Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Castillo VF, Saleeb R. Papillary. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/kidneytumormalignantrccpap.html. Accessed September 22nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Usually circumscribed malignant neoplasm characterized by predominantly papillary or tubulopapillary architecture
Essential features
- Predominantly papillary or tubulopapillary pattern lined by small, basophilic cells or large, eosinophilic cells
- Size cut off > 15 mm; often contain foamy histiocytes and psammoma bodies
- Must exclude other renal cell carcinomas (RCCs) with papillary architecture
- Alpha methyacyl CoA racemase (AMACR) positivity is a desirable feature
- Histologic subclassification to type 1 and type 2 is no longer recommended
- Due to poor interobserver reproducibility, the presence of overlapping features in a significant proportion of cases, the lack of prognostic significance and the historical inclusion of outliers (newly recognized entities) in the old type 2 category (Mod Pathol 2021;34:1392)
Terminology
- Not recommended: tubulopapillary renal cell carcinoma, renal papillary adenocarcinoma, chromophil renal cell carcinoma
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8260/3 - papillary renal cell carcinoma
- ICD-11: 2C90.0 & XH1D07 - renal cell carcinoma of kidney, except renal pelvis & papillary renal cell carcinoma
Epidemiology
- Second most common type of kidney tumors in adults; 15 - 20% of renal cell carcinoma (Curr Opin Urol 2022;32:344)
- Male predominance (M:F = 1.5 - 2:1) (Urol Oncol 2021;39:327)
Sites
- Renal cortex
Pathophysiology
- MET alterations are found mainly in low grade tumors
- CDKN2A, MYC pathway and NRF2-ARE pathway aberrations are observed in high grade tumors
- Other pathways or complexes implicated in papillary renal cell carcinoma (PRCC) are the Hippo signaling pathway, SWI / SNF complex and chromatin modifier pathways (N Engl J Med 2016;374:135)
Etiology
- No definite specific etiology but common in end stage kidney disease (ESRD)
- Could arise from progenitor-like cell population in proximal renal tubules in ESRD (Am J Pathol 2011;178:828, Am J Pathol 2019;189:2046)
Diagrams / tables
Clinical features
- Usually asymptomatic; incidental finding on imaging
- Maybe multifocal or bilateral in chronic kidney disease and hereditary PRCC (germline MET mutation)
Diagnosis
- Based on the assessment of both the morphology and immunohistochemical profile
- Essential to exclude outliers particularly in high grade lesions
Radiology description
- No specific radiologic findings
- Homogenous, solid mass with relative hypovascularity compared to nonpapillary RCC; may have cystic change and calcifications (Urol Oncol 2021;39:327)
Prognostic factors
- Generally thought to have a better prognosis than other clear cell RCC (Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:281)
- High WHO / ISUP grade, high stage and ATP binding cassette subfamily C member 2 (ABCC2) brush border are associated with worse prognosis (Hum Pathol 2022;120:57, Histopathology 2023 Sep 7 [Epub ahead of print])
Case reports
- 11 year old renal transplant boy with bilateral PRCC (European J Pediatr Surg Rep 2022;10:e160)
- 59 year old man with collision tumor of papillary and chromophobe RCCs (Oxf Med Case Reports 2022;2022:omac048)
- 63 year old man with PRCC with concurrent primary renal glomus tumor (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2022;15:459)
- 69 year old man with metastatic PRCC to testicle and penis (Urol Case Rep 2020;33:101362)
- 71 year old man with synchronous ipsilateral PRCC and urothelial carcinoma (Oncol Lett 2023;25:221)
Treatment
- Resection or ablation for localized disease
- Selective MET kinase inhibitor, MET / VEGF inhibitor, multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and PD-1 / PDL1 inhibitors for advanced or metastatic disease (Curr Opin Urol 2022;32:344)
- For advanced metastatic PRCC cabozantinib shows higher efficacy over sunitinib and other MET kinase inhibitors (Lancet 2021;397:695)
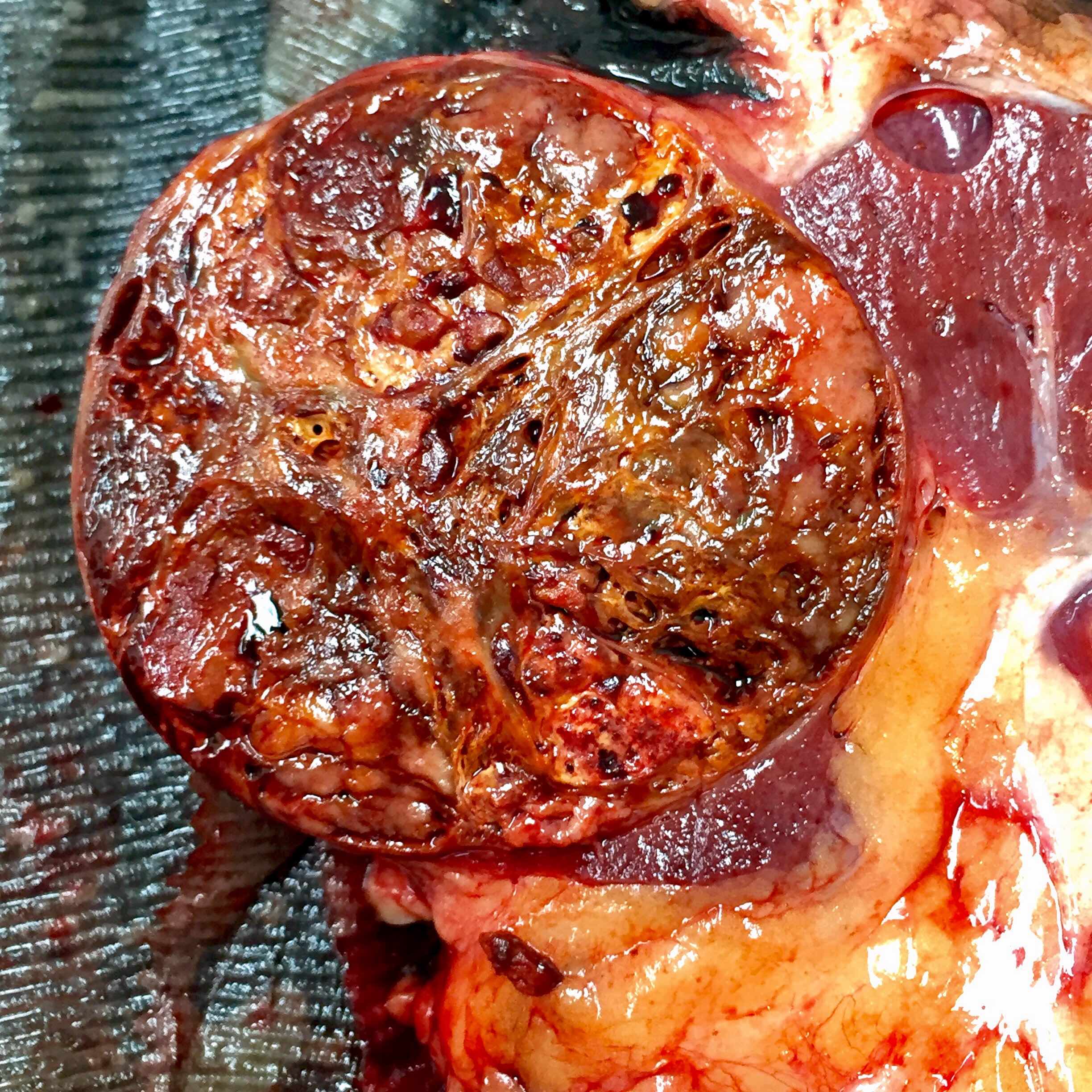
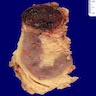
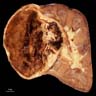
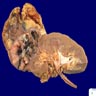
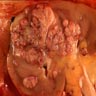
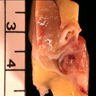
Gross description
- Most tumors are circumscribed, surrounded by a pseudocapsule (Adv Anat Pathol 2019;26:124)
- Yellow-tan, red-brown or variegated cut surfaces
- Granular or friable in appearance consistent with the papillary morphology
- Variable areas of necrosis and cystic degeneration (Cancer 1976;38:2469)
Gross images
Contributed by Nicole K. Andeen, M.D. and Maria Tretiakova, M.D., Ph.D.
