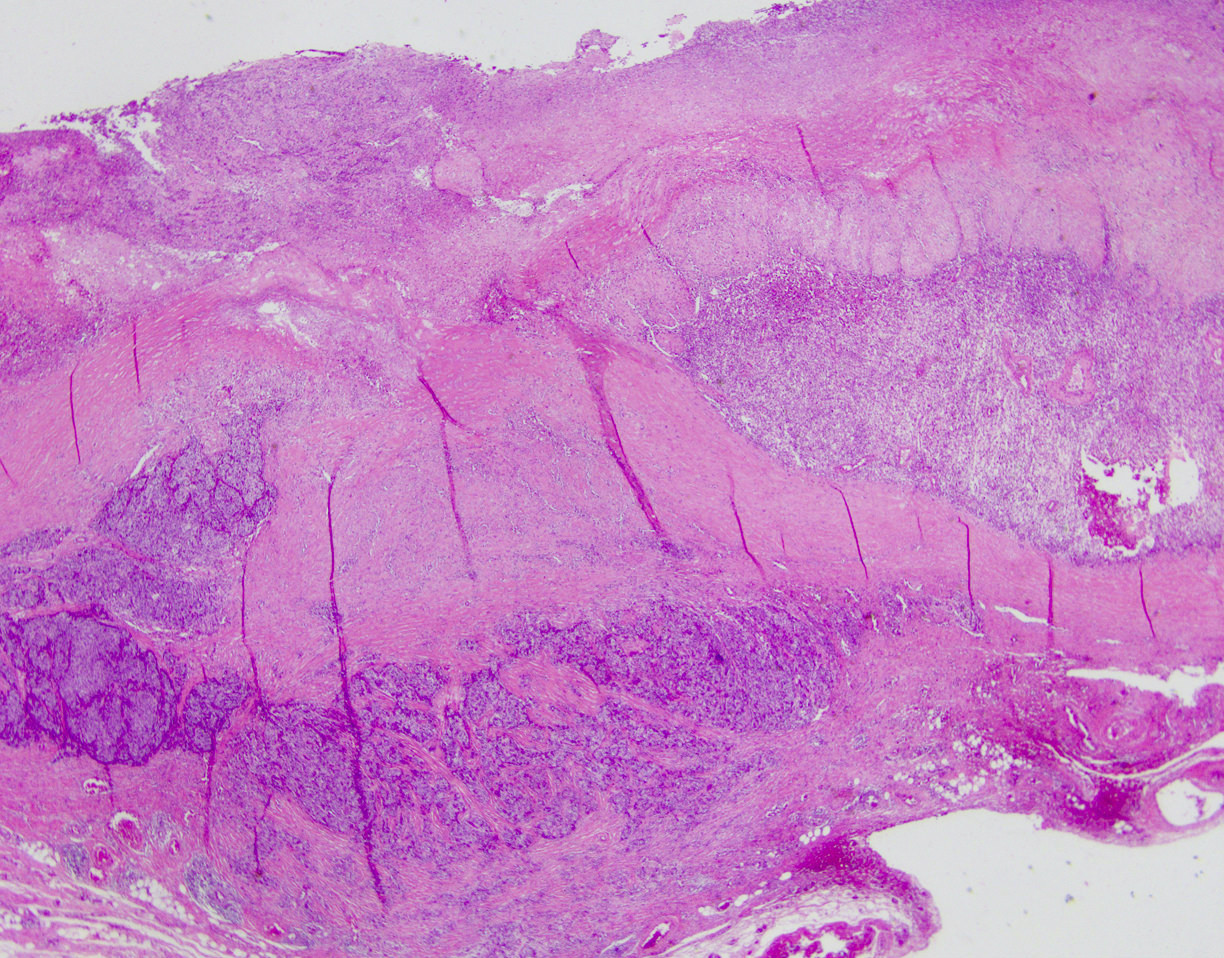
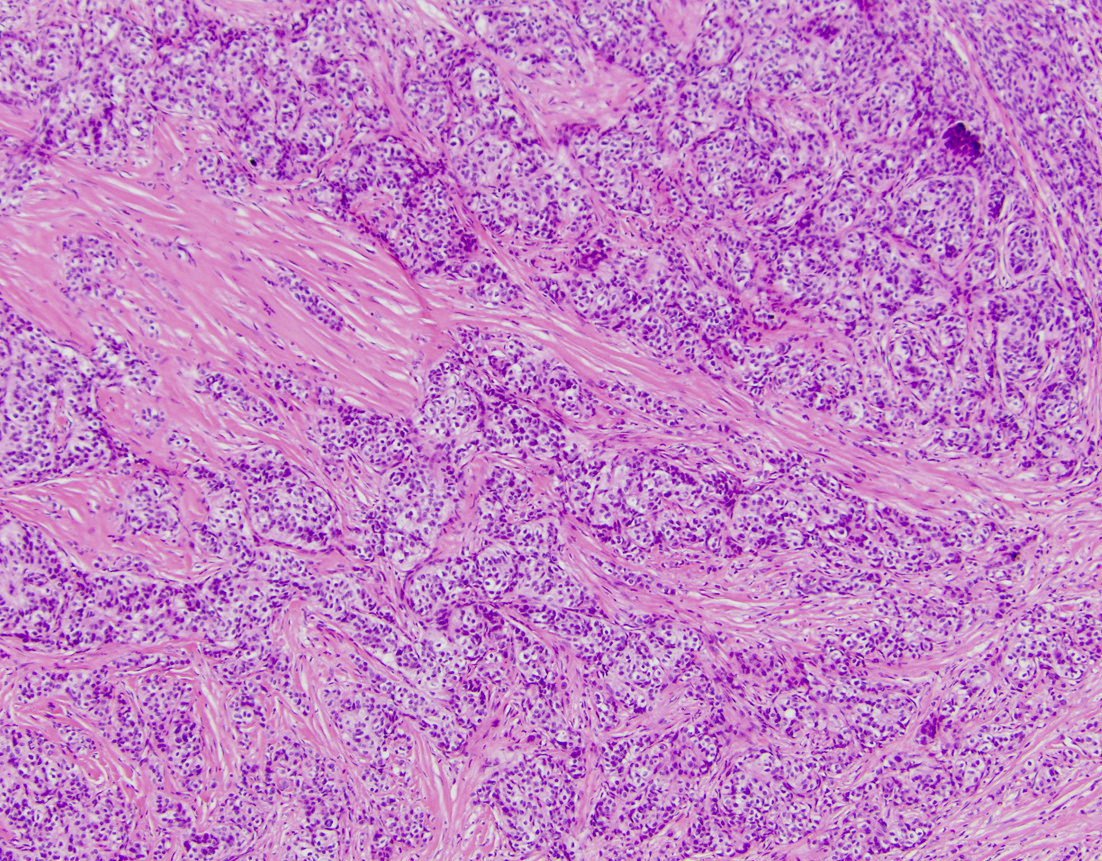
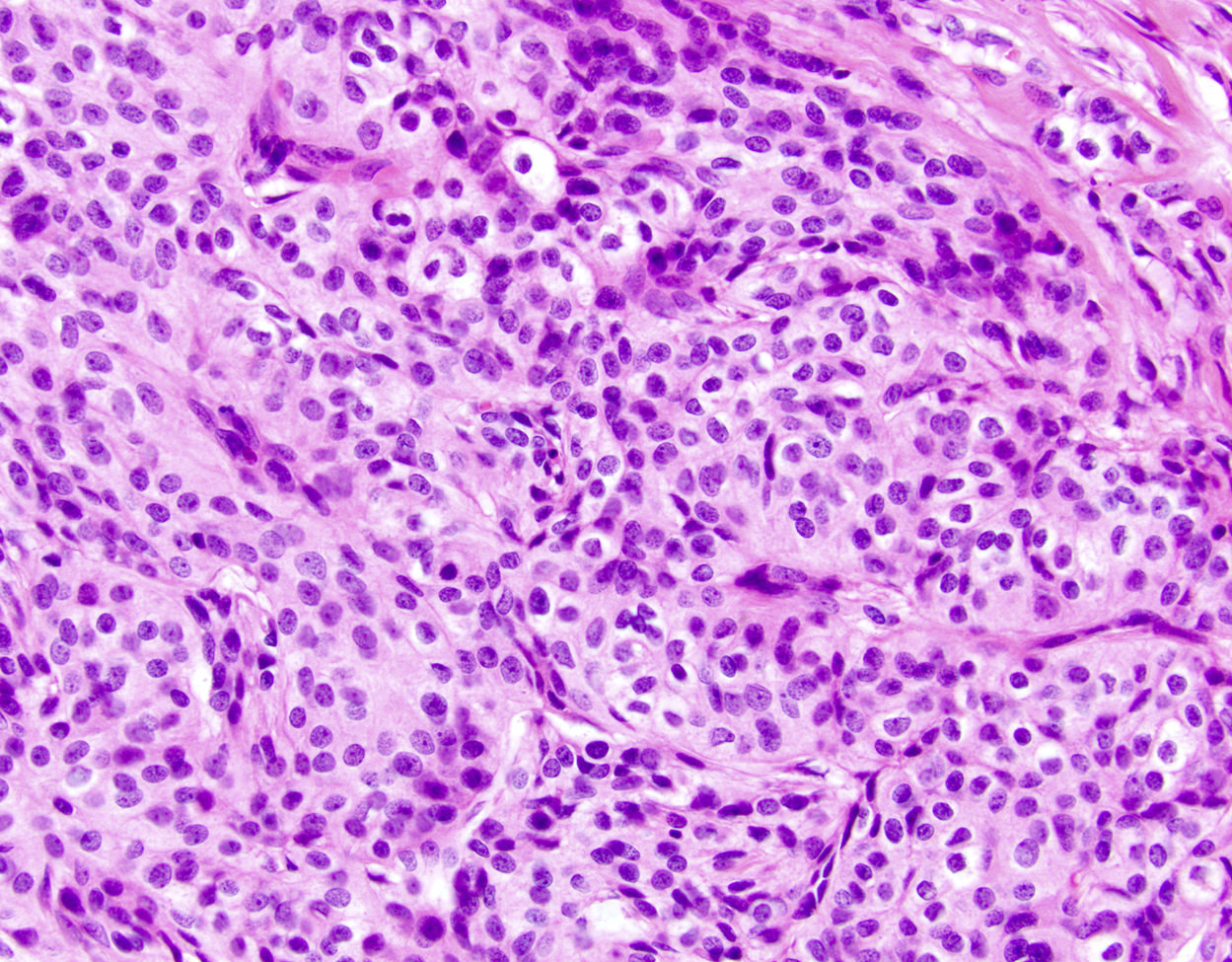
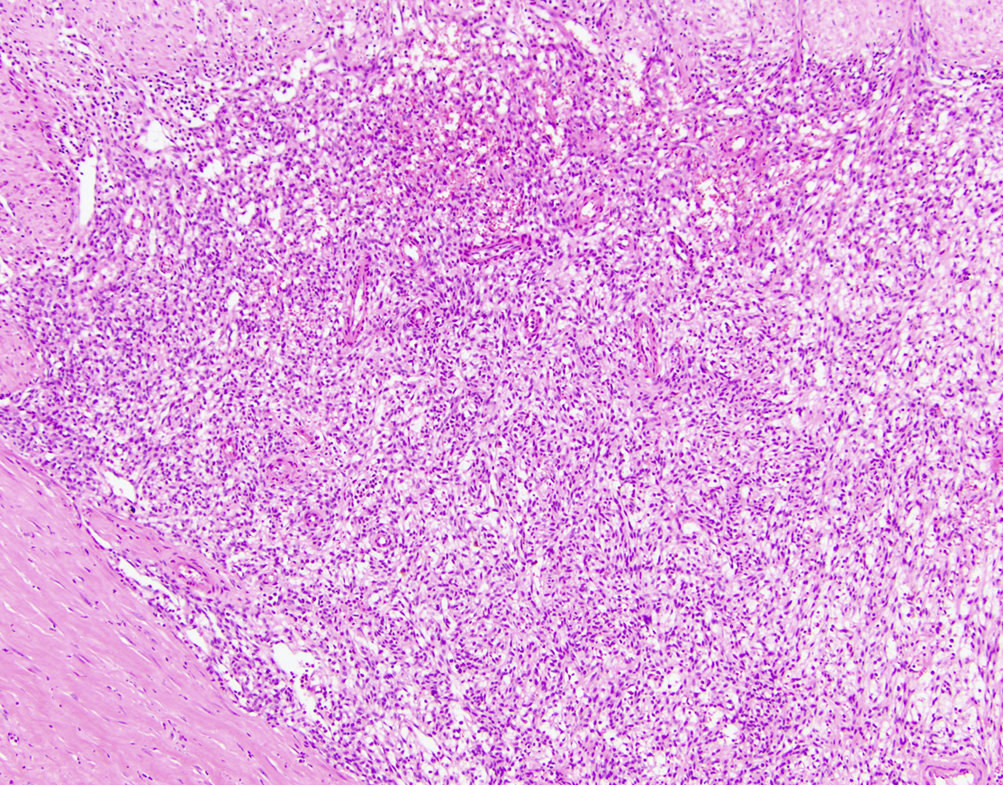
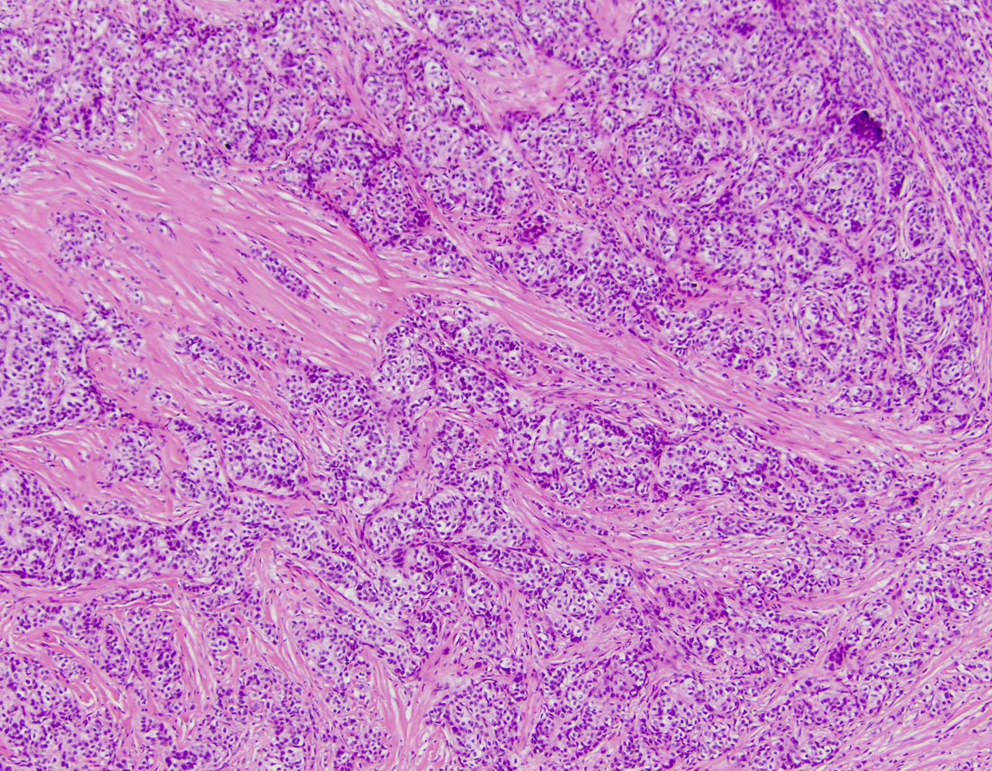
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Biphasic tumor
- Spindle cell component demonstrating sheets of monotonous spindled type cells
- Epithelial component demonstrating cords / clusters of epithelial type cells, some with vague to well formed gland formation, which may contain inspissated material
- Relatively low mitotic rate (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1370)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Epithelial component: various keratins (AE1 / AE3, CAM5.2, keratin 7 [partial], keratin 18), CD56 (focal), CD10 (focal) (Case Rep Pathol 2019;2019:4084196)
