Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Zuo C, Ye H. Adenocarcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bladderadeno.html. Accessed May 10th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Carcinoma derived from the urothelium and showing pure glandular differentiation
- Not including urachal adenocarcinoma or urothelial carcinoma with glandular differentiation
Essential features
- Rare, derived from the urothelium of the bladder with pure glandular differentiation
- Histology: intestinal (enteric) type, mucinous type, signet ring cell type, NOS and mixed
- Immunohistochemistry: often CK7+ and CK20+ or CK7- and CK20+, no nuclear staining for beta catenin
- Diagnosis made after excluding secondary adenocarcinoma either by metastasis or by direct extension
Terminology
- Primary adenocarcinoma of the bladder
- Primary adenocarcinoma of the ureter
- Primary adenocarcinoma of the renal pelvis
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Rare primary neoplasm, 0.5 - 2% of bladder malignancies (J Urol 2010;183:915)
- 0.7% of upper urinary tract tumors (Clin Genitourin Cancer 2021;19:117)
- M:F = 3:1
- Mean age 68 years (J Urol 2010;183:915, Cancer 1991;67:2165)
Sites
- Usually lateral, posterior wall or trigone of bladder (if dome, should consider urachal adenocarcinoma by default)
- Second most common site in urethra; rare in ureters and renal pelvis
Etiology
- Some cases may be due to progression of extensive intestinal metaplasia (cystitis glandularis) or villous adenoma; these cases arise at trigone and are usually enteric
- Exstrophy: diffuse intestinalization; 4 - 7% risk of developing adenocarcinoma, even after repair (J Urol 1970;104:699)
- Diverticula: usually develop urothelial carcinoma, occasionally adenocarcinoma
- Also Schistosoma haematobium (Urol Oncol 2006;24:13)
- Chronic irritation of bladder, including nonfunctioning bladder or obstruction (Urol Oncol 2006;24:13)
- Urethral adenocarcinomas may arise from metaplastic surface mucosa or from periurethral glands secondary to chronic inflammation, stricture, diverticula, fistula and infections
Clinical features
- Usually presents with hematuria, rarely with mucusuria, dysuria (Cancer 1991;67:2165)
- Patients are older and mucusuria is more common than in urachal adenocarcinoma
- 5 year disease free survival rate is 40 - 50% (Urol Oncol 2006;24:13)
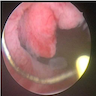
Diagnosis
- Screen test: urine cytology
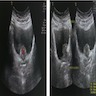
- Imaging modalities include ultrasound, computerized tomography (CT) urogram, retrograde pyelogram or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) urogram