Images hosted on other servers:
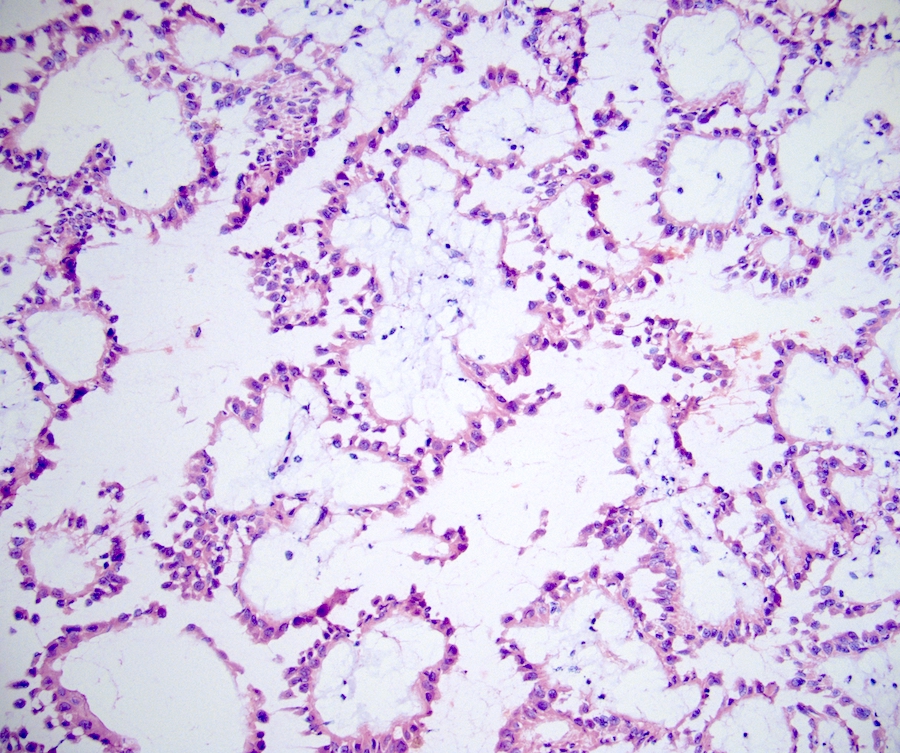
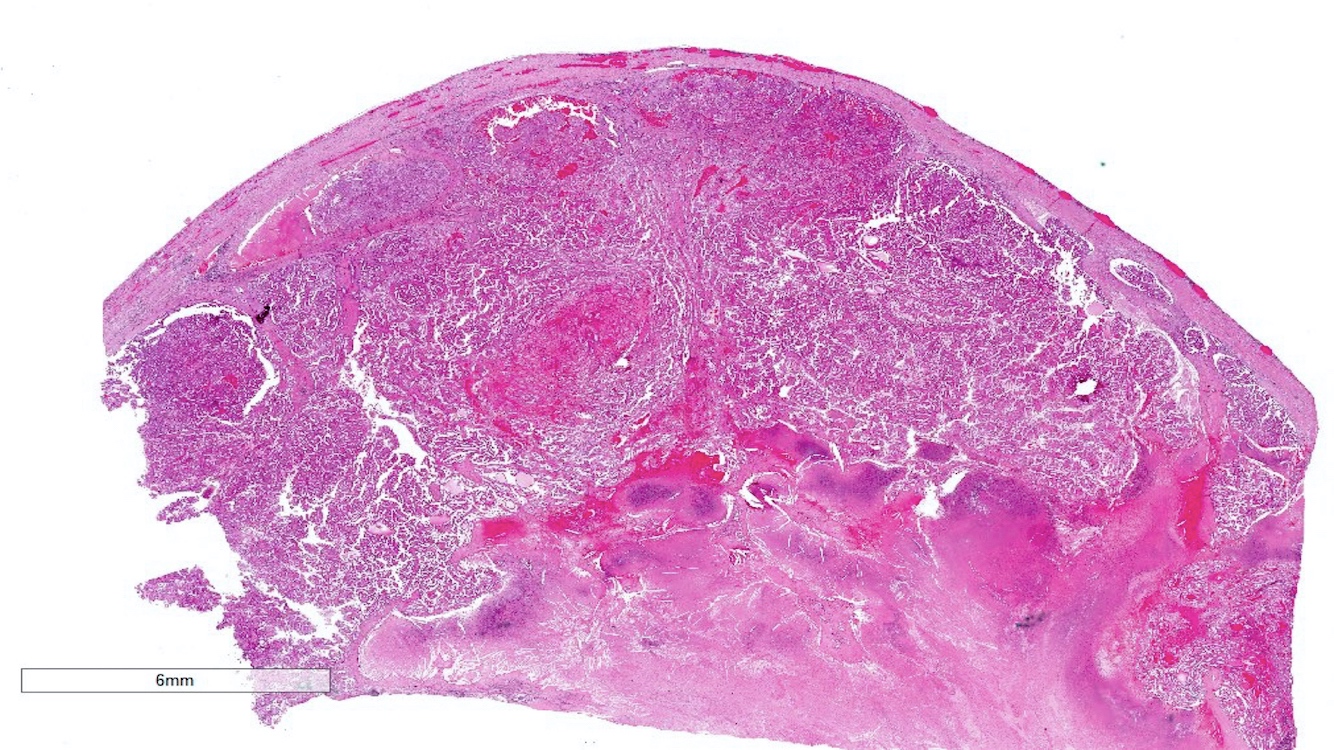
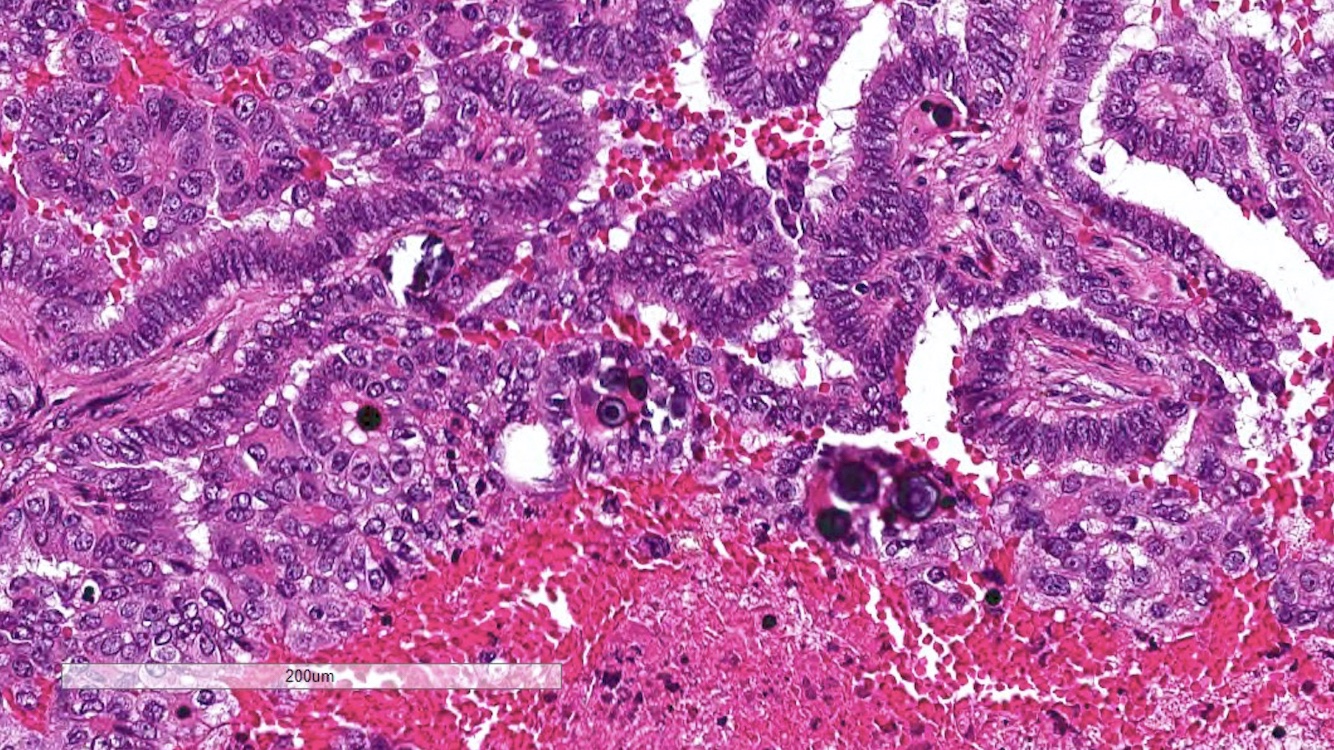
Microscopic (histologic) description
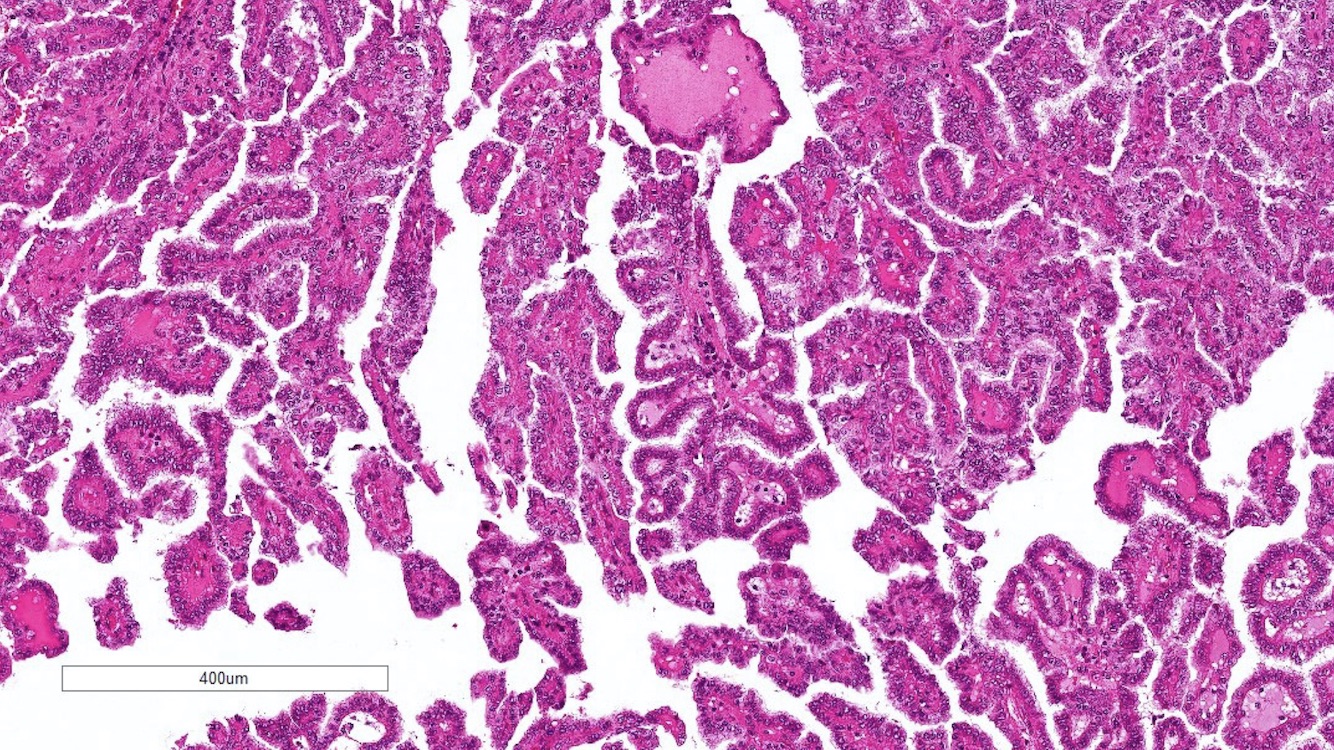
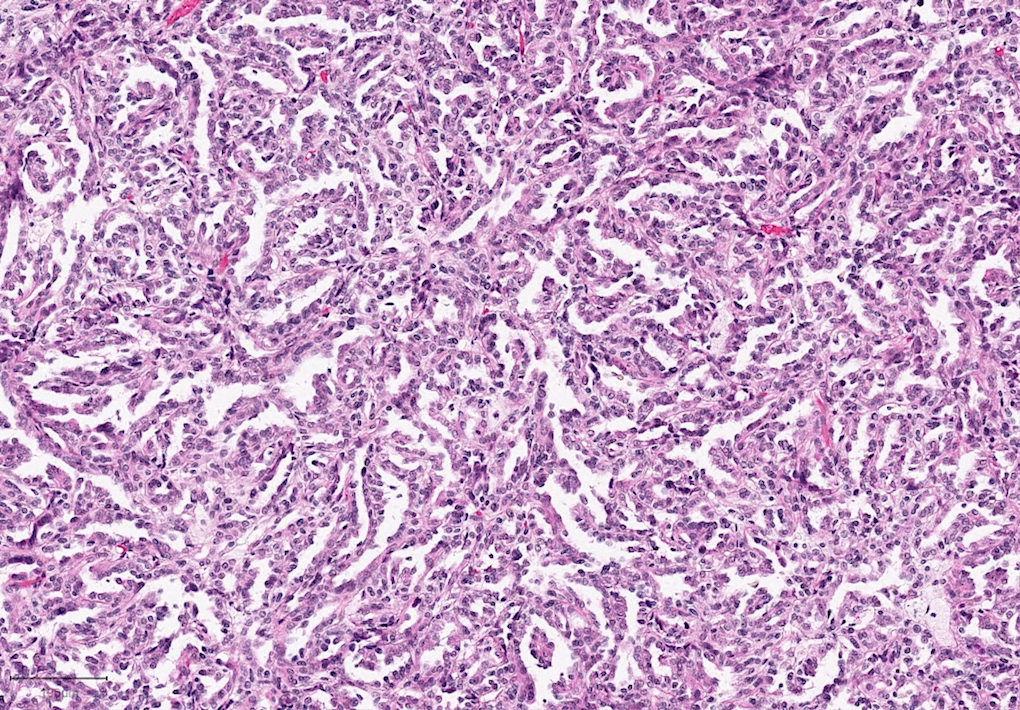
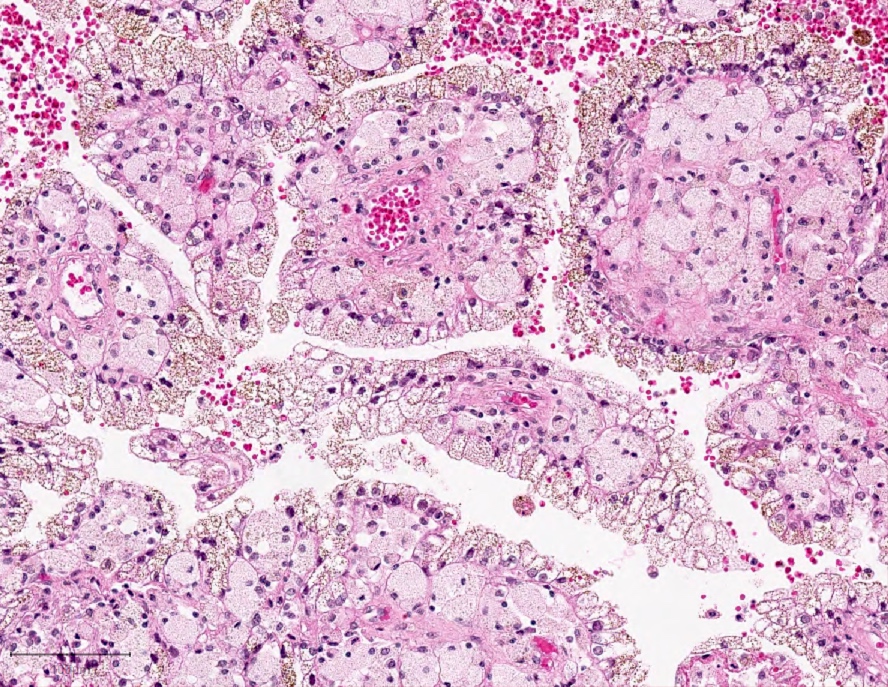
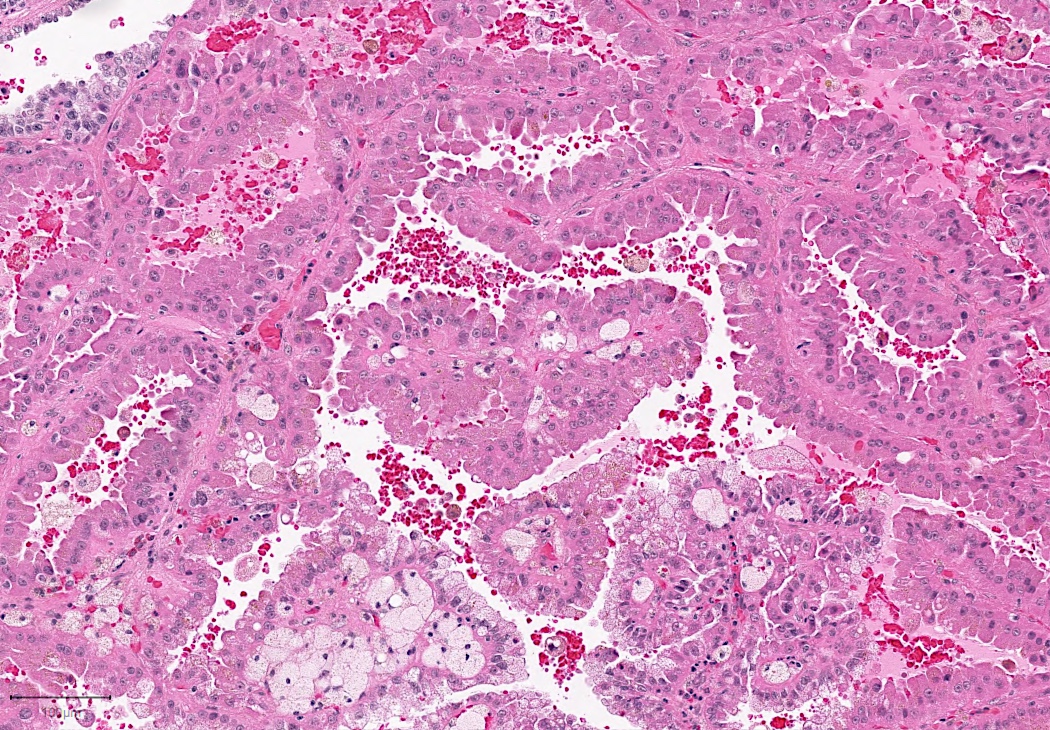
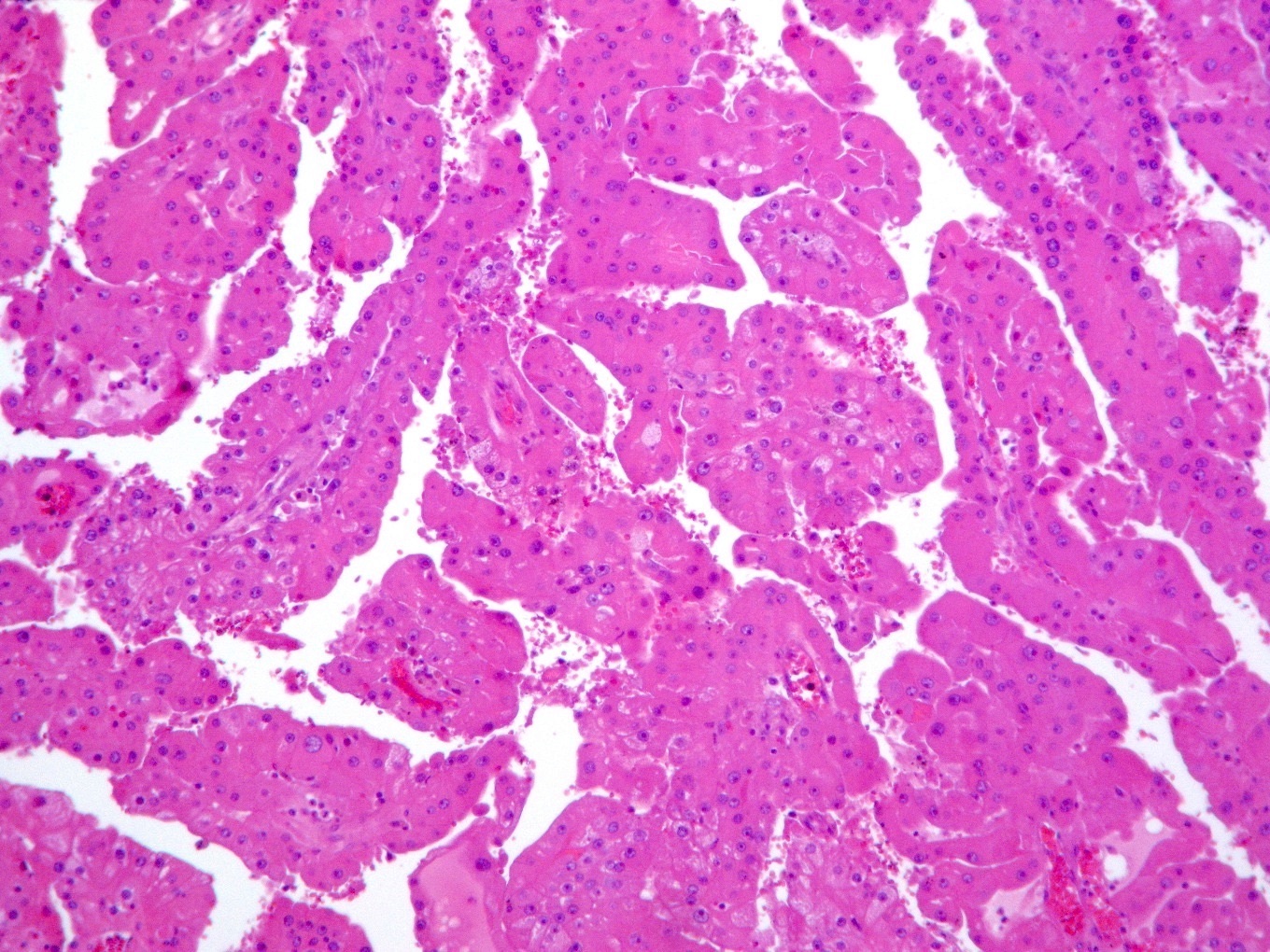
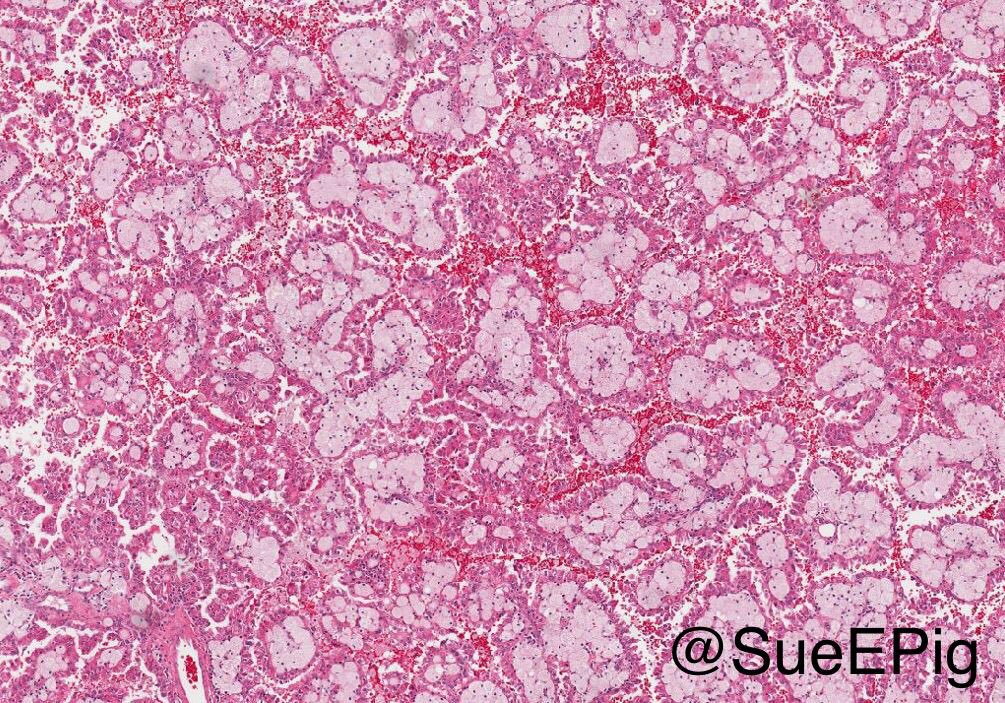
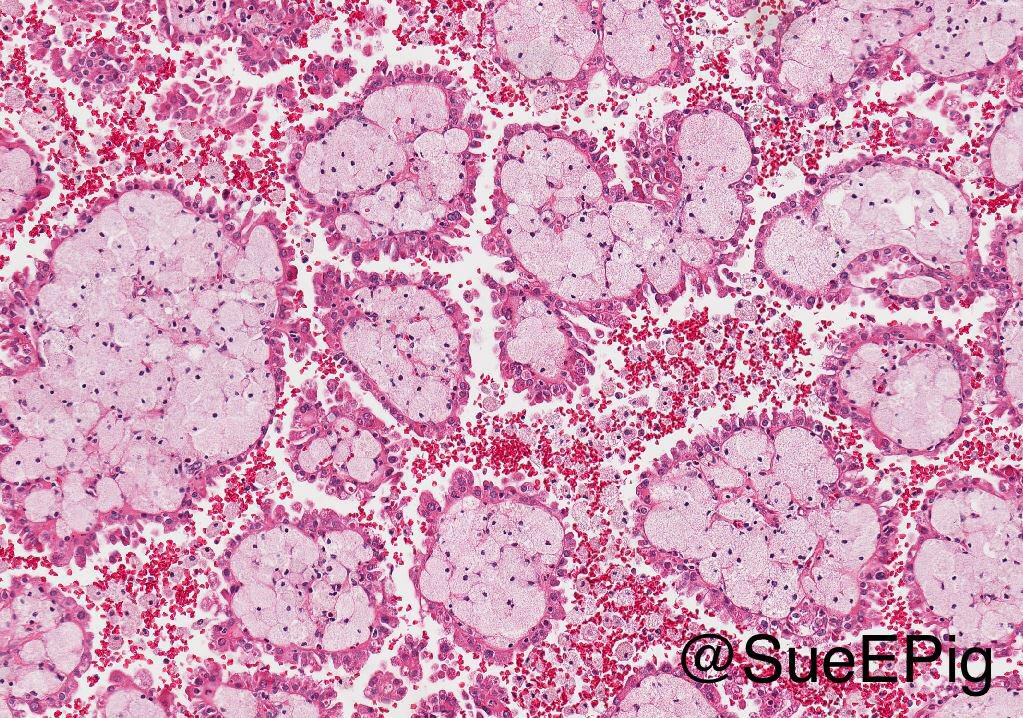
- Predominantly papillary or tubulopapillary architecture (Mod Pathol 2021;34:1392)
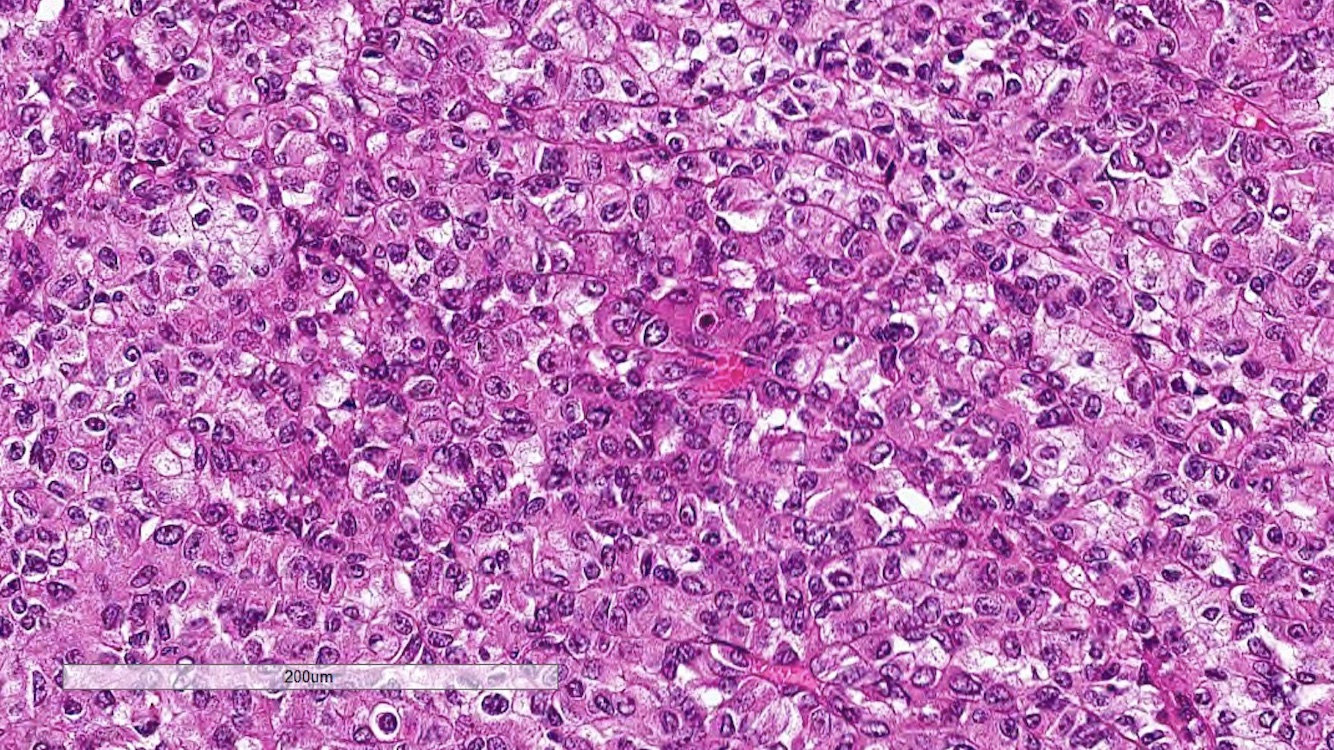
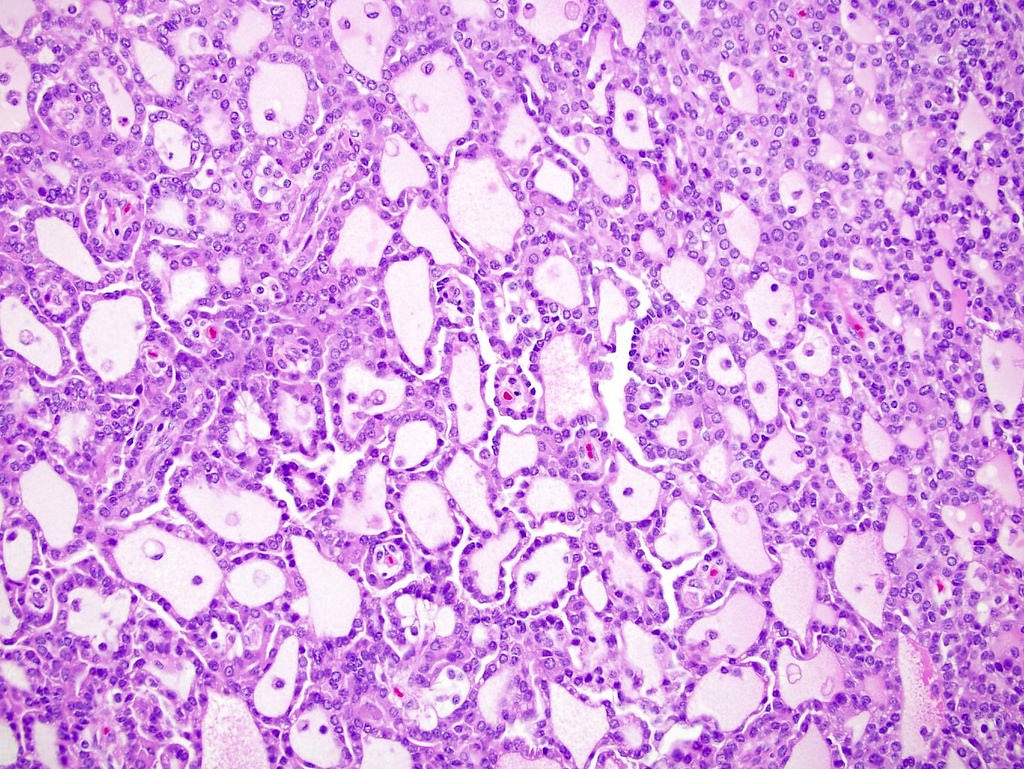
- Lined by cells with variation of morphologies, ranging from small, basophilic cuboidal cells with inconspicuous nucleoli to large, eosinophilic cells with prominent nucleoli; may have clear cytoplasm, known pitfall to have clearing in PRCC
- Cells can be arranged in linear or a pseudostratified pattern
- Heterogeneity and mixed morphology are very common (47 - 48% of cases), hence this is one of the reasons why typing is no longer favored (Mod Pathol 2021;34:1392, Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:887, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:1618)
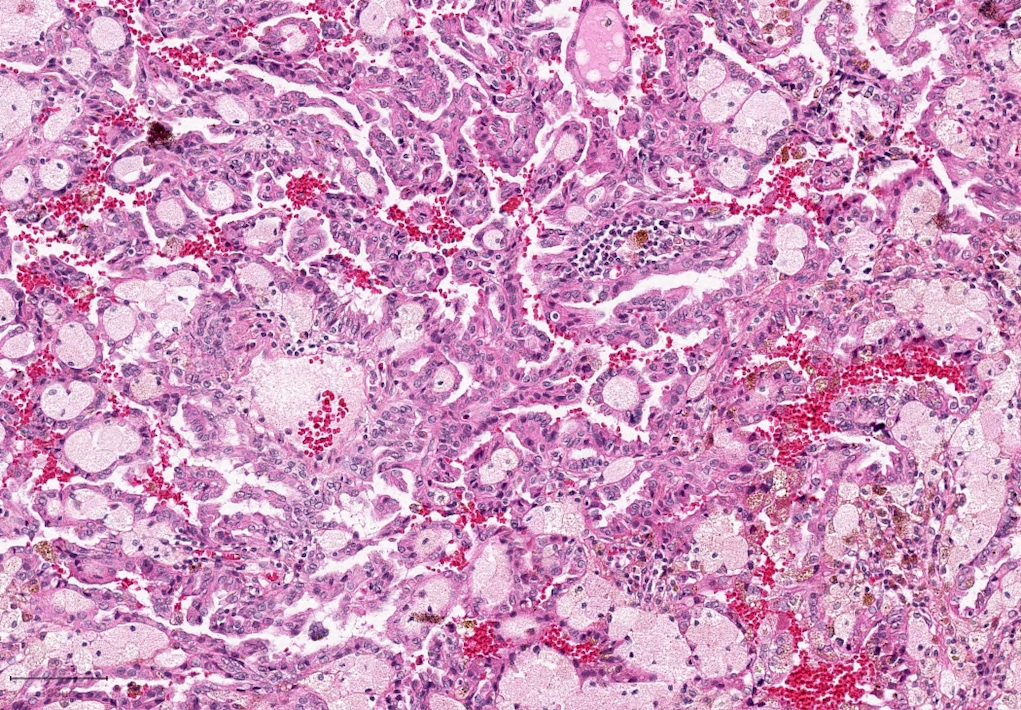
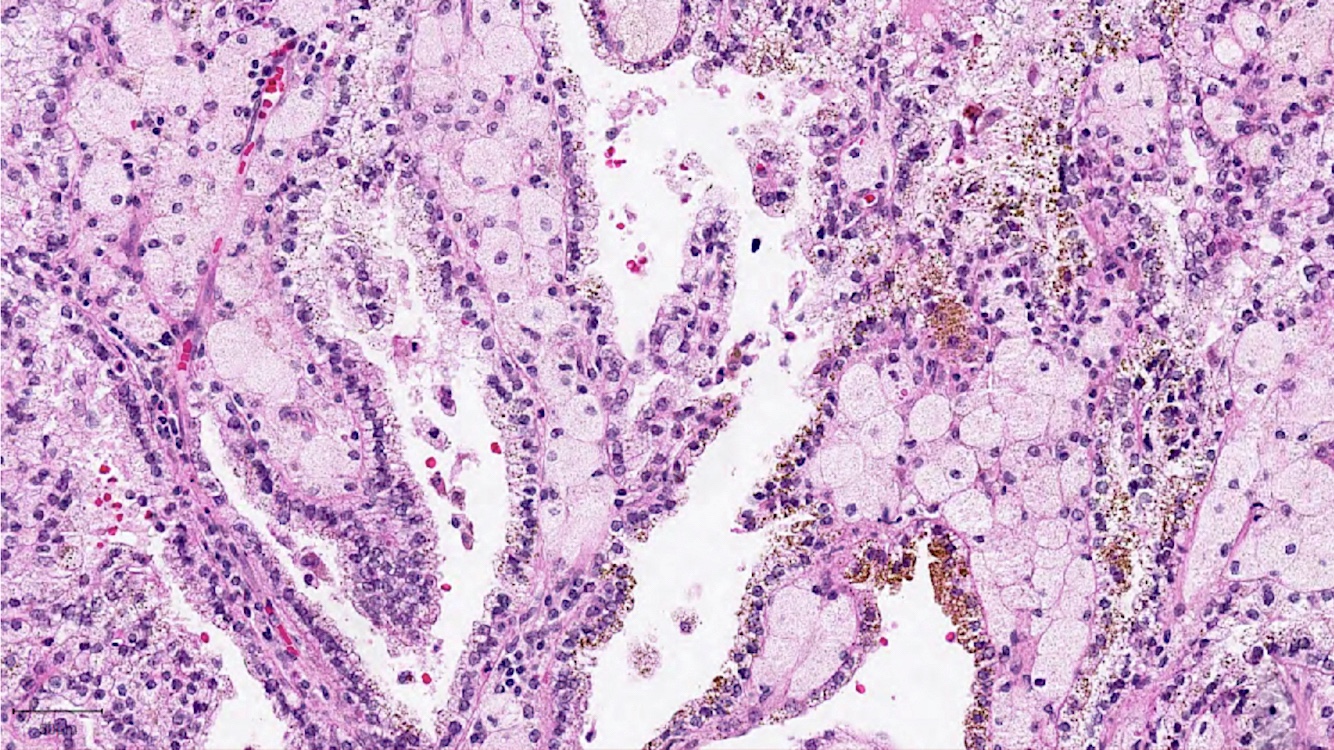
- Often infiltrated by foamy macrophages
- Psammoma bodies and hemosiderin pigments can be present
- Reported patterns (Mod Pathol 2021;34:1392)
- Biphasic (alveolar / squamoid) PRCC
- Dual cell populations, nests of larger (squamoid) eosinophilic cells surrounded by smaller amphophilic cells forming an alveolar pattern
- Evidence of aggressive behavior has been documented in up to 15% of the cases (Histopathology 2018;72:777)