- Spindle cell component: vimentin, CD10, CD56 (Case Rep Pathol 2019;2019:4084196)
- Both components: GLI1
Negative stains
- Epithelial component: CK5/6, CK20, EMA
- Both components: DOG1, CD34, CD99, ER, KIT, SMA, desmin, S100, p63, calretinin, chromogranin, synaptophysin, CDX2, TTF1, TLE1 and SS18 (Case Rep Pathol 2019;2019:4084196)
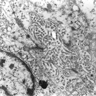
Electron microscopy description
- Tumor cells are joined by desmosomes and have microvilli (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1370)
Electron microscopy images
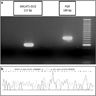
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Characteristic MALAT1::GLI1 fusion gene (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2022;61:285)
- Novel EWSR1::CTBP1 fusion gene was recently identified (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2021;60:640)
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Sample pathology report
- Stomach, partial gastrectomy:
- Gastroblastoma (see comment)
- Comment: H&E sections demonstrate a biphasic tumor with varied intermixed epithelial and stromal elements. The epithelial component is positive for keratin AE1 / AE3 while the stromal component is positive for vimentin. Both components are negative for KIT, CD34, desmin, S100, CD99 and SMA. Additional ancillary testing demonstrates the MALAT1::GLI1 fusion gene.
Differential diagnosis
- Biphasic synovial sarcoma:
- Usually monophasic in stomach (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1370)
- Translocation t(x;18), SYT::SSX1
- Carcinosarcoma:
- Overtly malignant epithelial and stromal tumor
- No characteristic translocation
- Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST):
- Plexiform fibromyxoma:
- Monophasic
- Plexiform growth pattern
- Can exhibit MALAT1::GLI1 fusion
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Which fusion gene typifies gastroblastoma?
- ASPL::TFE3
- BRAF::KIAA1549
- ETV6(TEL)::NTRK3
- MALAT1::GLI1
- SYT::SSX1
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
A large gastric antral tumor is excised in a 15 year old boy. Histologically, you identify 2 differing cellular components with spindled and epithelioid morphology (see image above). KIT, DOG1, SMA, desmin and S100 are negative. Which tumor type could this be?
- Gastroblastoma
- Gastrointestinal stromal tumor
- Granular cell tumor
- Leiomyoma
- Schwannoma
Board review style answer #2