- Cystoscopic examination of the entire urethra and bladder, with diagnostic specimens collected by either biopsy or transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT) (Eur Urol Focus 2021 [Epub ahead of print])
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Stage is most important prognostic factor
- Compared with urothelial carcinoma, patients with bladder adenocarcinoma have a worse prognosis, as they commonly present at a more advanced stage
- It is controversial whether it is more aggressive if controlled for tumor stage
- After adjusting pathologic stage, the presence of lymphovascular invasion and lymph node status, a study demonstrated that the primary adenocarcinoma has a worse prognosis than conventional urothelial carcinoma (J Urol 2006;175:2048)
Case reports
- 31 year old man with mucinous adenocarcinoma of renal pelvis (Ger Med Sci 2020;18:Doc11)
- 40 year old woman with primary mucinous adenocarcinoma (Case Rep Urol 2015;2015:783109)
- 53 year old man and 70 year old woman with primary signet ring cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder (Tunis Med 2019;97:167)
- 57 year old man with mucinous adenocarcinoma of the bladder with signet ring cells (Case Rep Urol 2016;2016:6080859)
- 62 year old woman with mucinous adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder (Am J Case Rep 2012;13:99)
- 65 year old man with primary upper urinary tract signet ring cell carcinoma (BMC Urol 2020;20:75)
Treatment
- Radical cystectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection
- Adjuvant therapy (radiation or chemotherapy) may be given in some cases
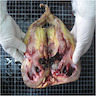
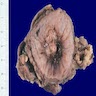
Gross description
- 67% are solitary lesions (while urothelial carcinoma tends to be multifocal)
- Tumor surface may be covered by gelatinous material
- Papillary, nodular, flat or ulcerated
Gross images
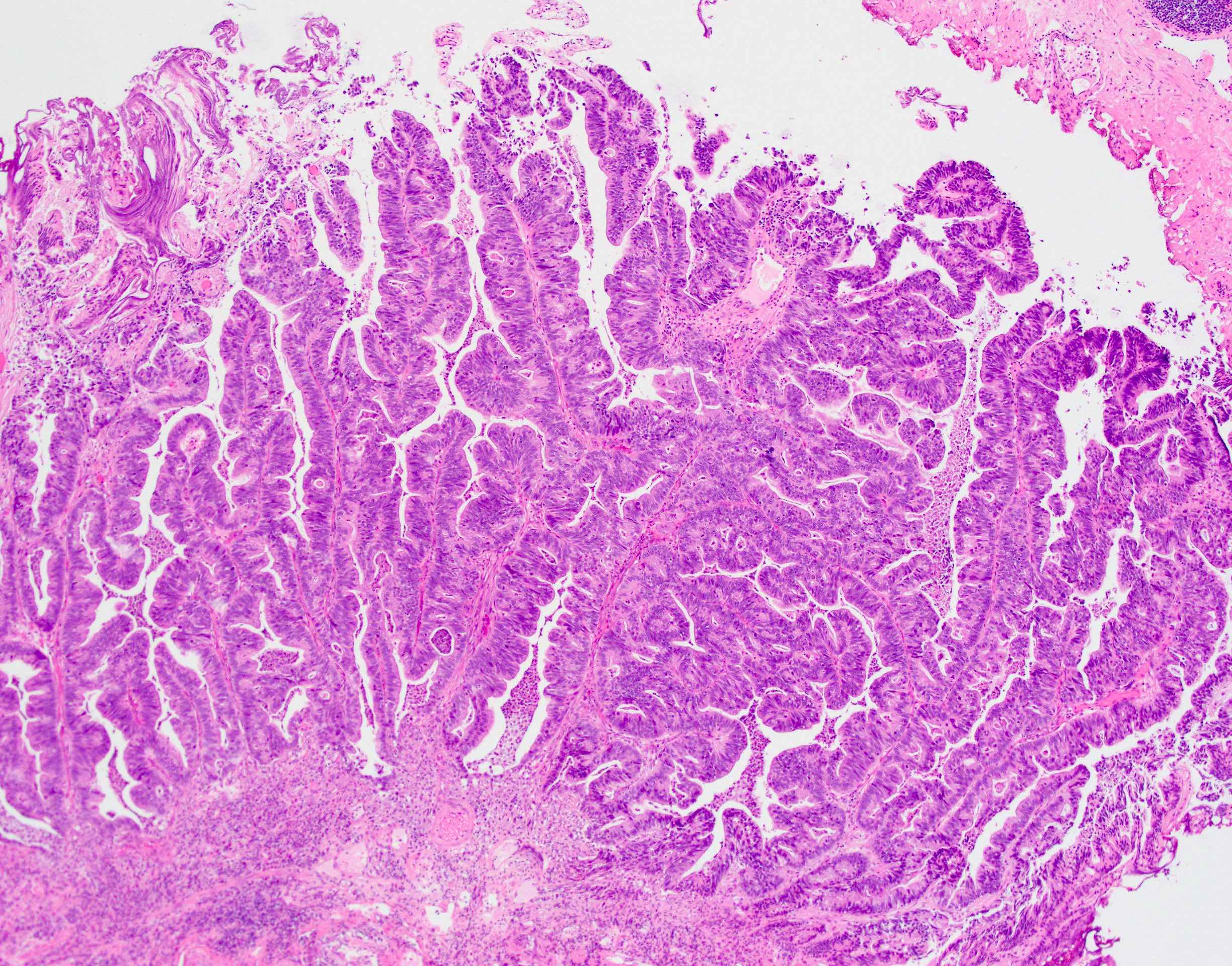
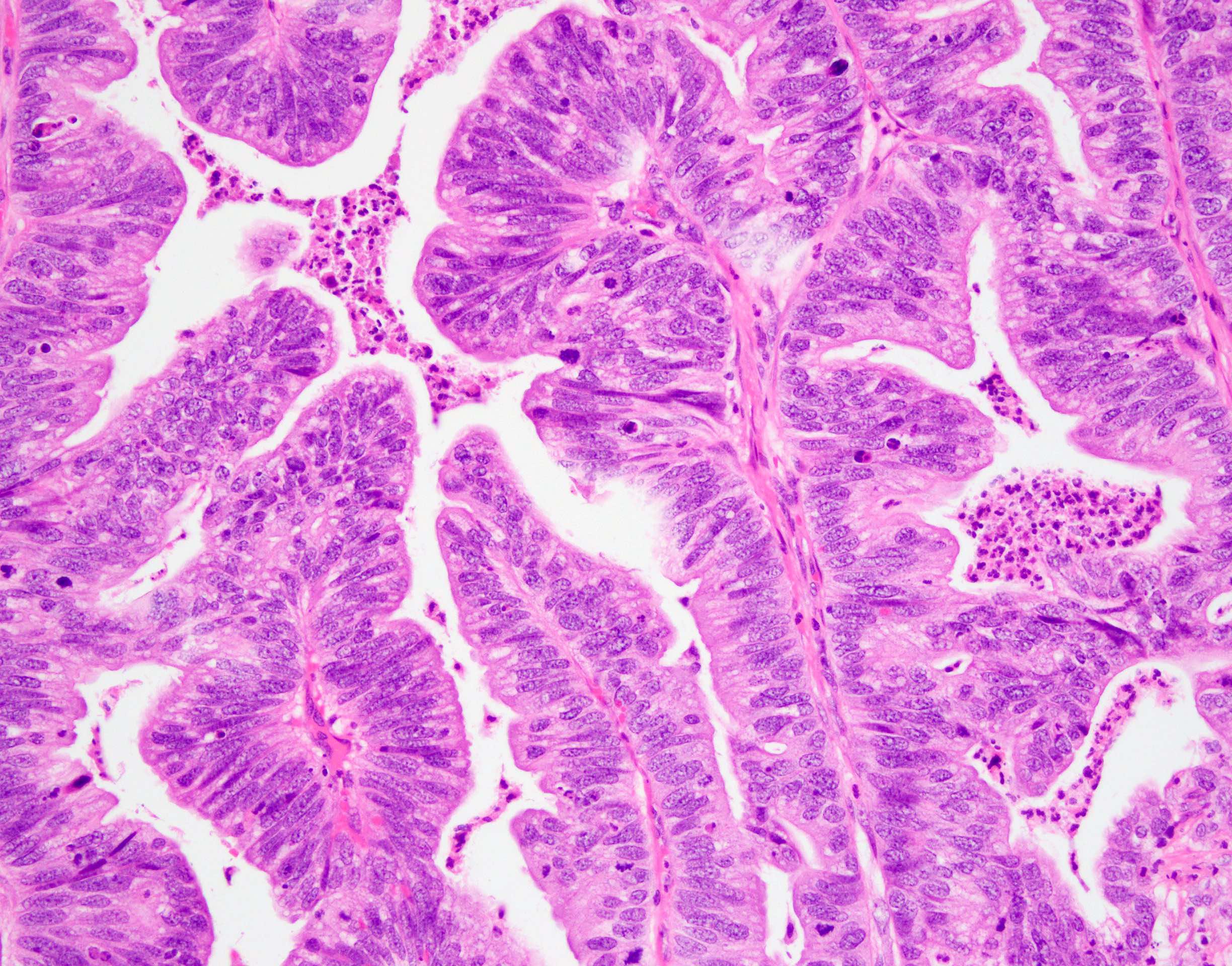
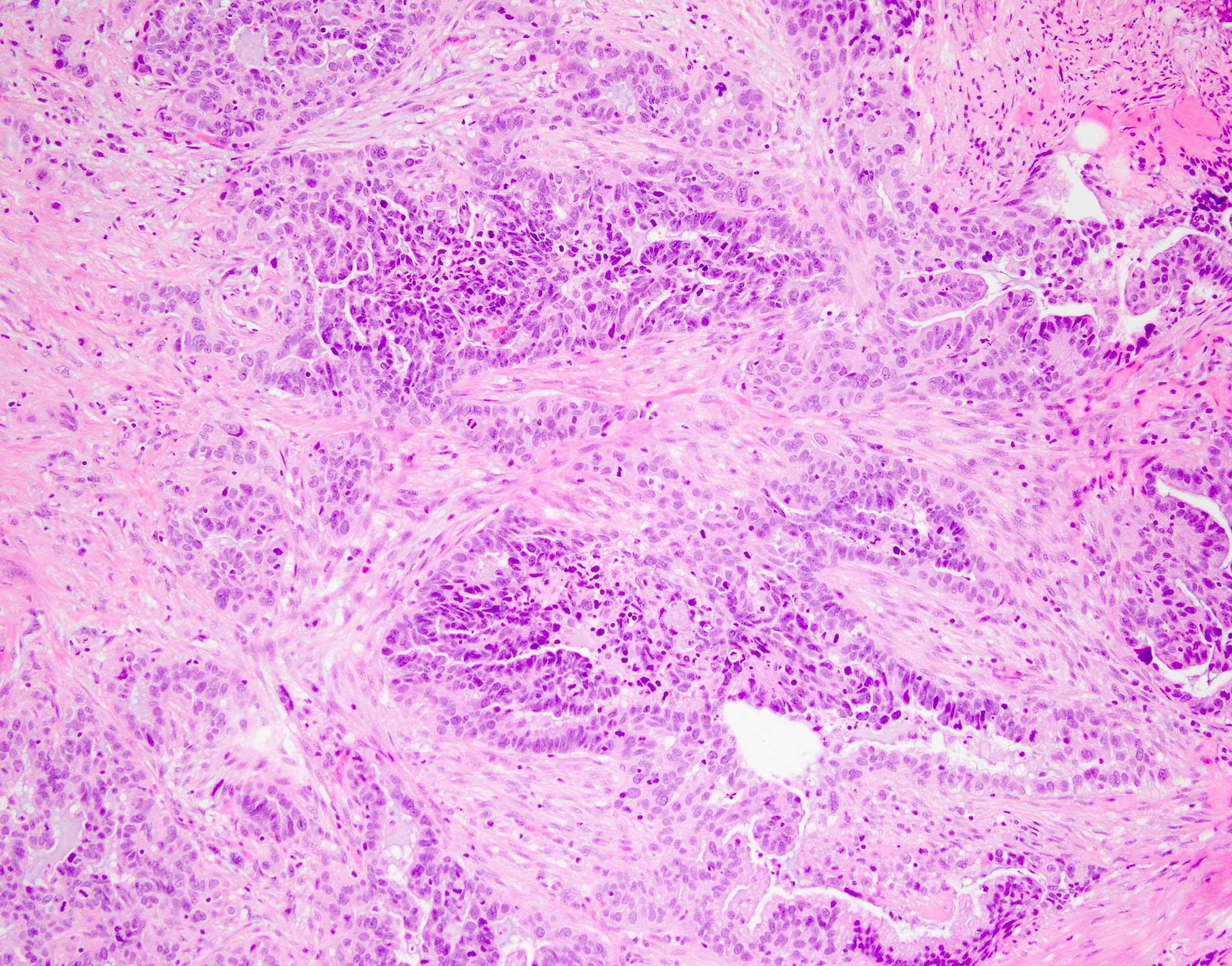
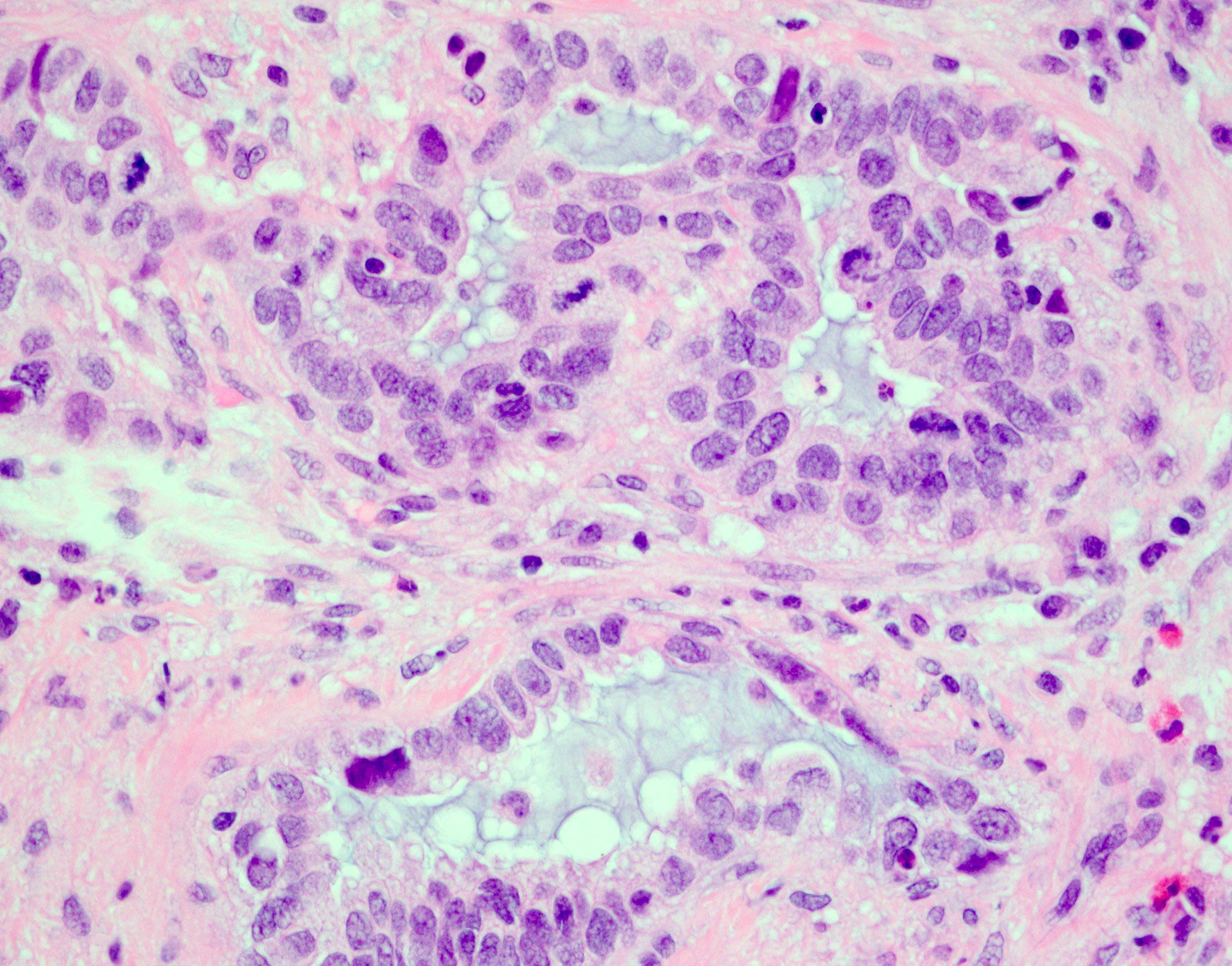
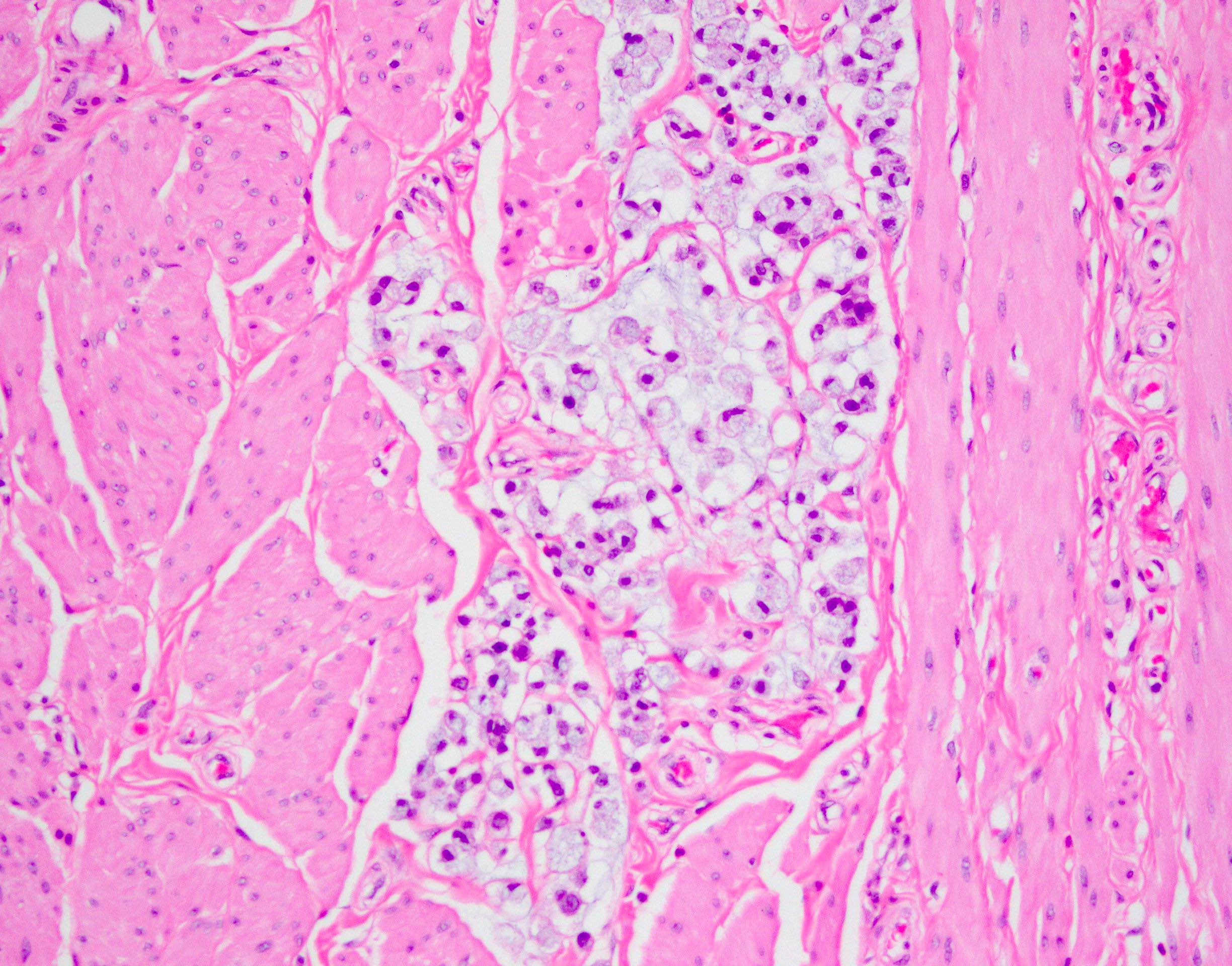
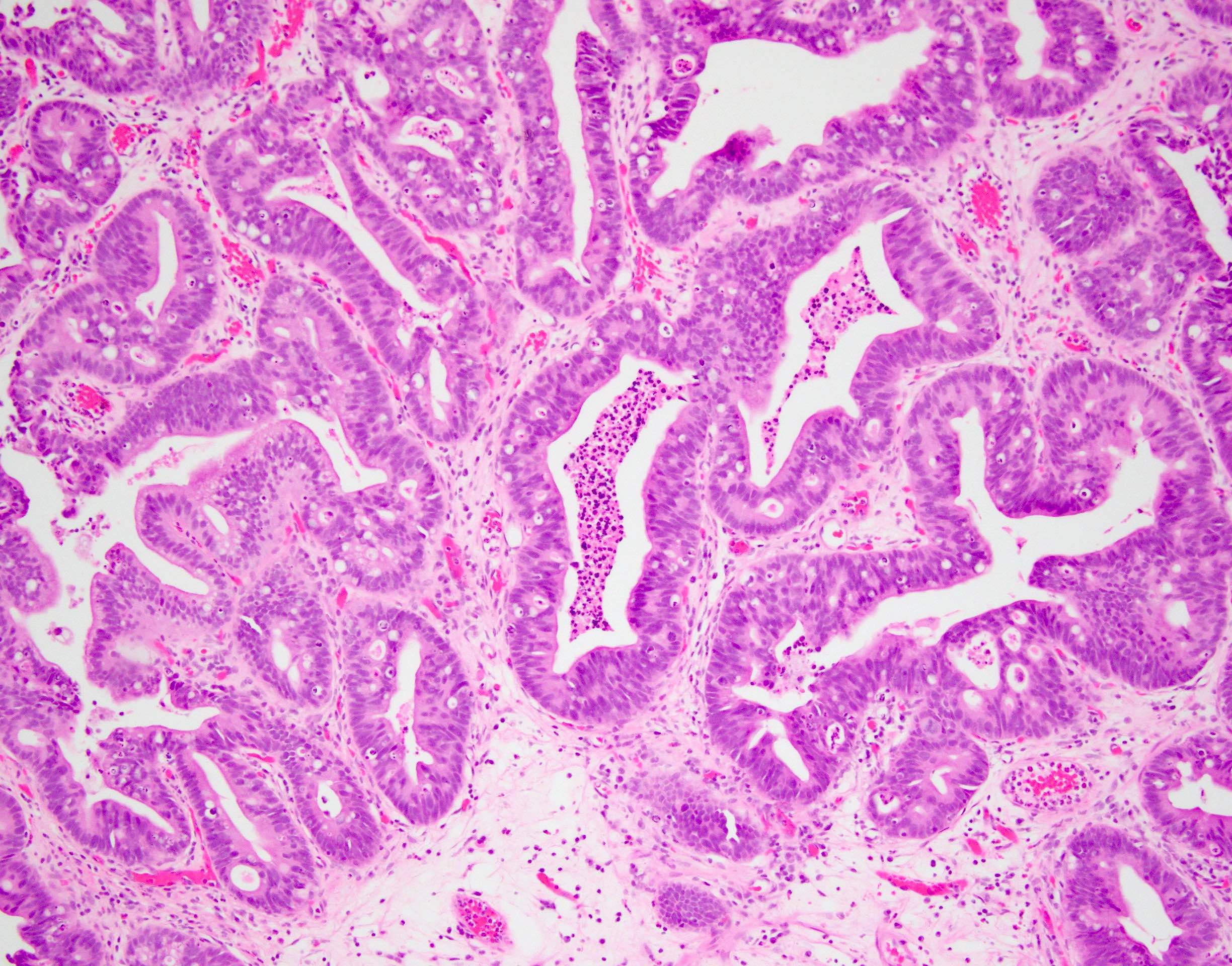
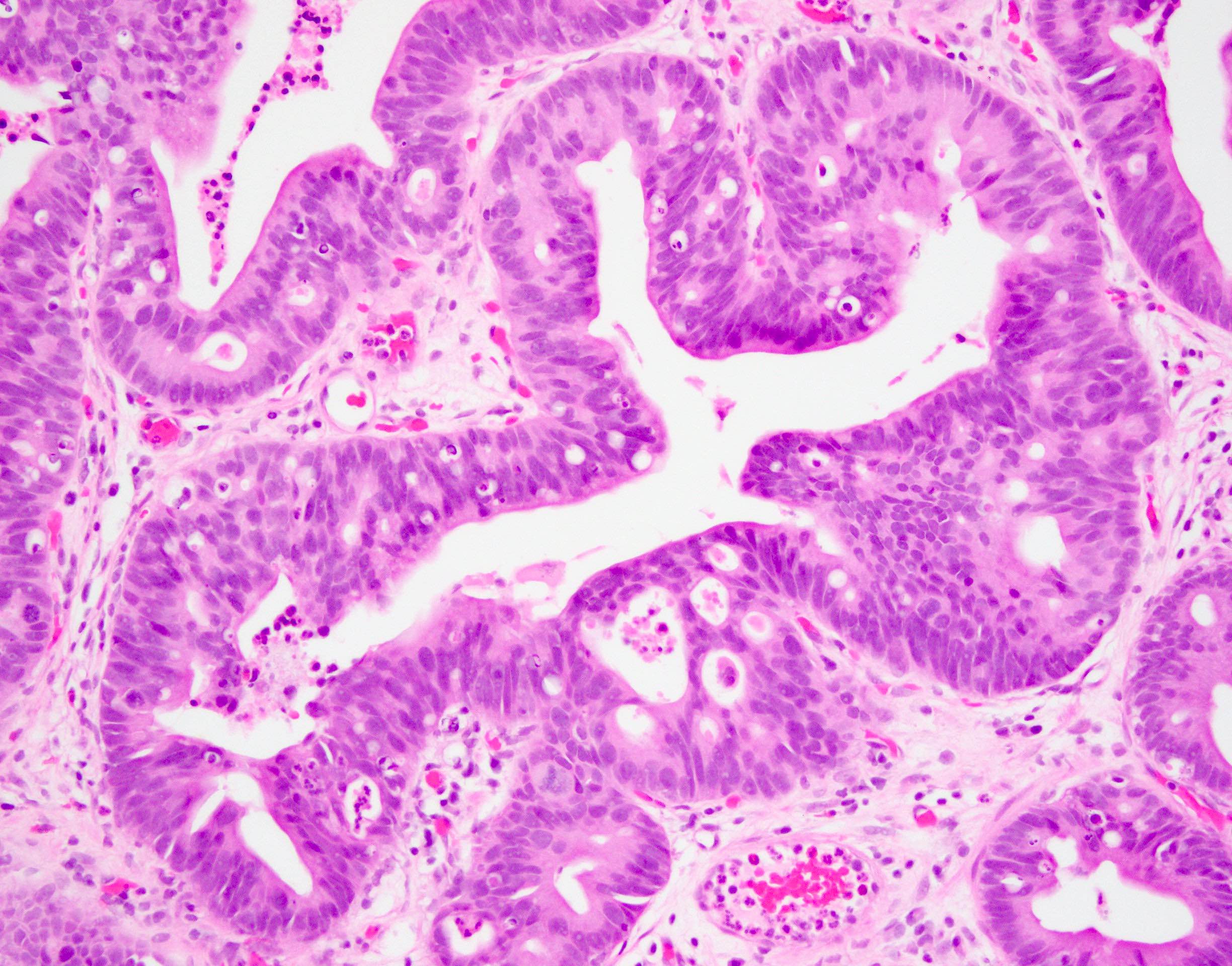
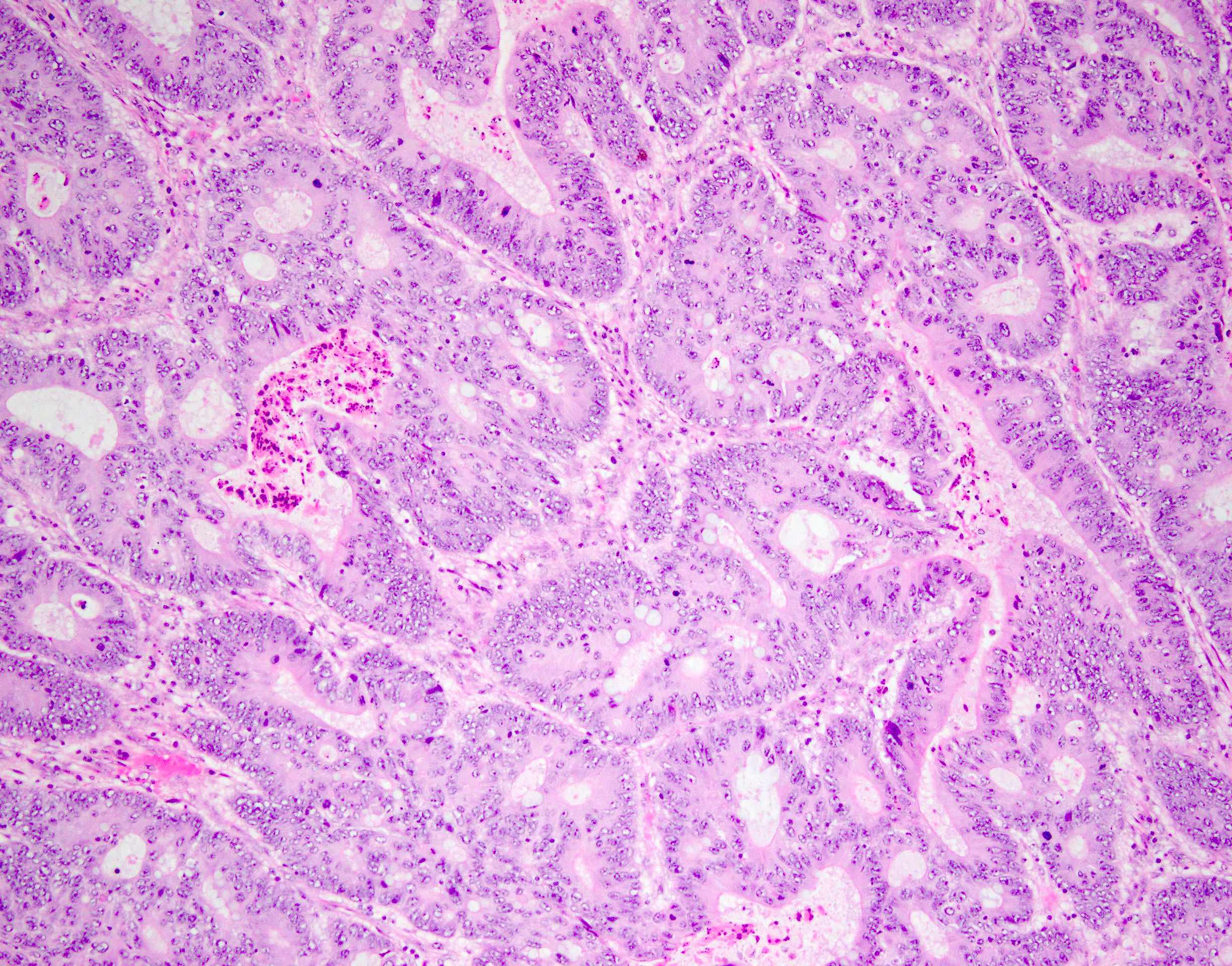
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Intestinal type (or enteric type):
- Resembles colonic adenocarcinoma (Cancer 1991;67:2165)
- Neoplastic glands are lined by pleomorphic mucin producing pseudostratified columnar epithelium
- Central dirty necrosis is commonly seen
- Mucinous (colloid) type:
- Nests of neoplastic cells floating in abundant extravasated mucin
- Singly dispersed or groups of signet ring cells can be seen in the mucin pools