- Warthin-like PRCC
- Eosinophilic papillae with dense lymphocytic infiltrates resembling Warthin tumor of the salivary gland
- Usually high grade tumors that can exhibit aggressive clinical behavior (Ann Diagn Pathol 2017;27:48)
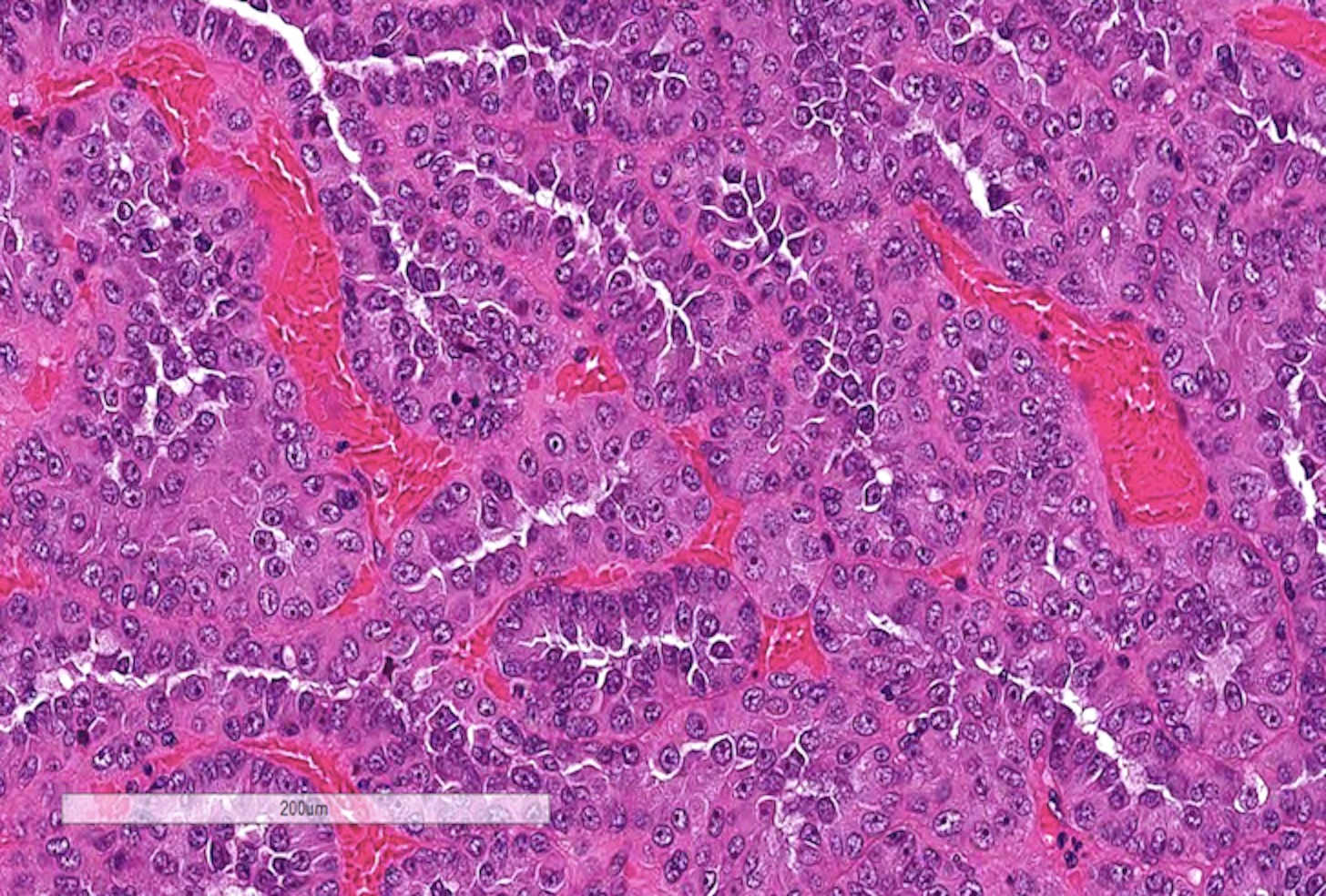
- Solid (pseudosolid) PRCC
- Solid architecture due to compressed tubular and papillary structures, lined by small cells with low grade nuclei
- Reported to have an indolent clinical behavior (Ann Diagn Pathol 2016;23:51)
- Biphasic (alveolar / squamoid) PRCC
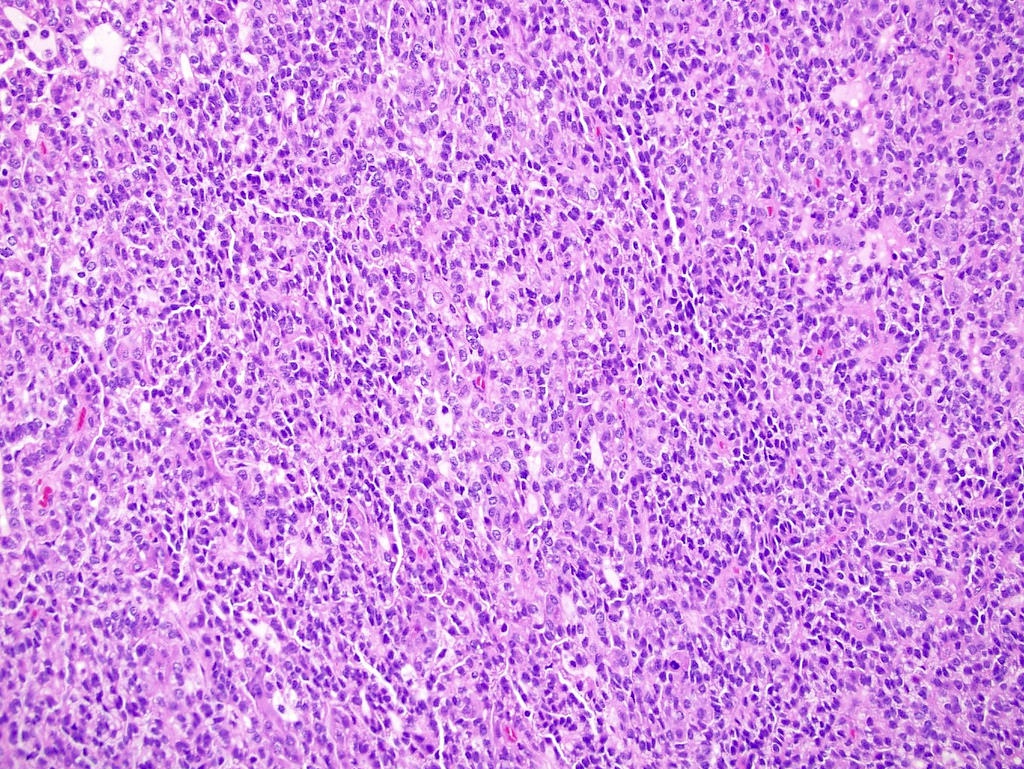
- Histologic patterns associated with worse prognosis: solid, micropapillary, hobnailing, microcystic architecture (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:582, Am J Surg Pathol 2022;46:392)
- WHO / ISUP grading system has been validated as a prognostic parameter for PRCC
- Based on nucleolar prominence (grades 1 - 3); nuclear pleomorphism or sarcomatoid / rhabdoid differentiation (grade 4) (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1490, Histopathology 2019;74:4)
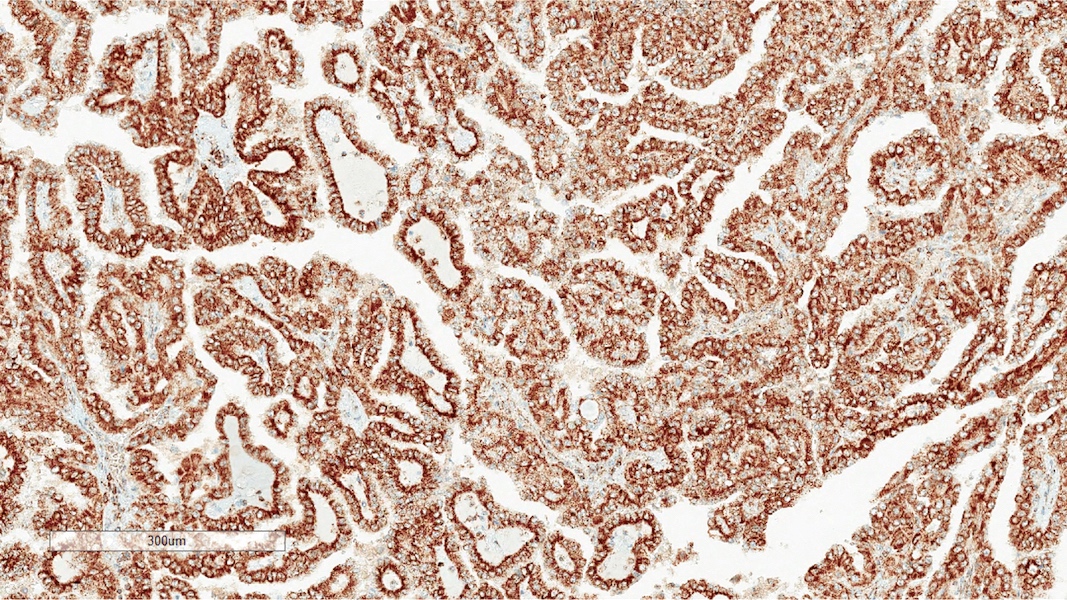
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Rola Saleeb, M.D., Ph.D., Vincent Francis Castillo, M.D., Nicole K. Andeen, M.D.,
Maria Tretiakova, M.D., Ph.D., Semir Vranić, M.D., Ph.D. and @SueEPig on Twitter
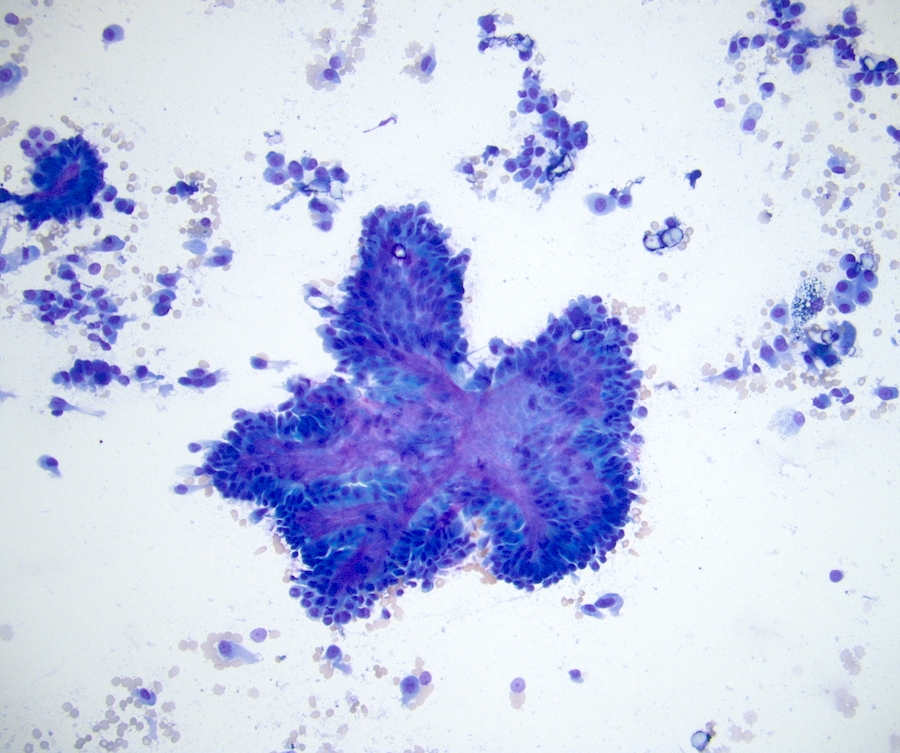
Cytology description
- Papillary fragments with fibrovascular cores
- Cohesive clusters of small cells with bland nuclei in low grade tumors
- Intracellular hemosiderin, foamy macrophages (Cancer 1998;84:303)
Cytology images
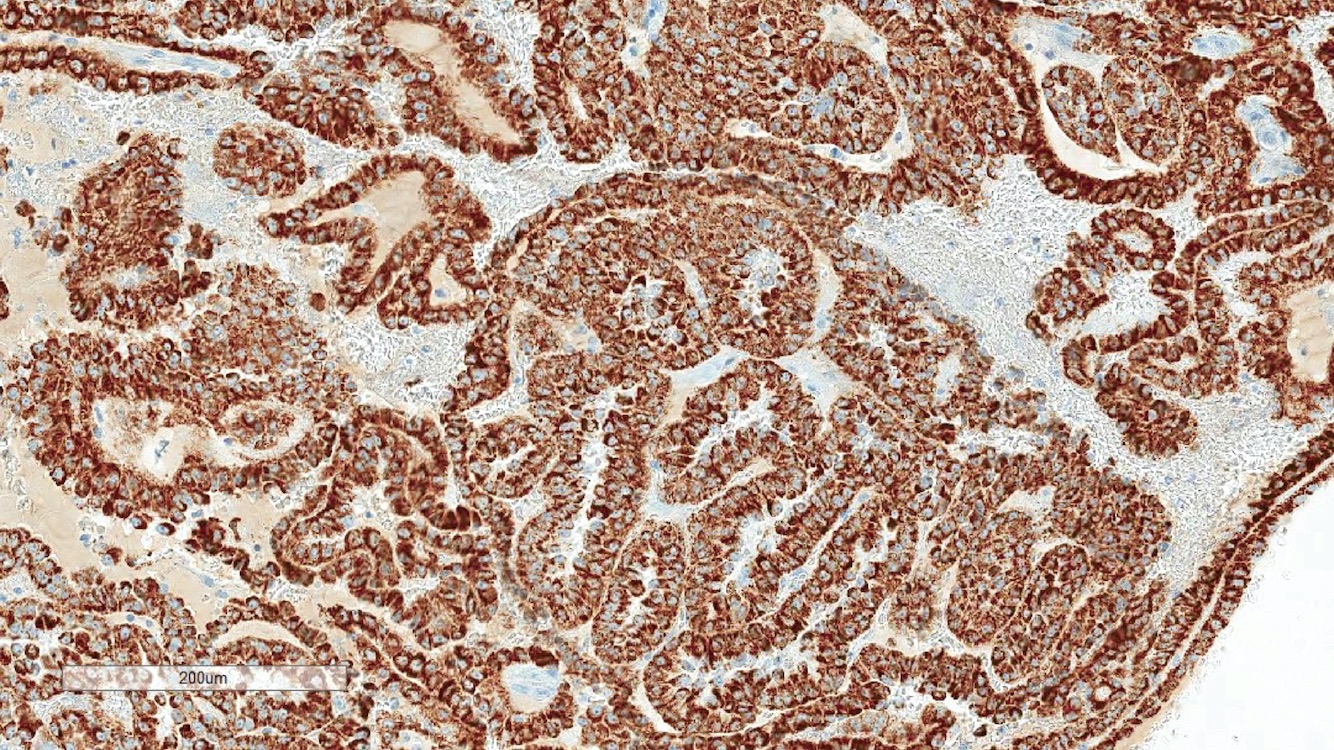
Positive stains
- AMACR
- Sensitive but not entirely specific (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:69)