- Mucin usually deeply invades muscularis propria
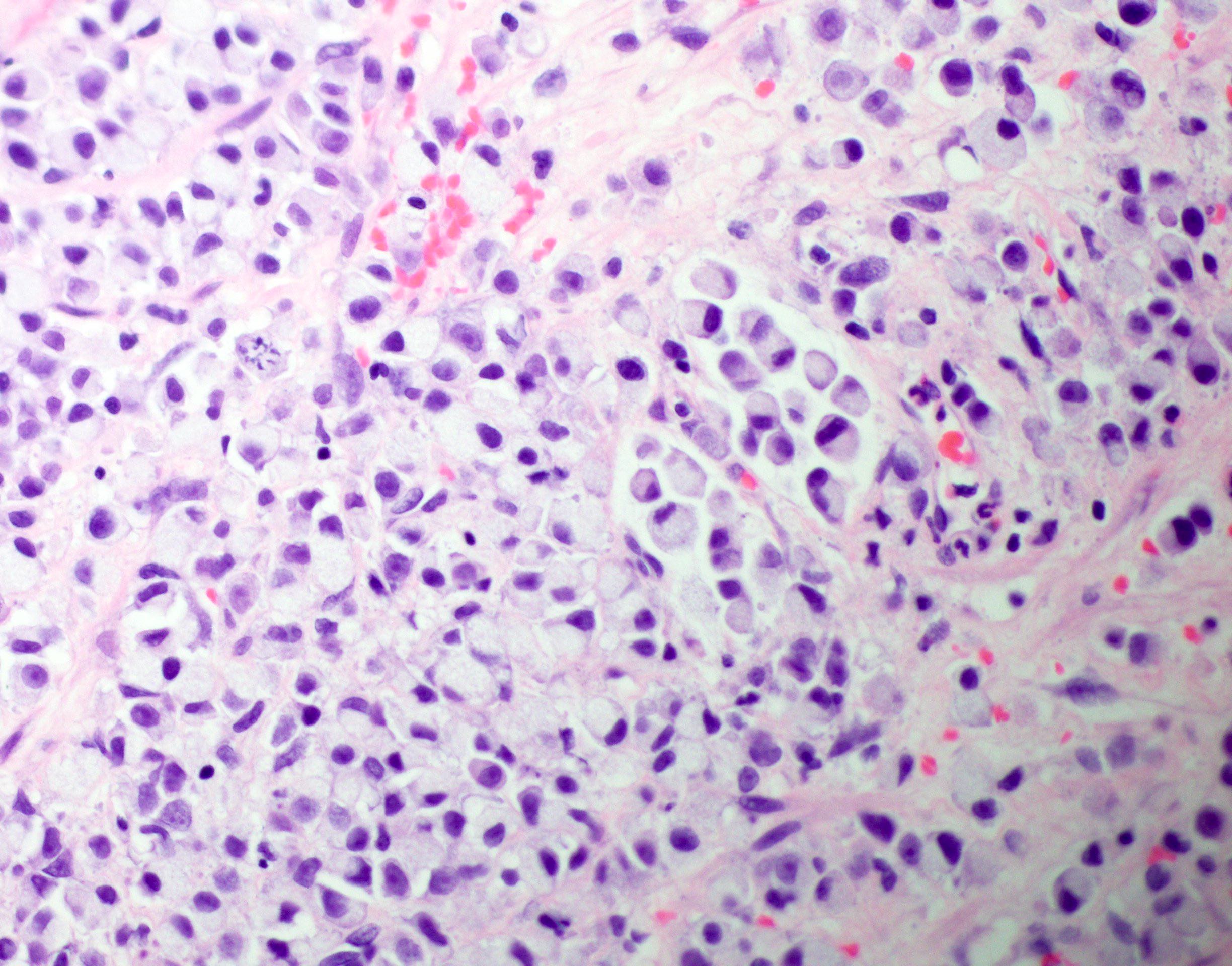
- Signet ring cell type (diffuse poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma):
- Discohesive round cells with large intracellular mucin vacuoles displacing nuclei to the periphery without extracellular mucin
- Diffusely infiltrating stromal tissue
- Association with in situ component is an important clue to differentiate primary adenocarcinoma of the bladder from secondary adenocarcinoma involving the bladder
- Intestinal metaplasia or villous adenoma may be seen
Microscopic (histologic) images
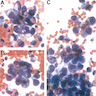
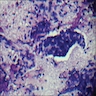
Cytology description
- Clusters of tumor cells, intracytoplasmic vacuoles, eccentrically located nuclei, hyperchromatic irregular nuclear contours, conspicuous to prominent nucleoli (Cancer 1998;84:335)
- Tumor cells of signet ring cell carcinoma show large intracytoplasmic mucin vacuole, hyperchromatic crescent shaped nuclei
- Background necrosis or mucin may be present, depending on the subtype
Positive stains
- CK7 (positive in more than half), CK20 (positive in more than half)
- Thrombomodulin (59%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:1380)
- SATB2 (49%) (Hum Pathol 2017;67:152)
- Variable CDX2 (Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:303, Mod Pathol 2005;18:1217)
Negative stains
- GATA3, p63, vimentin
- PSA, PSAP, PSMA, prostein (P501S), NKX3.1
- Beta catenin (usually no nuclear staining, only membranous staining) (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:e20)
- TTF1
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Harbors recurrent mutations in TP53, KRAS, PIK3CA, CTNNB1, APC and the promoter of TERT (Adv Anat Pathol 2020;27:303, Mod Pathol 2017;30:1133, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2013;110:17426)
- Most common abnormal FISH finding is 9p21 homozygous loss, followed by polysomy pattern (Diagn Pathol 2012;7:151)
Sample pathology report
- Bladder and prostate, radical cystoprostatectomy:
- Bladder, invasive adenocarcinoma, mixed mucinous type with signet ring cell component (see synoptic report)
- Prostate, negative for carcinoma
Differential diagnosis
- Urothelial carcinoma with predominantly glandular features / differentiation:
- Glandular differentiation in urothelial carcinoma is second most common after squamous differentiation
- Composed of enteric type glands with columnar epithelium and mucin production with typical urothelial carcinoma components present
- However, typical urothelial carcinoma components, such as invasive or noninvasive urothelial carcinoma, are present
- Examine the tumor specimen carefully to rule out any urothelial component
- Metastatic or local extension of colonic cancer:
- No in situ adenocarcinoma component or precursor lesion like villous adenoma
- Beta catenin nuclear staining (81%), CK7-, thrombomodulin, also CK20+ (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:1380, Am J Surg Pathol 1993;17:171)
- Metastatic or local extension of prostatic adenocarcinoma (particularly ductal type):
- PSA+, PSAP+, PSMA+, NKX3.1+, prostein (P501S)+, CDX2-, thrombomodulin-
- Nuclear NKX3.1 expression is specific for prostatic origin and retains even after heavily treated with androgen deprivation therapy, while hormonally treated prostate cancer often loses expression of PSA and PSAP
- Metastatic or local extension of endometrial and cervical adenocarcinoma:
- Endometrioid adenocarcinoma: ER+, PR+ and vimentin+
- Cervical adenocarcinoma: p16 strong nuclear and cytoplasmic immunoreactivity (some primary bladder adenocarcinoma can express p16), high risk HPV+ by chromogenic in situ hybridization (CISH)
- Other metastatic disease:
- Ovarian serous carcinoma: PAX8+, p53+ (or null type), WT1+, ER+, PR+
- Breast carcinoma: GATA3+, panel of ER variable, PR variable, HER2 variable, GCDFP-15 variable, mammaglobin variable, uroplakin II
- Ovarian and endometrial clear cell adenocarcinoma: napsin A+, HNF-1B+, p53+ (or null type)