- CK7
- Tends to be more positive in lower grade than higher grade tumors (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:887)
- PAX8, AE1 / AE3, EMA, CAM 5.2, vimentin
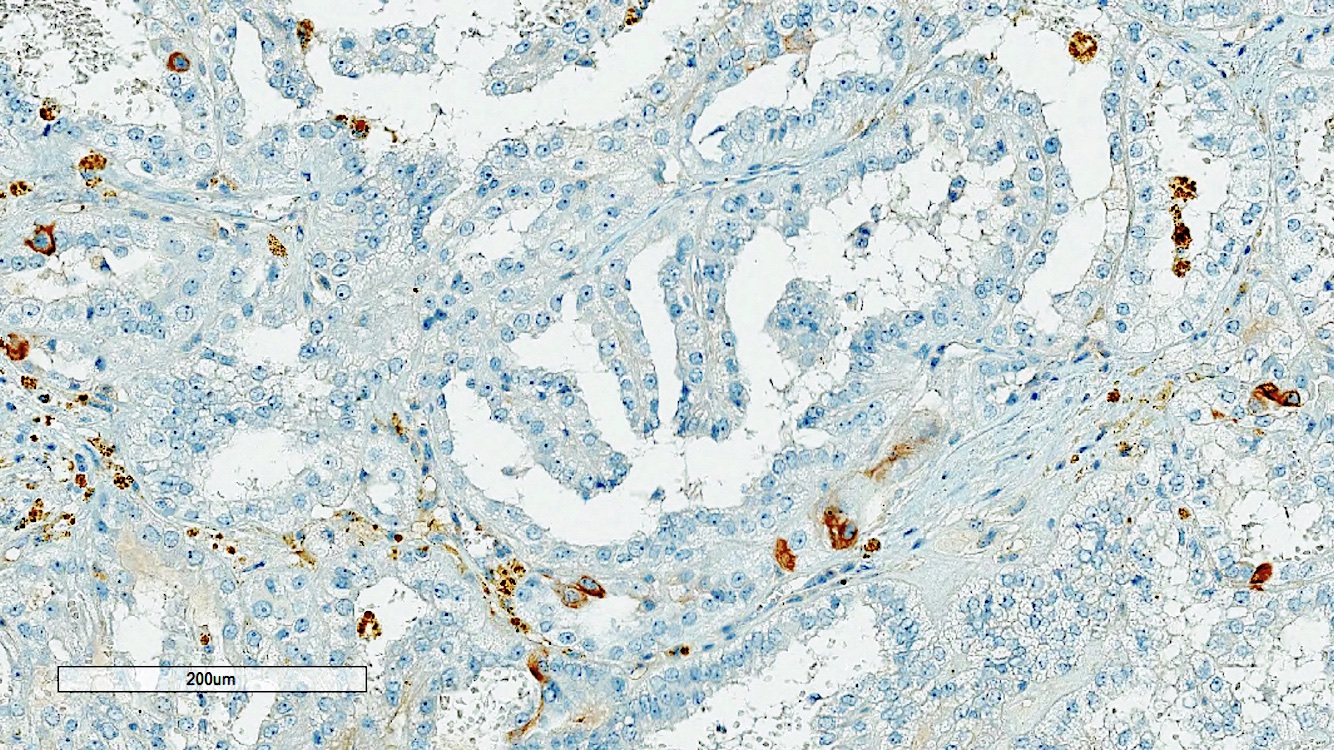
Negative stains
| Renal tumors | AMACR | CK7 | Vimentin | CAIX | CD117 | TFE3 | FH | SDH |
| Papillary RCC | + | Variable | + | - | - | - | + (retained) | + (retained) |
| Clear cell RCC | -/+ | - | + | + | - | - | + (retained) | + (retained) |
| Chromophobe RCC | - | + | - | - | + | - | + (retained) | + (retained) |
| Oncocytoma | - | - | - | - | + | - | + (retained) | + (retained) |
| TFE3 rearranged RCC | + | - | - | - | - | + | + (retained) | + (retained) |
| FH deficient RCC | Variable | - | Variable | - | - | - | - (loss) | + (retained) |
| SDH deficient RCC | - | - | - | - | - | - | + (retained) | - (loss) |
- References: Mod Pathol 2021;34:1392, Cancers (Basel) 2020;12:602
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- No molecular markers specific for the diagnosis of PRCC
- Chromosome 7 and 17 gains and loss of Y chromosome in low grade tumors (N Engl J Med 2016;374:135)
- MET mutations seen in former type 1 and low grade PRCC; CDKN2A mutation or promoter methylation in aggressive PRCC (N Engl J Med 2016;374:135)
- Exclude FH gene mutation and TFE3 rearrangements for high grade PRCC
Sample pathology report
- Right kidney (mass), biopsy:
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma
- WHO / ISUP grade 3 in this limited specimen
- Right kidney (mass), partial nephrectomy:
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma, pT1a (see synoptic report)
- WHO / ISUP grade 2
- Tumor size: 2.5 cm
- Tumor is limited to kidney
- Negative for sarcomatoid / rhabdoid features and necrosis
- Negative for vascular and lymphovascular invasion
- All margins are negative for tumor
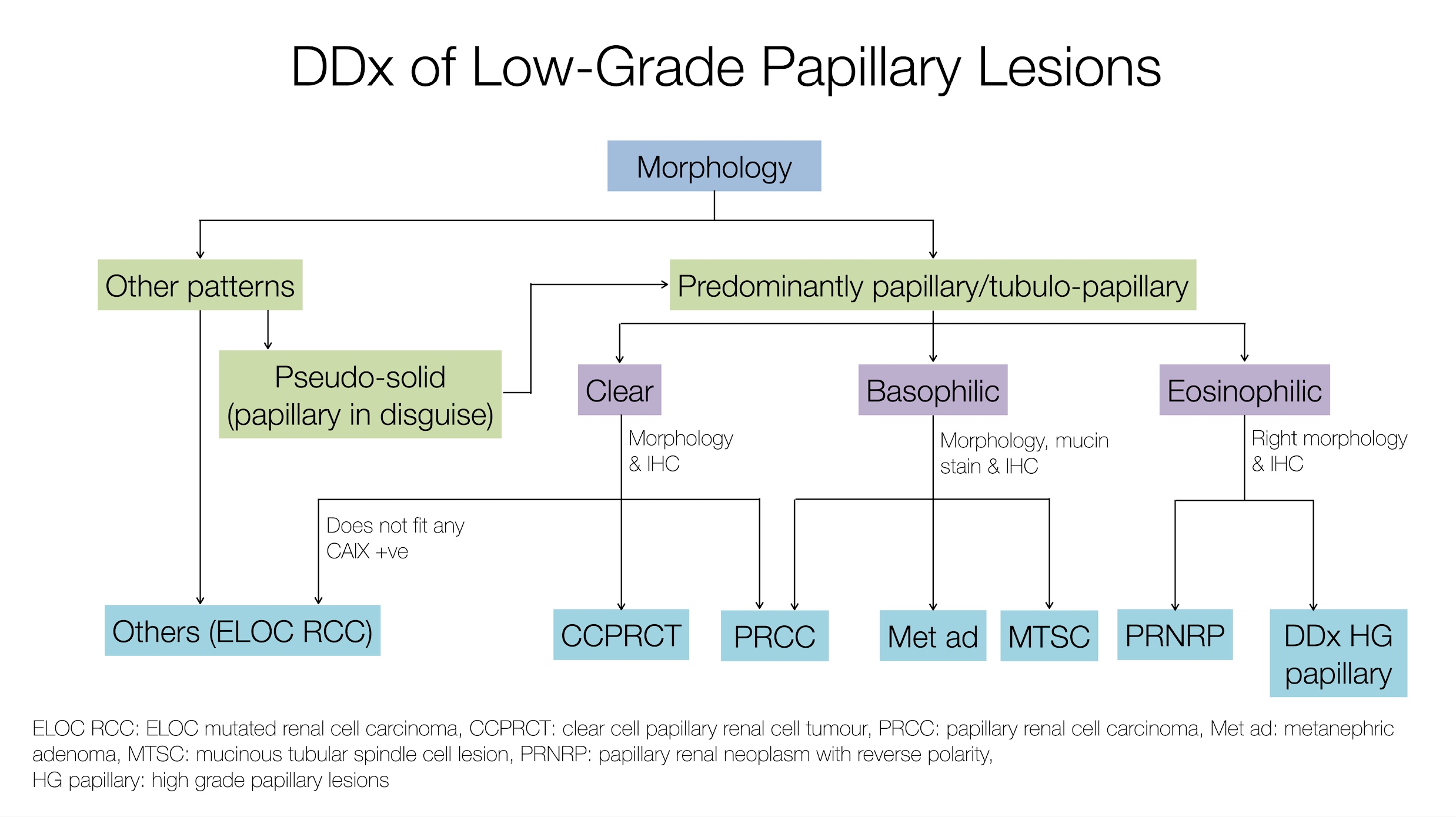
Differential diagnosis
- Main DDx for low grade PRCC (see Diagrams / tables)
- Clear cell papillary (CCP) renal cell tumor (Mod Pathol 2013;26:697):
- Metanephric adenoma (MA) (Mod Pathol 2015;28:1236):
- Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma (MTSC) (Diagn Pathol 2015;10:168):
- Anastomosing tubules lined by low grade cuboidal cells with bland spindle cells in a myxoid stroma; multiple chromosomal losses
- Mucin special stains are positive in MTSC and negative in PRCC
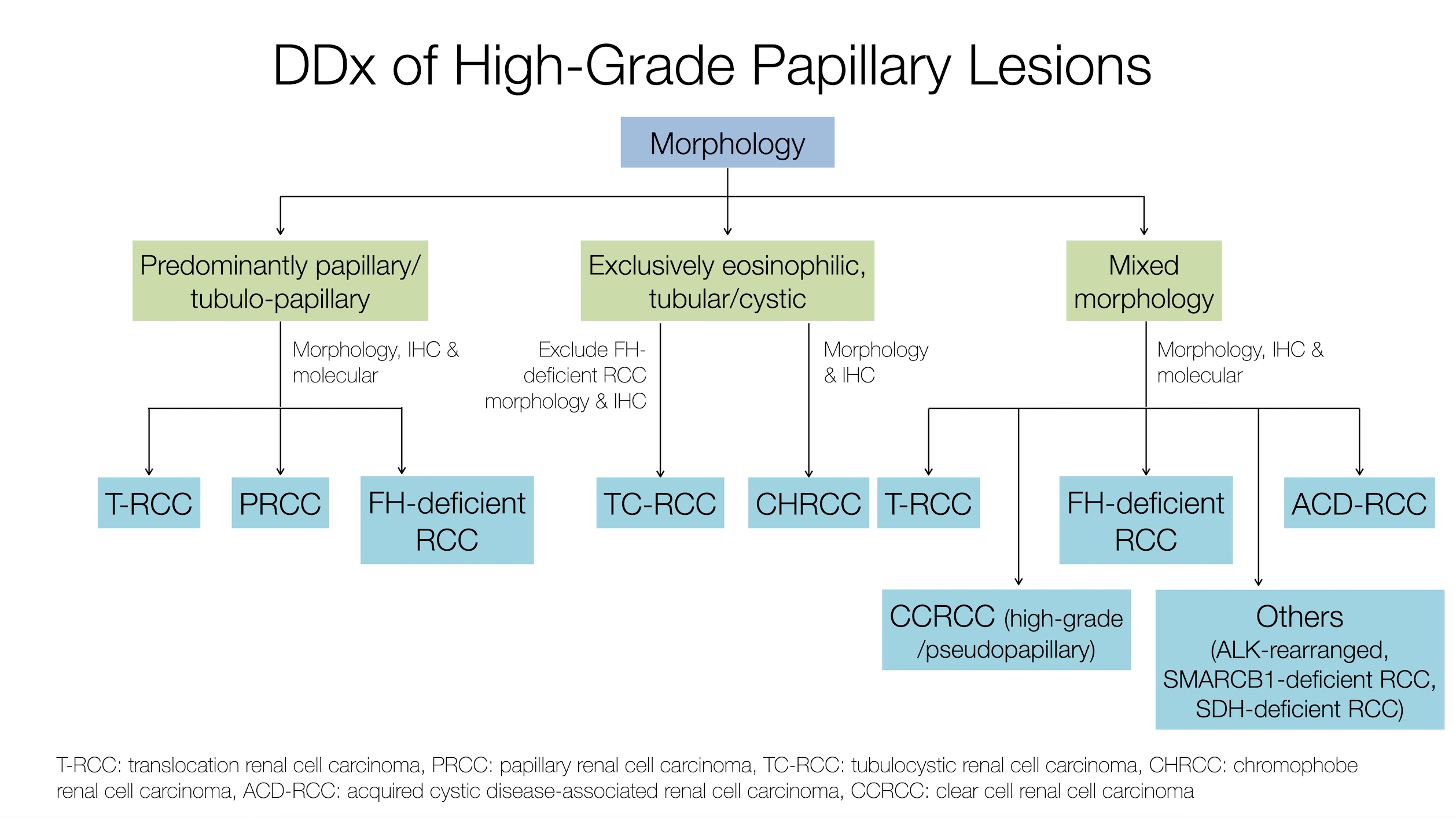
- Main DDx for high grade PRCC (see Diagrams / tables)
- FH deficient RCC (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:865):
- MiT family translocation RCC (mostly TFE3 rearranged RCC) (Semin Diagn Pathol 2015;32:103, Adv Anat Pathol 2022;29:131):
- Key feature is mixed histologic patterns including large nests, alveolar areas as well as papillary areas
- Commonly mixed areas of clear and eosinophilic cells
- Commonly associated with psammoma bodies, however, can also be observed in PRCC
- Often a panel of IHC stains is required to exclude translocation RCC; positive TFE3 (MRQ37 clone is known to be associated with false positive expression), cathepsin K (positive only in ~30% of the cases), weak / patchy keratins and often negative EMA
- In cases with ambiguous IHC profile, FISH studies are recommended
- Other possible DDx for high grade PRCC
- Acquired cystic disease associated RCC (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1156):
- Cribriform (sieve-like) appearance; high grade eosinophilic cells, oxalate crystals often present