- Lung adenocarcinoma: TTF1+
- Urachal adenocarcinoma:
- Located in urachus / dome
- Epicenter of the mass is usually in the muscular wall of the bladder
- CK7+ (variable), CK20+ (variable), CDX2 (variable), high molecular cytokeratin (variable), beta catenin negative for nuclear staining
- Müllerian type carcinoma of the bladder and the urethra:
- Most commonly arise from endometriosis
- Clear cell adenocarcinoma: PAX8+, HNF-1B+, AMACR+
- Villous adenoma:
- Rare benign neoplasm of the urinary tract and urachus
- No invasion
- Intestinal metaplasia:
- May mimic well differentiated adenocarcinoma due to widespread involvement with dissecting mucin pools
- However, minimal atypia, no mitoses, no signet ring cells, noninfiltrative, no muscle invasion (Hum Pathol 1997;28:1152)
- Florid cystitis glandularis:
- No nuclear anaplasia, rarely invades muscularis propria
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
A. Beta catenin. Up to 80% of metastatic colon cancers are positive for nuclear beta catenin (in addition to cytoplasmic stains), an indicator of WNT pathway activation. Primary adenocarcinoma of the bladder, intestinal type can express CK20, CDX2 and STAB2, however, lacks nuclear beta catenin staining.
Comment Here
Reference: Adenocarcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Adenocarcinoma