- Occurs in end stage kidneys
- Overlapping immunoprofile with high grade / eosinophilic PRCC
- Morphology and cystic ESRD are key clues to the diagnosis
- ALK rearranged RCC (Mod Pathol 2020;33:2564):
- Rare entity, morphology characterized by vacuoles, mucinous stroma, cribriform architecture and possibly some papillary morphology
- Sickle cell trait
- ALK IHC positive or ALK rearrangement by FISH
- Renal medullary carcinoma (Mod Pathol 2008;21:647):
- Infiltrative (noncircumscribed), high grade adenocarcinoma
- Sickle cell trait
- SMARCB1 (INI1) IHC loss (key feature); possible OCT4 positive staining
- Mixed, high grade infiltrative morphology is key to exclude PRCC
- Collecting duct carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:279):
- Infiltrative growth (noncircumscribed), adenocarcinoma, desmoplastic stroma
- Diagnosis of exclusion for high grade infiltrative lesions
- Mixed, high grade infiltrative morphology is key to exclude PRCC
- Acquired cystic disease associated RCC (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1156):
- Papillary renal neoplasm with reversed polarity (PRNRP):
- Papillary architecture lined by cells with abundant and eosinophilic cytoplasm and apically located linearly arranged nuclei (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1099)
- WHO / ISUP grade 1 - 2 (key feature)
- Positive for GATA3 nuclear staining (key feature), weak / negative AMACR and vimentin (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1099)
- GATA3 positive in papillary renal neoplasm with reversed polarity (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1099)
- Commonly harbor KRAS mutations (Mod Pathol 2020;33:1157, Mod Pathol 2020;33:690)
- Older terminologies: oncocytic low grade PRCC or type 4 PRCC (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:1618)
- Often smaller in size than classic PRCCs (most cases reported were pT1a disease)
- Indolent entity, no cases with disease progression reported to date (Front Oncol 2023;13:1101268)
- Important to recognize from eosinophilic PRCC, which is often a high grade lesion (Lab Investig 2023;103:S697)
Additional references
Practice question #1
A 65 year old man presented with an 8 cm kidney tumor located in the right lower pole extending to the renal sinus. Cut sections showed an encapsulated mass with brown-red surface and necrotic areas. Microscopic examination showed almost exclusively tubulopapillary architecture, which is lined by cells with voluminous, eosinophilic cytoplasm and nuclei with very prominent nucleoli. Calcifications were also noted. Which of the following IHC results are expected in PRCC?
- CAIX negative, CD117 negative, AMACR positive, CK7 negative, FH loss, TFE3 negative
- CAIX negative, CD117 negative, AMACR positive, CK7 negative, FH retained, TFE3 positive
- CAIX negative, CD117 negative, AMACR positive, CK7 patchy, FH retained, TFE3 negative
- CAIX negative, CD117 positive, AMACR negative, CK7 positive, FH retained, TFE3 negative
- CAIX positive, CD117 negative, AMACR negative, CK7 negative, FH retained, TFE3 negative
Practice answer #1
C. PRCC is CAIX negative, CD117 negative, AMACR positive, CK7 patchy, FH retained, TFE3 negative. While CK7 is usually positive in PRCC, it may be negative or focal in high grade PRCC.
Answer E is incorrect because clear cell RCC is CAIX positive, CD117 negative, AMACR negative, CK7 negative, FH retained, TFE3 negative.
Answer A is incorrect because FH deficient RCC is CAIX negative, CD117 negative, AMACR positive, CK7 negative, FH loss, TFE3 negative.
Answer D is incorrect because chromophobe RCC is CAIX negative, CD117 positive, AMACR negative, CK7 positive, FH retained, TFE3 negative.
Answer B is incorrect because TFE3 rearranged RCC is CAIX negative, CD117 negative, AMACR positive, CK7 negative, FH retained, TFE3 positive.
Comment Here
Reference: Papillary renal cell carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Papillary renal cell carcinoma
Practice question #2
Regarding papillary renal cell carcinoma, which of the following statements is true?
- CK7 is always positive in PRCC
- MET mutations are usually seen in aggressive PRCC
- Tumors with tubulopapillary, solid and cystic architecture lined by eosinophilic, high grade nuclei is diagnostic of PRCC and does not warrant further IHC studies
- WHO / ISUP nucleolar grading has prognostic significance in PRCC and should be reported
Practice answer #2
D. WHO / ISUP nucleolar grading is accepted as a prognostic histopathologic marker for PRCC and is recommended to be included in surgical pathology report. Answer B is incorrect because MET mutations are mostly observed in low grade PRCC. Answer C is incorrect because tumors composed of histologic patterns other than papillary or tubulopapillary like solid and cystic architecture should raise suspicion for potential mimickers of high grade PRCC. Therefore, IHC studies are recommended. Answer A is incorrect because CK7 can be negative or focal in PRCC with high grade features.
Comment Here
Reference: Papillary renal cell carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Papillary renal cell carcinoma